Interstitial Arabidopsis-Type Telomeric Repeats in Asteraceae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
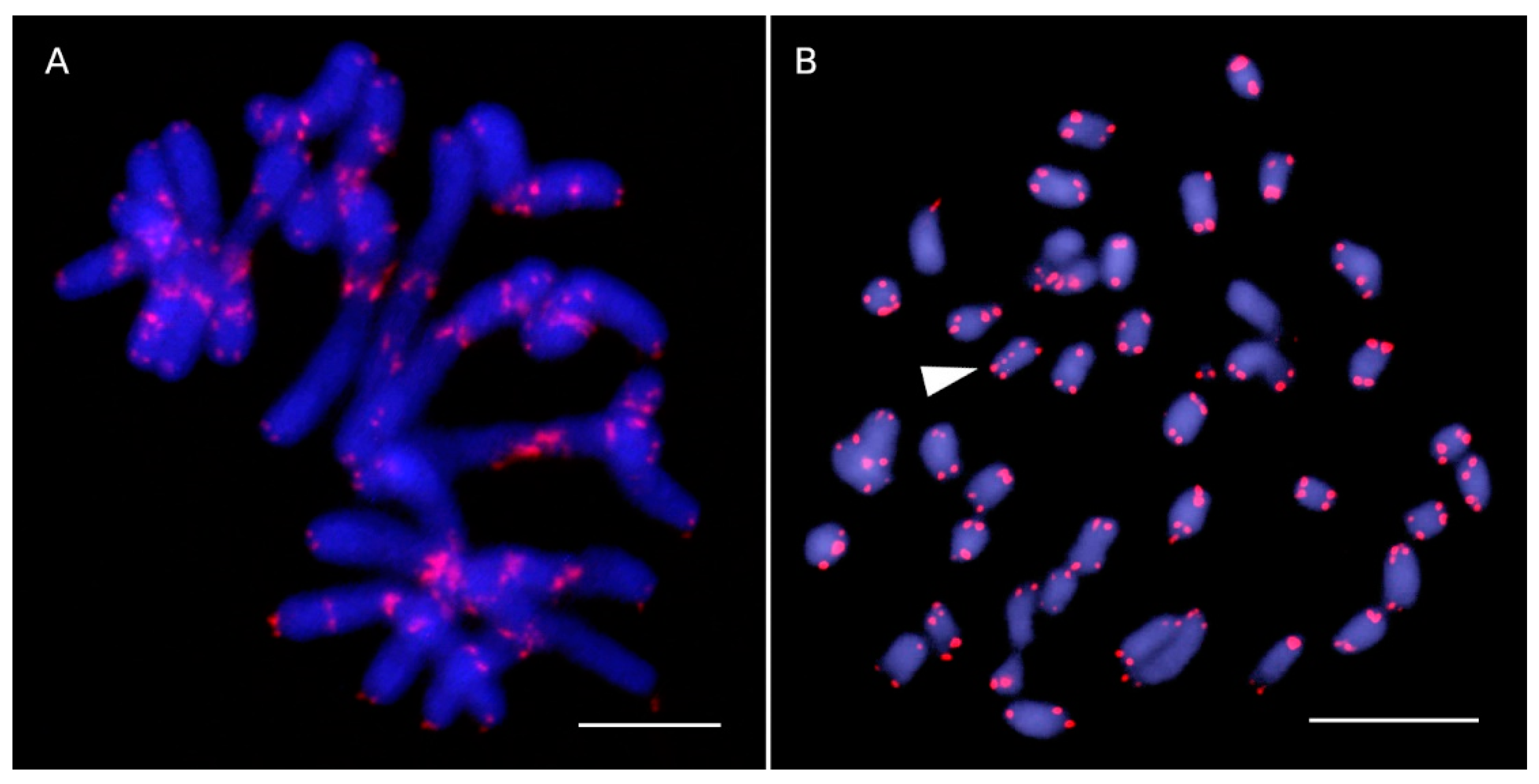
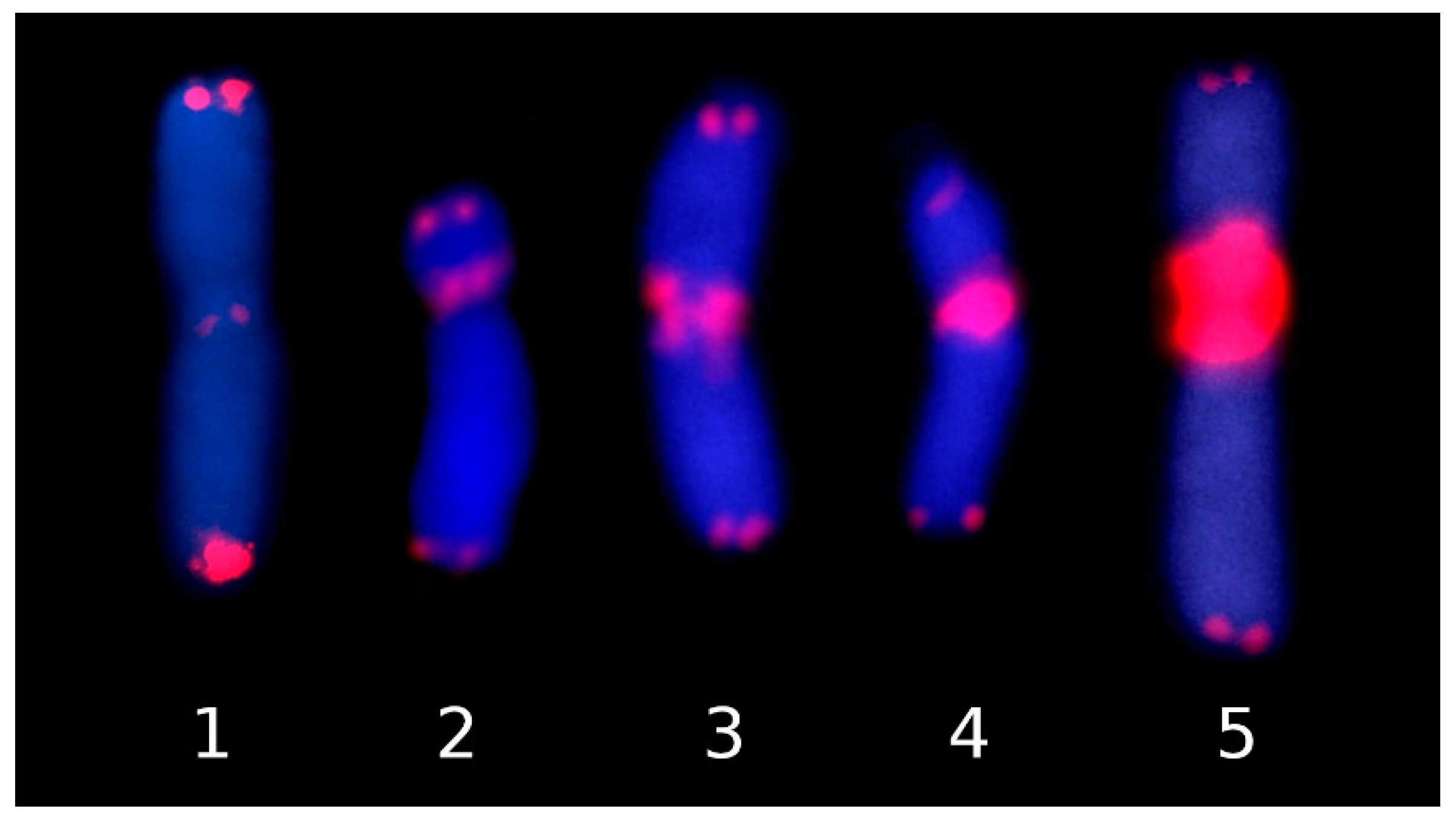
2.1. New Observations
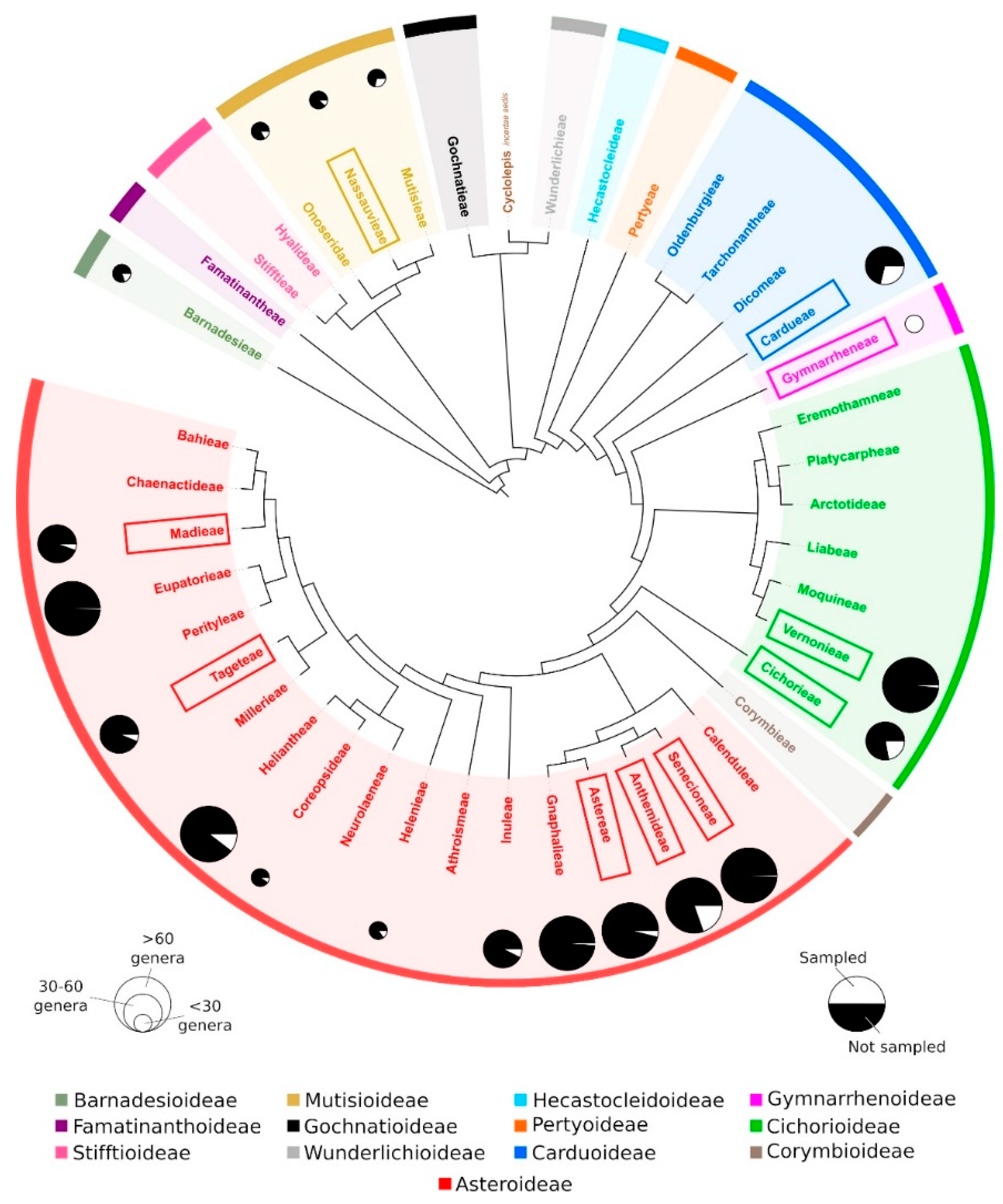
2.2. Patterns of ITR Variation in Asteraceae
3. Discussion
3.1. The Long Evolutionary History of Asteraceae May Have Erased Phylogenetic Signals of ITR Sites
3.2. Are Centromeric ITR Signals Remnants of Dysploidy in Asteraceae?
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. FISH Analysis
4.3. Karyotype Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blackburn, E.H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature 1991, 350, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.D.; Beilstein, M.A.; Shippen, D.E. Plant telomeres and telomerase. In Molecular Biology; Howell, S.H., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 25–49. [Google Scholar]
- O’Sullivan, R.J.; Karlseder, J. Telomeres: Protecting chromosomes against genome instability. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Fojtová, M.; Fajkus, J. Telomeres in plants and humans: Not so different, not so similar. Cells 2019, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajkus, J.; Sýkorová, E.; Leitch, A.R. Telomeres in evolution and evolution of telomeres. Chromosome Res. 2005, 13, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulnečková, J.; Ševčíková, T.; Fajkus, J.; Lukešova, A.; Lukeš, M.; Vlček, Č.; Lang, F.B.; Kim, E.; Eliáš, M.; Sýkorova, E. A broad phylogenetic survey unveils the diversity and evolution of telomeres in eukaryotes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 468–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, A.V.; Bennett, S.T.; Parokonny, A.S.; Kenton, A.; Callimassia, M.A.; Bennett, M.D. Comparison of plant telomere locations using a PCR-generated synthetic probe. Ann. Bot. 1993, 72, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, J.; Brandes, A.; Schubert, I. Telomere sequence localization and karyotype evolution in higher plants. Plant Syst. Evol. 1995, 196, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, H.; Scherthan, H. Aloe spp.—Plants with vertebrate-like telomeric sequences. Chromosome Res. 2002, 10, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puizina, J.; Weiss-Schneeweiss, H.; Pedrosa-Harand, A.; Kamenjarin, J.; Trinajstić, I.; Riha, K.; Schweizer, D. Karyotype analysis in Hyacinthella dalmatica (Hyacinthaceae) reveals vertebrate-type telomere repeats at the chromosome ends. Genome 2003, 46, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sýkorová, E.; Lim, K.Y.; Fajkus, J.; Leitch, A.R. The signature of the Cestrum genome suggests an evolutionary response to the loss of (TTTAGGG)n telomeres. Chromosoma 2003, 112, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajkus, P.; Peška, V.; Sitová, Z.; Fulnečková, J.; Dvořáčková, M.; Gogela, R.; Sýkorová, E.; Fajkus, J. Allium telomeres unmasked: The unusual telomeric sequence (CTCGGTTATGGG)n is synthesized by telomerase. Plant J. 2016, 85, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sýkorová, E.; Lim, K.Y.; Chase, M.W.; Knapp, S.; Leitch, I.J.; Leitch, A.R.; Fajkus, J. The absence of Arabidopsis-type telomeres in Cestrum and closely related genera Vestia and Sessea (Solanaceae): First evidence from eudicots. Plant J. 2003, 34, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sýkorová, E.; Lim, K.Y.; Kunická, Z.; Chase, M.W.; Bennett, M.D.; Fajkus, J.; Leitch, A.R. Telomere variability in the monocotyledonous plant order Asparagales. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 1893–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peška, V.; Sýkorová, E.; Fajkus, J. Two faces of Solanaceae telomeres: A comparison between Nicotiana and Cestrum telomeres and telomere-binding proteins. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2008, 122, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peška, V.; Fajkus, P.; Fojtová, M.; Dvořáčková, M.; Hapala, J.; Dvořáček, V.; Polanská, P.; Leitch, A.R.; Sýkorová, E.; Fajkus, J. Characterisation of an unusual telomere motif (TTTTTTAGGG)n in the plant Cestrum elegans (Solanaceae), a species with a large genome. Plant J. 2015, 82, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.D.; Cao, H.X.; Jovtchev, G.; Neumann, P.; Novák, P.; Fojtová, M.; Vu, G.T.H.; Macas, J.; Fajkus, J.; Schubert, I.; et al. Centromere and telomere sequence alterations reflect the rapid genome evolution within the carnivorous plant genus Genlisea. Plant J. 2015, 84, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peska, V.; García, S. Origin, diversity, and evolution of telomere sequences in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.W.; Yan, J. Endings in the middle: Current knowledge of interstitial telomeric sequences. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2008, 658, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyne, J.; Baker, R.J.; Hobart, H.H.; Hsu, T.C.; Ryder, O.A.; Ward, O.G.; Wiley, J.E.; Wurster-Hill, D.H.; Yates, T.L.; Moyzis, R.K. Distribution of non-telomeric sites of the (TTAGGG)n telomeric sequence in vertebrate chromosomes. Chromosoma 1990, 99, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksenova, A.Y.; Greenwell, P.W.; Dominska, M.; Shishkin, A.A.; Kim, J.C.; Petes, T.D.; Mirkin, S.M. Genome rearrangements caused by interstitial telomeric sequences in yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19866–19871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocalewicz, K. Telomeres in fishes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2013, 141, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolzán, A.D. Interstitial telomeric sequences in vertebrate chromosomes: Origin, function, instability and evolution. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2017, 773, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksenova, A.Y.; Mirkin, S.M. At the beginning of the end and in the middle of the beginning: Structure and maintenance of telomeric DNA repeats and interstitial telomeric sequences. Genes 2019, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Herrera, A.; Nergadze, S.G.; Santagostino, M.; Giulotto, E. Telomeric repeats far from the ends: Mechanisms of origin and role in evolution. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2008, 122, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitales, D.; D’Ambrosio, U.; Gálvez, F.; Kovařík, A.; García, S. Third release of the plant rDNA database with updated content and information on telomere composition and sequenced plant genomes. Plant Syst. Evol. 2017, 303, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, J.R.; Dikow, R.B.; Siniscalchi, C.M.; Thapa, R.; Watson, L.E.; Funk, V.A. A fully resolved backbone phylogeny reveals numerous dispersals and explosive diversifications throughout the history of Asteraceae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 14083–14088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raven, P.H.; Solbrig, O.T.; Kyhos, D.W.; Snow, R. Chromosome numbers in Compositae. I. Astereae. Am. J. Bot. 1960, 47, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, J.C.; Watanabe, K. A review of chromosome numbers in Asteraceae with hypotheses on chromosomal base number evolution. In Systematics, Evolution, and Biogeography of Compositae, 1st ed.; Funk, V.A., Susanna, A., Stuessy, T.F., Bayer, R.J., Eds.; International Association for Plant Taxonomy: Vienna, Austria, 2009; pp. 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bala, S.; Gupta, R.C. Male meiosis and chromosome number in Asteraceae family from district Kangra of HP (Western Himalayas). Int. J. Bot. Res. 2013, 3, 43–58. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.; Gao, T.; Qi, J.; Ma, H. Multiple polyploidization events across Asteraceae with two nested events in the early history revealed by nuclear phylogenomics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 2820–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houben, A.; Thompson, N.; Ahne, R.; Leach, C.R.; Verlin, D.; Timmis, J.N. A monophyletic origin of the B chromosomes of Brachycome dichromosomatica (Asteraceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 1999, 219, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.P.; Hartman, T.P.V.; Lim, K.Y.; Chase, M.W.; Bennett, M.D.; Leitch, I.J.; Leitch, A.R. Loss and recovery of Arabidopsis–type telomere repeat sequences 5′–(TTTAGGG)n–3′ in the evolution of a major radiation of flowering plants. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 268, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgen, L.; Leitch, I.; Santos-Guerra, A. Genome organization in diploid hybrid species of Argyranthemum (Asteraceae) in the Canary Islands. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2003, 141, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pires, J.C.; Lim, K.Y.; Kovarík, A.; Matyásek, R.; Boyd, A.; Leitch, A.R.; Bennett, N.D.; Soltis, P.S.; Soltis, D.E. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of recently evolved Tragopogon (Asteraceae) allopolyploids reveal a karyotype that is additive of the diploid progenitors. Am. J. Bot. 2004, 91, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Twab, M.H.; Kondo, K. FISH physical mapping of 5S, 45S and Arabidopsis-type telomere sequence repeats in Chrysanthemum zawadskii showing intra-chromosomal variation and complexity in nature. Chromosome Bot. 2006, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Twab, M.H.; Kondo, K. FISH physical mapping of 5S rDNA and telomere sequence repeats identified a peculiar chromosome mapping and mutation in Leucanthemella linearis and Nipponanthemum nipponicum in Chrysanthemum sensu lato. Chromosome Bot. 2007, 2, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanmoto, H.; Kataoka, R.; Ohmido, N.; Yonezawa, Y. Interstitial telomere-like repeats in the Haplopappus gracilis (Asteraceae) genome revealed by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cytologia 2007, 72, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matoba, H.; Mizutani, T.; Nagano, K.; Hoshi, Y.; Uchiyama, H. Chromosomal study of lettuce and its allied species (Lactuca spp.; Asteraceae) by means of karyotype analysis and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Hereditas 2007, 144, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Twab, M.H.; Kondo, K. Physical mapping of 5S, 45S, Arabidopsis-type telomere sequence repeats and AT-rich regions in Achillea millefolium showing intrachromosomal variation by FISH and DAPI. Chromosome Bot. 2009, 4, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dydak, M.; Kolano, B.; Nowak, T.; Siwinska, D.; Maluszynska, J. Cytogenetic studies of three European species of Centaurea L. (Asteraceae). Hereditas 2009, 146, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, S.; Garnatje, T.; Pellicer, J.; McArthur, E.D.; Siljak-Yakovlev, S.; Vallés, J. Ribosomal DNA, heterochromatin, and correlation with genome size in diploid and polyploid North American endemic sagebrushes (Artemisia, Asteraceae). Genome 2009, 52, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoba, H.; Uchiyama, H. Physical mapping of 5S rDNA, 18S rDNA and telomere sequences in three species of the genus Artemisia (Asteraceae) with distinct basic chromosome numbers. Cytologia 2009, 74, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, F.; Hizume, M. Survey of Arabidopsis- and human-type telomere repeats in plants using fluorescence in situ hybridisation. Cytologia 2011, 76, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, S.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Yang, F.; Ma, L.; Huang, J.; Li, L. Telomere and 45S rDNA sequences are structurally linked on the chromosomes in Chrysanthemum segetum L. Protoplasma 2012, 249, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuyacot, A.R.; Won, S.Y.; Park, S.K.; Sohn, S.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, H.H.; Lim, K.M.; Hwang, Y.J. The chromosomal distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in Chrysanthemum boreale revealed a characterization in its genome. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 198, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuyacot, A.R.; Lim, K.B.; Kim, H.H.; Hwang, Y.J. Chromosomal characterization based on repetitive DNA distribution in a tetraploid cytotype of Chrysanthemum zawadskii. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2017, 58, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancia, F.H.; Ju, Y.H.; Lim, K.B.; Kim, J.S.; Nam, S.Y.; Hwang, Y.J. Cytogenetic mapping of Carthamus tinctorius L. with tandemly repeated DNA sequences by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Korean J. Plant Res. 2017, 30, 654–661. [Google Scholar]
- Rosato, M.; Álvarez, I.; Nieto Feliner, G.; Rosselló, J.A. Inter- and intraspecific hypervariability in interstitial telomeric-like repeats (TTTAGGG)n in Anacyclus (Asteraceae). Ann. Bot. 2018, 122, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlinarec, J.; Skuhala, A.; Jurković, A.; Malenica, N.; McCann, J.; Weiss-Schneeweiss, H.; Bohanec, B.; Besendorfer, V. The repetitive DNA composition in the natural pesticide producer Tanacetum cinerariifolium: Interindividual variation of subtelomeric tandem repeats. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzacher, T.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S. In situ hybridization to plant telomeres using synthetic oligomers. Genome 1991, 34, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitch, A.R.; Schwarzacher, T.; Jackson, D.; Leitch, I.J. In Situ Hybridization: A Practical Guide; BIOS Scientific Publishers Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Maravilla, A.J.; Rosato, M.; Rosselló, J.A. Interstitial telomeric-like repeats (ITR) in seed plants as assessed by molecular cytogenetic techniques: A review. Plants 2021, 10, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlins, D.J.; Highett, M.I.; Shaw, P.J. Localization of telomeres in plant interphase nuclei by in situ hybridization and 3D confocal microscopy. Chromosoma 1991, 100, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.M.; Williams, K.; Harper, J.A. Labelling telomeres of cereals, grasses and clover by primed in situ DNA labelling. Chromosome Res. 1996, 4, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gortner, G.; Nenno, M.; Weising, K.; Zink, D.; Nagl, W.; Kahl, G. Chromosomal localization and distribution of simple sequence repeats and the Arabidopsis-type telomere sequence in the genome of Cicer arietinum L. Chromosome Res. 1998, 6, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nenno, M.; Zink, D.; Nagl, W. The Arabidopsis telomere sequence is highly abundant in the genome of Phaseolus acutifolius and preferentially located in the centromeres. Annu. Rep.—Bean Improv. Coop. 1998, 41, 103–104. [Google Scholar]
- Galasso, I.; Schmidt, T.; Pignone, D. Identification of Lens culinaris ssp. culinaris chromosomes by physical mapping of repetitive DNA sequences. Chromosome Res. 2001, 9, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pedrosa, A.; Sandal, N.; Stougaard, J.; Schweizer, D.; Bachmair, A. Chromosomal map of the model legume Lotus japonicus. Genetics 2002, 161, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdera, I.; Siwinska, D.; Hasterok, R.; Maluszynska, J. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of genome structure in Lupinus angustifolius and Lupinus cosentinii. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navrátilová, A.; Neumann, P.; Macas, J. Karyotype analysis of four Vicia species using in situ hybridization with repetitive sequences. Ann. Bot. 2003, 91, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macas, J.; Neumann, P.; Navrátilová, A. Repetitive DNA in the pea (Pisum sativum L.) genome: Comprehensive characterization using 454 sequencing and comparison to soybean and Medicago truncatula. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarek, A.; Naganowska, B.; Wolko, B. Karyotyping of the narrow-leafed lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.) by using FISH, PRINS and computer measurements of chromosomes. J. Appl. Genet. 2009, 50, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatloukalová, P.; Hřibová, E.; Kubaláková, M.; Suchánková, P.; Šimková, H.; Adoración, C.; Kahl, G.; Millán, T.; Doležel, J. Integration of genetic and physical maps of the chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) genome using flow-sorted chromosomes. Chromosome Res. 2011, 19, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonsêca, A.; Pedrosa-Harand, A. Karyotype stability in the genus Phaseolus evidenced by the comparative mapping of the wild species Phaseolus microcarpus. Genome 2013, 56, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Li, L.N.; Zhang, Z.X.; Liu, H.; Qin, L.; Huang, B.Y.; Dong, W.; Tang, F.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, X.Y. Chromosome painting of telomeric repeats reveals new evidence for genome evolution in peanut. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 2488–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonsêca, A.; Ferraz, M.E.; Pedrosa-Harand, A. Speeding up chromosome evolution in Phaseolus: Multiple rearrangements associated with a one-step descending dysploidy. Chromosoma 2016, 125, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Tia, L.; Chen, L.; Yu, W. Identification of peanut (Arachis hypogaea) chromosomes using a fluorescence in situ hybridization system reveals multiple hybridization events during tetraploid peanut formation. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 1424–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waminal, N.E.; Pellerin, R.J.; Kim, N.S.; Jayakodi, M.; Park, J.Y.; Yang, T.J.; Kim, H.H. Rapid and efficient FISH using pre-labeled oligomer probes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, S.M.; Kim, H.H. Chromosome karyotyping of Senna covesii and S. floribunda based on triple-color FISH mapping of rDNAs and telomeric repeats. Plant Breed. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, R.J.; Waminal, N.E.; Kim, H.H. FISH mapping of rDNA and telomeric repeats in 10 Senna species. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2019, 60, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falistocco, E. Insight into the chromosome structure of the cultivated tetraploid alfalfa (Medicago sativa subsp. sativa L.) by a combined use of GISH and FISH techniques. Plants 2020, 9, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Waminal, N.E.; Lee, D.S.; Pellerin, R.J.; Ta, T.D.; Campomayor, N.B.; Kang, B.Y.; Kim, H.H. Comparative triple-color FISH mapping in eleven Senna species using rDNA and telomeric repeat probes. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2021, 62, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waminal, N.E.; Pellerin, R.J.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, H.H. Chromosomal mapping of tandem repeats revealed massive chromosomal rearrangements and insights into Senna tora dysploidy. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panero, J.L.; Crozier, B.S. Macroevolutionary dynamics in the early diversification of Asteraceae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 99, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, M.S.; Kane, N.C.; Matvienko, M.; Kozik, A.; Michelmore, R.W.; Knapp, S.J.; Rieseberg, L.H. Multiple paleopolyploidizations during the evolution of the Compositae reveal parallel patterns of duplicate gene retention after millions of years. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 2445–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, M.S.; Li, Z.; Kidder, T.I.; Reardon, C.R.; Lai, Z.; Oliveira, L.O.; Scascitelli, M.; Rieseberg, L.H. Most Compositae (Asteraceae) are descendants of a paleohexaploid and all share a paleotetraploid ancestor with the Calyceraceae. Am. J. Bot. 2016, 103, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, I.; Lysak, M.A. Interpretation of karyotype evolution should consider chromosome structural constraints. Trends Genet. 2011, 27, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funk, V.A.; Bayer, R.J.; Keeley, S.; Chan, R.; Watson, L.; Gemeinholzer, B.; Schilling, E.; Panero, J.L.; Baldwin, B.G.; García-Jacas, N.; et al. Everywhere but Antarctica: Using a supertree to understand the diversity and distribution of the Compositae. Biol. Skr. 2005, 55, 343–374. [Google Scholar]
- Mota, L.; Torices, R.; Loureiro, J. The evolution of haploid chromosome numbers in the sunflower family. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 3516–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskina, O.; Barber, J.C.; Nevo, E.; Belyayev, A. Repetitive DNA and chromosomal rearrangements: Speciation-related events in plant genomes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2008, 120, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.S.; Bolshev, N.L.; Samatadze, T.E.; Nosov, N.N.; Nosova, I.V.; Zelenin, A.V.; Punina, E.O.; Muravenko, O.V.; Rodionov, A.V. The unique genome of two-chromosome grasses Zingeria and Colpodium, its origin, and evolution. Russ. J. Genet. 2009, 45, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.; Cusimano, N.; Renner, S.S. Combining FISH and model-based predictions to understand chromosome evolution in Typhonium (Araceae). Ann. Bot. 2014, 113, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amosova, A.V.; Bolsheva, N.L.; Samatadze, T.E.; Twardovska, M.O.; Zoshchuk, S.A.; Andreev, I.O.; Badaeva, E.D.; Kunakh, V.A.; Muravenko, O.V. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of Deschampsia antarctica Desv. (Poaceae), Maritime Antarctic. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockinger, A.; Sousa, A.; Carvalho, F.A.; Renner, S.S. Chromosome number reduction in the sister clade of Carica papaya with concomitant genome size doubling. Am. J. Bot. 2016, 103, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, G.; Vanzela, A.L.; Crosa, O.; Guerra, M. Interstitial telomeric sites and Robertsonian translocations in species of Ipheion and Nothoscordum (Amaryllidaceae). Genetica 2016, 144, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, M.; Castro, M.; Rosselló, J.A. Relationships of the woody Medicago species (section Dendrotelis) assessed by molecular cytogenetic analyses. Ann. Bot. 2008, 102, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, E.J.; Ausubel, F.M. Isolation of a higher eukaryotic telomere from Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell 1998, 53, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Fransz, P.F.; Wennekes-van Eden, J.; Zabel, P.; Van Kammen, A.; De Jong, H.J. High-resolution mapping on pachytene chromosomes extended DNA fibres by fluorescence in-situ hybridisation. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 1996, 14, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galián, J.A.; Rosato, M.; Rosselló, J.A. Incomplete sequence homogenization in 45S rDNA multigene families: Intermixed IGS heterogeneity within the single NOR locus of the polyploid species Medicago arborea (Fabaceae). Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roa, F.; Guerra, M. Distribution of 45S rDNA sites in chromosomes of plants: Structural and evolutionary implications. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, A. MicroMeasure: A new computer program for the collection and analysis of cytogenetic data. Genome 2001, 44, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Family | Subfamily | No. of Tribes | No. of Genera | No. of Species | No. of Subsp. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asteraceae | Asteroideae | 11 (2) | 62 (15) | 97 (24) | 1 |
| Carduoideae | 1 (1) | 21 (2) | 31 (2) | 1 | |
| Cichorioideae | 2 (2) | 21 (6) | 35 (8) | 1 | |
| Gymnarrhenoideae | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0 | |
| Mutisioideae | 3 (1) | 8 (1) | 10 (1) | 0 | |
| Barnadesioideae | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 2 (0) | 0 | |
| Calyceraceae | 1 (0) | 1(0) | 0 | ||
| Goodeniaceae | 2 (0) | 2(0) | 0 | ||
| Campanulaceae | 1 (0) | 1 (0) | 0 | ||
| Stylidaceae | 1 (0) | 1 (0) | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maravilla, A.J.; Rosato, M.; Álvarez, I.; Nieto Feliner, G.; Rosselló, J.A. Interstitial Arabidopsis-Type Telomeric Repeats in Asteraceae. Plants 2021, 10, 2794. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10122794
Maravilla AJ, Rosato M, Álvarez I, Nieto Feliner G, Rosselló JA. Interstitial Arabidopsis-Type Telomeric Repeats in Asteraceae. Plants. 2021; 10(12):2794. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10122794
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaravilla, Alexis J., Marcela Rosato, Inés Álvarez, Gonzalo Nieto Feliner, and Josep A. Rosselló. 2021. "Interstitial Arabidopsis-Type Telomeric Repeats in Asteraceae" Plants 10, no. 12: 2794. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10122794
APA StyleMaravilla, A. J., Rosato, M., Álvarez, I., Nieto Feliner, G., & Rosselló, J. A. (2021). Interstitial Arabidopsis-Type Telomeric Repeats in Asteraceae. Plants, 10(12), 2794. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10122794







