Mucoadhesive Rifampicin-Liposomes for the Treatment of Pulmonary Infection by Mycobacterium abscessus: Chitosan or ε-Poly-L-Lysine Decoration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Liposomes and Polymer-Decorated Liposomes
2.3. Determination of Drug Entrapment and In Vitro Drug Release
2.4. Size and ζ-Potential Measurements
2.5. Bilayer Characterization by DPH Fluorescence Anisotropy
2.6. Preparation of Mucin Solution and Mucoadhesive Studies
2.7. Morphological Investigation
2.8. Biological Evaluation
2.8.1. Bacterial Strains
2.8.2. Cell Line
2.8.3. Infection with Mabs
2.8.4. Stability of Liposomes in Culture Medium
2.8.5. Uptake of Liposomes in dTHP-1 Cells
2.8.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of Liposomes
3.2. Mucoadhesion Study
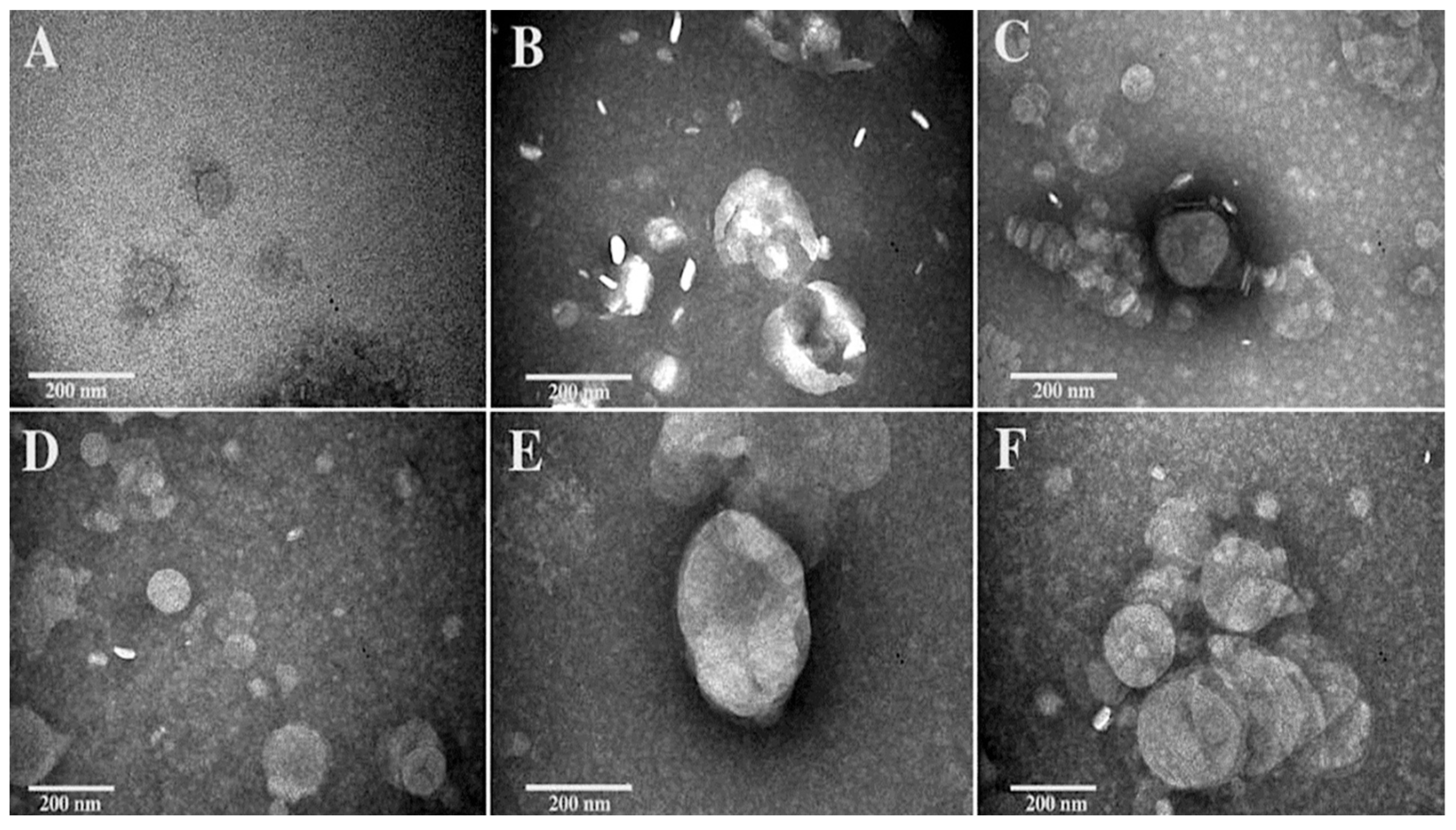
3.3. Morphological Investigation
3.4. Stability Studies
3.5. Release Studies
3.6. Biological Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Post Nebulization Studies
| Sample | DH ± SD (nm) | PDI ± SD | ζ-pot ± SD (mV) | E.E. % | Anisotropy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LipoRIF pre | 117 ± 2 | 0.22 ± 0.08 | −42 ± 2 | 96± 2 | 0.30 ± 0.01 |
| LipoRIF post | 114 ± 1 | 0.29 ± 0.04 | −47 ± 1 | 94 ± 1 | 0.33 ± 0.01 |
| LipoRIF + Chit pre | 277 ± 6 | 0.25 ± 0.04 | −32 ± 2 | 95 ± 1 | 0.37 ± 0.01 |
| LipoRIF + Chit post | 283 ± 23 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | −30 ± 2 | 92± 1 | 0.33 ± 0.01 |
| LipoRIF + ε-PLL pre | 150 ± 3 | 0.23 ± 0.07 | −37 ± 1 | 95 ± 2 | 0.32 ± 0.01 |
| LipoRIF + ε-PLL post | 146 ± 2 | 0.29 ± 0.04 | −40 ± 1 | 91 ± 1 | 0.36 ± 0.01 |

Appendix A.2. Mucoadhesion Studies

Appendix B
Biological Evaluation of Chit-Decorated Rifampicin-Liposomes

References
- Victoria, L.; Gupta, A.; Gómez, J.L.; Robledo, J. Mycobacterium Abscessus Complex: A Review of Recent Developments in an Emerging Pathogen. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 659997. [Google Scholar]
- Marianecci, C.; Marzio, L.D.; Rinaldi, F.; Carafa, M.; Alhaique, F. Pulmonary Delivery: Innovative Approaches and Perspectives. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 2, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, J.D.; van Ingen, J.; van der Laan, R.; Herrmann, J.-L. Liposomal Drug Delivery to Manage Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Disease and Other Chronic Lung Infections. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apolinario, A.C.; Hauschke, L.; Nunes, J.R.; Lopes, L.B. Lipid Nanovesicles for Biomedical Applications: ‘What Is in a Name’? Prog. Lipid Res. 2021, 82, 101096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, S.J.; Neville, M.E.; Gupta, R.; Bermudez, L.E. Delivery of Aerosolized Liposomal Amikacin as a Novel Approach for the Treatment of Nontuberculous Mycobacteria in an Experimental Model of Pulmonary Infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, J.S.; Devi, V.K.; Devi, K.; Sarasija, S. A Novel Approach for Lung Delivery of Rifampicin-Loaded Liposomes in Dry Powder Form for the Treatment of Tuberculosis. Lung India 2015, 32, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaru, M.; Sinico, C.; De Logu, A.; Caddeo, C.; Lai, F.; Manca, M.L.; Fadda, A.M. Rifampicin-Loaded Liposomes for the Passive Targeting to Alveolar Macrophages: In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. J. Liposome Res. 2009, 19, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemarchand, C.; Gref, R.; Couvreur, P. Polysaccharide-Decorated Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, P.L.; McKenzie, I.F.C. Mucins: Structure, Function, and Associations with Malignancy. BioEssays 1992, 14, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Suk, J.S. Enhancing Nanoparticle Penetration through Airway Mucus to Improve Drug Delivery Efficacy in the Lung. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guan, J.; Qin, L.; Zhang, X.; Mao, S. Physicochemical Properties Affecting the Fate of Nanoparticles in Pulmonary Drug Delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.D.; Nöjd, S.; Edman, M.; Lindell, K.; Topgaard, D.; Wahlgren, M. Mucoadhesion: Mucin-Polymer Molecular Interactions. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 610, 121245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, J.D. The Basics and Underlying Mechanisms of Mucoadhesion. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.R.; Muzzarelli, R.; Muzzarelli, C.; Sashiwa, H.; Domb, A.J. Chitosan Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Perspectives. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6017–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehr, C.-M.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Schacht, E.H.; Junginger, H.E. In Vitro Evaluation of Mucoadhesive Properties of Chitosan and Some Other Natural Polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 78, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkomy, M.H.; Ali, A.A.; Eid, H.M. Chitosan on the Surface of Nanoparticles for Enhanced Drug Delivery:A Comprehensive Review. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 923–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Dutta, J.; Dutta, P.K.; Koh, J. A Systematic Study on Chitosan-Liposome Based Systems for Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Huang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C. Recent Advances in Epsilon-Poly-L-Lysine and L-Lysine-Based Dendrimer Synthesis, Modification, and Biomedical Applications. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 659304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Nagasawa, T. ε-Poly-l-Lysine: Microbial Production, Biodegradation and Application Potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 62, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Shi, Y.; Xing, B.; Hou, Y.; Cui, J.; Jia, S. The Antimicrobial Effects and Mechanism of ε-Poly-Lysine against Staphylococcus Aureus. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2019, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, S.; Matsuoka, H.; Iwamoto, T.; Sakai, H. Antimicrobial Action of ε-Poly-L-Lysine. J. Antibiot. 1984, 37, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, I.-L.; Shen, M.-H.; Van, Y.-T. Microbial Synthesis of Poly(ε-Lysine) and Its Various Applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Korolev, N.; Eom, K.D.; Tam, J.P.; Nordenskiöld, L. Design and Biophysical Characterization of Novel Polycationic ϵ-Peptides for DNA Compaction and Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2007, 9, 321–330. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/bm700882g (accessed on 21 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- Gad, A.E.; Silver, B.L.; Eytan, G.D. Polycation-Induced Fusion of Negatively-Charged Vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1982, 690, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Sun, M.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yang, Z.; Jiao, X. ε-Polylysine-Coated Liposomes Loaded with a β-CD Inclusion Complex Loaded with Carvacrol: Preparation, Characterization, and Antibacterial Activities. LWT 2021, 146, 111422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennato, S.; Bordi, F.; Cametti, C.; Marianecci, C.; Carafa, M.; Cametti, M. Hybrid Niosome Complexation in the Presence of Oppositely Charged Polyions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 3720–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrati, C.; Marianecci, C.; Sennato, S.; Carafa, M.; Bordoni, V.; Cimini, E.; Tempestilli, M.; Pucillo, L.P.; Turchi, F.; Martini, F.; et al. Multicompartment Vectors as Novel Drug Delivery Systems: Selective Activation of Tγδ Lymphocytes after Zoledronic Acid Delivery. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2011, 7, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Bao, H. Rapidly in Situ Forming Chitosan/ε-Polylysine Hydrogels for Adhesive Sealants and Hemostatic Materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, F.; Hanieh, P.N.; Sennato, S.; De Santis, F.; Forte, J.; Fraziano, M.; Casciardi, S.; Marianecci, C.; Bordi, F.; Carafa, M. Rifampicin–Liposomes for Mycobacterium Abscessus Infection Treatment: Intracellular Uptake and Antibacterial Activity Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaru, M.; Manca, M.-L.; Fadda, A.M.; Antimisiaris, S.G. Chitosan-Coated Liposomes for Delivery to Lungs by Nebulisation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 71, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Peters, J.I.; Williams, R.O. Inhaled Nanoparticles—A Current Review. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 356, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Yin, S.; Xu, L.; Ma, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, G.; Li, J. Polylysine and Cysteine Functionalized Chitosan Nanoparticle as an Efficient Platform for Oral Delivery of Paclitaxel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraki, J. ε-Polylysine; Its Development and Utilization. Fine Chem. 2000, 29, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Koppel, D.E. Analysis of Macromolecular Polydispersity in Intensity Correlation Spectroscopy: The Method of Cumulants. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 57, 4814–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.J. Zeta Potential in Colloid Science: Principles and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4832-1408-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo, D.; Kiselev, M.A. Methods of Liposomes Preparation: Formation and Control Factors of Versatile Nanocarriers for Biomedical and Nanomedicine Application. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, F.; Hanieh, P.N.; Imbriano, A.; Passeri, D.; Del Favero, E.; Rossi, M.; Marianecci, C.; De Panfilis, S.; Carafa, M. Different Instrumental Approaches to Understand the Chitosan Coated Niosomes/Mucin Interaction. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poerio, N.; Riva, C.; Olimpieri, T.; Rossi, M.; Lorè, N.I.; De Santis, F.; Henrici De Angelis, L.; Ciciriello, F.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Lucidi, V.; et al. Combined Host- and Pathogen-Directed Therapy for the Control of Mycobacterium Abscessus Infection. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02546-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poerio, N.; Caccamo, N.R.; La Manna, M.P.; Olimpieri, T.; De Angelis, L.H.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Dieli, F.; Fraziano, M. Phosphatidylserine Liposomes Reduce Inflammatory Response, Mycobacterial Viability, and HIV Replication in Coinfected Human Macrophages. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 1675–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordi, F.; Sennato, S.; Truzzolillo, D. Polyelectrolyte-Induced Aggregation of Liposomes: A New Cluster Phase with Interesting Applications. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 203102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index on the Clinical Applications of Lipidic Nanocarrier Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinitzky, M.; Barenholz, Y. Fluidity Parameters of Lipid Regions Determined by Fluorescence Polarization. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Biomembr. 1978, 515, 367–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Xue, J.; Eric, K.; Feng, B.; Zhang, X.; Xia, S. Dual Effects of Chitosan Decoration on the Liposomal Membrane Physicochemical Properties As Affected by Chitosan Concentration and Molecular Conformation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6901–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, F.; Oliva, A.; Sabatino, M.; Imbriano, A.; Hanieh, P.N.; Garzoli, S.; Mastroianni, C.M.; De Angelis, M.; Miele, M.C.; Arnaut, M.; et al. Antimicrobial Essential Oil Formulation: Chitosan Coated Nanoemulsions for Nose to Brain Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.M.G.; Taylor, G.; Kellaway, I.W.; Stevens, J. The Stability of Liposomes to Nebulisation. Int. J. Pharm. 1990, 58, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niven, R.W.; Schreier, H. Nebulization of Liposomes. I. Effects of Lipid Composition. Pharm. Res. 1990, 7, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhissi, A.M.A.; Giebultowicz, J.; Stec, A.A.; Wroczynski, P.; Ahmed, W.; Alhnan, M.A.; Phoenix, D.; Taylor, K.M.G. Nebulization of Ultradeformable Liposomes: The Influence of Aerosolization Mechanism and Formulation Excipients. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaru, M.; Mourtas, S.; Klepetsanis, P.; Fadda, A.M.; Antimisiaris, S.G. Liposomes for Drug Delivery to the Lungs by Nebulization. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, M.L.; Sinico, C.; Maccioni, A.M.; Diez, O.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M. Composition Influence on Pulmonary Delivery of Rifampicin Liposomes. Pharmaceutics 2012, 4, 590–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, G.; Motta, S.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Brocca, P.; Rossi, S.; Ferrari, F.; Rondelli, V.; Cantù, L.; Caramella, C.; Del Favero, E. Chitosan-Coupled Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Tuning Nanostructure and Mucoadhesion. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 110, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, A.A.; Morgan, J.T.; Brown, P.H.; Adams, A.; Jayasekara, M.P.S.; Zhang, G.; Ackerson, C.J.; Kruhlak, M.J.; Leapman, R.D. Synthesis, Characterization, and Direct Intracellular Imaging of Ultrasmall and Uniform Glutathione-Coated Gold Nanoparticles. In Small; Sousa-Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/smll.201200071 (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Talmon, Y. Staining and Drying-Induced Artifacts in Electron Microscopy of Surfactant Dispersions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1983, 93, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jass, J.; Tjärnhage, T.; Puu, G. From Liposomes to Supported, Planar Bilayer Structures on Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Surfaces: An Atomic Force Microscopy Study. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 3153–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignataro, B.; Steinem, C.; Galla, H.-J.; Fuchs, H.; Janshoff, A. Specific Adhesion of Vesicles Monitored by Scanning Force Microscopy and Quartz Crystal Microbalance. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reviakine, I.; Brisson, A. Formation of Supported Phospholipid Bilayers from Unilamellar Vesicles Investigated by Atomic Force Microscopy. Langmuir 2000, 16, 1806–1815. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/la9903043 (accessed on 21 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- Dobrynin, A.; Deshkovski, A.; Rubinstein, M. Adsorption of Polyelectrolytes at Oppositely Charged Surfaces. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 3421–3436. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/ma0013713 (accessed on 26 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Ukidve, A.; Krishnan, V.; Mitragotri, S. Effect of Physicochemical and Surface Properties on in Vivo Fate of Drug Nanocarriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 143, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.H.T.; Santos, N.G.; Alves, J.P.H.; Garcia, C.A.B.; Romão, L.C.P.; Arguelho, M.L.P.M. Evaluation of the Physico-Chemical Properties of Chitosan as a Potential Carrier for Rifampicin, Using Voltammetric and Spectrophotometric Techniques. Bioelectrochemistry 2008, 72, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.C.; Reis, R.L.; Ferreira, H.; Neves, N.M. Cellular Uptake of Three Different Nanoparticles in an Inflammatory Arthritis Scenario versus Normal Conditions. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 3235–3246. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.1c00066 (accessed on 26 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.L.; Hanson, R.J. Solving Least Squares Problems; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1974; p. 263. [Google Scholar]





| Sample | DPPG mg/mL | HSPC mg/mL | RIF mg/mL | Chit mg/mL | εPLL mg/mL | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LipoRIF | 5 | 5 | 5 | - | - | 7.40 ± 0.01 |
| LipoRIF + Chit | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 0.037 | - | 5.90 ± 0.01 |
| LipoRIF + ε-PLL | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | - | 0.05 | 6.10 ± 0.01 |
| Sample | DH ± SD (nm) | PDI ± SD | ζ-pot ± SD (mV) | E.E. % | Anisotropy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LipoRIF | 117 ± 2 | 0.22 ± 0.08 | −2 ± 2 | 96 ± 2 | 0.34 ± 0.02 |
| LipoRIF + Chit | 277 ± 6 | 0.25 ± 0.04 | −32 ± 2 | 95 ± 1 | 0.37 ± 0.01 |
| LipoRIF + ε-PLL | 150 ± 3 | 0.23 ± 0.07 | −37 ± 1 | 95 ± 2 | 0.32 ± 0.01 |
| Sample | DH± SD (nm) | PDI± SD | ζ-pot ± SD (mV) | ∆A | ∆A % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LipoRIF + M | 161 ± 1 | 0.41 ± 0.02 | −14 ±1 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 8.0 ± 0.2 |
| LipoRIF + Chit + M | 361 ±3 | 0.41 ± 0.02 | −16 ± 1 | 0.31 ± 0.01 | 77.0 ± 0.5 |
| LipoRIF + ε-PLL + M | 230 ± 3 | 0.36 ± 0.04 | −18 ± 1 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 55.0 ± 0.5 |
| Mucin (M) | 1623 ± 60 | 0.45 ± 0.08 | −16 ± 1 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forte, J.; Hanieh, P.N.; Poerio, N.; Olimpieri, T.; Ammendolia, M.G.; Fraziano, M.; Fabiano, M.G.; Marianecci, C.; Carafa, M.; Bordi, F.; et al. Mucoadhesive Rifampicin-Liposomes for the Treatment of Pulmonary Infection by Mycobacterium abscessus: Chitosan or ε-Poly-L-Lysine Decoration. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060924
Forte J, Hanieh PN, Poerio N, Olimpieri T, Ammendolia MG, Fraziano M, Fabiano MG, Marianecci C, Carafa M, Bordi F, et al. Mucoadhesive Rifampicin-Liposomes for the Treatment of Pulmonary Infection by Mycobacterium abscessus: Chitosan or ε-Poly-L-Lysine Decoration. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(6):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060924
Chicago/Turabian StyleForte, Jacopo, Patrizia Nadia Hanieh, Noemi Poerio, Tommaso Olimpieri, Maria Grazia Ammendolia, Maurizio Fraziano, Maria Gioia Fabiano, Carlotta Marianecci, Maria Carafa, Federico Bordi, and et al. 2023. "Mucoadhesive Rifampicin-Liposomes for the Treatment of Pulmonary Infection by Mycobacterium abscessus: Chitosan or ε-Poly-L-Lysine Decoration" Biomolecules 13, no. 6: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060924
APA StyleForte, J., Hanieh, P. N., Poerio, N., Olimpieri, T., Ammendolia, M. G., Fraziano, M., Fabiano, M. G., Marianecci, C., Carafa, M., Bordi, F., Sennato, S., & Rinaldi, F. (2023). Mucoadhesive Rifampicin-Liposomes for the Treatment of Pulmonary Infection by Mycobacterium abscessus: Chitosan or ε-Poly-L-Lysine Decoration. Biomolecules, 13(6), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060924











