Oxidative Stress Reaction to Hypobaric–Hyperoxic Civilian Flight Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
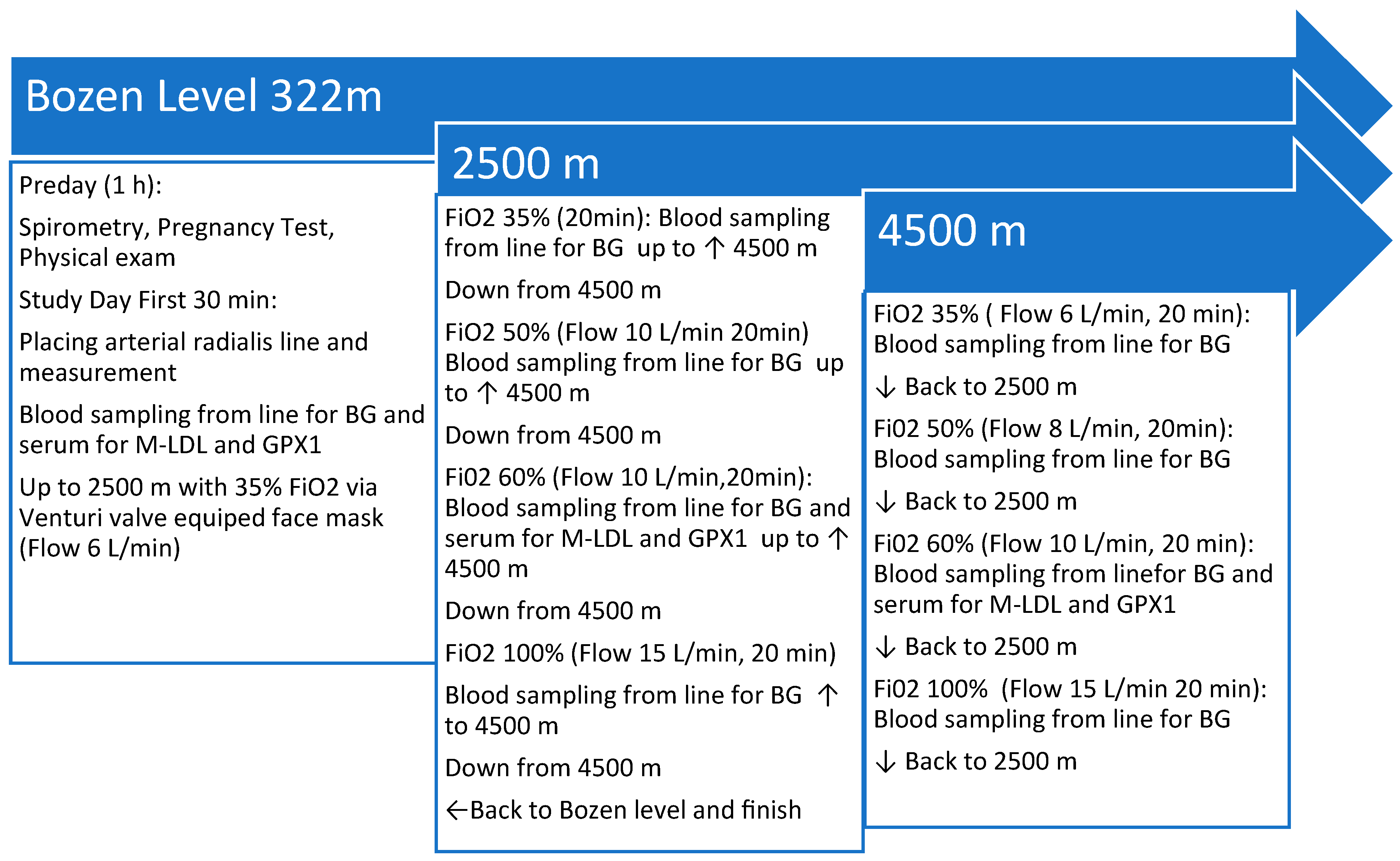
2.2. Study Site and Flight Simulation
2.3. Assessment of Oxidative Stress
2.4. Statistical Analyses
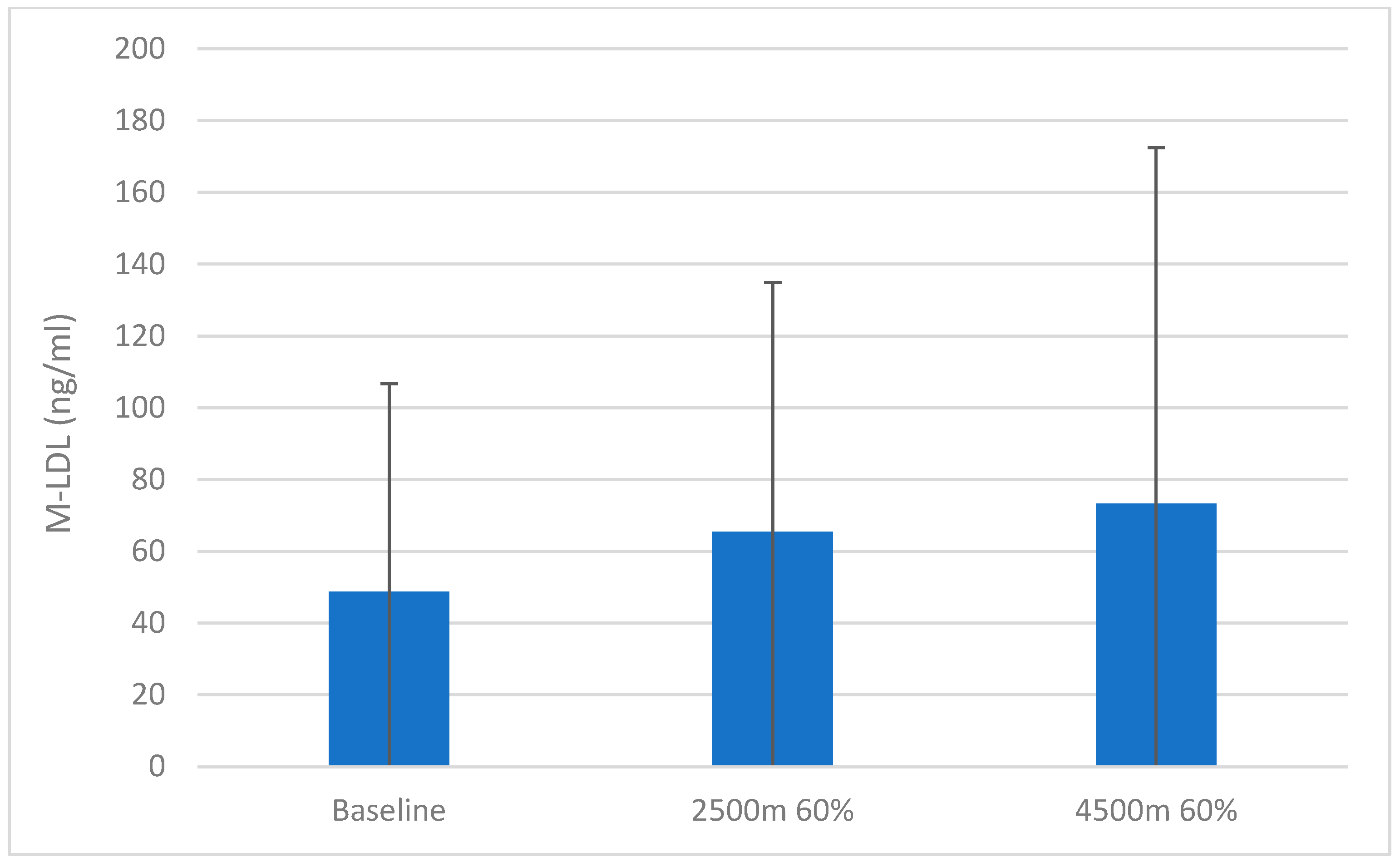
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouak, F.; Vartanian, O.; Hofer, K.; Cheung, B. Acute mild hypoxic hypoxia effects on cognitive and simulated aircraft pilot performance. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2018, 89, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, J.B. A strategy for in-flight measurements of physiology of pilots of high-performance fighter aircraft. J. Appl. Physiol. 1985, 115, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamma, G.; Valenti, G.; Grossini, E.; Donnini, S.; Marino, A.; Marinelli, R.A.; Calamita, G. Aquaporin Membrane Channels in Oxidative Stress, Cell Signaling, and Aging: Recent Advances and Research Trends. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 1501847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vottier, G.; Pham, H.; Pansiot, J.; Biran, V.; Gressens, P.; Charriaut-Marlangue, C.; Baud, O. Deleterious effect of hyperoxia at birth on white matter damage in the newborn rat. Dev. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, R.S.; Tenfen, L.; Joaquim, L.; Lanzzarin, E.V.R.; Bernardes, G.C.; Bonfante, S.R.; Mathias, K.; Biehl, E.; Bagio, É.; de Souza Stork, S.; et al. Hyperoxia by short-term promotes oxidative damage and mitochondrial dysfunction in rat brain. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2022, 306, 103963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Koppelmans, V.; Riascos, R.F.; Hasan, K.M.; Pasternak, O.; Mulavara, A.P.; Bloomberg, J.J.; Seidler, R.D. Spaceflight-Associated Brain White Matter Microstructural Changes and Intracranial Fluid Redistribution. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damato, E.G.; Fillioe, S.J.; Margevicius, S.P.; Mayes, R.S.; Somogyi, J.E.; Vannix, I.S.; Abdollahifar, A.; Turner, A.M.; Ilcus, L.S.; Decker, M.J. Increased Serum Levels of Proinflammatory Cytokines Are Accompanied by Fatigue in Military T-6A Texan II Instructor Pilots. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 876750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damato, E.G.; Fillioe, S.J.; Vannix, I.S.; Norton, L.K.; Margevicius, S.P.; Beebe, J.L.; Decker, M.J. Characterizing the Dose Response of Hyperoxia with Brain Perfusion. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2022, 93, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damato, E.G.; Flak, T.A.; Mayes, R.S.; Strohl, K.P.; Ziganti, A.M.; Abdollahifar, A.; Flask, C.A.; LaManna, J.C.; Decker, M.J. Neurovascular and cortical responses to hyperoxia: Enhanced cognition and electroencephalographic activity despite reduced perfusion. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 3941–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAR 91.211-Supplemental Oxygen. Available online: http://www.faa-aircraft-certification.com (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Available online: http://www.ainonline.com/aviation-news/air-transport/2020-05-13/faa-amends-oxygen-mask-rule-not-without-controversy (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Qian, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, W. Effects of acute mild hypoxia on cerebral blood flow in pilots. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, I.; Fujiwara, O.; Utsuki, N.; Mizumoto, C.; Arimori, T. Hypoxia-induced fatal aircraft accident revealed by voice analysis. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1980, 51, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rayman, R.B. Sudden incapacitation in flight, 1 January 1966–30 November 1971. Aerosp. Med. 1973, 44, 953–955. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rayman, R.B.; McNaughton, G.B. Hypoxia: USAF experience 1970–1980. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1983, 54, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin-Saint-Laurent, A.; Lavernhe, J.; Casano, G.; Simkoff, A. Clinical aspects of inflight incapacitations in commercial aviation. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1990, 61, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Available online: http://www.longislandpress.com/2023/06/06/loss-oxygen-virginia-plane-crash/ (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Aerospace Medical Association; Aviation Safety Committee; Civil Aviation Subcommittee. Cabin cruising altitudes for regular transport aircraft. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2008, 79, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: From basic research to clinical application. Am. J. Med. 1991, 91, 31S–38S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: Oxidants and antioxidants. Exp. Physiol. 1997, 82, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. Biological redox systems and oxidative stress. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 2181–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katerji, M.; Filippova, M.; Duerksen-Hughes, P. Approaches and Methods to Measure Oxidative Stress in Clinical Samples: Research Applications in the Cancer Field. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 1279250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert Koch-Institut. Oxidativer Stress und Möglichkeiten seiner Messung aus umweltmedizinischer Sicht: Mitteilung der Kommission “Methoden und Qualitätssicherung in der Umweltmedizin”. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 2008, 51, 1464–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmerich, W. StatisticGuru: Poweranalyse für Korrelationen 2018. Available online: https://statisticguru.deTrechner/poweranalyse-korrelationen.html (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Petraki, K.; Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Tekos, F.; Skaperda, Z.; Orfanou, M.; Mesnage, R.; Vassilakou, T.; Kouretas, D. Estimation of Redox Status in Military Pilots during Hypoxic Flight-Simulation Conditions—A Pilot Study. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, D.M.; Cabre, G.; Gant, N. Hypoxic Hypoxia and Brain Function in Military Aviation: Basic Physiology and Applied Perspectives. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 665821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, J.B. Cognitive Impairment of School Children at High Altitude: The Case for Oxygen Conditioning in Schools. High. Alt. Med. Biol. 2016, 17, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, J.B. High-altitude medicine. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, J.B. A new approach to very-high-altitude land travel: The train to Lhasa, Tibet. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 149, 898–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppelmans, V.; Mulavara, A.P.; Seidler, R.D.; De Dios, Y.E.; Bloomberg, J.J.; Wood, S.J. Cortical thickness of primary motor and vestibular brain regions predicts recovery from fall and balance directly after spaceflight. Brain Struct. Funct. 2022, 227, 2073–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.S.; Sun, X.Q.; Wu, X.Y.; Rao, Z.R.; Liu, H.L.; Xie, X.P. Influences of repeated lower +Gz exposures on high +Gz exposure induced brain injury in rats. Space Med. Med. Eng. 2002, 15, 339–342. [Google Scholar]
- Pashchenko, P.S.; Risman, B.V. Strukturnye preobrazovaniia v serom veshchestve spinnogo mozga posle vozdeĭstviia gravitatsionnykh peregruzok [Structural changes in spinal cord gray matter induced by gravitational overloads]. Morfologiia 2002, 121, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clément, G.R.; Boyle, R.D.; George, K.A.; Nelson, G.A.; Reschke, M.F.; Williams, T.J.; Paloski, W.H. Challenges to the central nervous system during human spaceflight missions to Mars. J. Neurophysiol. 2020, 123, 2037–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, K.E.P.; Anderson, E.E. Hyperventilation-Induced Hypocapnia in an Aviator. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2022, 93, 470–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, A.M.; Varis, N.O.; Kokki, H.J.; Leino, T.K. A New Method for Combined Hyperventilation and Hypoxia Training in a Tactical Fighter Simulator. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2022, 93, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varis, N.; Leinonen, A.; Parkkola, K.; Leino, T.K. Hyperventilation and Hypoxia Hangover during Normobaric Hypoxia Training in Hawk Simulator. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 942249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Netzer, N.C.; Jaekel, H.; Popp, R.; Gostner, J.M.; Decker, M.; Eisendle, F.; Turner, R.; Netzer, P.; Patzelt, C.; Steurer, C.; et al. Oxidative Stress Reaction to Hypobaric–Hyperoxic Civilian Flight Conditions. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040481
Netzer NC, Jaekel H, Popp R, Gostner JM, Decker M, Eisendle F, Turner R, Netzer P, Patzelt C, Steurer C, et al. Oxidative Stress Reaction to Hypobaric–Hyperoxic Civilian Flight Conditions. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(4):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040481
Chicago/Turabian StyleNetzer, Nikolaus C., Heidelinde Jaekel, Roland Popp, Johanna M. Gostner, Michael Decker, Frederik Eisendle, Rachel Turner, Petra Netzer, Carsten Patzelt, Christian Steurer, and et al. 2024. "Oxidative Stress Reaction to Hypobaric–Hyperoxic Civilian Flight Conditions" Biomolecules 14, no. 4: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040481
APA StyleNetzer, N. C., Jaekel, H., Popp, R., Gostner, J. M., Decker, M., Eisendle, F., Turner, R., Netzer, P., Patzelt, C., Steurer, C., Cavalli, M., Forstner, F., & Pramsohler, S., on behalf of the Hypoxiflight Study Group. (2024). Oxidative Stress Reaction to Hypobaric–Hyperoxic Civilian Flight Conditions. Biomolecules, 14(4), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040481









