Structural Characterization of Withanolide Glycosides from the Roots of Withania somnifera and Their Potential Biological Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
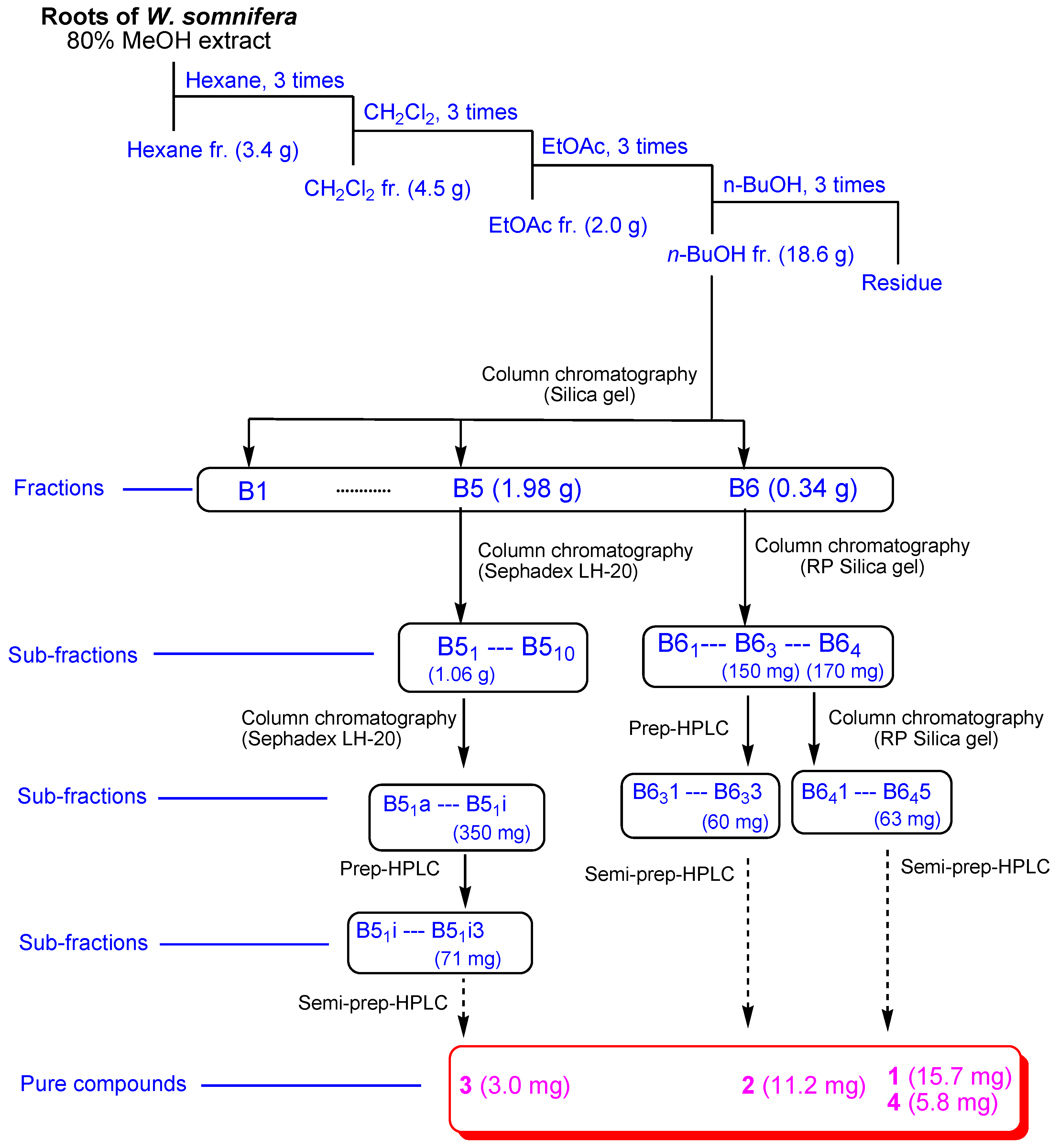
2.1. Isolation of Compounds 1–4
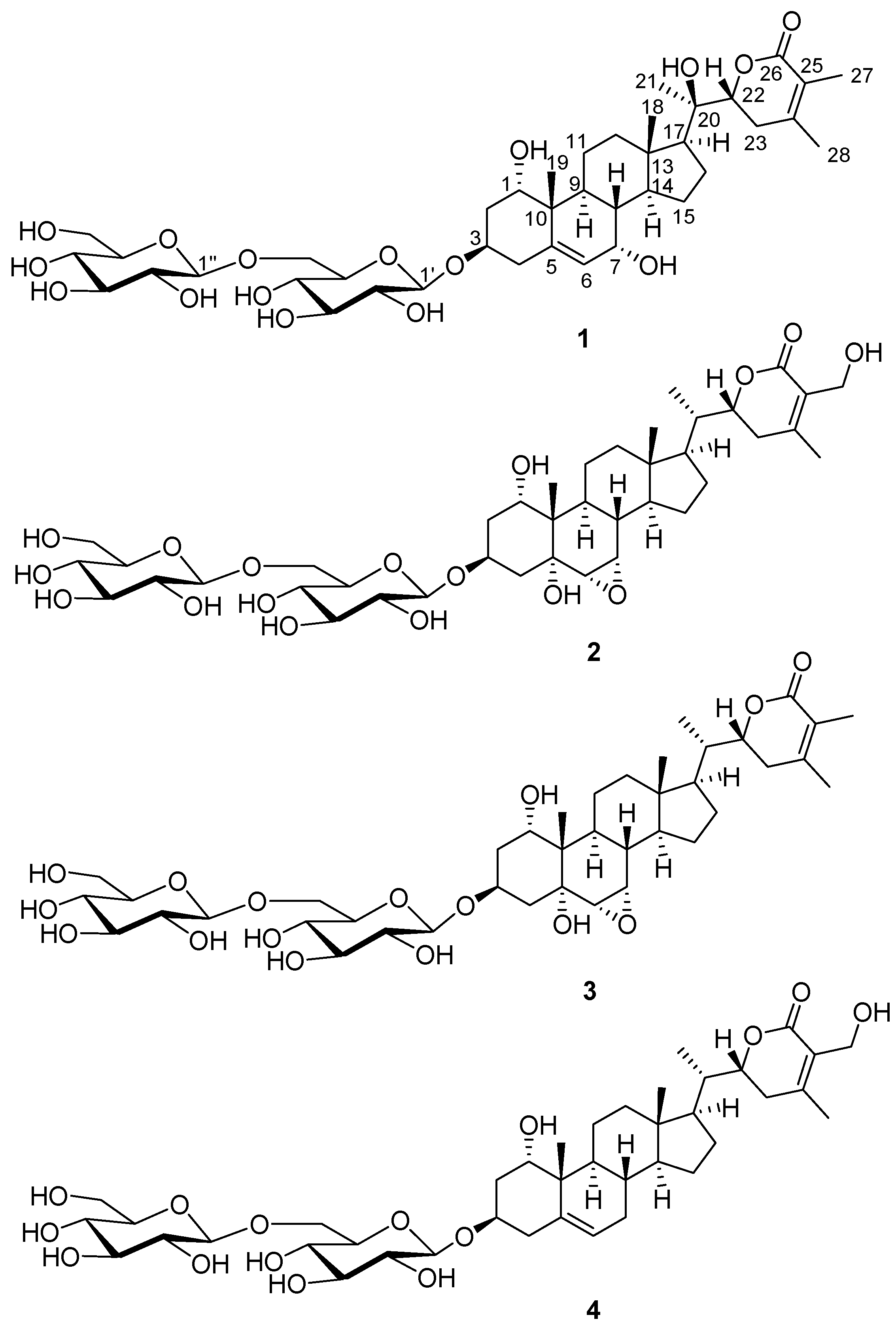
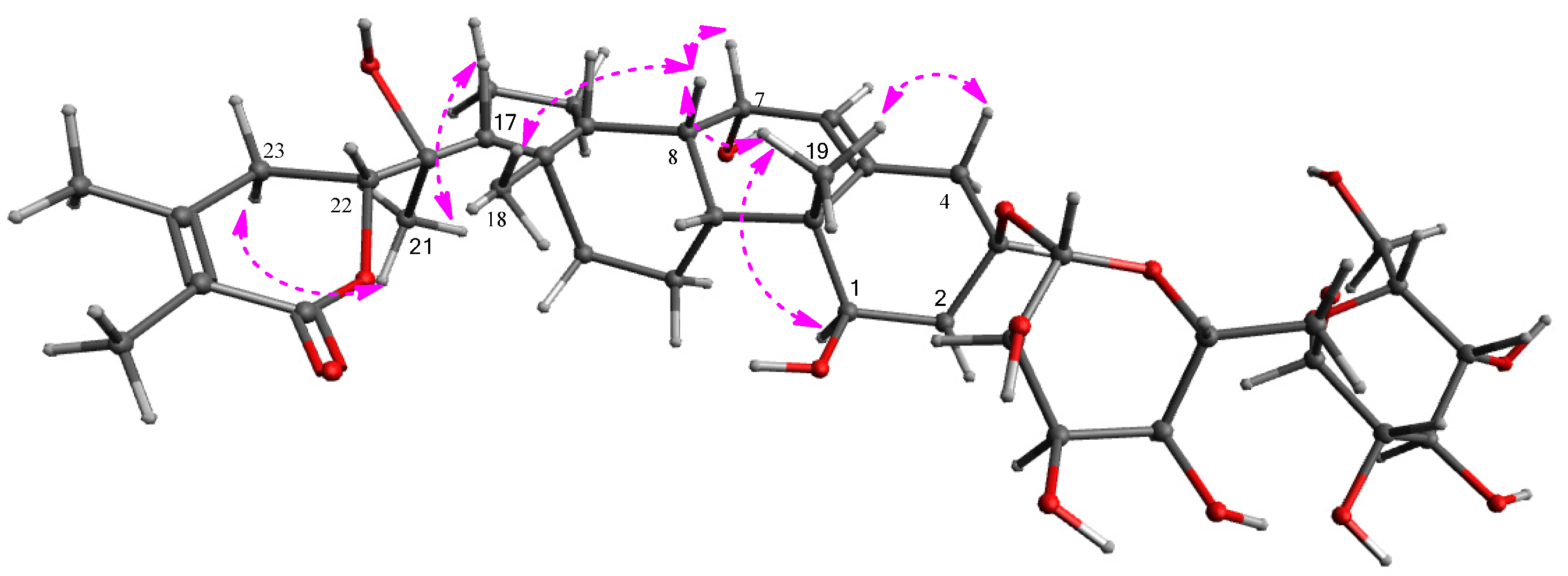
2.2. Structural Elucidation of the Isolated Compounds 1–4
2.3. Evaluation of Biological Activity of the Isolated Compounds
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedure and Plant Material
3.2. Extraction and Separation of the Compounds
3.2.1. Withanoside XII (1)
3.2.2. Withagenin A Diglucoside (2)
3.3. Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Absolute Configuration Determination of the Sugar Moieties of Compound 1
Withanoside XIIa (1a)
3.4. Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity
3.5. Antioxidant Activity Test with ABTS Radical
3.6. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kulkarni, S.; Dhir, A. Withania somnifera: An Indian ginseng. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiat. 2008, 32, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.; Ansari, W.A. Withania somnifera: Advances and implementation of molecular and tissue culture techniques to enhance its application. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glotter, E. Withanolides and related ergostane-type steroids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1991, 8, 415–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborti, S.; De Barun, K.; Bandyopadhyay, T. Variations in the antitumor constituents of Withania somnifera Dunal. Experientia 1974, 30, 852–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minguzzi, S.; Barata, E.S.L. Cytotoxic withanolides from Achnistus arborescens. Phytochemistry 2002, 59, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Nakamura, N. Withanolides derivatives from the roots of Withania somnifera and their neurite outgrowth activities. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, C.-M.; Gallagher, R.J.; Timmermann, B.N. Antiproliferative withanolides from several solanaceous species. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Zhang, W.-N.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C.; Lin, R.; Shan, S.-M.; Zhu, M.-D.; Luo, J.-G.; Kong, L.-Y. Cytotoxic withanolides from Physalis angulate var. villosa and the apoptosis-inducing effect via ROS generation and the activation of MAPK in human osteosarcoma cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 53089–53100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, V.; Beuerle, T. A validated HPTLC method for the simultaneous quantifications of three phenolic acids and three withanolides from Withania somnifera plants and its herbal products. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1124, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girme, A.; Verma, M.K. Investigating 11 Withanosides and Withanolides by UHPLC-PDA and Mass Fragmentation Studies from Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera). ACS Omega 2020, 5, 27933–27943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroya, A.S.; Singh, J. Neuropharmacology of Nardostachys jatamansi DC. In Pharmacotherapeutic Potential of Natural Products in Neurological Disorders; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Chikhale, R.V.; Gurav, S.S.; Patil, R.B.; Sinha, S.K.; Prasad, S.K.; Shakya, A.; Shrivastava, S.K.; Gurav, N.S.; Prasad, R.S. SARS-CoV-2 host entry and replication inhibitors from Indian ginseng: An in-silico approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 4510–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.K.; Singh, P.; Sharma, S.; Singh, T.P.; Ethayathulla, A.S.; Kaur, P. Identification of bioactive molecule from Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) as SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitor. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 5668–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.R.; Kang, H.S.; Yoo, M.J.; Yi, S.A.; Beemelmanns, C.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, K.H. Anti-adipogenic Pregnane Steroid from a Hydractinia-associated Fungus, Cladosporium sphaerospermum SW67. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2020, 26, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Ryoo, R.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.H. Trichothecene and tremulane sesquiterpenes from a hallucinogenic mushroom Gymnopilus junonius and their cytotoxicity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2020, 43, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.W.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Jang, W.; Kim, K.H. Mushrooms: An Important Source of Natural Bioactive Compounds. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2020, 26, 118–131. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.S.; Park, M.; Pang, C.; Rashan, L.; Jung, W.H.; Kim, K.H. Antifungal phenols from Woodfordia uniflora Collected in Oman. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2261–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yu, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, S.U.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.H. Cytotoxic withanolides from the roots of Indian ginseng (Withania somnifera). J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.C.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Jo, M.S.; Yu, J.S.; Ko, Y.J.; Cho, Y.C.; Kim, K.H. Withaninsams A and B: Phenylpropanoid esters from the roots of Indian ginseng (Withania somnifera). Plants 2019, 8, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.S.; Yoo, M.J.; Kang, H.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, S.; Yu, J.S.; Kim, J.C.; Jang, T.S.; Pang, C.; Kim, K.H. Withasomniferol D, a New Anti-adipogenic Withanolide from the Roots of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera). Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harinantenaina, L.R.R.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K. Ent-kaurane Diterpenoid Glycosides from the Leaves of Cussonia racemosa, a Malagasy Endemic Plant. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H.; Murakami, T.; Kishi, A.; Yoshikawa, M. Structures of withanosides I, II, III, IV, V, VI, and VII, new withanolide glycosides, from the roots of Indian Withania somnifera Dunal. and inhibitory activity for tachyphylaxis to clonidine in isolated guinea-pig ileum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.M.; Wijeratne, E.M.K.; Brooks, A.D.; Tewary, P.; Xuan, L.J.; Wang, W.Q.; Sayers, T.J.; Gunatilaka, A.A.L. Cytotoxic and other withanolides from aeroponically grown Physalis philadelphica. Phytochemistry 2018, 152, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta-ur-Rahman; Dur-e-Shahwar; Naz, A.; Choudhary, M.I. Withanolides from Withania coagulans. Phytochemistry 2003, 63, 387–390. [Google Scholar]
- Neogi, P.; Kawai, M.; Butsugan, Y.; Mori, Y.; Suzuki, M. Withacoagin, a new withanolide from Withania coagulans roots. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1988, 61, 4479–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, G.; Chien, N.Q.; Nguyen, H.K. Dunawithanine A and B, first plant withanolide glycosides from Dunalia australis. Naturwissenschaften 1981, 68, 425–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-F.; Ma, L.; Sun, L.-J.; Ali, M.; Arfan, M.; Liu, J.-W.; Hu, L.-H. Immunosuppressive withanolides from Withania coagulans. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velde, V.V.; Lavie, D. New withanolides of biogenetic interest from Withania somnifera. Phytochemistry 1981, 20, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nakashima, T.; Ueda, T.; Tomii, K.; Kouno, I. Facile Discrimination of Aldose Enantiomers by Reversed-Phase HPLC. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coxon, B. Two-Dimensional J-Resolved Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometry of Hydroxyl-Coupled α- and β-d-Glucose. Anal. Chem. 1983, 55, 2361–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolleddula, J. Identification of metabolites in Withania sominfera fruits by liquid chromatography and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, D.J.; George, A.E.; Trainor, E.A.; Horton, K.E.; Hildebrandt, E.; Testerman, T.L. Cholesterol enhances Helicobacter pylori resistance to antibiotics and LL-37. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2897–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Inhibitory effect of Korean Red Ginseng extract on DNA damage response and apoptosis in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, P.; Rawat, V. Antibacterial activity of Withania somnifera against Gram-positive isolates from pus samples. AYU 2014, 35, 330–332. [Google Scholar]
- Owais, M.; Sharad, K.S.; Shehbaz, A.; Saleemuddin, M. Antibacterial efficacy of Withania somnifera (ashwagandha) an indigenous medicinal plant against experimental murin salmonellosis. Phytomedicine 2005, 12, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, N.; Hossain, M.; Mottalib, M.A.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Gan, S.H.; Khalil, M.I. Methanolic extracts of Withania somnifera leaves, fruits and roots possess antioxidant properties and antibacterial activities. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Kim, T.-H.; Kang, M.-J.; Choi, J.-A.; Pack, D.-Y.; Lee, I.-R.; Kim, M.-G.; Han, S.-S.; Kim, B.-Y.; Oh, S.-M.; et al. Inhibitory effect of witaferin A on Helicobacter pylori-induced IL-8 production and NF-κB activation in gastric epithelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singh, D.; Aggarwal, A.; Maurya, R.; Naik, S. Withania somnifera inhibits NF-kappaB and AP-1 transcription factors in human peripheral blood and synovial fluid mononuclear cells. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.A.K.; Park, W.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.J.; Akter, K.M.; Goo, Y.M. A new anti-Helicobacter pylori juglone from Reynoutria japonica. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2019, 42, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.S.; Kim, H.-J.; Li, M.; Lim, D.H.; Kim, J.; Kwak, S.-S.; Kang, C.-M.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Ahn, M.-J. Two Classes of Pigments, Carotenoids and C-Phycocyanin, in Spirulina Powder and Their Antioxidant Activities. Molecules 2018, 23, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, J.K.; Yu, J.S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, J.C.; Ko, Y.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.H. Ginkwanghols A and B, osteogenic coumaric acid-aliphatic alcohol hybrids from the leaves of Ginkgo biloba. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2021, 44, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ) and HMBC (
) and HMBC ( ) correlations for 1.
) correlations for 1.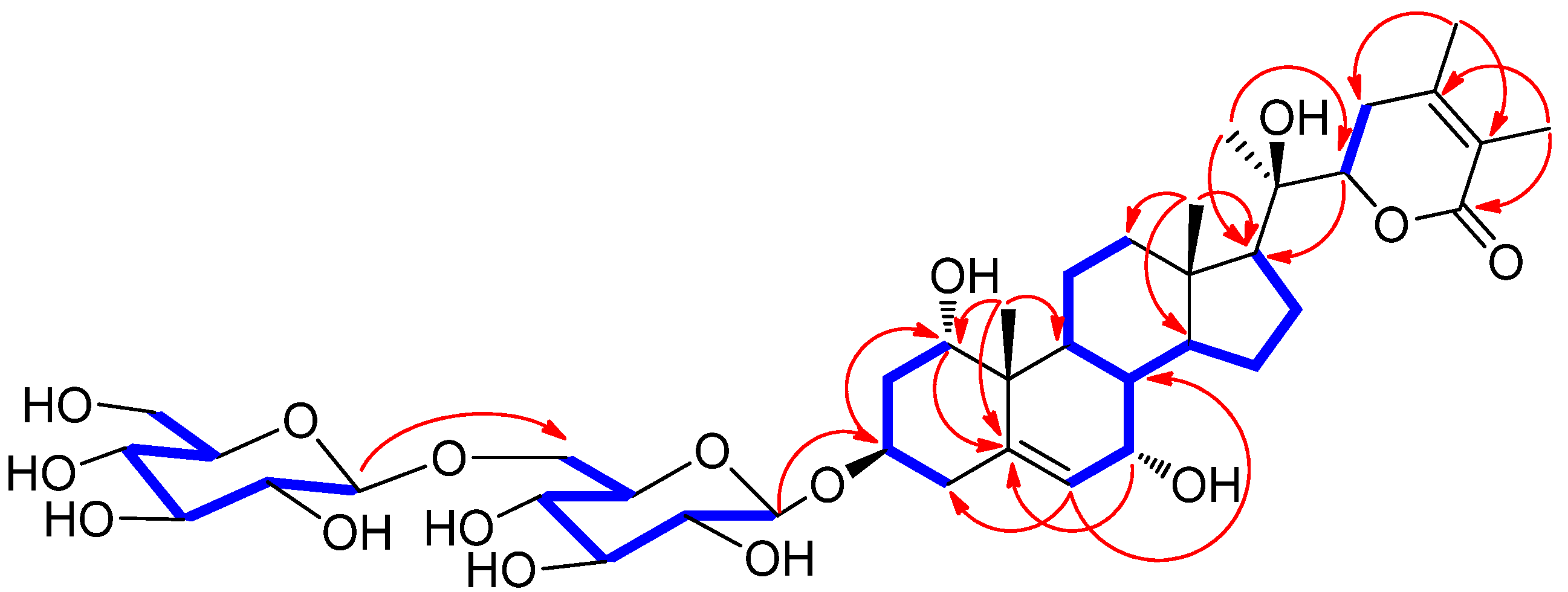
 ) and HMBC (
) and HMBC ( ) correlations for 1a.
) correlations for 1a.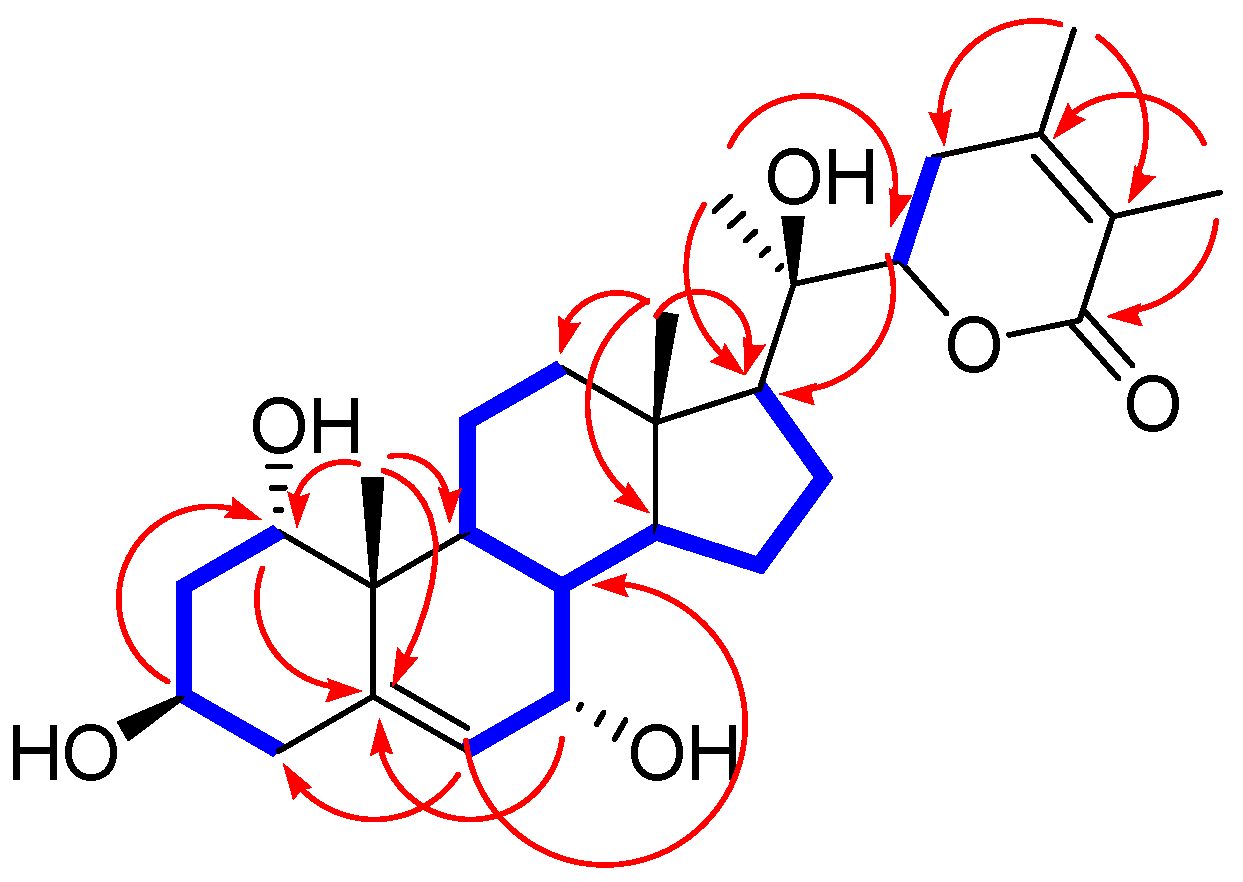
| Position | 1 | 1a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | |
| 1 | 3.86 dd (1.5, 1.5) | 72.2 d | 3.82 dd (1.0, 1.0) | 72.0 d |
| 2α | 2.55 ddd (13.0, 5.5, 1.5) | 37.7 t | 2.01 ddd (13.0, 5.5, 1.0) | 37.6 t |
| 2β | 2.40 ddd (13.0, 12.5, 1.5) | 1.73 ddd (13.0, 12.5, 1.0) | ||
| 3 | 4.09 dddd (12.5, 12.5, 5.5, 5.5) | 73.8 d | 3.91 dddd (12.5, 12.5, 5.5, 5.5) | 65.1 d |
| 4α | 2.23 dd (13.0, 5.5) | 36.1 t | 2.36 dd (13.0, 5.5) | 40.9 t |
| 4β | 1.85 dd (13.0, 12.5) | 2.32 dd (13.0, 12.5) | ||
| 5 | 142.7 s | 142.9 s | ||
| 6 | 5.77 d (4.0) | 126.2 d | 5.72 d (4.0) | 126.0 d |
| 7 | 3.75 t (4.0) | 64.4 d | 3.72 t (4.0) | 64.5 d |
| 8 | 1.44 m | 37.0 d | 1.46 m | 37.0 d |
| 9 | 1.92 m | 33.4 d | 1.92 m | 33.8 d |
| 10 | 41.8 s | 41.6 s | ||
| 11α | 1.57 m | 19.5 t | 1.51 m | 19.3 t |
| 11β | 1.52 m | 1.56 m | ||
| 12α | 1.37 m | 39.2 t | 2.00 m | 39.3 t |
| 12β | 2.01 m | 1.36 m | ||
| 13 | 42.3 s | 42.1 s | ||
| 14 | 1.57 m | 49.6 d | 1.57 m | 49.8 d |
| 15α | 1.86 m | 23.1 t | 1.19 m | 22.3 t |
| 15β | 1.22 m | 1.84 m | ||
| 16α | 1.70 m | 21.5 t | 1.69 m | 21.3 t |
| 16β | 1.91 m | 1.91 m | ||
| 17 | 1.82 m | 54.3 d | 1.82 m | 54.1 d |
| 18 | 0.89 s | 12.6 q | 0.89 s | 12.6 q |
| 19 | 1.02 s | 17.5 q | 1.02 s | 17.3 q |
| 20 | 74.9 s | 75.0 s | ||
| 21 | 1.29 s | 19.5 q | 1.28 s | 19.3 q |
| 22 | 4.27 dd (13.5, 3.5) | 81.2 d | 4.25 dd (13.5, 3.5) | 81.0 d |
| 23α | 2.32 m | 30.8 t | 2.32 m | 30.8 t |
| 23β | 2.56 m | 2.54 t (15.0) | ||
| 24 | 151.5 s | 151.2 s | ||
| 25 | 120.6 s | 120.6 s | ||
| 26 | 167.8 s | 167.6 s | ||
| 27 | 1.87 s | 11.1 q | 1.87 s | 10.8 q |
| 28 | 2.01 s | 19.2 q | 2.00 s | 19.1 q |
| 1′ | 4.40 d (8.0) | 101.8 d | ||
| 2′ | 3.18 dd (9.0, 8.0) | 73.8 d | ||
| 3′ | 3.38 overlap | 76.4 d | ||
| 4′ | 3.28 overlap | 70.3 d | ||
| 5′ | 3.49 overlap | 75.6 d | ||
| 6′ | 4.14 dd (12.0, 2.0); 3.80 dd (12.0, 6.0) | 68.5 t | ||
| 1″ | 4.41 d (8.0) | 103.5 d | ||
| 2″ | 3.23 (9.0, 8.0) | 73.8 d | ||
| 3″ | 3.36 overlap | 76.4 d | ||
| 4″ | 3.30 overlap | 70.0 d | ||
| 5″ | 3.28 overlap | 76.5 d | ||
| 6″ | 3.88 dd (12.0, 2.0); 3.69 dd (12.0, 5.5) | 61.3 t | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ha, J.W.; Yu, J.S.; Lee, B.S.; Kang, D.-M.; Ahn, M.-J.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, K.H. Structural Characterization of Withanolide Glycosides from the Roots of Withania somnifera and Their Potential Biological Activities. Plants 2022, 11, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11060767
Ha JW, Yu JS, Lee BS, Kang D-M, Ahn M-J, Kim JK, Kim KH. Structural Characterization of Withanolide Glycosides from the Roots of Withania somnifera and Their Potential Biological Activities. Plants. 2022; 11(6):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11060767
Chicago/Turabian StyleHa, Ji Won, Jae Sik Yu, Bum Soo Lee, Dong-Min Kang, Mi-Jeong Ahn, Jung Kyu Kim, and Ki Hyun Kim. 2022. "Structural Characterization of Withanolide Glycosides from the Roots of Withania somnifera and Their Potential Biological Activities" Plants 11, no. 6: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11060767
APA StyleHa, J. W., Yu, J. S., Lee, B. S., Kang, D.-M., Ahn, M.-J., Kim, J. K., & Kim, K. H. (2022). Structural Characterization of Withanolide Glycosides from the Roots of Withania somnifera and Their Potential Biological Activities. Plants, 11(6), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11060767










