Effects of A1 Milk, A2 Milk and the Opioid-like Peptide β-Casomorphin-7 on the Proliferation of Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. A1 and A2 Milk
2.2. In Vitro Digestion of A1 and A2 Milk
2.3. Detection of BCM-7 in Digested Milk Using In-House Competitive ELISA
2.4. Isolation of PBMCs from Human Blood Samples
2.5. In Vitro Cell Proliferation
2.6. Separation of CD4+ T Cells by Magnetic-Activated Cell Sorting (MACS)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ConA-Induced Proliferation of PBMCs
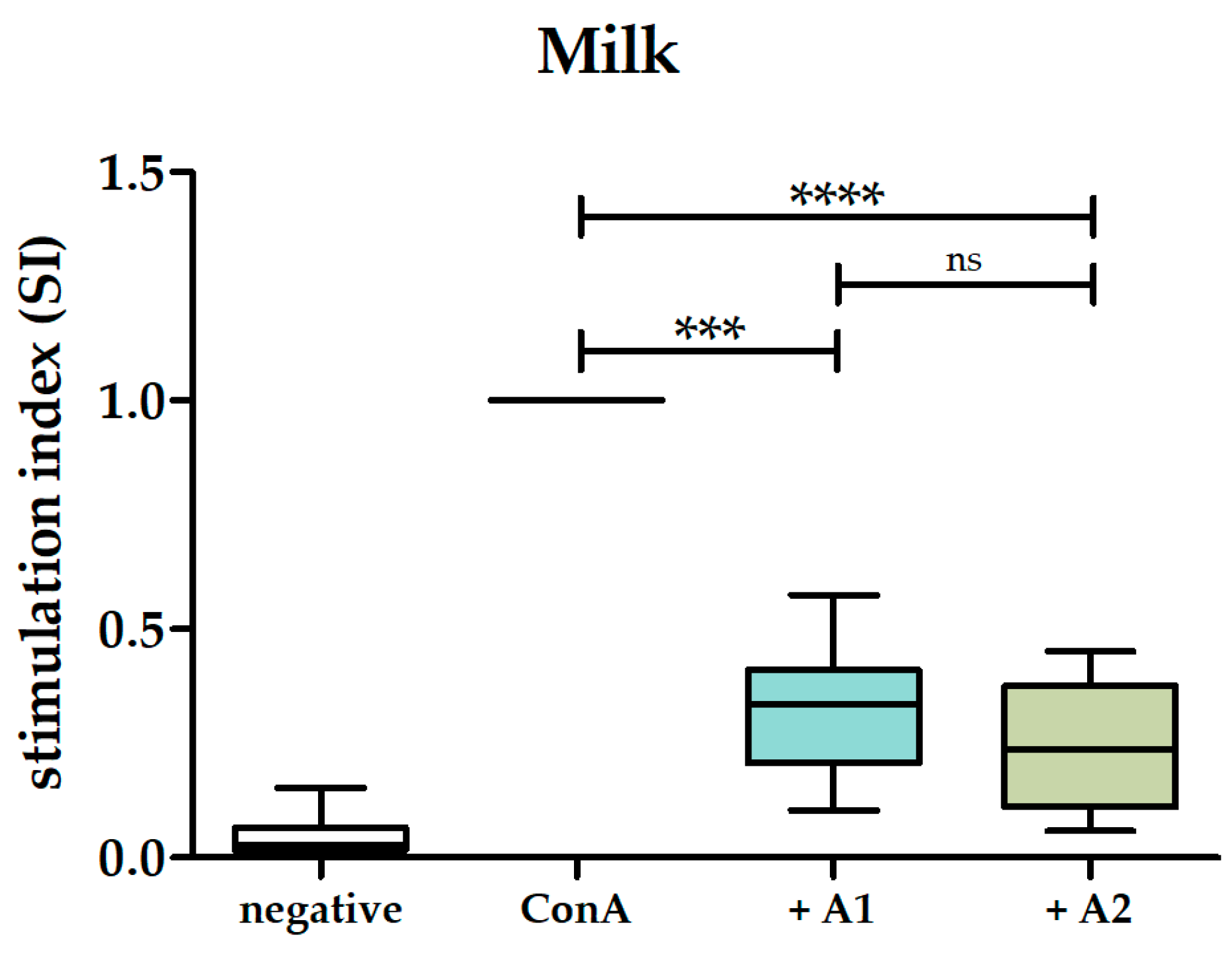
3.2. A1 and A2 Milk Inhibited Proliferation of PBMCs
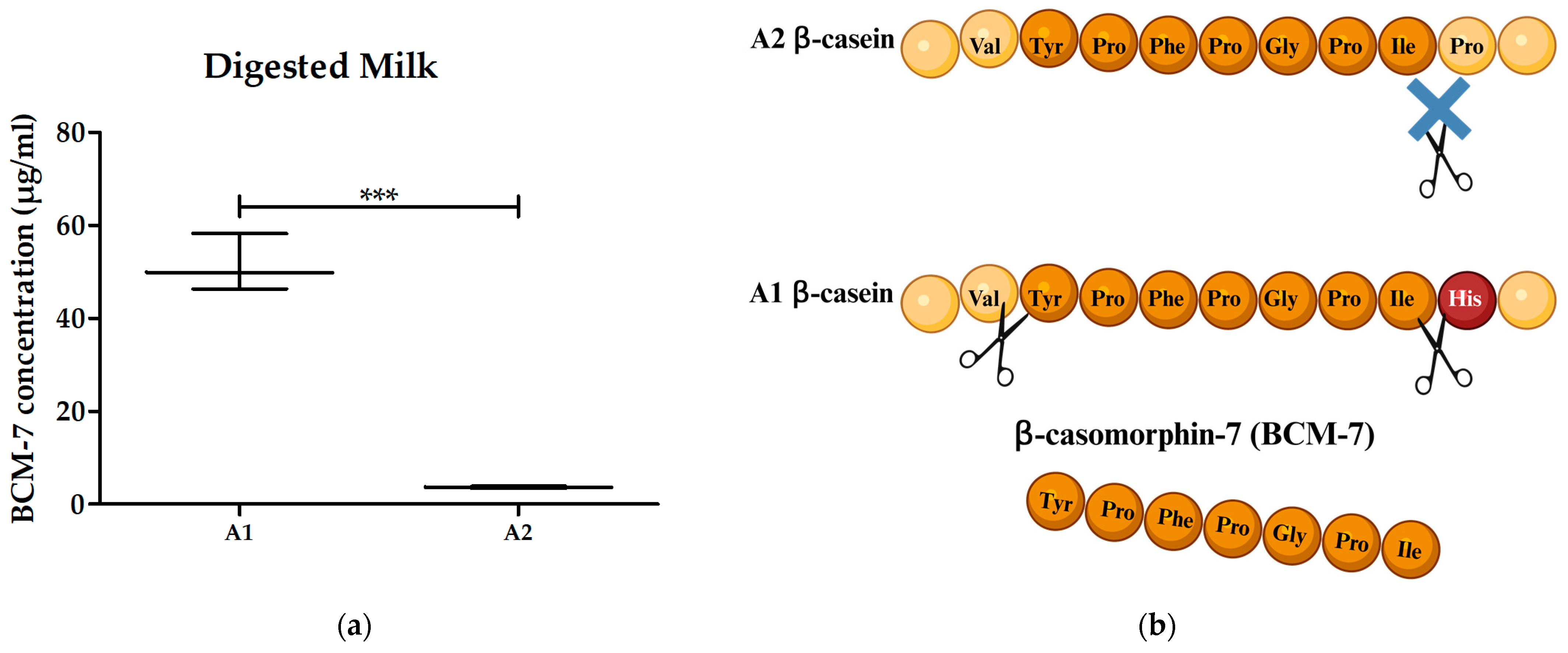
3.3. Digested A1 and A2 Milk Contained BCM-7 and Did Not Alter the Proliferation of PBMCs
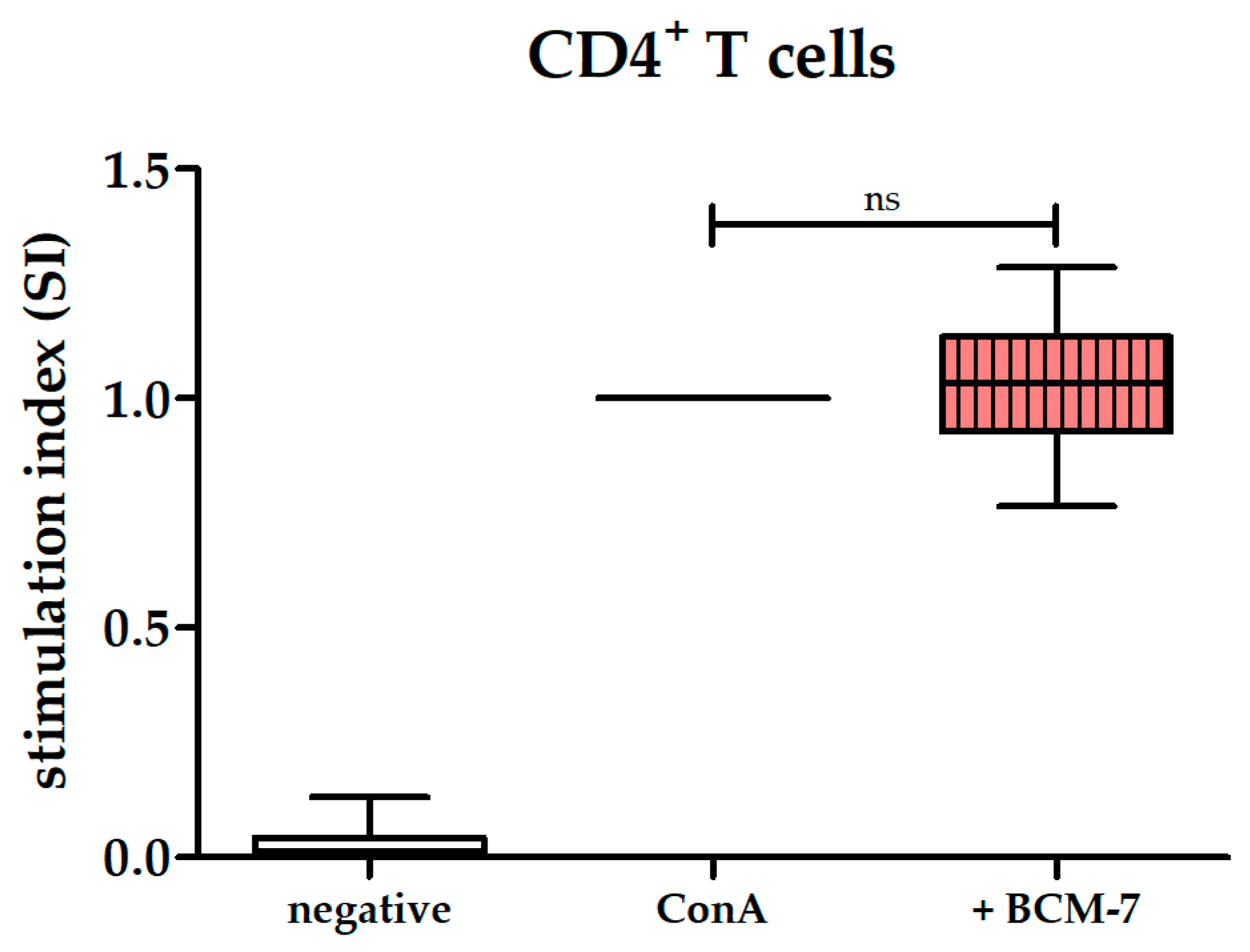
3.4. BCM-7 at Several Concentrations Did Not Alter the Proliferation of PBMCs and CD4+ T Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franzoi, M.; Niero, G.; Visentin, G.; Penasa, M.; Cassandro, M.; De Marchi, M. Variation of Detailed Protein Composition of Cow Milk Predicted from a Large Database of Mid-Infrared Spectra. Animals 2019, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroli, A.M.; Chessa, S.; Erhardt, G.J. Invited review: Milk protein polymorphisms in cattle: Effect on animal breeding and human nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 5335–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallinat, J.L.; Qanbari, S.; Drogemuller, C.; Pimentel, E.C.; Thaller, G.; Tetens, J. DNA-based identification of novel bovine casein gene variants. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jann, O.; Ceriotti, G.; Caroli, A.; Erhardt, G. A new variant in exon VII of bovine β-casein gene (CSN2) and its distribution among European cattle breeds. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2002, 119, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, M.; Zhou, X.; Dydak, U.; Savaiano, D.A. Gastric Emptying of New-World Milk Containing A1 and A2 Beta-Casein Is More Rapid as Compared to Milk Containing Only A2 Beta-Casein in Lactose Maldigesters: A Randomized, Cross-Over Trial Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Nutrients 2023, 15, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noni, I.D. Release of β-casomorphins 5 and 7 during simulated gastro-intestinal digestion of bovine β-casein variants and milk-based infant formulas. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslinska, A.; Kostyra, E.; Kostyra, H.; Olenski, K.; Fiedorowicz, E.; Kaminski, S. Milk from cows of different beta-casein genotypes as a source of beta-casomorphin-7. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 63, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asledottir, T.; Le, T.T.; Poulsen, N.A.; Devold, T.G.; Larsen, L.B.; Vegarud, G.E. Release of β-casomorphin-7 from bovine milk of different β-casein variants after ex vivo gastrointestinal digestion. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 81, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Haq, M.R.; Kapila, R.; Kapila, S. Release of beta-casomorphin-7/5 during simulated gastrointestinal digestion of milk beta-casein variants from Indian crossbred cattle (Karan Fries). Food Chem. 2015, 168, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantl, V.; Teschemacher, H. A material with opioid activity in bovine milk and milk products. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 1979, 306, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschemacher, H. Opioid receptor ligands derived from food proteins. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2003, 9, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappenheimer, J.R.; Dahl, C.E.; Karnovsky, M.L.; Maggio, J.E. Intestinal absorption and excretion of octapeptides composed of D amino acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1942–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M. Modulation of intestinal functions by food substances. Nahrung 1999, 43, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Son, D.O. Food-derived peptides and intestinal functions. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolov, O.; Kost, N.; Andreeva, O.; Korneeva, E.; Meshavkin, V.; Tarakanova, Y.; Dadayan, A.; Zolotarev, Y.; Grachev, S.; Mikheeva, I.; et al. Autistic children display elevated urine levels of bovine casomorphin-7 immunoreactivity. Peptides 2014, 56, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarmolowska, B.; Bukalo, M.; Fiedorowicz, E.; Cieslinska, A.; Kordulewska, N.K.; Moszynska, M.; Swiatecki, A.; Kostyra, E. Role of Milk-Derived Opioid Peptides and Proline Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Nutrients 2019, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedorowicz, E.; Kaczmarski, M.; Cieslinska, A.; Sienkiewicz-Szlapka, E.; Jarmolowska, B.; Chwala, B.; Kostyra, E. beta-casomorphin-7 alters mu-opioid receptor and dipeptidyl peptidase IV genes expression in children with atopic dermatitis. Peptides 2014, 62, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwan, M.; Jarmolowska, B.; Bielikowicz, K.; Kostyra, E.; Kostyra, H.; Kaczmarski, M. Transport of micro-opioid receptor agonists and antagonist peptides across Caco-2 monolayer. Peptides 2008, 29, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asledottir, T.; Picariello, G.; Mamone, G.; Ferranti, P.; Roseth, A.; Devold, T.G.; Vegarud, G.E. Degradation of beta-casomorphin-7 through in vitro gastrointestinal and jejunal brush border membrane digestion. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 8622–8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Ninkovic, J.; Banerjee, S.; Charboneau, R.G.; Das, S.; Dutta, R.; Kirchner, V.A.; Koodie, L.; Ma, J.; Meng, J.; et al. Opioid drug abuse and modulation of immune function: Consequences in the susceptibility to opportunistic infections. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2011, 6, 442–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.K.; Killam, K.F., Jr.; Chuang, L.F.; Kung, H.F.; Sheng, W.S.; Chao, C.C.; Yu, L.; Chuang, R.Y. Mu opioid receptor gene expression in immune cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 216, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elitsur, Y.; Luk, G.D. Beta-casomorphin (BCM) and human colonic lamina propria lymphocyte proliferation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1991, 85, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiedorowicz, E.; Jarmolowska, B.; Iwan, M.; Kostyra, E.; Obuchowicz, R.; Obuchowicz, M. The influence of mu-opioid receptor agonist and antagonist peptides on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Peptides 2011, 32, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayser, H.; Meisel, H. Stimulation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes by bioactive peptides derived from bovine milk proteins. FEBS Lett. 1996, 383, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutas, Y.; Soppi, E.; Korhonen, H.; Syvaoja, E.L.; Saxelin, M.; Rokka, T.; Isolauri, E. Suppression of lymphocyte proliferation in vitro by bovine caseins hydrolyzed with Lactobacillus casei GG-derived enzymes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 98, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deth, R.; Clarke, A.; Ni, J.; Trivedi, M. Clinical evaluation of glutathione concentrations after consumption of milk containing different subtypes of β-casein: Results from a randomized, cross-over clinical trial. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Rico, S.; Mondragón, A.d.C.; López-Santamarina, A.; Cardelle-Cobas, A.; Regal, P.; Lamas, A.; Ibarra, I.S.; Cepeda, A.; Miranda, J.M. A2 Milk: New Perspectives for Food Technology and Human Health. Foods 2022, 11, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carriere, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food—An international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, T.T. Processing affects beta-casomorphin peptide formation during simulated gastrointestinal digestion in both A1 and A2 milk. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 121, 105099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, R.S.; Bernstein, I.A. Thymidine incorporation into deoxyribonucleic acid by isolated rat liver mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 1970, 245, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, N.; Ronsmans, S.; Hoet, P. Methods to Assess Proliferation of Stimulated Human Lymphocytes In Vitro: A Narrative Review. Cells 2023, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninković, J.; Roy, S. Role of the mu-opioid receptor in opioid modulation of immune function. Amino Acids 2013, 45, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, P.J.; Davis, T.A.; Smoot, D.S.; Abe, R.; June, C.H.; Lee, K.P. Mitogenic stimulation of T cells reveals differing contributions for B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86) costimulation. Immunology 1997, 90, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarmołowska, B.; Bielikowicz, K.; Iwan, M.; Sidor, K.; Kostyra, E.; Kaczmarski, M. Serum activity of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV; EC 3.4.14.5) in breast-fed infants with symptoms of allergy. Peptides 2007, 28, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieslinska, A.; Fiedorowicz, E.; Rozmus, D.; Sienkiewicz-Szlapka, E.; Jarmolowska, B.; Kaminski, S. Does a Little Difference Make a Big Difference? Bovine beta-Casein A1 and A2 Variants and Human Health-An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogahawaththa, D.; Ashraf, R.; Chandrapala, J.; Donkor, O.; Vasiljevic, T. In vitro immunogenicity of various native and thermally processed bovine milk proteins and their mixtures. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8726–8736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otani, H.; Hata, I. Inhibition of proliferative responses of mouse spleen lymphocytes and rabbit Peyer’s patch cells by bovine milk caseins and their digests. J. Dairy Res. 1995, 62, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolk, K.; Kunz, S.; Asadullah, K.; Sabat, R. Cutting edge: Immune cells as sources and targets of the IL-10 family members? J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 5397–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Prete, G.; De Carli, M.; Almerigogna, F.; Giudizi, M.G.; Biagiotti, R.; Romagnani, S. Human IL-10 is produced by both type 1 helper (Th1) and type 2 helper (Th2) T cell clones and inhibits their antigen-specific proliferation and cytokine production. J. Immunol. 1993, 150, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabat, R.; Grütz, G.; Warszawska, K.; Kirsch, S.; Witte, E.; Wolk, K.; Geginat, J. Biology of interleukin-10. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, H.M.; Jimenez-Flores, R.; Bleck, G.T.; Brown, E.M.; Butler, J.E.; Creamer, L.K.; Hicks, C.L.; Hollar, C.M.; Ng-Kwai-Hang, K.F.; Swaisgood, H.E. Nomenclature of the Proteins of Cows’ Milk—Sixth Revision. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 1641–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemilar, M.; Khalili, M.; Rezaeimanesh, N.; Sadeghi Hokmabadi, E.; Rasulzade, S.; Shamshirgaran, S.M.; Taheraghdam, A.; Farhoudi, M.; Shaafi, S.; Shakouri, S.K.; et al. Effect of Whey Protein Supplementation on Inflammatory and Antioxidant Markers, and Clinical Prognosis in Acute Ischemic Stroke (TNS Trial): A Randomized, Double Blind, Controlled, Clinical Trial. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, E.K.; Vegarud, G.E.; Langsrud, T.; Almaas, H.; Lea, T. Effect of milk proteins and their hydrolysates on in vitro immune responses. Small Rumin. Res. 2008, 79, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, N.S.; Bailey, H.M.; Guardiola, L.V.; Stein, H.H. Values for Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score (DIAAS) Determined in Pigs Are Greater for Milk Than for Breakfast Cereals, but DIAAS Values for Individual Ingredients Are Additive in Combined Meals. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loveday, S.M. Protein digestion and absorption: The influence of food processing. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2023, 36, 544–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.P.; Mitsui, T.; Fujiki, K.; Ishiguro, H.; Kondo, T. Effect of lactase preparations in asymptomatic individuals with lactase deficiency--gastric digestion of lactose and breath hydrogen analysis. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2002, 65, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Horstman, A.M.H.; Huppertz, T. Milk proteins: Processing, gastric coagulation, amino acid availability and muscle protein synthesis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 10267–10282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, M.L. Gastrointestinal absorption of intact proteins. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1988, 8, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heppner, F.L.; Christ, A.D.; Klein, M.A.; Prinz, M.; Fried, M.; Kraehenbuhl, J.-P.; Aguzzi, A. Transepithelial prion transport by M cells. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 976–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, E.; Bendayan, M. Intestinal absorption of peptides through the enterocytes. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2000, 49, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballegaard, A.-S.R.; Bøgh, K.L. Intestinal protein uptake and IgE-mediated food allergy. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanuytsel, T.; Tack, J.; Farre, R. The Role of Intestinal Permeability in Gastrointestinal Disorders and Current Methods of Evaluation. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 717925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutrou, R.; Gaudichon, C.; Dupont, D.; Jardin, J.; Airinei, G.; Marsset-Baglieri, A.; Benamouzig, R.; Tome, D.; Leonil, J. Sequential release of milk protein-derived bioactive peptides in the jejunum in healthy humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, S.; Masotti, F.; Stuknytė, M.; De Noni, I. Impact of in vitro static digestion method on the release of β-casomorphin-7 from bovine milk and cheeses with A1 or A2 β-casein phenotypes. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asledottir, T.; Le, T.T.; Petrat-Melin, B.; Devold, T.G.; Larsen, L.B.; Vegarud, G.E. Identification of bioactive peptides and quantification of β-casomorphin-7 from bovine β-casein A1, A2 and I after ex vivo gastrointestinal digestion. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 71, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svedberg, J.; de Haas, J.; Leimenstoll, G.; Paul, F.; Teschemacher, H. Demonstration of β-casomorphin immunoreactive materials in in vitro digests of bovine milk and in small intestine contents after bovine milk ingestion in adult humans. Peptides 1985, 6, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lijnen, P.; Saavedra, A.; Petrov, V. In vitro proliferative response of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells to concanavalin A. Clin. Chim. Acta 1997, 264, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Yasuoka, C.; Mishima, T.; Ikematsu, T.; Uede, T.; Matsunaga, T.; Inobe, M. Concanavalin A-mediated T cell proliferation is regulated by herpes virus entry mediator costimulatory molecule. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. -Anim. 2014, 50, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unitt, J.; Hornigold, D. Plant lectins are novel Toll-like receptor agonists. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 81, 1324–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.M.; Martinez, G.J.; Chung, Y.; Dong, C. Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in T cells promotes autoimmune inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13064–13069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales-Malca, J.A.; Tirado-Kulieva, V.A.; Abanto-López, M.S.; Aldana-Juárez, W.L.; Palacios-Zapata, C.M. Worldwide research on the health effects of bovine milk containing A1 and A2 β-casein: Unraveling the current scenario and future trends through bibliometrics and text mining. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 7, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuellenberg de Gaudry, D.; Lohner, S.; Bischoff, K.; Schmucker, C.; Hoerrlein, S.; Roeger, C.; Schwingshackl, L.; Meerpohl, J.J. A1- and A2 beta-casein on health-related outcomes: A scoping review of animal studies. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Park, Y.-S.; Yoon, S.-S. A2 milk consumption and its health benefits: An update. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 33, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gard, F.; Flad, L.M.; Weißer, T.; Ammer, H.; Deeg, C.A. Effects of A1 Milk, A2 Milk and the Opioid-like Peptide β-Casomorphin-7 on the Proliferation of Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060690
Gard F, Flad LM, Weißer T, Ammer H, Deeg CA. Effects of A1 Milk, A2 Milk and the Opioid-like Peptide β-Casomorphin-7 on the Proliferation of Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(6):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060690
Chicago/Turabian StyleGard, Felix, Lili M. Flad, Tanja Weißer, Hermann Ammer, and Cornelia A. Deeg. 2024. "Effects of A1 Milk, A2 Milk and the Opioid-like Peptide β-Casomorphin-7 on the Proliferation of Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells" Biomolecules 14, no. 6: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060690
APA StyleGard, F., Flad, L. M., Weißer, T., Ammer, H., & Deeg, C. A. (2024). Effects of A1 Milk, A2 Milk and the Opioid-like Peptide β-Casomorphin-7 on the Proliferation of Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Biomolecules, 14(6), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060690






