Effects of 6-Benzyladenine (6-BA) on the Filling Process of Maize Grains Placed at Different Ear Positions under High Planting Density
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Yield and Yield Components
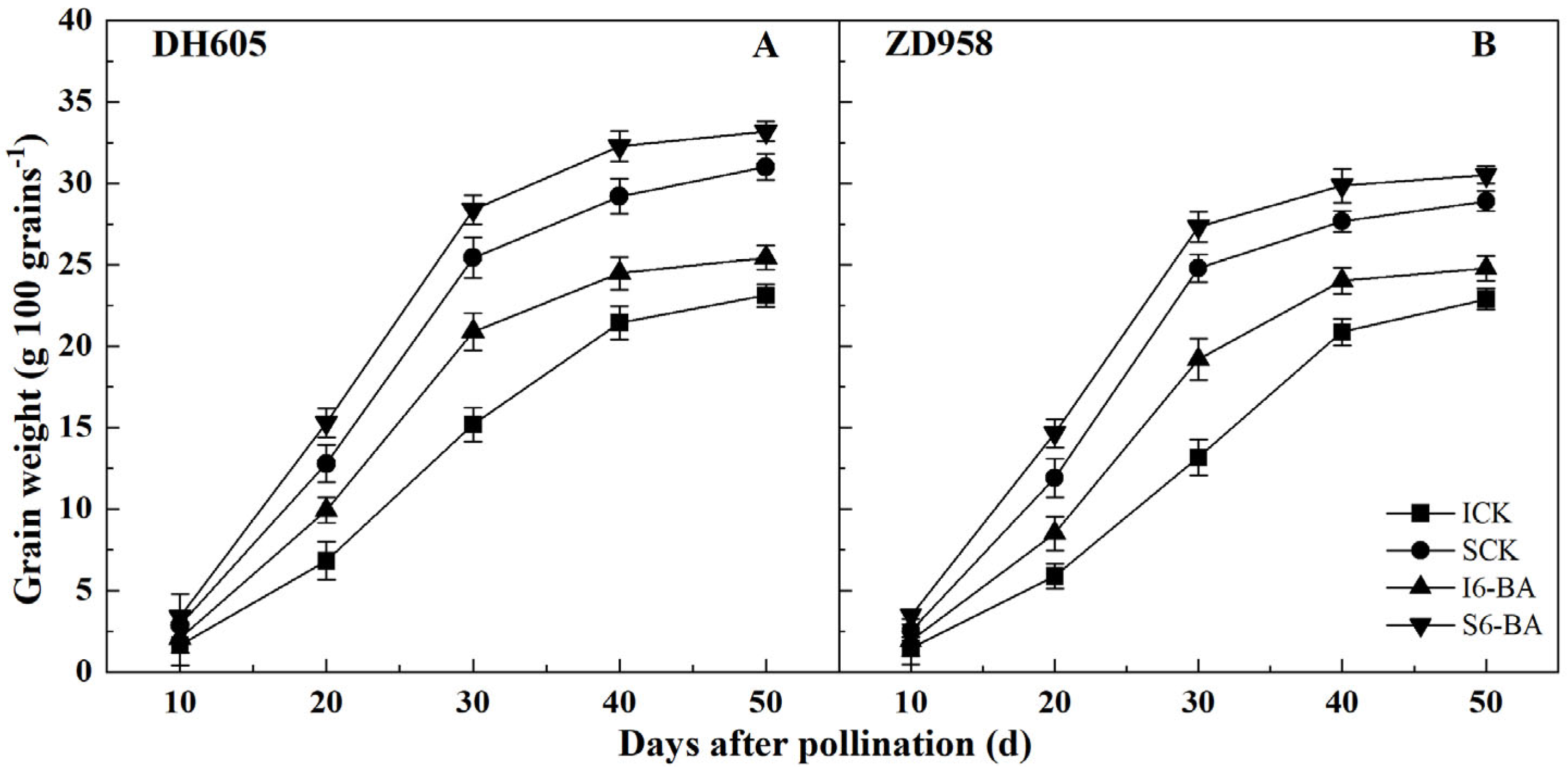
2.2. Grain Filling Process
2.3. Grain Starch Content and Starch Synthesis Critical Enzyme Activity
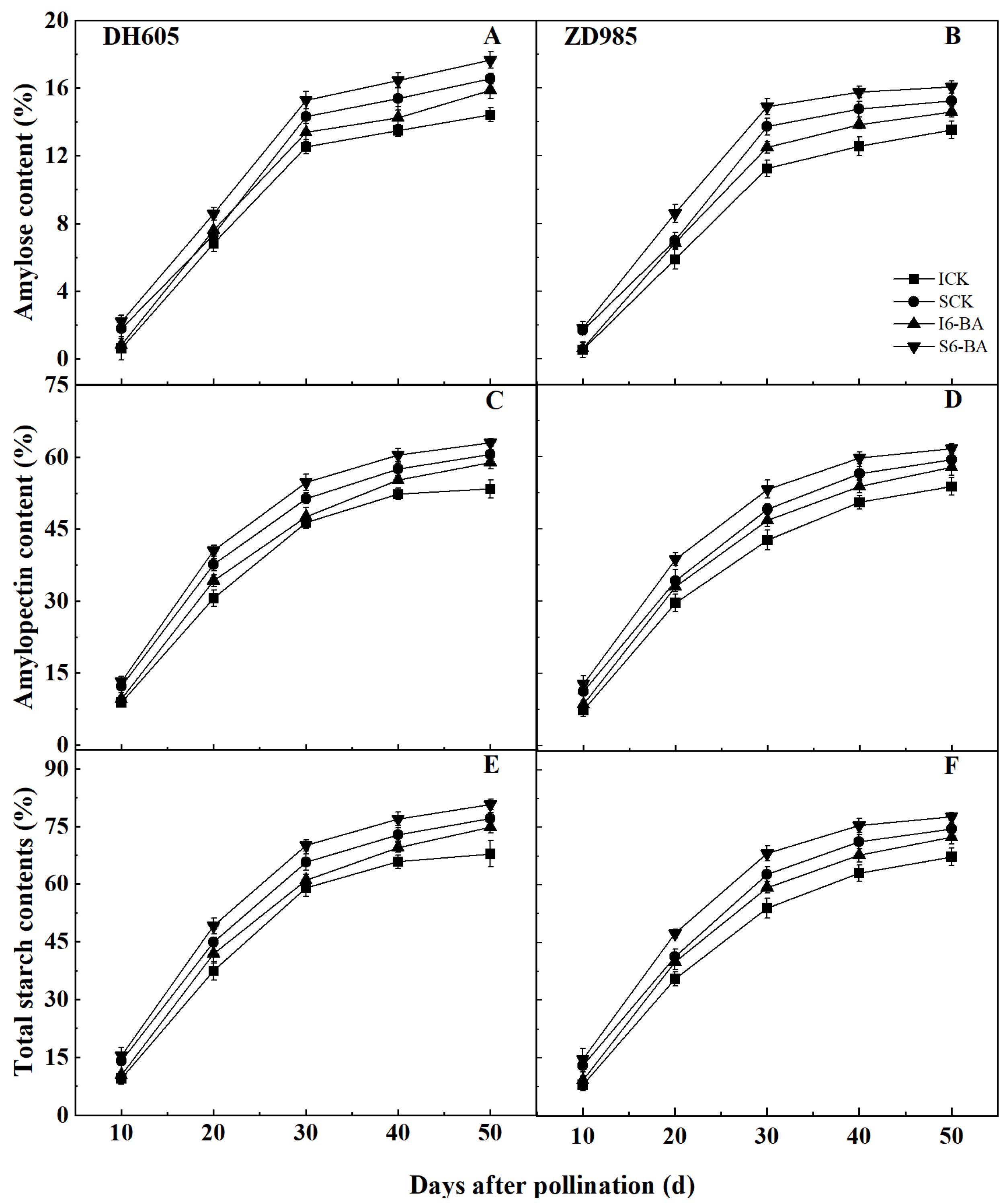
2.3.1. Starch Content
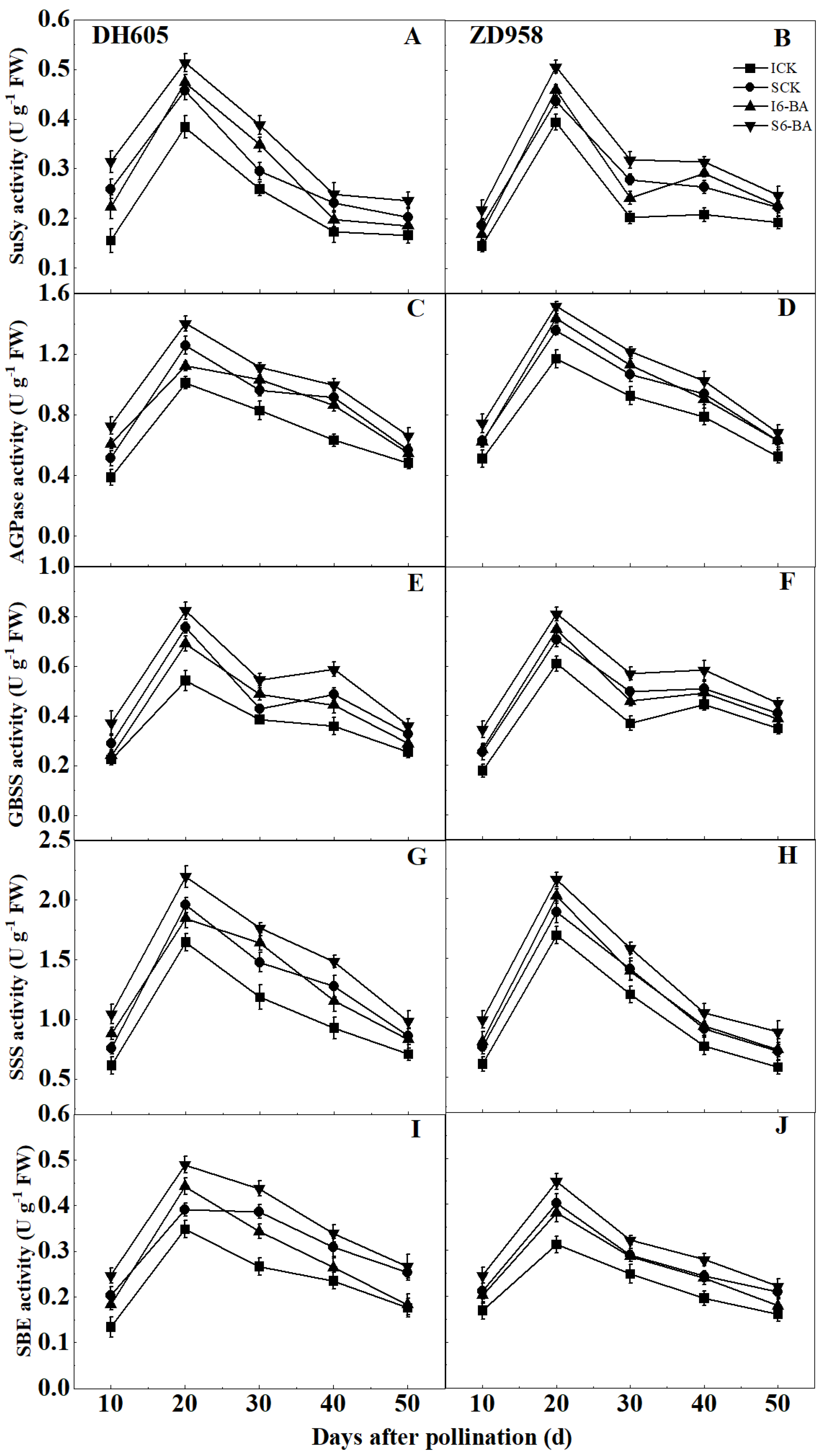
2.3.2. Starch Synthesis Critical Enzyme Activity
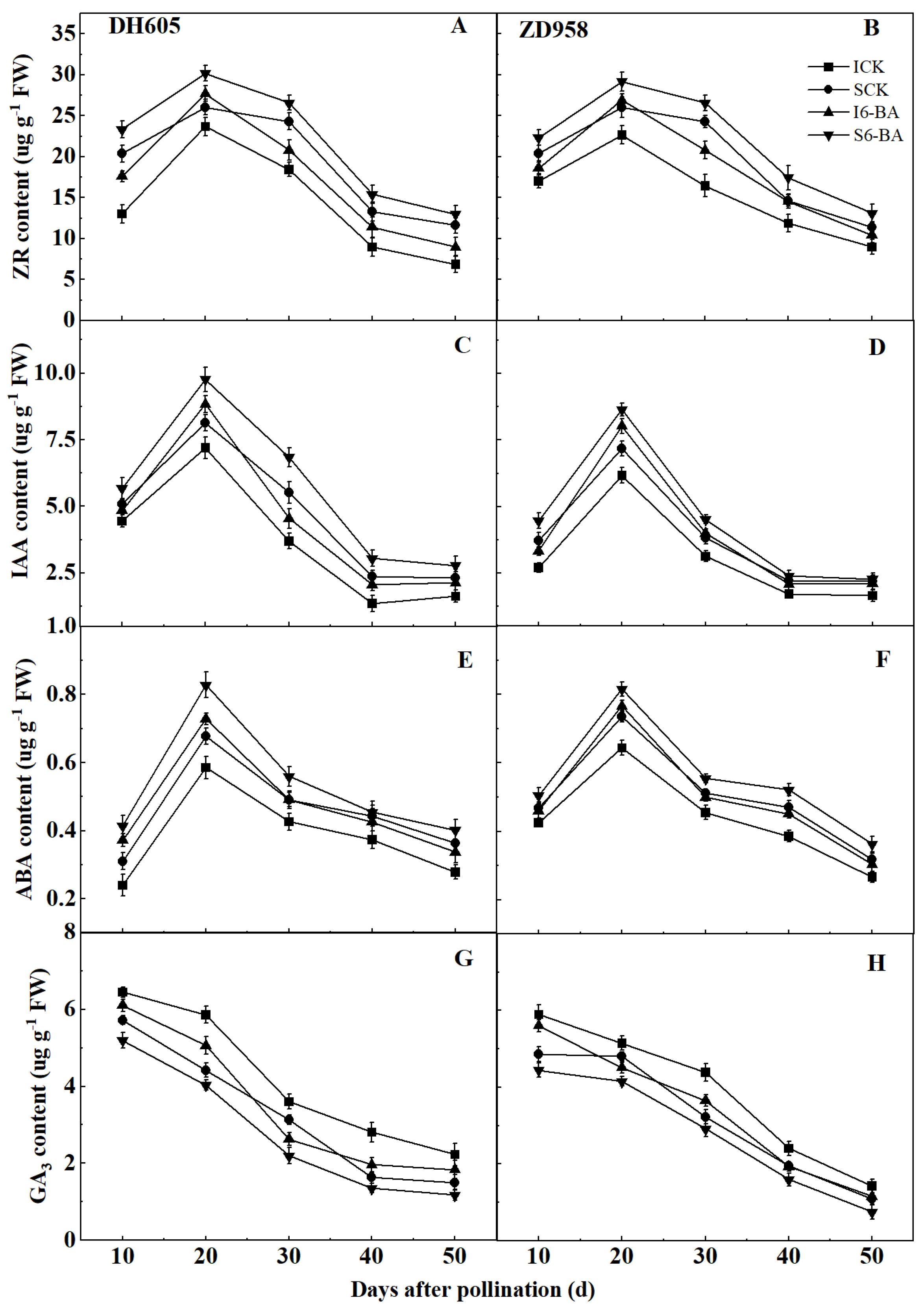
2.4. Grain Endogenous Hormones
2.4.1. ZR, IAA, and ABA Levels
2.4.2. GA3 Level
3. Discussion
3.1. Effect of Applying 6-BA on Grain Yield and Filling Process
3.2. Effect of Applying 6-BA on Grain Starch Accumulation
3.3. Effect of Applying 6-BA on Grain Endogenous Hormones
4. Materials and Methods
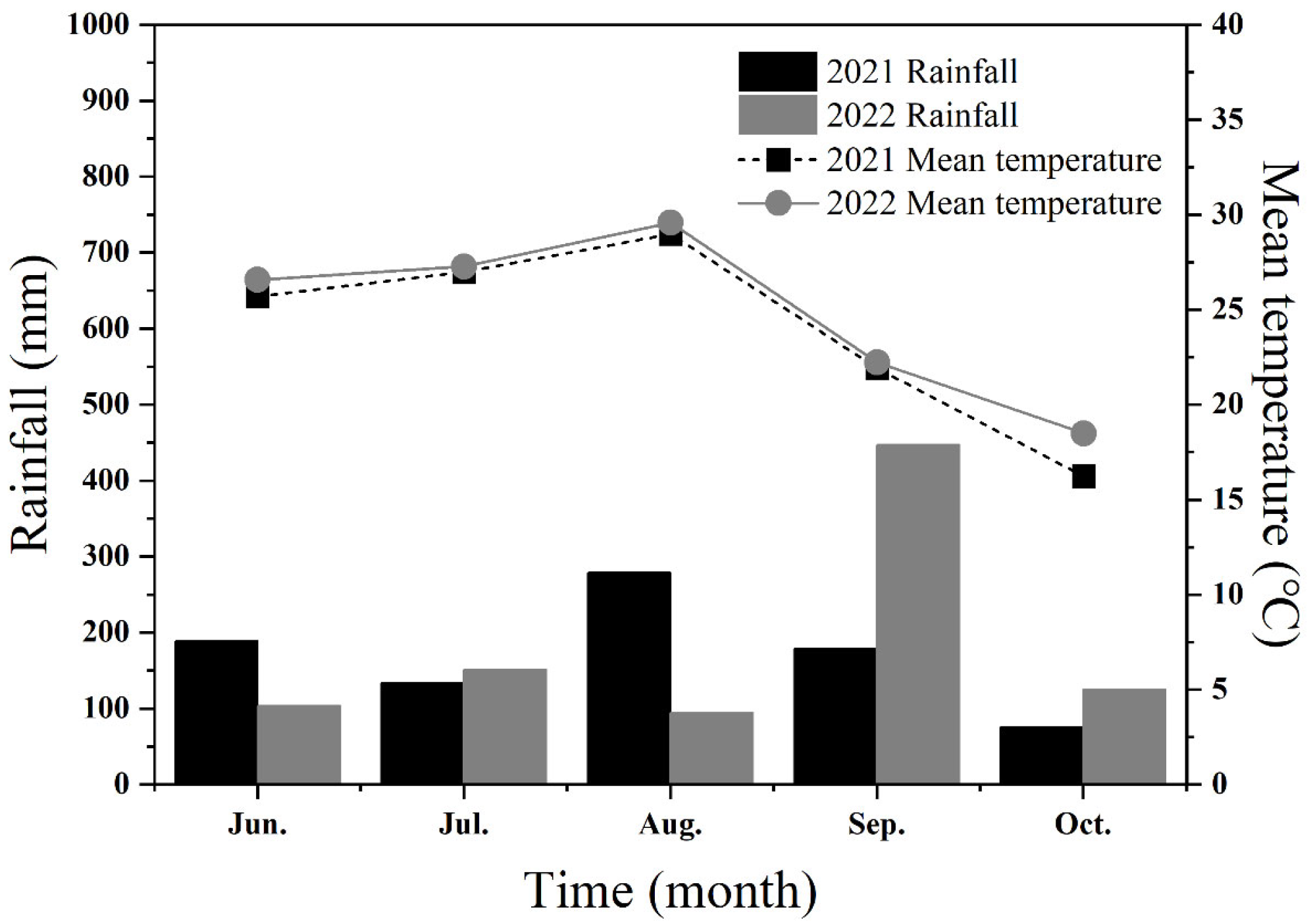
4.1. Test Site and Conditions
4.2. Experimental Design and Sampling
4.3. Test Items and Methods
4.3.1. Grain Filling Process
4.3.2. Starch Content and Starch Synthesis Critical Enzyme Activity
4.3.3. Endogenous Hormone Levels
4.3.4. Yield and Yield Components
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ten Berge, H.F.M.; Hijbeek, R.; Van Loon, M.P.; Van Loon, J.; Rurinda, K.; Tesfaye, S.; Zingore, P.; Craufurd, J.; Van Heerwaarden, F.; Brentrup, J.J.; et al. Maize crop nutrient input requirements for food security in sub-Saharan Africa. Glob. Food Secur. 2019, 23, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenstein, O.; Jaleta, M.; Sonder, K.; Mottaleb, K.; Prasanna, B.M. Global maize production, consumption and trade: Trends and R&D implications. Food Secur. 2022, 14, 1295–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Yue, Y.; Sun, X.; Ding, Z.; Ma, W.; Zhao, M. Maize kernel weight responses to sowing date-associated variation in weather conditions. Crop J. 2017, 5, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Du, L.; Feng, D.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Kong, F.; Yuan, J. Grain-filling characteristics and yield differences of maize cultivars with contrasting nitrogen efficiencies. Crop J. 2020, 8, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B.; Dong, S. Increased plant density and reduced N rate lead to more grain yield and higher resource utilization in summer maize. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 2515–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, G.; Reyneri, A.; Blandino, M. Maize grain yield enhancement through high plant density cultivation with different inter-row and intra-row spacings. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 72, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Shen, D.; Xie, R.; Ming, B.; Hou, P.; Xue, J.; Li, R.; Chen, J.; Wang, K.; Li, S. Optimizing planting density to improve nitrogen use of super high yield maize. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 4147–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, R.Z.; Wang, K.R.; Ming, B.; Guo, Y.Q.; Zhang, G.Q.; Li, S.K. Variations in maize dry matter, harvest index, and grain yield with plant density. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, Y.; Vara Prasad, P.V.; Carter, P.; Hinds, M.; Bhalla, G.; Schon, R.; Jeschke, M.; Paszkiewicz, S.; Ciampitti, I.A. Yield responses to planting density for US modern corn hybrids: A synthesis-analysis. Crop Sci. 2016, 56, 2802–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Sun, L.; Mou, H.; Ali, S.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ren, X.; Jia, Z. Effects of planting patterns and sowing densities on grain–filling, radiation use efficiency and yield of maize (Zea mays L.) in semi-arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 201, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wu, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhang, F.; Qiang, S.; Zheng, J.; Xiang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zou, H. Effects of water and fertilizer management on grain filling characteristics, grain weight and productivity of drip-fertigated winter wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, R.A.; Savin, R.; Cossani, C.M.; Slafer, G.A. Maize grain weight sensitivity to source-sink manipulations under a wide range of field conditions. Crop Sci. 2018, 58, 2542–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Harrison, M.T.; Yan, H.; Liu, D.L.; Meinke, H.; Hoogenboom, G.; Wang, B.; Peng, B.; Guan, K.; Jaegermeyr, J.; et al. Silver lining to a climate crisis in multiple prospects for alleviating crop waterlogging under future climates. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Jing, L.; Wang, D.; Bao, F.; Lu, W.; Wang, G. Grain and starch granule morphology in superior and inferior kernels of maize in response to nitrogen. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.M.; Chen, X.P.; Zou, C.Q. Soil application of zinc fertilizer increases maize yield by enhancing the kernel number and kernel weight of inferior grains. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Wang, Z.; Song, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, X. Tillage practices affects the grain filling of inferior kernel of summer maize by regulating soil water content and photosynthetic capacity. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Fang, C.; Qian, Z.; Guo, B.; Huo, Z. Differences in starch structure, physicochemical properties and texture characteristics in superior and inferior grains of rice varieties with different amylose contents. Food Hydrocolloid. 2021, 110, 106170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cai, T.; Wang, Z.; He, M. Physiological basis for the differences of productive capacity among tillers in winter wheat. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 1958–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Sun, H.; Qiao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Tang, G.; Zhao, Q. Differentially expressed microRNA cohorts in seed development may contribute to poor grain filling of inferior spikelets in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonelli, L.E.; Monzon, J.P.; Cerrudo, A.; Rizzalli, R.H.; Andrade, F.H. Maize grain yield components and source-sink relationship as affected by the delay in sowing date. Field Crops Res. 2016, 198, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Gu, X.; Ding, M.; Lu, W.; Lu, D. Heat stress during grain filling affects activities of enzymes involved in grain protein and starch synthesis in waxy maize. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.C.; Tan, H.Y.; Zhang, C.Q.; Li, Q.F.; Liu, Q.Q. Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperms: An updated review over the last decade. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.M.; Gu, W.R.; Li, C.F.; Jing, L.I.; Wei, S. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and chemical regulation on spring maize lodging characteristics, grain filling and yield formation under high planting density in Heilongjiang Province, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Wang, S.; Lu, D. Fertilization time of slow-release fertilizer affects the physicochemical properties of starch from spring-sown waxy maize. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Kamran, M.; Meng, X.; Ali, S.; Bilegjargal, B.; Cai, T.; Liu, T.; Han, Q. Effects of plant growth regulators on seed filling, endogenous hormone contents and maize production in semiarid regions. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 38, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, D.; Wu, W.; Wen, X.; Liao, Y. The relationship between polyamines and hormones in the regulation of wheat grain filling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Li, K.; Zhu, K.; Tian, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z. Effect of exogenous plant hormones on agronomic and physiological performance of a leaf early-senescent rice mutant osled. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 92, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, L. Correlation of cytokinin levels in the endosperms and roots with cell number and cell division activity during endosperm development in rice. Ann. Bot. 2002, 90, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lur, H.S.; Setter, T.L. Role of auxin in maize endosperm development (timing of nuclear DNA endoreduplication, zein expression, and cytokinin). Plant Physiol. 1993, 103, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.L.; Dong, N.Q.; Guo, T.; Ye, W.W.; Shan, J.X.; Lin, H.X. A quantitative trait locus GW6 controls rice grain size and yield through the gibberellin pathway. Plant J. 2020, 103, 1174–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, C.; Harshavardhan, V.T.; Rajesh, K.; Reddy, P.S.; Strickert, M.; Rolletschek, H.; Scholz, U.; Wobus, U.; Sreenivasulu, N. ABA biosynthesis and degradation contributing to ABA homeostasis during barley seed development under control and terminal drought-stress conditions. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 2615–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ning, T.; Ren, S.; Su, L.; Li, Z. Abscisic acid and aldehyde oxidase activity in maize ear leaf and grain relative to post-flowering photosynthetic capacity and grain-filling rate under different water/nitrogen treatments. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 70, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sui, Y.; Gu, D.; Wen, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Liao, Y. Effects of conservation tillage on grain filling and hormonal changes in wheat under simulated rainfall conditions. Field Crops Res. 2013, 144, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, F.U.; Xu, Y.J.; Chen, L.; Yuan, L.M.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yang, J.C. Changes in enzyme activities involved in starch synthesis and hormone concentrations in superior and inferior spikelets and their association with grain filling of super rice. Rice Sci. 2013, 20, 120–128. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X.; Han, J.; Liao, Y.; Liu, Y. Effect of phosphorus and potassium foliage application post-anthesis on grain filling and hormonal changes of wheat. Field Crops Res. 2017, 214, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Xu, H.; Peng, D.; Yin, Y.; Yang, W.; Ni, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, C.; Yang, D.; Cui, Z.; et al. Exogenous hormonal application improves grain yield of wheat by optimizing tiller productivity. Field Crops Res. 2014, 155, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yan, Y.; Lu, W.; Lu, D. Application of exogenous phytohormones at silking stage improve grain quality under post-silking drought stress in waxy maize. Plants 2020, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liao, Y.; Liu, Y. Exogenous spermidine regulates starch synthesis and the antioxidant system to promote wheat grain filling under drought stress. ACTA Physiol. Plant. 2020, 42, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Horgan, K.J.; Reynolds, P.H.S.; Jameson, P.E. 6-Benzyladenine metabolism during reinvigoration of mature Pinus radiata buds in vitro. Tree Physiol. 2010, 30, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ren, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B. Effects of spraying exogenous hormone 6-benzyladenine (6-BA) after waterlogging on grain yield and growth of summer maize. Field Crops Res. 2016, 188, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Liang, X.G.; Zhang, L.; Lin, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, L.L.; Shen, S.; Zhou, S.L. Spraying exogenous 6-benzyladenine and brassinolide at tasseling increases maize yield by enhancing source and sink capacity. Field Crops Res. 2017, 211, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani Javid, M.; Sorooshzadeh, A.; Modarres Sanavy, S.A.M.; Allahdadi, I.; Moradi, F. Effects of the exogenous application of auxin and cytokinin on carbohydrate accumulation in grains of rice under salt stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2011, 65, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, N.; Rafiqul Islam, M.; Abdul Karim, M.; Hossain, T. Alleviation of drought stress in maize by exogenous application of gibberellic acid and cytokinin. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 17, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ren, B.; Dong, S.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J. Comparative proteomic analysis reveals that exogenous 6-benzyladenine (6-BA) improves the defense system activity of waterlogged summer maize. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yang, S.; He, D.; Yi, Y.; Fu, Y.; Yin, D.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, C. Exogenous 6-benzyladenine treatment alleviates cold stress in early japonica rice at booting in Northeast China. Agron. J. 2022, 114, 2905–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B. Spraying exogenous synthetic cytokinin 6-benzyladenine following the waterlogging improves grain growth of waterlogged maize in the field. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2019, 205, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Cui, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, M.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wang, Z. Exogenous cytokinins increase grain yield of winter wheat cultivars by improving stay-green characteristics under heat stress. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, H.M.; Abbas, F.; Ahmad, A.; Bakhat, H.F.; Farhad, W.; Wilkerson, C.J.; Fahad, S.; Hoogenboom, G. Predicting kernel growth of maize under controlled water and nitrogen applications. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2020, 14, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Ma, S.; Fan, Y.; Huang, Z. Exogenous 6-benzylaminopurine enhances waterlogging and shading tolerance after anthesis by improving grain starch accumulation and grain filling. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1003920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; Qin, Y.; Jiang, D.; Dong, S. Plant density and nitrogen supply affect the grain-filling parameters of maize kernels located in different ear positions. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Liang, X.G.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.P.; Lin, S.; Gao, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhou, S.L. Intervening in sibling competition for assimilates by controlled pollination prevents seed abortion under postpollination drought in maize. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 903–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Zhang, L.; Liang, X.G.; Zhao, X.; Lin, S.; Qu, L.H.; Liu, Y.P.; Gao, Z.; Ruan, Y.L.; Zhou, S.L. Delayed pollination and low availability of assimilates are major factors causing maize kernel abortion. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 1599–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, X.; Liao, Y.; Liu, Y. Effect of non-structural carbohydrate accumulation in the stem pre-anthesis on grain filling of wheat inferior grain. Field Crops Res. 2017, 211, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liao, P.; Wang, W.; Xu, K.; Dai, Q.; et al. Excessive nitrogen application leads to lower rice yield and grain quality by inhibiting the grain filling of inferior grains. Agriculture 2022, 12, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.H.; Othman, Z.; Lee, J.S. Gamma irradiation of corn starches with different amylose-to-amylopectin ratio. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 6218–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhao, H. The influence of different plant hormones on biomass and starch accumulation of duckweed: A renewable feedstock for bioethanol production. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, L.C.; James, M. The complexities of starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperms. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008, 19, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.G.; Denyer, K.; Myers, A.M. Starch synthesis in the cereal endosperm. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, O.; Pan, D. Starch synthesis in maize endosperms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1995, 46, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Li, G.; Dong, S.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B. Proteomic analysis of maize grain development using iTRAQ reveals temporal programs of diverse metabolic processes. BMC Plant Boil. 2016, 16, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Li, G.; Liu, P.; Dong, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B. Proteomics analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) grain based on iTRAQ reveals molecular mechanisms of poor grain filling in inferior grains. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Teng, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Yi, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Yu, H.; Lv, J.; Wang, Y.; Duan, M.; Zhang, J.; et al. Excessive nitrogen in field-grown rice suppresses grain filling of inferior spikelets by reducing the accumulation of cytokinin and auxin. Field Crops Res. 2022, 283, 108542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Hu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Li, P. Sugars in postharvest lotus seeds were modified by 6-benzylaminopurine treatment through altering related enzymes involved in starch-sucrose metabolism. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 221, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Ye, N.; Yang, J.; Peng, X.; Zhang, J. Regulation of expression of starch synthesis genes by ethylene and ABA in relation to the development of rice inferior and superior spikelets. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3907–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Xue, H.; Zhang, F. An integrative overview of physiological and proteomic changes of cytokinin-induced potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tuber development in vitro. Physiol. Plantarum. 2020, 168, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Shi, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J. Grain development and endogenous hormones in summer maize (Zea mays L.) submitted to different light conditions. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2018, 62, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Gu, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Hormone contents in kernels at different positions on an ear and their relationship with endosperm development and kernel filling in maize. Acta Agron. Sin. 2013, 39, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, L. Abscisic acid and cytokinins in the root exudates and leaves and their relationship to senescence and remobilization of carbon reserves in rice subjected to water stress during grain filling. Planta 2002, 215, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, J.; Lam, H.M.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Hormonal changes are related to the poor grain filling in the inferior spikelets of rice cultivated under non-flooded and mulched condition. Field Crops Res. 2007, 101, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Koshiba, T. Complex regulation of ABA biosynthesis in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharis, R.P.; King, R.W. Gibberellins and reproductive development in seed plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1985, 36, 517–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Liu, D.; Gu, D.; Wang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Wen, X. Effect of plastic film mulching on the grain filling and hormonal changes of maize under different irrigation conditions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosakivska, I.V.; Vedenicheva, N.P.; Babenko, L.M.; Voytenko, L.V.; Romanenko, K.O.; Vasyuk, V.A. Exogenous phytohormones in the regulation of growth and development of cereals under abiotic stresses. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, B.B.; Sekhar, S.; Dash, S.K.; Behera, L.; Shaw, B.P. Biochemical and molecular characterisation of exogenous cytokinin application on grain filling in rice. BMC Plant Boil. 2018, 18, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agro-Chemistrical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 30–100. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Goudriaan, J.A.N.; Lantinga, E.A.; Vos, J.A.N.; Spiertz, H.J. A flexible sigmoid function of determinate growth. Ann. Bot. 2003, 91, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Jackson, D.S.; Wehling, R.L.; Geera, B. Comparison of amylose determination methods and the development of a dual wavelength iodine binding technique. Cereal Chem. 2008, 85, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Ren, H.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J.; Ren, B.; Liu, P. Maize (Zea mays L.) responses to heat stress: Mechanisms that disrupt the development and hormone balance of tassels and pollen. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2023, 209, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | Variety | Treatments | Ear Number (Ears hm−2) | Grains per Ear | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Yield (kg hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | DH605 | CK | 84,147.36 ± 214 a | 434.41 ± 7.63 a | 352.73 ± 3.14 c | 12,893.81 ± 439 b |
| 6-BA | 84,138.38 ± 304 a | 435.49 ± 3.46 a | 380.75 ±4.53 a | 13,951.43 ± 130 a | ||
| ZD958 | CK | 84,143.11 ± 488 a | 447.59 ± 6.67 a | 346.70 ± 3.67 c | 13,003.87 ± 237 b | |
| 6-BA | 84,558.38 ± 225 a | 443.80 ± 16.79 a | 370.09 ± 5.11 b | 13,884.28 ± 454 a | ||
| 2022 | DH605 | CK | 83,893.33 ± 101 a | 451.72 ± 17.99 a | 357.26 ± 3.03 c | 13,538.95 ± 563 bc |
| 6-BA | 83,903.47 ± 131 a | 453.04 ± 3.85 a | 384.75 ± 5.73 a | 14,625.20 ± 149 a | ||
| ZD958 | CK | 84,473.11 ± 581 a | 448.98 ± 6.64 a | 347.70 ± 5.73 d | 13,185.40 ± 268 c | |
| 6-BA | 84,948.38 ± 221 a | 451.98 ± 3.51 a | 366.09 ±4.84 b | 14,055.86 ± 489 ab |
| Variety | Treatments | Wmax (g 100 Grains−1) | Gmax (g 100 Grains−1 d−1) | Gave (g 100 Grains−1 d−1) | P (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DH605 | ICK | 10.89 ± 0.41 d | 0.73 ± 0.06 d | 0.44 ± 0.02 d | 44.60 ± 2.57 a |
| I6-BA | 12.70 ± 0.40 c | 0.87 ± 0.04 c | 0.52 ± 0.03 c | 44.02 ± 4.50 a | |
| SCK | 14.51 ± 0.90 b | 1.01 ± 0.03 b | 0.60 ± 0.03 b | 43.23 ± 6.00 a | |
| S-6BA | 16.57 ± 0.55 a | 1.13 ± 0.07 a | 0.68 ± 0.02 a | 43.87 ± 8.20 a | |
| ZD958 | ICK | 11.59 ± 0.26 d | 0.82 ± 0.04 d | 0.49 ± 0.03 d | 42.62 ± 4.21 a |
| I6-BA | 12.54 ± 0.35 c | 0.94 ± 0.03 c | 0.56 ± 0.01 c | 40.24 ± 6.82 a | |
| SCK | 14.36 ± 0.30 b | 1.04 ± 0.05 b | 0.62 ± 0.03 b | 41.40 ± 5.05 a | |
| S6-BA | 15.29 ± 0.21 a | 1.14 ± 0.02 a | 0.68 ± 0.01 a | 40.32 ± 6.47 a |
| SuSy | AGPase | GBSS | SSS | SBE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amylose | 0.931 ** | 0.751 * | 0.899 ** | 0.810 ** | 0.793 * |
| Amylopectin | 0.954 ** | 0.819 ** | 0.835 ** | 0.928 ** | 0.961 ** |
| Total starch | 0.951 ** | 0.804 ** | 0.885 ** | 0.931 ** | 0.965 ** |
| Wmax | Gmax | Gave | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZR | 0.817 * | 0.860 ** | 0.864 ** | 0.422 |
| IAA | 0.874 ** | 0.963 ** | 0.962 ** | 0.608 |
| ABA | 0.855 ** | 0.946 ** | 0.944 ** | 0.623 |
| GA3 | −0.832 * | −0.884 ** | −0.886 ** | −0.464 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, T.; Xin, Y.; Liu, P. Effects of 6-Benzyladenine (6-BA) on the Filling Process of Maize Grains Placed at Different Ear Positions under High Planting Density. Plants 2023, 12, 3590. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12203590
Yu T, Xin Y, Liu P. Effects of 6-Benzyladenine (6-BA) on the Filling Process of Maize Grains Placed at Different Ear Positions under High Planting Density. Plants. 2023; 12(20):3590. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12203590
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Tao, Yuning Xin, and Peng Liu. 2023. "Effects of 6-Benzyladenine (6-BA) on the Filling Process of Maize Grains Placed at Different Ear Positions under High Planting Density" Plants 12, no. 20: 3590. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12203590
APA StyleYu, T., Xin, Y., & Liu, P. (2023). Effects of 6-Benzyladenine (6-BA) on the Filling Process of Maize Grains Placed at Different Ear Positions under High Planting Density. Plants, 12(20), 3590. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12203590





