A Simple and Efficient One-Step Synthesis System for Flexible Production of Circular RNA in E. coli
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
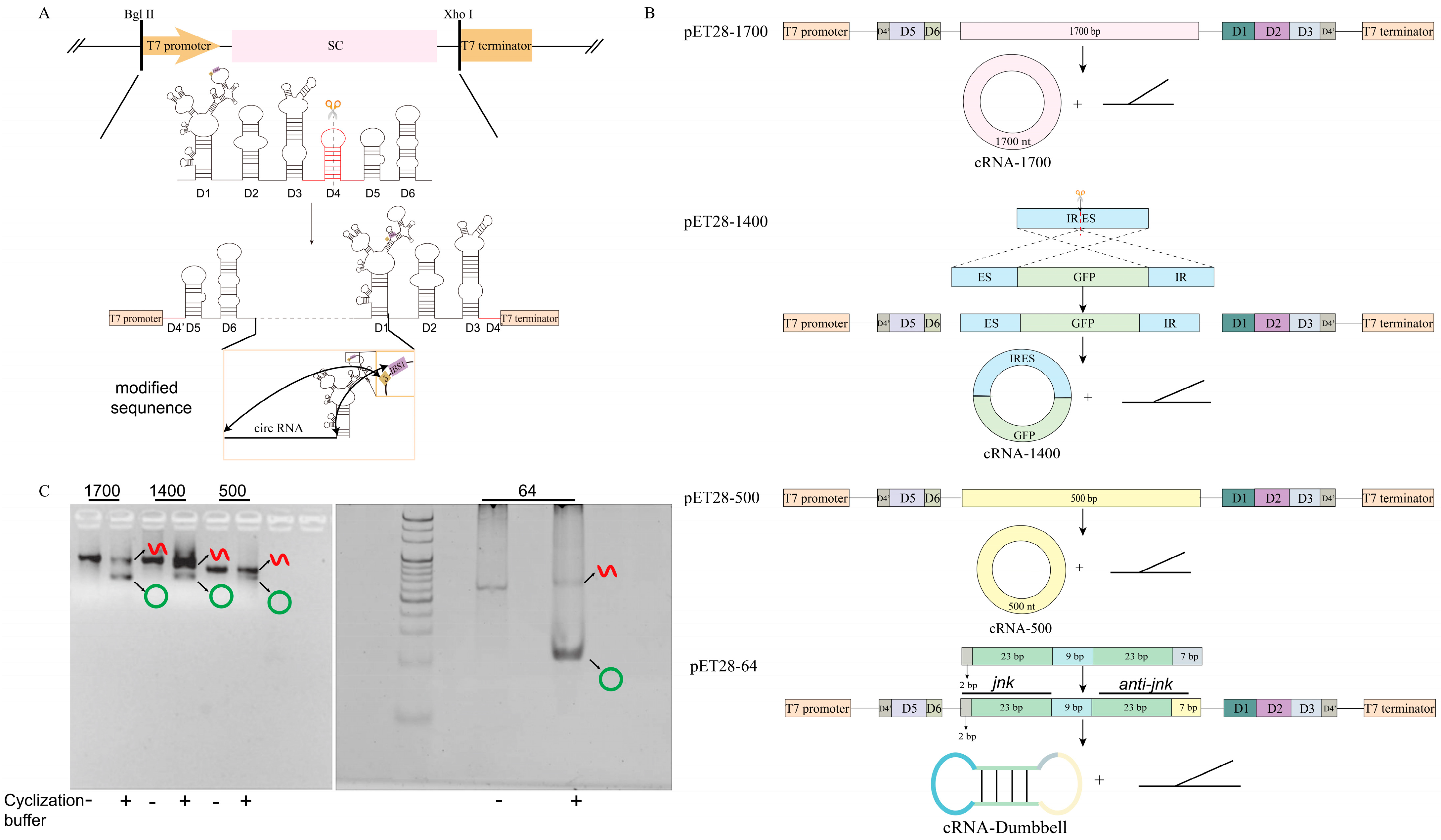
2.1. Vector Construction
2.2. In Vitro Transcription (IVT) and Circularization of RNA
2.3. Establishment and Optimization of In Vivo Circular RNA (circRNA) Production System
2.3.1. Establishment of the Expression Strain System
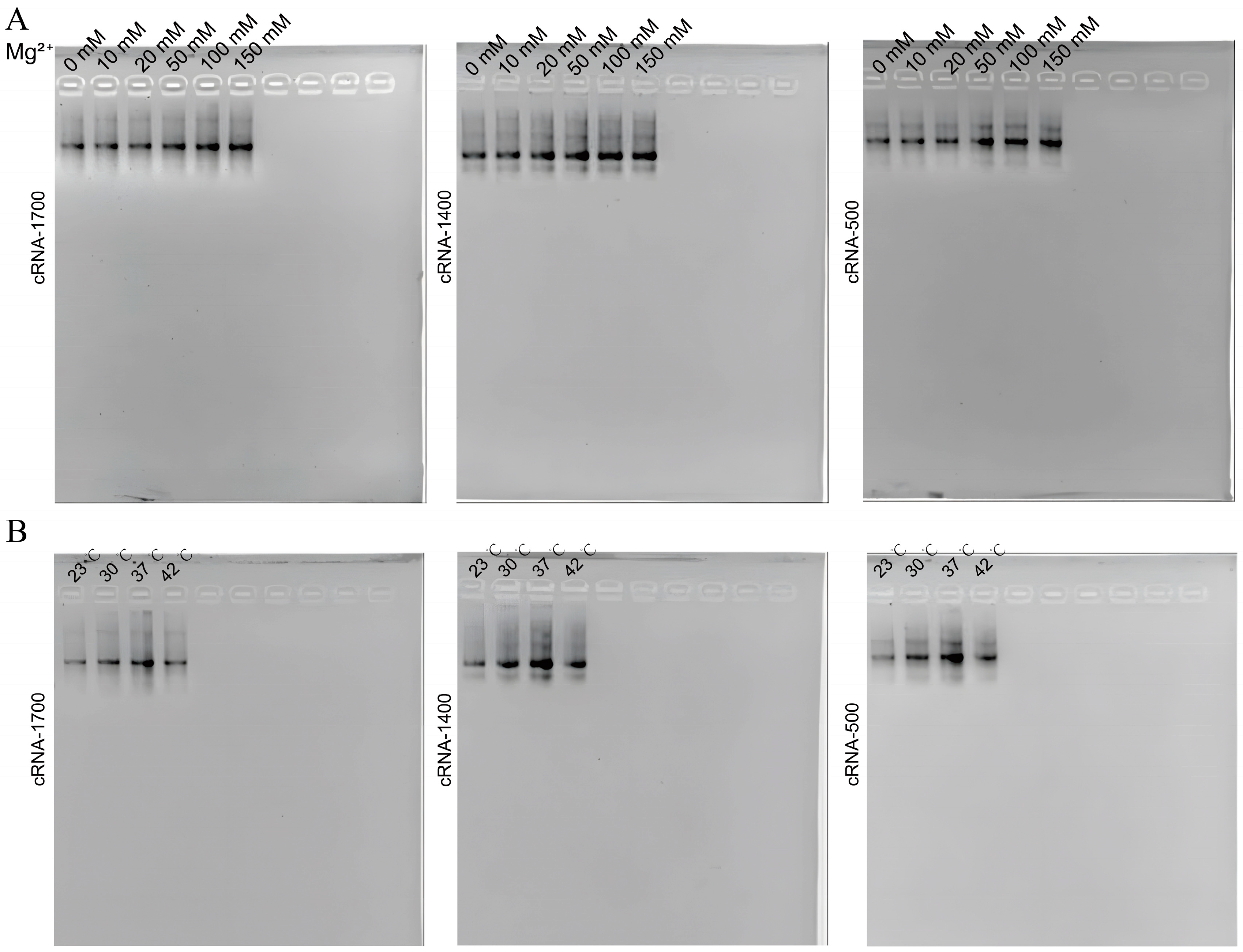
2.3.2. Extraction Solution Exploration
2.3.3. Exploration of Culture Medium Components
2.3.4. Exploration of Induction Temperature
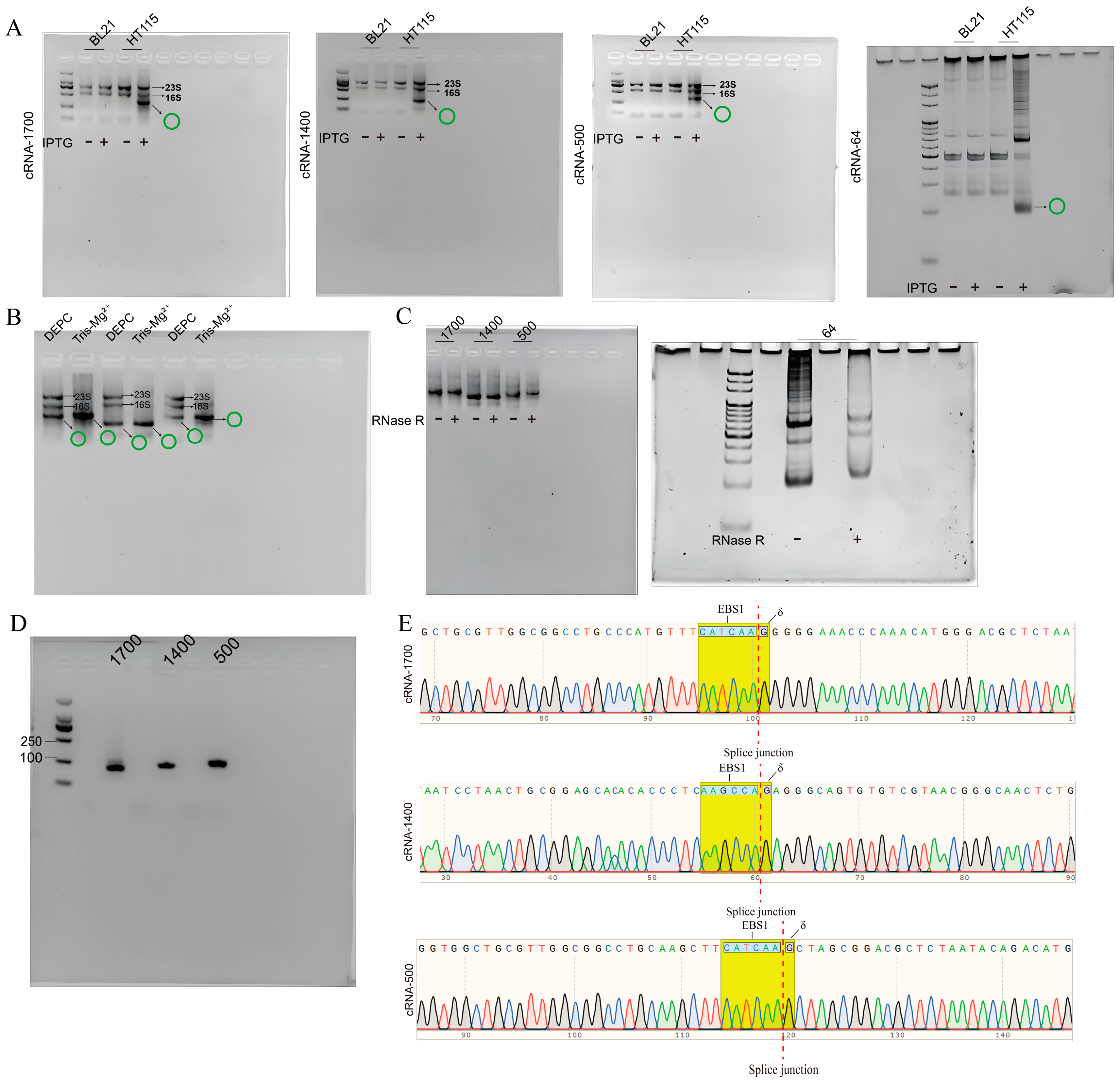
2.4. Validation of RNA Cyclization
2.4.1. RNase R Cleavage Assay
2.4.2. Assay of circRNA with Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.4.3. Sequencing of the PCR Products
2.5. Measurement of circRNA Translation and RNAi Effect
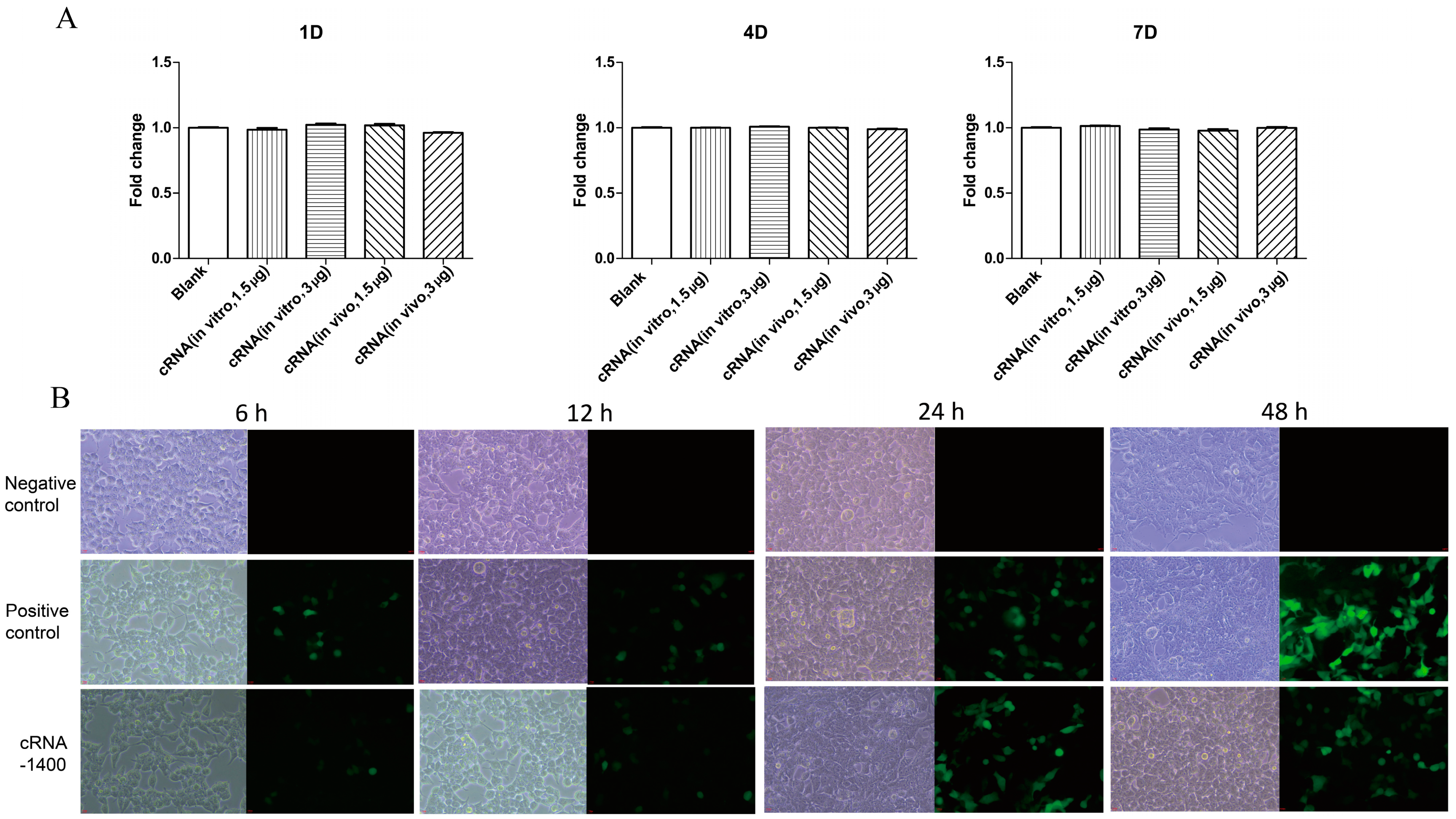
2.5.1. Cytotoxic Activity of circRNA
2.5.2. GFP Fluorescence Identification
2.5.3. qPCR Analysis
2.5.4. Analysis of Apoptosis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.6.1. Expression Analysis
2.6.2. Circularization Rate Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Construction and In Vitro Transcription Validation of Four Different-Sized Circular RNA Expression Plasmids
3.2. Synthesizing Four circRNAs Using E. coli
3.3. Optimization of circRNA Synthesis Efficiency In Vivo
3.4. CircRNA Expressed Protein and Showed Low Cytotoxicity in Cells
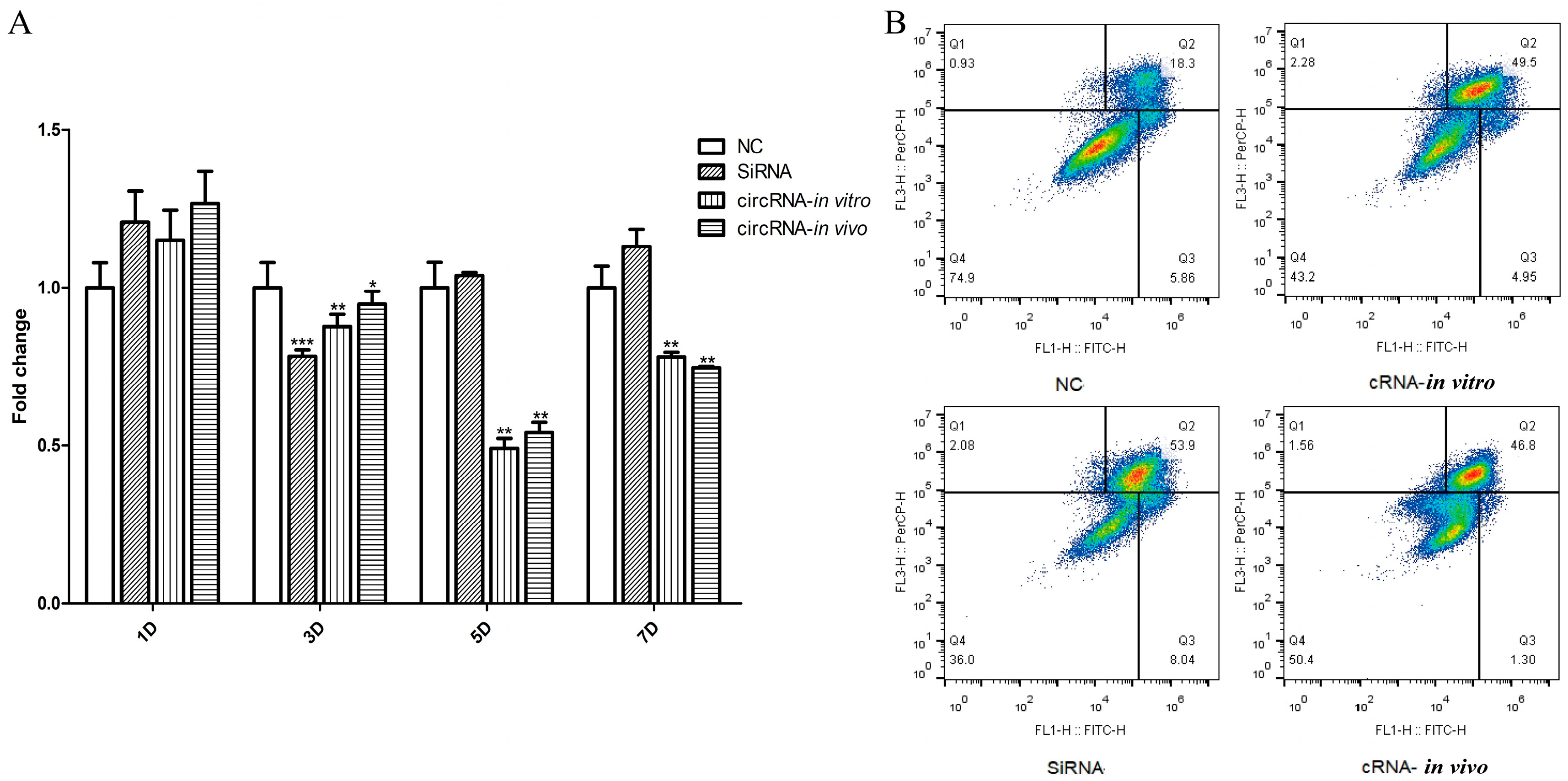
3.5. CRNA−Dumbbell Reduced Target Gene Expression and Induced Apoptosis in Hep 3B Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. The Biogenesis, functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, G.; Ling, Y.; Tan, W.; Tan, L.; Andrews, R.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, X.; Song, E.; et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_001783 regulates breast cancer progression via sponging miR-200c-3p. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seephetdee, C.; Bhukhai, K.; Buasri, N.; Leelukkanaveera, P.; Lerdwattanasombat, P.; Manopwisedjaroen, S.; Phueakphud, N.; Kuhaudomlarp, S.; Olmedillas, E.; Saphire, E.O.; et al. A circular mRNA vaccine prototype producing VFLIP-X spike confers a broad neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants by mouse sera. Antivir. Res. 2022, 204, 105370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Wang, S.K.; Belk, J.A.; Amaya, L.; Li, Z.; Cardenas, A.; Abe, B.T.; Chen, C.-K.; Wender, P.A.; Chang, H.Y. Engineering circular RNA for enhanced protein production. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Nishihara, M.; Nakano, Y.; Shibata, A.; Maruyama, H.; Shuto, S.; Matsuda, A.; Yoshida, M.; Ito, Y.; et al. Rolling circle translation of circular RNA in living human cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, N.; Abe, H.; Nagai, C.; Harada, M.; Hatakeyama, H.; Harashima, H.; Ohshiro, T.; Nishihara, M.; Furukawa, K.; Maeda, M.; et al. Synthesis, structure, and biological activity of dumbbell-shaped nanocircular RNAs for RNA interference. Bioconjugate Chem. 2011, 22, 2082–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahns, H.; Degaonkar, R.; Podbevsek, P.; Gupta, S.; Bisbe, A.; Aluri, K.; Szeto, J.; Kumar, P.; LeBlanc, S.; Racie, T.; et al. Small circular interfering RNAs (sciRNAs) as a potent therapeutic platform for gene-silencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 10250–10264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriero, S.; Damha, M.J. Template-mediated synthesis of lariat RNA and DNA. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 8328–8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.G.; Kim, M.V.; Chen, X.; Batista, P.J.; Aoyama, S.; Wilusz, J.E.; Iwasaki, A.; Chang, H.Y. Sensing self and foreign circular RNAs by intron identity. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 228–238.e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lyu, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Santos, C.; Yang, B.B. An improved model for circular RNA overexpression: Using the actin intron reveals high circularization efficiency. Adv. Genet. 2023, 4, 2200019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cheng, K.; Liu, X.; An, R.; Komiyama, M.; Liang, X. Preferential production of RNA rings by T4 RNA ligase 2 without any splint through rational design of precursor strand. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesselhoeft, R.A.; Kowalski, P.S.; Anderson, D.G. Engineering circular RNA for potent and stable translation in eukaryotic cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, W.; Zou, L.; Yu, X.; Xiao, F. A precise and efficient circular RNA synthesis system based on a ribozyme derived from Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diegelman, A.M.; Kool, E.T. Chemical and enzymatic methods for preparing circular single-stranded DNAs. In Current Protocols in Nucleic Acid Chemistry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, D.; Wilusz, J.E. Short intronic repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti Nagarjuna, R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litke, J.L.; Jaffrey, S.R. Highly efficient expression of circular RNA aptamers in cells using autocatalytic transcripts. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umekage, S.; Kikuchi, Y. In vivo circular RNA production using a constitutive promoter for high-level expression. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2009, 108, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, U.; Tomoe, U.; Yoshinobu, F.; Suzuki, H.; Kikuchi, Y. In vivo circular RNA expression by the permuted intron-exon method. In Innovations in Biotechnology; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; Chapter 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ortolá, B.; Cordero, T.; Hu, X.; Daròs, J.A. Intron-assisted, viroid-based production of insecticidal circular double-stranded RNA in Escherichia coli. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 1846–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikheeva, S.; Hakim-Zargar, M.; Carlson, D.; Jarrell, K. Use of an engineered ribozyme to produce a circular human exon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 5085–5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, N.; Hausner, G.; Zimmerly, S. Coevolution of group II intron RNA structures with their intron-encoded reverse transcriptases. RNA 2001, 7, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambowitz, A.M.; Zimmerly, S. Group II introns: Mobile ribozymes that invade DNA. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a003616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wei, H.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Wei, T.; Tang, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. A flexible, efficient, and scalable platform to produce circular RNAs as new therapeutics. bioRxiv 2022, 5, 494115. [Google Scholar]
- McNeil, B.A.; Zimmerly, S. Novel RNA structural features of an alternatively splicing group II intron from Clostridium tetani. RNA 2014, 20, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, S.O.; Xie, Q.; Fried, S.D. Optimized loopable translation as a platform for the synthesis of repetitive proteins. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 1736–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taracena, M.L.; Garcia Caffaro, I.; Paiva-Silva, G.O.; Oliveira, P.L.; Rendon, P.A.; Dotson, E.M.; Pennington, P.M. Delivery of double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) produced by Escherichia coli HT115(DE3) for nontransgenic RNAi-based insect pest management. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2360, 279–294. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.C.; Boone, M.; Meuris, L.; Lemmens, I.; Van Roy, N.; Soete, A.; Reumers, J.; Moisse, M.; Plaisance, S.; Drmanac, R.; et al. Genome dynamics of the human embryonic kidney 293 lineage in response to cell biology manipulations. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostain, W.; Shen, S.; Cordero, T.; Rodrigo, G.; Jaramillo, A. Engineering a circular riboregulator in Escherichia coli. BioDesign Res. 2020, 2020, 1916789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daròs, J.A.; Aragonés, V.; Cordero, T. A viroid-derived system to produce large amounts of recombinant RNA in Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, E.; Ares, M., Jr. Synthesis of circular RNA in bacteria and yeast using RNA cyclase ribozymes derived from a group I intron of phage T4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3117–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umekage, S.; Kikuchi, Y. In vitro and in vivo production and purification of circular RNA aptamer. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 139, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovic, S.; Müller, S. RNA self-processing: Formation of cyclic species and concatemers from a small engineered RNA. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 2435–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, K.; Honma, M.; Harumoto, T.; Harada, K.; Sawada, T.; Yamamoto, J.; Shinohara, F. Development of prodrug type circular siRNA for In vivo knockdown by systemic administration. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 30, 346–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, T.K.; Hausner, G. Using group II introns for attenuating the in vitro and in vivo expression of a homing endonuclease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cui, G.; Hua, D.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, T.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liao, J.; et al. A new EBS2b-IBS2b base paring (A(-8)/T(-8)) improved the gene-targeting efficiency of thermotargetron in Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. J. 2023, 11, e0315922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Ando, T.; Umekage, S.; Tanaka, T.; Kikuchi, Y. Extracellular production of an RNA aptamer by ribonuclease-free marine bacteria harboring engineered plasmids: A proposal for industrial RNA drug production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. J. 2010, 76, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wu, F.; Jin, W. A Simple and Efficient One-Step Synthesis System for Flexible Production of Circular RNA in E. coli. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14111416
Zhao X, Liu Y, Huang H, Sun Y, Wu F, Jin W. A Simple and Efficient One-Step Synthesis System for Flexible Production of Circular RNA in E. coli. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(11):1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14111416
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiayang, Yiqing Liu, Huanhui Huang, Yue Sun, Fangli Wu, and Weibo Jin. 2024. "A Simple and Efficient One-Step Synthesis System for Flexible Production of Circular RNA in E. coli" Biomolecules 14, no. 11: 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14111416
APA StyleZhao, X., Liu, Y., Huang, H., Sun, Y., Wu, F., & Jin, W. (2024). A Simple and Efficient One-Step Synthesis System for Flexible Production of Circular RNA in E. coli. Biomolecules, 14(11), 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14111416





