Diesel Exhaust Particulates Enhances Susceptibility of LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury through Upregulation of the IL-17 Cytokine-Derived TGF-β1/Collagen I Expression and Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
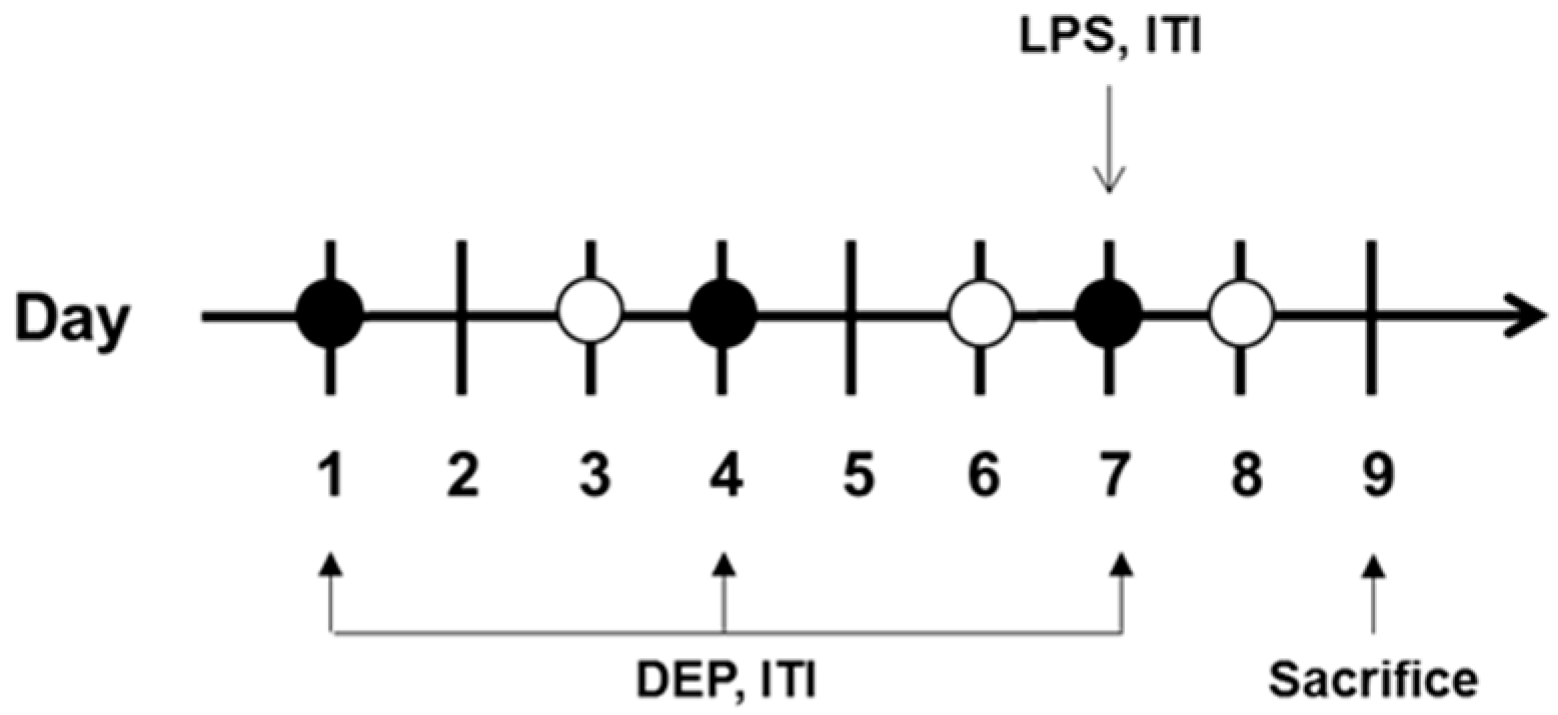
2.2. Study Protocol
2.3. DEP and LPS Instillation
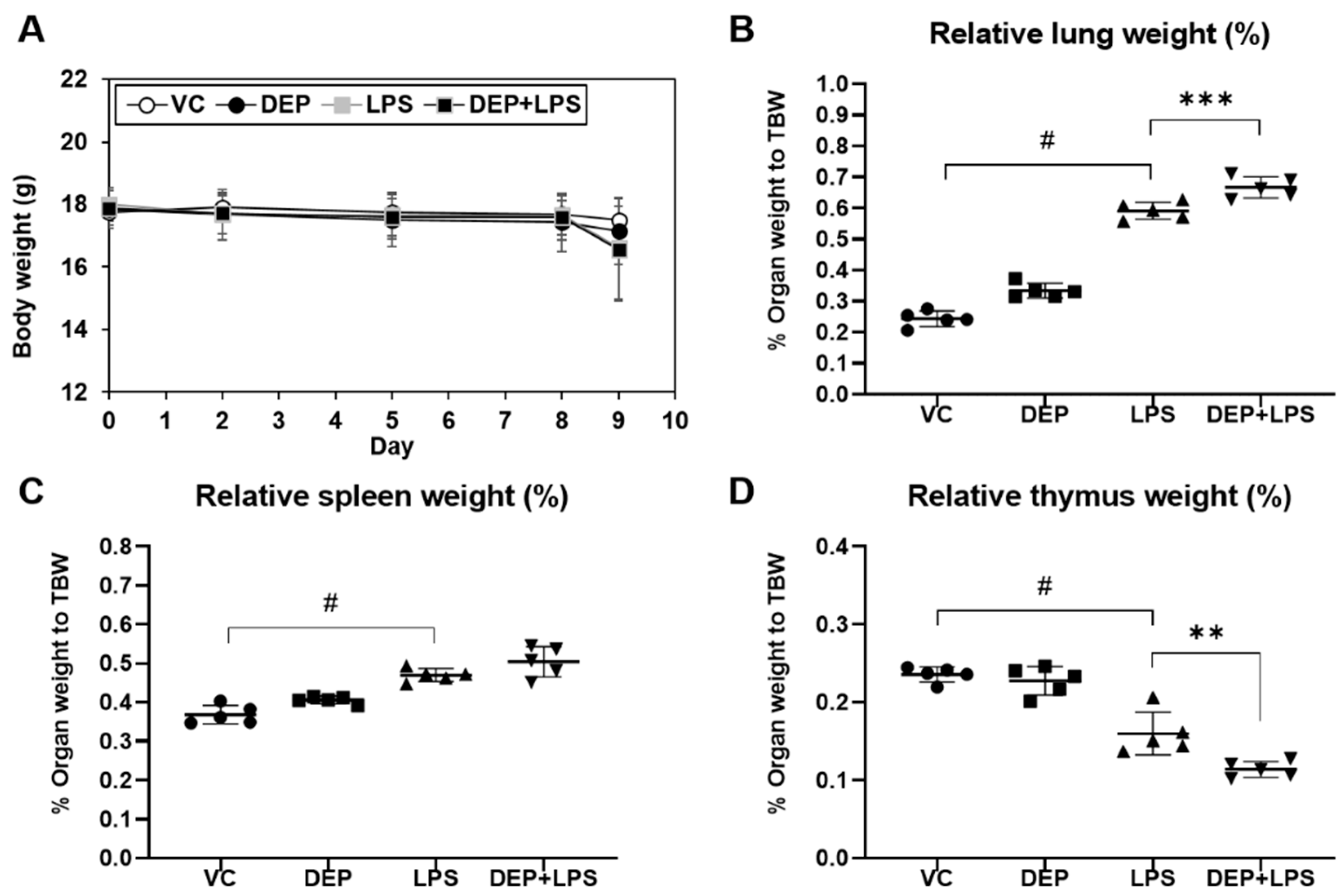
2.4. Measurement of Body and Organ Weights
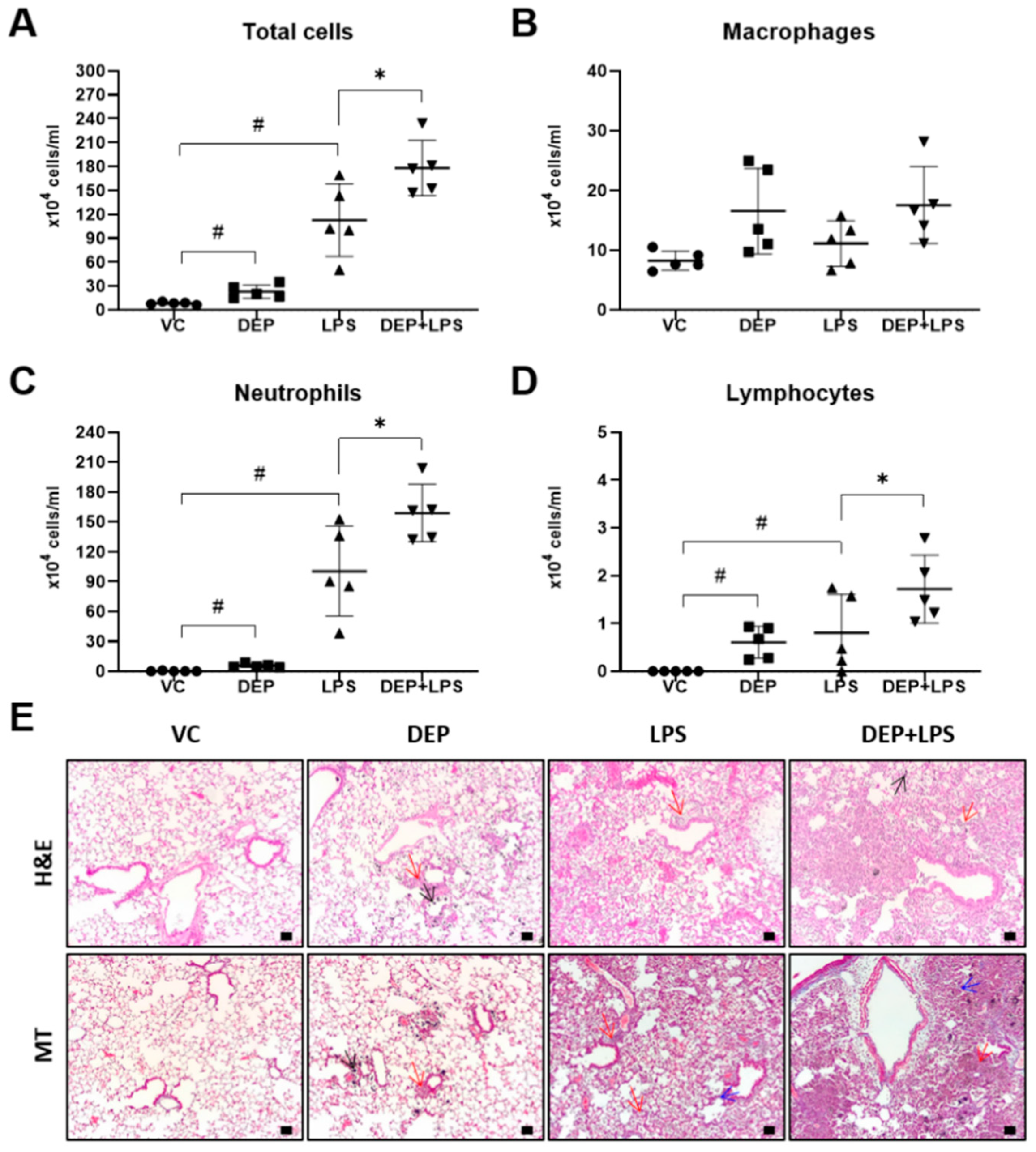
2.5. Preparation of BAL Fluid
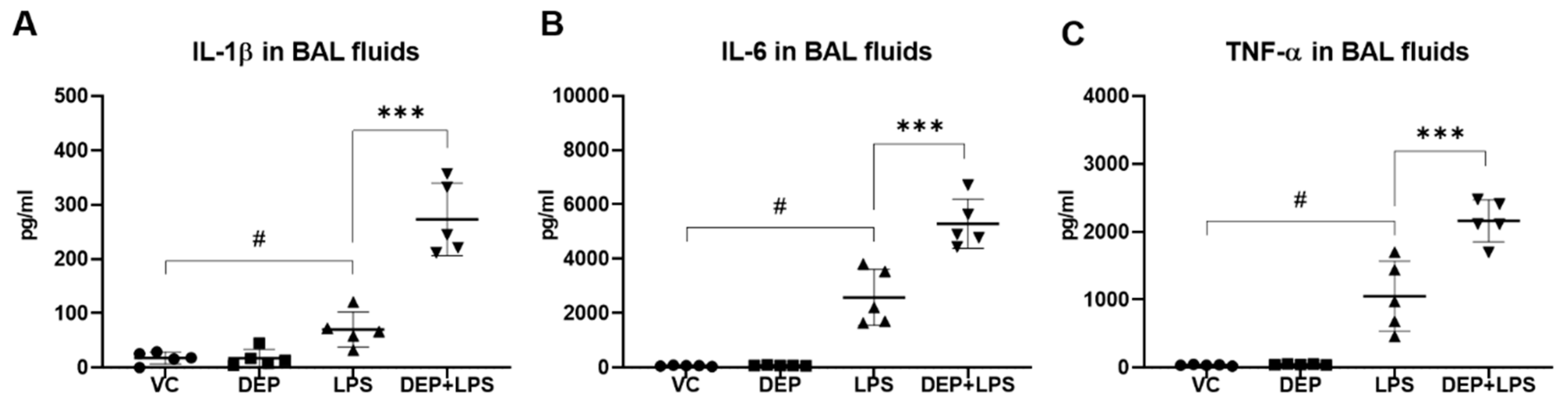
2.6. Measurement of Cytokine Levels
2.7. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.8. Preparation of Protein Extract and Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Body and Organ Weights
3.2. DEP Pre-Exposure Exacerbates LPS-Induced Acute Lung
3.3. DEP Pre-Exposure Upregulates Pro-Inflammatory Protein Expression in the BAL Fluid of LPS-Instilled Mice
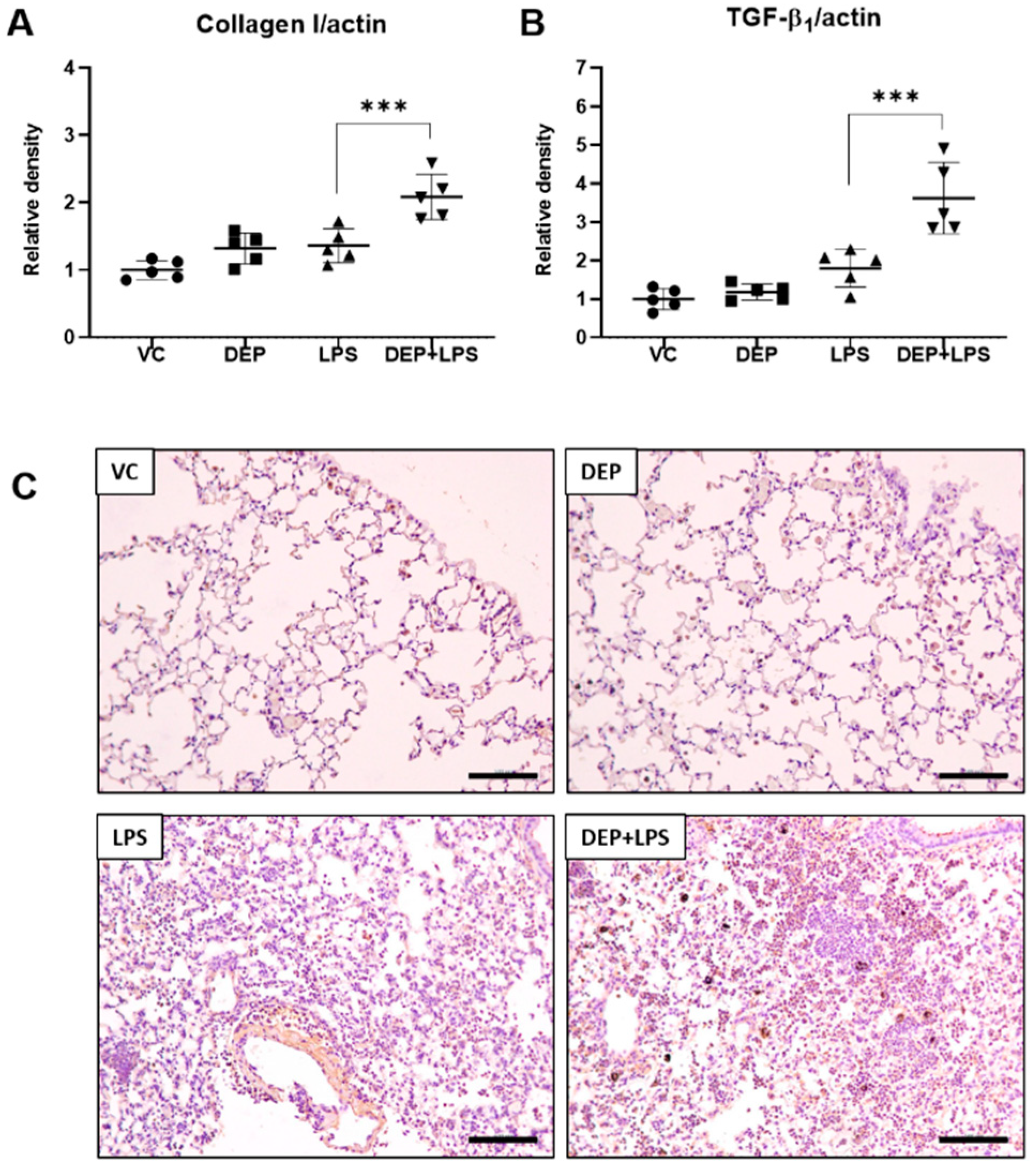
3.4. DEP Pre-Exposure Induces Lung Fibrosis by Upregulating Collagen I and TGF-β1 Protein Expression in LPS-Instilled Mice
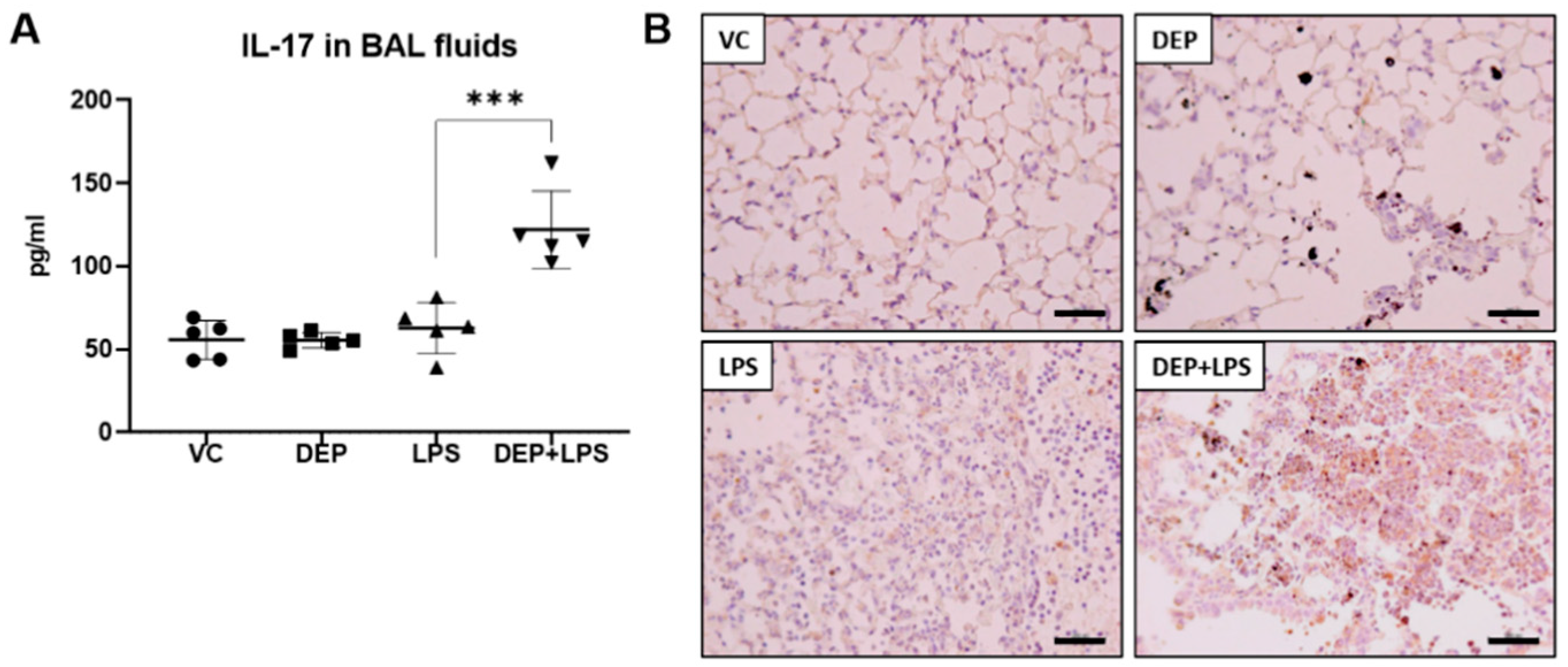
3.5. The Upregulation of IL-17 in the BAL Fluid Contributes to Fibrosis in the Lung of LPS-Instilled Mice Pre-Exposed to DEP
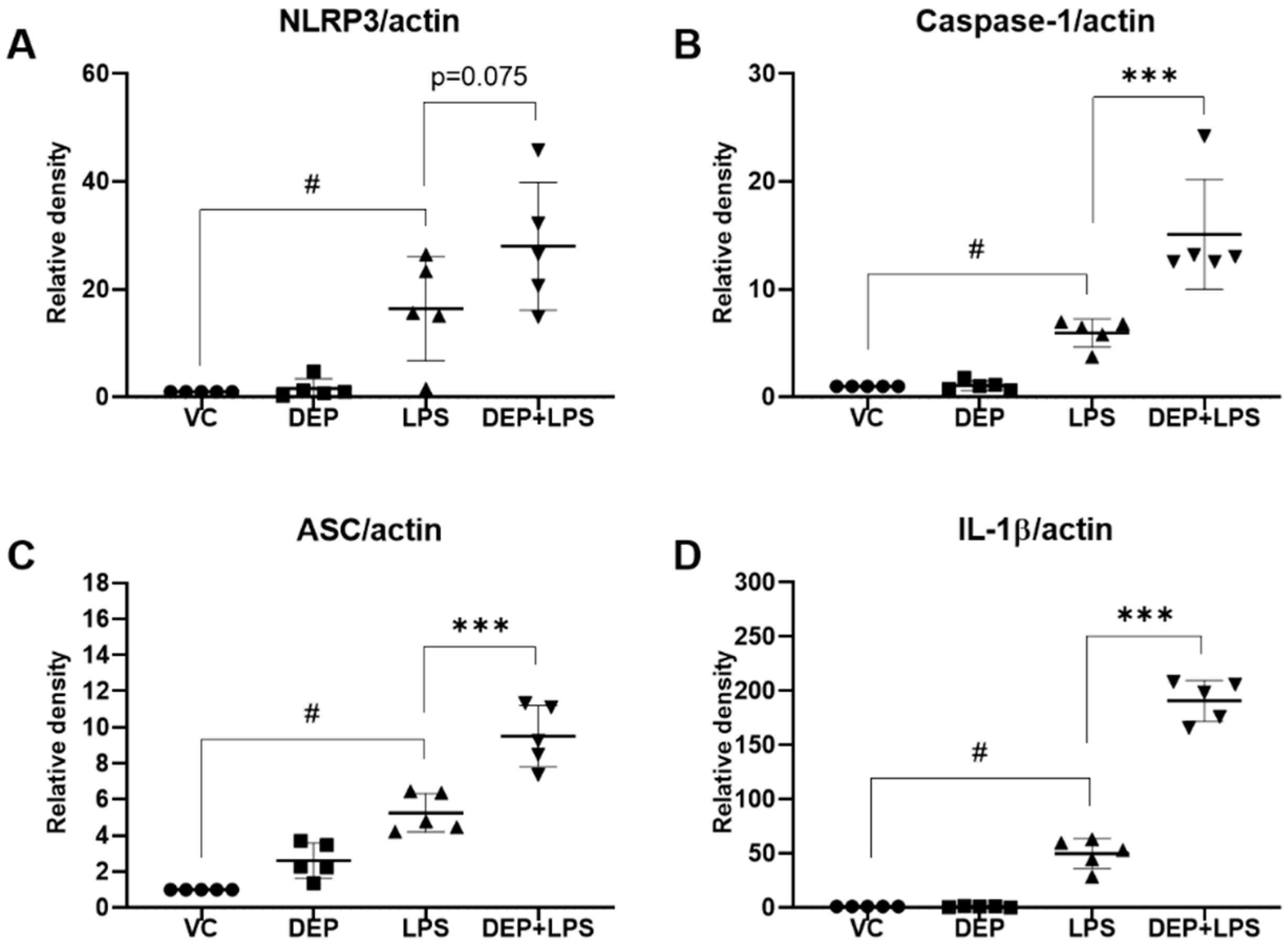
3.6. Effect of DEP Pre-Exposure on the NLRP3 Inflammasome in LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matthay, M.A.; Zemans, R.L.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Arabi, Y.M.; Beitler, J.R.; Mercat, A.; Herridge, M.; Randolph, A.G.; Calfee, C.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moazed, F.; Calfee, C.S. Environmental risk factors for ARDS. Clin. Chest Med. 2014, 35, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strosnider, H.M.; Chang, H.H.; Darrow, L.A.; Liu, Y.; Vaidyanathan, A.; Strickland, M.J. Age-specific associations of ozone and fine particulate matter with respiratory emergency department visits in the United States. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, F.; Gao, X.; Virzonis, D.; Damiati, S.; Schneider, M.R.; Kodzius, R. Air quality effects on human health and approaches for its assessment through microfluidic chips. Genes 2017, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Tao, J.; Kan, H.; Qian, Z.; Chen, A.; Du, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Ye, J.; et al. Ambient particulate matter air pollution associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome in Guangzhou, China. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, J.; Dominici, F.; Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J.; Wang, Y.; Di, Q.; Balmes, J.; Christiani, D.C. Impact of long-term exposures to ambient PM 2.5 and ozone on ARDS risk for older adults in the United States. Chest 2019, 156, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, J.P.; Zhao, Z.; Shashaty, M.G.S.; Koyama, T.; Christie, J.D.; Lanken, P.N.; Wang, C.; Balmes, J.R.; Matthay, M.A.; Calfee, C.S.; et al. Low to moderate air pollutant exposure and acute respiratory distress syndrome after severe trauma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, B.; McDermid, R.C.; Celi, L.A.; Walley, K.R.; Russell, J.A.; Boyd, J.H. Association between chronic exposure to air pollution and mortality in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Li, W.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, H. Exposure to particular matter increases susceptibility to respiratory Staphylococcus aureus infection in rats via reducing pulmonary natural killer cells. Toxicology 2014, 325, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigaud, S.; Goldsmith, C.W.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Z.; Fedulov, A.; Imrich, A.; Kobzik, L. Air pollution particles diminish bacterial clearance in the primed lungs of mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 223, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.M.; Antonini, J.M.; Barger, M.W.; Butterworth, L.; Roberts, B.R.; Ma, J.K.; Castranova, V.; Ma, J.Y. Diesel exhaust particles suppress macrophage function and slow the pulmonary clearance of Listeria monocytogenes in rats. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, R.; Takano, H.; Inoue, K.; Ichinose, T.; Sadakane, K.; Yoshino, S.; Yamaki, K.; Kumagai, Y.; Uchiyama, K.; Yoshikawa, T.; et al. Enhancement of acute lung injury related to bacterial endotoxin by components of diesel exhaust particles. Thorax 2003, 58, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takano, H.; Yanagisawa, R.; Ichinose, T.; Sadakane, K.; Yoshino, S.; Yoshikawa, T.; Morita, M. Diesel exhaust particles enhance lung injury related to bacterial endotoxin through expression of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and intercellular adhesion molecule-1. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, R.; Takano, H.; Inoue, K.; Ichinose, T.; Yoshida, S.; Sadakane, K.; Takeda, K.; Yoshino, S.; Yamaki, K.; Kumagai, Y.; et al. Complementary DNA microarray analysis in acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide and diesel exhaust particles. Exp. Biol. Med. 2004, 229, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurczynski, S.J.; Moore, B.B. IL-17 in the lung: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2018, 314, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artis, D.; Spits, H. The biology of innate lymphoid cells. Nature 2015, 517, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennard, S.I.; Fogarty, C.F.; Kelsen, S.; Long, W.; Ramsdell, J.; Allison, J.; Mahler, D.; Saadeh, C.; Siler, T.; Snell, P.; et al. The safety and efficacy of infliximab in moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mize, M.T.; Sun, X.L.; Simecka, J.W. Interleukin-17A exacerbates disease severity in BALB/c mice susceptible to lung infection with Mycoplasma pulmonis. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, e00292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseinian, N.; Cho, Y.; Lockey, R.F.; Kolliputi, N. The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in pulmonary diseases. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2015, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, R.; Tao, L.; Jian, H.; Chang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, H. NLRP3 inflammasome activation and lung fibrosis caused by airborne fine particulate matter. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Xie, M.; Wei, X. The NALP3 inflammasome is required for collagen synthesis via the NF-κB pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santos, G.D.; Kutuzov, M.A.; Ridge, K.M. The inflammasome in lung diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2012, 303, L627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, M.S.; Madala, S.K.; Ramalingam, T.R.; Gochuico, B.R.; Rosas, I.O.; Cheever, A.W.; Wynn, T.A. Bleomycin and IL-1–mediated pulmonary fibrosis is IL-17A dependent. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mi, S.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.P.; Ma, Y.G.; Wang, X.X.; Liu, H.Z.; Sun, W.; Hu, Z.W. Blocking IL-17A promotes the resolution of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis via TGF-b1–dependent and –independent mechanisms. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasse, P.; Riteau, N.; Vacher, R.; Michel, M.; Fautrel, A.; Padova, F.; Fick, L.; Charron, S.; Lagente, V.; Eberl, G.; et al. IL-1 and IL-23 mediate early IL-17A production in pulmonary inflammation leading to late fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrentraut, H.; Weisheit, C.K.; Frede, S.; Hilbert, T. Inducing acute lung injury in mice by direct intratracheal lipopolysaccharide instillation. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, M.; Kubo, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Ishizawa, K.; Numasaki, M.; Ueda, S.; Suzuki, T.; Sasaki, H. Bone marrow-derived progenitor cells are important for lung repair after lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury. J Immunol. 2004, 172, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bozinovski, S.; Jones, J.; Beavitt, S.; Cook, A.D.; Hamilton, J.A.; Anderson, G.P. Innate immune responses to LPS in mouse lung are suppressed and reversed by neutralization of GM-CSF via repression of TLR-4. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2004, 286, L877–L885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Du, J. Anti-inflammatory and protective effects of D-carvone on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury in mice. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 1592–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.I.; Song, M.K.; Kim, S.H.; Park, C.Y.; Lee, K. TF-343 alleviates diesel exhaust particulate-induced lung inflammation via modulation of nuclear factor-κB signaling. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 8315845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.I.; Song, M.K.; Kim, H.I.; Han, K.M.; Lee, K. Diesel exhaust particulates induce neutrophilic lung inflammation by modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated CXCL1/KC expression in alveolar macrophages. Molecules 2020, 25, 6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renne, R.; Brix, A.; Harkema, J.; Herbert, R.; Kittel, B.; Lewis, D.; March, T.; Nagano, K.; Pino, M.; Rittinghausen, S.; et al. Proliferative and non-proliferative lesions of the rat and mouse respiratory tract. Toxicol. Pathol. 2009, 37, 5S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashcroft, T.; Simpson, J.M.; Timbrell, V. Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J. Clin. Pathol. 1988, 41, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fedchenko, N.; Reifenrath, J. Different approaches for interpretation and reporting of immunohistochemistry analysis results in the bone tissue—A review. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butt, Y.; Kurdowska, A.; Allen, T.C. Acute lung injury: A clinical and molecular review. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2016, 140, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forrest, O.A.; Ingersoll, S.A.; Preininger, M.K.; Laval, J.; Limoli, D.H.; Brown, M.R.; Lee, F.E.; Bedi, B.; Sadikot, R.T.; Goldberg, J.B.; et al. Frontline science: Pathological conditioning of human neutrophils recruited to the airway milieu in cystic fibrosis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 104, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.M.; Gray, R.D. Neutrophil extracellular traps and the dysfunctional innate immune response of cystic fibrosis lung disease: A review. J. Inflamm. 2017, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Balakrishnan, L.; Datta, K.K.; Sahasrabuddhe, N.A.; Khan, A.A.; Sahu, A.; Singhal, A.; Getnet, D.; Raju, R.; Chatterjee, A.; et al. A knowledgebase resource for interleukin-17 family mediated signaling. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2015, 9, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, E.; Peng, N.; Xiao, F.; Hu, D.; Wang, X.; Lu, L. The roles of immune cells in the pathogenesis of fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Mark, R. IL-17 in lung disease: Friend or foe? Thorax 2013, 68, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Ramli, W.; Préfontaine, D.; Chouiali, F.; Martin, J.G.; Olivenstein, R.; Lemière, C.; Hamid, Q. T(H)17-associated cytokines (IL-17A and IL-17F) in severe asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; de Vleeschauwer, S.I.; Vos, R.; Meyts, I.; Bullens, D.M.; Reynders, V.; Wuyts, W.A.; Raemdonck, D.E.V.; Dupont, L.J.; Verleden, G.M. The role of the IL23/IL17 axis in bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, J.; Meng, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, H.; Wang, R. NLRP3 participates in the regulation of EMT in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 357, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togbe, D.; Besnard, A.; Madouri, F.; Couillin, I.; Gombault, A.; Baron, L.; Froux, N.; Maillard, A.; Erard, F.; Snick, J.V.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation leading to IL-1–IL-17 dependent lung inflammation and fibrosis. Curr. Respir. Med. Rev. 2014, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayan, M.; Mossman, B.T. The NLRP3 inflammasome in pathogenic particle and fibre-associated lung inflammation and diseases. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Group | VC | DEP | LPS | DEP + LPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black pigmented macrophages | 0 | 3.2 ± 0.45 ## | 0 | 3.4 ± 0.55 ** |
| Granulomatous inflammation/pulmonary fibrosis | 0 | 0.4 ± 0.55 | 0.4 ± 0.55 | 1.8 ± 0.45 ** |
| Acute inflammation, alveolar/interstitial | 0 | 0 | 2.6 ± 1.52 ## | 3.8 ± 0.45 |
| Infiltrate, neutrophilic cells, alveolar | 0 | 0 | 3.2 ± 0.84 ## | 3.6 ± 0.55 |
| Group | VC | DEP | LPS | DEP + LPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-17A | 0 | 0 | 1.2 ± 0.71 | 2.2 ± 0.45 ** |
| TGF-β1 | 0 | 0.2 ± 0.45 | 0.2 ± 0.45 | 3.4 ± 0.55 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.I.; Song, M.-K.; Lee, K. Diesel Exhaust Particulates Enhances Susceptibility of LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury through Upregulation of the IL-17 Cytokine-Derived TGF-β1/Collagen I Expression and Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling in Mice. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11010067
Kim DI, Song M-K, Lee K. Diesel Exhaust Particulates Enhances Susceptibility of LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury through Upregulation of the IL-17 Cytokine-Derived TGF-β1/Collagen I Expression and Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling in Mice. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(1):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11010067
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Dong Im, Mi-Kyung Song, and Kyuhong Lee. 2021. "Diesel Exhaust Particulates Enhances Susceptibility of LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury through Upregulation of the IL-17 Cytokine-Derived TGF-β1/Collagen I Expression and Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling in Mice" Biomolecules 11, no. 1: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11010067
APA StyleKim, D. I., Song, M.-K., & Lee, K. (2021). Diesel Exhaust Particulates Enhances Susceptibility of LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury through Upregulation of the IL-17 Cytokine-Derived TGF-β1/Collagen I Expression and Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling in Mice. Biomolecules, 11(1), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11010067




