Apoptotic, Anti-Inflammatory Activities and Interference with the Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling of Fractions from Pistacia lentiscus L. var. chia Leaves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
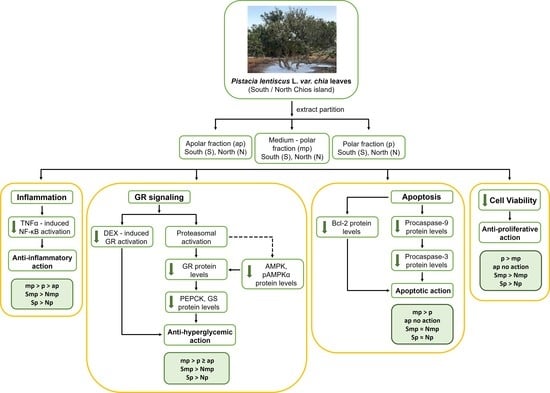
2. Results
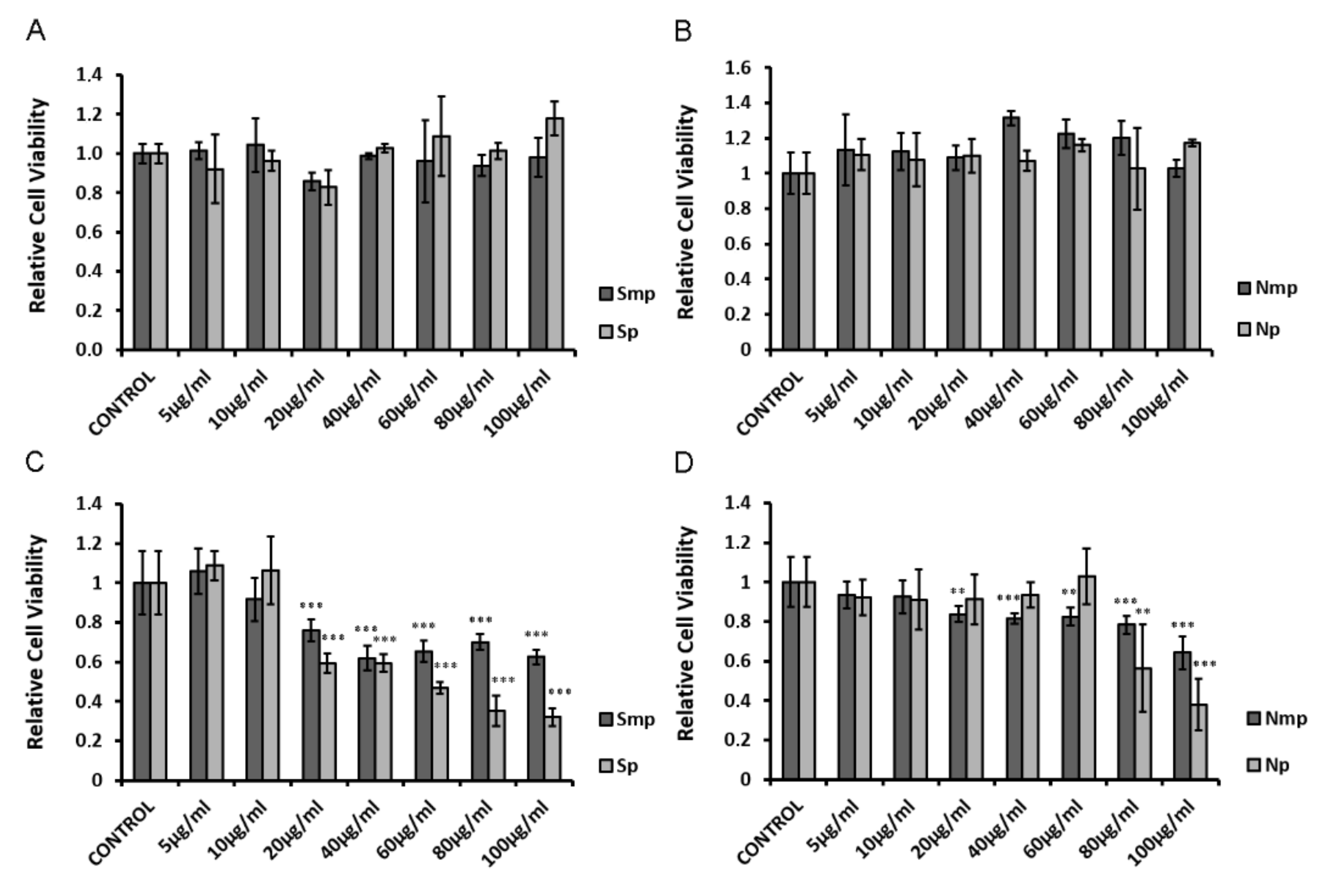
2.1. Effect of Chios Mastiha Tree Leaves Fractions on HEK293 Cell Viability
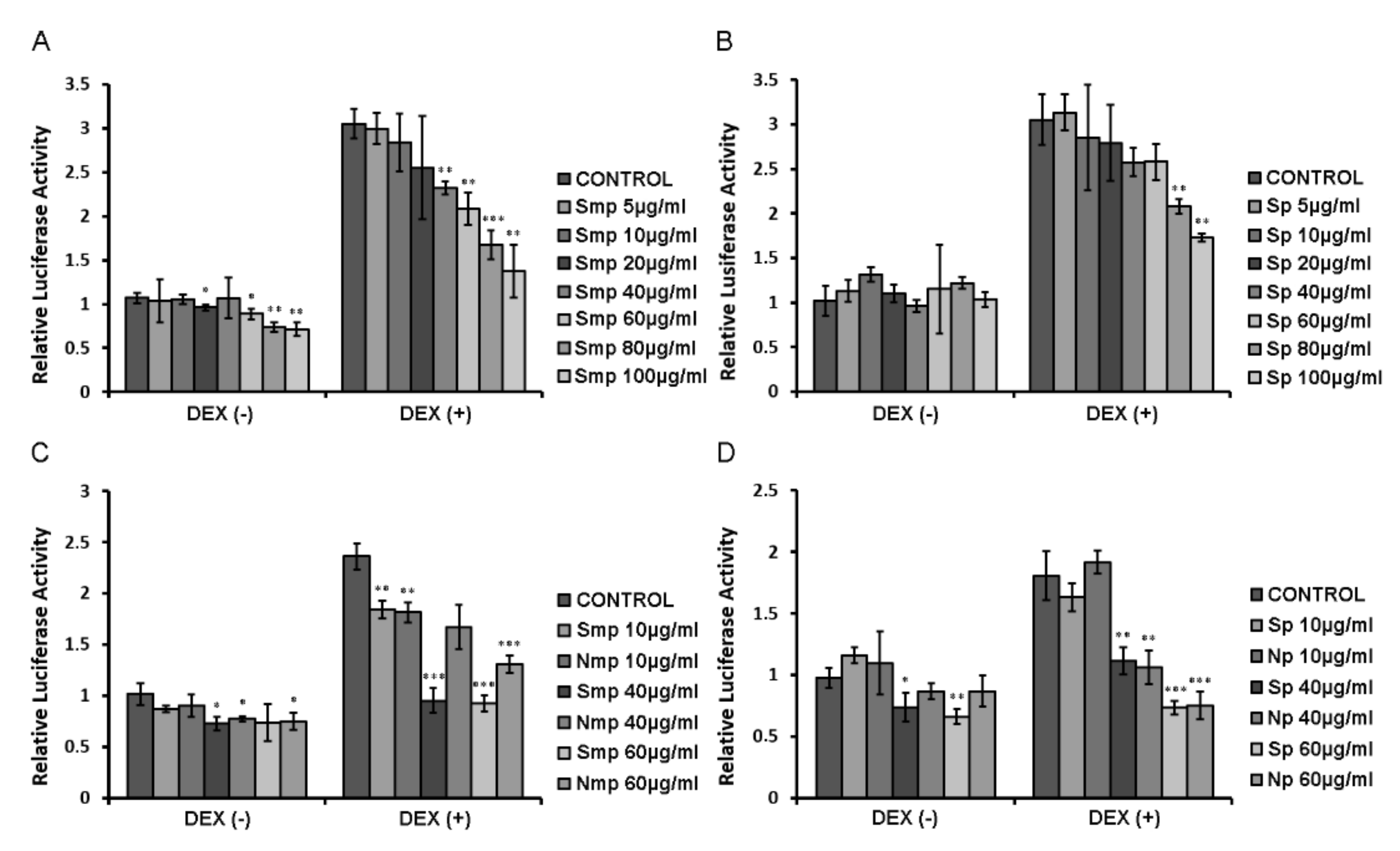
2.2. Chios Mastiha Tree Medium-Polar and Polar Leaves Fractions Suppressed the DEX-Induced GR Transcriptional Activation
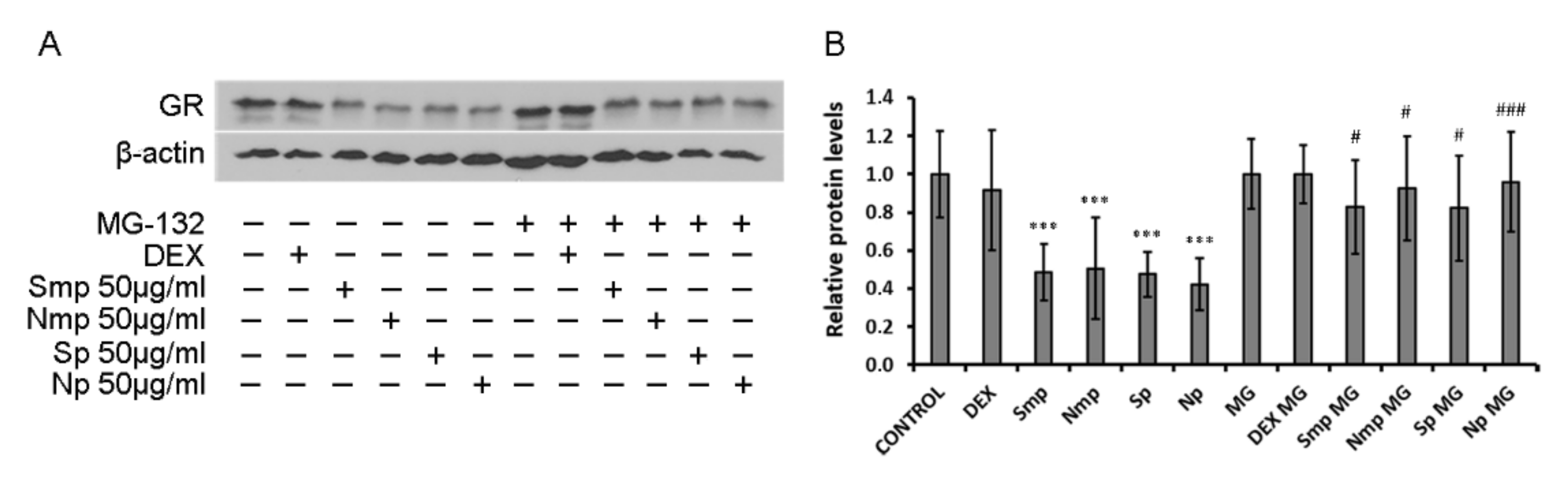
2.3. Proteasome Inhibitor MG-132 Inhibits Leaves Fractions-Induced GR Protein Levels Reduction
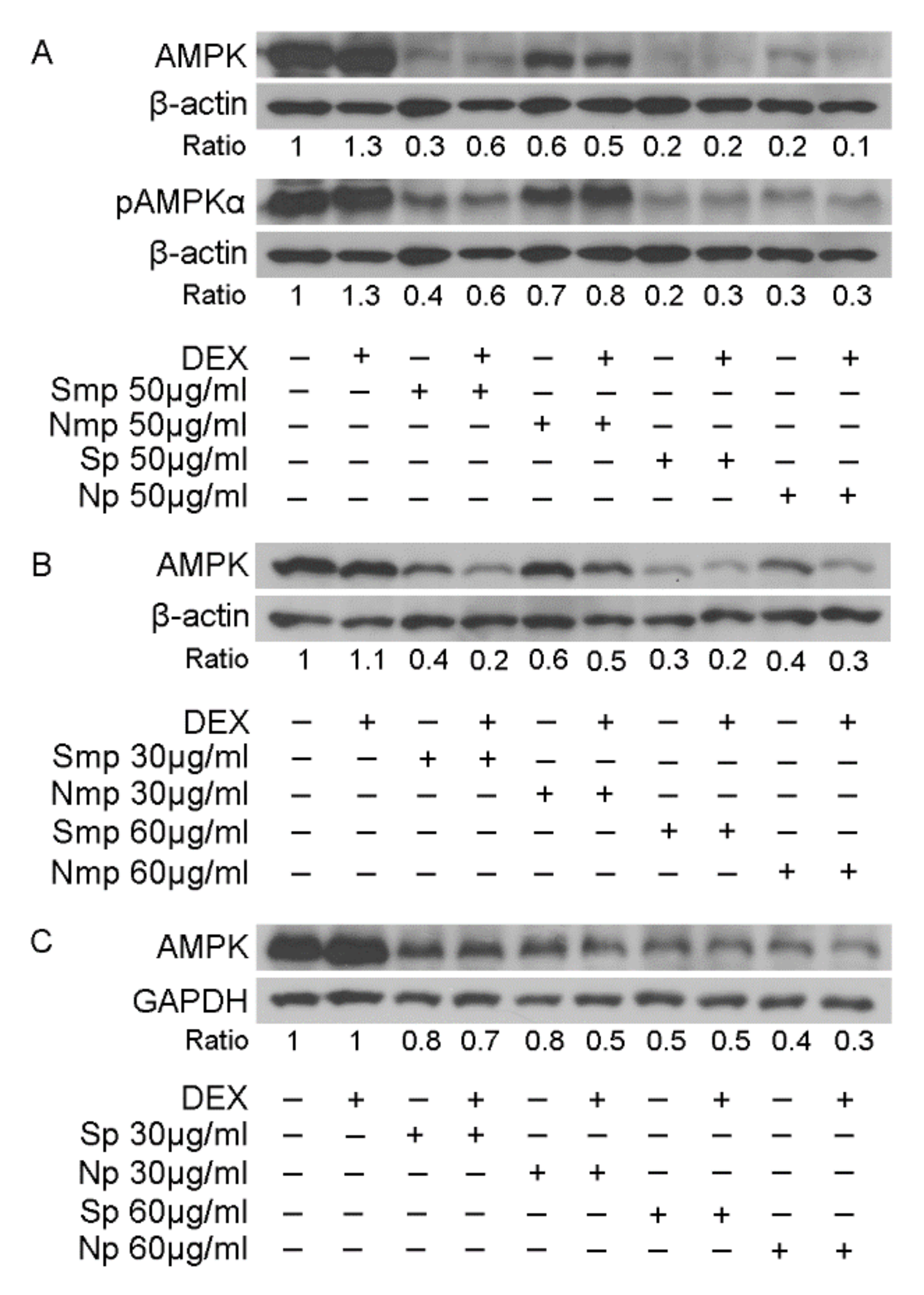
2.4. Effect of Leaves Fractions on Protein Levels of Energy Associated Molecules
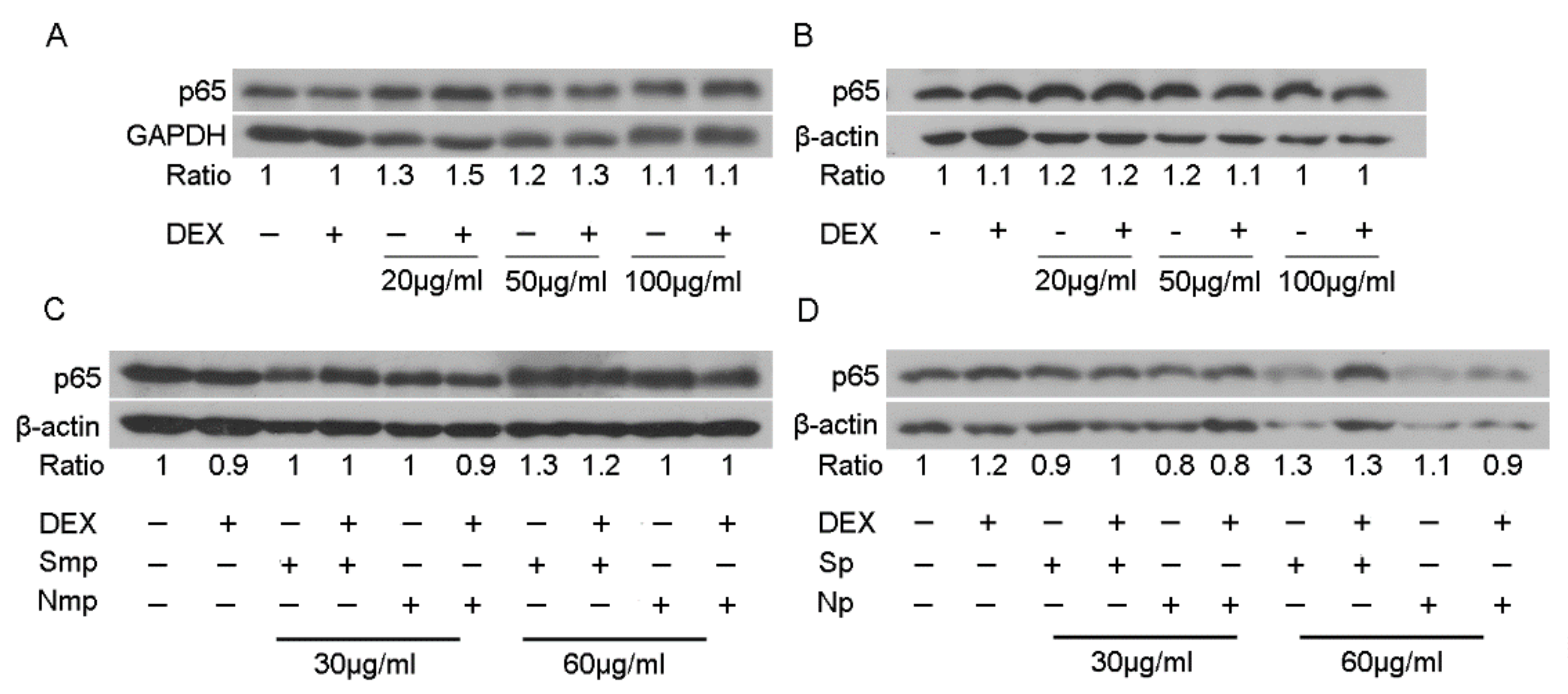
2.5. Anti-Inflammatory Actions of Chios Mastiha Tree Leaves Fractions via Suppression of the TNFα-Induced NF-κB Transcriptional Activation
2.6. Interference of Chios Mastiha Tree Medium-Polar and Polar Leaves Fractions with Apoptosis
2.7. Fractions Chemical Characterization
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Plant Material Fractionation
4.3. Chemical Characterization of Active Fractions
4.4. Antibodies
4.5. Cell Culture
4.6. Cell Viability Assay
4.7. GR and NF-κB Transactivation Measurement
4.8. Electrophoresis and Western Blotting
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papada, E.; Gioxari, A.; Amerikanou, C.; Forbes, A.; Tzavara, C.; Smyrnioudis, I.; Kaliora, A.C. Regulation of faecal biomarkers in inflammatory bowel disease patients treated with oral mastiha (Pistacia lentiscus) supplement: A double-blind and placebo-controlled randomised trial. Phytother. Res. PTR 2019, 33, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pachi, V.K.; Mikropoulou, E.V.; Gkiouvetidis, P.; Siafakas, K.; Argyropoulou, A.; Angelis, A.; Mitakou, S.; Halabalaki, M. Traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Chios mastic gum (Pistacia lentiscus var. Chia, Anacardiaceae): A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 254, 112485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bampouli, A.; Kyriakopoulou, K.; Papaefstathiou, G.; Louli, V.; Krokida, M.; Magoulas, K. Comparison of different extraction methods of Pistacia lentiscus var. chia leaves: Yield, antioxidant activity and essential oil chemical composition. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2014, 1, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bampouli, A.; Kyriakopoulou, K.; Papaefstathiou, G.; Louli, V.; Aligiannis, N.; Magoulas, K.; Krokida, M. Evaluation of total antioxidant potential of Pistacia lentiscus var. chia leaves extracts using UHPLC–HRMS. J. Food Eng. 2015, 167, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolella, S.; Nocera, P.; Carillo, P.; Woodrow, P.; Greco, V.; Manti, L.; Fiorentino, A.; Pacifico, S. An apolar Pistacia lentiscus L. leaf extract: GC-MS metabolic profiling and evaluation of cytotoxicity and apoptosis inducing effects on SH-SY5Y and SK-N-BE(2)C cell lines. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 95, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiatis, P.; Melliou, E.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Chinou, I.B.; Mitaku, S. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils of Pistacia lentiscus var. chia. Planta Med. 1999, 65, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgatza, D.; Gorgogietas, V.A.; Kylindri, P.; Charalambous, M.C.; Papadopoulou, K.K.; Hayes, J.M.; Psarra, A.G. The triterpene echinocystic acid and its 3-O-glucoside derivative are revealed as potent and selective glucocorticoid receptor agonists. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 79, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karra, A.G.; Tziortziou, M.; Kylindri, P.; Georgatza, D.; Gorgogietas, V.A.; Makiou, A.; Krokida, A.; Tsialtas, I.; Kalousi, F.D.; Papadopoulos, G.E.; et al. Boswellic acids and their derivatives as potent regulators of glucocorticoid receptor actions. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 695, 108656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baschant, U.; Culemann, S.; Tuckermann, J. Molecular determinants of glucocorticoid actions in inflammatory joint diseases. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 380, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.E.; Yun, J.S.; Patel, Y.M.; McGrane, M.M.; Hanson, R.W. Glucocorticoids regulate the induction of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene transcription during diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 12952–12957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkku, A.; Bodine, P.V.; Linnala-Kankkunen, A.; Mahonen, A. Glucocorticoids induce glutamine synthetase expression in human osteoblastic cells: A novel observation in bone. Bone 2004, 34, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianese, G.; Golin-Pacheco, S.D.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Collado, J.A.; Munoz, E.; Appendino, G.; Pollastro, F. Bioactive triterpenoids from the caffeine-rich plants guayusa and mate. Food Res. Int. 2019, 115, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, A.D.; Cao, Y.; Chandramouleeswaran, S.; Cidlowski, J.A. Lysine 419 targets human glucocorticoid receptor for proteasomal degradation. Steroids 2010, 75, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chui, A.J.; Okondo, M.C.; Rao, S.D.; Gai, K.; Griswold, A.R.; Johnson, D.C.; Ball, D.P.; Taabazuing, C.Y.; Orth, E.L.; Vittimberga, B.A.; et al. N-terminal degradation activates the NLRP1B inflammasome. Science 2019, 364, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, M.M.; Shaw, R.J. The AMPK signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nader, N.; Ng, S.S.; Lambrou, G.I.; Pervanidou, P.; Wang, Y.; Chrousos, G.P.; Kino, T. AMPK regulates metabolic actions of glucocorticoids by phosphorylating the glucocorticoid receptor through p38 MAPK. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 1748–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Lu, W.; Zhou, H.Y.; Long, L.H.; Hu, Z.L.; Ni, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.G.; et al. AMPK Mediates Glucocorticoids Stress-Induced Downregulation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor in Cultured Rat Prefrontal Cortical Astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraschos, S.; Magiatis, P.; Mitakou, S.; Petraki, K.; Kalliaropoulos, A.; Maragkoudakis, P.; Mentis, A.; Sgouras, D.; Skaltsounis, A.L. In vitro and in vivo activities of Chios mastic gum extracts and constituents against Helicobacter pylori. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kottakis, F.; Kouzi-Koliakou, K.; Pendas, S.; Kountouras, J.; Choli-Papadopoulou, T. Effects of mastic gum Pistacia lentiscus var. Chia on innate cellular immune effectors. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 21, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliora, A.C.; Stathopoulou, M.G.; Triantafillidis, J.K.; Dedoussis, G.V.; Andrikopoulos, N.K. Chios mastic treatment of patients with active Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioxari, A.; Kaliora, A.C.; Papalois, A.; Agrogiannis, G.; Triantafillidis, J.K.; Andrikopoulos, N.K. Pistacia lentiscus resin regulates intestinal damage and inflammation in trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis. J. Med. Food 2011, 14, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrikopoulos, N.K.; Kaliora, A.C.; Assimopoulou, A.N.; Papapeorgiou, V.P. Biological activity of some naturally occurring resins, gums and pigments against in vitro LDL oxidation. Phytother. Res. PTR 2003, 17, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedoussis, G.V.; Kaliora, A.C.; Psarras, S.; Chiou, A.; Mylona, A.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; Andrikopoulos, N.K. Antiatherogenic effect of Pistacia lentiscus via GSH restoration and downregulation of CD36 mRNA expression. Atherosclerosis 2004, 174, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loutrari, H.; Magkouta, S.; Pyriochou, A.; Koika, V.; Kolisis, F.N.; Papapetropoulos, A.; Roussos, C. Mastic oil from Pistacia lentiscus var. chia inhibits growth and survival of human K562 leukemia cells and attenuates angiogenesis. Nutr. Cancer 2006, 55, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balan, K.V.; Prince, J.; Han, Z.; Dimas, K.; Cladaras, M.; Wyche, J.H.; Sitaras, N.M.; Pantazis, P. Antiproliferative activity and induction of apoptosis in human colon cancer cells treated in vitro with constituents of a product derived from Pistacia lentiscus L. var. chia. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2007, 14, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, I.; Karatzas, T.; Korou, L.M.; Agrogiannis, G.; Vlachos, I.S.; Pantopoulou, A.; Tzanetakou, I.P.; Katsilambros, N.; Perrea, D.N. Evaluation of Chios mastic gum on lipid and glucose metabolism in diabetic mice. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartalis, A.; Didagelos, M.; Georgiadis, I.; Benetos, G.; Smyrnioudis, N.; Marmaras, H.; Voutas, P.; Zotika, C.; Garoufalis, S.; Andrikopoulos, G. Effects of Chios mastic gum on cholesterol and glucose levels of healthy volunteers: A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, pilot study (CHIOS-MASTIHA). Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2016, 23, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadou, I.; Mitakou, S.; Paraschos, S.; Efentakis, P.; Magiatis, P.; Kaklamanis, L.; Halabalaki, M.; Skaltsounis, L.; Iliodromitis, E.K. “Pistacia lentiscus L.” reduces the infarct size in normal fed anesthetized rabbits and possess antiatheromatic and hypolipidemic activity in cholesterol fed rabbits. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2016, 23, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadmiel, M.; Cidlowski, J.A. Glucocorticoid receptor signaling in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gruver-Yates, A.L.; Cidlowski, J.A. Tissue-specific actions of glucocorticoids on apoptosis: A double-edged sword. Cells 2013, 2, 202–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oray, M.; Abu Samra, K.; Ebrahimiadib, N.; Meese, H.; Foster, C.S. Long-term side effects of glucocorticoids. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2016, 15, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Kollner, T.G.; Chen, S.; Chen, F.; Chen, F. Characterization of Composition and Antifungal Properties of Leaf Secondary Metabolites from Thirteen Cultivars of Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. Molecules 2019, 24, 4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milia, E.; Bullitta, S.M.; Mastandrea, G.; Szotakova, B.; Schoubben, A.; Langhansova, L.; Quartu, M.; Bortone, A.; Eick, S. Leaves and Fruits Preparations of Pistacia lentiscus L.: A Review on the Ethnopharmacological Uses and Implications in Inflammation and Infection. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundahl, N.; Bridelance, J.; Libert, C.; De Bosscher, K.; Beck, I.M. Selective glucocorticoid receptor modulation: New directions with non-steroidal scaffolds. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 152, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, R.; Sharma, A.K.; Sharma, M.C.; Dobhal, M.P.; Gupta, R.S. Evaluation of antidiabetic and antioxidant potential of lupeol in experimental hyperglycaemia. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Jamil, U.; Butt, T.T.; Waquar, S.; Gan, S.H.; Shafique, H.; Jafar, T.H. In silico and in vitro studies of lupeol and iso-orientin as potential antidiabetic agents in a rat model. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 1501–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, R.G.; Silva Junior, W.F.; Veiga Junior, V.F.; Lima, A.A.; Lima, E.S. Physicochemical Characterization and Biological Activities of the Triterpenic Mixture alpha, beta-Amyrenone. Molecules 2017, 22, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehenni, C.; Atmani-Kilani, D.; Dumarcay, S.; Perrin, D.; Gerardin, P.; Atmani, D. Hepatoprotective and antidiabetic effects of Pistacia lentiscus leaf and fruit extracts. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, X.; Xie, L.; Deng, M.; Chen, H.; Song, J.; Long, J.; Li, X.; Luo, J. Lupeol and its derivatives as anticancer and anti-inflammatory agents: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic efficacy. Pharm. Res. 2021, 164, 105373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M. Lupeol, a novel anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer dietary triterpene. Cancer Lett. 2009, 285, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qabaha, K.; Ras, S.A.; Abbadi, J.; Al-Rimawi, F. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Eucalyptus Spp. And Pistascia Lentiscus Leaf Extracts. Afr. J. Tradit. Complementary Altern. Med. 2016, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Thompson, K.E.; Yates, C.R.; Miller, D.D. Synthesis and biological evaluation of quinic acid derivatives as anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5458–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Fang, X.; Ge, L.; Cao, F.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W. Antitumor, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of kaempferol and its corresponding glycosides and the enzymatic preparation of kaempferol. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotie, J.; Bohle, D.S.; Leimanis, M.L.; Georges, E.; Rukunga, G.; Nkengfack, A.E. Lupeol long-chain fatty acid esters with antimalarial activity from Holarrhena floribunda. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.G.; Velandia, J.R.; Oliviera, L.F.; Bezerra, F.B. Triterpenos isolados de Eschweilera longipes miers (Lecythidaceae). Química Nova 1998, 21, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cayme, J.C.; Ragasa, C.Y. Structure elucidation of β-stigmasterol and β-sitosterol from Sesbania grandiflora [Linn] Pers. and β-carotene from Heliotropium indicum Linn. by NMR spectroscopy. Kimika 2004, 20, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsialtas, I.; Gorgogietas, V.A.; Michalopoulou, M.; Komninou, A.; Liakou, E.; Georgantopoulos, A.; Kalousi, F.D.; Karra, A.G.; Protopapa, E.; Psarra, A.G. Neurotoxic effects of aluminum are associated with its interference with estrogen receptors signaling. Neurotoxicology 2020, 77, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgogietas, V.A.; Tsialtas, I.; Sotiriou, N.; Laschou, V.C.; Karra, A.G.; Leonidas, D.D.; Chrousos, G.P.; Protopapa, E.; Psarra, A.G. Potential interference of aluminum chlorohydrate with estrogen receptor signaling in breast cancer cells. J. Mol. Biochem. 2018, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar]



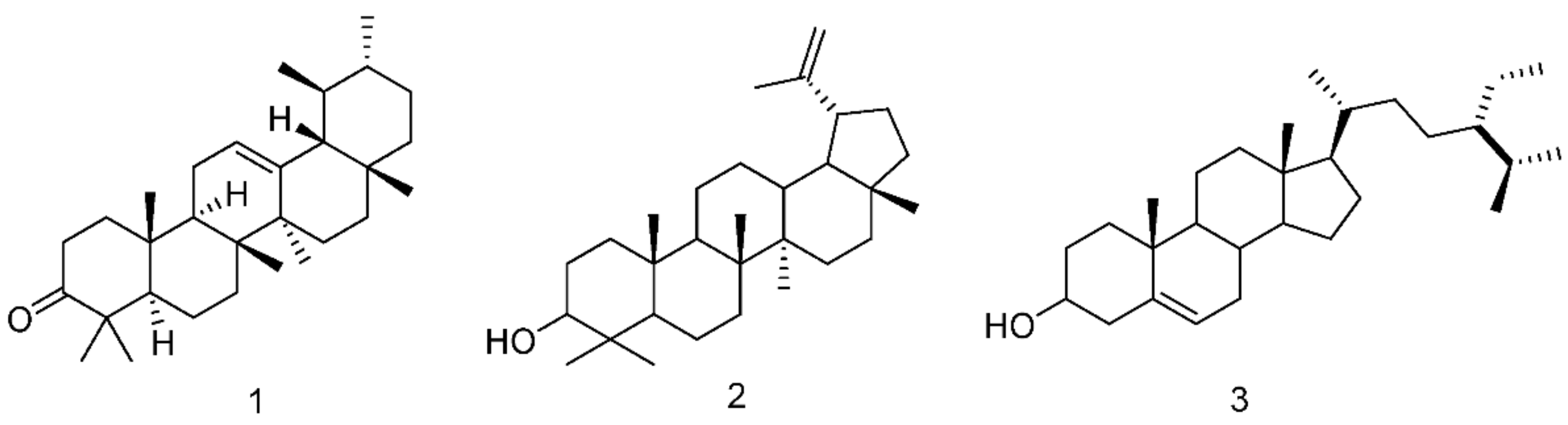
| Apolar Fraction Composition | Medium-Polar Fraction Composition | Polar Fraction Composition | |
|---|---|---|---|
| P. lentiscus leaves extracts from northern Chios island | Fatty acid triglycerides | Lupeol 0.073% | Phenolic compounds 36.58% |
| traces of triterpenoids | β-sitosterol 0.02% | traces of triterpenoids | |
| P. lentiscus leaves extracts from southern Chios island | Fatty acid triglycerides | Lupeol 16.54% | Phenolic compounds 25.97% |
| traces of triterpenoids | α-amyrenone 15.28% | traces of triterpenoids |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalousi, F.D.; Pollastro, F.; Christodoulou, E.C.; Karra, A.G.; Tsialtas, I.; Georgantopoulos, A.; Salamone, S.; Psarra, A.-M.G. Apoptotic, Anti-Inflammatory Activities and Interference with the Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling of Fractions from Pistacia lentiscus L. var. chia Leaves. Plants 2022, 11, 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11070934
Kalousi FD, Pollastro F, Christodoulou EC, Karra AG, Tsialtas I, Georgantopoulos A, Salamone S, Psarra A-MG. Apoptotic, Anti-Inflammatory Activities and Interference with the Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling of Fractions from Pistacia lentiscus L. var. chia Leaves. Plants. 2022; 11(7):934. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11070934
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalousi, Foteini D., Federica Pollastro, Evgenia C. Christodoulou, Aikaterini G. Karra, Ioannis Tsialtas, Achilleas Georgantopoulos, Stefano Salamone, and Anna-Maria G. Psarra. 2022. "Apoptotic, Anti-Inflammatory Activities and Interference with the Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling of Fractions from Pistacia lentiscus L. var. chia Leaves" Plants 11, no. 7: 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11070934
APA StyleKalousi, F. D., Pollastro, F., Christodoulou, E. C., Karra, A. G., Tsialtas, I., Georgantopoulos, A., Salamone, S., & Psarra, A.-M. G. (2022). Apoptotic, Anti-Inflammatory Activities and Interference with the Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling of Fractions from Pistacia lentiscus L. var. chia Leaves. Plants, 11(7), 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11070934