Switching to a Standard Chow Diet at Weaning Improves the Effects of Maternal and Postnatal High-Fat and High-Sucrose Diet on Cardiometabolic Health in Adult Male Mouse Offspring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Switching to a Standard Chow Diet at Weaning from Maternal HFHS did Not Alter Physical Characteristics
2.2. Postweaning Control Diet Improved Glucose and Insulin Tolerance Tests
2.3. Postweaning Control Diet Improved Hyperlipidemia and Hyperinsulinemia
2.4. Cardiac Systolic Function and Molecular Markers of Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy Were Not Altered by Either Maternal or Postnatal Diet
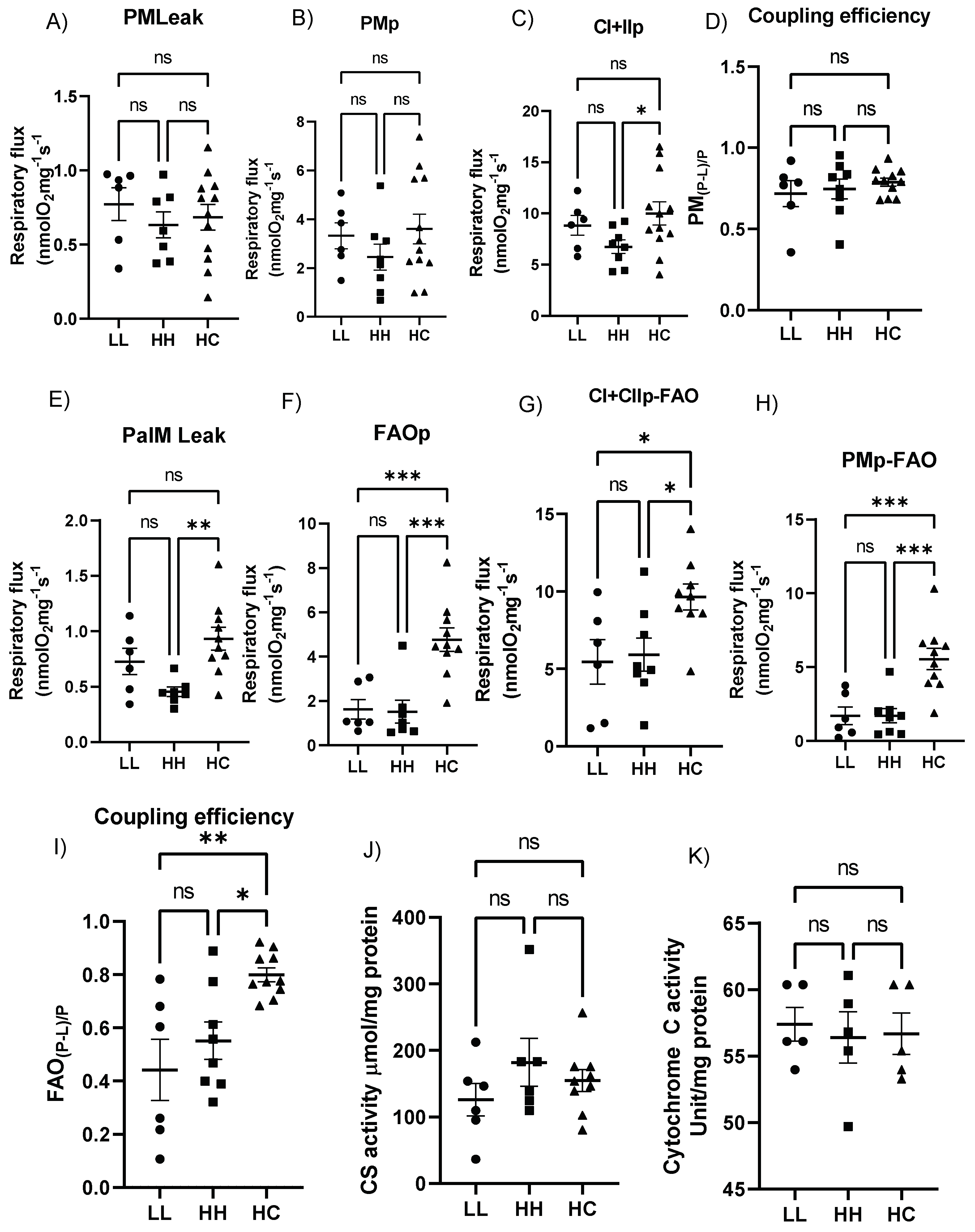
2.5. Postweaning Control Diet Modulates the Cardiac Mitochondrial Respiratory Function
2.6. Postweaning Control Diet Alters Genes Regulating Mitochondrial Function and Metabolism
2.7. Proteins Regulating Fatty Acid Metabolism Are Altered with Maternal and Postweaning Diet
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Group
4.2. Intraperitoneal Glucose—And Insulin Tolerance Tests
4.3. Assessment of Cardiac Function
4.4. Sample Collection
4.5. Plasma Analyses
4.6. Assessment of Mitochondrial Respiratory Function
4.7. Biochemical Assays
4.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.9. Protein Analyses
4.10. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Menting, M.D.; Mintjens, S.; van de Beek, C.; Frick, C.J.; Ozanne, S.E.; Limpens, J.; Roseboom, T.J.; Hooijmans, C.R.; van Deutekom, A.W.; Painter, R.C. Maternal obesity in pregnancy impacts offspring cardiometabolic health: Systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ainge, H.; Thompson, C.; Ozanne, S.E.; Rooney, K.B. A systematic review on animal models of maternal high fat feeding and offspring glycaemic control. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turdi, S.; Ge, W.; Hu, N.; Bradley, K.M.; Wang, X.; Ren, J. Interaction between maternal and postnatal high fat diet leads to a greater risk of myocardial dysfunction in offspring via enhanced lipotoxicity, IRS-1 serine phosphorylation and mitochondrial defects. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2013, 55, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kislal, S.; Jin, W.; Maesner, C.; Edlow, A.G. Mismatch between obesogenic intrauterine environment and low-fat postnatal diet may confer offspring metabolic advantage. Obes. Sci. Pr. 2021, 7, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvreur, O.; Ferezou, J.; Gripois, D.; Serougne, C.; Crepin, D.; Aubourg, A.; Gertler, A.; Vacher, C.M.; Taouis, M. Unexpected long-term protection of adult offspring born to high-fat fed dams against obesity induced by a sucrose-rich diet. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.Y.; Dekou, V.; Douglas, G.; Jensen, R.; Hanson, M.A.; Poston, L.; Taylor, P.D. A high-fat diet during rat pregnancy or suckling induces cardiovascular dysfunction in adult offspring. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 288, R127–R133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boudina, S.; Sena, S.; O’Neill Brian, T.; Tathireddy, P.; Young Martin, E.; Abel, E.D. Reduced Mitochondrial Oxidative Capacity and Increased Mitochondrial Uncoupling Impair Myocardial Energetics in Obesity. Circulation 2005, 112, 2686–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mdaki, K.S.; Larsen, T.D.; Wachal, A.L.; Schimelpfenig, M.D.; Weaver, L.J.; Dooyema, S.D.; Louwagie, E.J.; Baack, M.L. Maternal high-fat diet impairs cardiac function in offspring of diabetic pregnancy through metabolic stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2016, 310, H681–H692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferey, J.L.A.; Boudoures, A.L.; Reid, M.; Drury, A.; Scheaffer, S.; Modi, Z.; Kovacs, A.; Pietka, T.; DeBosch, B.J.; Thompson, M.D.; et al. A maternal high-fat, high-sucrose diet induces transgenerational cardiac mitochondrial dysfunction independently of maternal mitochondrial inheritance. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2019, 316, H1202–H1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.; Gonzalez, K.; Ullevig, S.L.; Zhang, J.; Umeda, M. Obesity, not a high fat, high sucrose diet alone, induced glucose intolerance and cardiac dysfunction during pregnancy and postpartum. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, M.S.; Kalashyan, H.; Choy, J.; Chiew, S.K.; Shawki, A.-H.; Dawood, A.H.; Becher, H. Left ventricular relative wall thickness versus left ventricular mass index in non-cardioembolic stroke patients. Medicine 2015, 94, e872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenz, M.; Robbins, J. Impact of beta-myosin heavy chain expression on cardiac function during stress. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 2390–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vigelsø, A.; Andersen, N.B.; Dela, F. The relationship between skeletal muscle mitochondrial citrate synthase activity and whole body oxygen uptake adaptations in response to exercise training. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. PHarmacol. 2014, 6, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, G.G.; Dawson, N.J.; Head, A.; Scott, G.R.; Scott, A.L. Astrocyte-mediated disruption of ROS homeostasis in Fragile X mouse model. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 146, 105036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.L.; Purpera, M.N.; Morrison, C.D. Maternal obesity is necessary for programming effect of high-fat diet on offspring. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 296, R1464–R1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sertie, R.; Kang, M.; Antipenko, J.P.; Liu, X.; Maianu, L.; Habegger, K.; Garvey, W.T. In utero nutritional stress as a cause of obesity: Altered relationship between body fat, leptin levels and caloric intake in offspring into adulthood. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, S.; Mauro, A.G.; Mezzaroma, E.; Kraskauskas, D.; Marchetti, C.; Buzzetti, R.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Abbate, A.; Toldo, S. A high-sugar and high-fat diet impairs cardiac systolic and diastolic function in mice. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 198, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loche, E.; Blackmore, H.L.; Carpenter, A.A.M.; Beeson, J.H.; Pinnock, A.; Ashmore, T.J.; Aiken, C.E.; de Almeida-Faria, J.; Schoonejans, J.; Giussani, D.A.; et al. Maternal diet-induced obesity programmes cardiac dysfunction in male mice independently of post-weaning diet. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blackmore, H.L.; Niu, Y.; Fernandez-Twinn, D.S.; Tarry-Adkins, J.L.; Giussani, D.A.; Ozanne, S.E. Maternal diet-induced obesity programs cardiovascular dysfunction in adult male mouse offspring independent of current body weight. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 3970–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, G.; Hill, M.A.; Sowers, J.R. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: An update of mechanisms contributing to this clinical entity. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, R.; Steegers, E.A.; Franco, O.H.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W. Maternal weight gain in different periods of pregnancy and childhood cardio-metabolic outcomes. The Generation R Study. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, V.; Dakin, R.S.; Liu, L.; Hadoke, P.W.; Walker, B.R.; Seckl, J.R.; Norman, J.E.; Drake, A.J. Maternal obesity has little effect on the immediate offspring but impacts on the next generation. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 2514–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boudina, S.; Han, Y.H.; Pei, S.; Tidwell, T.J.; Henrie, B.; Tuinei, J.; Olsen, C.; Sena, S.; Abel, E.D. UCP3 regulates cardiac efficiency and mitochondrial coupling in high fat-fed mice but not in leptin-deficient mice. Diabetes 2012, 61, 3260–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, E.J.; Yamazaki, H.; Neufer, P.D. Induction of endogenous uncoupling protein 3 suppresses mitochondrial oxidant emission during fatty acid-supported respiration. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 31257–31266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warden, C.H.; Fisler, J.S. Comparisons of diets used in animal models of high-fat feeding. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reeves, P.G.; Nielsen, F.H.; Fahey, G.C., Jr. AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: Final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, L.; Menikdiwela, K.R.; Clevenger, S.; Eboh, T.; Allen, L.; Koboziev, I.; Scoggin, S.; Rashid, A.M.; Moussa, H.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Maternal and postnatal supplementation of fish oil improves metabolic health of mouse male offspring. Obesity 2018, 26, 1740–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Nutrition during Pregnancy. Available online: https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/nutrition-during-pregnancy (accessed on 9 June 2022).
- Chassaing, B.; Miles-Brown, J.; Pellizzon, M.; Ulman, E.; Ricci, M.; Zhang, L.; Patterson, A.D.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Gewirtz, A.T. Lack of soluble fiber drives diet-induced adiposity in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G528–G541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, C.A.; Choudhury, M. Advancing metabolism research to overcome low litter survival in metabolically stressed mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 317, E261–E268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Suhett, C.P.; Scott, J.M.; Graham, A.; Chen, Y.; Deuster, P.A. Control diet in a high-fat diet study in mice: Regular chow and purified low-fat diet have similar effects on phenotypic, metabolic, and behavioral outcomes. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluckman, P.D.; Hanson, M.A.; Spencer, H.G. Predictive adaptive responses and human evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudina, S.; Abel, E.D. Diabetic cardiomyopathy revisited. Circulation 2007, 115, 3213–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, H.; Yokoyama, T.; Sekiguchi, K.; Iijima, D.; Sunaga, H.; Maniwa, M.; Ueno, M.; Iso, T.; Arai, M.; Kurabayashi, M. Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD1) augments saturated fatty acid-induced lipid accumulation and inhibits apoptosis in cardiac myocytes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCurdy, C.E.; Schenk, S.; Hetrick, B.; Houck, J.; Drew, B.G.; Kaye, S.; Lashbrook, M.; Bergman, B.C.; Takahashi, D.L.; Dean, T.A.; et al. Maternal obesity reduces oxidative capacity in fetal skeletal muscle of Japanese macaques. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e86612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereyra, A.S.; Hasek, L.Y.; Harris, K.L.; Berman, A.G.; Damen, F.W.; Goergen, C.J.; Ellis, J.M. Loss of cardiac carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2 results in rapamycin-resistant, acetylation-independent hypertrophy. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 18443–18456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, M.M.; Byrne, N.J.; Kim, T.T.; Levasseur, J.; Masson, G.; Boisvenue, J.J.; Febbraio, M.; Dyck, J.R. Cardiomyocyte-specific ablation of CD36 accelerates the progression from compensated cardiac hypertrophy to heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017, 312, H552–H560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Littlejohns, B.; Pasdois, P.; Duggan, S.; Bond, A.R.; Heesom, K.; Jackson, C.L.; Angelini, G.D.; Halestrap, A.P.; Suleiman, M.S. Hearts from mice fed a non-obesogenic high-fat diet exhibit changes in their oxidative state, calcium and mitochondria in parallel with Increased susceptibility to reperfusion injury. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anedda, A.; Lopez-Bernardo, E.; Acosta-Iborra, B.; Suleiman, M.S.; Landazuri, M.O.; Cadenas, S. The transcription factor Nrf2 promotes survival by enhancing the expression of uncoupling protein 3 under conditions of oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 61, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, L.; Kwong, M.; Hou, S.; Lee, C.; Chan, J.Y. Deficiency of the Nrf1 and Nrf2 transcription factors results in early embryonic lethality and severe oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 48021–48029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Gong, Q.; Stice, J.P.; Knowlton, A.A. Mitochondrial OPA1, apoptosis, and heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 84, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, A.J.; Le, C.H.; Schlater, A.; Nguyen, A.; Kaye, S.; Beals, J.W.; Scalzo, R.L.; Bell, C.; Gnaiger, E.; Costa, D.P.; et al. High fatty acid oxidation capacity and phosphorylation control despite elevated leak and reduced respiratory capacity in northern elephant seal muscle mitochondria. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 2947–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, E.; Joiner, H.E.; Skelton, T.; Looten, K.D.; Manczak, M.; Reddy, P.H. Maternal exercise upregulates mitochondrial gene expression and increases enzyme activity of fetal mouse hearts. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| LL | HH | HC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 122.3 ± 12.5 (6) | 216.1 ± 19.1 * (8) | 128.8 ± 7.4 + (8) |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 20.80 ± 0.92 (6) | 43.38 ± 5.94 * (8) | 22.38 ± 2.02 + (8) |
| Non-essential fatty acids (µM) | 320.8 ± 18.0 (5) | 368.1 ± 28.8 (8) | 383.7 ± 39.9 (9) |
| Triglycerides (ng/mL) | 149.0 ± 2.8 (5) | 108.1 ± 19.6 (8) | 113.3 ± 13.8 (8) |
| Insulin (ng/mL) | 4.26 ± 1.08 (6) | 17.76 ± 2.51 * (7) | 6.53 ± 2.24 + (3) |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 4.12 ± 1.09 (6) | 13.82 ± 1.24 * (7) | 12.48 ± 0.52 * (6) |
| M-Mode Parameters | LL (n = 12) | HH (n = 15) | HC (n = 12) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LV IVS (cm) | |||
| Diastolic | 0.104 ± 0.006 | 0.105 ± 0.004 | 0.113 ± 0.005 |
| Systolic | 1.154 ± 0.003 | 0.147 ± 0.006 | 0.155 ± 0.007 |
| LV PW (cm) | |||
| Diastolic | 0.113 ± 0.010 | 0.119 ± 0.007 | 0.115 ± 0.007 |
| Systolic | 0.164 ± 0.009 | 0.166 ± 0.010 | 0.170 ± 0.011 |
| LV diameter (cm) | |||
| Diastolic | 0.446 ± 0.011 | 0.473 ± 0.006 * | 0.469 ± 0.012 |
| Systolic | 0.304 ± 0.009 | 0.342 ± 0.012 * | 0.332 ± 0.014 |
| RWT | 0.47 ± 0.02 | 0.47 ± 0.02 | 0.448 ± 0.02 |
| LV, %FS | 32.28 ± 1.31 | 28.83 ± 1.73 | 30.10 ± 1.86 |
| LV, %EF | 64.52 ± 1.88 | 59.89 ± 3.75 | 63.81 ± 2.14 |
| HR, bpm | 532.8 ± 16.8 | 523.8 ± 15.9 | 557.9 ± 13.96 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiñas Merlin, A.; Gonzalez, K.; Mockler, S.; Perez, Y.; Jia, U.-T.A.; Chicco, A.J.; Ullevig, S.L.; Chung, E. Switching to a Standard Chow Diet at Weaning Improves the Effects of Maternal and Postnatal High-Fat and High-Sucrose Diet on Cardiometabolic Health in Adult Male Mouse Offspring. Metabolites 2022, 12, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060563
Chiñas Merlin A, Gonzalez K, Mockler S, Perez Y, Jia U-TA, Chicco AJ, Ullevig SL, Chung E. Switching to a Standard Chow Diet at Weaning Improves the Effects of Maternal and Postnatal High-Fat and High-Sucrose Diet on Cardiometabolic Health in Adult Male Mouse Offspring. Metabolites. 2022; 12(6):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060563
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiñas Merlin, Andrea, Kassandra Gonzalez, Sarah Mockler, Yessenia Perez, U-Ter Aondo Jia, Adam J. Chicco, Sarah L. Ullevig, and Eunhee Chung. 2022. "Switching to a Standard Chow Diet at Weaning Improves the Effects of Maternal and Postnatal High-Fat and High-Sucrose Diet on Cardiometabolic Health in Adult Male Mouse Offspring" Metabolites 12, no. 6: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060563
APA StyleChiñas Merlin, A., Gonzalez, K., Mockler, S., Perez, Y., Jia, U.-T. A., Chicco, A. J., Ullevig, S. L., & Chung, E. (2022). Switching to a Standard Chow Diet at Weaning Improves the Effects of Maternal and Postnatal High-Fat and High-Sucrose Diet on Cardiometabolic Health in Adult Male Mouse Offspring. Metabolites, 12(6), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060563






