The Binding of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Platelet Factor 4: A Proposed Mechanism for the Generation of Pathogenic Antibodies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM)
2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.5. Isothermal Spectral Shift Analysis (ISSA)
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
3. Results
3.1. The Binding of SARS-CoV-2 SP to PF4 by the Mean of the Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM)
3.2. The Binding of SARS-CoV-2 SP to PF4 Alters Protein Structures
3.3. The Confirmation of PF4–SP Binding in the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
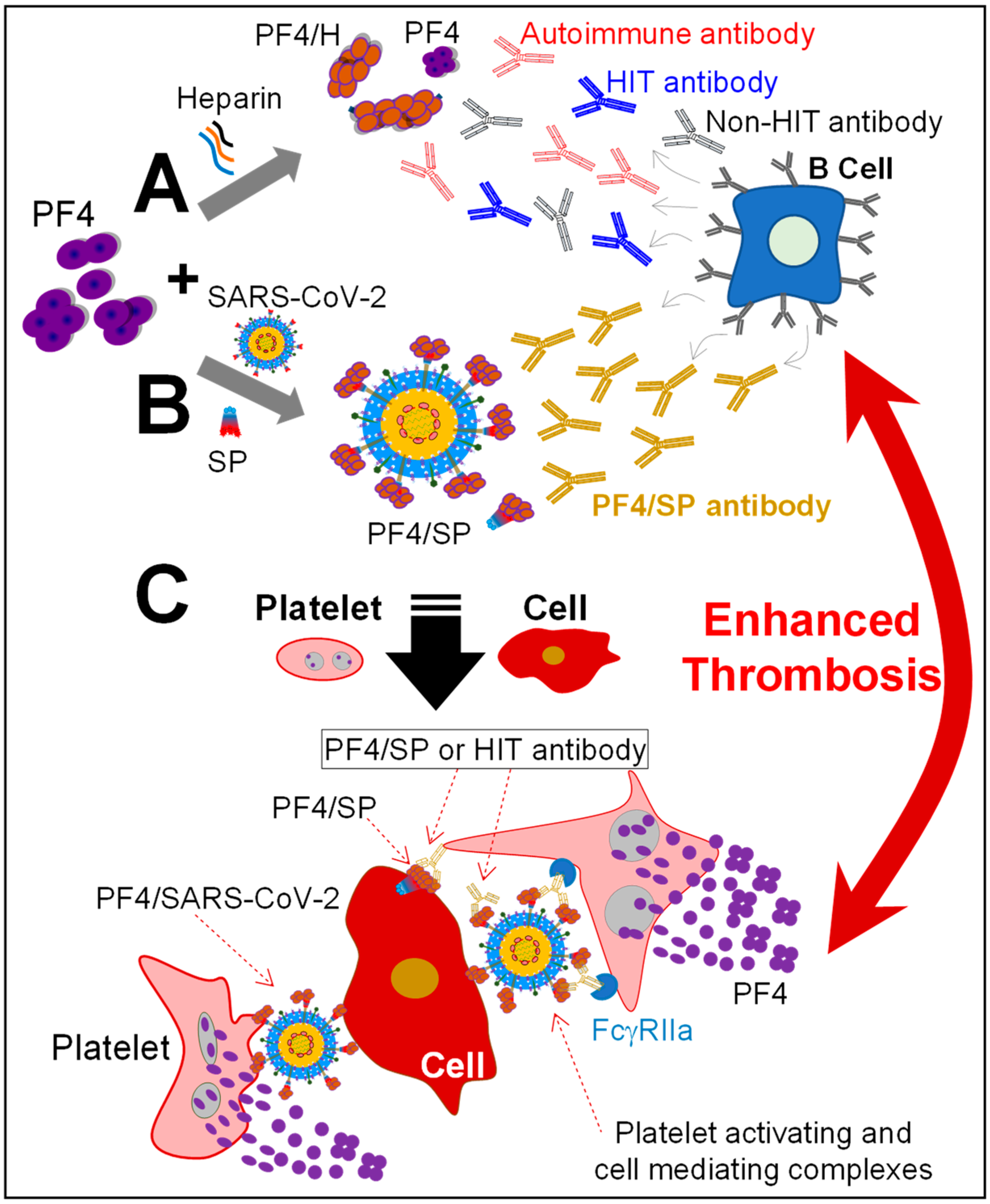
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 4 October 2023).
- Hanif, A.; Khan, S.; Mantri, N.; Hanif, S.; Saleh, M.; Alla, Y.; Chinta, S.; Shrestha, N.; Ji, W.; Attwood, K.; et al. Thrombotic complications and anticoagulation in COVID-19 pneumonia: A New York City hospital experience. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 2323–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Yu, Y.; Shang, Y. Thrombocytopenia and Its Association with Mortality in Patients with COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, N.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J. Thromb. Heamost. 2020, 18, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, F. Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1421–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middeldorp, S.; Coppens, M.; van Haaps, T.F.; Foppen, M.; Vlaar, A.P.; Muller, M.C.A.; Bouman, C.C.S.; Beenen, L.F.M.; Kootte, R.S.; Heijmans, J.; et al. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klok, F.A.; Kruip, M.; van der Meer, N.J.M.; Arbous, M.S.; Gommers, D.; Kant, K.M.; Kaptein, F.H.J.; van Paassen, J.; Stals, M.A.M.; Huisman, M.V.; et al. Confirmation of the high cumulative incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19: An updated analysis. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkentin, T.E.; Kaatz, S. COVID-19 versus HIT hypercoagulability. Thromb. Res. 2020, 196, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkentin, T.E.; Levine, M.N.; Hirsh, J.; Horsewood, P.; Roberts, R.S.; Gent, M.; Kelton, J.G. Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia in Patients Treated with Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin or Unfractionated Heparin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Khan, N.; Lindenbauer, A.; Nguyen, T.H. When Will Fondaparinux Induce Thrombocytopenia? Bioconjug. Chem. 2022, 33, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkentin, T.E.; Kelton, J.G. A 14-year study of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Am. J. Med. 1996, 101, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragonetti, D.; Guarini, G.; Pizzuti, M. Detection of anti-heparin-PF4 complex antibodies in COVID-19 patients on heparin therapy. Blood Transfus. 2020, 18, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althaus, K.; Marini, I.; Zlamal, J.; Pelzl, L.; Singh, A.; Haberle, H.; Mehrlander, M.; Hammer, S.; Schulze, H.; Bitzer, M.; et al. Antibody-induced procoagulant platelets in severe COVID-19 infection. Blood 2021, 137, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Miao, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Gerber, G.F.; Follmann, D.; Ji, H.; Zeger, S.L.; Chertow, D.S.; Quinn, T.C.; et al. Anti-PF4 antibodies associated with disease severity in COVID-19. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2213361119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueland, T.; Hausberg, I.; Mortberg, T.V.; Dahl, T.B.; Lerum, T.V.; Michelsen, A.; Ranheim, T.; Nezvalova Henriksen, K.; Dyrhol-Riise, A.M.; Holme, P.A.; et al. Anti-PF4/polyanion antibodies in COVID-19 patients are associated with disease severity and pulmonary pathology. Platelets 2022, 33, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thachil, J.; Tang, N.; Gando, S.; Falanga, A.; Cattaneo, M.; Levi, M.; Clark, C.; Iba, T. ISTH interim guidance on recognition and management of coagulopathy in COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, M.; Bertinato, E.M.; Birocchi, S.; Brizio, C.; Malavolta, D.; Manzoni, M.; Muscarella, G.; Orlandi, M. Pulmonary Embolism or Pulmonary Thrombosis in COVID-19? Is the Recommendation to Use High-Dose Heparin for Thromboprophylaxis Justified? Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 1230–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldenburg, J.; Klamroth, R.; Langer, F.; Albisetti, M.; von Auer, C.; Ay, C.; Korte, W.; Scharf, R.E.; Potzsch, B.; Greinacher, A. Diagnosis and Management of Vaccine-Related Thrombosis following AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccination: Guidance Statement from the GTH. Hamostaseologie 2021, 41, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greinacher, A.; Thiele, T.; Warkentin, T.E.; Weisser, K.; Kyrle, P.A.; Eichinger, S. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCov-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2092–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, M.; Singh, D.; Lown, R.; Poles, A.; Solomon, T.; Levi, M.; Goldblatt, D.; Kotoucek, P.; Thomas, W.; Lester, W. Pathologic Antibodies to Platelet Factor 4 after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2202–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althaus, K.; Moller, P.; Uzun, G.; Singh, A.; Beck, A.; Bettag, M.; Bosmuller, H.; Guthoff, M.; Dorn, F.; Petzold, G.C.; et al. Antibody-mediated procoagulant platelets in SARS-CoV-2- vaccination associated immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia. Haematologica 2021, 106, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Estes, S.K.; Ali, R.A.; Gandhi, A.A.; Yalavarthi, S.; Shi, H.; Sule, G.; Gockman, K.; Madison, J.A.; Zuo, M.; et al. Prothrombotic autoantibodies in serum from patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eabd3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H. Single-molecule force spectroscopy applied to heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J. Mol. Recognit. 2017, 30, e2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Greinacher, A. Effect of pH and ionic strength on the binding strength of anti-PF4/polyanion antibodies. Eur. Biophys. J. 2017, 46, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Greinacher, A. Platelet factor 4/heparin complexes present epitopes differently on solid-phase vs platelet surfaces. Blood 2017, 129, 3498–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, V.C.; Nguyen, T.H. The Role of Single-Molecule Force Spectroscopy in Unraveling Typical and Autoimmune Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauova, L.; Poncz, M.; McKenzie, S.E.; Reilly, M.P.; Arepally, G.; Weisel, J.W.; Nagaswami, C.; Cines, D.B.; Sachais, B.S. Ultralarge complexes of PF4 and heparin are central to the pathogenesis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood 2005, 105, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greinacher, A. Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Greinacher, A.; Delcea, M. Quantitative description of thermodynamic and kinetic properties of the platelet factor 4/heparin bonds. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10130–10139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, M.; Sheppard, J.I.; Li, N.; Warkentin, T.E. Neutrophil and Monocyte Counts in Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, B.H.; Pitney, W.R.; Castaldi, P.A.; Warkentin, T.E.; Kelton, J.G.; Warkentin, T.E. Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia: To w a rds Consensus. Thromb. Haemost. 1998, 79, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cines, D.B. Disorders Associated with Antibodies to Endothelial-Cells. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1989, 11, S705–S711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, G.P.; Ford, S.E.; Scott, J.P.; Aster, R.H. Antibodies from Patients with Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia/Thrombosis Are Specific for Platelet Factor-4 Complexed with Heparin or Bound to Endothelial-Cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkentin, T.E.; Basciano, P.A.; Knopman, J.; Bernstein, R.A. Spontaneous heparin-induced thrombocytopenia syndrome: 2 new cases and a proposal for defining this disorder. Blood 2014, 123, 3651–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Medvedev, N.; Delcea, M.; Greinacher, A. Anti-platelet factor 4/polyanion antibodies mediate a new mechanism of autoimmunity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, A.; Bartoschik, T.; Cehlar, O.; Duhr, S.; Baaske, P.; Streicher, W. A New Spectral Shift-Based Method to Characterize Molecular Interactions. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2022, 20, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Wesche, J.; Raschke, R.; Strobel, U.; Bui, V.C.; Delcea, M.; Greinacher, A. Reactivity of platelet-activating and nonplatelet-activating anti-PF4/heparin antibodies in enzyme immunosorbent assays under different conditions. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Xu, Y.; Brandt, S.; Mandelkow, M.; Raschke, R.; Strobel, U.; Delcea, M.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Greinacher, A. Characterization of the interaction between platelet factor 4 and homogeneous synthetic low molecular weight heparins. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vayne, C.; Nguyen, T.H.; Rollin, J.; Charuel, N.; Poupon, A.; Pouplard, C.; Normann, N.; Gruel, Y.; Greinacher, A. Characterization of New Monoclonal PF4-Specific Antibodies as Useful Tools for Studies on Typical and Autoimmune Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 121, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Greinacher, A. Distinct Binding Characteristics of Pathogenic Anti-Platelet Factor-4/Polyanion Antibodies to Antigens Coated on Different Substrates: A Perspective on Clinical Application. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 12030–12041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.Z.; Chen, L.Y.; Lindenbauer, A.; Pliquett, U.; Rothe, H.; Nguyen, T.H. Label-Free Detection and Characterization of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT)-like Antibodies. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 25926–25939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.Z.; Martin, D.; Pliquett, U.; Zaikou, Y.; Thomas, N.; Heinrich, D.; Kohler, J.M.; Nguyen, T.H. High-frequency Contactless Sensor for the Detection of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Antibodies via Platelet Aggregation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passariello, M.; Vetrei, C.; Amato, F.; De Lorenzo, C. Interactions of Spike-RBD of SARS-CoV-2 and Platelet Factor 4: New Insights in the Etiopathogenesis of Thrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.; Peacock, T.P.; Harvey, W.T.; Hughes, J.; Wright, D.W.; Consortium, C.-G.U.; Willett, B.J.; Thomson, E.; Gupta, R.K.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant evasion of monoclonal antibodies based on in vitro studies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Iketani, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Bowen, A.D.; Liu, M.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; et al. Alarming antibody evasion properties of rising SARS-CoV-2 BQ and XBB subvariants. Cell 2023, 186, 279–286.e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Kempf, A.; Nehlmeier, I.; Schulz, S.R.; Jack, H.M.; Pohlmann, S.; Hoffmann, M. Omicron sublineage BQ.1.1 resistance to monoclonal antibodies. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 22–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, V.C.; Gebicka, P.; Hippe, H.; Raschke, R.; Nguyen, T.L.; Greinacher, A.; Nguyen, T.H. Physicochemical Characteristics of Platelet Factor 4 under Various Conditions are Relevant for Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Testing. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 1438–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarna, S.; Espinasse, B.; Qi, R.; Lubica, R.; Poncz, M.; Cines, D.B.; Wiesner, M.R.; Arepally, G.M. Determinants of PF4/heparin immunogenicity. Blood 2007, 110, 4253–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-On, Y.M.; Flamholz, A.; Phillips, R.; Milo, R. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) by the numbers. eLife 2020, 9, e57309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Y.; Schirmer, U.; Widder, M.; Gruel, Y.; Rollin, J.; Zipfel, P.F.; Nguyen, T.H. Breast cancer cell-based ELISA: A potential material for better detection of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia antibodies. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 7708–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Y.; Apte, G.; Lindenbauer, A.; Frant, M.; Nguyen, T.H. Effect of HIT Components on the Development of Breast Cancer Cells. Life 2021, 11, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleem, A.; Nadeem, A.J. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia (VITT); StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Swank, Z.; Senussi, Y.; Manickas-Hill, Z.; Yu, X.G.; Li, J.Z.; Alter, G.; Walt, D.R. Persistent Circulating Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Spike Is Associated With Post-acute Coronavirus Disease 2019 Sequelae. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, e487–e490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaid, Y.; Puhm, F.; Allaeys, I.; Naya, A.; Oudghiri, M.; Khalki, L.; Limami, Y.; Zaid, N.; Sadki, K.; Ben El Haj, R.; et al. Platelets Can Associate with SARS-CoV-2 RNA and Are Hyperactivated in COVID-19. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 1404–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.Y.; Echtermeyer, D.; Pliquett, U. Modulating SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Reactivity through Moderate Electric Fields: A Pathway to Innovative Therapies. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 45952–45960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
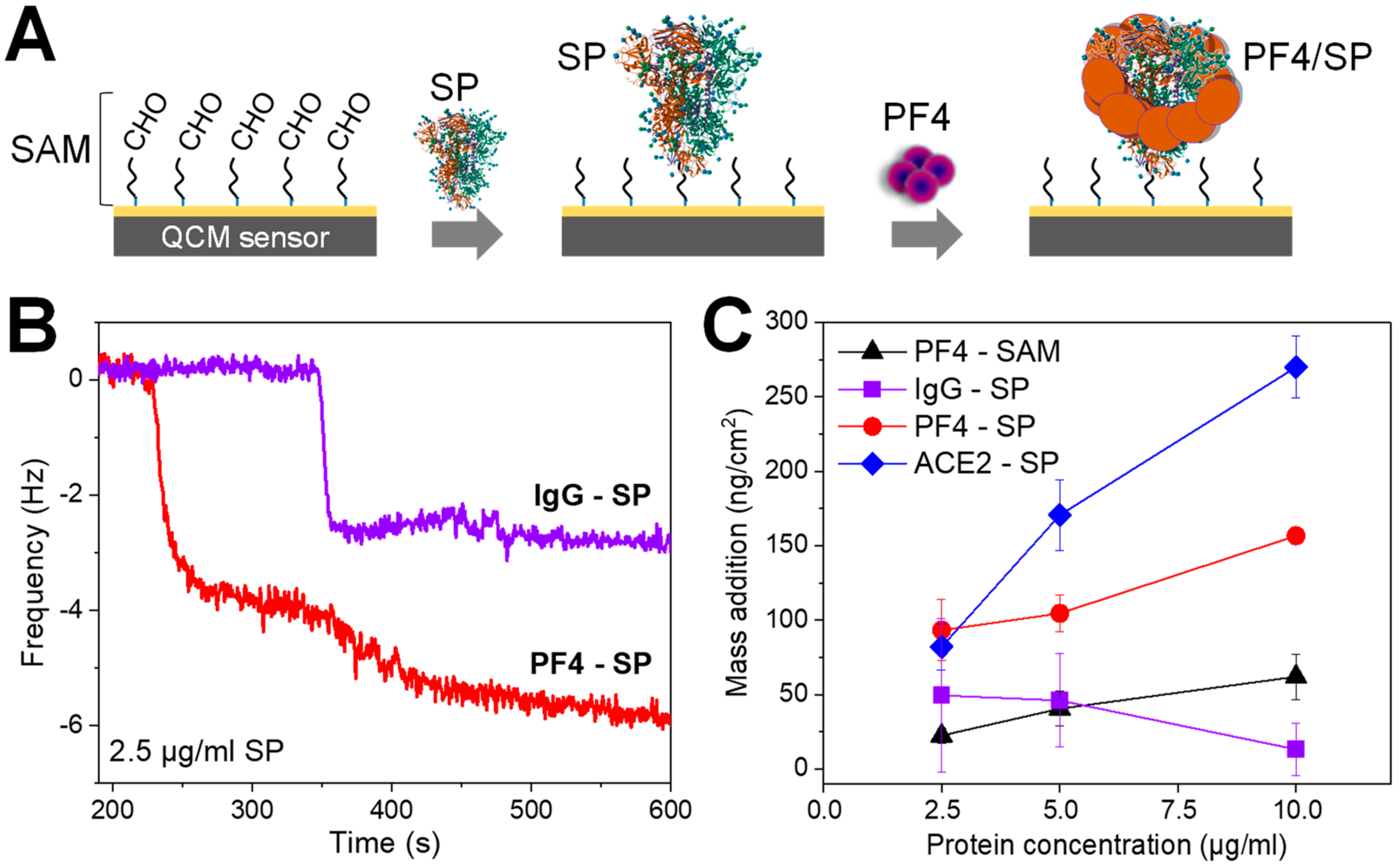
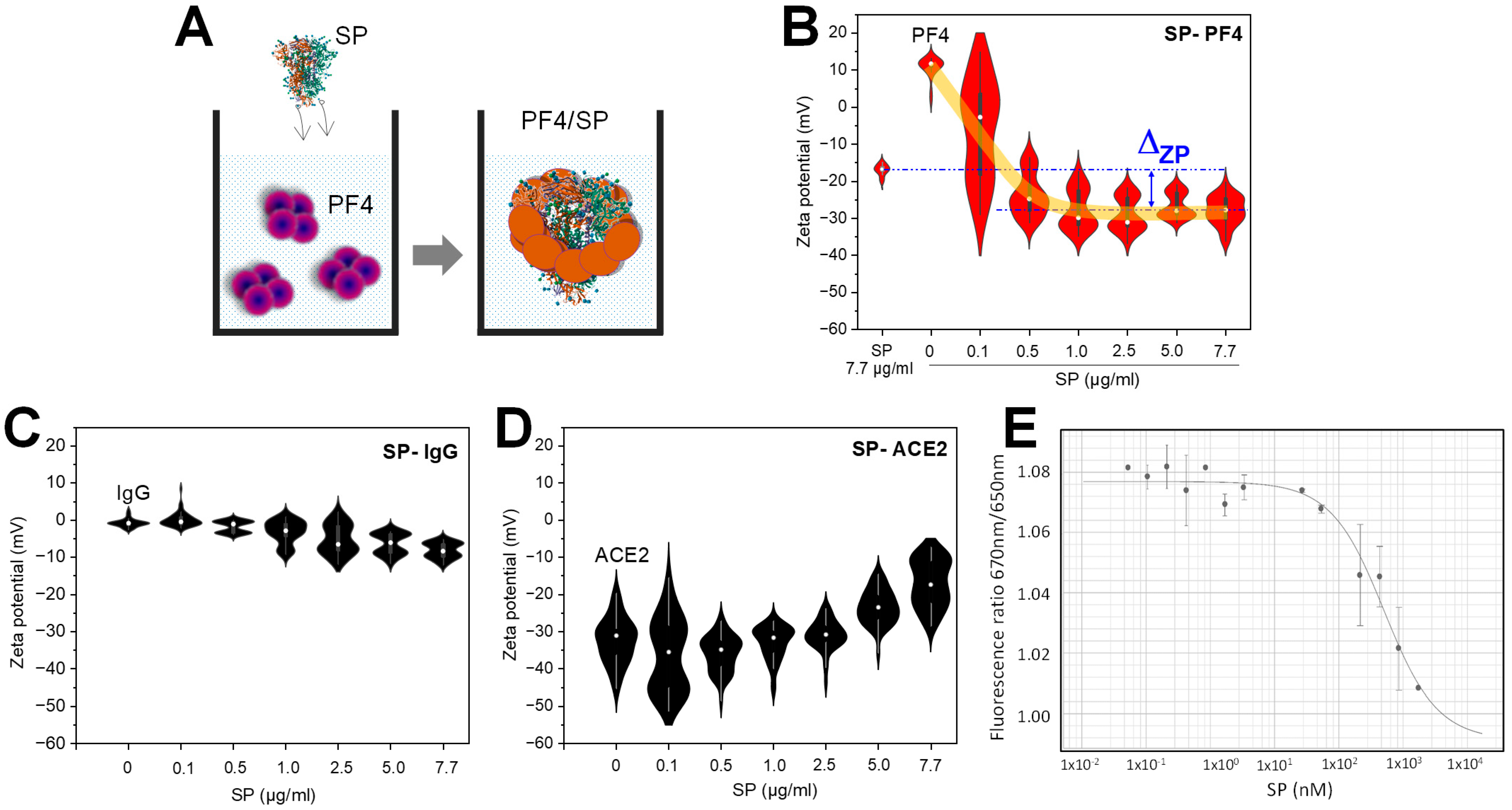
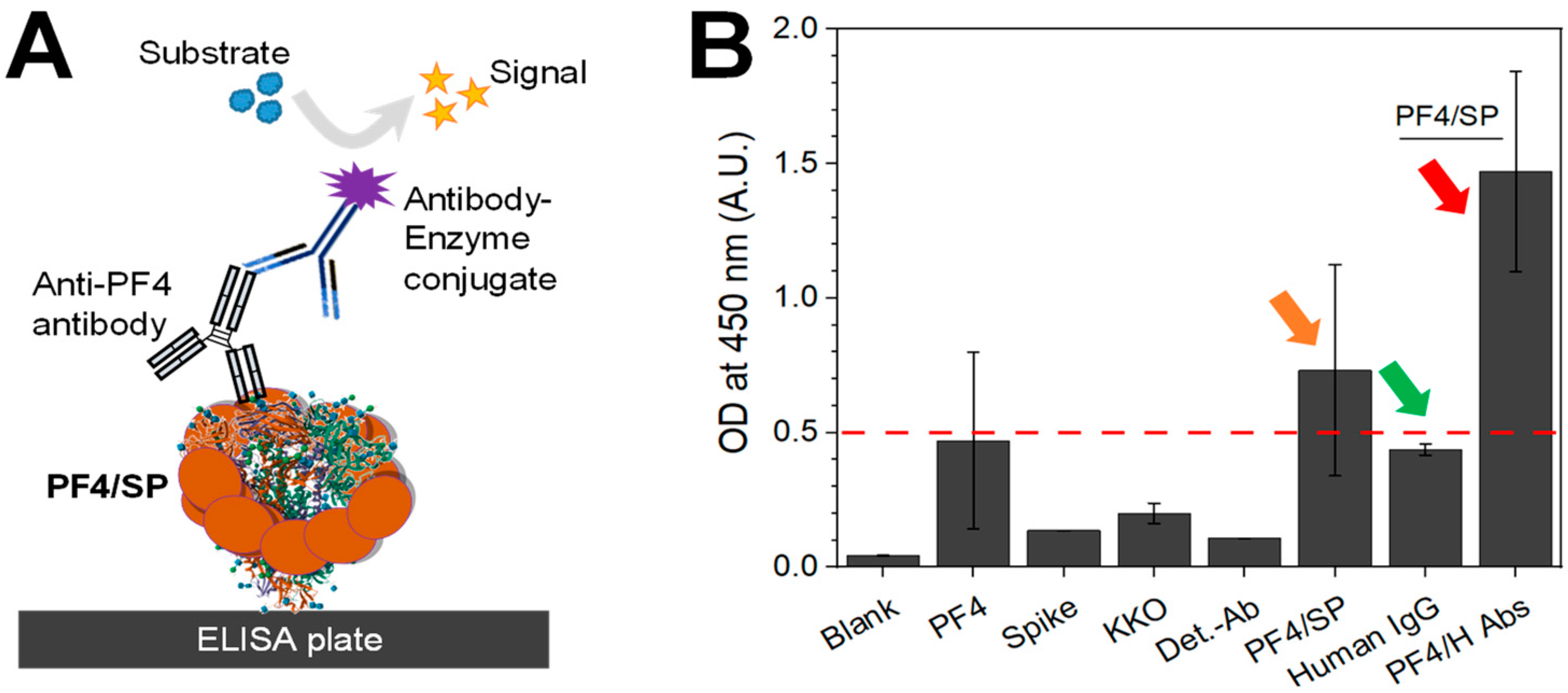
| Adding Material | Blank | Spike Control (SpikeCon) | KKO Control (KKOCon) | Detection Ab Control (Det-AbCon) | PF4/SP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP | - | + | + | - | + |
| PF4 | - | - | - | - | + |
| KKO | - | - | + | - | + |
| Detection Ab | - | + | + | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.-H.; Chen, L.-Y.; Khan, N.Z.; Lindenbauer, A.; Bui, V.-C.; Zipfel, P.F.; Heinrich, D. The Binding of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Platelet Factor 4: A Proposed Mechanism for the Generation of Pathogenic Antibodies. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030245
Nguyen T-H, Chen L-Y, Khan NZ, Lindenbauer A, Bui V-C, Zipfel PF, Heinrich D. The Binding of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Platelet Factor 4: A Proposed Mechanism for the Generation of Pathogenic Antibodies. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(3):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030245
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thi-Huong, Li-Yu Chen, Nida Zaman Khan, Annerose Lindenbauer, Van-Chien Bui, Peter F. Zipfel, and Doris Heinrich. 2024. "The Binding of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Platelet Factor 4: A Proposed Mechanism for the Generation of Pathogenic Antibodies" Biomolecules 14, no. 3: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030245
APA StyleNguyen, T.-H., Chen, L.-Y., Khan, N. Z., Lindenbauer, A., Bui, V.-C., Zipfel, P. F., & Heinrich, D. (2024). The Binding of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Platelet Factor 4: A Proposed Mechanism for the Generation of Pathogenic Antibodies. Biomolecules, 14(3), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030245






