Distribution and Biodiversity of Seed-Borne Pathogenic and Toxigenic Fungi of Maize in Egypt and Their Correlations with Weather Variables
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
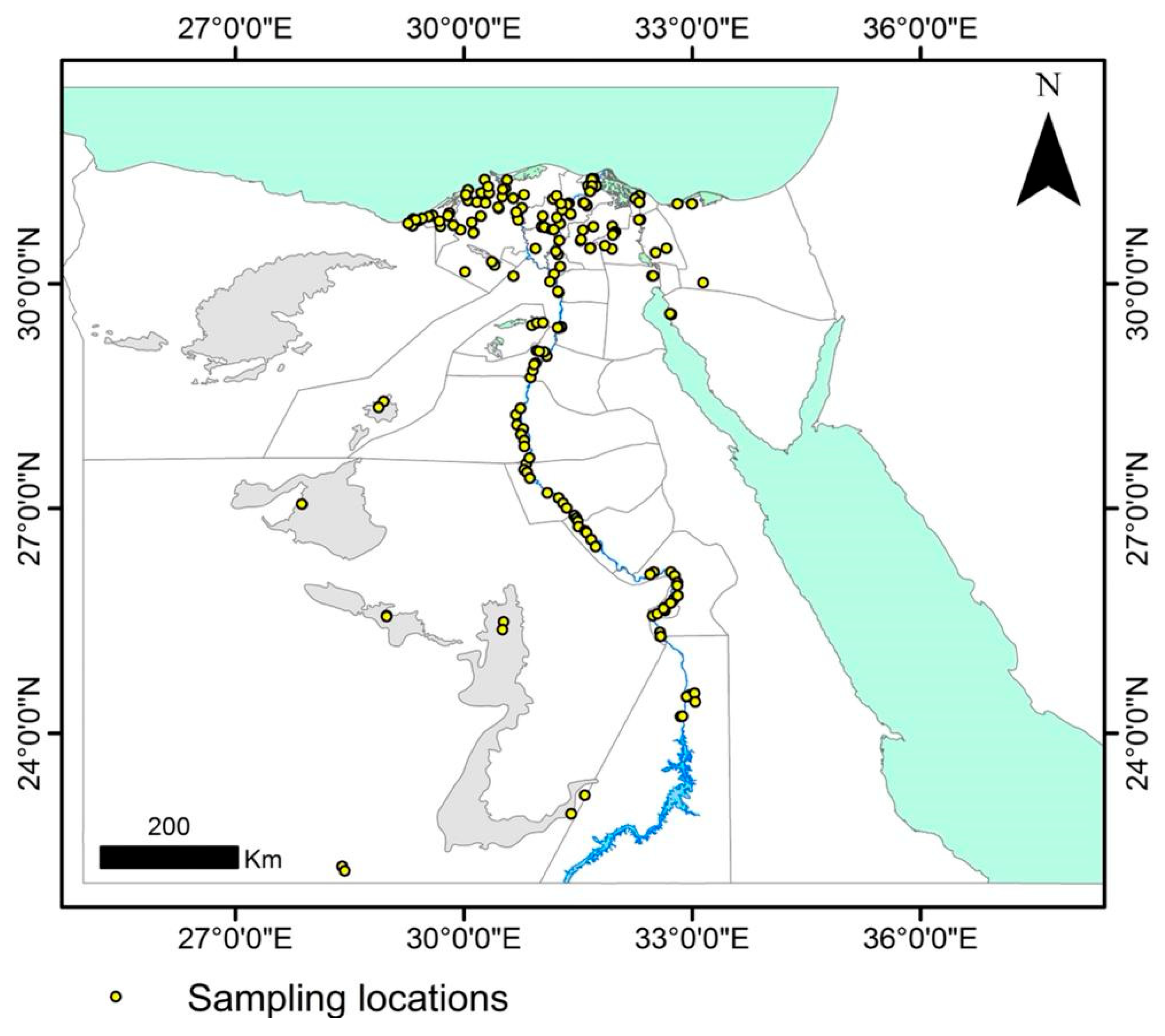
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Meteorological Conditions
2.3. Sampling Process
2.4. Seed Health Testing
2.4.1. Deep-Freezing Blotter (DFB) Technique
2.4.2. Washing Test
2.4.3. Identification of Seed-Borne Fungi
2.5. Biodiversity Metrics
2.6. Pathogenicity Test
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of Maize Seed-Borne Mycobiota
3.2. Biodiversity of Maize Seed-Borne Fungi
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.4. Pathogenicity Test
3.5. Correlations between the Occurrence of Maize Fungal Pathogens and Weather Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT © FAO. Statistics Division. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Arab Republic of Egypt, Ministry of Agriculture and Land Reclamation, Economic Affairs Sector. Bulletin of the Agricultural statistics, part 2, summer and Nile crops 2018/2019. Available online: https://moa.gov.eg/media/utblrjfm/2019 (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Pratap, P.; Kumar, J. Alien Gene Transfer in Crop Plants Vol. 2 Achievements and Impacts; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Krnjaja, V.; Stanojkovic, A.; Stankovic, S.; Lukic, M.; Bijelic, Z.; Mandic, V.; Micic, N. Fungal contamination of maize grain samples with a special focus on toxigenic genera. Biotehnol. U Stoc. 2017, 33, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Díaz, M.; Gil-Serna, J.; Vázquez, C.; Botia, M.N.; Patiño, B. A Comprehensive Study on the Occurrence of Mycotoxins and Their Producing Fungi during the Maize Production Cycle in Spain. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurney, A.L.; Grimanelli, D.; Kanampiu, F.; Hoisington, D.; Scholes, J.D.; Press, M.C. Novel sources of resistance to Striga hermonthica in Tripsacum dactyloides, a wild relative of maize. New Phytol. 2003, 160, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, J.F.; Summerell, B.A. The Fusarium Laboratory Manual; Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IA, USA, 2006; 388p. [Google Scholar]
- Gai, X.; Dong, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Gao, Z. Infection cycle of maize stalk rot and ear rot caused by Fusarium verticillioides. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.; Raizada, M. Fungal Pathogens of Maize Gaining Free Passage Along the Silk Road. Pathogens 2018, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degani, O. A Review: Late Wilt of Maize—The Pathogen, the Disease, Current Status, and Future Perspective. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degani, O.; Cernica, G. Diagnosis and Control of Harpophora maydis, the Cause of Late Wilt in Maize. Adv. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Aroca, T.; Doyle, V.; Singh, R.; Price, T.; Collins, K. First Report of Curvularia Leaf Spot of Corn, Caused by Curvularia lunata, in the United States. Plant Health Prog. 2018, 19, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-Y.; Liu, S.-S.; Shi, J.; Guo, N.; Zhang, H.-J.; Chen, J. A new Curvularia lunata variety discovered in Huanghuaihai Region in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Qi, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Wu, C.; Chang, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Gong, G. Etiology and Symptoms of Maize Leaf Spot Caused by Bipolaris spp. in Sichuan, China. Pathogens 2020, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.U.; Adnan, M.; Kalsoom, M.; Naz, N.; Husnain, M.G.; Ilahi, H.; Ilyas, M.A.; Yousaf, G.; Tahir, R.; Ahmad, U. Seed-Borne Fungal Diseases of Maize (Zea mays L.): A Review. Agrinula J. Agroteknologi Dan Perkeb. 2021, 4, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frąc, M.; Hannula, S.E.; Bełka, M.; Jędryczka, M. Fungal Biodiversity and Their Role in Soil Health. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Askar, A.A.; Ghoneem, K.M.; Rashad, Y.M.; Abdulkhair, W.M.; Hafez, E.; Shabana, Y.; Baka, Z.A. Occurrence and distribution of tomato seed-borne mycoflora in S audi A rabia and its correlation with the climatic variables. Microb. Biotechnol. 2014, 7, 556–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabana, Y.M.; Rashad, Y.M.; Ghoneem, K.M.; Arafat, N.S.; Aseel, D.G.; Qi, A.; Richard, B.; Fitt, B.D.L. Biodiversity of patho-genic and toxigenic seed-borne mycoflora of wheat in Egypt and their correlations with weather variables. Biology 2021, 10, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassman, N.A.; Leite, M.; Pan, Y.; De Hollander, M.; Van Veen, J.A.; Kuramae, E.E. Plant and soil fungal but not soil bacterial communities are linked in long-term fertilized grassland. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, B.D.; Nilsson, H.; Tedersoo, L.; Abarenkov, K.; Carlsen, T.; Kjøller, R.; Kõljalg, U.; Pennanen, T.; Rosendahl, S.; Stenlid, J.; et al. Fungal community analysis by high-throughput sequencing of amplified markers—A user’s guide. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AQUASTAT FAO’s Information System on Water and Agriculture, Climate Information Tool. Available online: http://www.fao.org/aquastat/en/ (accessed on 16 March 2017).
- ISTA. International rules for seed testing. Seed Sci. Technol. 1999, 27, 1–333. [Google Scholar]
- Raper, K.E.; Fennel, D.I. The Genus Aspergillus; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, C. Fusarium, Laboratory Guide to the Identification of the Major Species. Mycologia 1977, 69, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domsch, K.H.; Gams, W.; Anderson, T.H. Compendium of Soil Fungi; Lubrecht & Cramer Ltd.: Port Jervis, NY, USA, 1980; Volume 1, p. 1264. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Dudley, J.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) Software Version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J. 2020 Raster: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling, R Package Version 3.1–5; R Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pebesma, E.J.; Bivand, R.S. Classes and Methods for Spatial Data in R, R News 5: 1–5; R Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277. Available online: https://ggplot2.org (accessed on 3 November 2021).
- CoStat. CoHort Software, version 6.4; CoHort: Monterey, CA, USA, 2008. Available online: https://www.cohortsoftware.com/costat.html (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L. Vegan: Community Ecology Package (2020) R Package Version 2.5-7. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 3 November 2021).
- Rahm, M.A.; Gh, K.M.; Reha, N.A.E. Prevalence and Transmission of Seed-borne Fungi of Maize and Their Control by Phenolic Antioxidants. Plant Pathol. J. 2020, 19, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galletti, S.; Paris, R.; Cianchetta, S. Selected isolates of Trichoderma gamsii induce different pathways of systemic resistance in maize upon Fusarium verticillioides challenge. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 233, 126406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaige, A.R.; Todd, T.; Stack, J.P. Interspecific Competition for Colonization of Maize Plants Between Fusarium proliferatum and Fusarium verticillioides. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.M.; Ameye, M.; Landschoot, S.; Devlieghere, F.; De Saeger, S.; Eeckhout, M.; Audenaert, K. Molecular Insights into Defense Responses of Vietnamese Maize Varieties to Fusarium verticillioides Isolates. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frommer, D.; Veres, S.; Radócz, L. Susceptibility of stem infected sweet corn hybrids to common smut disease. Acta Agrar. Debr. 2018, 74, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansfield, M.A.; Jones, A.D.; Kuldau, G.A. Contamination of Fresh and Ensiled Maize by Multiple Penicillium Mycotoxins. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfordt, A.; Schiwek, S.; Rathgeb, A.; Rodemann, C.; Bollmann, N.; Buchholz, M.; Karlovsky, P.; Von Tiedemann, A. Occurrence, Pathogenicity, and Mycotoxin Production of Fusarium temperatum in Relation to Other Fusarium Species on Maize in Germany. Pathogens 2020, 9, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogórek, R.; Lejman, A.; Pusz, W.; Miłuch, A.; Miodyńska, P. Characteristics and taxonomy of Cladosporium fungi. Mikol. Lek. 2012, 19, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Gulbis, K.; Bankina, B.; Bimšteina, G.; Neusa-Luca, I.; Roga, A.; Fridmanis, D. Fungal Diversity of Maize (Zea mays L.) Grains. Rural Sustain. Res. 2016, 35, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Amatulli, M.T.; Fanelli, F.; Moretti, A.; Mule, G.; Logrieco, A.F. Alternaria species and mycotoxins associated to black point of cereals. JSM Mycotoxins 2013, 63, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, T.; Bhaskaran, R.; Karthikeyan, T.G.; Rajesh, M.; Senthilraja, G. Production of Cell Wall Degrading Enzymes and Toxins by Colletotrichum Capsici and Alternaria Alternata Causing Fruit ROT of Chillies. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2008, 48, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-R.; Shin, J.; Guevarra, R.B.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Seol, K.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.B.; Isaacson, R.E. Deciphering Diversity Indices for a Better Understanding of Microbial Communities. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 2089–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goko, M.L.; Murimwa, J.C.; Gasura, E.; Rugare, J.T.; Ngadze, E. Identification and Characterisation of Seed-Borne Fungal Pathogens Associated with Maize (Zea mays L.). Int. J. Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, P.M.; Cannon, P.F.; Minter, D.W.; Stalpers, J.A. Ainsworth & Bisby’s Dictionary of the Fungi, 10th ed.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2008; Available online: http://www.slideshare.net/fitolima/dictionary-of-fungi-kirk-et-al-2008-10a-edicao (accessed on 5 August 2019).
- Manamgoda, D.S.; Cai, L.; Bahkali, A.H.; Chukeatirote, E.; Hyde, K.D. Cochliobolus: An overview and current status of species. Fungal Divers. 2011, 51, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manamgoda, D.S.; Cai, L.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Crous, P.W.; Madrid, H.; Chukeatirote, E.; Shivas, R.G.; Tan, Y.P.; Hyde, K.D. A phylogenetic and taxonomic re-evaluation of the Bipolaris—Cochliobolus—Curvularia Complex. Fungal Divers. 2012, 56, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.J.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Lee, H.B. Phylogenetic Status of an Unrecorded Species of Curvularia, C. spicifera, Based on Current Classification System of Curvularia and Bipolaris Group Using Multi Loci. Mycobiology 2015, 43, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, N.; Sandoval-Denis, M.; Lombard, L.; Visagie, C.; Wingfield, B.; Crous, P. Redefining species limits in the Fusarium fujikuroi species complex. Pers.-Mol. Phylogeny Evol. Fungi 2021, 46, 129–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, M.; Saremi, H.; Javan-Nikkhah, M.; Somma, S.; Haidukowski, M.; Logrieco, A.F.; Moretti, A. Isolation, Molecular Identification and Mycotoxin Profile of Fusarium Species Isolated from Maize Kernels in Iran. Toxins 2019, 11, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, A.N. Taxonomy of Fusarium genus: A continuous fight between lumpers and splitters. Zb. Matic-Srp. Za Přír. Nauk. 2009, 117, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Yonezawa, T.; Lee, K.-I.; Kumagai, S.; Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Goto, K.; Hara-Kudo, Y. Molecular phylogeny of the higher and lower taxonomy of the Fusarium genus and differences in the evolutionary histories of multiple genes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, A.; Gené, J.; Sutton, D.; Madrid, H.; de Hoog, G.; Cano, J.; Decock, C.; Crous, P.; Guarro, J. Phylogeny of Sarocladium (Hypocreales). Pers.-Mol. Phylogeny Evol. Fungi 2015, 34, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerbell, R.C.; Gueidan, C.; Schroers, H.-J.; de Hoog, G.S.; Starink, M.; Rosete, Y.A.; Guarro, J.; Scott, J.A. Acremonium phylogenetic overview and revision of Gliomastix, Sarocladium, and Trichothecium. Stud. Mycol. 2011, 68, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, C.A.L.; Faria, C.B.; De Castro, F.F.; De Souza, S.R.; dos Santos, F.C.; Da Silva, C.N.; Tessmann, D.J.; Barbosa-Tessmann, I.P. Fungi Isolated from Maize (Zea mays L.) Grains and Production of Associated Enzyme Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 15328–15346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicklow, D.T.; Poling, S.M. Antimicrobial Activity of Pyrrocidines from Acremonium zeae Against Endophytes and Pathogens of Maize. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błaszczyk, L.; Waśkiewicz, A.; Gromadzka, K.; Mikołajczak, K.; Chełkowski, J. Sarocladium and Lecanicillium Associated with Maize Seeds and Their Potential to Form Selected Secondary Metabolites. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinn-Gofroń, A.; Bosiacka, B. Effects of meteorological factors on the composition of selected fungal spores in the air. Aerobiologia 2014, 31, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore-Landecker, E. Fundamentals of the Fungi, 3rd ed.; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1990; 561p. [Google Scholar]
- Noblin, X.; Yang, S.; Dumais, J. Surface tension propulsion of fungal spores. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 2835–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Félix, C.; Duarte, A.S.; Vitorino, R.; Guerreiro, A.C.L.; Domingues, P.; Correia, A.C.M.; Alves, A.; Esteves, A.C. Temperature Modulates the Secretome of the Phytopathogenic Fungus Lasiodiplodia theobromae. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-H.; Li, C.-S. Associations of Fungal Aerosols, Air Pollutants, and Meteorological Factors. Aerosol. Sci. Technol. 2000, 32, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hadi, A.; Schmidt-Heydt, M.; Parra, R.; Geisen, R.; Magan, N. A systems approach to model the relationship between aflatoxin gene cluster expression, environmental factors, growth and toxin production by Aspergillus flavus. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, A.; Schmidt-Heydt, M.; Cárdenas-Chávez, D.L.; Parra, R.; Geisen, R.; Magan, N. Integrating toxin gene expression, growth and fumonisin B1 and B2 production by a strain of Fusarium verticillioides under different environmental factors. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20130320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanubile, A.; Giorni, P.; Bertuzzi, T.; Marocco, A.; Battilani, P. Fusarium verticillioides and Aspergillus flavus Co-Occurrence Influences Plant and Fungal Transcriptional Profiles in Maize Kernels and In Vitro. Toxins 2021, 13, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Fungus | Code | Pre-Emergence Damping Off (%) | Post-Emergence Damping Off (%) | Survival (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alternaria alternata | EG1M1-1 | 6.8 l | 6.7 ij | 86.5 b |
| Bipolaris maydis | EG2M1-1 | 23.4 ef | 13.4 f | 63.2 hi |
| EG2M1-2 | 22.3 f–h | 17.3 e | 60.4 i–k | |
| EG2M1-3 | 20.0 hi | 21.7 cd | 58.3 jk | |
| Cephalosporium acremonium | EG11M1-1 | 13.6 k | 2.1 lm | 84.0 bc |
| Exerohilum rostratum | EG4M1-1 | 21.0 gh | 21.2 d | 57.8 jk |
| EG4M1-2 | 23.1 e–g | 25.2 b | 51.7 l | |
| Fusarium chlamydosporum | EG5M1-1 | 12.6 k | 5.0 jk | 82.4 c |
| Fusarium incarnatum | EG5M3-1 | 25.0 de | 30.0 a | 45.0 m |
| EG5M3-2 | 20.0 hi | 10.0 gh | 70.0 f | |
| EG5M3-3 | 25.0 de | 23.3 c | 51.7 l | |
| Fusarium nygami | EG5M6-1 | 20.0 hi | 22.9 cd | 57.1 k |
| Fusarium proliferatum | EG5M4-1 | 18.5 ij | 13.3 f | 68.2 fg |
| EG5M4-2 | 26.6 cd | 8.3 hi | 65.1 gh | |
| EG5M4-3 | 33.1 a | 6.4 j | 60.5 ij | |
| Fusarium verticillioides | EG5M5-1 | 29.8 b | 5.0 jk | 65.2 gh |
| EG5M5-2 | 25.9 d | 17.1 e | 57.0 k | |
| EG5M5-3 | 25.5 de | 3.7 kl | 70.8 ef | |
| Sarocladium zeae | EG6M2-1 | 16.2 j | 10.2 gh | 73.6 de |
| EG6M2-2 | 28.4 bc | 11.8 fg | 59.8 jk | |
| EG6M2-3 | 17.3 j | 8.3 hi | 74.4 d | |
| EG6M2-4 | 23.2 e–g | 10.0 gh | 66.8 g | |
| Control (without infection) | 4.0 mc | 0.7 m | 95.3 a | |
| Temperature | Relative Humidity | Precipitation | Wind Speed | Solar Radiation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 1 a | |||||||
| Relative Humidity | −0.91 | *** | 1 | |||||
| Precipitation | 0.10 | −0.22 | * | 1 | ||||
| Wind speed | 0.15 | * | −0.23 | * | −0.09 | 1 | ||
| Solar Radiation | 0.60 | *** | −0.70 | *** | −0.11 | 0.18 | * | 1 |
| Axis | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eigenvalue | 0.120 | 0.051 | 0.025 | 0.012 | 0.002 |
| Species-environment correlations | 0.575 | 0.496 | 0.399 | 0.311 | 0.155 |
| Cumulative percentage variance of species—weather relation | 57.1 | 81.1 | 93.0 | 98.9 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shabana, Y.M.; Ghoneem, K.M.; Rashad, Y.M.; Arafat, N.S.; Fitt, B.D.L.; Richard, B.; Qi, A. Distribution and Biodiversity of Seed-Borne Pathogenic and Toxigenic Fungi of Maize in Egypt and Their Correlations with Weather Variables. Plants 2022, 11, 2347. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11182347
Shabana YM, Ghoneem KM, Rashad YM, Arafat NS, Fitt BDL, Richard B, Qi A. Distribution and Biodiversity of Seed-Borne Pathogenic and Toxigenic Fungi of Maize in Egypt and Their Correlations with Weather Variables. Plants. 2022; 11(18):2347. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11182347
Chicago/Turabian StyleShabana, Yasser M., Khalid M. Ghoneem, Younes M. Rashad, Nehal S. Arafat, Bruce D. L. Fitt, Benjamin Richard, and Aiming Qi. 2022. "Distribution and Biodiversity of Seed-Borne Pathogenic and Toxigenic Fungi of Maize in Egypt and Their Correlations with Weather Variables" Plants 11, no. 18: 2347. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11182347
APA StyleShabana, Y. M., Ghoneem, K. M., Rashad, Y. M., Arafat, N. S., Fitt, B. D. L., Richard, B., & Qi, A. (2022). Distribution and Biodiversity of Seed-Borne Pathogenic and Toxigenic Fungi of Maize in Egypt and Their Correlations with Weather Variables. Plants, 11(18), 2347. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11182347







