Primary Nucleation of Polymorphic α-Synuclein Dimers Depends on Copper Concentrations and Definite Copper-Binding Site
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Constructions of Cu2+-Bound AS1–140 Fibril-Like Dimer Models
2.2. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations Protocol
2.3. Structural Analyses
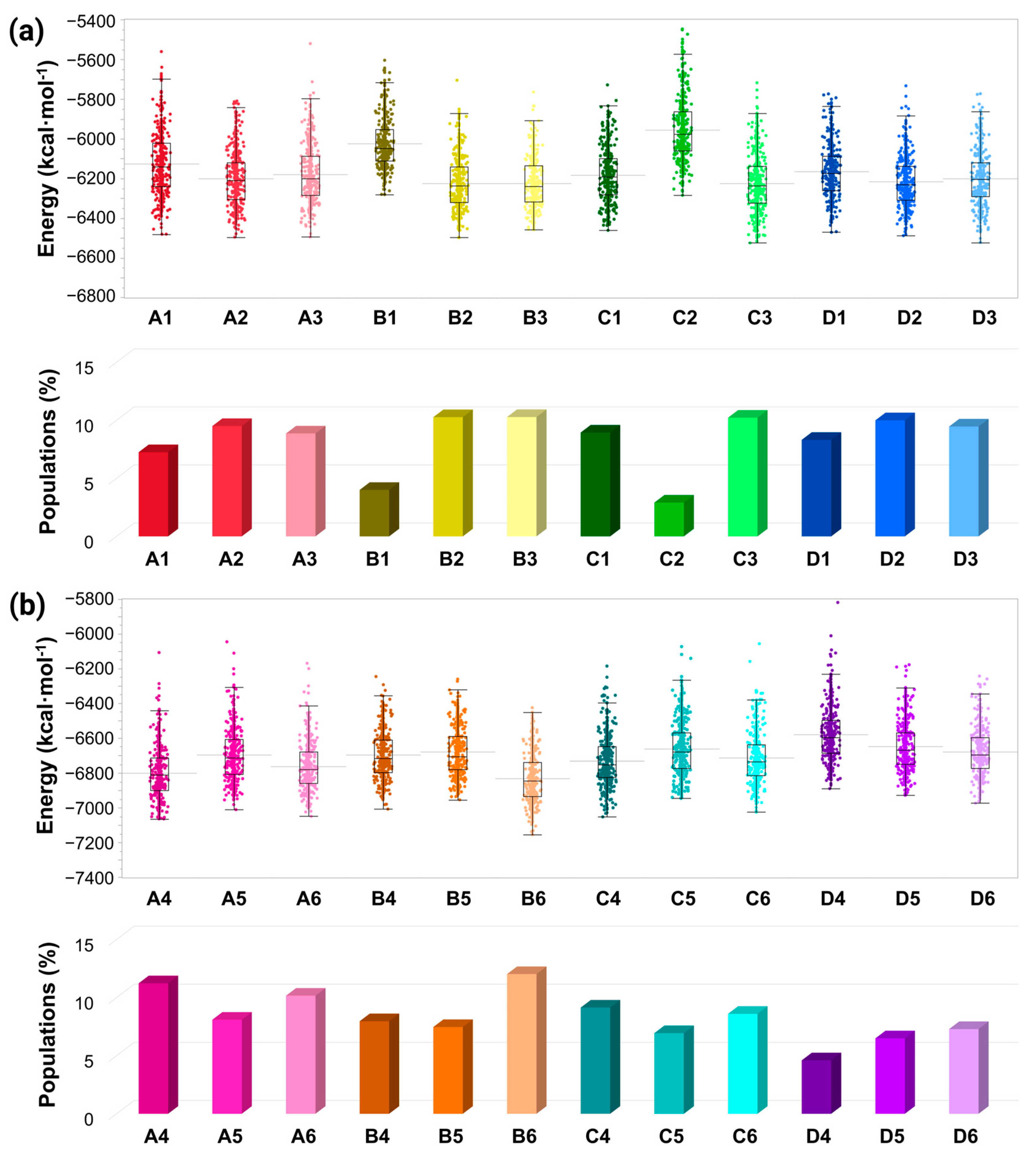
2.4. Determining the Conformational Energies and Populations for the Simulated Cu2+-Bound AS Dimers
3. Results and Discussion
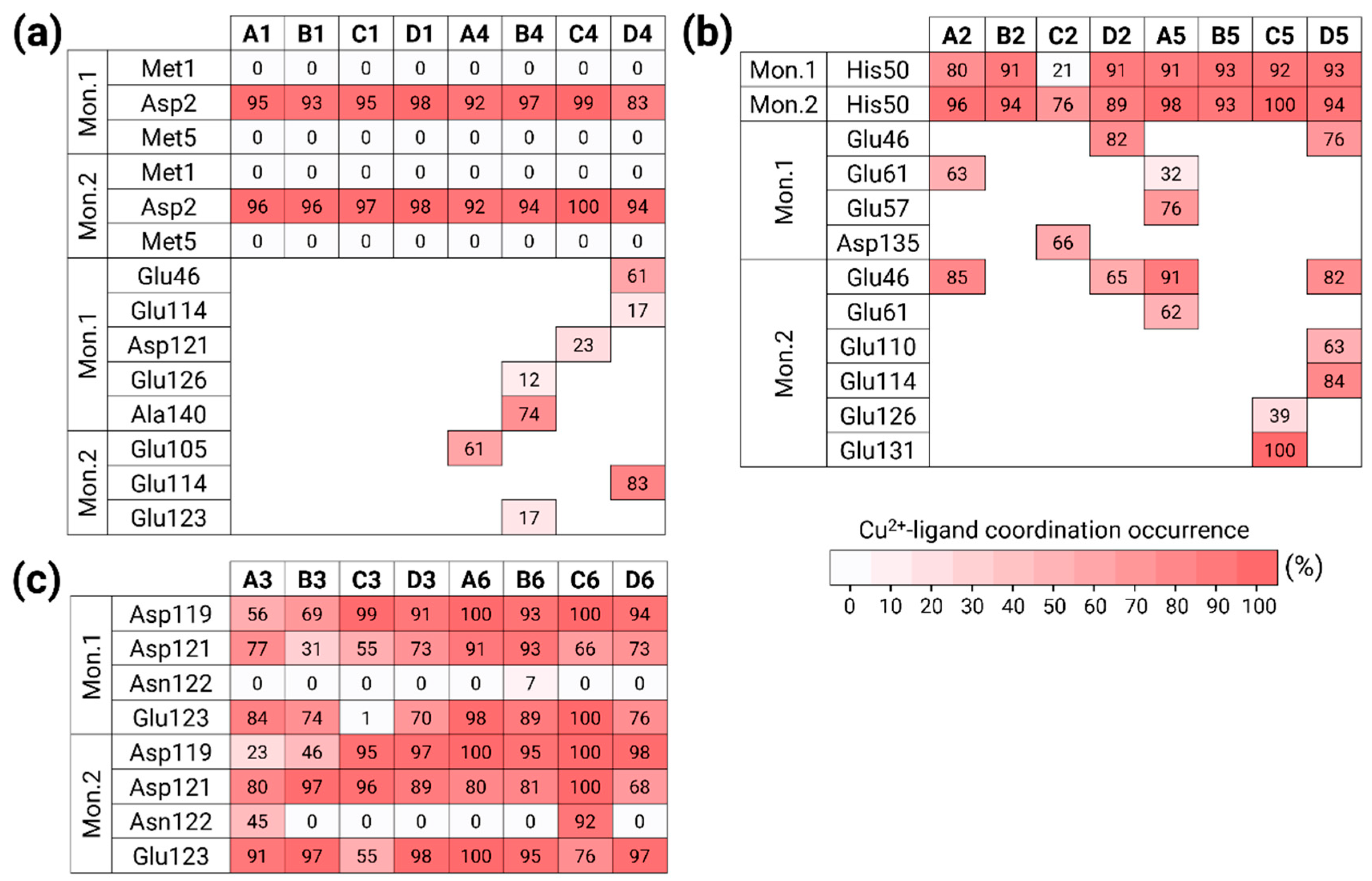
3.1. Copper Concentrations Affect the Metal-Binding Sites
3.2. Copper-Binding Sites at Different Concentrations Affect the Primary Nucleation of AS Aggregation
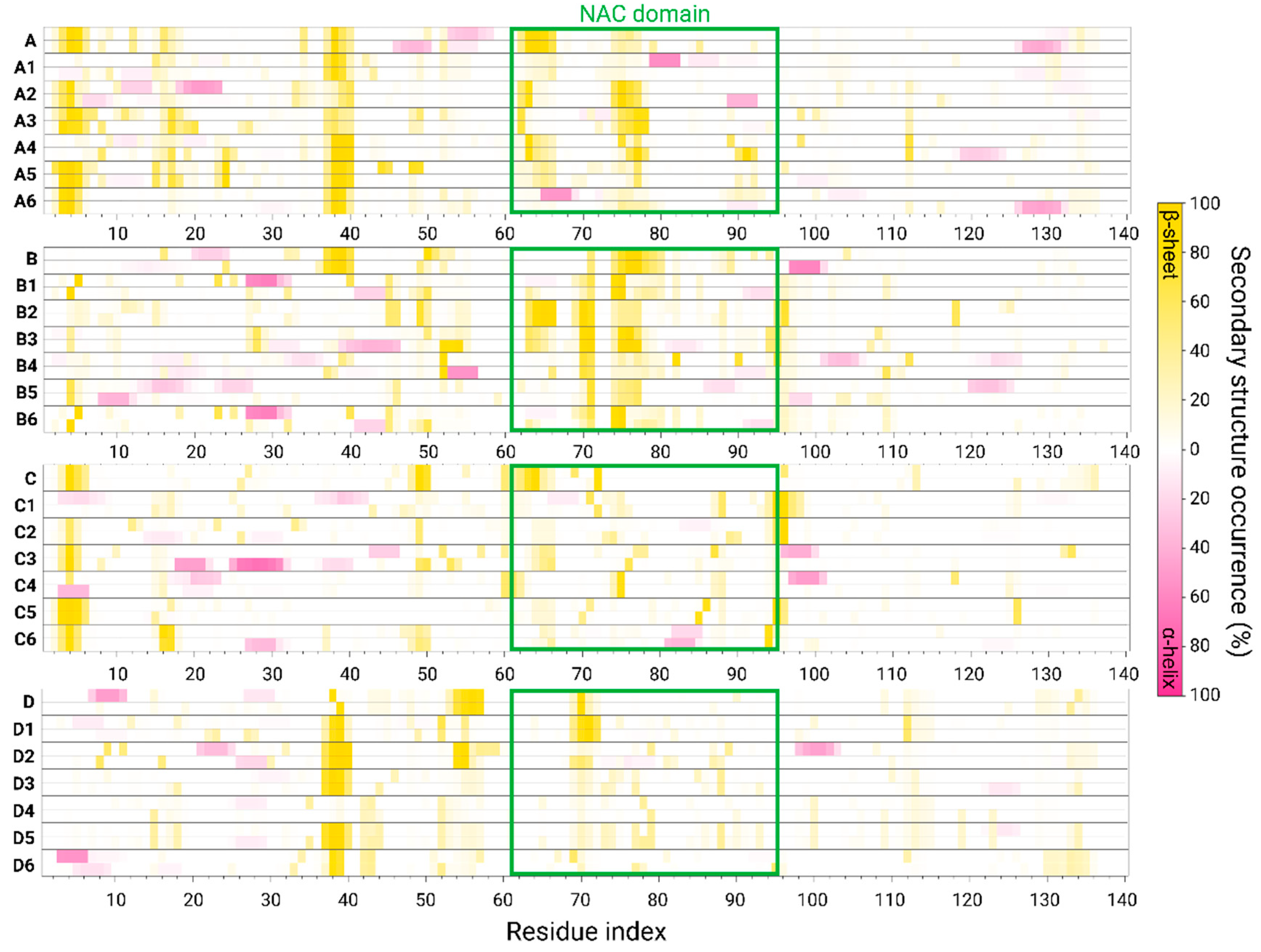
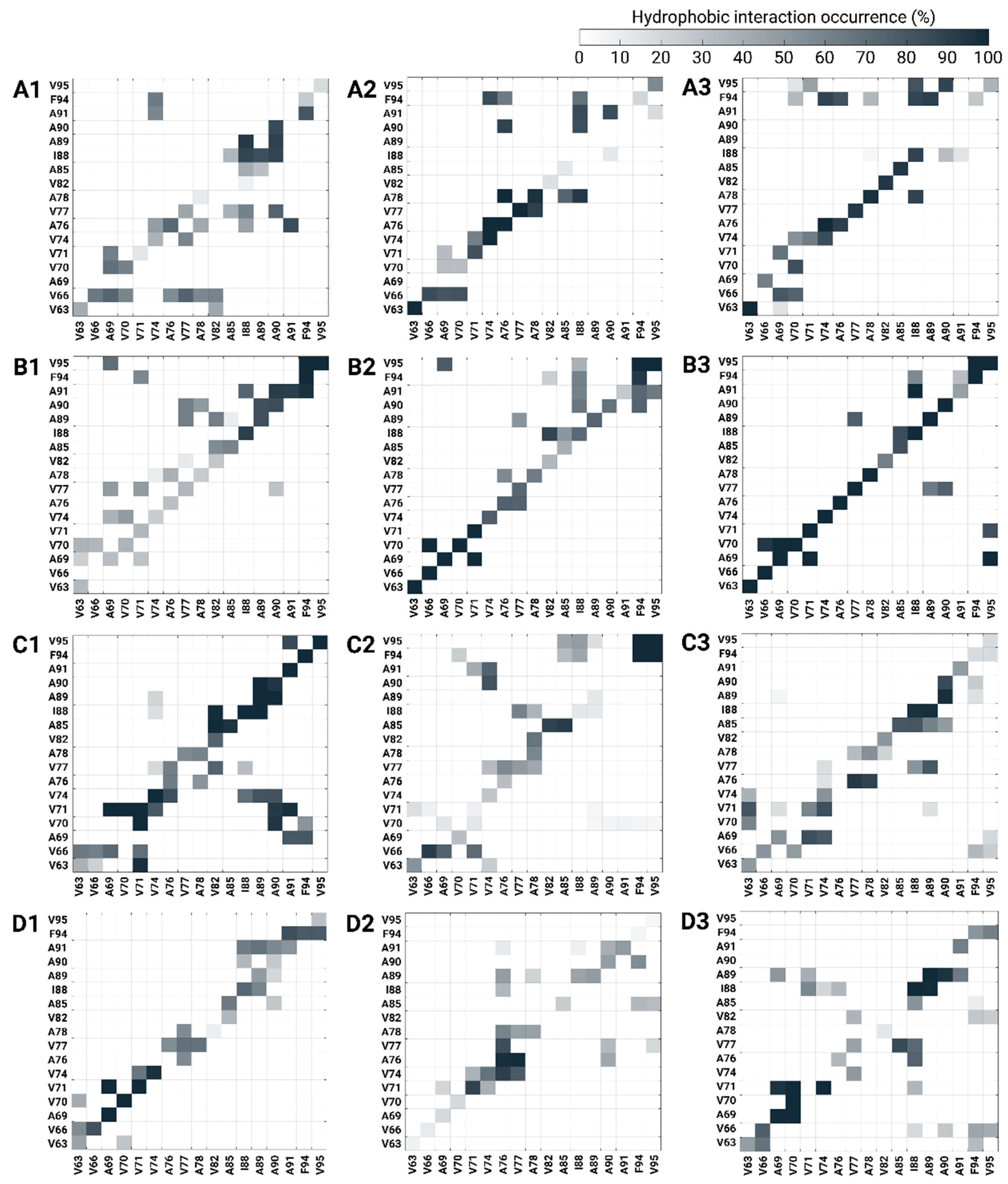
3.3. The Preference of Copper-Binding Site at Low Copper Concentrations Depends on Hydrophobic Contacts between the NAC Domains
3.4. Copper-Binding Site at the C-Terminus at High Concentrations Is Preferred Due to Conservation of Hydrophobic Contacts in the NAC Domain
3.5. The Preference of Copper-Binding Sites Depends on Copper Concentrations and on the Polymorphic AS Dimers
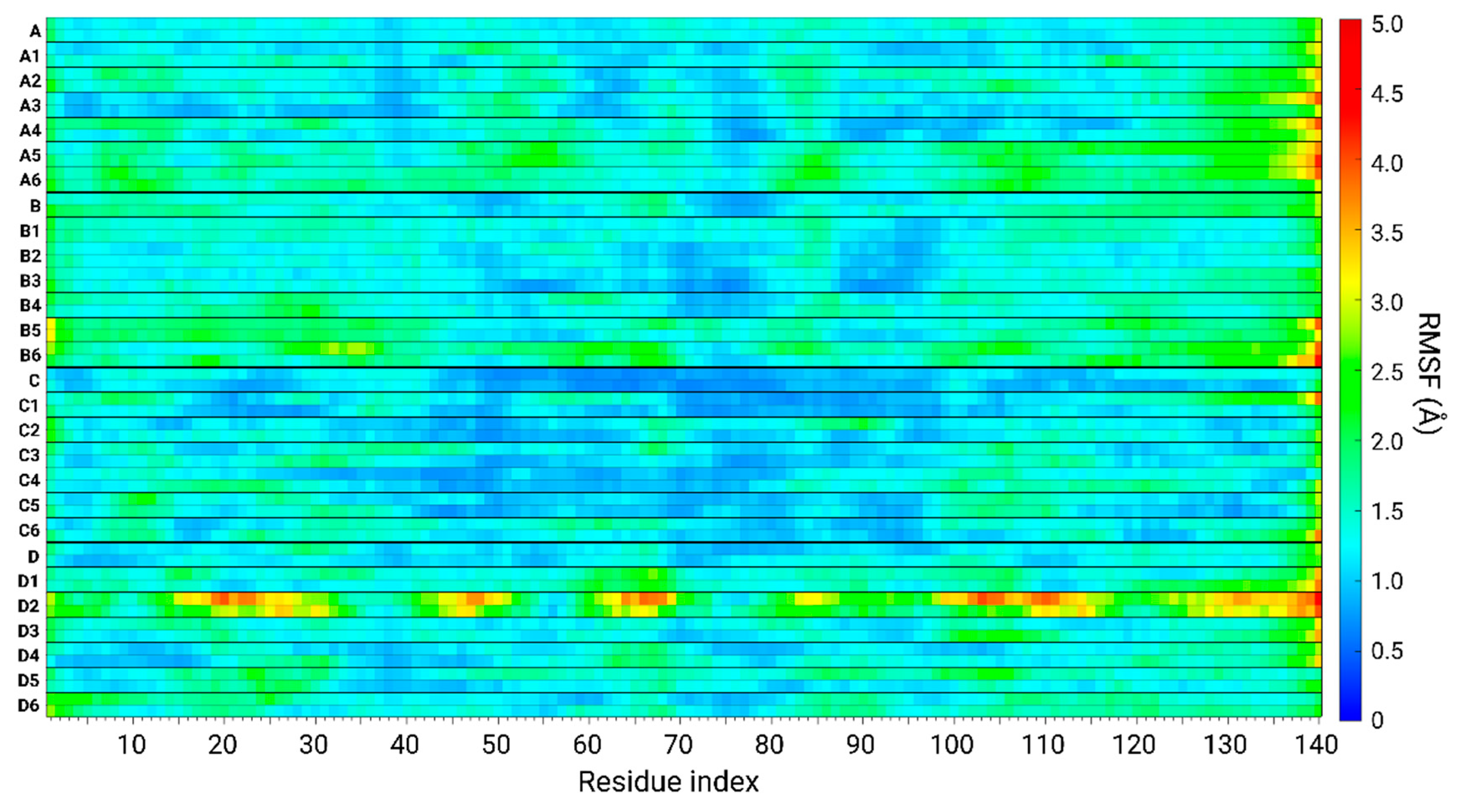
3.6. The Original Structure of AS Dimer Affects the Flexibility or Rigidity of Copper-AS Dimer Complexes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Hasegawa, M.; Goedert, M. alpha-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with lewy bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6469–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winner, B.; Jappelli, R.; Maji, S.K.; Desplats, P.A.; Boyer, L.; Aigner, S.; Hetzer, C.; Loher, T.; Vilar, M.; Campioni, S.; et al. In vivo demonstration that alpha-synuclein oligomers are toxic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4194–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camino, J.D.; Gracia, P.; Chen, S.W.; Sot, J.; de la Arada, I.; Sebastian, V.; Arrondo, J.L.R.; Goni, F.M.; Dobson, C.M.; Cremades, N. The extent of protein hydration dictates the preference for heterogeneous or homogeneous nucleation generating either parallel or antiparallel beta-sheet alpha-synuclein aggregates. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 11902–11914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan-Mark, S.; Miller, Y. Insights into the Interactions that Trigger the Primary Nucleation of Polymorphic alpha-Synuclein Dimers. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pall, H.S.; Williams, A.C.; Blake, D.R.; Lunec, J.; Gutteridge, J.M.; Hall, M.; Taylor, A. Raised cerebrospinal-fluid copper concentration in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 1987, 2, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnal, N.; Cristalli, D.O.; de Alaniz, M.J.; Marra, C.A. Clinical utility of copper, ceruloplasmin, and metallothionein plasma determinations in human neurodegenerative patients and their first-degree relatives. Brain Res. 2010, 1319, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Shi, M.; Chung, K.A.; Quinn, J.F.; Peskind, E.R.; Galasko, D.; Jankovic, J.; Zabetian, C.P.; Leverenz, J.B.; Baird, G.; et al. DJ-1 and alpha-synuclein in human cerebrospinal fluid as biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2010, 133, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, M.; Kato-Negishi, M.; Tanaka, K. Cross talk between neurometals and amyloidogenic proteins at the synapse and the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Metallomics 2017, 9, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosi, N.; Rossi, L. Copper at synapse: Release, binding and modulation of neurotransmission. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 90, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorklund, G.; Stejskal, V.; Urbina, M.A.; Dadar, M.; Chirumbolo, S.; Mutter, J. Metals and Parkinson’s Disease: Mechanisms and Biochemical Processes. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 2198–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasia, R.M.; Bertoncini, C.W.; Marsh, D.; Hoyer, W.; Cherny, D.; Zweckstetter, M.; Griesinger, C.; Jovin, T.M.; Fernandez, C.O. Structural characterization of copper(II) binding to alpha-synuclein: Insights into the bioinorganic chemistry of Parkinson’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4294–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uversky, V.N.; Li, J.; Fink, A.L. Metal-triggered structural transformations, aggregation, and fibrillation of human alpha-synuclein. A possible molecular NK between Parkinson’s disease and heavy metal exposure. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 44284–44296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, Y.; Rcom-H’cheo-Gauthier, A.N.; Goulding, M.; Chung, R.S.; Faller, P.; Pountney, D.L. Metallothionein, Copper and Alpha-Synuclein in Alpha-Synucleinopathies. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synhaivska, O.; Bhattacharya, S.; Campioni, S.; Thompson, D.; Nirmalraj, P.N. Single-Particle Resolution of Copper-Associated Annular alpha-Synuclein Oligomers Reveals Potential Therapeutic Targets of Neurodegeneration. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 1410–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyechova, E.Y.; Miliukhina, I.V.; Orlov, I.A.; Muruzheva, Z.M.; Puchkova, L.V.; Karpenko, M.N. A low blood copper concentration is a co-morbidity burden factor in Parkinson’s disease development. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 135, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Oh, S.B.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Ryu, H.S.; Kim, M.S.; Ayton, S.; Bush, A.I.; Lee, J.Y.; Chung, S.J. Association of metals with the risk and clinical characteristics of Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2018, 55, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittung-Stafshede, P. Crossroads between copper ions and amyloid formation in Parkinson’s disease. Essays Biochem. 2022, 66, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, D.N.; Kolkowska, P.; Tessari, I.; Baratto, M.C.; Sinicropi, A.; Bubacco, L.; Mangani, S.; Pozzi, C.; Valensin, D.; Miller, Y. Fibrils of alpha-Synuclein Abolish the Affinity of Cu2+-Binding Site to His50 and Induce Hopping of Cu2+ Ions in the Termini. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 10920–10927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, G.M.; Minetti, C.A.; Remeta, D.P.; Baum, J. A revised picture of the Cu(II)-alpha-synuclein complex: The role of N-terminal acetylation. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 2815–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valensin, D.; Dell’Acqua, S.; Kozlowski, H.; Casella, L. Coordination and redox properties of copper interaction with alpha-synuclein. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 163, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, X.; Sheveleva, A.; Tuna, F.; Willison, K.R.; Ying, L. Acetylation Rather than H50Q Mutation Impacts the Kinetics of Cu(II) Binding to alpha-Synuclein. Chemphyschem 2021, 22, 2413–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, R.J.; Paskins, A.R.; Dalton, C.F.; Smith, D.P. Copper Binding and Subsequent Aggregation of alpha-Synuclein Are Modulated by N-Terminal Acetylation and Ablated by the H50Q Missense Mutation. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 4737–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Prudent, M.; Fauvet, B.; Lashuel, H.A.; Girault, H.H. Phosphorylation of alpha-Synuclein at Y125 and S129 alters its metal binding properties: Implications for understanding the role of alpha-Synuclein in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease and related disorders. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeyawardhane, D.L.; Heitger, D.R.; Fernandez, R.D.; Forney, A.K.; Lucas, H.R. C-Terminal Cu(II) Coordination to alpha-Synuclein Enhances Aggregation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehra, S.; Gadhe, L.; Bera, R.; Sawner, A.S.; Maji, S.K. Structural and Functional Insights into alpha-Synuclein Fibril Polymorphism. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziaunys, M.; Sakalauskas, A.; Mikalauskaite, K.; Smirnovas, V. Polymorphism of Alpha-Synuclein Amyloid Fibrils Depends on Ionic Strength and Protein Concentration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Ferreira, R.; Taylor, N.M.; Arteni, A.A.; Kumari, P.; Mona, D.; Ringler, P.; Britschgi, M.; Lauer, M.E.; Makky, A.; Verasdonck, J.; et al. Two new polymorphic structures of human full-length alpha-synuclein fibrils solved by cryo-electron microscopy. Elife 2019, 8, e48907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, Y.; Ma, B.; Nussinov, R. Polymorphism in Alzheimer Abeta amyloid organization reflects conformational selection in a rugged energy landscape. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4820–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, Y.; Ma, B.; Nussinov, R. Zinc ions promote Alzheimer Abeta aggregation via population shift of polymorphic states. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9490–9495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.M.; Lin, Y.; Heo, Y.; Lee, Y.H. Polymorphism in alpha-synuclein oligomers and its implications in toxicity under disease conditions. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 959425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.; Sengupta, U.; Puangmalai, N.; Bhatt, N.; Kayed, R. Polymorphic Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers: Characterization and Differential Detection with Novel Corresponding Antibodies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 2691–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walke, G.; Kumar, R.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Copper ion incorporation in alpha-synuclein amyloids. Protein Sci. 2024, 33, e4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, D.N.; Miller, Y. Study of Molecular Mechanisms of alpha-Synuclein Assembly: Insight into a Cross-beta Structure in the N-Termini of New alpha-Synuclein Fibrils. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3363–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttle, M.D.; Comellas, G.; Nieuwkoop, A.J.; Covell, D.J.; Berthold, D.A.; Kloepper, K.D.; Courtney, J.M.; Kim, J.K.; Barclay, A.M.; Kendall, A.; et al. Solid-state NMR structure of a pathogenic fibril of full-length human alpha-synuclein. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Ge, P.; Murray, K.A.; Sheth, P.; Zhang, M.; Nair, G.; Sawaya, M.R.; Shin, W.S.; Boyer, D.R.; Ye, S.; et al. Cryo-EM of full-length alpha-synuclein reveals fibril polymorphs with a common structural kernel. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolus, M.; Bisaglia, M.; Zoleo, A.; Fittipaldi, M.; Benfatto, M.; Bubacco, L.; Maniero, A.L. Structural characterization of a high affinity mononuclear site in the copper(II)-alpha-synuclein complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18057–18066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, S.C.; Leong, S.L.; Pham, C.L.; Tew, D.J.; Masters, C.L.; Miles, L.A.; Cappai, R.; Barnham, K.J. Cu2+ binding modes of recombinant alpha-synuclein--insights from EPR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7766–7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, Y.; Ma, B.; Nussinov, R. Metal binding sites in amyloid oligomers: Complexes and mechanisms. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wineman-Fisher, V.; Bloch, D.N.; Miller, Y. Challenges in studying the structures of metal-amyloid oligomers related to type 2 diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 327-328, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalé, L.; Skeel, R.; Bhandarkar, M.; Brunner, R.; Gursoy, A.; Krawetz, N.; Phillips, J.; Shinozaki, A.; Varadarajan, K.; Schulten, K. NAMD2: Greater Scalability for Parallel Molecular Dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1999, 151, 283–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, M.W.; Jorgensen, W.L. A five-site model for liquid water and the reproduction of the density anomaly by rigid, nonpolarizable potential functions. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 112, 8910–8922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, S.E.; Zhang, Y.; Pastor, R.W.; Brooks, B.R. Constant pressure molecular dynamics simulation: The Langevin piston method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 4613–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, K.; Tobias, D.J.; Klein, M.L. Constant pressure and temperature molecular dynamics simulation of a fully hydrated liquid crystal phase dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer. Biophys. J. 1995, 69, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N log (N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckaert, J.-P.; Ciccotti, G.; Berendsen, H.J. Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: Molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, W.; Sander, C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: Pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers 1983, 22, 2577–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.; Pashley, R. The hydrophobic interaction is long range, decaying exponentially with distance. Nature 1982, 300, 341–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloof, H.; Nilsson, L.; Rigler, R. Molecular-Dynamics Simulation of Galanin in Aqueous and Nonaqueous Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 4028–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Feig, M.; Salsbury, F.R.; Brooks, C.L. New analytic approximation to the standard molecular volume definition and its application to generalized born calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Salsbury, F.R.; Brooks, C.L. Novel generalized Born methods. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 116, 10606–10614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, J.; Shenkin, P.S.; Still, W.C. Optimization of Gaussian surface calculations and extension to solvent-accessible surface areas. J. Comput. Chem. 1999, 20, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Ma, L.; Zheng, J.; Petersen, R.B.; Zheng, L.; et al. Copper and iron ions accelerate the prion-like propagation of alpha-synuclein: A vicious cycle in Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binolfi, A.; Quintanar, L.; Bertoncini, C.W.; Griesinger, C.; Fernández, C.O. Bioinorganic chemistry of copper coordination to alpha-synuclein: Relevance to Parkinson’s disease. Coordin Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 2188–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, F.; Hodak, M.; Bernholc, J. Mechanism of copper(II)-induced misfolding of Parkinson’s disease protein. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, E.J.; Wilkinson, M.; Radford, S.E.; Sobott, F. Taking Charge: Metal Ions Accelerate Amyloid Aggregation in Sequence Variants of alpha-Synuclein. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2023, 34, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisaglia, M.; Bubacco, L. Copper Ions and Parkinson’s Disease: Why Is Homeostasis So Relevant? Biomolecules 2020, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Garcia, M.; Fusco, G.; De Simone, A. Metal interactions of alpha-synuclein probed by NMR amide-proton exchange. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1167766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulson, B.G.; Szczepski, K.; Lachowicz, J.I.; Jaremko, L.; Emwas, A.H.; Jaremko, M. Aggregation of biologically important peptides and proteins: Inhibition or acceleration depending on protein and metal ion concentrations. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Ferreira, R.; Taylor, N.M.; Mona, D.; Ringler, P.; Lauer, M.E.; Riek, R.; Britschgi, M.; Stahlberg, H. Cryo-EM structure of alpha-synuclein fibrils. Elife 2018, 7, e36402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.S.; Calkins, E. Electron microscopic observations on a fibrous component in amyloid of diverse origins. Nature 1959, 183, 1202–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
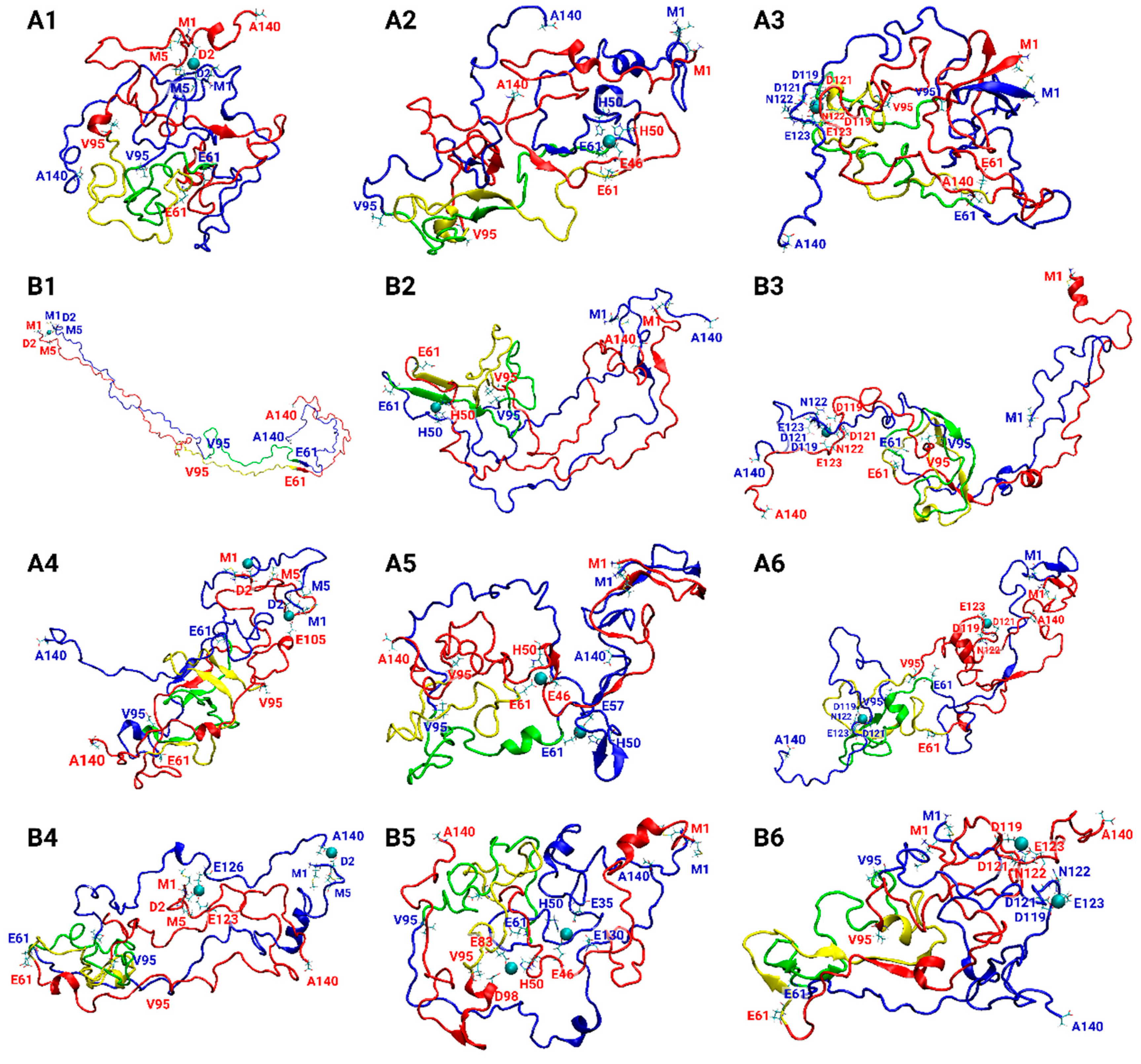
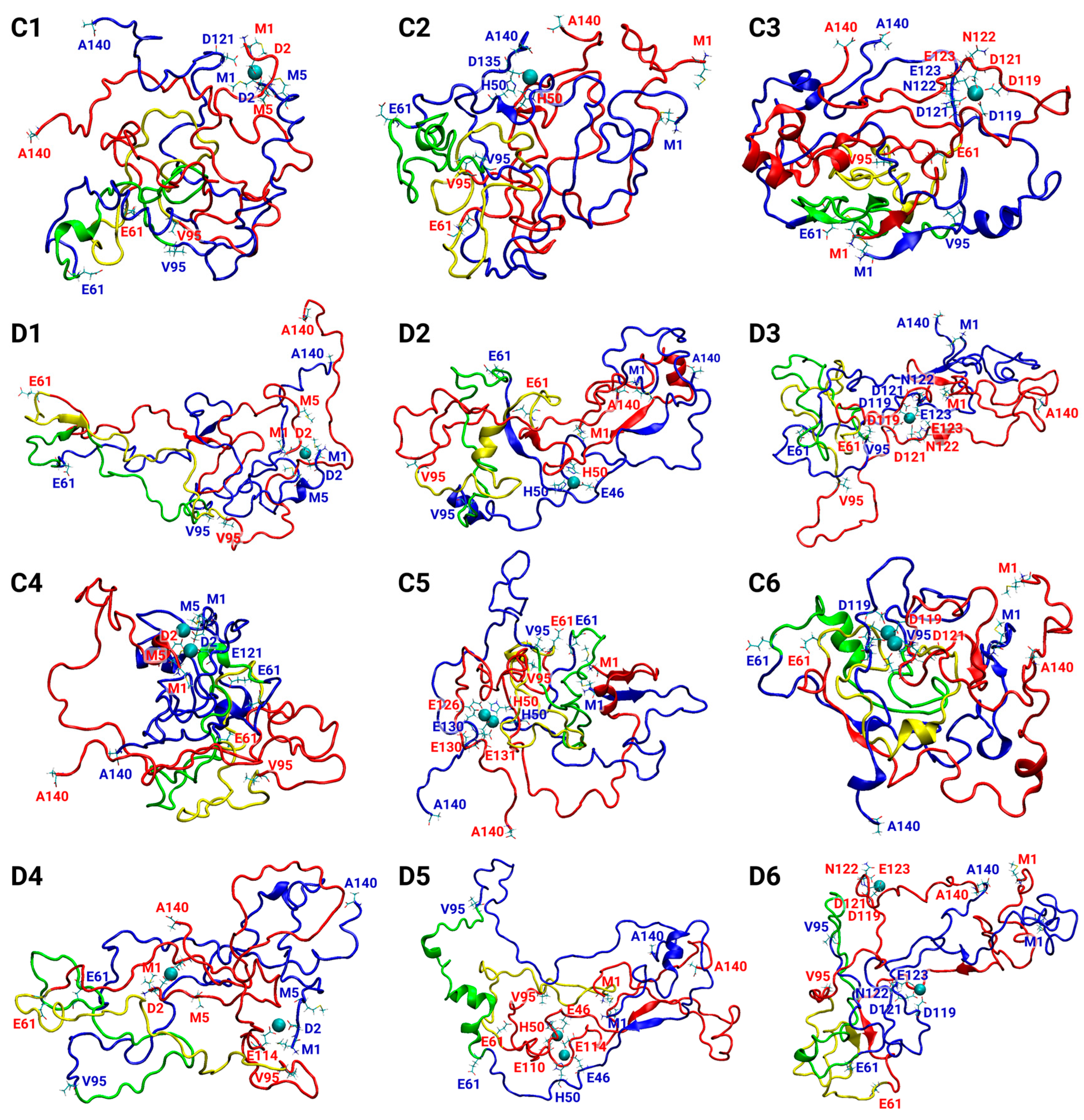


| Cu2+ Binding Site | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymorph-Based Fibril | Cu2+:AS Ratio | Met1, Asp2, Met5 | His50 | Asp119, Asp121, Asn122, Glu123 |
| A | 1:2 | A1 | A2 | A3 |
| 1:1 | A4 | A5 | A6 | |
| B | 1:2 | B1 | B2 | B3 |
| 1:1 | B4 | B5 | B6 | |
| C | 1:2 | C1 | C2 | C3 |
| 1:1 | C4 | C5 | C6 | |
| D | 1:2 | D1 | D2 | D3 |
| 1:1 | D4 | D5 | D6 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blacher, C.; Abramov-Harpaz, K.; Miller, Y. Primary Nucleation of Polymorphic α-Synuclein Dimers Depends on Copper Concentrations and Definite Copper-Binding Site. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060627
Blacher C, Abramov-Harpaz K, Miller Y. Primary Nucleation of Polymorphic α-Synuclein Dimers Depends on Copper Concentrations and Definite Copper-Binding Site. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(6):627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060627
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlacher, Carmia, Karina Abramov-Harpaz, and Yifat Miller. 2024. "Primary Nucleation of Polymorphic α-Synuclein Dimers Depends on Copper Concentrations and Definite Copper-Binding Site" Biomolecules 14, no. 6: 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060627
APA StyleBlacher, C., Abramov-Harpaz, K., & Miller, Y. (2024). Primary Nucleation of Polymorphic α-Synuclein Dimers Depends on Copper Concentrations and Definite Copper-Binding Site. Biomolecules, 14(6), 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060627










