Single-Molecule Long-Read Sequencing of Purslane (Portulaca oleracea) and Differential Gene Expression Related with Biosynthesis of Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
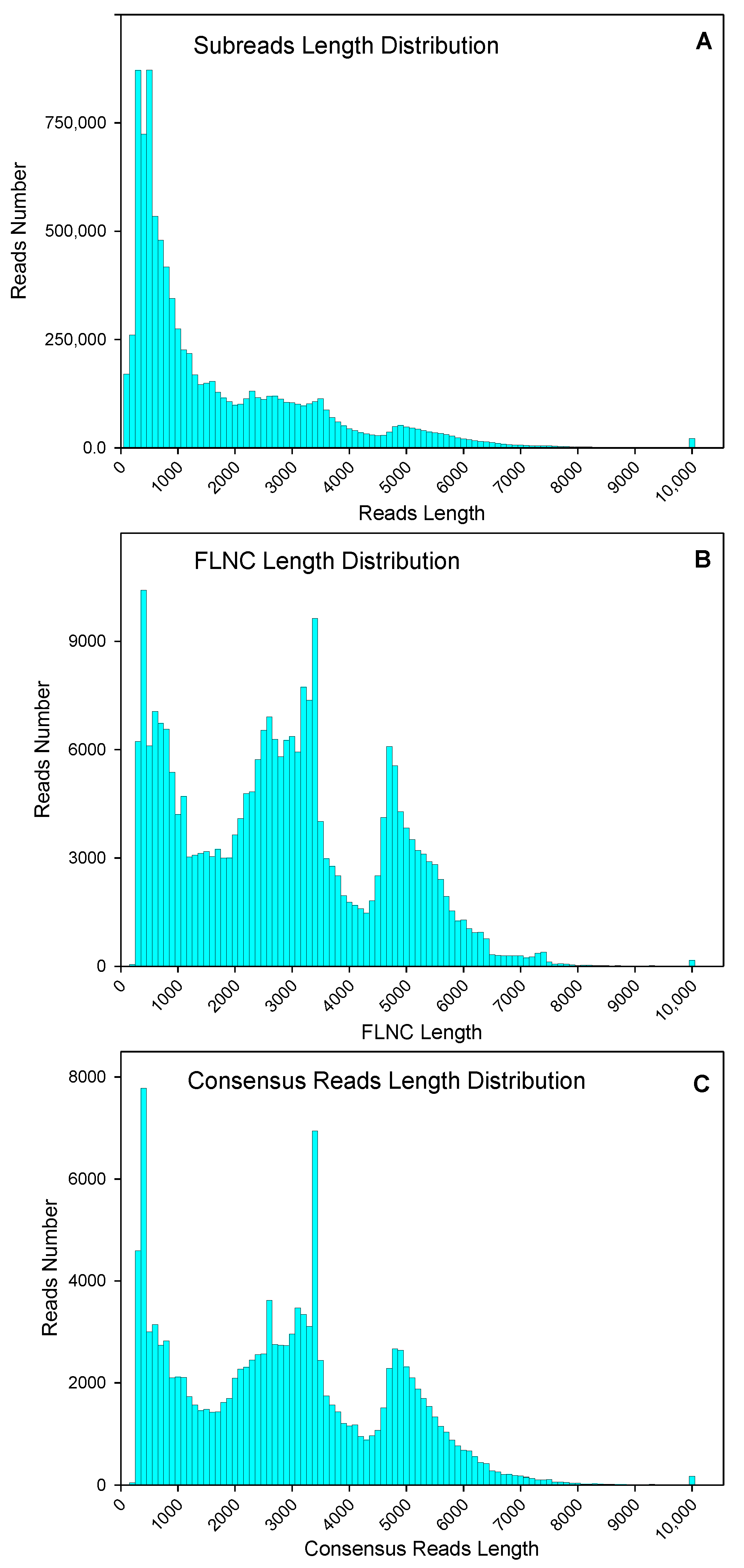
2.1. Single-Molecule Real-Time Sequencing of Purslane
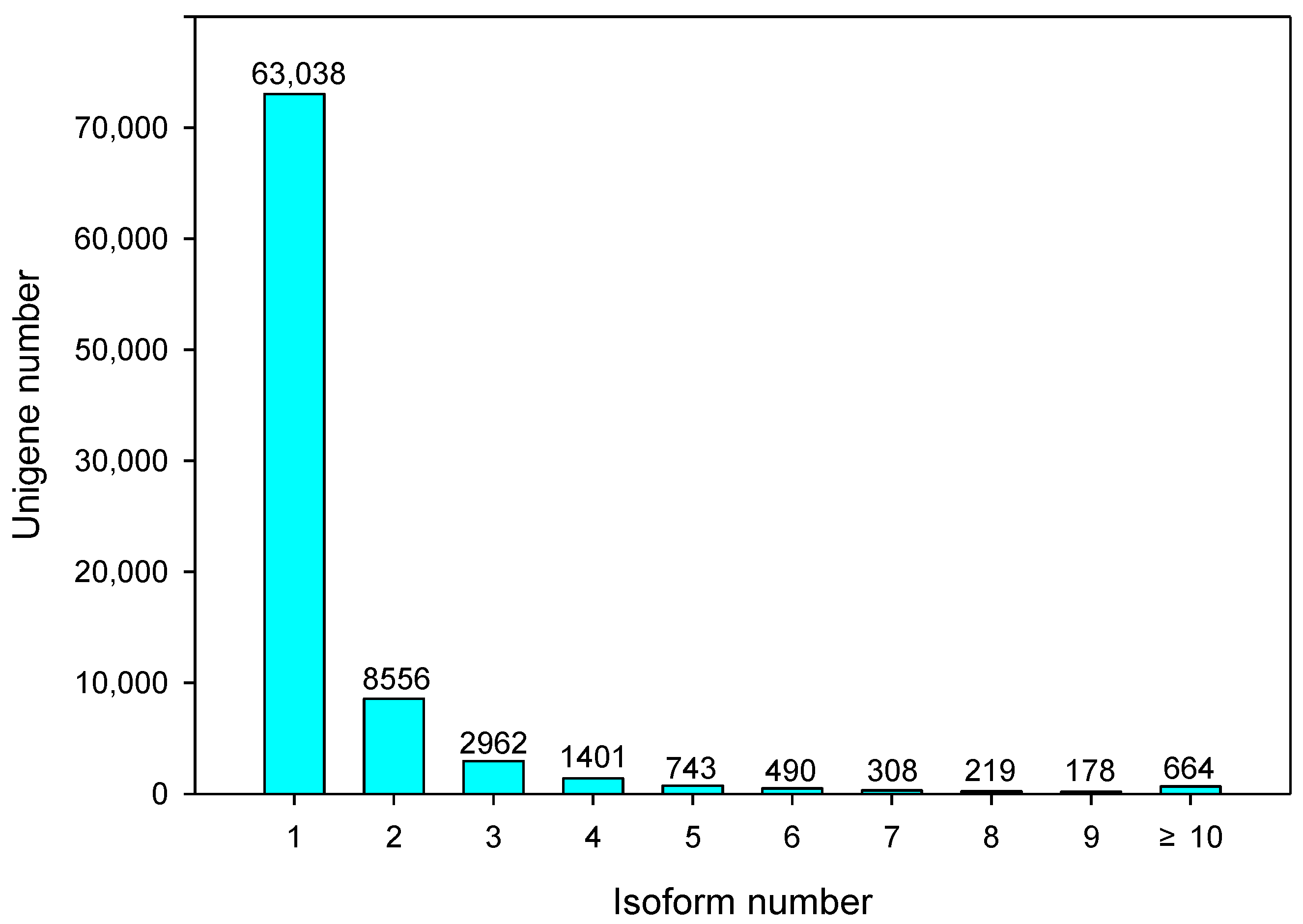
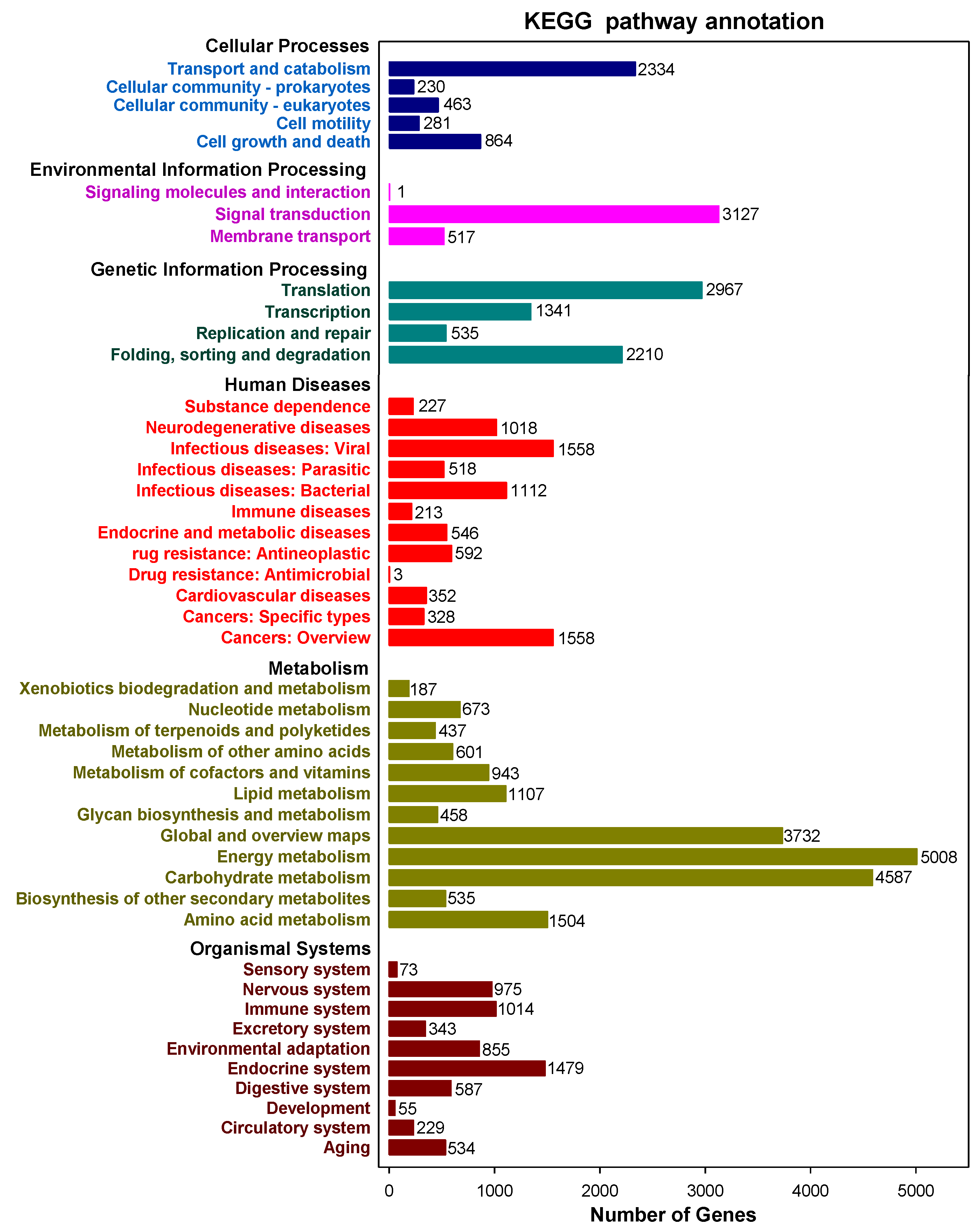
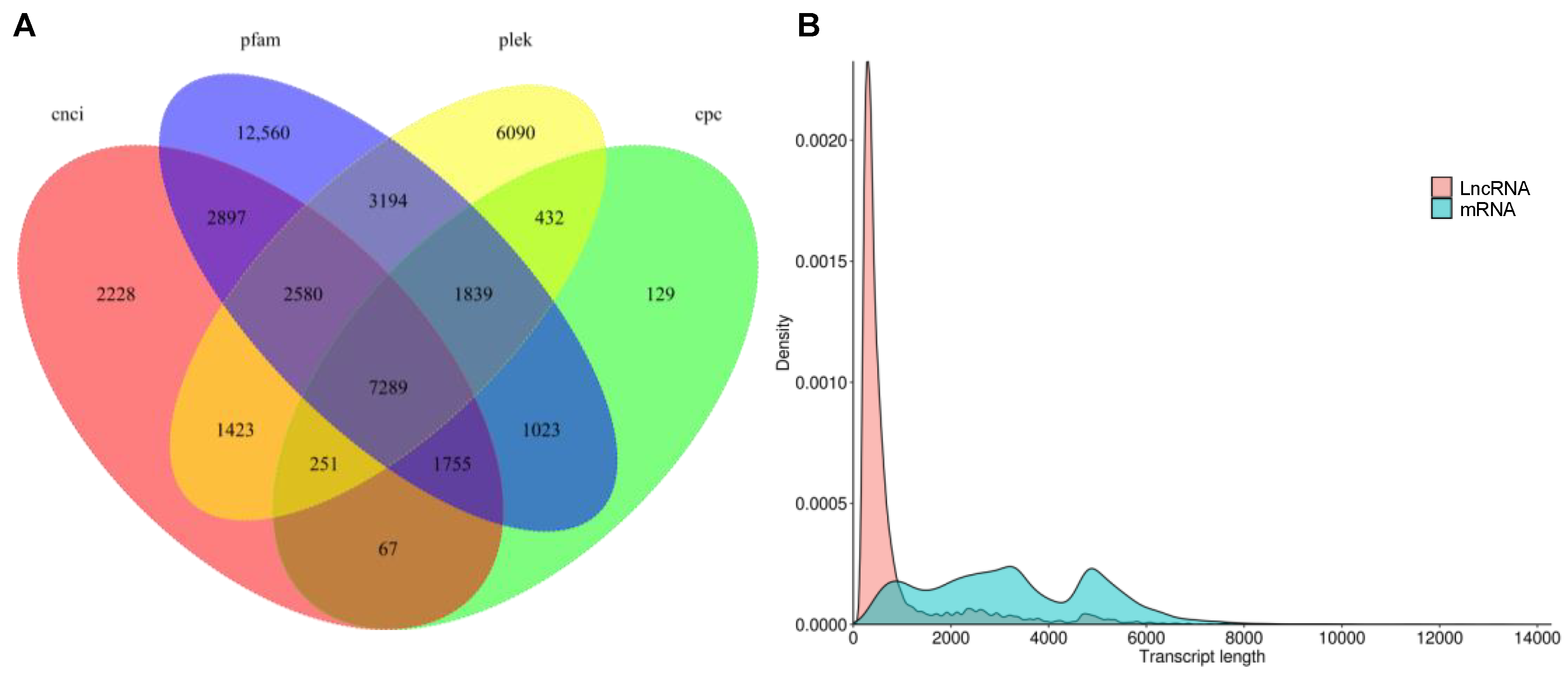
2.2. Functional Annotation of Full-Length Transcripts
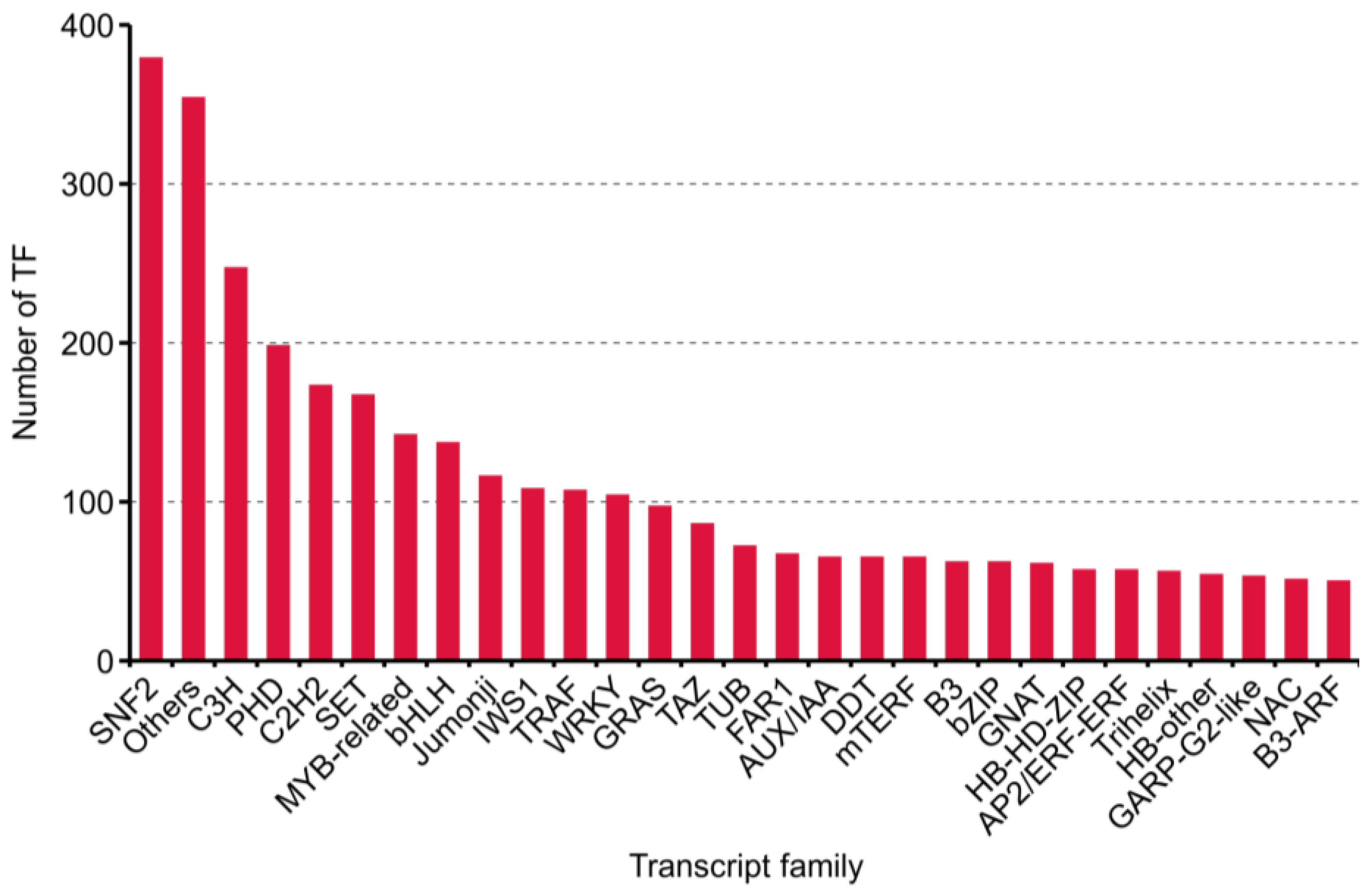
2.3. Results of Transcript Factors, Long Non-Coding RNAs and Simple Sequence Repeat
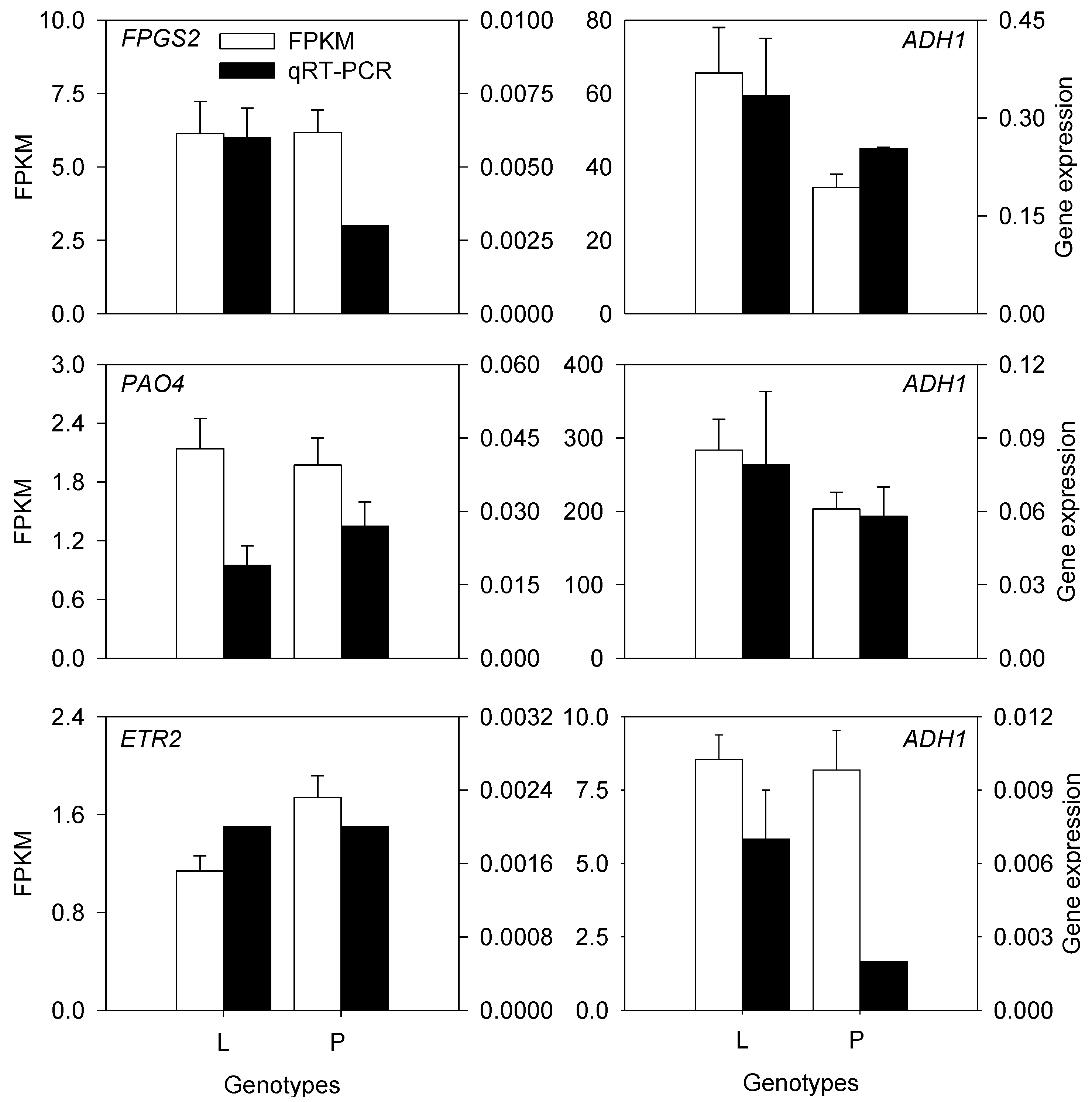
2.4. qRT–PCR Validation of Selected Genes
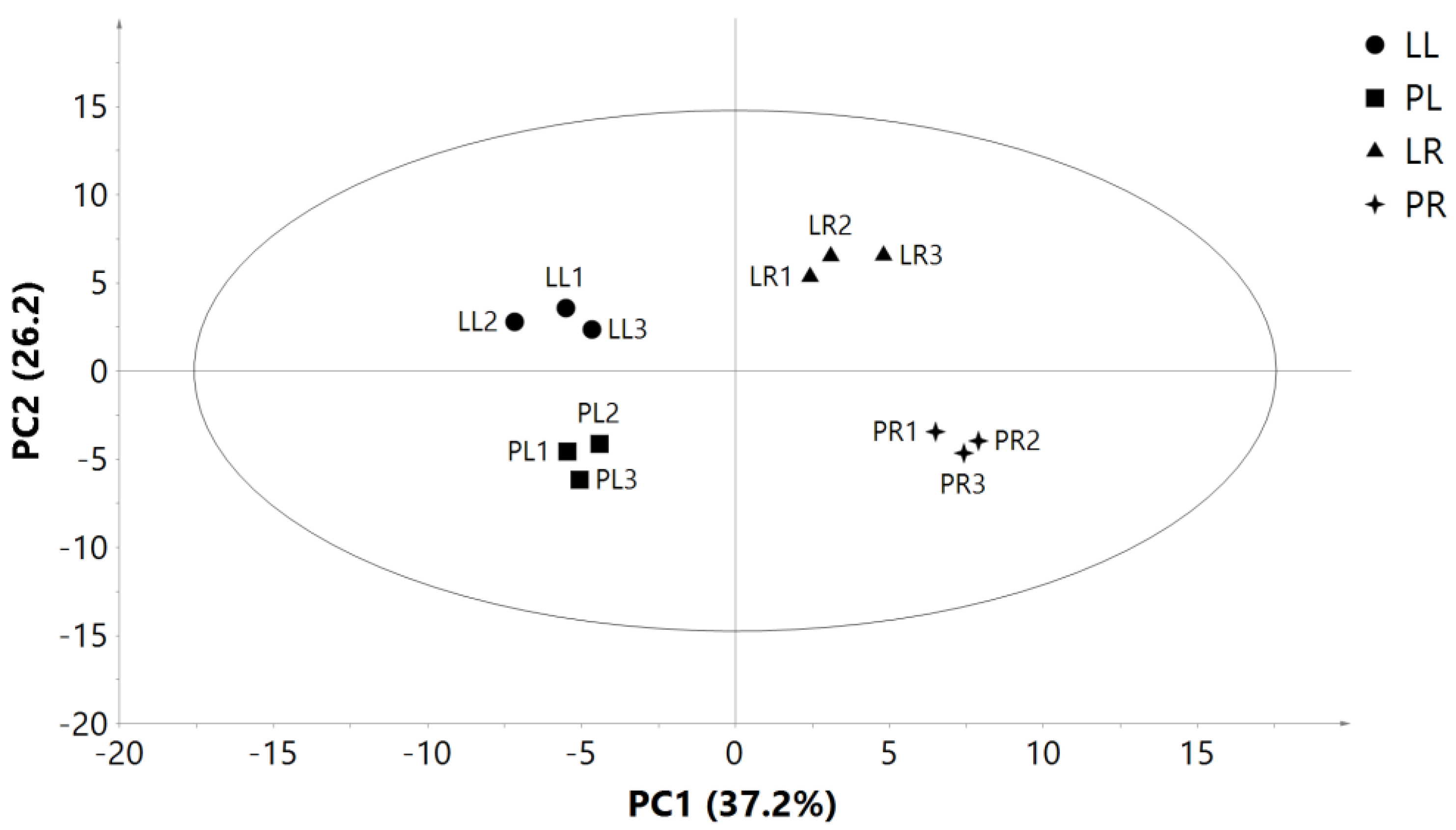
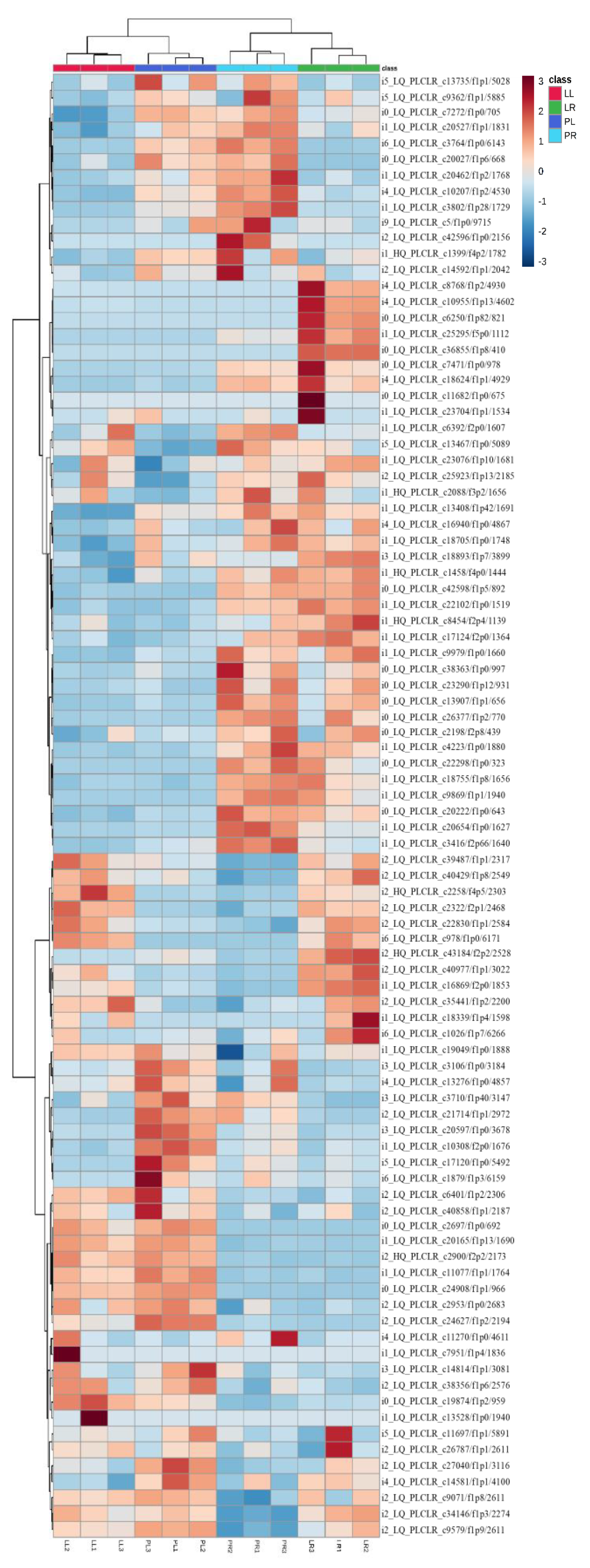
2.5. Illumina Sequencing Results and Differential Gene Expression in Leaves and Roots of Two Purslane Genotypes
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis in the Pathway of Biosynthesis of Unsaturated Fatty Acids
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plants Samples and Treatment
4.2. RNA Extraction, Library Construction and SMART Sequencing
4.3. Functional Annotation of Transcripts
4.4. Identification of Transcript Factors, Long Non-Coding RNAs and Simple Sequence Repeat
4.5. Illumina cDNA Library Construction and Second-Generation Sequencing Analysis
4.6. Quantitative RT–PCR Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ezekwe, M.O.; Omara-Alwala, T.R.; Membrahtu, T. Nutritive characterization of purslane accessions as influenced by planting date. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1999, 54, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P.; Norman, H.A.; Gillaspy, J.E. Purslane in human nutrition and its potential for world agriculture. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1995, 77, 47–74. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.; Juraimi, A.S.; Hossain, M.S.; Nahar, M.; Ali, M.; Rahman, M. Purslane weed (Portulaca oleracea): A prospective plant source of nutrition, omega-3 fatty acid, and antioxidant attributes. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 951019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.S.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kang, D.G.; Lee, H.S. Anti-TNF-α activity of Portulaca oleracea in vascular endothelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 5628–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayat, M.Q.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, M.; Shaheen, N.; Yasmin, G.; Akhter, S. Ethnotaxonomical approach in the identification of useful medicinal flora of tehsil Pindigheb (District Attock) Pakistan. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2008, 6, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, K.; Nisar, M.F.; Majeed, A.; Nawaz, K.; Bhatti, K.H. Ethnomedicinal survey for important plants of Jalalpur Jattan, district Gujrat, Punjab, Pakistan. Ethnobot. Leafl. 2010, 14, 807–825. [Google Scholar]
- Ercisli, S.; Coruh, I.; Gormez, A.; Sengul, M. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of Portulaca oleracea L. Grown wild in Turkey. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2008, 20, 533–542. [Google Scholar]
- Grieve, C.M.; Suarez, D.L. Purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.): A halophytic crop for drainage water reuse systems. Plant Soil 1997, 192, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Juraimi, A.S.; Rafii, M.Y.; Hamid, A.A. Effect of salinity on biomass yield and physiological and stem-root anatomical characteristics of purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) accessions. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 105695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kafi, M.; Rahimi, Z. Effect of salinity and silicon on root characteristics, growth, water status, proline content and ion accumulation of purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.). Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2011, 57, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulry, K.R.; Hanson, B.A.; Dudle, D.A. Alternative strategies in response to saline stress in two varieties of Portulaca oleracea (Purslane). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138723. [Google Scholar]
- Yazici, I.; Türkan, I.; Sekmen, A.H.; Demiral, T. Salinity tolerance of purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) is achieved by enhanced antioxidative system, lower level of lipid peroxidation and proline accumulation. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 61, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium. Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome. Nature 2004, 431, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharshini, S.; Chakravarthi, M.; Manoj, V.; Naveenarani, M.; Kumar, R.; Meena, M.; Ram, B.; Appunu, C. De novo sequencing and transcriptome analysis of a low temperature tolerant Saccharum spontaneum clone IND 00–1037. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 231, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Zou, X.; Zhang, X. Transcriptome analysis of canola (Brassica napus) under salt stress at the germination stage. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Jing, Y.; Wu, K.; Liang, J.; He, S.; Wang, G.; Mo, Z.; Tan, F. De novo analysis of transcriptome reveals genes associated with leaf abscission in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.). BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Li, B.; Meng, Y.; Ma, X.; Lai, Y.; Si, E.; Yang, K.; Ren, P.; Shang, X.; Wang, H. Transcriptomic profiling of the salt-stress response in the halophyte Halogeton glomeratus. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, J.C.; Zhao, B.Q.; Dong, J.; Liu, C.; Wen, Z.G.; Zhu, X.M.; Ding, H.R.; He, T.T.; Yang, H.; Wang, M.W.; et al. Transcriptome and metabolome profiles revealed molecular mechanisms underlying tolerance of Portulaca oleracea to saline stress. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2020, 67, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.B.; Schneeberger, K. The impact of third generation genomic technologies on plant genome assembly. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 36, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatko, B.E.; Gardner, A.F.; Ausubel, F.M. Overview of next-generation sequencing technologies. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2018, 122, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tseng, E.; Regulski, M.; Clark, T.A.; Hon, T.; Jiao, Y.; Lu, Z.; Olson, A.; Stein, J.C.; Ware, D. Unveiling the complexity of the maize transcriptome by single-molecule long-read sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, L.; Teng, K.; Tan, P.; Chao, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Han, L. PacBio single-molecule long-read sequencing shed new light on the transcripts and splice isoforms of the perennial ryegrass. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2020, 295, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Tang, L.; Mei, X.; Liu, H.; Luo, H.; Deng, Y.; Su, J. Single-molecule long-read sequencing of the full-length transcriptome of Rhododendron lapponicum L. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, H.; Yu, H.; Huang, T.; Shen, X.; Xia, J.; Pang, F.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M. The complexity of the Fragaria × ananassa (octoploid) transcriptome by single-molecule long-read sequencing. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, N.; Hou, C.; Ma, F.F.; Liu, C.X.; Tian, Y.X. Molecule long-read sequencing reveals the diversity of full-length transcripts in leaves of Gnetum (Gnetales). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiao, C.; Sun, H.; Rosli, H.G.; Pombo, M.A.; Zhang, P.; Banf, M.; Dai, X.; Martin, G.B.; Giovannoni, J.J.; et al. iTAK: A program for genome-wide prediction and classification of plant transcription factors, transcriptional regulators, and protein kinases. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, Y.; Yuan, J.; Li, S.; Jia, S.; Han, L.; Xu, L. Analysis of transcripts and splice isoforms in red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) by single-molecule long-read sequencing. BMC Plant Bio. 2018, 18, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Workman, R.E.; Myrka, A.M.; Wong, G.W.; Tseng, E.; Welch, J.K.C.; Timp, W. Single-molecule, full-length transcript sequencing provides insight into the extreme metabolism of the ruby-throated hummingbird Archilochus colubris. GigaScience 2018, 7, giy009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Chen, X.; Peng, J.; Yang, C.; Peng, M.; Zhu, W.; Xie, D.; He, P.; Wei, P.; Lin, Y.; et al. Single-molecule long-read sequencing facilitates shrimp transcriptome research. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, C.; Blow, M.; Sreedasyam, A.; Kuo, R.C.; Ramamoorthy, G.K.; Torres-Jerez, I.; Li, G.; Wang, M.; Dilworth, D.; Barry, K.; et al. Revealing the transcriptomic complexity of switchgrass by PacBio long-read sequencing. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chekanova, J.A. Long non-coding RNAs and their functions in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 27, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlik, E.; Marakli, S.; Gozukirmizi, N. Two lncRNAs expression profiles in salt stressed barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) roots. Cytologia 2018, 83, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Lin, J.; Kan, J.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Li, H.; Chang, Y. Genome-wide identification and functional prediction of novel drought-responsive LncRNAs in Pyrus betulifolia. Genes 2018, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kachroo, A.; Shanklin, J.; Whittle, E.; Lapchyk, L.; Hildebrand, D.; Kachroo, P. The Arabidopsis stearoyl-acyl carrier protein-desaturase family and the contribution of leaf isoforms to oleic acid synthesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 63, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanklin, J.; Cahoon, E.B. Desaturation and related modifications of fatty acids. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 49, 611–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Liu, A. Expression of genes controlling unsaturated fatty acids biosynthesis and oil deposition in developing seeds of sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.). Lipids 2014, 49, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Maximova, S.N.; Guiltinan, M.J. Characterization of a stearoyl-acyl carrier protein desaturase gene family from chocolate tree, Theobroma cacao L. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Rivas, J.M.; Martínez, R. Spatial and temporal regulation of three different microsomal oleate desaturase genes (FAD2) from normal-type and high-oleic varieties of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Mol. Breed. 2001, 8, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Pirtle, I.L.; Park, S.J.; Nampaisansuk, M.; Neogi, P.; Wanjie, S.W.; Pirtle, R.M.; Chapman, K.D. Identification and expression of a new delta-12 fatty acid desaturase (FAD2-4) gene in upland cotton and its functional expression in yeast and Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 47, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.C.; Coelho, N.; Olsson, M.E.; Brodelius, P.E.; Carvalho, I.S.; Brodelius, M. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of three omega-6 desaturase genes from purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.). Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Hu, H.; Yang, L. Cloning and expression of three fatty acid desaturase genes from cold-sensitive lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.). Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Q.Q.; Du, H.M. Content analysis of fatty acids and oxalic acid in ten different types of purslane (Portulaca oleracea). Guihaia 2019, 39, 1550–1557, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Raheja, R.K.; Batta, S.K.; Ahuja, K.L.; Labana, K.S.; Singh, M. Comparison of oil content and fatty acid composition of peanut genotypes differing in growth habit. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1987, 37, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meï, C.; Michaud, M.; Cussac, M.; Albrieux, C.; Gros, V.; Maréchal, E.; Block, M.A.; Jouhet, J.; Rébeillé, F. Levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids correlate with growth rate in plant cell cultures. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.; Dong, R.; Liu, L.; Hu, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Ding, X.; Chu, Z. A novel mutant allele of SSI2 confers a better balance between disease resistance and plant growth inhibition on Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaman, S.; Hu, S.; Alam, M.A.; Du, H.; Che, S. The accumulation of fatty acids in different organs of purslane under salt stress. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 250, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, S.E.; del Rio, A.H.; Bamberg, J.B.; Palta, J.P. Evidence for the up-regulation of stearoyl-ACP (Δ9) desaturase gene expression during cold acclimation. Am. J. Potato Res. 2004, 81, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miquel, M.; James, D.; Dooner, H. Arabidopsis requires polyunsaturated lipids for low-temperature survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6208–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallis, J.G.; Browse, J. Mutants of Arabidopsis reveal many roles for membrane lipids. Prog. Lipid Res. 2002, 41, 254–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, A.; Chen, H.; Shen, G.; Hu, Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, J. Expression of fatty acid synthesis genes and fatty acid accumulation in Haematococcus pluvialis under different stressors. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2012, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Li, B.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H. Arabidopsis fatty acid desaturase FAD2 is required for salt tolerance during seed germination and early seedling growth. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Q.Q.; Du, H.M. The effects of NaCl treatment on growth of purslane (Portulaca oleracea). J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Agri. Sci.) 2018, 36, 67–72, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Yang, M.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, T. Characterization of the whole transcriptome of whelk Rapana venosa by single-molecule mRNA sequencing. Mar. Genom. 2019, 44, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jaroszewski, L.; Godzik, A. Tolerating some redundancy significantly speeds up clustering of large protein databases. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatusov, R.L.; Fedorova, N.D.; Jackson, J.D.; Jacobs, A.R.; Kiryutin, B.; Koonin, E.V.; Krylov, D.M.; Mazumder, R.; Mekhedov, S.L.; Nikolskaya, A.N. The COG database: An updated version includes eukaryotes. BMC Bioinform. 2003, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bairoch, A.; Apweiler, R. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence database and its supplement TrEMBL in 2000. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Kawashima, S.; Okuno, Y.; Hattori, M. The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D277–D280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T. Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Bu, D.; Zhao, G.; Luo, H.; Yu, K.; Sun, L.; Chen, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e166. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.Q.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhao, S.Q.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC: Assess the protein-coding potential of transcripts using sequence features and support vector machine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W345–W349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Mistry, J.; Mitchell, A.L.; Potter, S.C.; Punta, M.; Qureshi, M.; Sangrador-Vegas, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database: Towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, D279–D285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z. PLEK: A tool for predicting long non-coding RNAs and messenger RNAs based on an improved k-mer scheme. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, J.; Zwinderman, A. On the Benjamini-Hochberg method. Ann. Stat. 2006, 34, 1827–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Su, N.; Jia, L.; Tian, J.; Li, H.; Huang, L.; Shen, Z.; Cui, J. Transcriptome analysis of radish sprouts hypocotyls reveals the regulatory role of hydrogen-rich water in anthocyanin biosynthesis under UV-A. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Mapping Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | |||
| “LCL”, 1 | 62,777,144 | 47,789,582 | 76.13 |
| “LCL”, 2 | 60,625,062 | 45,707,454 | 75.39 |
| “LCL”, 3 | 54,712,526 | 40,774,382 | 74.52 |
| “PL”, 1 | 54,782,840 | 41,921,110 | 76.52 |
| “PL”, 2 | 61,500,192 | 47,256,666 | 76.84 |
| “PL”, 3 | 59,127,304 | 44,841,760 | 75.84 |
| Roots | |||
| “LCL”, 1 | 58,010,278 | 34,114,332 | 58.81% |
| “LCL”, 2 | 56,153,952 | 34,729,076 | 61.85% |
| “LCL”, 3 | 59,146,128 | 37,448,562 | 63.32% |
| “PL”, 1 | 63,212,838 | 38,289,822 | 60.57% |
| “PL”, 2 | 48,132,318 | 28,489,398 | 59.19% |
| “PL”, 3 | 42,508,608 | 24,481,842 | 57.59% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, H.; Zaman, S.; Hu, S.; Che, S. Single-Molecule Long-Read Sequencing of Purslane (Portulaca oleracea) and Differential Gene Expression Related with Biosynthesis of Unsaturated Fatty Acids. Plants 2021, 10, 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040655
Du H, Zaman S, Hu S, Che S. Single-Molecule Long-Read Sequencing of Purslane (Portulaca oleracea) and Differential Gene Expression Related with Biosynthesis of Unsaturated Fatty Acids. Plants. 2021; 10(4):655. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040655
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Hongmei, Shah Zaman, Shuiqingqing Hu, and Shengquan Che. 2021. "Single-Molecule Long-Read Sequencing of Purslane (Portulaca oleracea) and Differential Gene Expression Related with Biosynthesis of Unsaturated Fatty Acids" Plants 10, no. 4: 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040655
APA StyleDu, H., Zaman, S., Hu, S., & Che, S. (2021). Single-Molecule Long-Read Sequencing of Purslane (Portulaca oleracea) and Differential Gene Expression Related with Biosynthesis of Unsaturated Fatty Acids. Plants, 10(4), 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040655








