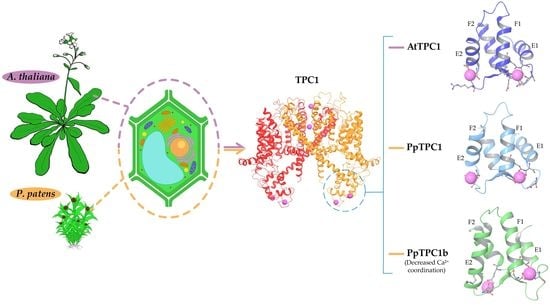
TPC1-Type Channels in Physcomitrium patens: Interaction between EF-Hands and Ca2+
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Nine TPC1-Like Channels in P. patens
2.2. Analysis of the Identity and Similarity of the EF-Hands of AtTPC1 and PpTPC1s
2.3. Electrostatic Surface of EF-Hands of TPC1- and TPC1b-Type Channels
2.4. Analysis of Molecular Dynamics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. TPC1 Sequences of Physcomitrium patens
4.2. EF-Hand Domain Identification and Clustering
4.3. Model Building
4.4. System Preparation
4.5. Molecular Simulation
4.6. Trajectory Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, F.H.; Catterall, W.A. The VGL-chanome: A protein superfamily specialized for electrical signaling and ionic homeostasis. Sci. STKE 2004, 2004, re15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedrich, R.; Marten, I. TPC1—SV Channels Gain Shape. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiter, E.; Maathuis, F.J.M.; Mills, L.N.; Knight, H.; Pelloux, J.; Hetherington, A.M.; Sanders, D. The vacuolar Ca2+-activated channel TPC1 regulates germination and stomatal movement. Nature 2005, 434, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrich, R.; Neher, E. Cytoplasmic calcium regulates voltage-dependent ion channels in plant vacuoles. Nature 1987, 329, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradogna, A.; Carpaneto, A. Electrophysiology and fluorescence to investigate cation channels and transporters in isolated plant vacuoles. Stress Biol. 2022, 2, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottosin, I.; Dobrovinskaya, O. Major vacuolar TPC1 channel in stress signaling: What matters, K+, Ca2+ conductance or an ion-flux independent mechanism? Stress Biol. 2022, 2, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintzer, A.F.; Stroud, R.M. Structure, inhibition and regulation of two-pore channel TPC1 from Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 2016, 531, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zeng, W.; Chen, Q.; Lee, C.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Cang, C.; Ren, D.; Jiang, Y. Structure of the voltage-gated two-pore channel TPC1 from Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 2016, 531, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaślan, D.; Mueller, T.D.; Becker, D.; Schultz, J.; Cuin, T.A.; Marten, I.; Dreyer, I.; Schönknecht, G.; Hedrich, R. Gating of the two-pore cation channel AtTPC1 in the plant vacuole is based on a single voltage-sensing domain. Plant Biol. 2016, 18, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaślan, D.; Dreyer, I.; Lu, J.; O’Malley, R.; Dindas, J.; Marten, I.; Hedrich, R. Voltage-dependent gating of SV channel TPC1 confers vacuole excitability. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Retamal, C.; Schott-Verdugo, S.; Gohlke, H.; Dreyer, I. Computational Analyses of the AtTPC1 (Arabidopsis Two-Pore Channel 1) Permeation Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.J.; Zhao, F.G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, K.; Kleist, T.J.; Lemaux, P.G.; Luan, S. A calcium signalling network activates vacuolar K+ remobilization to enable plant adaptation to low-K environments. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, C.; Sticht, H.; Meyerhoff, P.; Dietrich, P. Differential contribution of EF-hands to the Ca2+-dependent activation in the plant two-pore channel TPC1. Plant J. 2011, 68, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyota, M.; Spencer, D.; Sawai-Toyota, S.; Jiaqi, W.; Zhang, T.; Koo, A.J.; Howe, G.A.; Gilroy, S. Glutamate triggers long-distance, calcium-based plant defense signaling. Science 2018, 361, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.-G.; Toyota, M.; Kim, S.-H.; Hilleary, R.; Gilroy, S. Salt stress-induced Ca2+ waves are associated with rapid, long-distance root-to-shoot signaling in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6497–6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Cai, X.; Brailoiu, G.C.; Abood, M.E.; Brailoiu, E.; Patel, S. Two-pore channels provide insight into the evolution of voltage-gated Ca2+ and Na+ channels. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, ra109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, I.; Sussmilch, F.C.; Fukushima, K.; Riadi, G.; Becker, D.; Schultz, J.; Hedrich, R. How to Grow a Tree: Plant Voltage-Dependent Cation Channels in the Spotlight of Evolution. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Dong, X.P.; Samie, M.; Li, X.; Cheng, X.; Goschka, A.; Shen, D.; Zhou, Y.; Harlow, J.; et al. TPC Proteins Are Phosphoinositide- Activated Sodium-Selective Ion Channels in Endosomes and Lysosomes. Cell 2012, 151, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Navarro, B.; Seo, Y.J.; Aranda, K.; Shi, L.; Battaglia-Hsu, S.; Nissim, I.; Clapham, D.E.; Ren, D. mTOR Regulates Lysosomal ATP-Sensitive Two-Pore Na+ Channels to Adapt to Metabolic State. Cell 2013, 152, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Ward, J.; Schroeder, J. Magnesium Sensitizes Slow Vacuolar Channels to Physiological Cytosolic Calcium and Inhibits Fast Vacuolar Channels in Fava Bean Guard Cell Vacuoles. Plant Physiol. 1999, 121, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, V.; Wherrett, T.; Shabala, S.; Muñiz, J.; Dobrovinskaya, O.; Pottosin, I. Homeostatic control of slow vacuolar channels by luminal cations and evaluation of the channel-mediated tonoplast Ca2+ fluxes in situ. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 3845–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottosin, I.I.; Martínez-Estévez, M.; Dobrovinskaya, O.R.; Muñiz, J.; Schönknecht, G. Mechanism of luminal Ca2+ and Mg2+ action on the vacuolar slowly activating channels. Planta 2004, 219, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagné, S.M.; Li, M.X.; Sykes, B.D. Mechanism of Direct Coupling between Binding and Induced Structural Change in Regulatory Calcium Binding Proteins. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 4386–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biekofsky, R.R.; Martin, S.R.; Browne, J.P.; Bayley, P.M.; Feeney, J. Ca2+ coordination to backbone carbonyl oxygen atoms in calmodulin and other EF-hand proteins: 15N chemical shifts as probes for monitoring individual-site Ca2+ coordination. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 7617–7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Koselski, M.; Tsuboyama, S.; Dziubinska, H.; Trȩbacz, K.; Kuchitsu, K. Functional Analyses of the Two Distinctive Types of Two-Pore Channels and the Slow Vacuolar Channel in Marchantia polymorpha. Plant Cell Physiol. 2022, 63, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, H.; Kretsinger, R.H. Structural and functional diversity of EF-hand proteins: Evolutionary perspectives. Protein Sci. 2017, 26, 1898–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, I.S.; Reddy, V.S.; Shad Ali, G.; Reddy, A. Analysis of EF-hand-containing proteins in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintzer, A.F.; Green, E.M.; Dominik, P.K.; Bridges, M.; Armache, J.P.; Deneka, D.; Kim, S.S.; Hubbell, W.; Kossiakoff, A.A.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Structural basis for activation of voltage sensor domains in an ion channel TPC1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E9095–E9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, H.; Kretsinger, R. Calcium-binding proteins. 1: EF-hands. Protein Profile 1994, 1, 343–517. [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki, H.; Kretsinger, R. Calcium-binding proteins 1: EF-hands. Protein Profile 1995, 2, 297–490. [Google Scholar]
- Grabarek, Z. Structure of a Trapped Intermediate of Calmodulin: Calcium Regulation of EF-hand Proteins from a New Perspective. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 346, 1351–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabarek, Z. Structural Basis for Diversity of the EF-hand Calcium-binding Proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 359, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.R.; Chazin, W.J. Structures of EF-hand Ca 2+-binding proteins: Diversity in the organization, packing and response to Ca 2+ Binding. Biometals 1998, 11, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.R.; Chazin, W.J. An interaction-based analysis of calcium-induced conformational changes in Ca2+ sensor proteins. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadacz-Narloch, B.; Beyhl, D.; Larisch, C.; López-Sanjurjo, E.J.; Reski, R.; Kuchitsu, K.; Müller, T.D.; Becker, D.; Schönknecht, G.; Hedrich, R. A novel calcium binding Site in the slow vacuolar cation channel TPC1 senses luminal calcium levels. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2696–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, F.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Zeng, W.; Gan, N.; Zhao, C.; Yang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, J. Voltage-gating and cytosolic Ca2+ activation mechanisms of arabidopsis two-pore channel AtTPC1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2113946118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kintzer, A.F.; Stroud, R.M. On the structure and mechanism of two-pore channels. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zeng, W.; Jiang, Y. Tuning the ion selectivity of two-pore channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koselski, M.; Trebacz, K.; Dziubinska, H. Cation-permeable vacuolar ion channels in the moss Physcomitrella patens: A patch-clamp study. Planta 2013, 238, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koselski, M.; Trebacz, K.; Dziubinska, H. Vacuolar ion channels in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha: Influence of ion channel inhibitors. Planta 2017, 245, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koselski, M.; Trebacz, K.; Dziubinska, H. The role of vacuolar ion channels in salt stress tolerance in the liverwort Conocephalum conicum. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koselski, M.; Pupkis, V.; Hashimoto, K.; Lapeikaite, I.; Hanaka, A.; Wasko, P.; Plukaite, E.; Kuchitsu, K.; Kisnieriene, V.; Trebacz, K. Impact of Mammalian Two-Pore Channel Inhibitors on Long-Distance Electrical Signals in the Characean Macroalga Nitellopsis obtusa and the Early Terrestrial Liverwort Marchantia polymorpha. Plants 2021, 10, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirdita, M.; Schütze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: Making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, V.; Biasini, M.; Barbato, A.; Schwede, T. lDDT: A local superposition-free score for comparing protein structures and models using distance difference tests. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2722–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; Hermans, J. Interaction Models for Water in Relation to Protein Hydration. In Intermolecular Forces. The Jerusalem Symposia on Quantum Chemistry and Biochemistry; Pullman, B., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1981; pp. 331–342. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mérida-Quesada, F.; Vergara-Valladares, F.; Rubio-Meléndez, M.E.; Hernández-Rojas, N.; González-González, A.; Michard, E.; Navarro-Retamal, C.; Dreyer, I. TPC1-Type Channels in Physcomitrium patens: Interaction between EF-Hands and Ca2+. Plants 2022, 11, 3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11243527
Mérida-Quesada F, Vergara-Valladares F, Rubio-Meléndez ME, Hernández-Rojas N, González-González A, Michard E, Navarro-Retamal C, Dreyer I. TPC1-Type Channels in Physcomitrium patens: Interaction between EF-Hands and Ca2+. Plants. 2022; 11(24):3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11243527
Chicago/Turabian StyleMérida-Quesada, Franko, Fernando Vergara-Valladares, María Eugenia Rubio-Meléndez, Naomí Hernández-Rojas, Angélica González-González, Erwan Michard, Carlos Navarro-Retamal, and Ingo Dreyer. 2022. "TPC1-Type Channels in Physcomitrium patens: Interaction between EF-Hands and Ca2+" Plants 11, no. 24: 3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11243527
APA StyleMérida-Quesada, F., Vergara-Valladares, F., Rubio-Meléndez, M. E., Hernández-Rojas, N., González-González, A., Michard, E., Navarro-Retamal, C., & Dreyer, I. (2022). TPC1-Type Channels in Physcomitrium patens: Interaction between EF-Hands and Ca2+. Plants, 11(24), 3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11243527