Genome-Wide Identification of the TIFY Gene Family in Brassiceae and Its Potential Association with Heavy Metal Stress in Rapeseed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
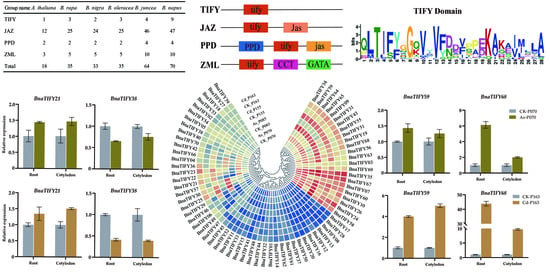
2.1. Identification of TIFY Family Genes in Brassiceae Species
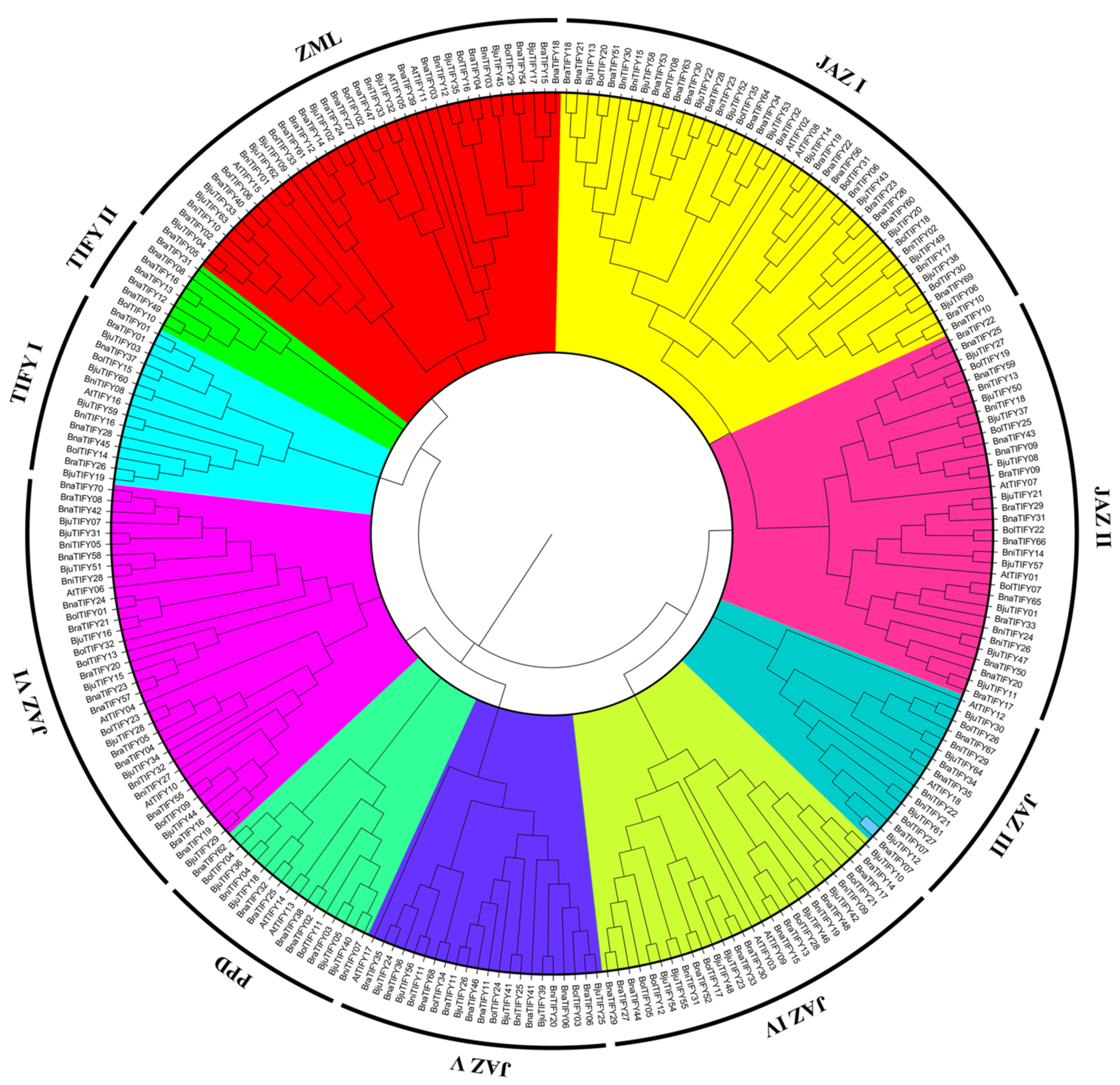
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of TIFY Genes in Brassiceae Species
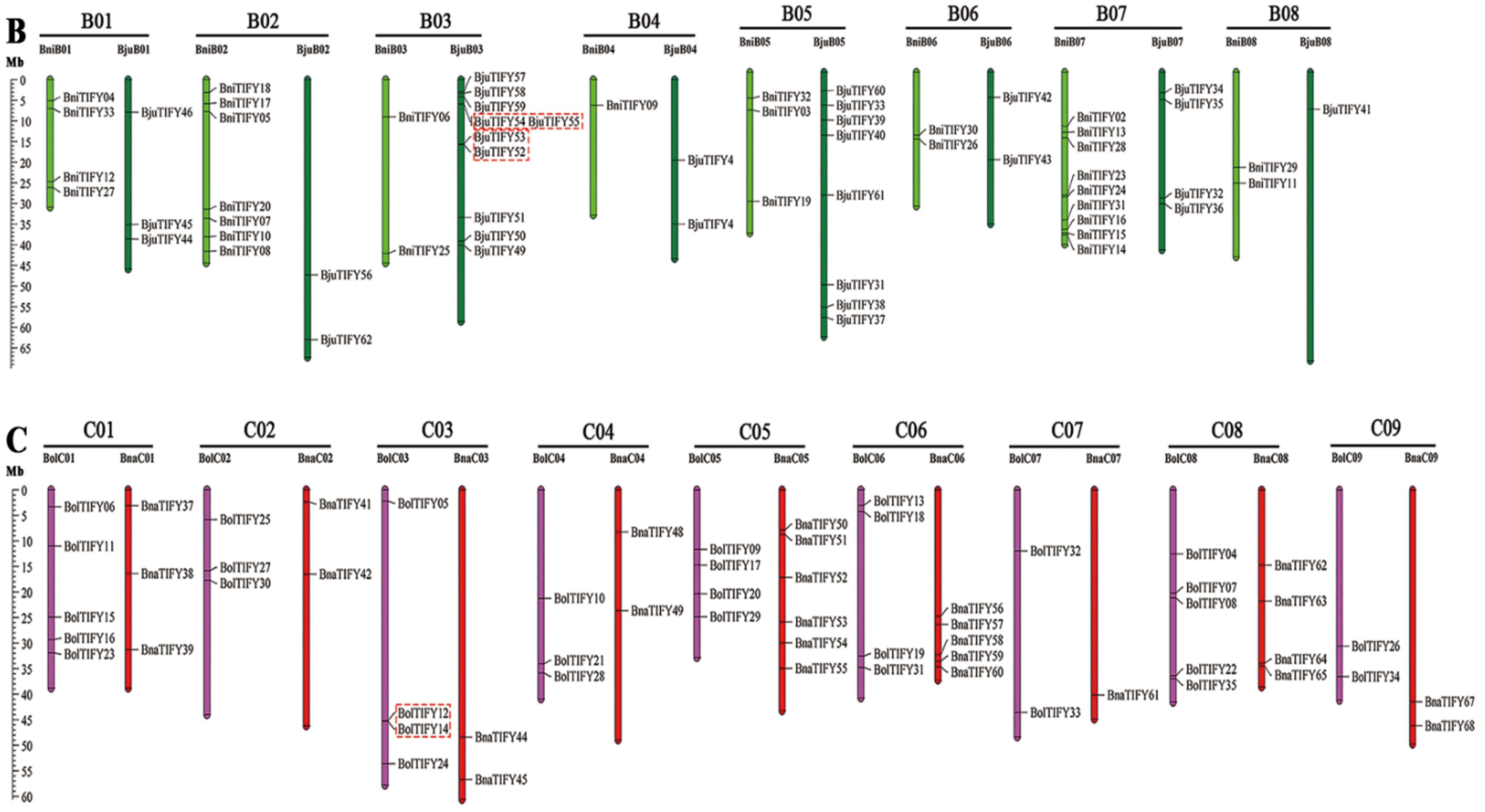
2.3. Chromosome Distributions of TIFY Family Genes in Brassiceae Species
2.4. Synteny and Duplicated Gene Analysis of TIFY Genes in Brassiceae Species
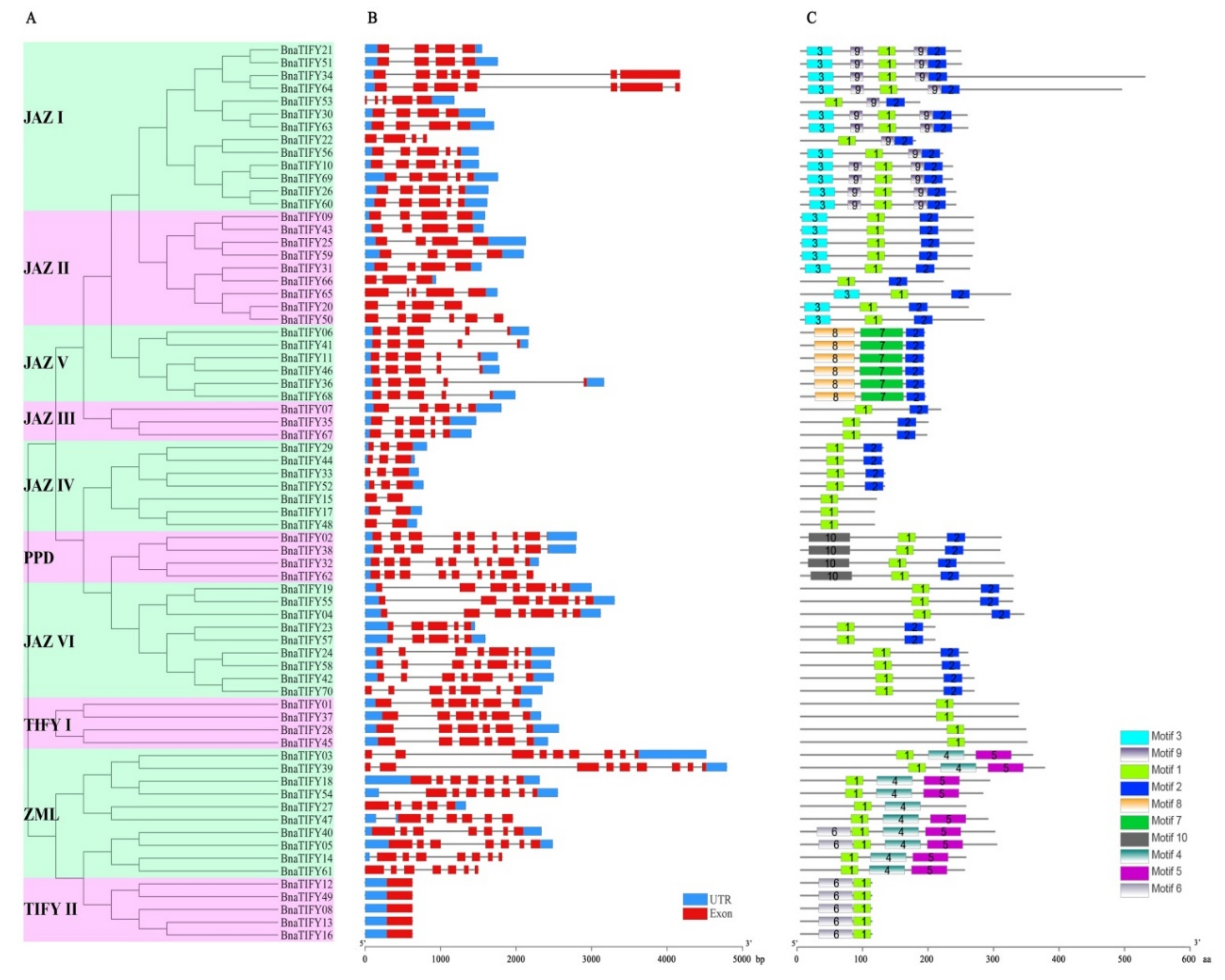
2.5. Gene Structural and Conserved Motif Analysis of TIFY Family Genes in B. napus
2.6. Expression Profiles of BnaTIFY Genes in B. napus
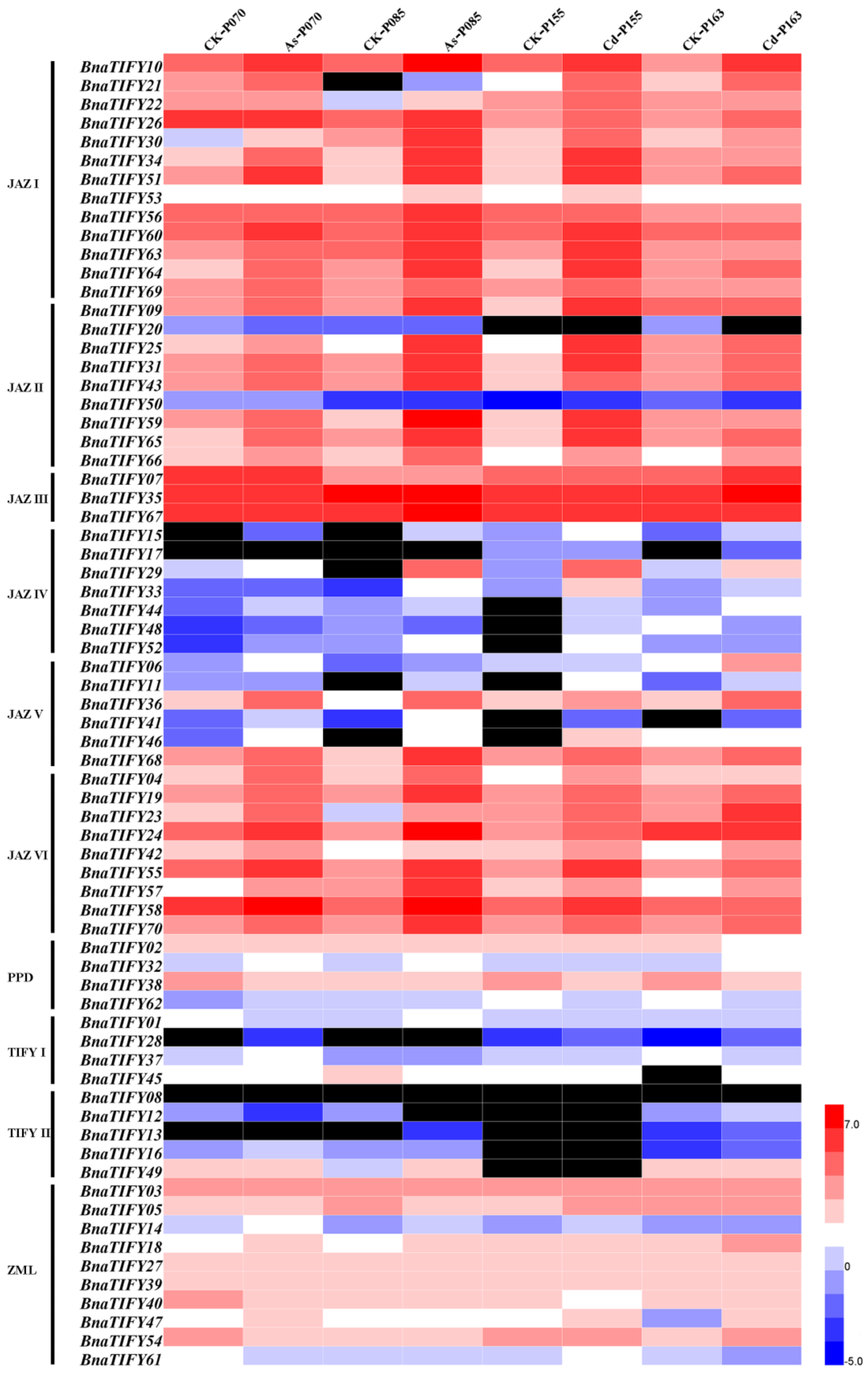
2.7. Expression Profiles of BnaTIFY Genes in Response to As3+ and Cd2+ Treatments
2.8. Cis-Element Analysis of BnTIFY Promotors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. TIFY Family Genes Identification and Annotation
4.2. Sequence Analysis of TIFY Gene Family
4.3. Conserved Motif Gene Structure Analysis of TIFY Gene Family
4.4. Chromosomal Locations, Tandem Duplication and Synteny of TIFY Gene Family
4.5. Expression Profiles Analysis of TIFY Gene Family
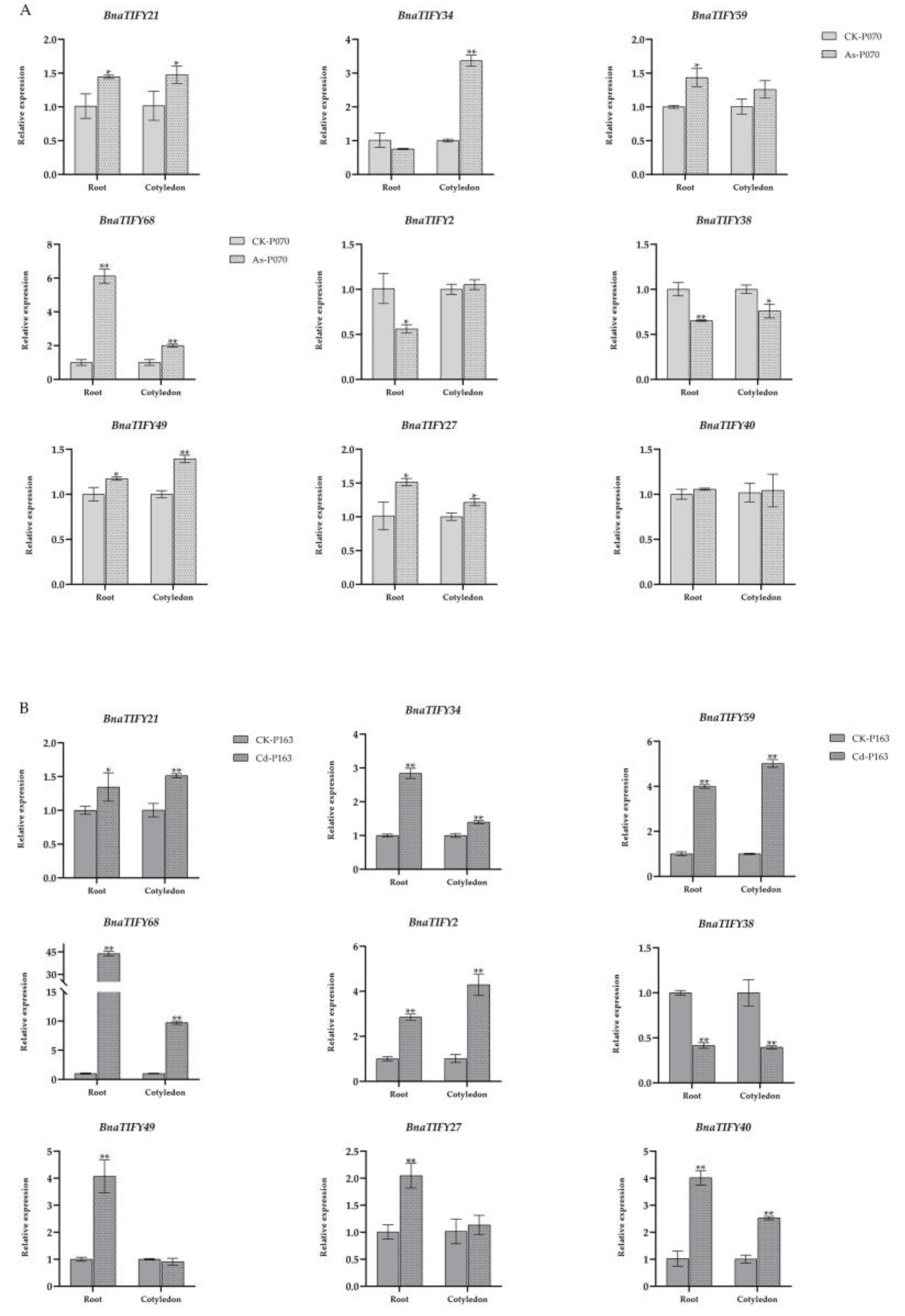
4.6. Quantitative qRT-PCR Validation Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishii, A.; Takemura, M.; Fujita, H.; Shikata, M.; Yokota, A.; Kohchi, T. Characterization of a novel gene encoding a putative single zinc-finger protein, ZIM, expressed during the reproductive phase in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vanholme, B.; Grunewald, W.; Bateman, A.; Kohchi, T.; Gheysen, G. The tify family previously known as ZIM. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Meng, Y.; Huang, D.; Qi, Y.; Chen, M. Origin and evolutionary analysis of the plant-specific TIFY transcription factor family. Genomics 2011, 98, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staswick, P. JAZing up jasmonate signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, A.; Boter, M.; Solano, R. Plant oxylipins: COI1/JAZs/MYC2 as the core jasmonic acid-signalling module. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 4682–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikata, M.; Matsuda, Y.; Ando, K.; Nishii, A.; Takemura, M.; Yokota, A.; Kohchi, T. Characterization of Arabidopsis ZIM, a member of a novel plant-specific GATA factor gene family. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Niu, Y.; Browse, J.; Howe, G. Top hits in contemporary JAZ: An update on jasmonate signaling. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorenzo, O.; Chico, J.; Sanchez-Serrano, J.; Solano, R. Jasmonate-insensitive1 encodes a MYC transcription factor essential to discriminate between different jasmonate-regulated defense responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1938–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsir, L.; Schilmiller, A.; Staswick, P.; He, S.; Howe, G. COI1 is a critical component of a receptor for jasmonate and the bacterial virulence factor coronatine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7100–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Jin, X.; Chen, Y.; Wei, M.; Liao, W.; Zhao, S.; Fu, C.; Yu, L. TcMYC2a, a basic helix loop helix transcription factor, transduces JA-signals and regulates taxol biosynthesis in Taxus chinensis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, A.; Fonseca, S.; Fernandez, G.; Adie, B.; Chico, J.; Lorenzo, O.; Garcia-Casado, G.; Lopez-Vidriero, I.; Lozano, F.; Ponce, M.; et al. The JAZ family of repressors is the missing link in jasmonate signalling. Nature 2007, 448, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oblessuc, P.; Obulareddy, N.; DeMott, L.; Matiolli, C.; Thompson, B.; Melotto, M. JAZ4 is involved in plant defense, growth, and development in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2020, 101, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lei, Y.; Lu, C.; Wang, L.; Wu, J. MYC2, MYC3, and MYC4 function additively in wounding-induced jasmonic acid biosynthesis and catabolism. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 1159–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Huang, H.; Song, S.; Xie, D. Regulation of jasmonate-mediated stamen development and seed production by a bHLH-MYB complex in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 1620–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, S.; Qi, T.; Huang, H.; Ren, Q.; Wu, D.; Chang, C.; Peng, W.; Liu, Y.; Peng, J.; Xie, D. The Jasmonate-ZIM domain proteins interact with the R2R3-MYB transcription factors MYB21 and MYB24 to Affect Jasmonate-regulated stamen development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1000–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, T.; Song, S.; Ren, Q.; Wu, D.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Fan, M.; Peng, W.; Ren, C.; Xie, D. The Jasmonate-ZIM-domain proteins interact with the WD-repeat/bHLH/MYB complexes to regulate Jasmonate-mediated anthocyanin accumulation and trichome initiation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1795–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, T.; Huang, H.; Wu, D.; Yan, J.; Qi, Y.; Song, S.; Xie, D. Arabidopsis DELLA and JAZ proteins bind the WD-repeat/bHLH/MYB complex to modulate gibberellin and Jasmonate signaling synergy. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, D.W. PEAPOD regulates lamina size and curvature in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13238–13243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, I.; Muthukumar, M.; Rajan, S. In-silico mining and characterisation of TIFY genes in mango. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 16, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.; Du, H.; Tang, N.; Li, X.; Xiong, L. Identification and expression profiling analysis of TIFY family genes involved in stress and phytohormone responses in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 71, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebel, C.; BenFeki, A.; Hanin, M.; Solano, R.; Chini, A. Characterization of wheat (Triticum aestivum) TIFY family and role of Triticum Durum TdTIFY11 a in salt stress tolerance. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0200566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Pandey, B.; Deveshwar, P.; Narnoliya, L.; Parida, S.; Giri, J. JAZ Repressors: Potential involvement in nutrients deficiency response in rice and chickpea. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peethambaran, P.; Glenz, R.; Honinger, S.; Islam, S.; Hummel, S.; Harter, K.; Kolukisaoglu, U.; Meynard, D.; Guiderdoni, E.; Nick, P.; et al. Salt-inducible expression of OsJAZ8 improves resilience against salt-stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Pan, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Kong, F.; Sun, X.; Wang, F. Overexpression of a TIFY family gene, GsJAZ2, exhibits enhanced tolerance to alkaline stress in soybean. Mol. Breed. 2020, 40, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Hu, F.; Dossa, K.; Wang, Z.; Ke, T. Genome-wide analysis of UDP-glycosyltransferase super family in Brassica rapa and Brassica oleracea reveals its evolutionary history and functional characterization. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mourato, M.; Moreira, I.; Leitao, I.; Pinto, F.; Sales, J.; Martins, L. Effect of Heavy Metals in Plants of the Genus Brassica. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 17975–17998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Wang, R.; Liang, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, J. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the EIN3/EIL gene family in allotetraploid Brassica napus reveal its potential advantages during polyploidization. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Z.; Ji, R.; Havlickova, L.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Lee, H.; Song, J.; Koh, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, M.; et al. Genome structural evolution in Brassica crops. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, F.; Trick, M.; Drou, N.; Lim, Y.; Park, J.; Kwon, S.; Kim, J.; Scott, R.; Pires, J.; Paterson, A.; et al. Comparative analysis between homoeologous genome segments of Brassica napus and its progenitor species reveals extensive sequence-level divergence. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1912–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hakata, M.; Muramatsu, M.; Nakamura, H.; Hara, N.; Kishimoto, M.; Iida-Okada, K.; Kajikawa, M.; Imai-Toki, N.; Toki, S.; Nagamura, Y.; et al. Overexpression of TIFY genes promotes plant growth in rice through jasmonate signaling. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, D.; Bai, X.; Luo, X.; Chen, Q.; Cai, H.; Ji, W.; Zhu, Y. Identification of wild soybean (Glycine soja) TIFY family genes and their expression profiling analysis under bicarbonate stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yin, X.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Guo, C.; Gao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Fan, C.; Wang, X. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.) TIFY gene family. Tree Genet. Genom. 2015, 11, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, F.; Chen, D.; Chu, W.; Liu, H.; Xiang, Y. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the Populus trichocarpa TIFY gene family. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shu, S.; Bai, S.; Tao, R.; Qian, M.; Teng, Y. Genome-wide survey and analysis of the TIFY gene family and its potential role in anthocyanin synthesis in Chinese sand pear (Pyrus pyrifolia). Tree Genet. Genom. 2018, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Yu, R.; Han, M.; Wu, Z. Isolation, structural analysis, and expression characteristics of the maize TIFY gene family. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2015, 290, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalhoub, B.; Denoeud, F.; Liu, S.; Parkin, I.; Tang, H.; Wang, X.; Chiquet, J.; Belcram, H.; Tong, C.; Samans, B.; et al. Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 2014, 345, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, F.; Sun, R.; Hou, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Liang, J.; Zhuang, M.; Liu, Y.; et al. Subgenome parallel selection is associated with morphotype diversification and convergent crop domestication in Brassica rapa and Brassica oleracea. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, T.; Beilstein, M.; Tang, M.; McKain, M.; Pires, J. Diversification times among Brassica (Brassicaceae) crops suggest hybrid formation after 20 million years of divergence. Am. J. Bot. 2014, 101, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Bai, X.; Zhu, Y.; Cai, H.; Li, Y.; Ji, W.; Chen, C.; An, L.; Zhu, Y. Isolation and functional analysis of GsTIFY11b relevant to salt and alkaline stress from Glycine soja. Yi Chuan 2012, 34, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Bai, X.; Chen, C.; Chen, Q.; Cai, H.; Li, Y.; Ji, W.; Zhai, H.; Lv, D.; Luo, X.; et al. GsTIFY10, a novel positive regulator of plant tolerance to bicarbonate stress and a repressor of jasmonate signaling. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 77, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Kang, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, W.; Xie, P.; Liao, L.; Huang, L.; Yao, M.; Qian, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the TIFY gene family in the response to multiple stresses in Brassica napus L. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, G.; Park, J.; Kayum, M.; Nou, I. A Genome-wide analysis reveals stress and hormone responsive patterns of TIFY family genes in Brassica rapa. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lv, H. Genome-wide identification, expression profile of the TIFY gene family in Brassica oleracea var. capitata, and their divergent response to various pathogen infections and phytohormone treatments. Genes 2020, 11, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Singh, R.; Singh, V.; Prasad, S. Heavy metal tolerance in plants: Role of transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and ionomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, V.; Mahajan, M.; Yadav, S. Toxic metals accumulation, tolerance and homeostasis in Brassicaoilseed species: Overview of physiological, biochemical and molecular mechanisms. In The Plant Family Brassicaceae; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 171–211. [Google Scholar]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Bo, Y.; Han, L.; He, J.; Lanczycki, C.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.; Geer, R.; Gonzales, N.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: Functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architectures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D200–D203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larkin, M.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, T.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.; Noble, W. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.; Frank, M.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorrips, R. MapChart: Software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xia, J.; Shen, S.; Guan, M.; Zhu, M.; Qiao, C.; Sun, F.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of phosphorus transporter genes in Brassica and their roles in heavy metal stress tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.; Rinn, J.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, S.; Sun, F.; Zhu, M.; Chen, S.; Guan, M.; Chen, R.; Tang, F.; Yin, N.; Xu, X.; Tang, Z.; et al. Genome-wide identification AINTEGUMENTA-like (AIL) genes in Brassica species and expression patterns during reproductive development in Brassica napus L. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0234411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Fu, F.; Lu, K.; Zhang, K.; Wang, R.; Xu, X.; Wang, M.; Lu, J.; Wan, H.; Tang, Z.; et al. Differential accumulation of phenolic compounds and expression of related genes in black- and yellow-seeded Brassica napus. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 2885–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Group Name | A. thaliana | B. rapa | B. nigra | B. oleracea | B. juncea | B. napus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JAZ I | 2 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 11 | 13 |
| JAZ II | 2 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 9 | 9 |
| JAZ III | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
| JAZ IV | 2 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 7 |
| JAZ V | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 6 |
| JAZ VI | 3 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 9 | 9 |
| PPD | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| TIFY I | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| TIFY II | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 |
| ZML | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 10 |
| Total | 18 | 35 | 33 | 35 | 64 | 70 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wan, Y.; Hu, R.; Shen, S.; Chen, S.; Yin, N.; Tang, Y.; Liang, Y.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of the TIFY Gene Family in Brassiceae and Its Potential Association with Heavy Metal Stress in Rapeseed. Plants 2022, 11, 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11050667
Sun F, Chen Z, Zhang Q, Wan Y, Hu R, Shen S, Chen S, Yin N, Tang Y, Liang Y, et al. Genome-Wide Identification of the TIFY Gene Family in Brassiceae and Its Potential Association with Heavy Metal Stress in Rapeseed. Plants. 2022; 11(5):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11050667
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Fujun, Zhiyou Chen, Qianwei Zhang, Yuanyuan Wan, Ran Hu, Shulin Shen, Si Chen, Nengwen Yin, Yunshan Tang, Ying Liang, and et al. 2022. "Genome-Wide Identification of the TIFY Gene Family in Brassiceae and Its Potential Association with Heavy Metal Stress in Rapeseed" Plants 11, no. 5: 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11050667
APA StyleSun, F., Chen, Z., Zhang, Q., Wan, Y., Hu, R., Shen, S., Chen, S., Yin, N., Tang, Y., Liang, Y., Lu, K., Qu, C., Hua, W., & Li, J. (2022). Genome-Wide Identification of the TIFY Gene Family in Brassiceae and Its Potential Association with Heavy Metal Stress in Rapeseed. Plants, 11(5), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11050667