Essential Oil of Croton zehntneri Prevents Conduction Alterations Produced by Diabetes Mellitus on Vagus Nerve
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
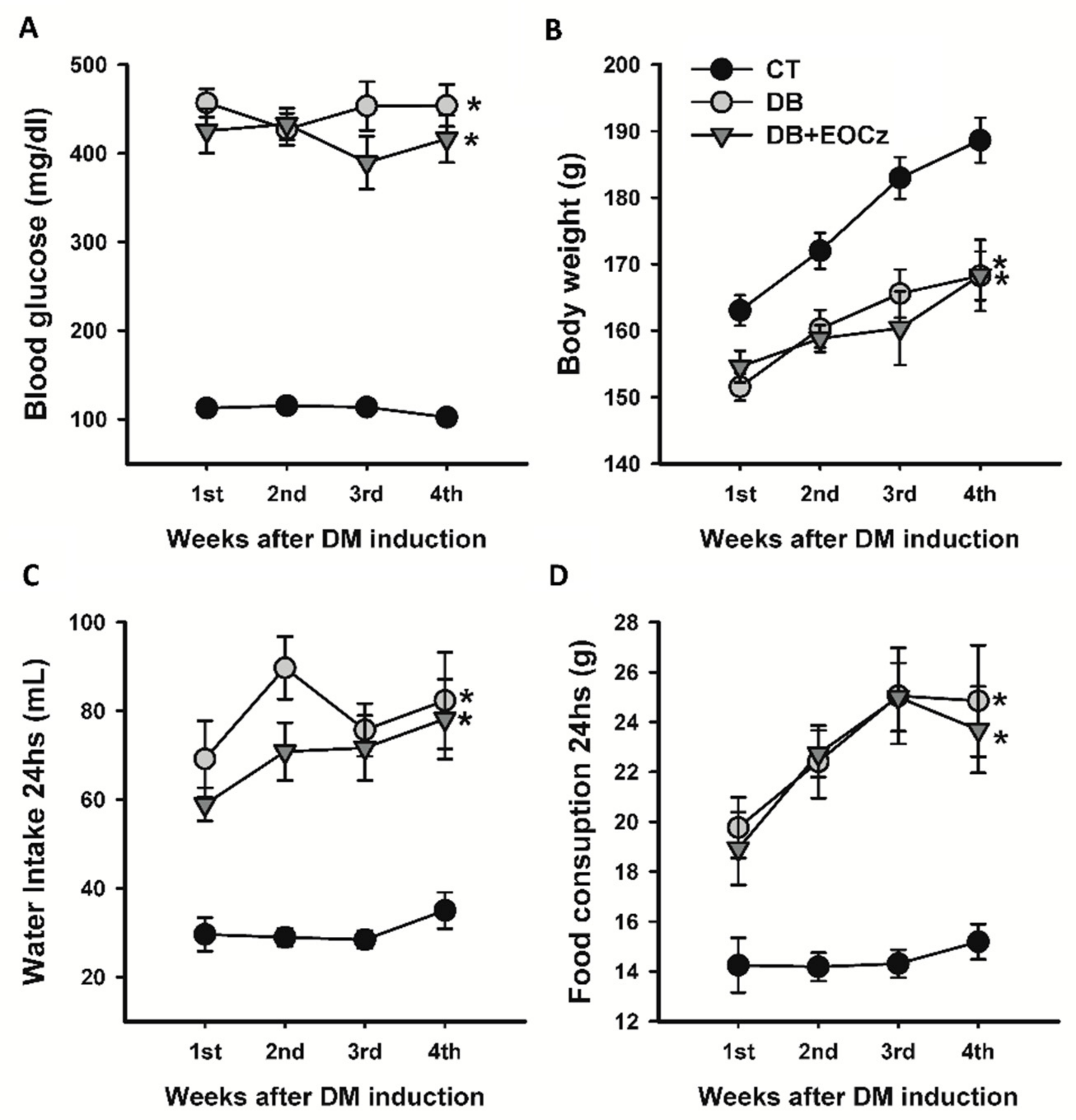
2.1. Streptozotocin-Induced DM Model and EOCz Effects
2.2. Characterization of Compound Action Potential (CAP)
2.3. DM Effects on CAP of Vagal Fibers and EOCz Prevention
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Extraction and EOCz Analysis and Composition Determination
4.2. Animals and DM Induction
4.3. Electrophysiology
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pasnoor, M.; Dimachkie, M.M.; Kluding, P.M.; Barohn, R.J. Diabetic Neuropathy Part 1. Overview and Symmetric Phenotypes. Neurol. Clin. 2013, 31, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Boulton, A.J.; Feldman, E.L.; Bril, V.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bodman, M.A.; Varacallo, M. Peripheral Diabetic Neuropathy; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, G.M.; Kahn, L.B.; Baxter, J.; Marshall, J.A.; Hamman, R.F. Sensory Neuropathy in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The San Luis Valley Diabetes Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1990, 131, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, J.R.; Smith, A.G.; Russell, J.W.; Feldman, E.L. Microvascular Complications of Impaired Glucose Tolerance. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2867–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira-Da-Silva, F.W.; Da Silva-Alves, K.S.; Lemos-Dos-Santos, M.; De Oliveira, K.A.; Joca, H.C.; Vale, O.C.D.; Coelho-De-Souza, A.N.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H. n5-STZ Diabetic Model Develops Alterations in Sciatic Nerve and Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons of Wistar Rats. ISRN Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stino, A.M.; Smith, A.G. Peripheral neuropathy in prediabetes and the metabolic syndrome. J. Diabetes Investig. 2017, 8, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.K.; Rohatgi, A.; Sharma, D. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy: A clinical update. J. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 2020, 50, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinik, A.I.; Maser, R.E.; Mitchell, B.D.; Freeman, R. Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1553–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freeman, R. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Neuroparasitol. Trop. Neurol. 2014, 126, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Park, J.; Baek, H. Can diabetic neuropathy be prevented? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2004, 66, S53–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.L.; Vincent, A.M.; Cheng, H.T.; Feldman, E.L. Diabetic neuropathy: Mechanisms to management. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 120, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yorek, M.; Malik, R.A.; Calcutt, N.A.; Vinik, A.; Yagihashi, S. Diabetic Neuropathy: New Insights to Early Diagnosis and Treatments. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, S. Inflammation: Therapeutic Targets for Diabetic Neuropathy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 49, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Lian, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Cai, Y.; Ma, H.; Yu, X. Understanding Diabetic Neuropathy: Focus on Oxidative Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stino, A.M.; Rumora, A.E.; Kim, B.; Feldman, E.L. Evolving concepts on the role of dyslipidemia, bioenergetics, and inflammation in the pathogenesis and treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2020, 25, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukami, H.; Osonoi, S. Collateral Glucose-Utilizing Pathways in Diabetic Polyneuropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Cardoso, J.H.; Fonteles, M.C. Pharmacological effects of essential oils of plants of the northeast of Brazil. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 1999, 71, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Leal-Cardoso, J.H.; Albuquerque, A.A.C.; Ceccatto, V.M.; Coelho-De-Souza, A.N. Croton zehntneri Pax et Hoffm. (canela-de-cunhã). In Plantas Medicinais da Caatinga: Atividades Biológicas e Potencial Terapêutico; Viana, G.S.B., Leal, L.K.A.M., Vasconcelos, S.M.M., Eds.; Expressão Gráfica e Editora: Fortaleza, Brazil, 2013; pp. 125–162. [Google Scholar]
- Morais, S.M.; Catunda-Junior, F.E.A.; Silva, A.R.A.; Martins-Neto, J.S.; Rondina, D.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H. Atividade antioxidante de óleos essenciais de espécies de Croton do Nordeste do Brasil. Quím. Nova 2006, 29, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serra, D.S.; Gomes, M.D.M.; Cavalcante, F.S. Ávila; Leal-Cardoso, J.H. Essential oil of Croton Zehntneri attenuates lung injury in the OVA-induced asthma model. J. Asthma 2018, 56, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.; Leal-Cardoso, J.; Santos, C.; Morais, S.; Coelho-De-Souza, A. Antinociceptive effects of the essential oil of Croton zehntneri in mice. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2001, 34, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalcanti, J.M.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H.; Diniz, L.R.L.; Portella, V.G.; Costa, C.O.; Linard, C.F.B.M.; Alves, K.; Rocha, M.V.A.D.P.; Lima, C.C.; Cecatto, V.M.; et al. The essential oil of Croton zehntneri and trans-anethole improves cutaneous wound healing. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 144, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva-Alves, K.; Ferreira-Da-Silva, F.; Coelho-De-Souza, A.; Albuquerque, A.; Vale, O.D.; Leal-Cardoso, J. Essential Oil of Croton zehntneri and Its Main Constituent Anethole Block Excitability of Rat Peripheral Nerve. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Alves, K.; Ferreira-Da-Silva, F.; Peixoto-Neves, D.; Viana-Cardoso, K.; Moreira-Júnior, L.; Oquendo, M.; Oliveira-Abreu, K.; Albuquerque, A.; Coelho-De-Souza, A.; Leal-Cardoso, J. Estragole blocks neuronal excitability by direct inhibition of Na+ channels. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2013, 46, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponte, E.L.; Sousa, P.L.; Rocha, M.V.; Soares, P.M.; Coelho-De-Souza, A.N.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H.; Assreuy, A.M. Comparative study of the anti-edematogenic effects of anethole and estragole. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho-De-Souza, A.N.; Rocha, M.V.A.; Oliveira, K.A.; Vasconcelos, Y.A.; Santos, E.C.; Silva-Alves, K.S.; Diniz, L.R.L.; Ferreira-Da-Silva, F.W.; Oliveira, A.C.; Ponte, E.L.; et al. Volatile oil of Croton zehntneri per oral sub-acute treatment offers small toxicity: Perspective of therapeutic use. Rev. Bras. Farm. 2019, 29, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge, D. Nerve and Muscle Excitation, 2nd ed.; Sinauer Associates Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Schoonhoven, R.; Stegeman, D.F. Models and analysis of compound nerve action potentials. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1991, 19, 47–111. [Google Scholar]
- Erlanguer, J.; Gasser, H.S. Electrical Signs of Nervous Activity; University of Pennsylvania Press: Oxford, UK, 1937. [Google Scholar]
- Hursh, J.B. Conduction velocity and diameter of nerve fibers. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1939, 127, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Karakida, T.; Homma, S. Conduction velocity of motor nerve and cervical sympathetic and vagus nerve in streptozotocin diabetic rats. Neurosci. Lett. 1990, 113, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, R.; Charlesworth, G.; Farrag, K.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Costa, S. The use of the rat isolated vagus nerve for functional measurements of the effect of drugs in vitro. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2005, 51, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Cardoso, J.H.; da Silva-Alves, K.S.; Ferreira-Da-Silva, F.W.; dos Santos-Nascimento, T.; Joca, H.C.; de Macedo, F.H.P.; de Albuquerque-Neto, P.M.; Magalhães, P.J.C.; Lahlou, S.; Cruz, J.S.; et al. Linalool blocks excitability in peripheral nerves and voltage-dependent Na+ current in dissociated dorsal root ganglia neurons. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 645, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, V.; Uchoa, P.; Aquino, C.; Britto, L.; Fonteles, M.; Leal-Cardoso, J.; Silva-Alves, K.; Havt, A.; Prata, M.; Heimark, D.; et al. Expression of myo-inositol cotransporters in the sciatic nerve and dorsal root ganglia in experimental diabetes. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, e8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Ong, L.; Smith, M.T.; Ross, F.B.; Schmid, K.L.; Hoey, A.J.; Burstow, D.J.; Brown, L.C. The streptozotocin-diabetic rat as a model of the chronic complications of human diabetes. Hear. Lung Circ. 2003, 12, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Norouzian, D.; Mehrabi, M.R.; Jamshidi, S.; Farhangi, A.; Verdi, A.A.; Mofidian, S.M.A.; Rad, B.L. Induction of diabetes by Streptozotocin in rats. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 22, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Awar, A.; Kupai, K.; Veszelka, M.; Szűcs, G.; Attieh, Z.; Murlasits, Z.; Török, S.; Pósa, A.; Varga, C. Experimental Diabetes Mellitus in Different Animal Models. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Julu, P.O.O. The correlation between sensory nerve conduction velocities and three metabolic indices in rats treated with streptozotocin. Diabetology 1988, 31, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaman, M.; Uluduz, D.; Yuksel, S.; Pay, G.; Kızıltan, M.E. The cutaneous silent period in diabetes mellitus. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 419, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, F.; Kojima, R.; Taniguchi, M.; Kosaka, A.; Uetake, H.; Tavakoli, M. The Expanded Bead Size of Corneal C-Nerve Fibers Visualized by Corneal Confocal Microscopy Is Associated with Slow Conduction Velocity of the Peripheral Nerves in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tesfaye, S.; Boulton, A.J.; Dyck, P.J.; Freeman, R.; Horowitz, M.; Kempler, P.; Lauria, G.; Malik, R.A.; Spallone, V.; Vinik, A.; et al. Diabetic Neuropathies: Update on Definitions, Diagnostic Criteria, Estimation of Severity, and Treatments. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.; Morrow, T.J.; Paulson, P.E.; Isom, L.L.; Wiley, J.W. Early Painful Diabetic Neuropathy Is Associated with Differential Changes in Tetrodotoxin-sensitive and -resistant Sodium Channels in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons in the Rat. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 29341–29350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.; Wiley, J.W. Altered expression and function of sodium channels in large DRG neurons and myelinated A-fibers in early diabetic neuropathy in the rat. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 339, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zochodne, D.W.; Ramji, N.; Toth, C. Neuronal Targeting in Diabetes Mellitus: A Story of Sensory Neurons and Motor Neurons. Neuroscientist 2008, 14, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, R.; Kojima, H.; Nakamura, K.; Arahata, A.; Fujita, Y.; Tokuyama, Y.; Saito, T.; Furudate, S.-I.; Kurihara, T.; Yagishita, S.; et al. Alterations in mRNA Expression of Myelin Proteins in the Sciatic Nerves and Brains of Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rats. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumy, L.F.; Bampton, E.T.; Tolkovsky, A.M. Hyperglycaemia inhibits Schwann cell proliferation and migration and restricts regeneration of axons and Schwann cells from adult murine DRG. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008, 37, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Rouen, S.; Dobrowsky, R.T. Hyperglycemia and downregulation of caveolin-1 enhance neuregulin-induced demyelination. Glia 2008, 56, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, H.C. Schwann Cells as a Therapeutic Target for Peripheral Neuropathies. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2010, 9, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.E.; Plurad, D.A.; Plurad, S.B.; Cogswell, B.E.; Diani, A.R.; Roth, K.A. Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical characterization of autonomic neuropathy in genetically diabetic Chinese hamsters. Lab. Investig. 1989, 61, 77–92. [Google Scholar]
- Murinson, B.B.; Griffin, J.W. C-Fiber Structure Varies with Location in Peripheral Nerve. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 63, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Julu, P.O. Latency of neuroactivity and optimum period of treatment with evening primrose oil in diabetic rats. J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal. 1996, 13, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruvilla, R.; Peterson, R.; Kincaid, J.; Eichberg, J. Evening primrose oil treatment corrects reduced conduction velocity but not depletion of arachidonic acid in nerve from streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 1998, 59, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, I.; Cotter, M.A.; Cameron, N.E.; Greaves, M. The effects of treatment with [alpha]-lipoic acid or evening primrose oil on vascular hemostatic and lipid risk factors, blood flow, and peripheral nerve conduction in the streptozotocin-diabetic rat. Metabolism 2001, 50, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batatinha, M.; De Souza-Spinosa, H.; Bernardi, M. Croton zehntneri: Possible central nervous system effects of the essential oil in rodents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1995, 45, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.C.; De Holanda-Angelin-Alves, C.M.; Pereira-Gonçalves, Á.; Kennedy-Feitosa, E.; Evangelista-Costa, E.; Bezerra, M.A.C.; Coelho-De-Souza, A.N.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H. Antispasmodic effects of the essential oil of Croton zehnteneri, anethole, and estragole, on tracheal smooth muscle. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho-De-Souza, A.N.; Criddle, D.N.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H. Selective Modulatory Effects of the Essential Oil of Croton zehntneri on Isolated Smooth Muscle Preparations of the Guinea-pig. Phytother. Res. 1998, 12, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, P.H.B.; Campos, R.D.M.; Fonteles, M.C.; Santos, C.F.; Cardoso, J.H.L.; Nascimento, N.R.F.D. Effects of the essential oil of Croton zehntneri and its major components, anethole and estragole, on the rat corpora cavernosa. Life Sci. 2014, 112, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto-Neves, D.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H.; Jaggar, J.H. Eugenol Dilates Rat Cerebral Arteries by Inhibiting Smooth Muscle Cell Voltage-dependent Calcium Channels. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 64, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peixoto-Neves, D.; Wang, Q.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H.; Rossoni, L.V.; Jaggar, J.H. Eugenol dilates mesenteric arteries and reduces systemic BP by activating endothelial cell TRPV4 channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3484–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chainy, G.B.; Manna, S.K.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Anethole blocks both early and late cellular responses transduced by tumor necrosis factor: Effect on NF-κB, AP-1, JNK, MAPKK and apoptosis. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2943–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, G.; Yang, M.; Liu, N.; Li, Y.-X.; Ma, H.; Ma, L.; Sun, T.; Tan, H.; Yu, J. Neuroprotective Effect of Anethole Against Neuropathic Pain Induced by Chronic Constriction Injury of the Sciatic Nerve in Mice. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 2404–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, M.; Cruz, G.; Lopes, M.; Albuquerque, A.; Leal-Cardoso, J. Effects of terpineol on the compound action potential of the rat sciatic nerve. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2001, 34, 1337–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leal-Cardoso, J.; Moreira, M.; Da Cruz, G.P.; De Morais, S.; Lahlou, M.; Coelho-De-Souza, A. Effects of essential oil of Alpinia zerumbet on the compound action potential of the rat sciatic nerve. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva-Alves, K.S.; Ferreira-da-Silva, F.W.; Coelho-de-Souza, A.N.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H. Essential Oil of Croton zehntneri Prevents Conduction Alterations Produced by Diabetes Mellitus on Vagus Nerve. Plants 2021, 10, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050893
Silva-Alves KS, Ferreira-da-Silva FW, Coelho-de-Souza AN, Leal-Cardoso JH. Essential Oil of Croton zehntneri Prevents Conduction Alterations Produced by Diabetes Mellitus on Vagus Nerve. Plants. 2021; 10(5):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050893
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva-Alves, Kerly Shamyra, Francisco Walber Ferreira-da-Silva, Andrelina Noronha Coelho-de-Souza, and José Henrique Leal-Cardoso. 2021. "Essential Oil of Croton zehntneri Prevents Conduction Alterations Produced by Diabetes Mellitus on Vagus Nerve" Plants 10, no. 5: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050893
APA StyleSilva-Alves, K. S., Ferreira-da-Silva, F. W., Coelho-de-Souza, A. N., & Leal-Cardoso, J. H. (2021). Essential Oil of Croton zehntneri Prevents Conduction Alterations Produced by Diabetes Mellitus on Vagus Nerve. Plants, 10(5), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050893





