Dry–Wet Changes in a Typical Agriculture and Pasture Ecotone in China between 1540 and 2019
Abstract
:1. Introduction
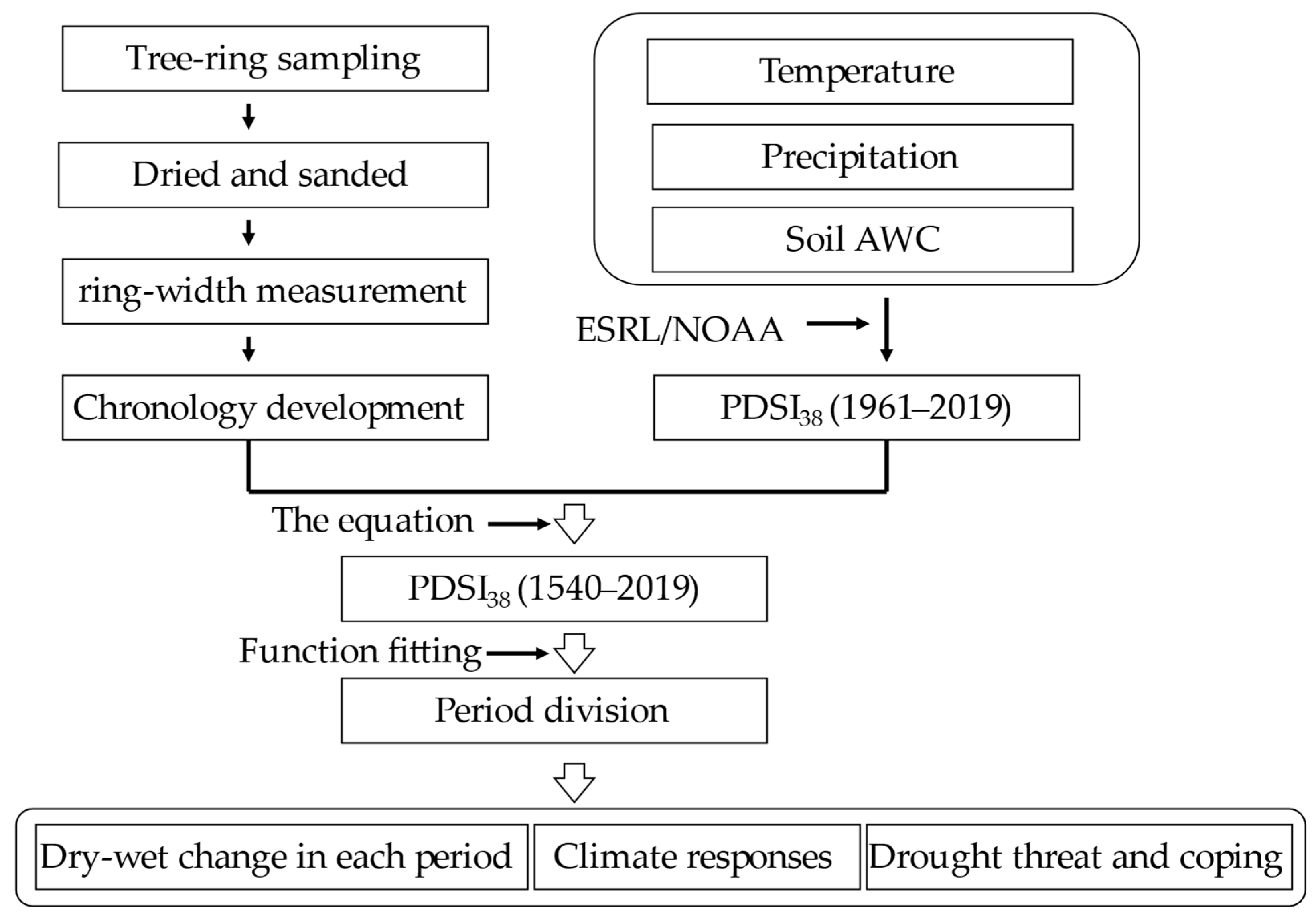
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Tree-Ring Sampling
2.3. Chronology Development
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Reconstruction of PDSI38
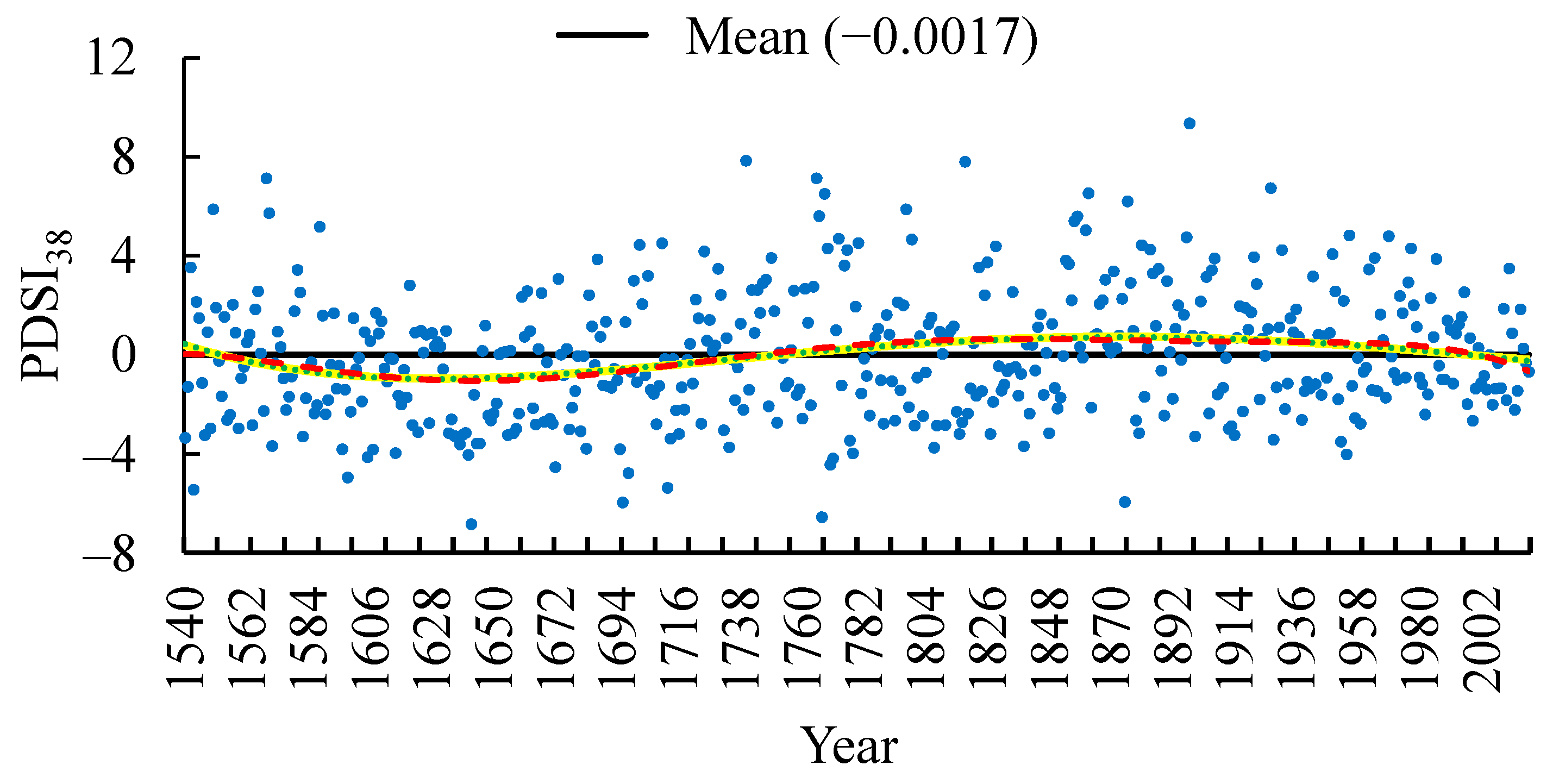
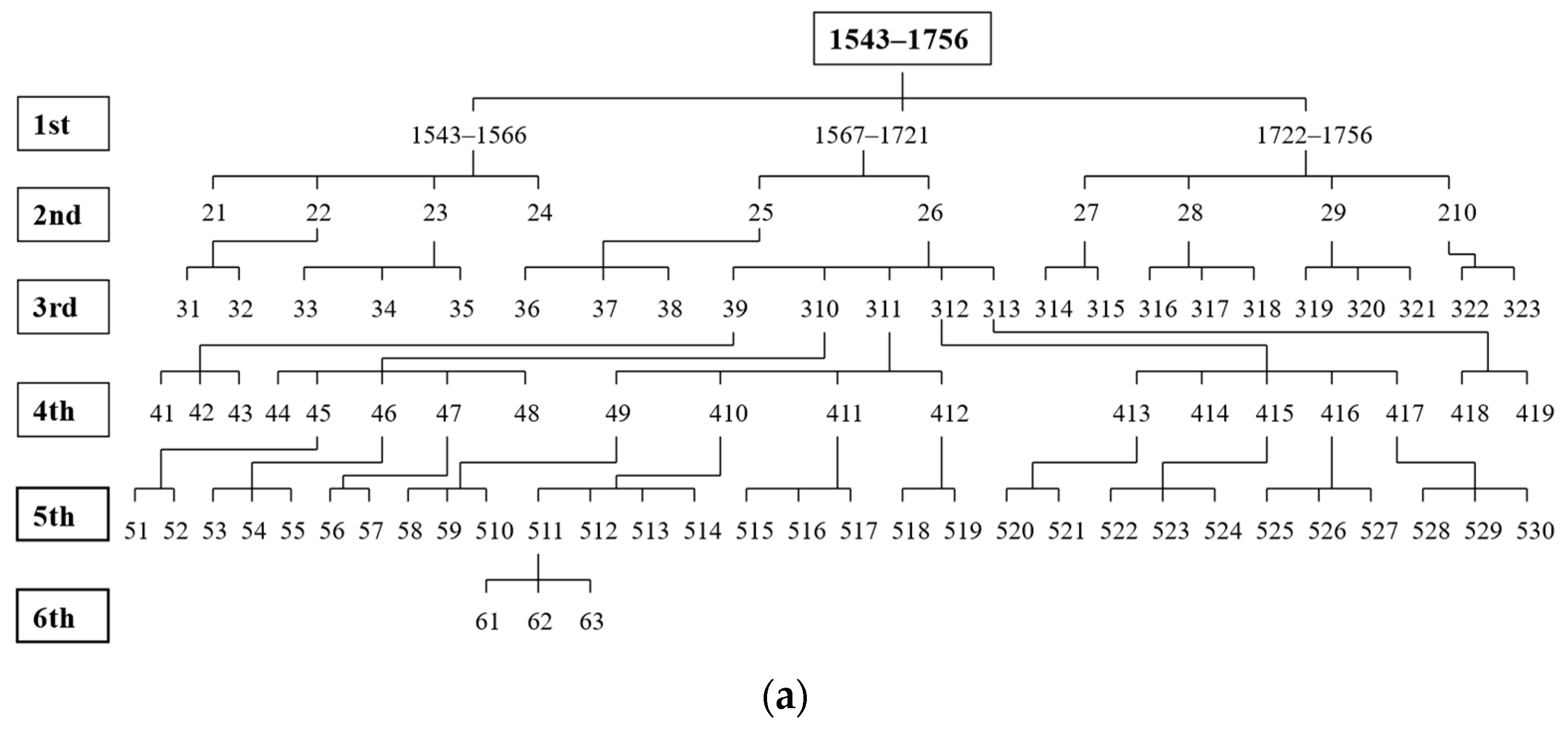
2.4.2. Period Division of the PDSI38 Related to Dry–Wet Changes
Division Using Function Fitting Methods
Division Process of Function Fitting
Analysis Methods
3. Results
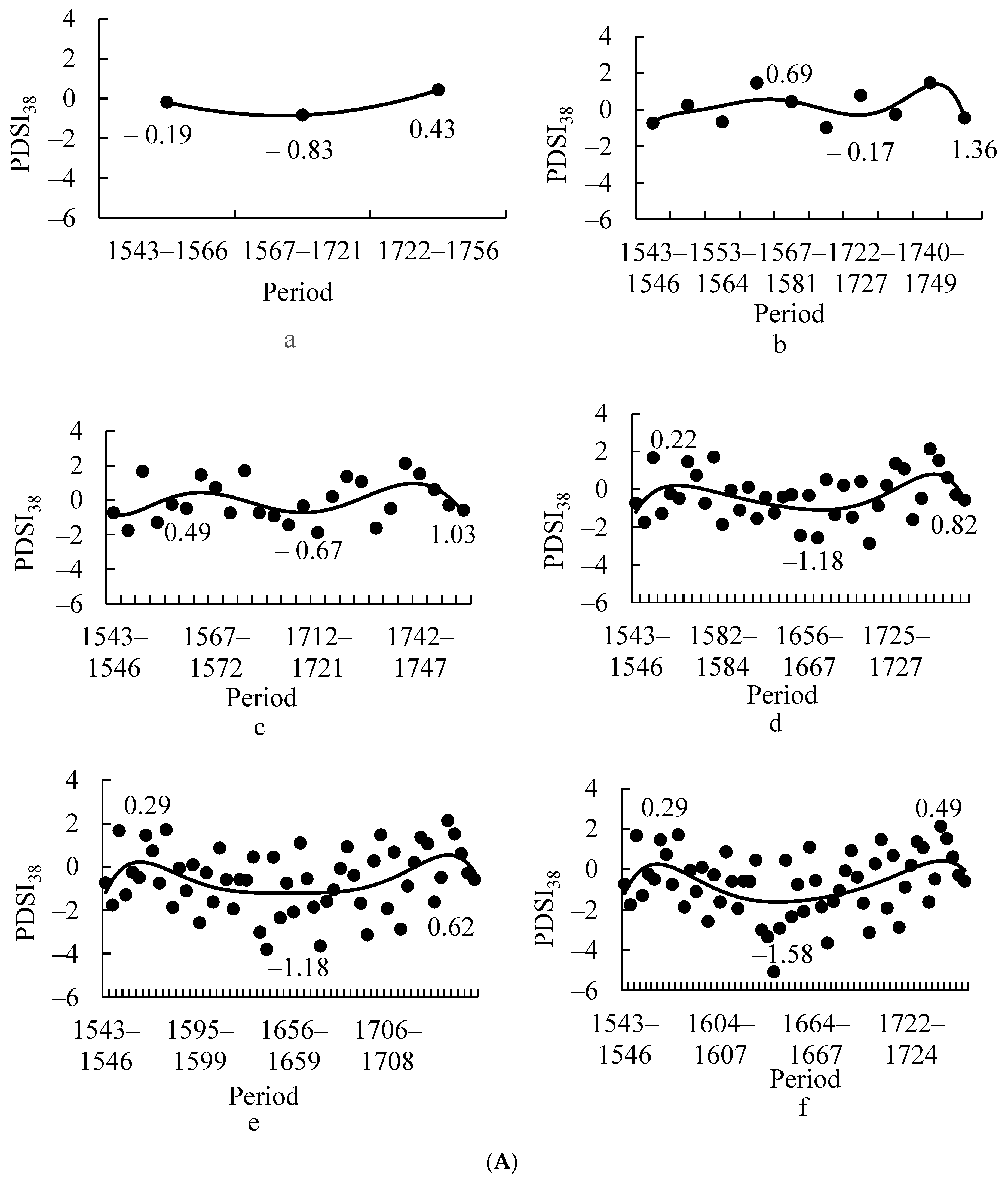
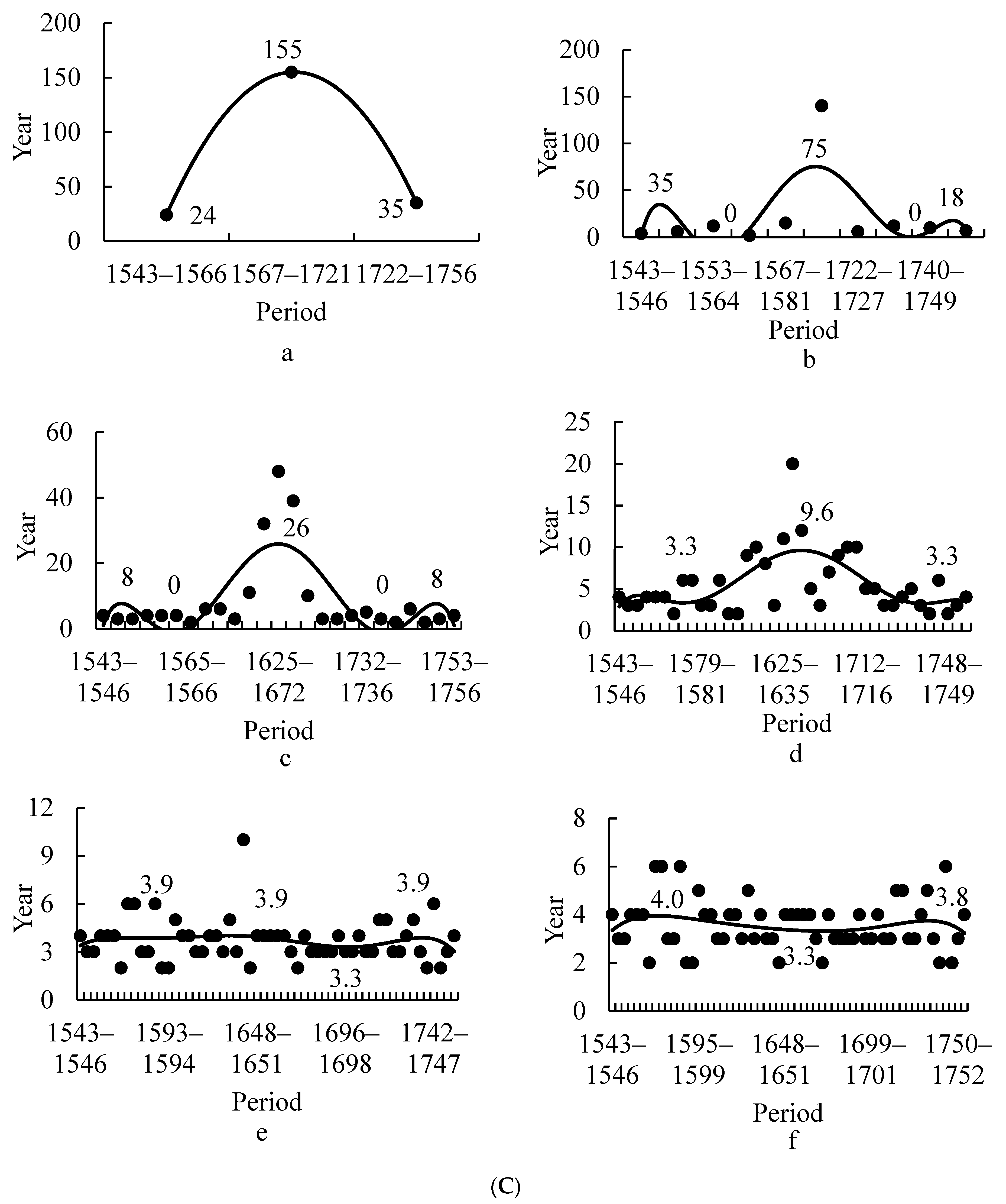
3.1. First Dry Period
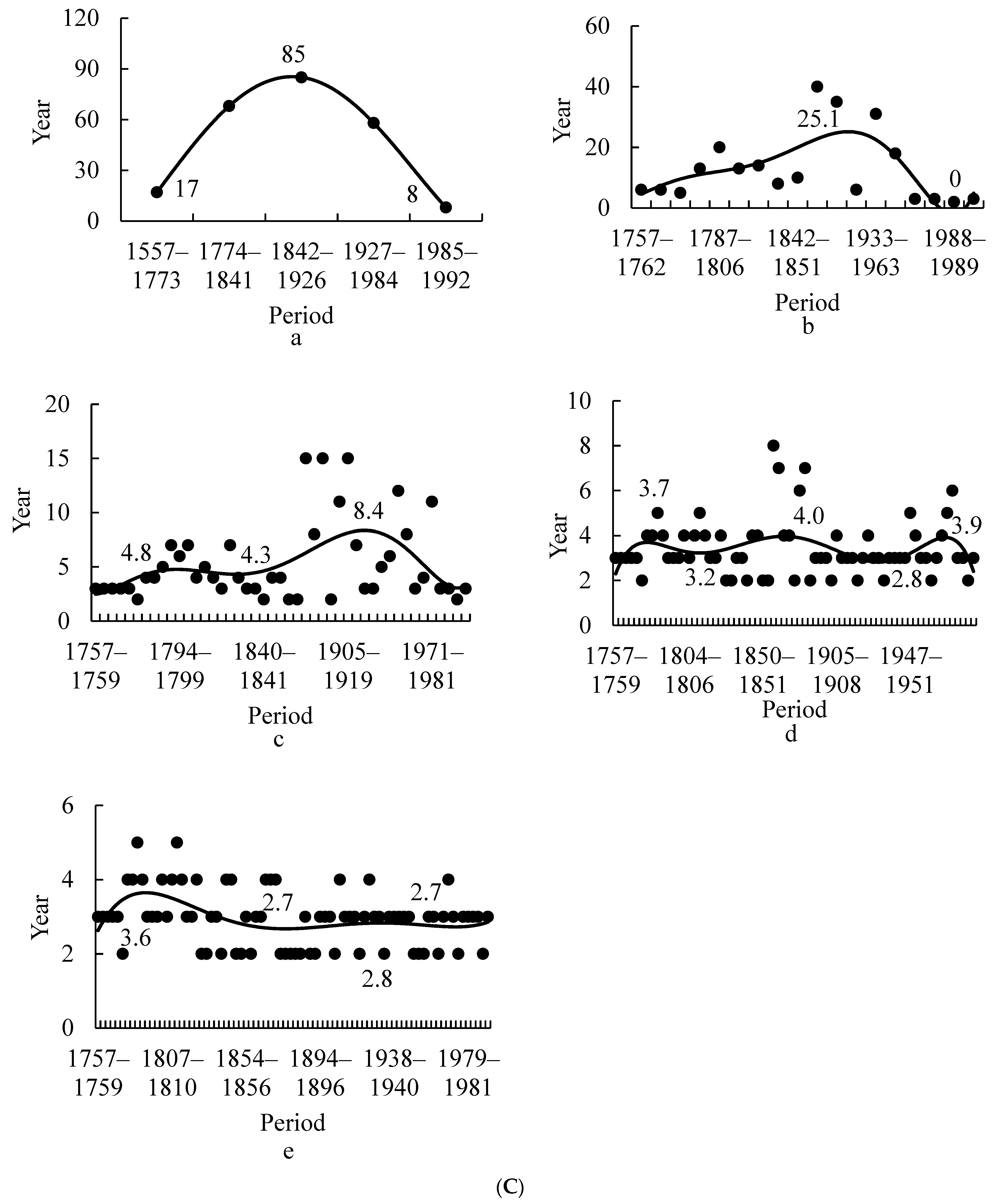
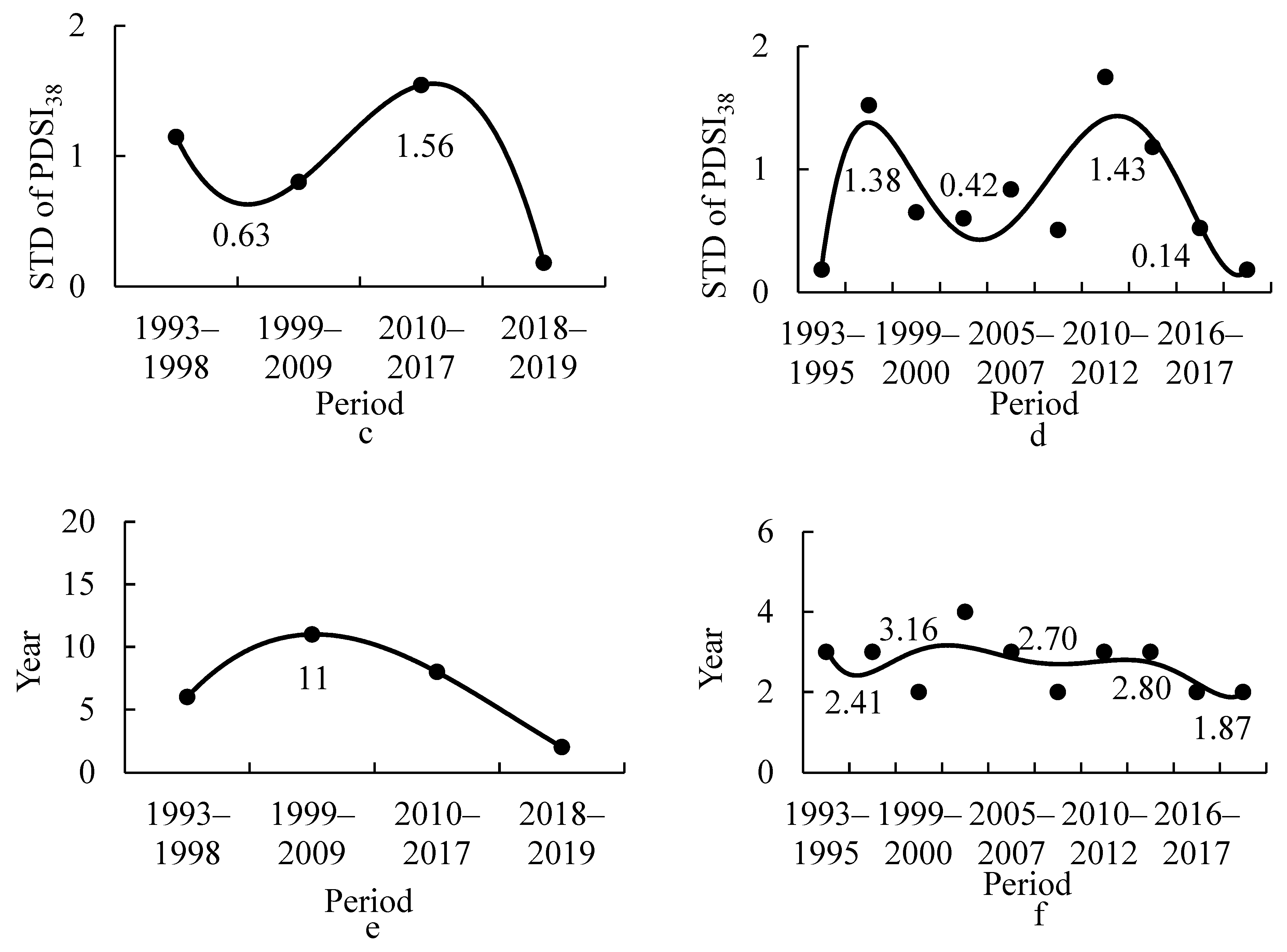
3.1.1. Change in the Mean of the PDSI38 in All Periods
3.1.2. Change in the Standard Deviation (SD) of the PDSI38 in All Periods
3.1.3. Change in the Duration of the PDSI38 in All Periods
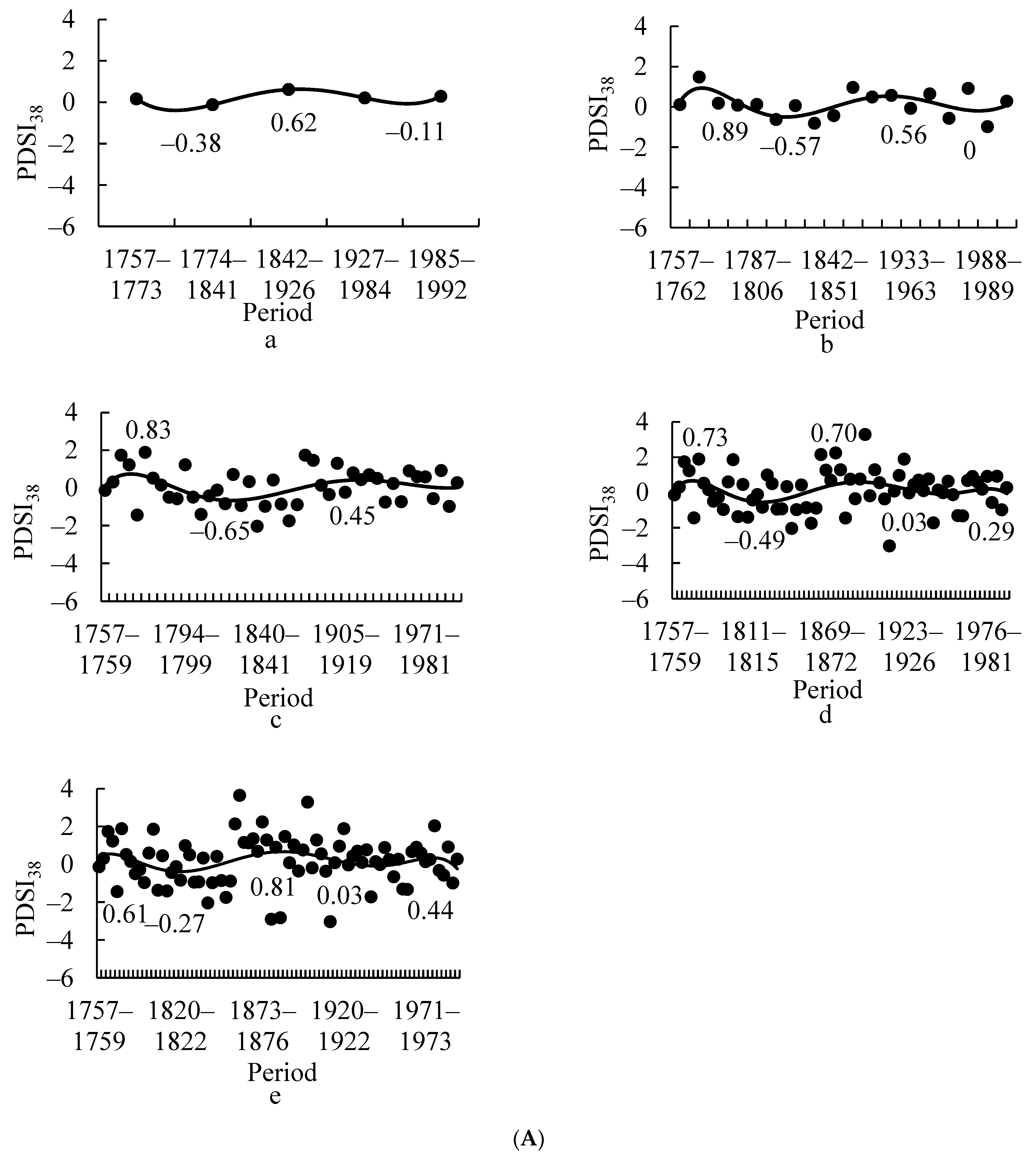
3.2. First Wet Cycle
3.2.1. Changes in the Mean PDSI38 in All Periods
3.2.2. Changes in the SD of the PDSI38 in All Periods
3.2.3. Change in the Duration of the PDSI38 in All Periods
3.3. Second Dry Period
4. Discussion
4.1. Climate Responses
4.2. Drought Threat
4.3. Strategies to Address Severe Droughts
4.4. Period of Dry–Wet Change
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Z.Y.; Zhou, J.J.; Zhang, L.L.; Wei, W.; Cao, J.J. Climate dry-wet change and dry evolution characteristics of different dry-wet areas in northern China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 1908–1919, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Misra, V.; Solomon, S.; Mall, A.K.; Prajapati, C.P.; Hashem, A.; Allah, E.F.; Ansari, M.I. Morphological assessment of water stressed sugarcane: A comparison of waterlogged and dry affected crop. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.F.; Chen, X.H. Spatiotemporal trends of dryness/wetness duration and severity: The respective contribution of precipitation and temperature. Atmos. Res. 2019, 216, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.F.; Wang, Y.; Yu, S.Y.; Kang, Z.H. Synchronous droughts and floods in the southern Chinese Loess Plateau since 1646 CE in phase with decadal solar activities. Glob. Plant Change 2019, 183, 103033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P.; Shi, P.J.; Zheng, Y.J. Variations of dryness/wetness across China: Changing properties, drought risks, and causes. Glob. Planet Change 2017, 115, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Long, S.F.; Ma, J.W.; Song, J.Y.; Liu, Z.W. Temporal-spatial variability in correlations of drought and flood during recent 500 years in Inner Mongolia, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.P.; Gao, L.; Zuo, X.A.; Zhong, F.L. Statistical analyses of spatial and temporal variabilities in total, daytime, and nighttime precipitation indices and of extreme dry/wet association with large-scale circulations of Southwest China, 1961–2016. Atmos. Res. 2019, 219, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, V.G.; Jain, K. Unravelling the teleconnections between ENSO and dry/wet conditions over India using nonlinear Granger causality. Atmos. Res. 2021, 247, 105168. [Google Scholar]
- Melsen, L.A.; Teuling, A.J.; Torfs, P.J.J.F.; Zappa, M.; Mizukami, N.; Mendoza, P.A.; Clark, M.P.; Uijlenhoet, R. Subjective modeling decisions can significantly impact the simulation of flood and drought events. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.Y.; Wei, H.; Lam, S.K.; Li, P.; Zong, Y.Z.; Zhang, D.S.; Li, F.Y. Enhancement of no-tillage, crop straw return and manure application on field organic matter content overweigh the adverse effects of climate change in the arid and semi-arid Northwest China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 295, 108199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.C.; Ge, Q.S.; Zheng, J.Y.; Liu, C.W. Reviews of agricultural drought risk assessment. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2010, 6, 263–270, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.J.; Liu, Y.T.; Shi, X.L. Contributions of climate change to the boundary shifts in the farming-pastoral ecotone in northern China since 1970. Agric. Syst. 2018, 161, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.F.; Su, B.D.; Zhai, J.Q.; Jiang, T.; Wen, S.S. Variation of drys in Luanhe river basin, 1961–2012. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2015, 29, 180–185, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.Q.; Zhang, B. Spatio-temporal changes of the extreme drought and wet events in Northern China from 1960 to 2016. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 1543–1554, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.G.; Dan, L.; Hu, Y.W. The extreme dry/wet events in northern China during recent 100 years. J. Geogr. Sci. 2004, 3, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.G.; Huang, G.; Gan, W.Q.; Chen, M.L. Multi-Scale temporal characteristics of the dryness /wetness over northern China during the last century. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 29, 671–681, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.B.; Fang, X.Q.; Ye, Y. Reclamation and revolt: Social responses in Eastern Inner Mongolia to flood/dry-induced refugees from the North China Plain 1644–1911. J. Arid. Environ. 2013, 88, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhou, T.; Yi, C.X.; Shi, P.J.; Fang, W.; Liu, R.S.; Liang, E.Y.; Camarero, J.J. Asymmetric impacts of dryness and wetness on tree growth and forest coverage. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 288–289, 107980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klippel, L.; George, S.S.; Buntgen, U.; Krusic, P.J.; Esper, J. Differing pre-industrial cooling trends between tree rings and lower-resolution temperature proxies. Clim. Past 2020, 16, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, J.T.; Harley, G.L.; Matheus, T.J.; Strange, B.M.; Van Aken, K.; Au, T.F.; Bregy, J.C. Sampling density and date along with species selection influence spatial representation of tree-ring reconstructions. Clim. Past 2020, 5, 1901–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaco, E.; Miley, N.; Biondi, F. Reconstruction of seasonal and water-year precipitation anomalies from tree-ring records of the southwestern United States. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2020, 547, 109689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadava, A.K.; Misra, K.G.; Singh, V.; Misra, S.; Sharma, Y.K.; Kotlia, B.S. 244-YEAR long tree-ring based drought records from Uttarakhand, western Himalaya, India. Quat. Int. 2021, 599–600, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Sun, Z.G.; Tan, M.H.; Guo, L.L.; Zhang, X.B. Changing patterns in farming pastoral ecotones in China between 1990 and 2010. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Wang, K.; Sun, Y.M. Study on the change of temperature time series in medium section of agro-pastoral ectone of Northern China during the last 60 years. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2016, 4, 747–753, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.M.; Zhang, A.; Zhao, X.Y. Analysis of vulnerable characteristics in Chinese northern farming-pastoral region based on coordinated regional downscaling experiment. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2017, 53, 1099–1107, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shelach-Lavi, G.; Tu, D.D. Food, pots and socio-economic transformation: The beginning and intensification of pottery production in North China. Archaeol. Res. Asia 2017, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.J.; Huang, D.; Tang, S.M.; Li, S.Y.; Guo, J.X.; Yang, Y.J.; Liu, H.F.; Li, J.S.; Wang, K. The emerge of metabolism in different ecosystems under the same environmental conditions in the agro-pastoral ecotone of northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 74, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, M.; Harlan, T.; Harris, M.; Storey, J.B. Datability of pecan tree ring. HortScience 1995, 30, 523–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmex, Inc. The Velmex “TA” System for Research and Non-Contact Measurement Analysis; Velmex Inc.: Bloomfield, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Fritts, H.C. Tree Rings and Climate; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, R. Computer assisted quality control. Tree-Ring Bull. 1983, 43, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Camarero, J.J.; Martin, E.; Gil-Pelegrin, E. The impact of a needleminer (Epinotia subsequana) outbreak on radial growth of silver fir (Abies alba) in the Aragon Pyrenees: A dendrochronological assessment. Dendrochronologia 2003, 21, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, E.R.; Kairiukstis, L.A. Methods of Dendrochronology: Applications in the Environmental Sciences; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Helama, S.; Begin, Y.; Vartiainen, M.; Peltola, H.; Kolstrom, T.; Merilainen, J. Quantifications of dendrochronological information from contrasting microdensitometric measuring circumstances of experimental wood samples. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2012, 70, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davi, N.K.; Jacoby, G.C.; Wiles, G.C. Boreal temperature variability inferred from maximum latewood density and tree-ring width data, Wrangell Mountain region, Alaska. Quat. Res. 2003, 60, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigley, T.; Briffa, K.R.; Jones, P.D. On the average value of correlated time series, with applications in dendroclimatology and hydrometeorology. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1984, 23, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.G. Drought under global warming: A review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Change 2011, 2, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobler, L. Global Soil Types, 1-Degree Grid; Oak Ridge National Laboratory Distributed Active Archive Center: Auckland, New Zealand, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.X.; Brauning, A.; Tian, Q.H.; Yang, B.; Cao, K.F. Tree ring recorded May-August temperature variations since A.D. 1585 in the Gaoligong Mountains, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2010, 296, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromer, T.L. A periodicity threshold theorem for a volterra integral equation. Appl. Anal. 1986, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.Y. The geographical distribution of floods and droughts in Chinese history, 206 B.C.-A.D. 1911. Far East. Q. 1943, 4, 357–378. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.Q.; Wang, X.J.; Yin, Y.X.; Shahid, S. Analysis of historical drought and flood characteristics of Hengshui during the period 1649–2018: A typical city in North China. Nat. Hazards 2021, 108, 2081–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Li, D.L.; Wang, J.D. Spatiotemporal characteristics of dry over China during 1961–2009. J. Desert Res. 2012, 32, 473–483, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.D.; Ren, G.Y.; Yang, Y.D.; Bing, H.; Hao, Z.X.; Zhang, P.F. Extreme historical droughts and floods in the Hanjiang River Basin, China, since 1426. Clim. Past 2022, 18, 1775–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Niu, J.J.; Fang, K.Y.; Li, X.L.; Li, Y.; Bu, W.L.; Li, Y.H. Climate-adial growth relationship of Larix principis-upprechtii at different altitudes on Luya Mountain. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 1608–1618, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Stjepanovic, S.; Matovic, B.; Stojanovic, D.; Lalic, B.; Levanic, T.; Orlovic, S.; Gutalj, M. The Impact of Adverse Weather and Climate on the Width of European Beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) Tree Rings in Southeastern Europe. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.B.; Wang, X.P.; Cheng, J.F.; Lin, X.; Wu, Y.L.; Yin, W.L. Alpine timberline ecotone tree growth in relation to climatic variability for Picea crassifolia forests in the middle Qilian Mountains, northwestern China. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2012, 34, 50–56, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood, B.R.; Leblanc, D.C. Radial growth-climate relationships of white ash (Fraxinus americana L. Oleaceae) in the eastern United States. J. Torrey Bot Soc. 2017, 144, 267–279. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.H.; Wang, M.M.; Wang, H.J.; Bai, J.; Cui, H.T. Climate changes and their ecological impacts of the last 50 years in semihumid and semiarid transitional zones of the east part of north west China. Quat. Sci. 2009, 29, 920–930. [Google Scholar]
- Gaire, N.P.; Dhakal, Y.R.; Shah, S.K.; Fan, Z.X.; Brauning, A.; Thapa, U.K.; Bhandari, S.; Aryal, S.; Bhuju, D.R. Drought (scPDSI) reconstruction of trans-Himalayan region of central Himalaya using Pinus wallichiana tree-rings. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2019, 514, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.Q.; Xiao, L.B.; Su, Y.; Zheng, J.Y.; Wei, Z.D.; Yin, J. Social impacts of climate change on the history of China. J. Palaeogeogr. 2017, 19, 729–736, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. The influence of natural disasters on the extinction of the Ming Dynasty. J. Suizhou Univ. 2016, 31, 73–77, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jia, T.F.; Shi, W.Y.; Zheng, X.Y.; Zhang, W.G.; Yu, L.Z. The flood and drought disasters of the Chaohu lake basin in the past 600 years. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2012, 32, 66–73, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.Y.; Sun, L.Y.; Wang, C.L.; Zhai, Z.H.; Wu, J.D. Analysis of drought characteristics in Guangdong in recent 40 years based on PDSI index. J. Meteorol. Res. Appl. 2022, 43, 36–40, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Arsalani, M.; Grieinger, J.; Pourtahmasi, K.; Brauning, A. Multi-centennial reconstruction of drought events in South-Western Iran using tree rings of Mediterranean cypress (Cupressus sempervirens L). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2021, 567, 110296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadad, M.A.; Gonzalez-Reyes, A.; Roig, F.A.; Matskovsky, V.; Cherubini, P. Tree-ring-based hydroclimatic reconstruction for the northwest Argentine Patagonia since 1055 CE and its teleconnection to large-scale atmospheric circulation. Glob. Planet Change 2021, 202, 103496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buntgen, U.; Trouet, V.; Frank, D.; Leuschner, H.H.; Friedrichs, D.; Luterbacher, U.; Esper, J. Tree-ring indicators of German summer drought over the last millennium. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2010, 29, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, R.P.H.; Lee, H.F. Drought-induced spatio-temporal synchrony of plague outbreak in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanitsch-Ackerl, S.; Mayer, K.; Gauster, T.; Laaha, G.; Holawe, F.; Wimmer, R.; Grabner, M. A 400-year reconstruction of spring–summer precipitation and summer low flow from regional tree-ring chronologies in North-Eastern Austria. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stager, J.C.; Ryves, D.B.; King, C.; Madson, J.; Hazzard, M.; Neumann, F.H.; Maud, R. Late Holocene precipitation variability in the summer rainfall region of South Africa. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 67, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutheimer, C.M.; Meunier, J.; Hotchkiss, S.C.; Rebitzke, E.; Radeloff, V.C. Historical fire regimes of North American hemiboreal peatlands. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 498, 119561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.J.; Chen, Z.M.; Chen, X.L.; Zou, M.; Jiang, J.; Hu, S. Interpreting IPCC AR6: Future global climate based on projection under scenarios and on near-term information. Clim. Change Res. 2021, 17, 652–663. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.Y. Analysis on the change of crops structure in Chengdu plain in little ice age of Ming and Qing dynasties. Agric. Archaeol. 2018, 4, 66–71, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.Y. The she people’s acculturation during the little ice age in the Ming and Qing dynasties: Environmental change and ethnic relations in the juncture areas of Fujian, Guangdong, Jiangxi and Hunan Provinces. Guangxi Ethn. Stud. 2019, 146, 96–102, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Locosselli, G.M.; Brienen, R.J.W.; Martins, V.T.S.; Gloor, E.; Boom, A.; Camargo, E.P.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Buckeridge, M.S. Intra-annual oxygen isotopes in the tree rings record precipitation extremes and water reservoir levels in the Metropolitan Area of Sao Paulo, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigozon, N.R.; Prestes, A.; Nordemann, D.J.R.; Silva, H.E.; Echer, M.P.S.; Echer, E. Solar maximum epoch imprints in tree-ring width from Passo Fundo, Brazil (1741–2004). J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys 2008, 70, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, X.H.; He, Y.H.; Wang, J.W.; Lai, C.G. Reconstruction of annual runoff since CE 1557 using tree-ring chronologies in the upper Lancang-Mekong River basin. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, A.V.; Perrone, L.; Nusinov, A.A. Thermospheric parameters’ long-term variations over the period including the 24/25 solar cycle minimum. Whether the CO2 increase effects are seen? J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys 2021, 223, 105736. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Du, S.C.; Jia, W.J. Multiscale variability of China historical flood/drought index and precipitation teleconnections with ENSO using wavelet analyses. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 149, 1583–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Li, F.M.; Cheng, H.; Ma, Z.B.; Cai, B.G.; Xiao, J.L. Summer monsoon precipitation variability during recent 700 years recorded in a high-resolution stalagmite from southwestern Yunnan, China. Quat. Sci. 2021, 41, 398–410, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, B.R.B.; Patterson, R.T.; Galloway, J.M.; Reinhardt, E.G. The impact of cyclical, multi-decadal to centennial climate variability on arsenic sequestration in lacustrine sediments. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2021, 565, 110189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Wen, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Hu, H.N. Analysis of drought and flood variations on a 200-Year scale based on historical environmental information in western China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Li, J.; Huang, Z.Q.; Zhong, R.D.; Chen, J.Y.; Qiu, Z.H. Spatiotemporal variations analysis of meteorological drought in China based on scPDSI. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 161–168, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Franchi, F.; Ahad, J.M.E.; Geris, J.; Jhowa, G.; Petros, A.K.; Comte, J.C. Modern sediment records of hydroclimatic extremes and associated potential contaminant mobilization in semi-arid environments: Lessons learnt from recent flood-dry cycles in southern Botswana. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 1632–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, M.; Liberato, M.L.R.; Sori, R.; Vazquez, M.; Phan-Van, T.; Hieu, D.; Hoang, C.T.; Nguyen, P.N.B.; Raquel, N.; Luis, G. Trends and extremes of dry episodes in vietnam sub-regions during 1980–2017 at different timescales. Water 2020, 3, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
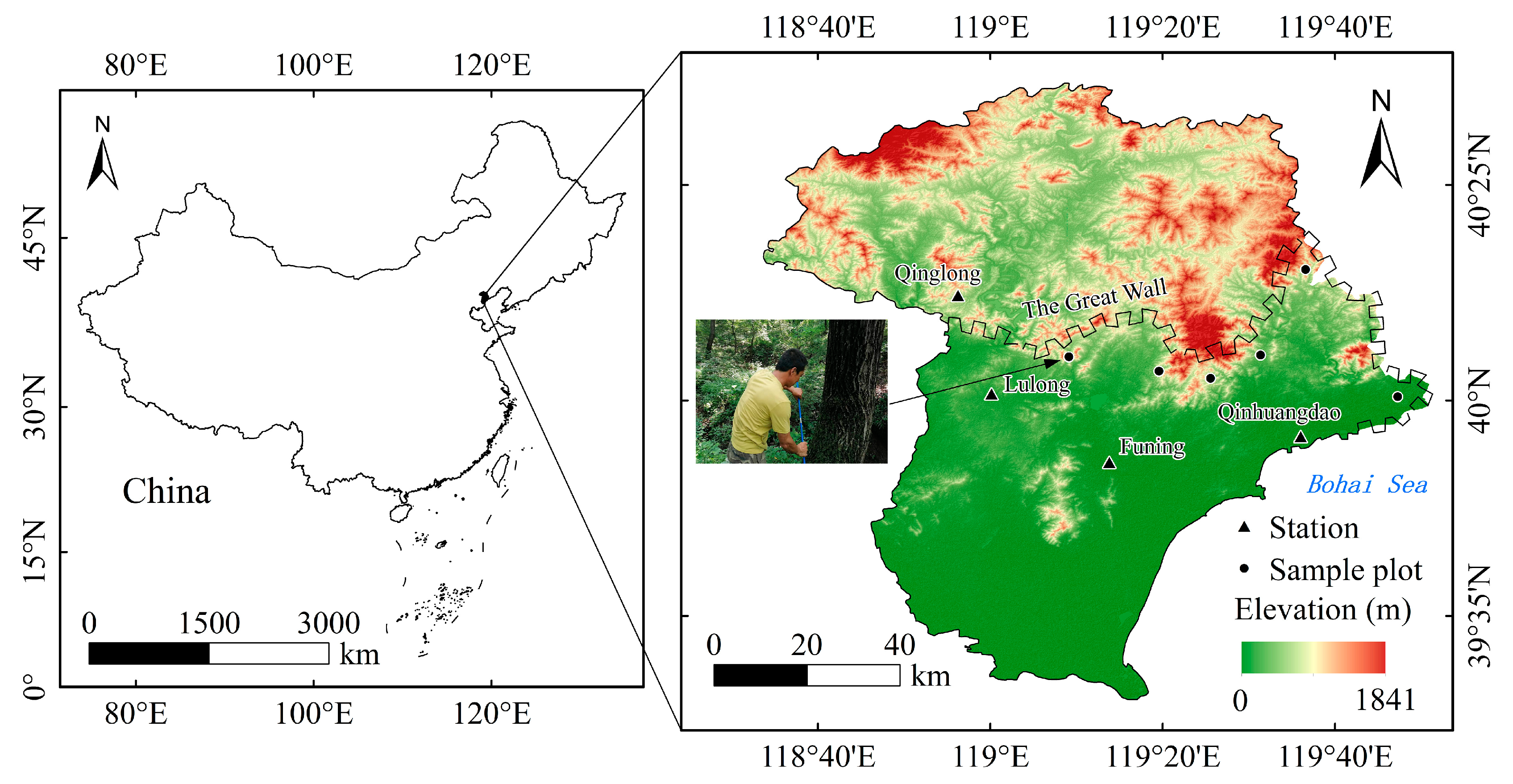

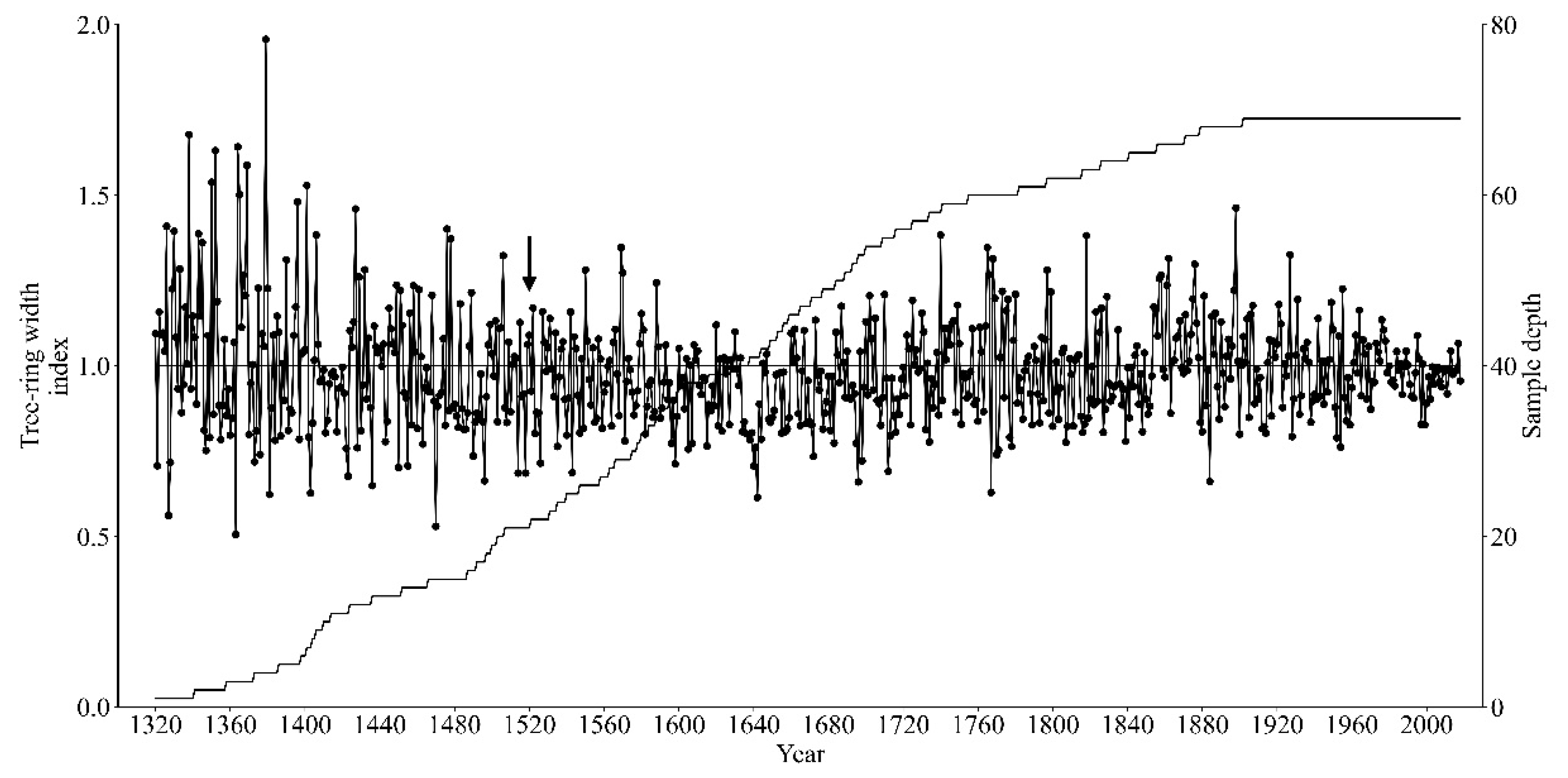





| Plot | Longitude (E) | Latitude (N) | C/T | NCC | RP (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 119.162693 | 40.217760 | 18/9 | 18 | 1320–2018 |
| 2 | 119.446449 | 40.144764 | 20/10 | 18 | 1341–2018 |
| 3 | 119.530907 | 40.204247 | 20/10 | 20 | 1373–2018 |
| 4 | 119.561806 | 40.219650 | 24/12 | 22 | 1410–2018 |
| 5 | 119.620185 | 40.481356 | 16/8 | 16 | 1503–2018 |
| 6 | 119.742050 | 40.044175 | 22/11 | 22 | 1531–2018 |
| r | R2 | R2adj | RE | ST | PMT | DW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | 0.69 ** | 0.479 | 0.470 | ||||
| Verification | 0.67 ** | 0.449 | 0.407 | 0.342 | 30+/29− * | 3.534 * | 1.720 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Song, Y.; An, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, X. Dry–Wet Changes in a Typical Agriculture and Pasture Ecotone in China between 1540 and 2019. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13060191
Wang X, Song Y, An Y, Liu X, Li X. Dry–Wet Changes in a Typical Agriculture and Pasture Ecotone in China between 1540 and 2019. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2024; 13(6):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13060191
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaodong, Yujia Song, Yu An, Xiaohui Liu, and Xiaoqiang Li. 2024. "Dry–Wet Changes in a Typical Agriculture and Pasture Ecotone in China between 1540 and 2019" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 13, no. 6: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13060191
APA StyleWang, X., Song, Y., An, Y., Liu, X., & Li, X. (2024). Dry–Wet Changes in a Typical Agriculture and Pasture Ecotone in China between 1540 and 2019. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 13(6), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13060191








