Crataegus oxyacantha Extract as a Biostimulant to Enhance Tolerance to Salinity in Tomato Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effects of Crataegus oxyacantha Extract on Physiological Parameters of Tomato Plants under Salt Stress
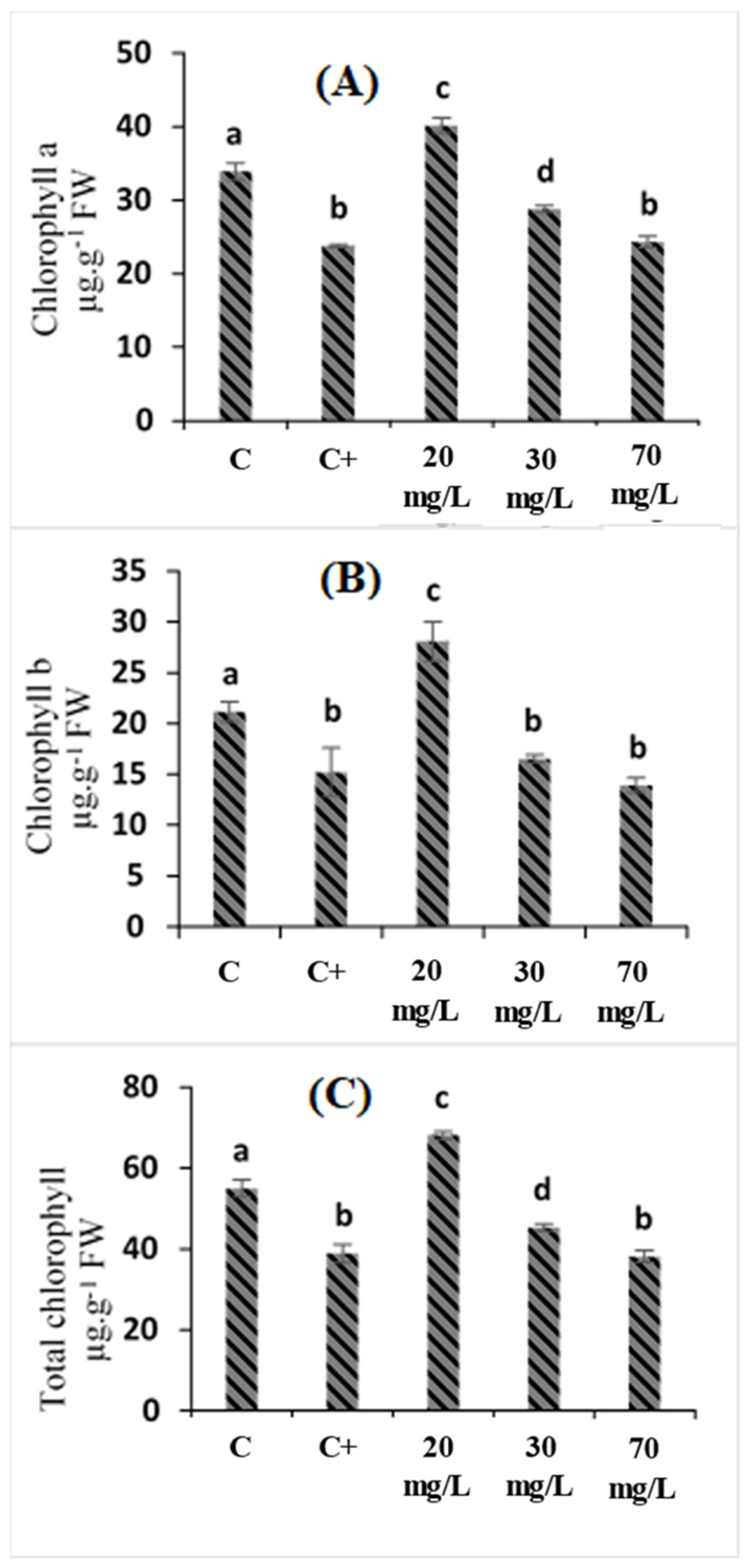
2.2. Effects of Cataegus oxyacantha Extract on Photosynthetic Pigment (Chlorophyll a, Chlorophyll b, and Total Chlorophyll) Enzymes in Tomato Seedlings under Salt Stress
2.3. Effects of C. oxyacantha Extract on Malondialdehyde (MDA), Soluble Sugar, and Amino Acid Content in Tomato Seedlings under Salt Stress
2.4. Effects of C. oxyacantha Extract on Antioxidant Enzymes in Tomato Plants under Salt Stress
3. Material and Methods
3.1. C. oxyacantha Collection and Preparation of Extracts
3.2. Plant Material and Bioassays for Tomato Growth and Treatments
- Plants only treated with water (control);
- Plants treated with 75 mM of NaCl;
- Plants treated with 75 mM of NaCl + 20 mg/L COE (irrigation);
- Plants treated with 75 mM of NaCl + 30 mg/L COE (irrigation);
- Plants treated with 75 mM of NaCl + 70 mg/L COE (irrigation).
3.3. Determination of Chlorophyll Content
3.4. Determination of MDA Content
3.5. Determination of Soluble Sugar and Amino Acid Content
3.6. Enzyme Extraction and Assays
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gull, A.; Lone, A.A.; Wani, N.U.I. Biotic and Abiotic Stresses in Plants; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahbaz, M.; Ashraf, M. Improving Salinity Tolerance in Cereals. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2013, 32, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, M.D.; Yadav, R.K.; Narjary, B.; Yadav, G.; Jat, H.S.; Sheoran, P.; Meena, M.K.; Antil, R.S.; Meena, B.L.; Singh, H.V.; et al. Municipal Solid Waste (MSW): Strategies to Improve Salt Affected Soil Sustainability: A Review. Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.; Roychoudhury, A. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Response of Antioxidants as ROS-Scavengers during Environmental Stress in Plants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mushtaq, Z.; Faizan, S.; Gulzar, B. Salt Stress, Its Impacts on Plants and the Strategies Plants Are Employing against It: A Review. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Rome, I. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Duke University: Durham, NC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Iovieno, P.; Punzo, P.; Guida, G.; Mistretta, C.; Van Oosten, M.J.; Nurcato, R.; Bostan, H.; Colantuono, C.; Costa, A.; Bagnaresi, P.; et al. Transcriptomic Changes Drive Physiological Responses to Progressive Drought Stress and Rehydration in Tomato. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patanè, C.; Scordia, D.; Testa, G.; Cosentino, S.L. Physiological Screening for Drought Tolerance in Mediterranean Long-Storage Tomato. Plant Sci. 2016, 249, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colla, G.; Nardi, S.; Cardarelli, M.; Ertani, A.; Lucini, L.; Canaguier, R.; Rouphael, Y. Protein Hydrolysates as Biostimulants in Horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Jardin, P. Plant Biostimulants: Definition, Concept, Main Categories and Regulation. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Q.; Zuo, Z.; Harrison, F.; Chow, M.S.S. Hawthorn. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 42, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Habtemariam, S.; Ahmed, T.; Sureda, A.; Daglia, M.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Nabavi, S.M. Polyphenolic Composition of Crataegus Monogyna Jacq.: From Chemistry to Medical Applications. Nutrients 2015, 7, 7708–7728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, F.; Perrone, A.; Yousefi, S.; Papini, A.; Castiglione, S.; Guarino, F.; Cicatelli, A.; Aelaei, M.; Arad, N.; Gholami, M.; et al. Botanical, Phytochemical, Anti-Microbial and Pharmaceutical Characteristics of Hawthorn (Crataegus monogyna Jacq.), Rosaceae. Molecules 2021, 26, 7266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.; Fahim, M. Chapter 22—Physiological Modification of Plants through Small RNA. In Plant Small RNA; Guleria, P., Kumar, V., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 493–519. ISBN 978-0-12-817112-7. [Google Scholar]
- Alzahib, R.H.; Migdadi, H.M.; Al Ghamdi, A.A.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Al-Selwey, W.A. Assessment of Morpho-Physiological, Biochemical and Antioxidant Responses of Tomato Landraces to Salinity Stress. Plants 2021, 10, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarini, C.; Antognoni, F.; Biondi, S.; Fraternale, A.; Verardo, G.; Gorassini, A.; Scoccianti, V. Polyphenol-Enriched Spelt Husk Extracts Improve Growth and Stress-Related Biochemical Parameters under Moderate Salt Stress in Maize Plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. PPB 2019, 141, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozfidan-Konakci, C.; Yildiztugay, E.; Kucukoduk, M. Upregulation of Antioxidant Enzymes by Exogenous Gallic Acid Contributes to the Amelioration in Oryza Sativa Roots Exposed to Salt and Osmotic Stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 1487–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Mrid, R.; Benmrid, B.; Hafsa, J.; Boukcim, H.; Sobeh, M.; Yasri, A. Secondary metabolites as biostimulant and bioprotectant agents: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Latef, A.; Mostofa, M.; Rahman, M.; Abdel-Farid, I.; Tran, L.-S. Extracts from Yeast and Carrot Roots Enhance Maize Performance under Seawater-Induced Salt Stress by Altering Physio-Biochemical Characteristics of Stressed Plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 38, 966–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzouk, S.; Dobrev, P.; Djazouli, Z.-E.; Motyka, V. Positive Impact of Vermicompost Leachate on Salt Stress Resistance in Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum L.) at the Seedling Stage: A Phytohormonal Approach. Plant Soil 2020, 446, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.-B.; Cai, W.-J.; Wang, J.-W.; Hong, G.-J.; Tao, X.-Y.; Wang, L.-J.; Huang, Y.-P.; Chen, X.-Y. Silencing a Cotton Bollworm P450 Monooxygenase Gene by Plant-Mediated RNAi Impairs Larval Tolerance of Gossypol. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkarnaini, Z.M.; Sakimin, S.Z.; Mohamed, M.T.M.; Jaafar, H.Z.E. Relationship between Chlorophyll Content and Soil Plant Analytical Development Values in Two Cultivars of Fig (Ficus carica L.) as Brassinolide Effect at an Open Field. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 250, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacha, H.; Tekaya, M.; Drine, S.; Guasmi, F.; Touil, L.; Enneb, H.; Triki, T.; Cheour, F.; Ferchichi, A. Impact of Salt Stress on Morpho-Physiological and Biochemical Parameters of Solanum Lycopersicum Cv. Microtom Leaves. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 108, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latique, S.; Ben Mrid, R.; Kabach, I.; Kchikich, A.; Sammama, H.; Yasri, A.; Nhiri, M.; El Kaoua, M.; Douira, A.; Selmaoui, K. Foliar Application of Ulva Rigida Water Extracts Improves Salinity Tolerance in Wheat (Triticum durum L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri, R.; Hatami, A.; Oloumi, H.; Naghizadeh, M.; Nasibi, F.; Tahmasebi, Z. Foliar Application of Melatonin Induces Tolerance to Drought Stress in Moldavian Balm Plants (Dracocephalum moldavica) through Regulating the Antioxidant System. Folia Hortic. 2018, 30, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mokhtari, N.; Rahimmalek, M.; Talebi, M.; Khorrami, M. Assessment of Genetic Diversity among and within Carthamus Species Using Sequence-Related Amplified Polymorphism (SRAP) Markers. Plant Syst. Evol. 2013, 299, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Liu, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Hailin, F. Non-Destructive Determination of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Distribution in Oilseed Rape Leaves by Laboratory Scale NIR Hyperspectral Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ren, S.; Tang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Chen, C.; Li, W. Supplementation of American Ginseng Berry Extract Mitigated Cisplatin-Evoked Nephrotoxicity by Suppressing ROS-Mediated Activation of MAPK and NF-ΚB Signaling Pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 110, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawaz, A.; Amjad, M.; Jahangir, M.M.; Khan, S.M.; Cui, H.; Hu, J. Induction of Salt Tolerance in Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) Seeds through Sand Priming. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2012, 6, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar]
- Manai, J.; Kalai, T.; Gouia, H.; Corpas, F.J. Exogenous Nitric Oxide (NO) Ameliorates Salinity-Induced Oxidative Stress in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) Plants. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2014, 14, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, S.M.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Parvin, K.; Fujita, M. Pretreatment of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Seedlings with 2,4-D Improves Tolerance to Salinity-Induced Oxidative Stress and Methylglyoxal Toxicity by Modulating Ion Homeostasis, Antioxidant Defenses, and Glyoxalase Systems. Plant Physiol. Biochem. PPB 2020, 152, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Al Hassan, M.; Naranjo, M.A.; Agrawal, V.; Boscaiu, M.; Vicente, O. Effects of Salinity and Drought on Growth, Ionic Relations, Compatible Solutes and Activation of Antioxidant Systems in Oleander (Nerium oleander L.). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Giraldo, J.P.; Shabala, S. It Is Not All about Sodium: Revealing Tissue Specificity and Signalling Roles of Potassium in Plant Responses to Salt Stress. Plant Soil 2018, 431, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, A.; Xu, Y.; AL-Bukhaiti, W.Q.; Abed, S.M.; Ali, A.H.; Ramadhan, A.H.; Xia, W. Influence of Enzymatic Hydrolysis Conditions on the Degree of Hydrolysis and Functional Properties of Protein Hydrolysate Obtained from Chinese Sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) by Using Papain Enzyme. Process Biochem. 2018, 67, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.; Prado, C.; Podazza, G.; Interdonato, R.; González, J.A.; Hilal, M.; Prado, F.E. Soluble Sugars—Metabolism, Sensing and Abiotic Stress. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murshed, R.; Lopez-Lauri, F.; Sallanon, H. Effect of Salt Stress on Tomato Fruit Antioxidant Systems Depends on Fruit Development Stage. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2014, 20, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alscher, R.G.; Erturk, N.; Heath, L.S. Role of Superoxide Dismutases (SODs) in Controlling Oxidative Stress in Plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Khan, W.U.; Ali Shah, A.; Yasin, N.A.; Naz, S.; Ali, A.; Tahir, A.; Iram Batool, A. Synergistic Effects of Nitric Oxide and Silicon on Promoting Plant Growth, Oxidative Stress Tolerance and Reduction of Arsenic Uptake in Brassica Juncea. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Omari, R.; Ben Mrid, R.; Chibi, F.; Nhiri, M. Involvement of Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase and Antioxydants Enzymes in Nitrogen Nutrition Tolerance in Sorghum Bicolor Plants. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 63, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noctor, G.; Gomez, L.; Vanacker, H.; Foyer, C.H. Interactions between Biosynthesis, Compartmentation and Transport in the Control of Glutathione Homeostasis and Signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 1283–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.-M.; Nie, Y.-X.; Zhang, J.; Yin, J.-S.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.-J.; Bai, J.-G. Ferulic Acid Pretreatment Enhances Dehydration-Stress Tolerance of Cucumber Seedlings. Biol. Plant. 2013, 57, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Hu, R.; Zhang, J.; Guo, H.-B.; Cheng, H.; Li, L.; Borland, A.M.; Qin, H.; Chen, J.-G.; Muchero, W.; et al. Overexpression of an Agave Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase Improves Plant Growth and Stress Tolerance. Cells 2021, 10, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Asthir, B.; Bains, N.S. Modulation of Proline Metabolism under Drought and Salt Stress Conditions in Wheat Seedlings. IJBB 2018, 55, 114–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Mrid, R.; El Omari, R.; El Mourabit, N.; Bouargalne, Y.; Nhiri, M. Changes in the antioxidant and glyoxalase enzyme activities in leaves of two Moroccan sorghum ecotypes with differential tolerance to nitrogen stress. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2018, 12, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, C.P.; Arya, V.; Thakur, N. Ethnomedicinal and Phytopharmacological Potential of Crataegus Oxyacantha Linn—A Review. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2 (Suppl. S2), S1194–S1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, D.I. Copper enzymes in Isolated Chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta Vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1949, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yemm, E.W.; Willis, A.J. The Estimation of Carbohydrates in Plant Extracts by Anthrone. Biochem. J. 1954, 57, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.D.; Bridou, R.; Johs, A.; Parks, J.M.; Elias, D.A.; Hurt, R.A.; Brown, S.D.; Podar, M.; Wall, J.D. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of HgcA and HgcB Reveals Amino Acid Residues Important for Mercury Methylation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3205–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouchmaa, N.; Ben Mrid, R.; Boukharsa, Y.; Nhiri, M.; Ait Mouse, H.; Taoufik, J.; Ansar, M.; Zyad, A. Cytotoxicity of New Pyridazin-3(2H)-One Derivatives Orchestrating Oxidative Stress in Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (MDA-MB-468). Arch. Pharm. 2018, 351, e1800128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.V.; Paliyath, G.; Ormrod, D.P. Ultraviolet-B- and Ozone-Induced Biochemical Changes in Antioxidant Enzymes of Arabidopsis Thaliana. Plant Physiol. 1996, 110, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben Mrid, R.; Bouargalne, Y.; El Omari, R.; El Mourabit, N.; Nhiri, M. Activities of Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism Enzymes of Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) During Seed Development. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 21, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Control (Water) | Control + 75 mM NaCl | 20 mg/L + 75 mM NaCl | 30 mg/L + 75 mM NaCl | 70 mg/L + 75 mM NaCl | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant Fresh Weight (mg) | 882 ± 48 a | 547 ± 35 b | 1153 ± 210 a | 493 ± 55 b | 304 ± 27 b |
| Plant Height (cm) | 17.8 ± 1.4 a | 14.5 ± 1.9 b | 14.7 ± 1.7 bc | 14.7 ± 0.5 c | 17 ± 1.3 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naboulsi, I.; Ben Mrid, R.; Ennoury, A.; Zouaoui, Z.; Nhiri, M.; Ben Bakrim, W.; Yasri, A.; Aboulmouhajir, A. Crataegus oxyacantha Extract as a Biostimulant to Enhance Tolerance to Salinity in Tomato Plants. Plants 2022, 11, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11101283
Naboulsi I, Ben Mrid R, Ennoury A, Zouaoui Z, Nhiri M, Ben Bakrim W, Yasri A, Aboulmouhajir A. Crataegus oxyacantha Extract as a Biostimulant to Enhance Tolerance to Salinity in Tomato Plants. Plants. 2022; 11(10):1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11101283
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaboulsi, Imane, Reda Ben Mrid, Abdelhamid Ennoury, Zakia Zouaoui, Mohamed Nhiri, Widad Ben Bakrim, Abdelaziz Yasri, and Aziz Aboulmouhajir. 2022. "Crataegus oxyacantha Extract as a Biostimulant to Enhance Tolerance to Salinity in Tomato Plants" Plants 11, no. 10: 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11101283
APA StyleNaboulsi, I., Ben Mrid, R., Ennoury, A., Zouaoui, Z., Nhiri, M., Ben Bakrim, W., Yasri, A., & Aboulmouhajir, A. (2022). Crataegus oxyacantha Extract as a Biostimulant to Enhance Tolerance to Salinity in Tomato Plants. Plants, 11(10), 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11101283





