MBD3 Regulates Male Germ Cell Division and Sperm Fertility in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
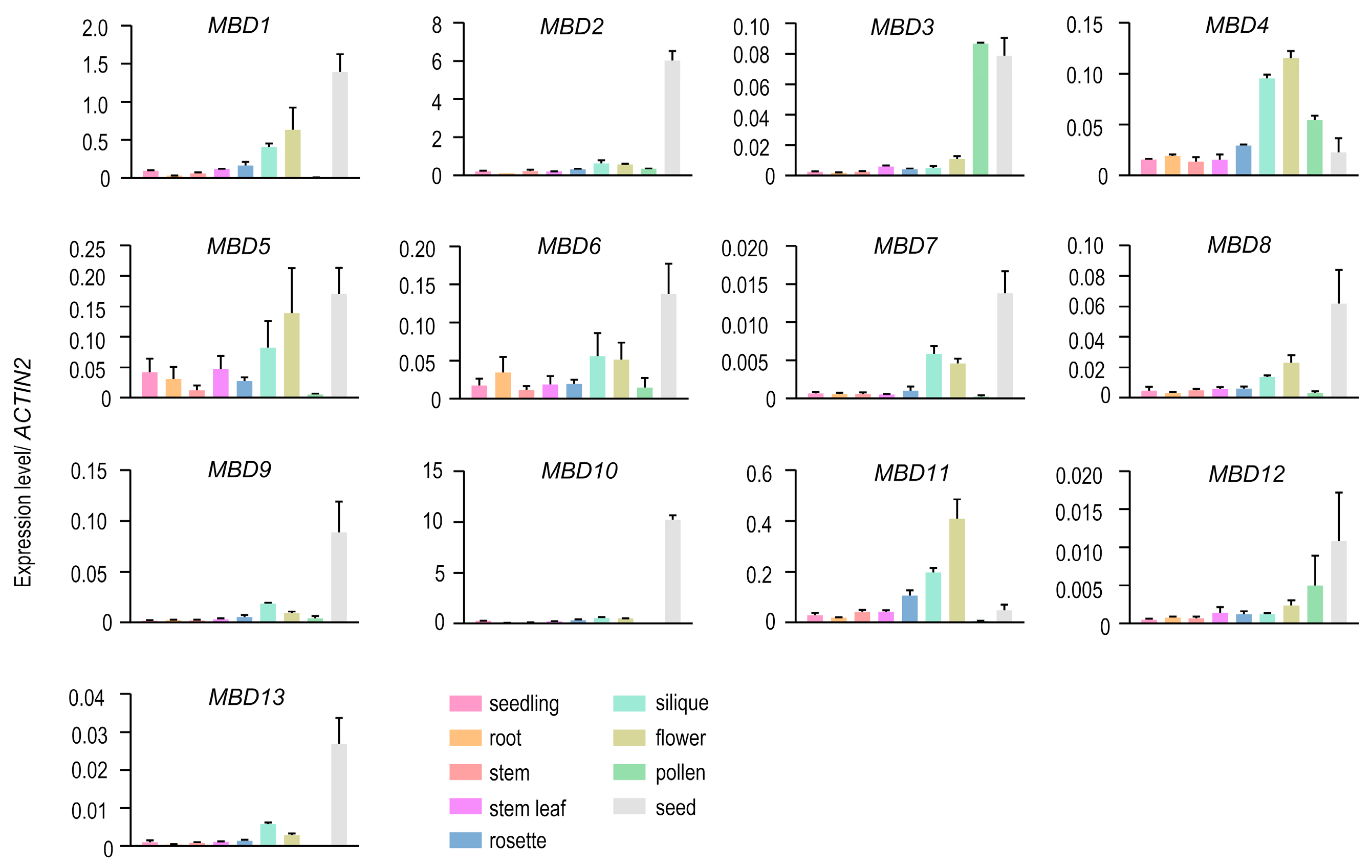
2.1. AtMBD3 Was Highly Expressed in Pollen and Seeds
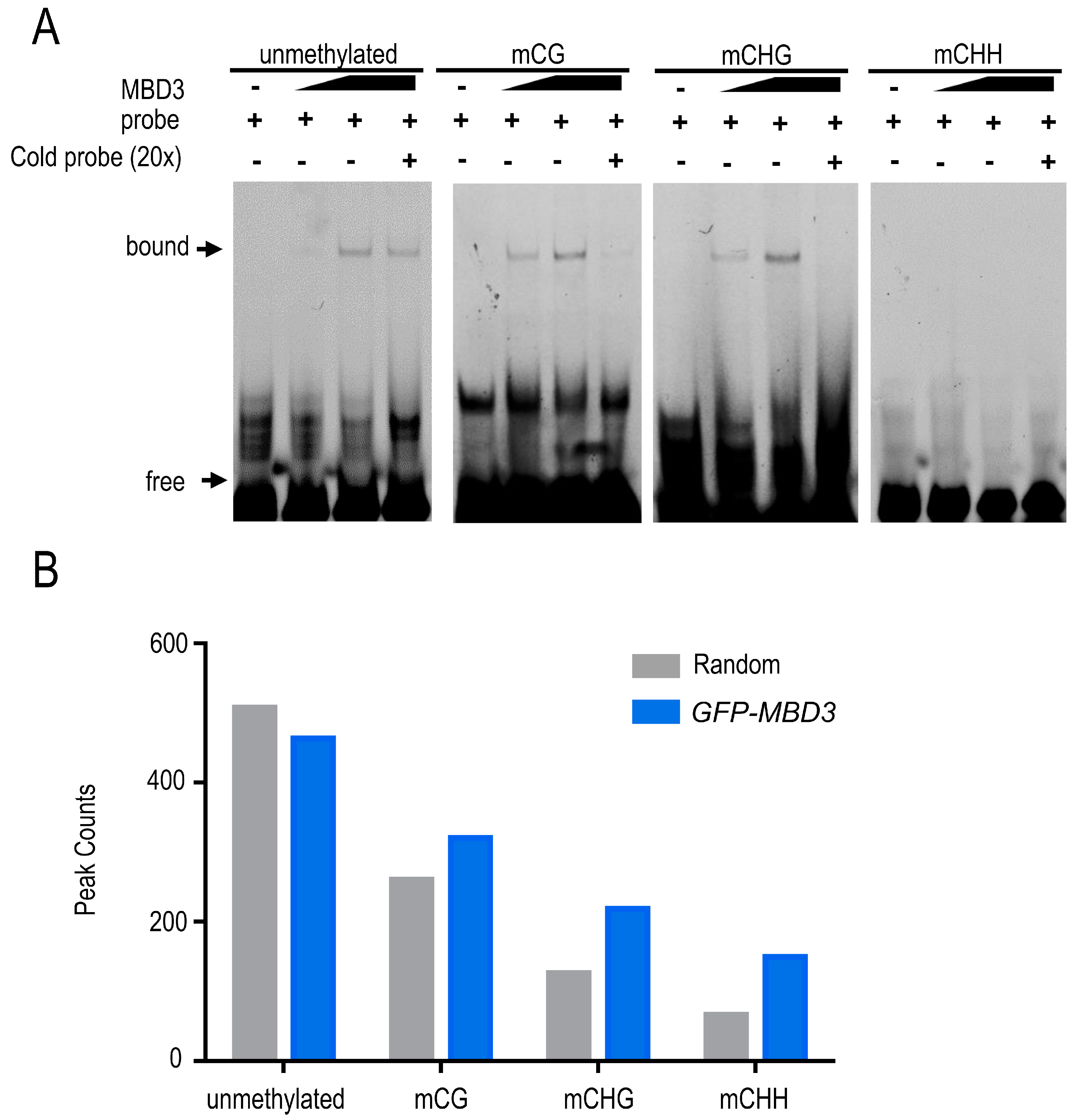
2.2. AtMBD3 Preferred to Bind Symmetric Methylated and Unmethylated Sequences
2.3. MBD3 Is Important for Plant Embryo Development
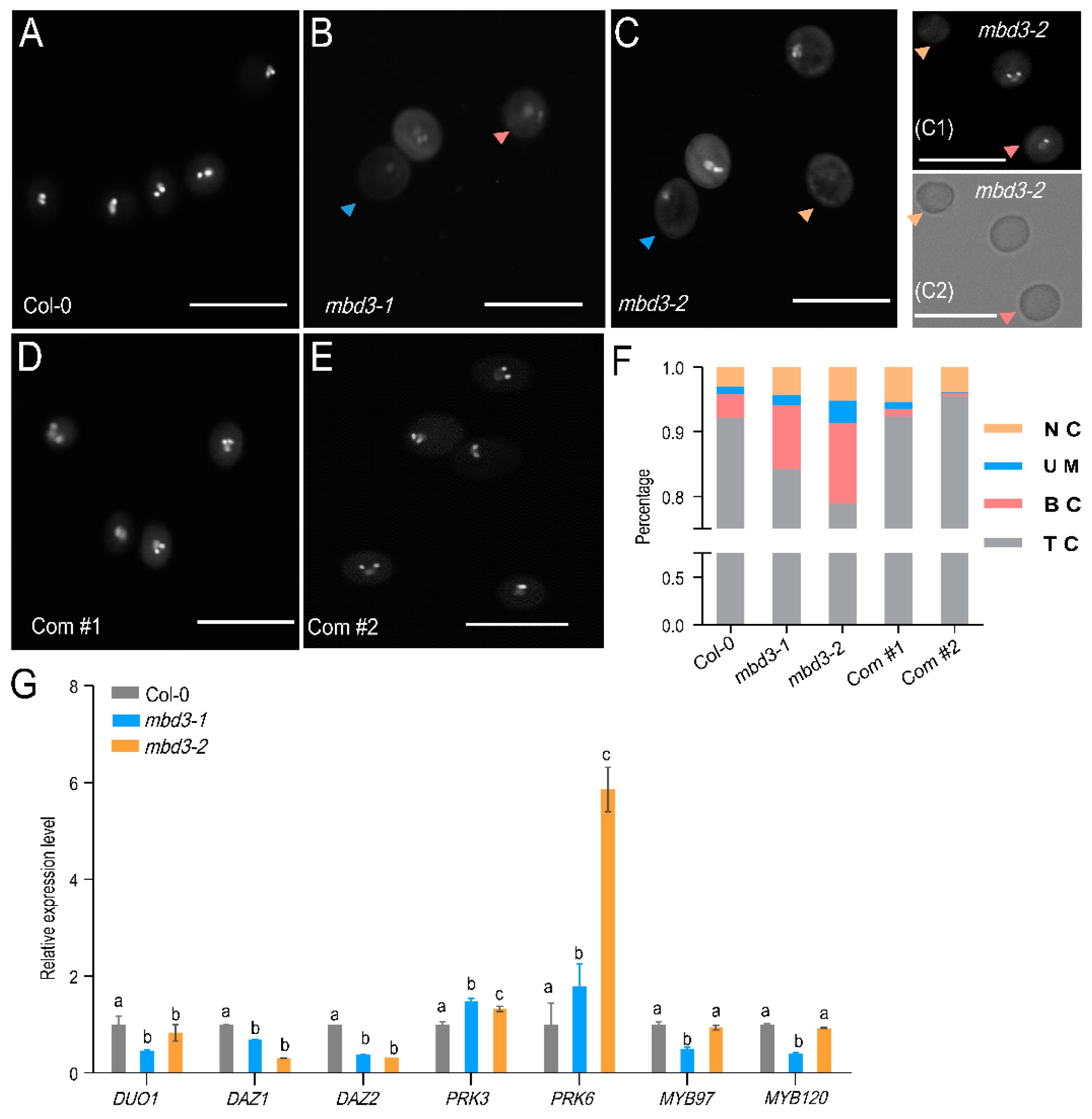
2.4. MBD3 Mutation Impairs Pollen Development
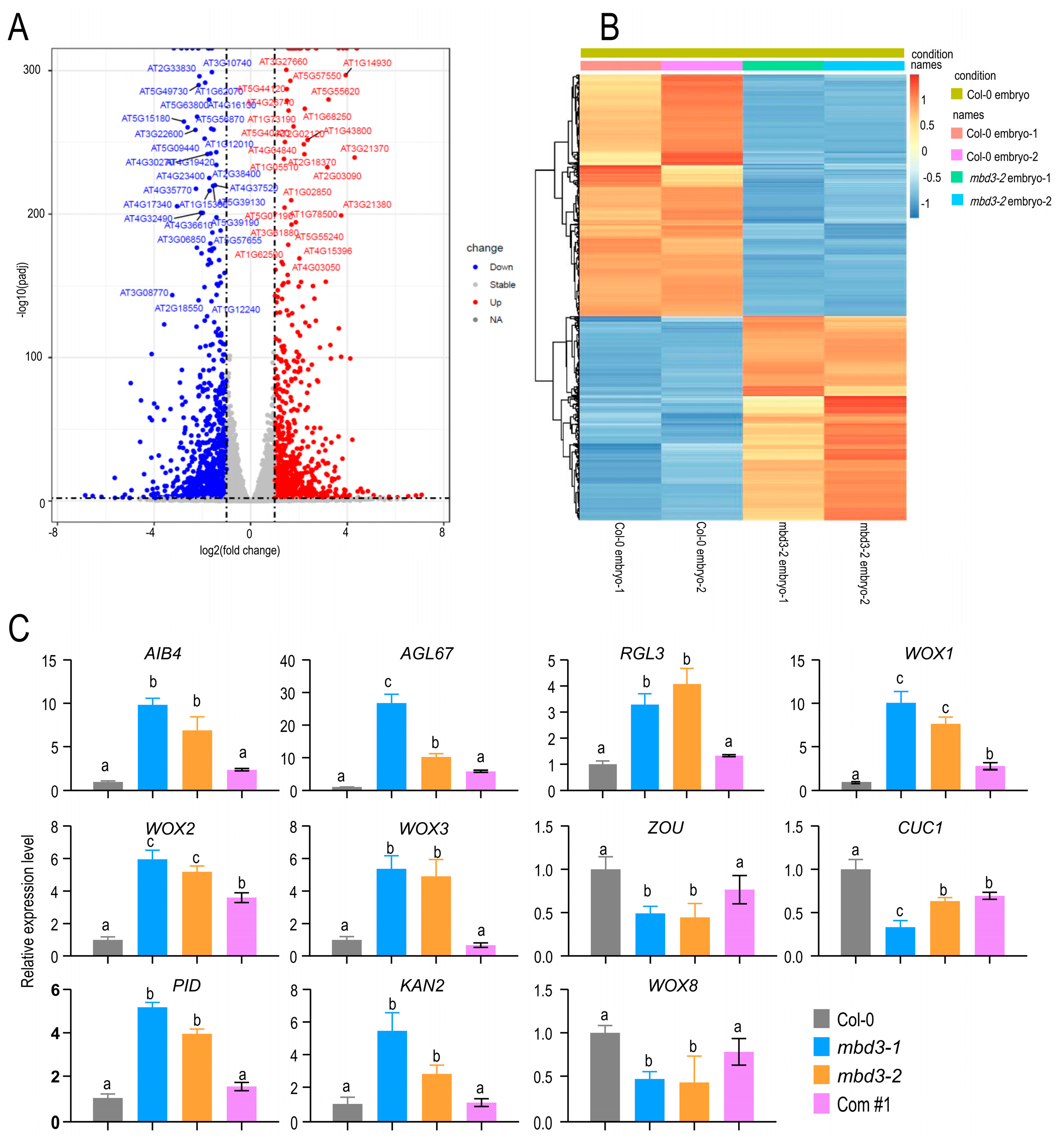
2.5. mbd3 Embryo Development Delay Caused by Asymmetric Divisions
2.6. Interaction Protein Screening of AtMBD3
3. Discussion
3.1. MBD3 Have the Ability to Bind Sequences More than Methylated DNA
3.2. MBD3 Participates in Embryo Development with Other Genes
3.3. MBD3 Regulates Pollen and Embryo Development with Other Genes
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of MBD Genes
4.3. Generation of the CRISPR Allele of mbd3 Mutants
4.4. ChIP-seq
4.5. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
4.6. Affinity Purification and Mass Spectrometry
4.7. Microscopy Analysis
4.8. Alexander Dye and 4′,6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole Staining
4.9. In Vitro Pollen Germination Analysis
4.10. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR (qPCR)
4.11. Yeast Two-Hybrid Screening
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suzuki, M.M.; Bird, A. DNA methylation landscapes: Provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Custard, K.D.; Brown, R.C.; Lemmon, B.E.; Harada, J.J.; Goldberg, R.B.; Fischer, R.L. DNA methylation is critical for Arabidopsis embryogenesis and seed viability. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamauchi, T.; Johzuka-Hisatomi, Y.; Terada, R.; Nakamura, I.; Iida, S. The MET1b gene encoding a maintenance DNA methyltransferase is indispensable for normal development in rice. Plant. Mol. Biol. 2014, 85, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Tarutani, Y.; Miyao, A.; Ito, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Sakai, H.; Fukai, E.; Hirochika, H. Loss of function mutations in the rice chromomethylase OsCMT3a cause a burst of transposition. Plant J. 2015, 83, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Eichten, S.R.; Hermanson, P.J.; Zaunbrecher, V.M.; Song, J.; Wendt, J.; Rosenbaum, H.; Madzima, T.F.; Sloan, A.E.; Huang, J.; et al. Genetic perturbation of the maize methylome. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 4602–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Yazaki, J.; Sundaresan, A.; Cokus, S.; Chan, S.W.L.; Chen, H.; Henderson, I.R.; Shinn, P.; Pellegrini, M.; Jacobsen, S.E.; et al. Genome-wide High-Resolution Mapping and Functional Analysis of DNA Methylation in Arabidopsis. Cell 2006, 126, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cokus, S.J.; Feng, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Merriman, B.; Haudenschild, C.D.; Pradhan, S.; Nelson, S.F.; Pellegrini, M.; Jacobsen, S.E. Shotgun bisulphite sequencing of the Arabidopsis genome reveals DNA methylation patterning. Nature 2008, 452, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bogdanović, O.; Veenstra, G.J.C. DNA methylation and methyl-CpG binding proteins: Developmental requirements and function. Chromosoma 2009, 118, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unoki, M.; Nishidate, T.; Nakamura, Y. ICBP90, an E2F-1 target, recruits HDAC1 and binds to methyl-CpG through its SRA domain. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7601–7610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filion, G.J.P.; Zhenilo, S.; Salozhin, S.; Yamada, D.; Prokhortchouk, E.; Defossez, P.-A. A Family of Human Zinc Finger Proteins That Bind Methylated DNA and Repress Transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bird, A.; Nan, X.; Ng, H.-H.; Johnson, C.A.; Laherty, C.D.; Turner, B.M.; Eisenman, R.N. Transcriptional repression by the methyl-CpG-binding protein MeCP2 involves a histone deacetylase complex. Nature 1998, 393, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolffe, A.P.; Jones, P.L.; Jan Veenstra, G.C.; Wade, P.A.; Vermaak, D.; Kass, S.U.; Landsberger, N.; Strouboulis, J. Methylated DNA and MeCP2 recruit histone deacetylase to repress transcription. Nat. Genet. 1998, 19, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, N.M.; Kaeppler, S.M. Evolutionary Divergence of Monocot and Dicot Methyl-CpG-Binding Domain Proteins. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zemach, A.; Gideon, G. Characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana methyl-CpG-binding domain (MBD) proteins. Plant J. 2003, 34, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemach, A.; Grafi, G. Methyl-CpG-binding domain proteins in plants: Interpreters of DNA methylation. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, A.P.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, A.K. AtMBD4: A methylated DNA binding protein negatively regulates a subset of phosphate starvation genes. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, A.; Kodama, Y.; Koike, A.; Shinya, T.; Kim, H.-J.; Matsumoto, M.; Ogita, S.; Wada, Y.; Ohad, N.I.R.; Sano, H. Interaction Between Methyl CpG-Binding Protein and Ran GTPase during Cell Division in Tobacco Cultured Cells. Ann. Bot. 2006, 98, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Dong, X.; Jin, D.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, S.; Li, X.; He, X.; Lang, Z.; Lai, J.; Zhu, J.-K.; et al. Methyl-CpG-Binding Domain Protein MBD7 Is Required for Active DNA Demethylation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lang, Z.; Lei, M.; Wang, X.; Tang, K.; Miki, D.; Zhang, H.; Mangrauthia, S.K.; Liu, W.; Nie, W.; Ma, G.; et al. The Methyl-CpG-Binding Protein MBD7 Facilitates Active DNA Demethylation to Limit DNA Hyper-Methylation and Transcriptional Gene Silencing. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stangeland, B.; Rosenhave, E.M.; Winge, P.; Berg, A.; Amundsen, S.S.; Karabeg, M.; Mandal, A.; Bones, A.M.; Grini, P.E.; Aalen, R.B. AtMBD8 is involved in control of flowering time in the C24 ecotype of Arabidopsis thaliana. Physiol. Plant 2009, 136, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Cui, Y.; Bi, Y.M.; Rothstein, S.J. AtMBD9: A protein with a methyl-CpG-binding domain regulates flowering time and shoot branching in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2006, 46, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.; Meza, T.J.; Mahic, M.; Thorstensen, T.; Kristiansen, K.; Aalen, R.B. Ten members of the Arabidopsis gene family encoding methyl-CpG-binding domain proteins are transcriptionally active and at least one, AtMBD11, is crucial for normal development. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 5291–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hendrich, B.; Guy, J.; Ramsahoye, B.; Wilson, V.A.; Bird, A. Closely related proteins MBD2 and MBD3 play distinctive but interacting roles in mouse development. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, P.; Kapoor, S.; Tyagi, A.K. Transcription factors regulating the progression of monocot and dicot seed development. Bioessays 2011, 33, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrash, E.B.; Bergmann, D.C. Asymmetric cell divisions: A view from plant development. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjamins, R.; Quint, A.; Weijers, D.; Hooykaas, P.; Offringa, R. The PINOID protein kinase regulates organ development in Arabidopsis by enhancing polar auxin transport. Development 2001, 128, 4057–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penfield, S.; Li, Y.; Gilday, A.D.; Graham, S.; Graham, I.A. Arabidopsis ABA INSENSITIVE4 Regulates Lipid Mobilization in the Embryo and Reveals Repression of Seed Germination by the Endosperm. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 1887–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Johnston, N.; Talideh, E.; Mitchell, S.; Jeffree, C.; Goodrich, J.; Ingram, G. The endosperm-specific ZHOUPI gene of Arabidopsis thaliana regulates endosperm breakdown and embryonic epidermal development. Development 2008, 135, 3501–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehti-Shiu, M.D.; Adamczyk, B.J.; Fernandez, D.E. Expression of MADS-box genes during the embryonic phase in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 58, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lang, Z.; Zhu, J.-K. Dynamics and function of DNA methylation in plants. Nat. Rev. 2018, 19, 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scebba, F.; Bernacchia, G.; De Bastiani, M.; Evangelista, M.; Cantoni, R.M.; Cella, R.; Locci, M.T.; Pitto, L. Arabidopsis MBD proteins show different binding specificities and nuclear localization. Plant Mol. Biol. 2003, 53, 755–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, H.L.; McNae, L.W.; Schmiedeberg, L.; Klose, R.J.; Bird, A.; Walkinshaw, M.D. MeCP2 binding to DNA depends upon hydration at methyl-CpG. Mol. Cell 2008, 29, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ichino, L.; Boone, B.A.; Strauskulage, L.; Harris, C.J.; Kaur, G.; Gladstone, M.A.; Tan, M.; Feng, S.; Jami-Alahmadi, Y.; Duttke, S.H.; et al. MBD5 and MBD6 couple DNA methylation to gene silencing through the J-domain protein SILENZIO. Science 2021, 372, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Li, N.; Xu, C.; Zhong, S.; Lin, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, T.; Yuliang, A.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.-R.; et al. Mutation of a major CG methylase in rice causes genome-wide hypomethylation, dysregulated genome expression, and seedling lethality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10642–10647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Chory, J.; Weigel, D. Combinations of WOX activities regulate tissue proliferation during Arabidopsis embryonic development. Dev. Biol. 2007, 309, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, S.K.; Dagenais, N.; Chory, J.; Weigel, D. Regulation of Auxin Response by the Protein Kinase PINOID. Cell 2000, 100, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friml, J.Y.X.; Michniewicz, M.; Weijers, D.; Quint, A.; Tietz, O.; Benjamins, R.; Ouwerkerk, P.B.; Ljung, K.; Sandberg, G.; Hooykaas, P.J.; et al. A PINOID-dependent binary switch in apical-basal PIN polar targeting directs auxin efflux. Science 2004, 306, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, S.; Fei, Z.; Chen, Y.R.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, M.; Vrebalov, J.; McQuinn, R.; Gapper, N.; Liu, B.; Xiang, J.; et al. Single-base resolution methylomes of tomato fruit development reveal epigenome modifications associated with ripening. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Butel, N.; Santos-Gonzalez, J.; Borges, F.; Yi, J.; Martienssen, R.A.; Martinez, G.; Kohler, C. Polymerase IV Plays a Crucial Role in Pollen Development in Capsella. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 950–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, J.; Gao, H.; Zhang, J.; Aldridge, B.; Vickers, M.; Higgins, J.D.; Feng, X. Sexual-lineage-specific DNA methylation regulates meiosis in Arabidopsis. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Lan, Z.; Qian, W. Deciphering the synergistic and redundant roles of CG and non-CG DNA methylation in plant development and transposable element silencing. New Phytol. 2022, 233, 722–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichino, L.; Picard, C.L.; Yun, J.; Chotai, M.; Wang, S.; Lin, E.K.; Papareddy, R.K.; Xue, Y.; Jacobsen, S.E. Single-nucleus RNA-seq reveals that MBD5, MBD6, and SILENZIO maintain silencing in the vegetative cell of developing pollen. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Wei, S.; Wu, Y.; Hu, R.; Li, H.; Yang, W.; Xie, Q. High-efficiency genome editing in Arabidopsis using YAO promoter-driven CRISPR/Cas9 system. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1820–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method forAgrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana: Floral dip transformation of Arabidopsis. Plant. J. Cell Mol. Biol. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, T.; Wang, D.; Tian, G.; Sun, L.; Yang, M.; Yin, X.; Xiao, J.; Sheng, Y.; Zhu, D.; He, H.; et al. Chromatin remodeling complexes regulate genome architecture in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 2638–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Zeng, J.; Cao, Z.; Li, Y.; Qian, W. Regulation of Active DNA Demethylation by a Methyl-CpG-Binding Domain Protein in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stroud, H.; Do, T.; Du, J.; Zhong, X.; Feng, S.; Johnson, L.; Patel, D.J.; Jacobsen, S.E. Non-CG methylation patterns shape the epigenetic landscape in Arabidopsis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

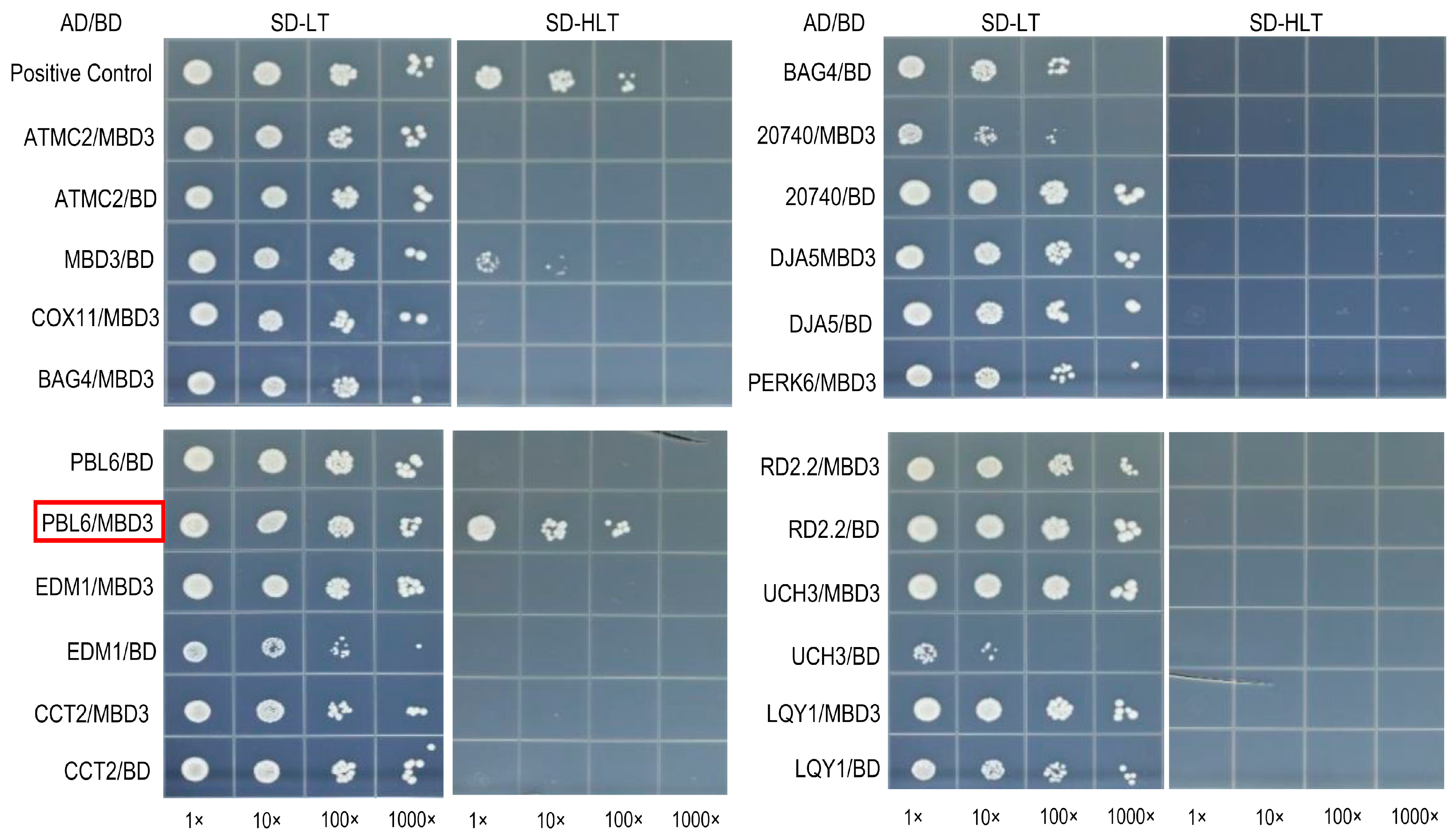
| Frequency | ID | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | AT4G25110 | ATMC2 | Encodes a type I metacaspase. |
| 11 | AT2G21620 | RD2 | Encodes a gene that is induced in response to desiccation |
| 4 | AT5G20740 | Plant invertase/pectin methylesterase inhibitor superfamily protein | |
| 4 | AT3G51780 | BAG4 | Plant homologs of mammalian regulators of apoptosis |
| 3 | AT2G28590 | PBL6 | Protein kinase superfamily protein |
| 2 | AT3G18810 | PERK6 | Encodes a member of the PERK family |
| 2 | AT4G39960 | DJA5 | Molecular chaperone Hsp40/DnaJ family protein |
| 2 | AT1G75690 | LQY1 | DnaJ/Hsp40 cysteine-rich domain superfamily protein |
| 2 | AT1G02410 | COX11 | Encodes a member of the cytochrome c oxidase 11 protein family |
| 2 | AT4G17510 | UCH3 | Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase 3 |
| 2 | AT5G20890 | CCT2 | TCP-1/cpn60 chaperonin family protein |
| 2 | AT4G11260 | EDM1 | Functions in plant-disease-resistance signaling |
| ID | Gene | Description | Unique Peptides |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT2G28590.1 | PBL6 | Protein kinase superfamily protein | 40 |
| AT4G00416.1 | MBD3 | Methyl-CPG-binding domain 3 | 7 |
| AT5G59380.1 | MBD6 | Methyl-CPG-binding domain 6 | 5 |
| AT3G46580.1 | MBD5 | Methyl-CPG-binding domain 5 | 2 |
| AT5G20890.1 | CCT2 | TCP-1/cpn60 chaperonin family protein | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, J.; Yin, X.; Liu, Y.; Mi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, A.; Guo, H.; Dong, J. MBD3 Regulates Male Germ Cell Division and Sperm Fertility in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants 2023, 12, 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12142654
Shu J, Yin X, Liu Y, Mi Y, Zhang B, Zhang A, Guo H, Dong J. MBD3 Regulates Male Germ Cell Division and Sperm Fertility in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants. 2023; 12(14):2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12142654
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Jia, Xiaochang Yin, Yannan Liu, Yingjie Mi, Bin Zhang, Aoyuan Zhang, Hongbo Guo, and Juane Dong. 2023. "MBD3 Regulates Male Germ Cell Division and Sperm Fertility in Arabidopsis thaliana" Plants 12, no. 14: 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12142654
APA StyleShu, J., Yin, X., Liu, Y., Mi, Y., Zhang, B., Zhang, A., Guo, H., & Dong, J. (2023). MBD3 Regulates Male Germ Cell Division and Sperm Fertility in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants, 12(14), 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12142654








