Effect of Linoleic Acid on Cholesterol Levels in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia Rat Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. High-Fat Diet Preparation
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Biochemical Measurements of Serum Lipid Profile and Liver Function Test
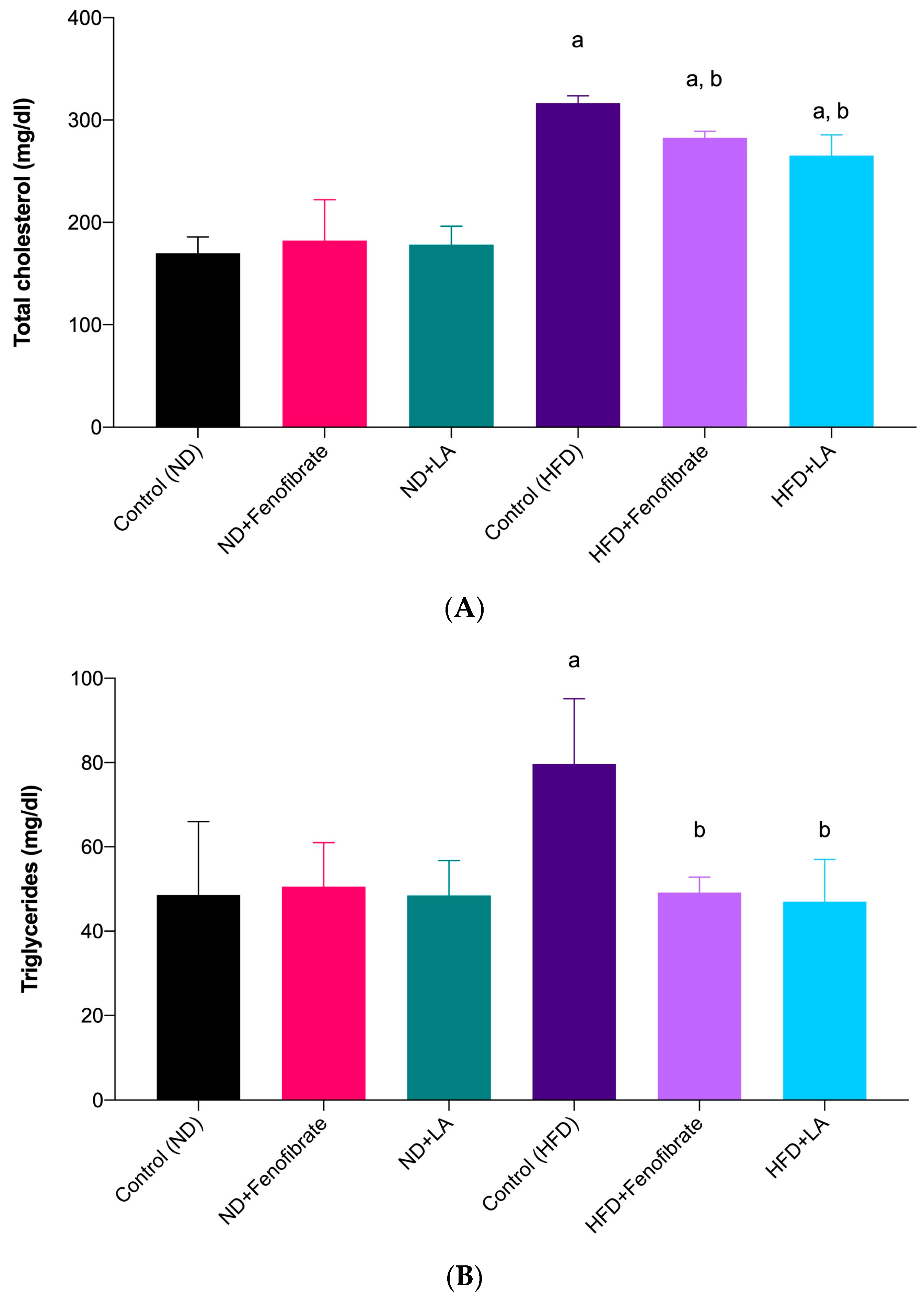
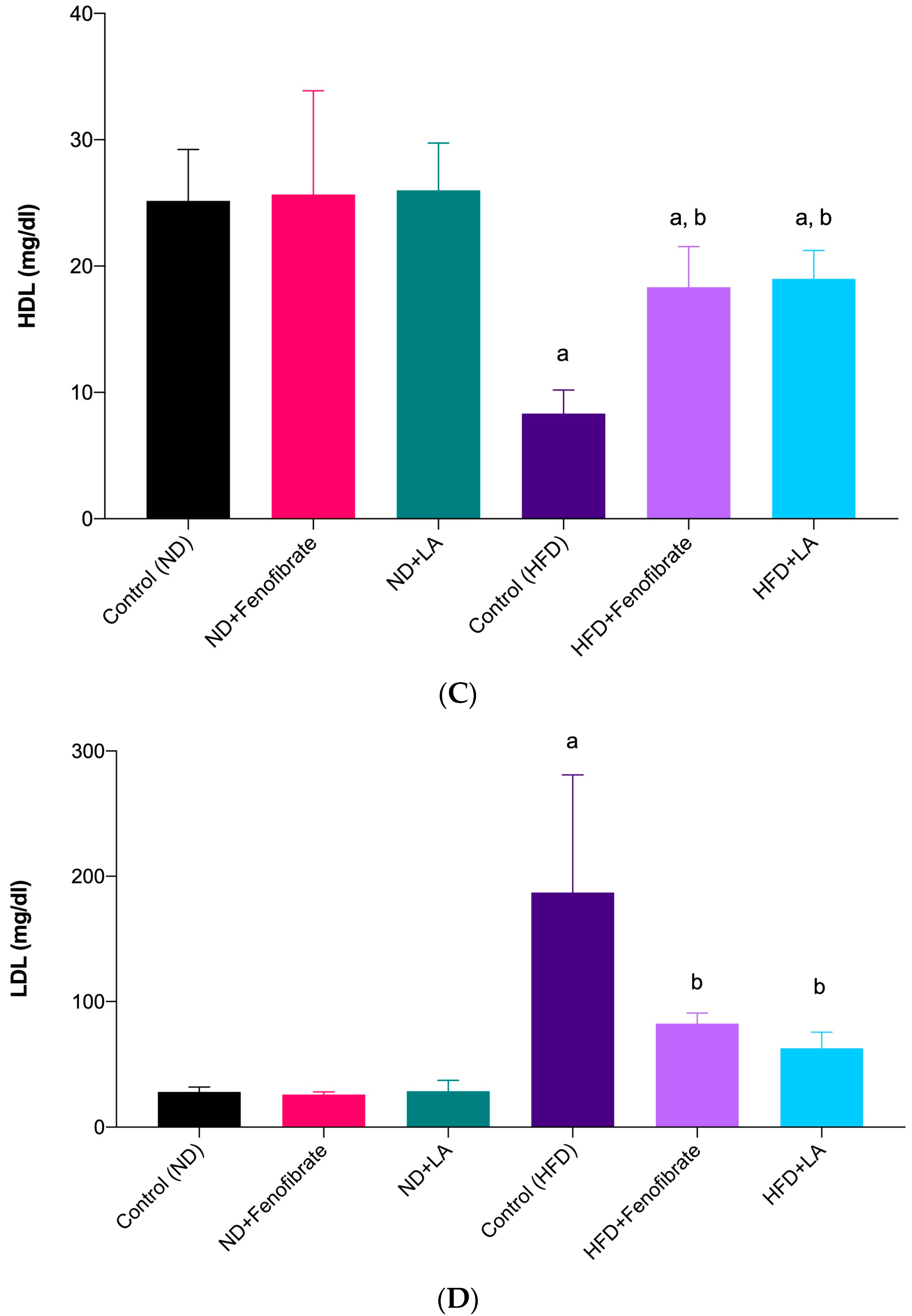
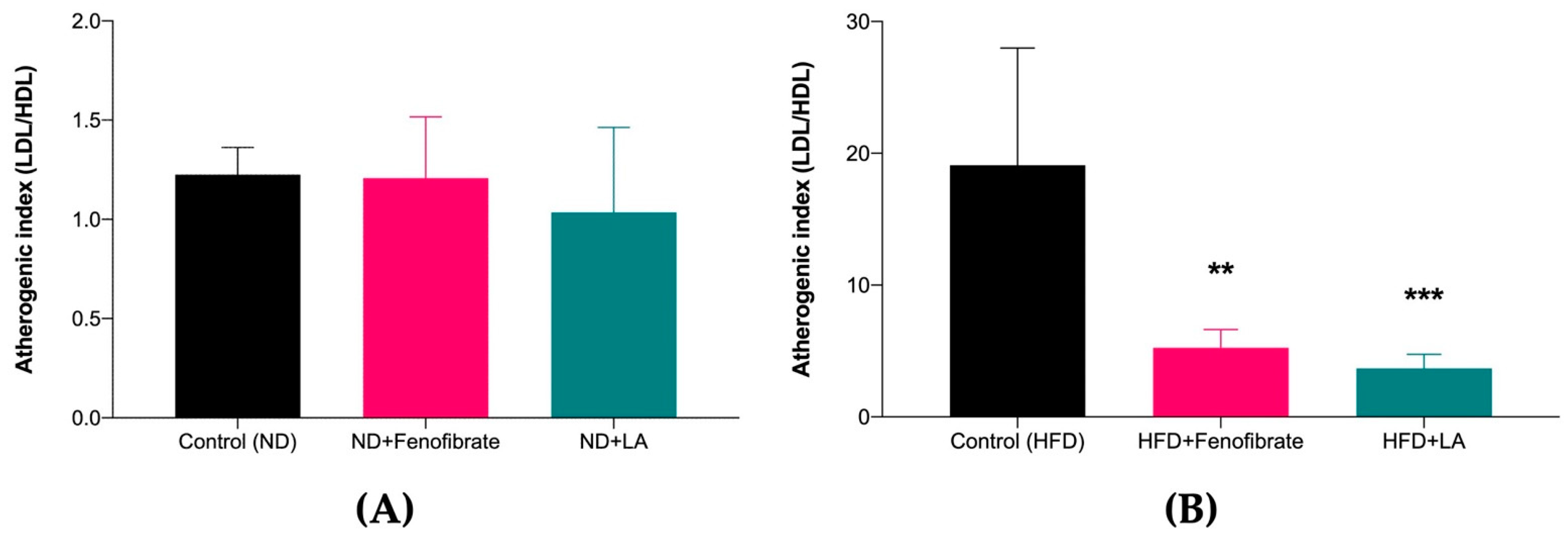
2.3.1. Serum Lipid Profile and Atherogenic Index (AI)
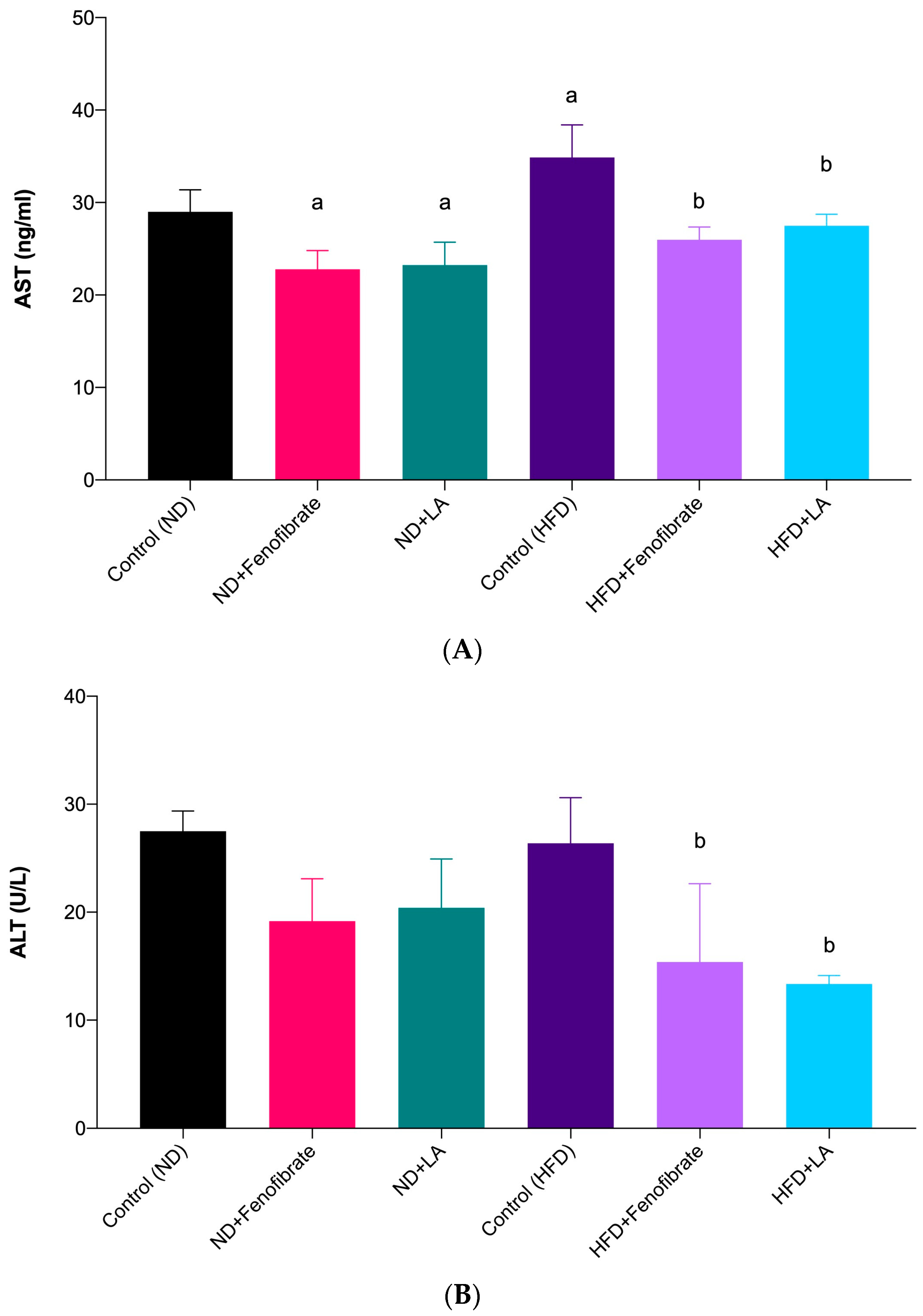
2.3.2. Liver Function Test
2.4. Histopathology
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Linoleic Acid and Fenofibrate on Body and Organ Weight
3.2. Effect of Linoleic Acid and Fenofibrate on Serum Lipid Profile and AI
3.3. Effect of Linoleic Acid and Fenofibrate on Liver Function Test
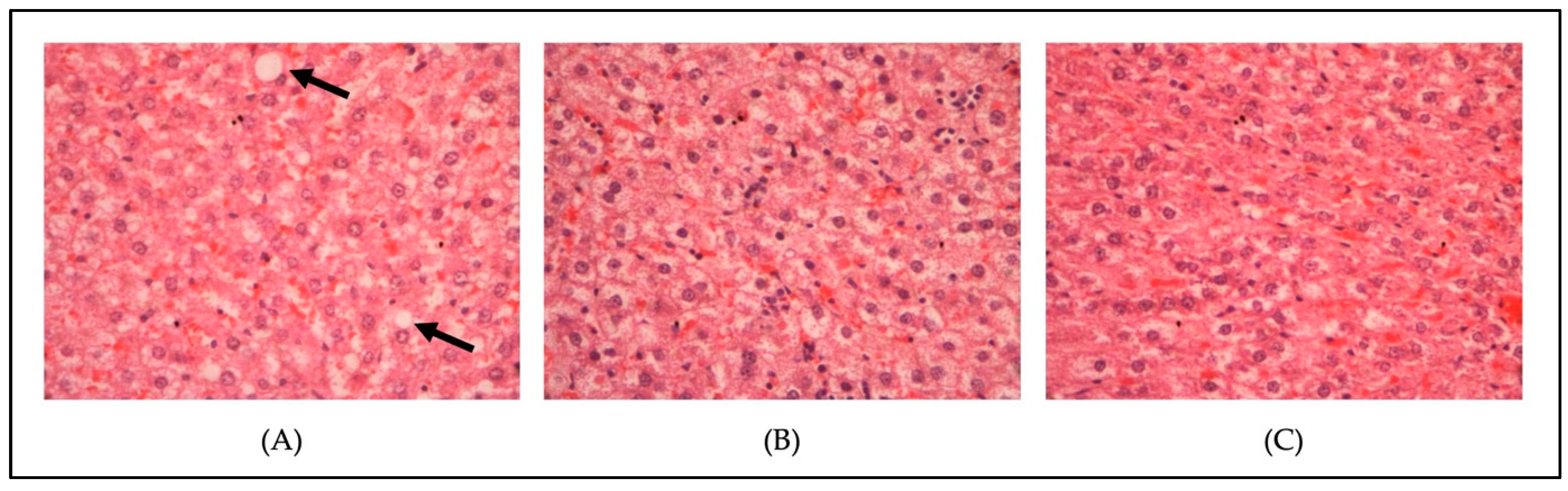
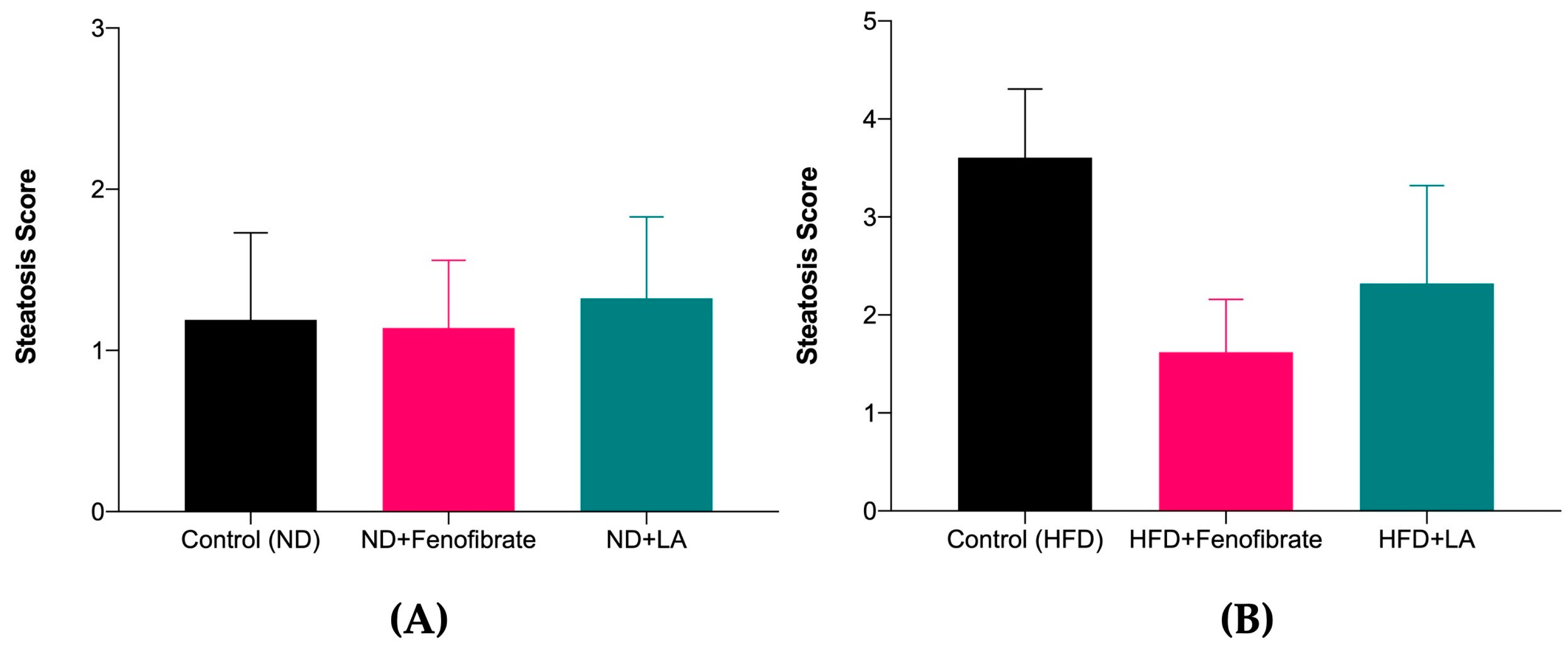
3.4. Histopathological Changes in the Liver Tissue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Su, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, J.; Zhu, M.; He, X.; Zhang, B.; Xu, H.; Yang, X.; et al. Intermittent Fasting Inhibits High-Fat Diet–Induced Atherosclerosis by Ameliorating Hypercholesterolemia and Reducing Monocyte Chemoattraction. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flora, G.D.; Nayak, M.K. A Brief Review of Cardiovascular Diseases, Associated Risk Factors and Current Treatment Regimes. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 4063–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visseren, F.L.J.; MacH, F.; Smulders, Y.M.; Carballo, D.; Koskinas, K.C.; Bäck, M.; Benetos, A.; Biffi, A.; Boavida, J.M.; Capodanno, D.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice. Eur Heart. J. 2021, 42, 3227–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguila, M.B.; Loureiro, C.C.; Pinheiro, A.d.R.; Mandarim-De-Lacerda, C.A. Lipid Metabolism in Rats Fed Diets Containing Different Types of Lipids. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2002, 78, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, X.J.; Du, Y.; Jiang, H.J.; Li, Y.Z.; Xu, Y.N.; Si, S.Y.; Wang, L.; Hong, B. Identification of Novel Compounds Enhancing SR-BI MRNA Stability through High-Throughput Screening. SLAS Discov. 2020, 25, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, P.; Khetarpal, S.A.; Larach, D.B.; Hancock-Cerutti, W.F.; Millar, J.S.; Cuchel, M.; DerOhannessian, S.; Kontush, A.; Surendran, P.; Saleheen, D.; et al. Rare Variant in Scavenger Receptor BI Raises HDL Cholesterol and Increases Risk of Coronary Heart Disease. Science 2016, 351, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Brewer, H.B.; Ansell, B.J.; Barter, P.; Chapman, M.J.; Heinecke, J.W.; Kontush, A.; Tall, A.R.; Webb, N.R. Dysfunctional HDL and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajkovska, K.T.; Topuzovska, S. High-Density Lipoprotein Metabolism and Reverse Cholesterol Transport: Strategies for Raising HDL Cholesterol. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2017, 18, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokoła-Wysoczańska, E.; Wysoczański, T.; Wagner, J.; Czyż, K.; Bodkowski, R.; Lochyński, S.; Patkowska-Sokoła, B. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Potential Therapeutic Role in Cardiovascular System Disorders—A Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, J.S.; Griffith, T.A.; Naghipour, S.; Vider, J.; Toit, E.F.D.; Patel, H.H.; Peart, J.N.; Headrick, J.P. Dietary α-Linolenic Acid Counters Cardioprotective Dysfunction in Diabetic Mice: Unconventional Pufa Protection. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, N.R.; Fischer, M.H. The Role of Essential Fatty Acids in Human Health. J. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 18, 268–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Mechanisms of Action of (n-3) Fatty Acids. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 592S–599S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jump, D.B.; Depner, C.M.; Tripathy, S. Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation and Cardiovascular Disease: Thematic Review Series: New Lipid and Lipoprotein Targets for the Treatment of Cardiometabolic Diseases. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2525–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farvid, M.S.; Ding, M.; Pan, A.; Sun, Q.; Chiuve, S.E.; Steffen, L.M.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Dietary Linoleic Acid and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Circulation 2014, 130, 1568–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez, M.L.; West, K.L. Mechanisms by Which Dietary Fatty Acids Modulate Plasma Lipids. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 2075–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mustad, V.A.; Ellsworth, J.L.; Cooper, A.D.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Etherton, T.D. Dietary Linoleic Acid Increases and Palmitic Acid Decreases Hepatic LDL Receptor Protein and MRNA Abundance in Young Pigs. J. Lipid Res. 1996, 37, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froyen, E.; Burns-Whitmore, B. The Effects of Linoleic Acid Consumption on Lipid Risk Markers for Cardiovascular Disease in Healthy Individuals: A Review of Human Intervention Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zock, P.L.; Katan, M.B. Hydrogenation Alternatives: Effects of Trans Fatty Acids and Stearic Acid versus Linoleic Acid on Serum Lipids and Lipoproteins in Humans. J. Lipid Res. 1992, 33, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, T.A.B.; Oakley, F.R.; Miller, G.J.; Mitropoulos, K.A.; Crook, D.; Oliver, M.F. Influence of N-6 versus n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Diets Low in Saturated Fatty Acids on Plasma Lipoproteins and Hemostatic Factors. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1997, 17, 3449–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, J.M.; Dougherty, R.M. Lack of Effect of Linoleic Acid on the High-Density-Lipoprotein-Cholesterol Fraction of Plasma Lipoproteins. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chroni, A.; Liu, T.; Gorshkova, I.; Kan, H.Y.; Uehara, Y.; von Eckardstein, A.; Zannis, V.I. The Central Helices of ApoA-I Can Promote ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter A1 (ABCA1)-Mediated Lipid Efflux. Amino Acid Residues 220-231 of the Wild-Type ApoA-I Are Required for Lipid Efflux in Vitro and High Density Lipoprotein Formation in Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 6719–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chambenoit, O.; Hamon, Y.; Marguet, D.; Rigneault, H.; Rosseneu, M.; Chimini, G. Specific Docking of Apolipoprotein A-I at the Cell Surface Requires a Functional ABCA1 Transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 9955–9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Batal, R.; Tremblay, M.; Krimbou, L.; Marner, O.; Davignon, J.; Genest, J.; Cohn, J.S. Familial HDL Deficiency Characterized by Hypercatabolism of Mature ApoA- I but Not ProApoA-I. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, B.; Yang, Z.; Liu, L.; Yao, D.; Cui, G.; Sun, J.; Wu, Z. Metabolomic Analysis of Simvastatin and Fenofibrate Intervention in High-Lipid Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia Rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arca, M.; Montali, A.; Pigna, G.; Antonini, R.; Antonini, T.M.; Luigi, P.; Fraioli, A.; Mastrantoni, M.; Maddaloni, M.; Letizia, C. Comparison of Atorvastatin versus Fenofibrate in Reaching Lipid Targets and Influencing Biomarkers of Endothelial Damage in Patients with Familial Combined Hyperlipidemia. Metabolism 2007, 56, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooistra, T.; Verschuren, L.; de Vries-Van Der Weij, J.; Koenig, W.; Toet, K.; Princen, H.M.G.; Kleemann, R. Fenofibrate Reduces Atherogenesis in ApoE*3Leiden Mice: Evidence for Multiple Antiatherogenic Effects besides Lowering Plasma Cholesterol. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azemi, A.K.; Mokhtar, S.S.; Sharif, S.E.T.; Rasool, A.H.G. Clinacanthus Nutans Attenuates Atherosclerosis Progression in Rats with Type 2 Diabetes by Reducing Vascular Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Pharm. Biol. 2021, 59, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghibu, S.; Ilie, I.; Mureșan, A.; Mogoșan, C. Perspectives in the Experimental Study of the Metabolic Syndrome. Farmacia 2015, 63, 482–486. [Google Scholar]
- Getz, G.S.; Reardon, C.A. Diet and Murine Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramani, C.; Rajakkannu, A.; Rathinam, A.; Gaidhani, S.; Raju, I.; Kartar Singh, D.V. Anti-atherosclerotic activity of root bark of Premna integrifolia Linn. in high fat diet induced atherosclerosis model rats. J. Pharm. Anal. 2017, 7, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Miranda, J.; Pérez-Martínez, P.; Marin, C.; Fuentes, F.; Delgado, J.; Pérez-Jiménez, F. Dietary Fat, Genes and Insulin Sensitivity. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 85, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, A.C.; Roche, H.M. The Potential Role of Olive Oil-Derived MUFA in Insulin Sensitivity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassoued, I.; Trigui, M.; Ghlissi, Z.; Nasri, R.; Jamoussi, K.; Kessis, M.; Sahnoun, Z.; Rebai, T.; Boualga, A.; Lamri-Senhadji, M.; et al. Evaluation of Hypocholesterolemic Effect and Antioxidant Activity of Boops Boops Proteins in Cholesterol-Fed Rats. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, K.Y.; Clanton, E.C.; Clements, K.P.; Granger, D.N. Role of Interferon-γ in Hypercholesterolemia-Induced Leukocyte-Endothelial Cell Adhesion. Circulation 2003, 107, 2140–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asahina, M.; Sato, M.; Imaizumi, K. Genetic Analysis of Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia in Exogenously Hypercholesterolemic Rats. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 2289–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samat, S.; Kanyan Enchang, F.; Nor Hussein, F.; Wan Ismail, W.I. Four-Week Consumption of Malaysian Honey Reduces Excess Weight Gain and Improves Obesity-Related Parameters in High Fat Diet Induced Obese Rats. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 1342150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godea (Lupei), S.; Ciubotariu, D.; Danciu, M.; Lupuşoru, R.V.; Ghiciuc, C.M.; Cernescu, I.; Gheţu, N.; Lupei, M.; Lupuşoru, C.E. Improvement in Serum Lipids and Liver Morphology after Supplementation of the Diet with Fish Oil Is More Evident under Regular Feeding Conditions than under High-Fat or Mixed Diets in Rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Lu, X.; Ma, H.; Shi, H.; Li, H.; Xie, D.; Dong, L.; Liang, C. Treatment with PPARδ Agonist Alleviates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating Glucose and Fatty Acid Metabolic Enzymes in a Rat Model. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.A.; Haider, A.; Mahmood, W.; Roome, T.; Abbas, G. Gamma-Linolenic Acid Ameliorated Glycation-Induced Memory Impairment in Rats. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 1817–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierno, S.; Camerino, G.M.; Cippone, V.; Rolland, J.F.; Desaphy, J.F.; de Luca, A.; Liantonio, A.; Bianco, G.; Kunic, J.D.; George, A.L.; et al. Statins and Fenofibrate Affect Skeletal Muscle Chloride Conductance in Rats by Differently Impairing ClC-1 Channel Regulation and Expression. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 156, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azemi, A.K.; Mokhtar, S.S.; Rasool, A.H.G. Clinacanthus Nutans Leaves Extract Reverts Endothelial Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Rats by Improving Protein Expression of ENOS. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oztürk, Z.; Gurpinar, T.; Vural, K.; Boyacıoglu, S.; Korkmaz, M.; Var, A. Effects of Selenium on Endothelial Dysfunction and Metabolic Profile in Low Dose Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats Fed a High Fat Diet. Biotech. Histochem. 2015, 90, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, Z.A.; Sahmat, A.; Azmi, A.H.; Nur Zainol, A.S.; Omar, M.H.; Balan, T.; Sulistyorini, L.; Azizah, R.; Abdullah, M.N.H. Polyphenolics and Triterpenes Presence in Chloroform Extract of Dicranopteris Linearis Leaves Attenuated Paracetamol-Induced Liver Intoxication in Rat. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omagari, K.; Suzuta, M.; Taniguchi, A.; Kumamoto, R.; Koyama, Y.; Fukuda, A.; Suruga, K.; Ichimura-Shimizu, M.; Tsuneyama, K. A Non-Obese, Diet-Induced Animal Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Wistar/ST Rats Compared to Sprague-Dawley Rats. Clin. Nutr. Exp. 2020, 30, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassir, F.; Rector, R.S.; Hammoud, G.M.; Ibdah, J.A. Pathogenesis and Prevention of Hepatic Steatosis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 11, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- O’Reilly, M.E.; Lenighan, Y.M.; Dillon, E.; Kajani, S.; Curley, S.; Bruen, R.; Byrne, R.; Heslin, A.M.; Moloney, A.P.; Roche, H.M.; et al. Conjugated Linoleic Acid and Alpha Linolenic Acid Improve Cholesterol Homeostasis in Obesity by Modulating Distinct Hepatic Protein Pathways. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, e1900599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.K.; Flintoff-Dye, N.; Omaye, S.T. Conjugated Linoleic Acid Modulation of Risk Factors Associated with Atherosclerosis. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 5, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banu, J.; Bhattacharya, A.; Rahman, M.; Fernandes, G. Beneficial Effects of Conjugated Linoleic Acid and Exercise on Bone of Middle-Aged Female Mice. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2008, 26, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaya, N.; Chen, S. Conjugated Linoleic Acid Reduces Body Weight Gain in Ovariectomized Female C57BL/6J Mice. Nutr. Res. 2010, 30, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munro, I.A.; Garg, M.L. Weight Loss and Metabolic Profiles in Obese Individuals Using Two Different Approaches. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzickova, J.; Rossmeisl, M.; Prazak, T.; Flachs, P.; Sponarova, J.; Vecka, M.; Tvrzicka, E.; Bryhn, M.; Kopecky, J. Omega-3 PUFA of marine origin limit diet-induced obesity in mice by reducing cellularity of adipose tissue. Lipids 2004, 39, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raclot, T.; Groscolas, R.; Langin, D.; Ferré, P. Site-Specific Regulation of Gene Expression by n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Rat White Adipose Tissues. J. Lipid Res. 1997, 38, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynés, B.; Palou, M.; Palou, A. Gene Expression Modulation of Lipid and Central Energetic Metabolism Related Genes by High-Fat Diet Intake in the Main Homeostatic Tissues. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 629–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taranto, M.P.; Medici, M.; Perdigon, G.; Ruiz Holgado, A.P.; Valdez, G.F. Evidence for Hypocholesterolemic Effect of Lactobacillus Reuteri in Hypercholesterolemic Mice. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 2336–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiruchenduran, M.; Vijayan, N.A.; Sawaminathan, J.K.; Devaraj, S.N. Protective Effect of Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins against Cholesterol Cholic Acid Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia in Rats. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2011, 20, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, W.; Binczek, E.; Schmidt-Soltau, I.; Brodesser, S.; Wegner, I. High Fat/High Cholesterol Diet Does Not Provoke Atherosclerosis in the Ω3-and Ω6-Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Synthesis–Inactivated Δ6-Fatty Acid Desaturase–Deficient Mouse. Mol. Metab. 2021, 54, 101335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gåfvels, M.; Rudling, M.; Murphy, C.; Björkhem, I.; Einarsson, C.; Eggertsen, G. Critical Role of Cholic Acid for Development of Hypercholesterolemia and Gallstones in Diabetic Mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 342, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spady, D.K.; Kearney, D.M.; Hobbs, H.H. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Up-Regulate Hepatic Scavenger Receptor B1 (SR-BI) Expression and HDL Cholesteryl Ester Uptake in the Hamster. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H. Black Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Reduces Obesity and Improves Lipid Metabolism in C57BL/6J Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schalkwijk, D.B.; Pasman, W.J.; Hendriks, H.F.J.; Verheij, E.R.; Rubingh, C.M.; van Bochove, K.; Vaes, W.H.J.; Adiels, M.; Freidig, A.P.; de Graaf, A.A. Dietary Medium Chain Fatty Acid Supplementation Leads to Reduced VLDL Lipolysis and Uptake Rates in Comparison to Linoleic Acid Supplementation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, C.B.; Amigo, N.; Wood, L.G.; Correig, X.; Garg, M.L. Effect of Diets Rich in Either Saturated Fat or N-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Supplemented with Long-Chain n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Plasma Lipoprotein Profiles. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.Q.; Li, Y.F.; Jiang, Z.L. Β3-Adrenoceptor Activation Upregulates Apolipoprotein A-I Expression in HepG2 Cells, Which Might Further Promote Cholesterol Efflux from Macrophage Foam Cells. Drug. Des. Devel. Ther. 2017, 11, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.J.; Hu, J.; Hu, Z.; Kraemer, F.B.; Azhar, S. Scavenger Receptor Class B Type i (SR-BI): A Versatile Receptor with Multiple Functions and Actions. Metabolism 2014, 63, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, K.; Inoue, N.; Wang, Y.M.; Shirouchi, B.; Yanagita, T. Dietary Conjugated Linoleic Acid Alleviates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Zucker (Fa/Fa) Rats. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Candido, C.J.; Figueiredo, P.S.; Silva, R.D.C.; Portugal, L.C.; Jaques, J.A.D.S.; de Almeida, J.A.; Penteado, B.d.B.; Dias, D.A.; Marcelino, G.; Pott, A.; et al. Protective Effect of α-Linolenic Acid on Non-Alcoholic Hepatic Steatosis and Interleukin-6 and -10 in Wistar Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeyapal, S.; Kona, S.R.; Mullapudi, S.V.; Putcha, U.K.; Gurumurthy, P.; Ibrahim, A. Substitution of Linoleic Acid with α-Linolenic Acid or Long Chain n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Prevents Western Diet Induced Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, E.A. Review on Liver Steatosis and Its Impact on Liver Transplantation. J. Liver Res. Disord. Ther. 2017, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Sub-Group | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Non-hypercholesterolemic | 1 | Control normal diet-fed rats (Control (ND)) |
| 2 | Normal diet-fed rats treated with 60 mg/kg daily of fenofibrate (ND + Fenofibrate) | |
| 3 | Normal diet-fed rats treated with 5 mg/kg daily of linoleic acid (ND + LA) | |
| Hypercholesterolemic | 1 | Control high-fat diet-fed rats (Control (HFD)) |
| 2 | High-fat diet-fed rats treated with 60 mg/kg daily of fenofibrate (HFD + Fenofibrate) | |
| 3 | High-fat diet-fed rats treated with 5 mg/kg daily of linoleic acid (HFD + LA) |
| Control | Fenofibrate (60 mg/kg) | Linoleic Acid (5 mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Diet | |||
| Initial body weight (Week 0), (g) | 269.40 ± 30.32 | 281.80 ± 16.09 | 273.30 ± 42.63 |
| Final body weight (Week 6), (g) | 291.40 ± 32.34 | 298.40 ± 20.53 | 293.90 ± 41.80 |
| High-fat diet | |||
| Initial body weight (Week 0), (g) | 278.10 ± 25.44 | 268.40 ± 11.99 | 267.90 ± 26.38 |
| Final body weight (Week 6), (g) | 339.90 ± 15.37 | 282.80 ± 6.25 * | 274.10 ± 23.92 ** |
| Normal diet | |||
| Liver weight (g) | 2.68 ± 0.76 | 3.55 ± 1.67 | 2.76 ± 0.38 |
| High-fat diet | |||
| Liver weight (g) | 3.24 ± 0.36 | 3.02 ± 0.58 | 2.99 ± 0.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azemi, N.A.; Azemi, A.K.; Abu-Bakar, L.; Sevakumaran, V.; Muhammad, T.S.T.; Ismail, N. Effect of Linoleic Acid on Cholesterol Levels in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia Rat Model. Metabolites 2023, 13, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010053
Azemi NA, Azemi AK, Abu-Bakar L, Sevakumaran V, Muhammad TST, Ismail N. Effect of Linoleic Acid on Cholesterol Levels in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia Rat Model. Metabolites. 2023; 13(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010053
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzemi, Nurul Adila, Ahmad Khusairi Azemi, Luqman Abu-Bakar, Vigneswari Sevakumaran, Tengku Sifzizul Tengku Muhammad, and Noraznawati Ismail. 2023. "Effect of Linoleic Acid on Cholesterol Levels in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia Rat Model" Metabolites 13, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010053
APA StyleAzemi, N. A., Azemi, A. K., Abu-Bakar, L., Sevakumaran, V., Muhammad, T. S. T., & Ismail, N. (2023). Effect of Linoleic Acid on Cholesterol Levels in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia Rat Model. Metabolites, 13(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010053







