The Influence of Elevated CO2 on Volatile Emissions, Photosynthetic Characteristics, and Pigment Content in Brassicaceae Plants Species and Varieties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Influence of Elevated Carbon Dioxide on Photosynthetic Parameters
2.2. The Emission of Volatile Organic Compounds from Plants under Elevated Carbon Dioxide
2.3. The Influence of Elevated Carbon Dioxide on Chlorophylls and β-Carotene
2.4. The Change in Total Phenol Concentration for Plants Grown at Different Carbon Dioxide Concentration
2.5. The Influence of Elevated Carbon Dioxide on Flavonoids Content in the Leaves of Brasicacea Plants
2.6. Microscopic Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Photosynthetic Measurements
4.3. Volatile Sampling and GC–MS Analyses
4.4. Chromatographic Analysis of Photosynthetic Pigments
4.5. Flavonoid Content Analysis
4.6. Total Phenolic Content—Folin–Ciocalteu Method
4.7. Microscopy Analyses
4.8. Statistical Analysis and Data Handling
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; p. 1132. [Google Scholar]
- Ishigooka, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Kuwagata, T.; Nishimori, M.; Wakatsuki, H. Revision of estimates of climate change impacts on rice yield and quality in Japan by considering the combined effects of temperature and CO2 concentration. J. Agric. Meteorol. 2021, 77, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyer, C.P.O.; Leuzinger, S.; Rammig, A.; Wolf, A.; Bartholomeus, R.P.; Bonfante, A.; de Lorenzi, F.; Dury, M.; Gloning, P.; Abou Jaoudé, R.; et al. A plant’s perspective of extremes: Terrestrial plant responses to changing climatic variability. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlyn, B.E.; Barton, C.V.M.; Broadmeadow, M.S.J.; Ceulemans, R.; De Angelis, P.; Forstreuter, M.; Freeman, M.; Jackson, S.B.; Kellomäki, S.; Laitat, E.; et al. Stomatal conductance of forest species after long-term exposure to elevated CO2 concentration: A synthesis. New Phytol. 2001, 149, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, B.G.; Gonzàlez-Meler, M.A.; Long, S.P. More efficient plants: A Consequence of Rising Atmospheric CO2? Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1997, 48, 609–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cernusak, L.A.; Haverd, V.; Brendel, O.; Le Thiec, D.; Guehl, J.M.; Cuntz, M. Robust response of terrestrial plants to rising CO2. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainsworth, E.A.; Leakey, A.D.B.; Ort, D.R.; Long, S.P. FACE-ing the facts: Inconsistencies and interdependence among field, chamber and modeling studies of elevated [CO2] impacts on crop yield and food supply. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Heckathorn, S.A.; Wang, X.; Philpott, S.M. A meta-analysis of plant physiological and growth responses to temperature and elevated CO2. Oecologia 2012, 169, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, E.A.; Rogers, A.; Blum, H.; Nösberger, J.; Long, S.P. Variation in acclimation of photosynthesis in Trifolium repens after eight years of exposure to Free Air CO2 Enrichment (FACE). J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 2769–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.; Humphries, S.W. A mechanistic evaluation of photosynthetic acclimation at elevated CO2. Glob. Change Biol. 2000, 6, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peña-Rojas, K.; Aranda, X.; Fleck, I. Stomatal limitation to CO2 assimilation and down-regulation of photosynthesis in Quercus ilex resprouts in response to slowly imposed drought. Tree Physiol. 2004, 24, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, F.; Hao, L.; Yu, J.; Guo, L.; Zhou, H.; Ma, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, M. Elevated CO2 concentration induces photosynthetic down-regulation with changes in leaf structure, non-structural carbohydrates and nitrogen content of soybean. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copolovici, L.; Popitanu, A.C.; Copolovici, D.-M. Volatile organic compound emission and residual substances from plants in light of the globally increasing CO2 level. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2021, 19, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantz, A.T.; Solomon, C.; Gog, L.; McClain, A.M.; Weraduwage, S.M.; Cruz, J.A.; Sharkey, T.D. Isoprene suppression by CO2 is not due to triose phosphate utilization (TPU) limitation. Front. For. Glob. Change 2019, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Martin, C.; Fingu Mabola, J.C.; Verheggen, F.; Wang, Z.; He, K.; Francis, F. Effects of host plants reared under elevated CO2 concentrations on the foraging behavior of different stages of corn leaf aphids Rhopalosiphum maidis. Insects 2019, 10, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daussy, J.; Staudt, M. Do future climate conditions change volatile organic compound emissions from Artemisia annua? Elevated CO2 and temperature modulate actual VOC emission rate but not its emission capacity. Atmos. Environ. X 2020, 7, 100082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, M.; Pokharel, S.S.; Li, C.; Parajulee, M.N.; Chen, F.; Fang, W. Effects of elevated CO2 on foliar soluble nutrients and functional components of tea, and population dynamics of tea aphid, Toxoptera aurantii. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 145, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.C.; War, A.R.; Pathania, M.; Sharma, S.P.; Akbar, S.M.; Munghate, R.S. Elevated CO2 influences host plant defense response in chickpea against Helicoverpa armigera. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2016, 10, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, Y.; Arantes-Garcia, L.; Costa, M.; Nunes, B.; Rúbia, B.; Gélvez-Zúñiga, I.; Franco, A.; Fernandes, G. CO2 fertilizer effect on growth, polyphenols, and endophytes in two Baccharis species. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2020, 63, e20190302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynul Haque, M.; Hamid, A.; Khanam, M.; Biswas, D.K.; Karim, M.A.; Khaliq, Q.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Uprety, D.C. The effect of elevated CO2 concentration on leaf chlorophyll and nitrogen contents in rice during post-flowering phases. Biol. Plant. 2006, 50, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanoue, J.; Leonardos, E.D.; Khosla, S.; Hao, X.; Grodzinski, B. Effect of elevated CO2 and spectral quality on whole plant gas exchange patterns in tomatoes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-Y.; Wong, S.-L.; Weng, J.-H. Rapid light-response curve of chlorophyll fluorescence in terrestrial plants: Relationship to CO2 exchange among five woody and four fern species adapted to different light and water regimes. Plants 2021, 10, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, A.; Mina, U.; Kumar, V.; Tomer, R.; Kumar, A.; Chakrabarti, B.; Singh, R.N.; Singh, B. Effect of elevated ozone and carbon dioxide interaction on growth, yield, nutrient content and wilt disease severity in chickpea grown in Northern India. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Shang, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Song, H.; Zheng, S.; Li, M.; Xing, G. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of elevated CO2 in promoting the growth of pak choi (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis). Sci. Hortic. 2021, 288, 110318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramat, S.; Eshghizadeh, H.R.; Zahedi, M.; Nematpour, A. Growth and biochemical changes of sorghum genotypes in response to carbon dioxide and salinity interactions. Cereal Res. Commun. 2020, 48, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jia, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Cao, K.; Zhang, N.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z. The combined effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 and cadmium exposure on flavonoids in the leaves of Robinia pseudoacacia L. seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 210, 111878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, M.; Yoshida, H.; Fujiuchi, N.; Ariizumi, T.; Ezura, H.; Fukuda, N. Continuous blue lighting and elevated carbon dioxide concentration rapidly increase chlorogenic acid content in young lettuce plants. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 272, 109550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, S.; Abuelsoud, W.; Al-Sanea, M.M.; AbdElgawad, H. Elevated CO2 differently suppresses the arsenic oxide nanoparticles-induced stress in C3 (Hordeum vulgare) and C4 (Zea maize) plants via altered homeostasis in metabolites specifically proline and anthocyanin metabolism. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 166, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, E.A.; Long, S.P. What have we learned from 15 years of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE)? A meta-analytic review of the responses of photosynthesis, canopy properties and plant production to rising CO2. New Phytol. 2005, 165, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, S.; Jellings, A.; Fuller, M. Positive effects of elevated CO2 and its interaction with nitrogen on safflower physiology and growth. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radoglou, K.M.; Aphalo, P.; Jarvis, P.G. Response of photosynthesis, stomatal conductance and water use efficiency to elevated CO2 and nutrient supply in acclimated seedlings of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Ann. Bot. 1992, 70, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centritto, M.; Nascetti, P.; Petrilli, L.; Raschi, A.; Loreto, F. Profiles of isoprene emission and photosynthetic parameters in hybrid poplars exposed to free air CO2 enrichmen. Plant Cell Environ. 2004, 27, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Hüve, K.; Vislap, V.; Niinemets, Ü. Elevated CO2 magnifies isoprene emissions under heat and improves thermal resistance in hybrid aspen. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 5509–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomson, G.; Mollah, M.R.; Partington, D.L.; Jones, R.; Argall, R.; Tregenza, J.; Fitzgerald, G.J. Effects of elevated carbon dioxide and soil nitrogen on growth of two leafy Brassica vegetables. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2013, 41, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karowe, D.N.; Grubb, C. Elevated CO2 increases constitutive phenolics and trichomes, but decreases inducibility of phenolics in Brassica rapa (Brassicaceae). J. Chem. Ecol. 2011, 37, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.-G.; Long, S.P.; Ort, D.R. Improving photosynthetic efficiency for greater yield. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 235–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirose, T.; Ackerly, D.D.; Traw, M.B.; Bazzaz, F.A. Effects of CO2 elevation on canopy development in the stands of two co-occurring annuals. Oecologia 1996, 108, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baligar, V.C.; Elson, M.K.; Almeida, A.-A.F.; de Araujo, Q.R.; Ahnert, D.; He, Z. The Impact of carbon dioxide concentrations and low to adequate photosynthetic photon flux density on growth, physiology and nutrient use efficiency of juvenile cacao genotypes. Agronomy 2021, 11, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Gruda, N.; Lam, S.K.; Li, X.; Duan, Z. Effects of elevated CO2 on nutritional quality of vegetables: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, B.; Zhou, G. Elevated-CO2 response of stomata and its dependence on environmental factors. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negi, J.; Hashimoto-Sugimoto, M.; Kusumi, K.; Iba, K. New approaches to the biology of stomatal guard cells. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 55, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Negi, J.; Wang, C.; Isogai, Y.; Schroeder, J.I.; Iba, K. The transmembrane region of guard cell SLAC1 channels perceives CO2 signals via an ABA-independent pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wand, S.J.E.; Midgley, G.F.; Jones, M.H.; Curtis, P.S. Responses of wild C4 and C3 grass (Poaceae) species to elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration: A meta-analytic test of current theories and perceptions. Glob. Change Biol. 1999, 5, 723–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sreeharsha, R.V.; Sekhar, K.M.; Reddy, A.R. Delayed flowering is associated with lack of photosynthetic acclimation in Pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan L.) grown under elevated CO2. Plant Sci. 2015, 231, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Negi, J.; Young, J.; Israelsson, M.; Schroeder, J.I.; Iba, K. Arabidopsis HT1 kinase controls stomatal movements in response to CO2. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cao, J.; Wu, Y.; Kong, F.; Li, L. Review on plant terpenoid emissions worldwide and in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popitanu, C.; Lupitu, A.; Copolovici, L.; Bungău, S.; Niinemets, Ü.; Copolovici, D.M. Induced volatile emissions, photosynthetic characteristics, and pigment content in Juglans regia leaves infected with the Erineum-forming mite Aceria erinea. Forests 2021, 12, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Staudt, M. BVOCs and global change. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuorinen, T.; Reddy, G.V.P.; Nerg, A.-M.; Holopainen, J.K. Monoterpene and herbivore-induced emissions from cabbage plants grown at elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himanen, S.J.; Nerg, A.-M.; Nissinen, A.I.; Pinto, D.M.L.; Stewart, C.N.; Poppy, G.M.; Holopainen, J.K. Effects of elevated carbon dioxide and ozone on volatile terpenoid emissions and multitrophic communication of transgenic insecticidal oilseed rape (Brassica napus). New Phytol. 2009, 181, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudt, M.; Joffre, R.; Rambal, S.; Kesselmeier, J. Effect of elevated CO2 on monoterpene emission of young Quercus ilex trees and its relation to structural and ecophysiological parameters. Tree Physiol. 2001, 21, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loreto, F.; Fischbach, R.J.; Schnitzler, J.-P.; Ciccioli, P.; Brancaleoni, E.; Calfapietra, C.; Seufert, G. Monoterpene emission and monoterpene synthase activities in the Mediterranean evergreen oak Quercus ilex L. grown at elevated CO2 concentrations. Glob. Change Biol. 2001, 7, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety, D.C.; Mahalaxmi, V. Effect of elevated CO2 and nitrogen nutrition on photosynthesis, growth and carbon-nitrogen balance in Brassica juncea. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2000, 184, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, W.J.; Julkunen-Tiitto, R.; Herms, D.A. CO2 enrichment and carbon partitioning to phenolics: Do plant responses accord better with the protein competition or the growth differentiation balance models? Oikos 2005, 111, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goufo, P.; Pereira, J.; Moutinho-Pereira, J.; Correia, C.M.; Figueiredo, N.; Carranca, C.; Rosa, E.A.S.; Trindade, H. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) phenolic compounds under elevated carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 99, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, K.L.; Anderson, O.R.; Gastrich, M.D.; Lewis, J.D.; Lin, G.; Schuster, W.; Seemann, J.R.; Tissue, D.T.; Turnbull, M.H.; Whitehead, D. Plant growth in elevated CO2 alters mitochondrial number and chloroplast fine structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2473–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Copolovici, L.; Pag, A.; Kännaste, A.; Bodescu, A.; Tomescu, D.; Copolovici, D.; Soran, M.-L.; Niinemets, Ü. Disproportionate photosynthetic decline and inverse relationship between constitutive and induced volatile emissions upon feeding of Quercus robur leaves by large larvae of gypsy moth (Lymantria dispar). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2017, 138, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niinemets, Ü.; Copolovici, L.; Hüve, K. High within-canopy variation in isoprene emission potentials in temperate trees: Implications for predicting canopy-scale isoprene fluxes. J. Geophys. Res.-Biogeosci. 2010, 115, G04029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Copolovici, L.; Lupitu, A.; Moisa, C.; Taschina, M.; Copolovici, D.M. The effect of antagonist abiotic stress on bioactive compounds from basil (Ocimum basilicum). Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opriş, O.; Copaciu, F.; Soran, M.L.; Ristoiu, D.; Niinemets, Ü.; Copolovici, L. Influence of nine antibiotics on key secondary metabolites and physiological characteristics in Triticum aestivum: Leaf volatiles as a promising new tool to assess toxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 87, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisa, C.; Copolovici, L.; Pop, G.; Imbrea, I.; Lupitu, A.; Nemeth, S.; Copolovici, D. Wastes resulting from aromatic plants distillation-bio-sources of antioxidants and phenolic compounds with biological active principles. Farmacia 2018, 66, 289–295. [Google Scholar]
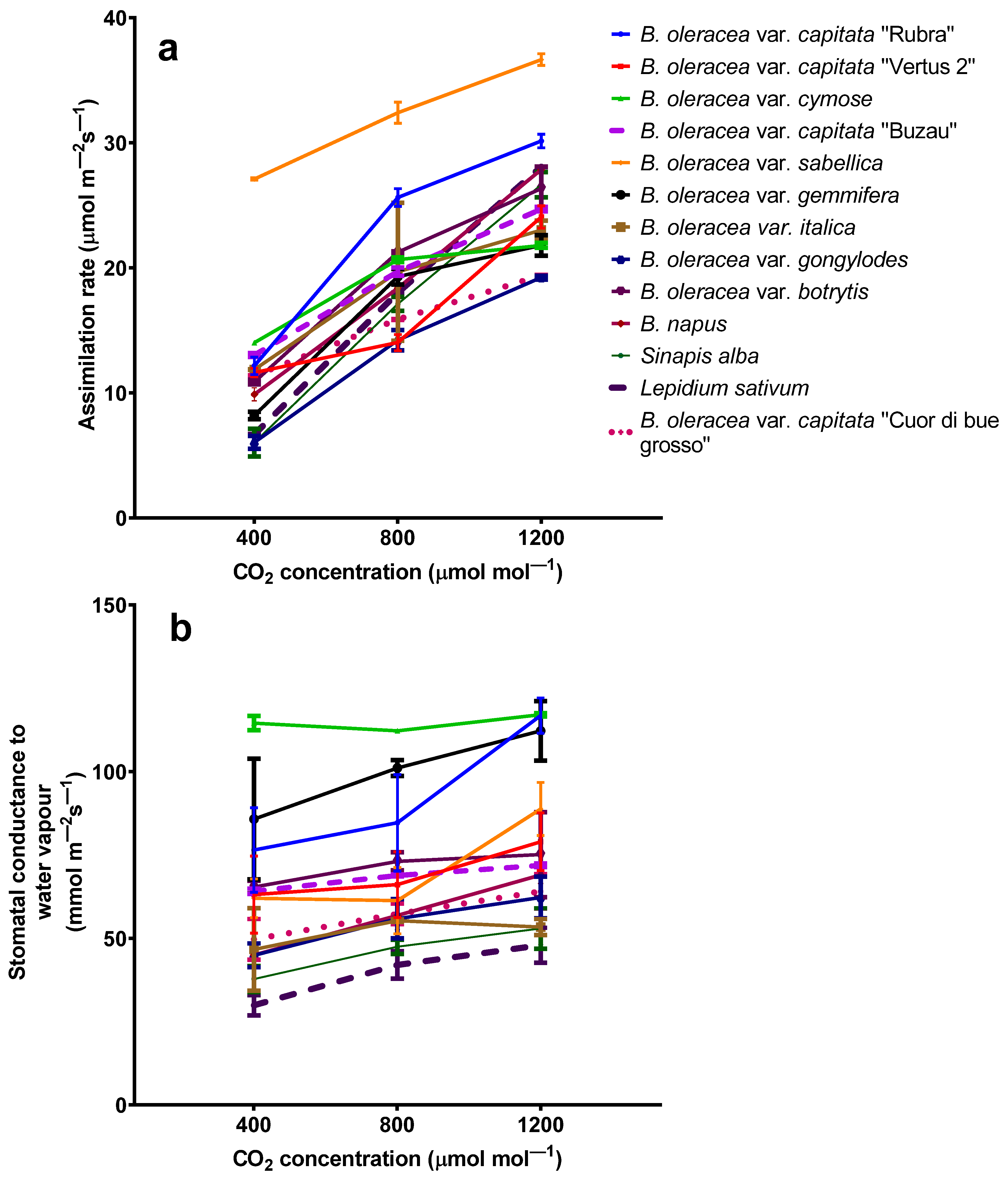

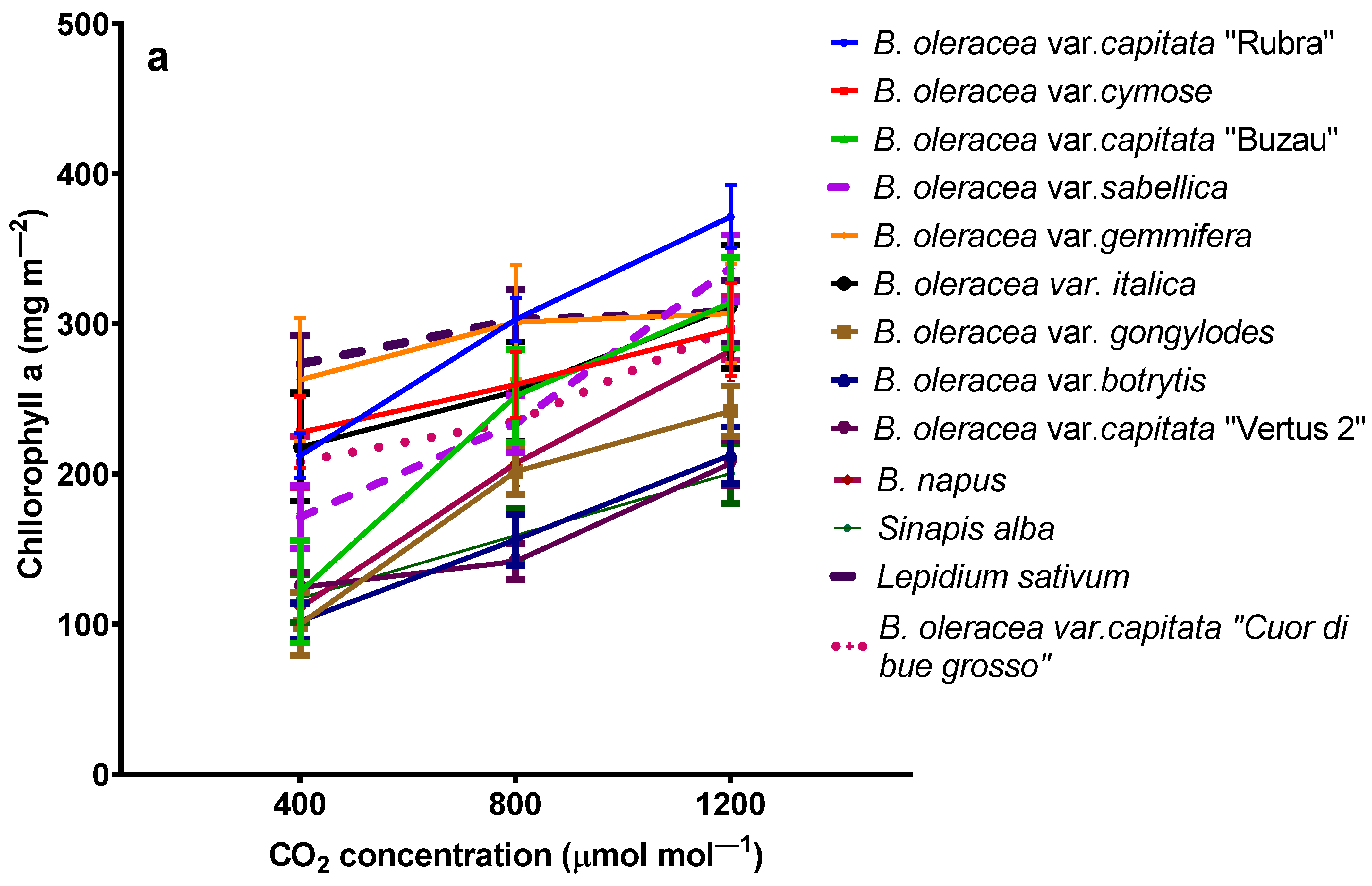





| Plant Characteristic | Effect * | Species | Elevated Carbon Dioxide Concentration (ppmv) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assimilation rate | ↑ | Trifolium repens | 600 | [9] |
| ↑ | Triticum aestivum | 583 | [7] | |
| ↑ | Oryza sativa | 475–600 | [29] | |
| ↑ | Glycine max | 475–600 | [29] | |
| ↑ | Carthamus tinctorius | 1000 | [30] | |
| ↑ | Phaseolus vulgaris L. | 700 | [31] | |
| ↑ | Populus × euroamericana | 550 | [32] | |
| ↑ | Camellia sinensis | 770 | [17] | |
| ↑ | Oryza sativa L. | 570 | [20] | |
| Isoprene emission | ↓ | Phragmites australis | 800 | [14] |
| ↓ | Platanus × acerfolia | 800 | [14] | |
| ↓ | Populas nigra × maximowiczii NM6 | 800 | [14] | |
| ↓ | Populus × euroamericana | 550 | [32] | |
| ↔ | Populus tremula × Populus tremuloides | 780 | [33] | |
| Total phenols | ↑ | Camellia sinensis | 770 | [17] |
| ↑ | Cicer arietinum | 750 | [18] | |
| ↑ | Baccharis dracunculifolia | 750–800 | [19] | |
| ↑ | Baccharis platypoda | 750–800 | [19] | |
| Chlorophylls concentration | ↓ | Oryza sativa L. | 570 | [20] |
| ↓ | Solanum lycopersicum | 1000 | [21] | |
| ↑ | Cicer arietinum | 700 | [23] | |
| ↑ | Brassica rapa | 800 | [24] | |
| ↑ | Sorghum bicolor | 700 | [25] | |
| ↔ | Carthamus tinctorius | 1000 | [30] | |
| Total flavonoids | ↑ | Robinia pseudoacacia L. | 750 | [26] |
| ↓ | Hordeum vulgare | 620 | [28] | |
| ↓ | Zea maize | 620 | [28] |
| Source of Variation | Assimilation Rate | Stomata Conductance | Monoterpene Emission | Chlorophyll a | Chlorophyll b | β-carotene | Flavonoids | Polyphenols |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df, MS, F, p Value | df, MS, F, p Value | df, MS, F, p Value | df, MS, F, p Value | df, MS, F, p Value | df, MS, F, p Value | df, MS, F, p Value | df, MS, F, p Value | |
| Carbon dioxide | 2, 3182, 2849, <0.0001 | 2, 4907, 97.81, <0.0001 | 2, 0.0406, 1671, <0.0001 | 2, 119,198, 214.2, <0.0001 | 2, 39,098, 130.2, <0.0001 | 2, 1127, 44.26, <0.0001 | 2, 0.00333, 265.4, <0.0001 | 2, 2573, 5178, <0.0001 |
| Species/varieties | 12, 313.2, 280.4, <0.0001 | 12, 7206, 143.6, <0.0001 | 12, 0.0724, 2979, <0.0001 | 12, 25,178, 45.24, <0.0001 | 12, 10,211, 34.01, <0.0001 | 12, 389.9, 15.31, <0.0001 | 12, 0.00629, 501.0, <0.0001 | 12, 22,126, 44,530, <0.0001 |
| Error | 174.2 | 7827 | 0.001895 | 43,406 | 23,416 | 1986 | 0.001958 | 38.76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lupitu, A.; Moisa, C.; Gavrilaş, S.; Dochia, M.; Chambre, D.; Ciutină, V.; Copolovici, D.M.; Copolovici, L. The Influence of Elevated CO2 on Volatile Emissions, Photosynthetic Characteristics, and Pigment Content in Brassicaceae Plants Species and Varieties. Plants 2022, 11, 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11070973
Lupitu A, Moisa C, Gavrilaş S, Dochia M, Chambre D, Ciutină V, Copolovici DM, Copolovici L. The Influence of Elevated CO2 on Volatile Emissions, Photosynthetic Characteristics, and Pigment Content in Brassicaceae Plants Species and Varieties. Plants. 2022; 11(7):973. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11070973
Chicago/Turabian StyleLupitu, Andreea, Cristian Moisa, Simona Gavrilaş, Mihaela Dochia, Dorina Chambre, Virgiliu Ciutină, Dana Maria Copolovici, and Lucian Copolovici. 2022. "The Influence of Elevated CO2 on Volatile Emissions, Photosynthetic Characteristics, and Pigment Content in Brassicaceae Plants Species and Varieties" Plants 11, no. 7: 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11070973
APA StyleLupitu, A., Moisa, C., Gavrilaş, S., Dochia, M., Chambre, D., Ciutină, V., Copolovici, D. M., & Copolovici, L. (2022). The Influence of Elevated CO2 on Volatile Emissions, Photosynthetic Characteristics, and Pigment Content in Brassicaceae Plants Species and Varieties. Plants, 11(7), 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11070973








