Preparation of Chlorophyll Nanoemulsion from Pomelo Leaves and Its Inhibition Effect on Melanoma Cells A375
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. HPLC Analysis of Chlorophylls in Pomelo Leaves
2.2. Chlorophyll Nanoemulsion Characteristics
2.3. Cell Tolerance to Sample Solvent and Blank Nanoemulsion
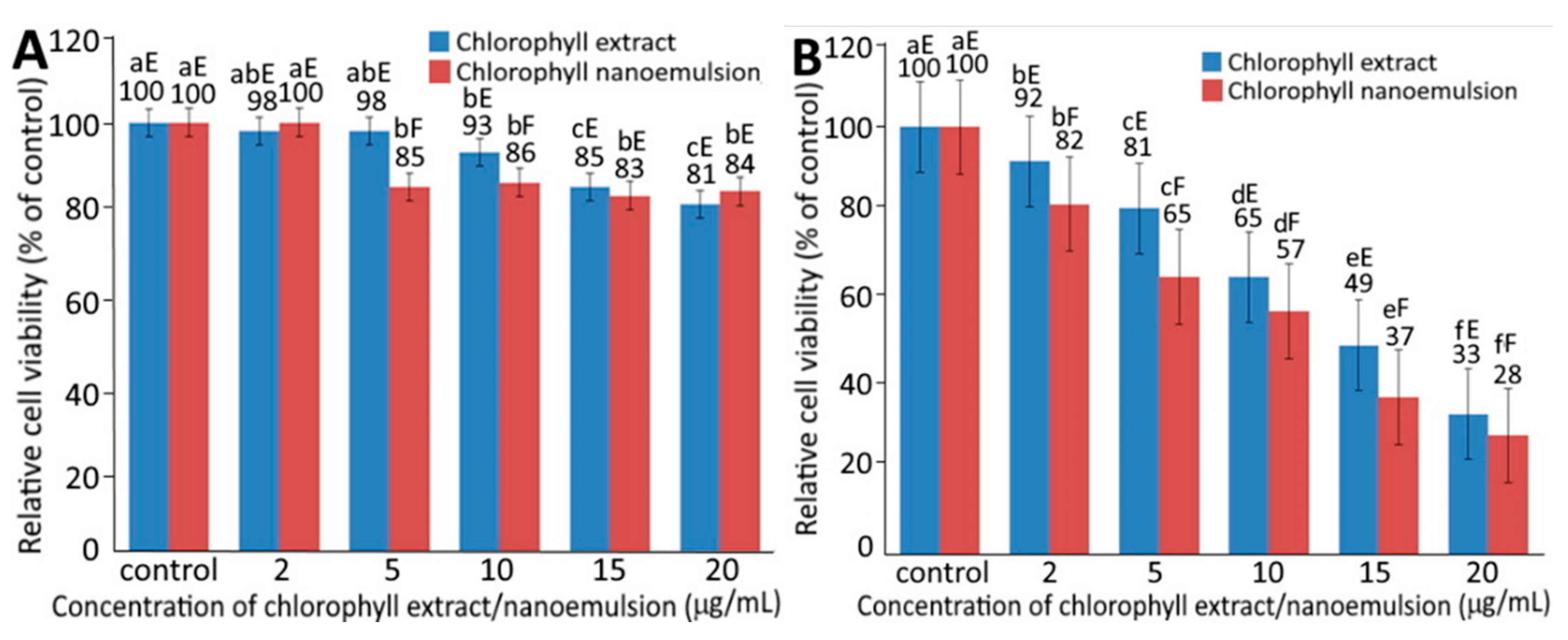
2.4. Cell Growth Inhibition Assay
2.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.6. Expression of Cell Cycle- and Apoptosis-Related Proteins
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Pomelo Leave Extraction and Analysis
3.4. Preparation of Chlorophylls from Pomelo Leave Extract by Preparative Column Chromatography
3.5. HPLC Analysis of Chlorophylls
3.6. Preparation of Chlorophyll Nanoemulsion
3.7. Determination of Nanoemulsion Characteristics
3.8. Cell Culture Study
3.9. MTT Assay
3.10. Cell Cycle Analysis
3.11. Western Blotting
3.12. Activities of Caspase-3, Caspase-8 and Caspase-9
3.13. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ladaniya, M.S. Commercial Fresh Citrus Cultivars and Producing Countries; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, J. Food Chemistry; New Wenjing Development Publishing: Taipei, Taiwan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Negishi, T.; Nakano, H.; Kitamura, A.; Itome, C.; Shiotani, T.; Hayatsu, H. Inhibitory activity of chlorophyllin on the genotoxicity of carcinogens in Drosophila. Cancer Lett. 1994, 83, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.L.; Chen, J.K.; Ong, T.; Brockman, H.E.; Whong, W.Z. Antitransforming activity of chlorophyllin against selected carcinogens and complex mixtures. Teratog Carcinog Mutagen 1994, 14, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashwood, R.H.; Breinholt, V.; Bailey, G.S. Chemopreventive properties of chlorophyllin: Inhibition of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1)-DNA binding in vivo and anti-mutagenic activity against AFB1 and two heterocyclic amines in the Salmonella mutagenicity assay. Carcinogenesis 1991, 12, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breinholt, V.; Hendricks, J.; Pereira, C.; Arbogast, D.; Bailey, G. Dietary chlorophyllin is a potent inhibitor of aflatoxin B1 hepatocarcinogenesis in rainbow trout. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Gong, M.W.; Peng, Z.F.; Zhou, T.; Ying, M.G.; Zheng, Q.H.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhang, Q.Q. The marine fungal metabolite, dicitrinone B, induces A375 cell apoptosis through the ROS-related caspase pathway. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1939–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, C.P.; Lu, Y.Y.; Ji, L.N.; Mao, Z.W. Metallomics insights into the programmed cell death induced by metal-based anticancer compounds. Metallomics 2014, 6, 978–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, G.D.; Li, Q.; Dashwood, R.H. Caspase-8 and apoptosis-inducing factor mediate a cytochrome c-independent pathway of apoptosis in human colon cancer cells induced by the dietary phytochemical chlorophyllin. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1254. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, J.Y.; Tang, P.M.; Hon, P.M.; Au, S.W.; Tsui, S.K.; Waye, M.M.; Kong, S.K.; Mak, T.C.; Fung, K.P. Pheophorbide a, a major antitumor component purified from Scutellaria barbata, induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Planta Med. 2006, 72, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, L.C.; Kong, C.K.; Ooi, V.E. The chlorophyllin-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells is associated with ERK deactivation and cyclin D1 depletion. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 16, 735–740. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.-J.; Ng, L.-T.; Wang, G.-H.; Huang, Y.-J.; Chen, J.-L.; Sun, F.-M. Chlorophyll a, an active anti-proliferative compound of Ludwigia octovalvis, activates the CD95 (APO-1/CD95) system and AMPK pathway in 3T3-L1 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferruzzi, M.G.; Blakeslee, J. Digestion, absorption, and cancer preventative activity of dietary chlorophyll derivatives. Nutr. Res. 2007, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, A.; Armentano, M.F.; Miglionico, R.; Caddeo, C.; Chirollo, C.; Gualtieri, M.J.; Ostuni, A.; Bisaccia, F.; Faraone, I.; Milella, L. Hura crepitans L. extract: Phytochemical characterization, antioxidant activity, and nanoformulation. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinisgalli, C.; Faraone, I.; Vassallo, A.; Caddeo, C.; Bisaccia, F.; Armentano, M.F.; Milella, L.; Ostuni, A. Phytochemical profile of Capsicum annuum L. cv Senise, incorporation into liposomes, and evaluation of cellular antioxidant activity. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Hung, C.F.; Chen, B.H. Preparation of coffee oil-algae oil-based nanoemulsions and the study of their inhibition effect on UVA-induced skin damage in mice and melanoma cell growth. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 6559–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delpino-Rius, A.; Cosovanu, D.; Eras, J.; Vilaró, F.; Balcells, M.; Canela-Garayoa, R. A fast and reliable ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography method to assess the fate of chlorophylls in teas and processed vegetable foodstuff. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1568, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arechabala, B.; Coiffard, C.; Rivalland, P.; Coiffard, L.J.; de Roeck-Holtzhauer, Y. Comparison of cytotoxicity of various surfactants tested on normal human fibroblast cultures using the neutral red test, MTT assay and LDH release. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1999, 19, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Le Maux, S.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J. Emulsion-based delivery systems for tributyrin, a potential colon cancer preventative agent. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9243–9249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Violante, G.; Zerrouk, N.; Richard, I.; Provot, G.; Chaumeil, J.C.; Arnaud, P. Evaluation of the cytotoxicity effect of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) on Caco2/TC7 colon tumor cell cultures. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 1600–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, R.F.; Wei, Y.J.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B.H. Inhibition of colon cancer cell growth by nanoemulsion carrying gold nanoparticles and lycopene. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 2823–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.-H.; Zhang, L.-J.; Sun, J.-J.; Yan, Y.-J.; Zhang, L.-X.; Chen, N.; Chen, Z.-L. Photodynamic efficiency of a chlorophyll-a derivative in vitro and in vivo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 81, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, M.; Ferruzzi, M.G. Update on the bioavailability and chemopreventative mechanisms of dietary chlorophyll derivatives. Nutr. Res. 2020, 81, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albino, A.P.; Juan, G.; Traganos, F.; Reinhart, L.; Connolly, J.; Rose, D.P.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of melanoma cells by docosahexaenoic acid: Association with decreased pRb phosphorylation. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 4139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, R.A.; Jenski, L.J.; Harvey, K.A.; Wiesehan, J.D.; Stillwell, W.; Zaloga, G.P. Cell-cycle arrest in Jurkat leukaemic cells: A possible role for docosahexaenoic acid. Biochem. J. 2003, 371, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merendino, N.; Loppi, B.; D’Aquino, M.; Molinari, R.; Pessina, G.; Romano, C.; Velotti, F. Docosahexaenoic acid induces apoptosis in the human PaCa-44 pancreatic cancer cell line by active reduced glutathione extrusion and lipid peroxidation. Nutr. Cancer 2005, 52, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughees, M.; Wajid, S. Herbal based polymeric nanoparticles as a therapeutic remedy for breast cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Yang, L.; Li, D.; Yang, L.; Su, Y.; Su, X. Cell cycle regulation by berberine in human melanoma A375 cells. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 169, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, A.; Zhang, R. Diosmetin inhibits cell proliferation, induces cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in liver cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 3537–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Duan, X. Cardamonin as a potential treatment for melanoma induces human melanoma cell apoptosis. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Fu, Q.R.; Huang, Z.J.; Lin, J.Y.; Chen, Q.X.; Wang, Q.; Shen, D.Y. Apoptosis induced by ursodeoxycholic acid in human melanoma cells through the mitochondrial pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Do, B.H.; Nguyen, T.P.T.; Ho, N.Q.C.; Le, T.L.; Hoang, N.S.; Doan, C.C. Mitochondria-mediated caspase-dependent and caspase-independent apoptosis induced by aqueous extract from Moringa oleifera leaves in human melanoma cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 3675–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbaraj, B.S.; Lu, H.; Hung, C.F.; Wu, W.B.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, B.H. Determination of carotenoids and their esters in fruits of Lycium barbarum Linnaeus by HPLC-DAD-APCI-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, C.H.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Liu, M.H.; Chen, B.H. Determination of chlorophylls in Taraxacum formosanum by high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection-mass spectrometry and preparation by column chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6108–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SAS. SAS Procedures and SAS/Graph User’s Guide; Version 6; SAS Institute Inc.: Gary, NC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
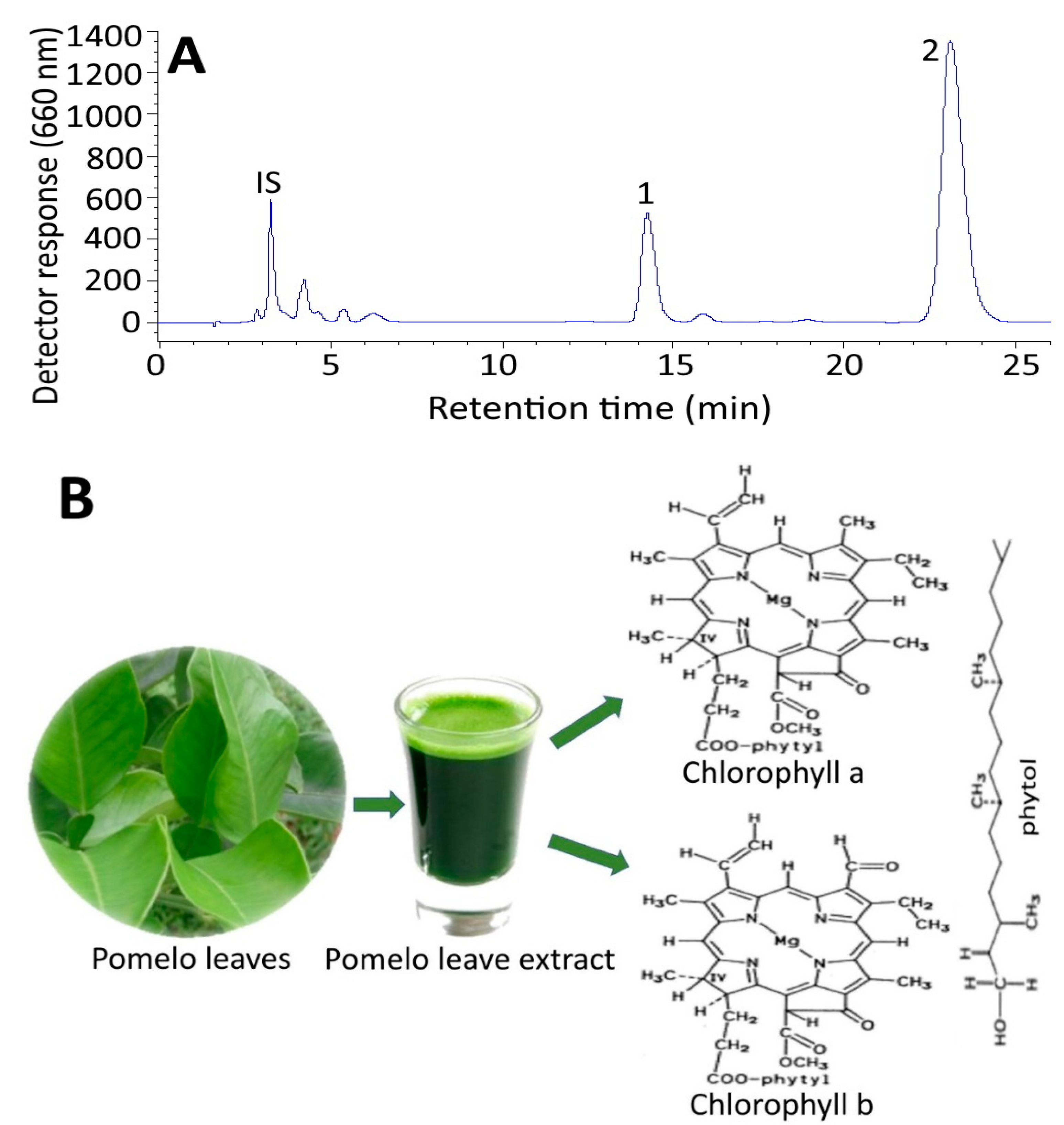




| Peak No | Compound | tR (min) | Retention Factor (k) a | Content (µg/g) b | m/z Found | m/z Reported | λmax (On-Line) | λmax (Reported) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chlorophyll b | 13.92 | 3.35 | 785.8 | 907.4 [M + H] 630.4 [M + H−278] | 907.4 [M + H] 629.4 [M + H−278] c | 464, 600, 648 | 464, 599, 648 c |
| 2 | Chlorophyll a | 22.54 | 6.04 | 2278.3 | 894.6 [M + H] | 893.6 [M + H] c | 430, 618, 664 | 431, 617, 663 c |
| Average Particle Size a | PDI a | Zeta Potential a | pH a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 13.2 ± 0.10 A | 0.15 ± 0.01 A | −64.4 ± 1.10 A | 4.85 ± 0.08 A |
| 7 | 13.5 ± 0.15 A | 0.183 ± 0.01 AB | −66.1 ± 0.82 B | 4.80 ± 0.13 AB |
| 14 | 14.6 ± 0.38 B | 0.193 ± 0.01 AB | −66.2 ± 1.36 B | 4.77 ± 0.14 AB |
| 21 | 15.0 ± 0.40 B | 0.21 ± 0.01 BC | −66.1 ± 0.75 B | 4.75 ± 0.11 AB |
| 28 | 15.7 ± 0.44 CD | 0.235 ± 0.04 BC | −67.3 ± 0.21 BC | 4.58 ± 0.17 BC |
| 35 | 15.7 ± 0.44 CD | 0.268 ± 0.03 BC | −68.6 ± 0.26 C | 4.52 ± 0.35 BC |
| 42 | 16.0 ± 0.93 CDE | 0.278 ± 0.04 BC | −70.4 ± 0.61 D | 4.50 ± 0.34 CD |
| 60 | 16.4 ± 0.26 DE | 0.289 ± 0.04 BC | −73.3 ± 1.20 D | 4.44 ± 0.12 CD |
| 90 | 16.6 ± 0.46 E | 0.295 ± 0.07 C | −75.1 ± 0.51 D | 4.40 ± 0.07 D |
| Temp. (°C) | Particle Size (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heating Time | Heating Time | |||||||||
| 0 h | 0.5 h | 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | 0 h | 0.5 h | 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | |
| 40 | 13.2 | 13.5 | 15.5 | 16.5 | 16.4 | −64.6 | −75.4 | −73.3 | −72.9 | −67.5 |
| 60 | 13.2 | 13.8 | 13.7 | 12.6 | 12.4 | −64.6 | −64.4 | −68.1 | −64.1 | −61.8 |
| 80 | 13.2 | 14.6 | 13.7 | 13.4 | 13.2 | −64.6 | −34.4 | −33.3 | −32.0 | −28.6 |
| 100 | 13.2 | 14.3 | 14.2 | 13.7 | 12.6 | −64.6 | −44.6 | −37.4 | −35.5 | −25.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.-H.; Li, Y.-F.; Chen, B.-H. Preparation of Chlorophyll Nanoemulsion from Pomelo Leaves and Its Inhibition Effect on Melanoma Cells A375. Plants 2021, 10, 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081664
Liu M-H, Li Y-F, Chen B-H. Preparation of Chlorophyll Nanoemulsion from Pomelo Leaves and Its Inhibition Effect on Melanoma Cells A375. Plants. 2021; 10(8):1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081664
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Man-Hai, Yi-Fen Li, and Bing-Huei Chen. 2021. "Preparation of Chlorophyll Nanoemulsion from Pomelo Leaves and Its Inhibition Effect on Melanoma Cells A375" Plants 10, no. 8: 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081664
APA StyleLiu, M.-H., Li, Y.-F., & Chen, B.-H. (2021). Preparation of Chlorophyll Nanoemulsion from Pomelo Leaves and Its Inhibition Effect on Melanoma Cells A375. Plants, 10(8), 1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081664







