Inheritance of Fruit Red-Flesh Patterns in Peach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
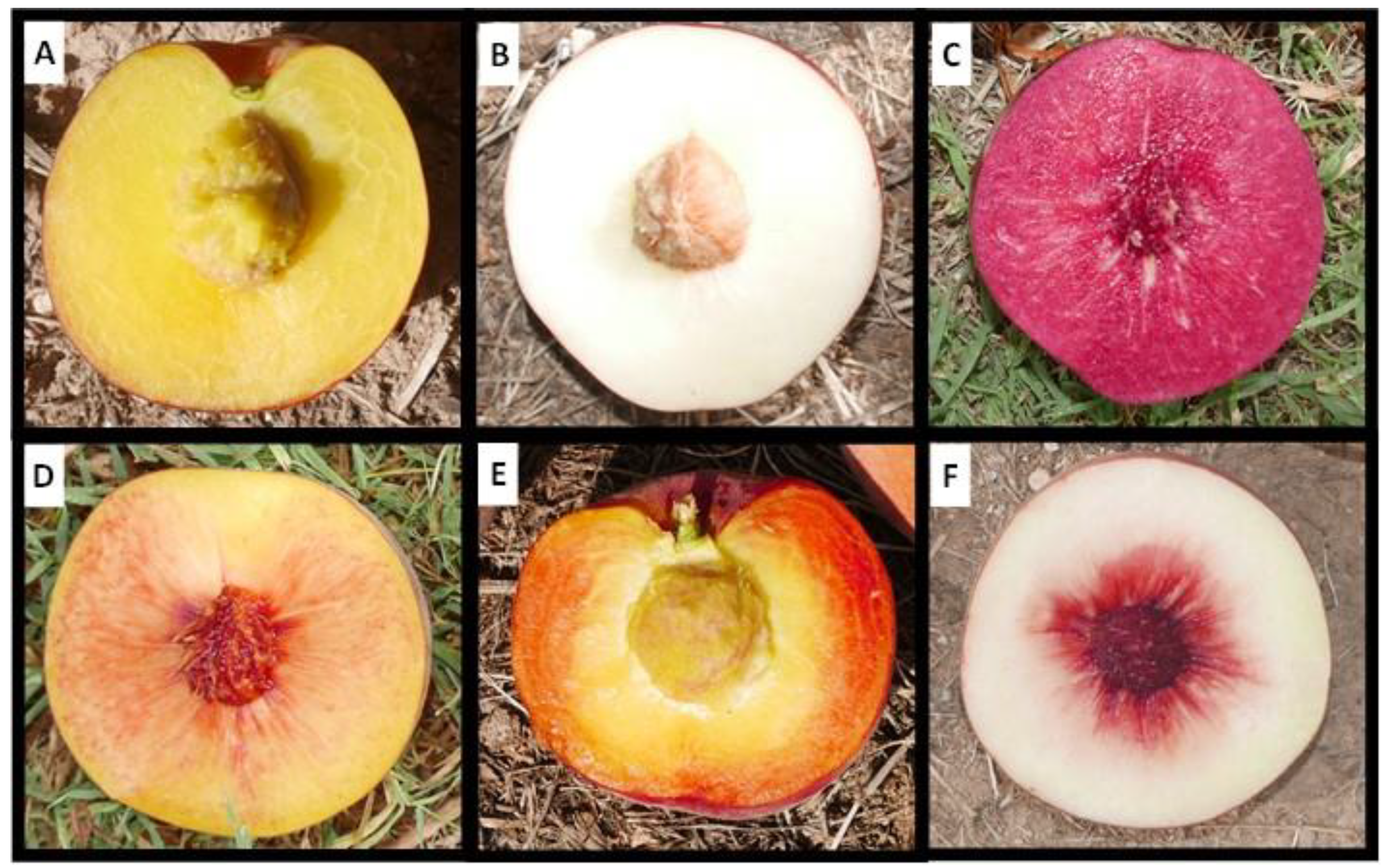
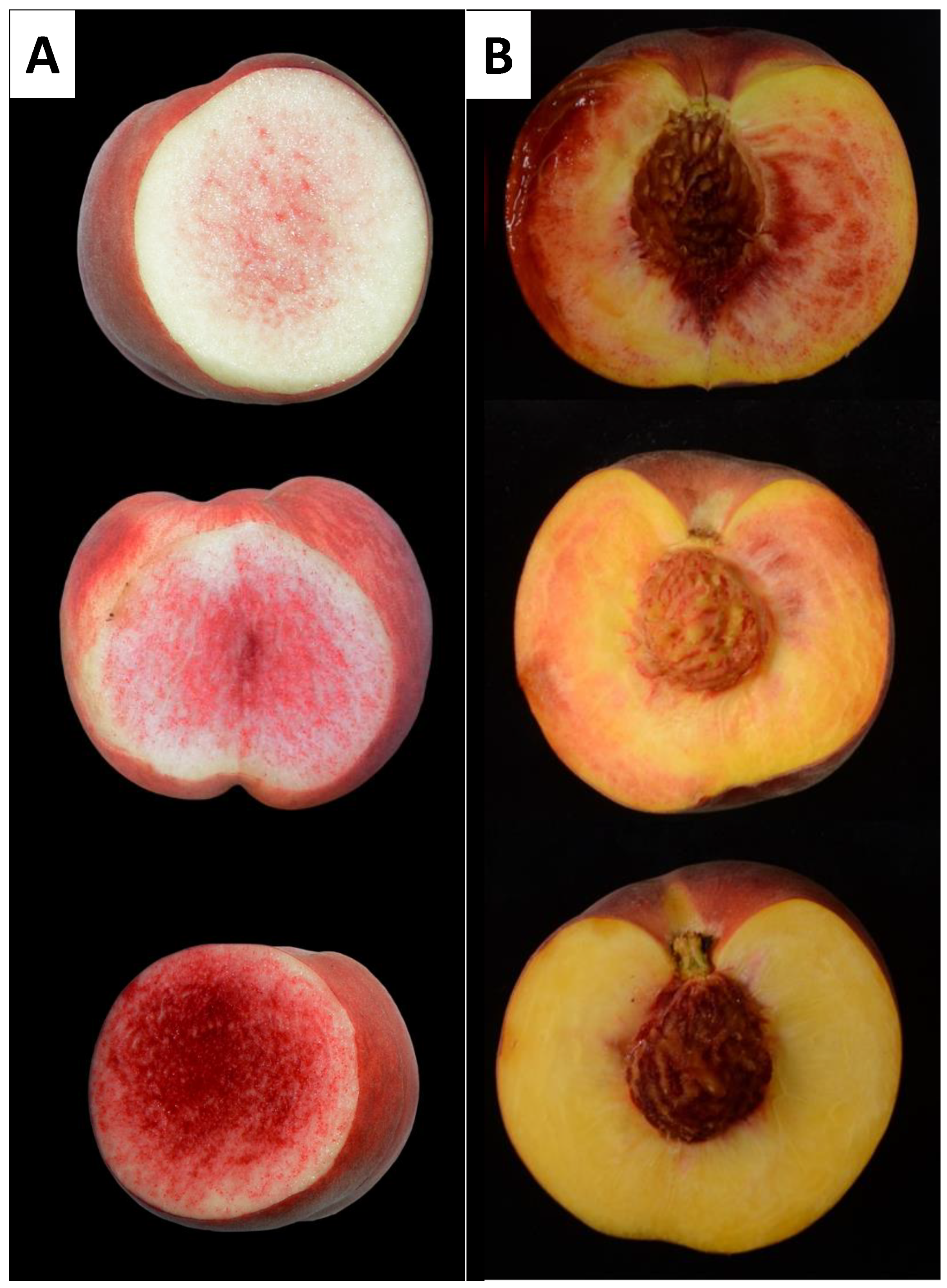
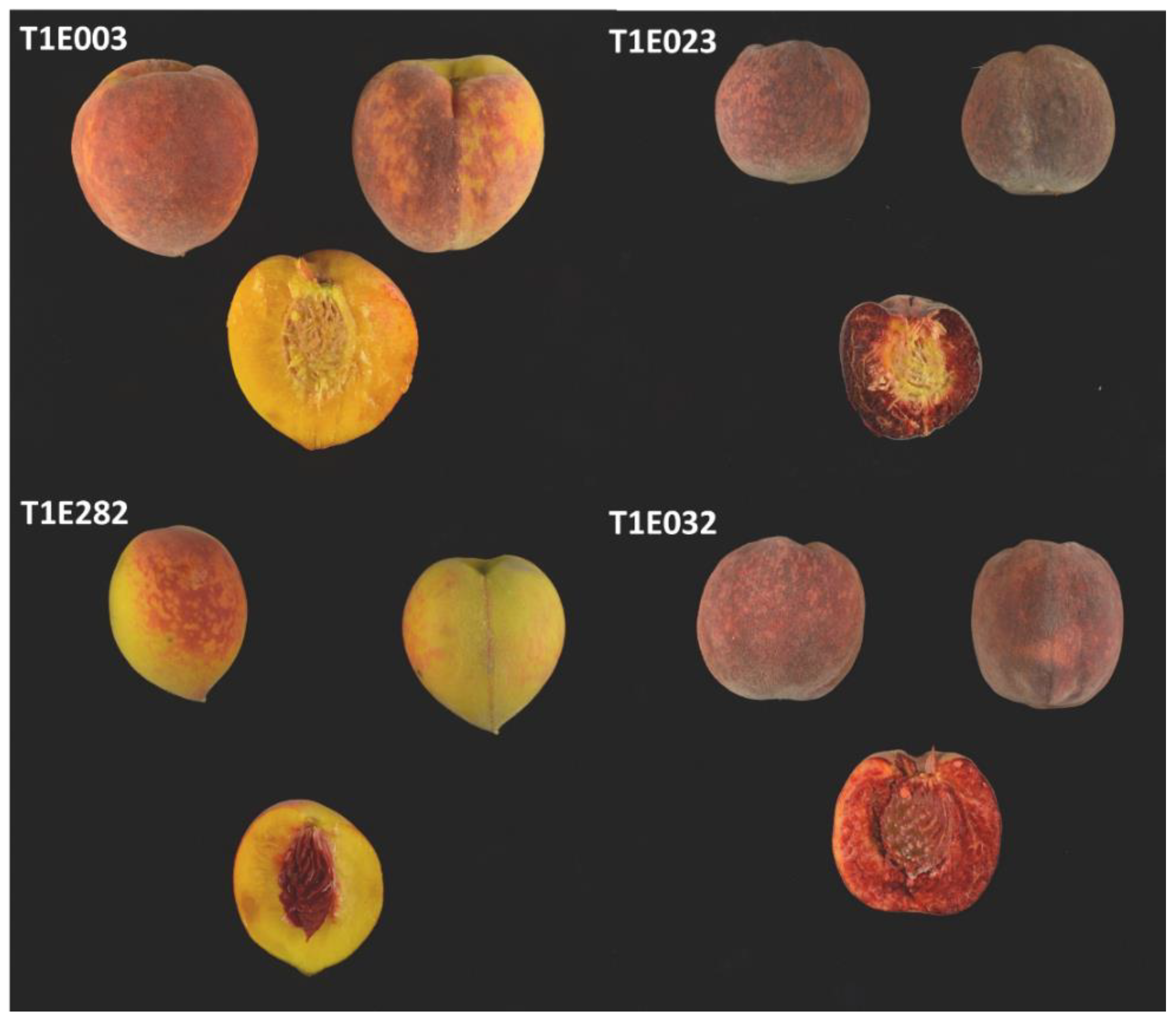
2.1. Description of Peach Flesh Color Patterns Identified in the IRTA Peach Cultivar Collection
2.2. QTL Analysis of RDF (Red Dots in the Flesh) in Bb × Nl and in SDF2
2.3. QTL Analysis of Cs in SDF2 and in T1E
3. Discussion
3.1. Peach Red Flesh Patterns
3.2. Relationship between RDF and DBF in Peach
3.3. Relationship between Cs and MD in Peach
3.4. Red Dots under the Skin (RDS)
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Plant Material
5.2. Phenotyping
5.3. QTL Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shulaev, V.; Korban, S.S.; Sosinski, B.R.; Abbott, A.G.; Aldwinckle, H.S.; Folta, K.M.; Iezzoni, A.F.; Main, D.; Arús, P.; Dandekar, A.M.; et al. Multiple models for Rosaceae genomics. Plant. Physiol. 2008, 147, 985–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reig, G.; Alegre, S.; Gatius, F.; Iglesias, I. Agronomical performance under Mediterranean climatic conditions among peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] cultivars originated from different breeding programmes. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 150, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peace, C. DNA-informed breeding of rosaceous crops: Promises.; progress and prospects. Hortic. Res. 2017, 4, 17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranzana, M.J.; Decroocq, V.; Dirlewanger, E.; Eduardo, I.; Gao, Z.S.; Gasic, K.; Iezzoni, A.; Jung, S.; Peace, C.; Prieto, H.; et al. Prunus genetics and applications after de novo genome sequencing: Achievements and prospects. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eduardo, I.; de Tomás, C.; Alexiou, K.G.; Giovannini, D.; Pietrella, M.; Carpenedo, S.; Bassols Raseira, M.C.; Batlle, I.; Cantín, C.M.; Aranzana, M.J.; et al. Fine mapping of the peach pollen sterility gene (Ps/ps) and detection of markers for marker-assisted selection. Mol. Breed 2020, 40, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, D.; Liverani, A.; Bassi, D.; Lateur, M. ECPGR Priority Descriptors for Peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch). In European Cooperative Programme for Plant Genetic Resources; 2013; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.; Butelli, E.; Petroni, K.; Tonelli, C. How can research on plants contribute to promoting human health? Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connors, C.H. Some notes on the inheritance of unit characters in the peach. Proc. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1920, 16, 24–36. [Google Scholar]
- Bliss, F.A.; Arulsekar, S.; Foolad, M.R.; Becerra, V.; Gillen, A.M.; Warburton, M.L.; Dandekar, A.M.; Kocsisne, G.M.; Mydin, K.K. An expanded genetic linkage map of Prunus based on an interspecific cross between almond and peach. Genome 2002, 45, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, M.; De Franceschi, P.; Brandi, F.; Liverani, A.; Giovannini, D.; Rosati, C.; Dondini, L.; Tartarini, S. Identifying a carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase (ccd4) gene controlling yellow/white fruit flesh color of peach. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 31, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, R.; Vendramin, E.; Zanon, L.; Scalabrin, S.; Cipriani, G.; Verde, I.; Vizzotto, G.; Morgante, M. Three distinct mutational mechanisms acting on a single gene underpin the origin of yellow flesh in peach. Plant J. 2013, 76, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, D.J.; Creller, M.A.; Chaparro, J.X. Inheritance of the Blood-flesh trait in peach. Hortscience 1998, 33, 1243–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillen, A.M.; Bliss, F.A. Identification and mapping of markers linked to the Mi gene for root-knot nematode resistance in peach. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2005, 130, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Confolent, C.; Lambert, P.; Poëssel, J.L.; Quilot-Turion, B.; Yu, M.; Ma, R.; Pascal, T. Characterization and genetic mapping of a new blood-flesh trait controlled by the single dominant locus DBF in peach. Tree Genet. Genomes 2013, 9, 1435–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoso, J.M.; Picañol, R.; Serra, O.; Howad, W.; Alegre, S.; Arús, P.; Eduardo, I. Exploring almond genetic variability useful for peach improvement: Mapping major genes and QTLs in two interspecific almond × peach populations. Mol. Breed 2016, 36, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Shimada, T.; Imai, T.; Yaegaki, H.; Haji, T.; Matsuta, N.; Yamaguchi, M.; Hayashi, T. Characterization of morphological traits based on a genetic linkage map in peach. Breed Sci. 2001, 51, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Hayashi, T. An integrated genetic linkage map of peach by SSR.; STS.; AFLP and RAPD. J. Jpn. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2005, 74, 204213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Cao, K.; Deng, C.; Li, Y.; Zhu, G.; Fang, W.; Wang, L. An integrated peach genome structural variation map uncovers genes associated with fruit traits. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, I.; Jenkins, J.; Dondini, L.; Micali, S.; Pagliarani, G.; Vendramin, E.; Paris, R.; Aramini, V.; Gazza, L.; Rossini, L.; et al. The Peach v2.0 release: High-resolution linkage mapping and deep resequencing improve chromosome-scale assembly and contiguity. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Lin-Wang, K.; Wang, H.; Gu, C.; Dare, A.P.; Espley, R.V.; He, H.; Allan, A.C.; Han, Y. Molecular genetics of blood-fleshed peach reveals activation of anthocyanin biosynthesis by NAC transcription factors. Plant J. 2015, 82, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.A.; Busatto, N.; Trainotti, L. Regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in peach fruits. Planta 2014, 240, 913–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretó, M.P.; Cantín, C.M.; Iglesias, I.; Arús, P.; Eduardo, I. Mapping a major gene for red skin color suppression (highlighter) in peach. Euphytica 2017, 213, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, T.; Li, J.; Tian, J.; Jin, K.; Yao, Y. Low medium pH value enhances anthocyanin accumulation in Malus crabapple leaves. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cao, K.; Zhu, G.; Fang, W.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Genome-wide Association Analysis of Red Flesh Character Based on Resequencing Approach in Peach. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2019, 144, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilot, B.; Wu, B.H.; Kervella, J.; Génard, M.; Foulongne, M.; Moreau, K. QTL analysis of quality traits in an advanced backcross between Prunus persica cultivars and the wild relative species P. davidiana. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirona, R.; Eduardo, I.; Pacheco, I.; Linge, C.D.S.; Miculan, M.; Verde, I.; Tartarini, S.; Dondini, L.; Pea, G.; Bassi, D.; et al. Fine mapping and identification of a candidate gene for a major locus controlling maturity date in peach. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, N.; Eduardo, I.; Arús, P. Comparative QTL analysis in peach ‘Earlygold’ F2 and backcross progenies. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 293, 110726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagné, D.; Carlisle, C.M.; Blond, C.; Volz, R.K.; Whitworth, C.J.; Oraguzie, N.C.; Crowhurst, R.N.; Allan, A.C.; Espley, R.V.; Hellens, R.P.; et al. Mapping a candidate gene (MdMYB10) for red flesh and foliage colour in apple. BMC Genomics 2007, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagné, D.; Lin-Wang, K.; Espley, R.V.; Volz, R.K.; How, N.M.; Rouse, S.; Brendolise, C.; Carlisle, C.M.; Kumar, S.; De Silva, N.; et al. An ancient duplication of apple MYB transcription factors is responsible for novel red fruit-flesh phenotypes. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espley, R.V.; Brendolise, C.; Chagné, D.; Kutty-Amma, S.; Green, S.; Volz, K.R.; Putterill, J.; Schouten, H.J.; Gardiner, S.E.; Hellens, R.P.; et al. Multiple repeats of a promoter segment causes transcription factor autoregulation in red apples. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eduardo, I.; Picañol, R.; Rojas, E.; Batlle, I.; Howad, W.; Aranzana, M.J.; Arús, P. Mapping of a major gene for the slow ripening character in peach: Co-location with the maturity date gene and development of a candidate gene-based diagnostic marker for its selection. Euphytica 2015, 205, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Mora, J.R.; Micheletti, D.; Bink, M.; Van de Weg, E.; Cantín, C.; Nazzicari, N.; Caprera, A.; Dettori, M.T.; Micali, S.; Banchi, E.; et al. Integrated QTL detection for key breeding traits in multiple peach progenies. BMC Genom. 2017, 8, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eduardo, I.; Alegre, S.; Alexiou, K.G.; Arús, P. Resynthesis: Marker-based partial reconstruction of elite genotypes in clonally reproducing plant species. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Ooijen, J.W. Multipoint maximum likelihood mapping in a full-sib family of an outbreeding species. Genet. Res. 2011, 93, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ooijen, J.W. MapQTL ® 5.; Software for the Mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci in Experimental Populations; Kyazma BV: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Voorrips, R.E. Mapchart: Software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaracho, N.; Reig, G.; Kalluri, N.; Arús, P.; Eduardo, I. Inheritance of Fruit Red-Flesh Patterns in Peach. Plants 2023, 12, 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12020394
Zaracho N, Reig G, Kalluri N, Arús P, Eduardo I. Inheritance of Fruit Red-Flesh Patterns in Peach. Plants. 2023; 12(2):394. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12020394
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaracho, Nathalia, Gemma Reig, Naveen Kalluri, Pere Arús, and Iban Eduardo. 2023. "Inheritance of Fruit Red-Flesh Patterns in Peach" Plants 12, no. 2: 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12020394
APA StyleZaracho, N., Reig, G., Kalluri, N., Arús, P., & Eduardo, I. (2023). Inheritance of Fruit Red-Flesh Patterns in Peach. Plants, 12(2), 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12020394






