Medium-Term Effects of Sprinkler Irrigation Combined with a Single Compost Application on Water and Rice Productivity and Food Safety
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site, Experimental Design and Field Management
2.2. Data Collection
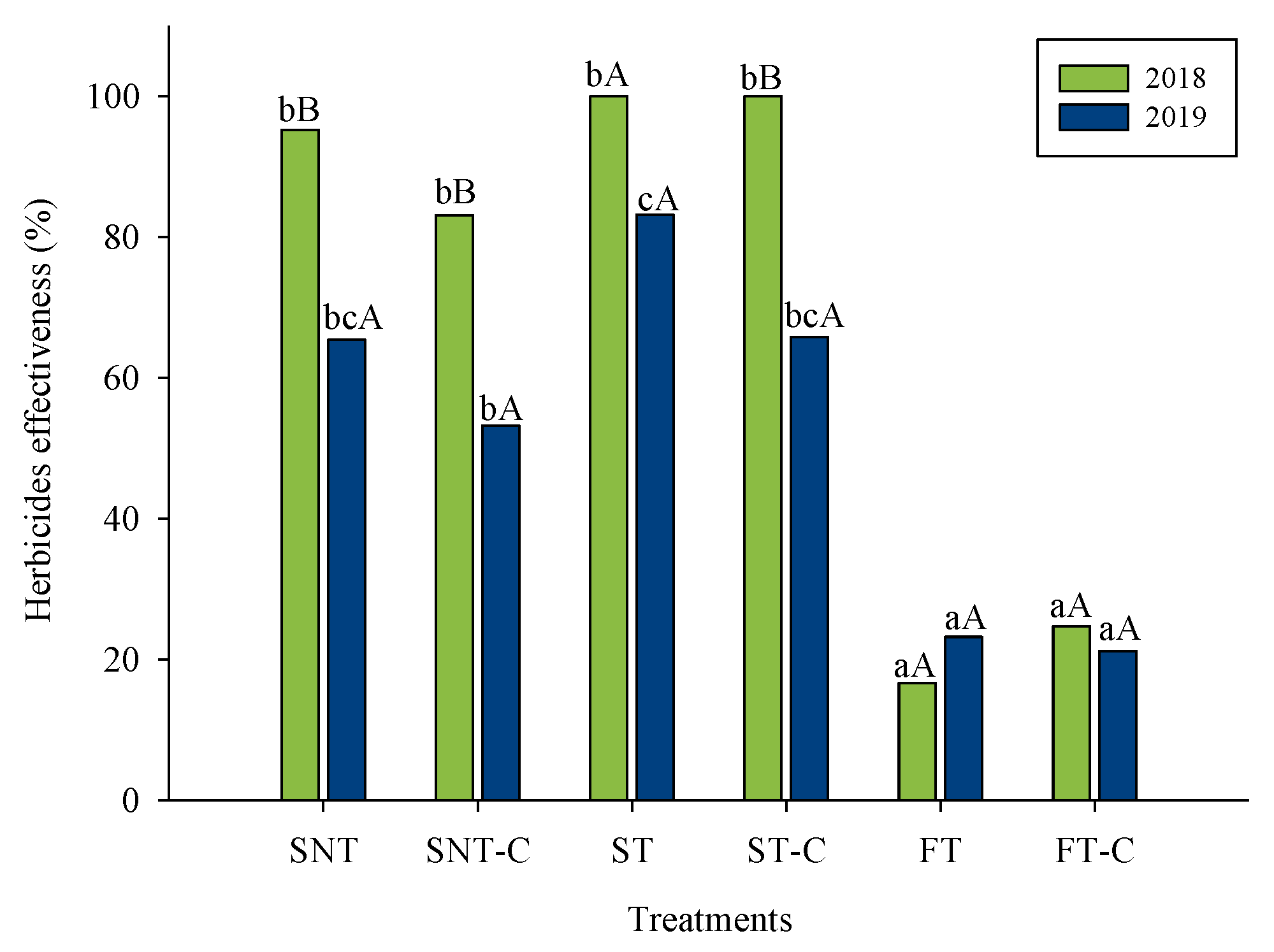
2.2.1. Weed Control Efficiency
2.2.2. Agronomic Parameters
2.2.3. Arsenic and Cadmium in Soil and Rice Grain
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Weed Control Efficiency
3.2. Agronomic Parameters
3.3. Arsenic and Cadmium in Soil and Rice Grain
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campillo, C.; Gordillo, J.; Santiago, L.M.; Cordoba, A.; Martinez, L.; Prieto, M.H.; Fortes, R. Development of an efficient water management system in commercial processing tomato farms. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1159, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, N.; Yadav, S.; Singh, V.K.; Kumar, A. Effective crop management and modern breeding strategies to ensure higher crop productivity under direct seeded rice cultivation system: A review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Hussain, S.; Guo, R.; Sarwar, M.; Ren, X.; Krstic, D.; Aslam, Z.; Zulifqar, U.; Rauf, A.; Hano, C.; et al. Carbon sequestration to avoid soil degradation: A review on the role of conservation tillage. Plants 2021, 10, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merante, P.; Van Passel, S.; Pacini, C. Using agro-environmental models to design a sustainable benchmark for the sustainable value method. Agric. Syst. 2015, 136, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rato Nunes, J.; Cabral, F.; López-Piñeiro, A. Short-term effects on soil properties and wheat production from secondary paper sludge application on two Mediterranean agricultural soils. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4935–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zou, Y.; Jiang, P.; Xia, B.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Mo, Y. Effect of tillage on soil and crop properties of wet-seeded flooded rice. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 129, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Llerena, J.; López-Piñeiro, A.; Albarrán, Á.; Peña, D.; Becerra, D.; Rato-Nunes, J.M. Short and long-term effects of different irrigation and tillage systems on soil properties and rice productivity under Mediterranean conditions. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 77, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Bhullar, M.S.; Chauhan, B.S. Influence of tillage, cover cropping, and herbicides on weeds and productivity of dry direct-seeded rice. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 147, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Zheng, X.; Lv, W.; Qin, Q.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Xue, Y. Effects of tillage and straw return on water-stable aggregates, carbon stabilization and crop yield in an estuarine alluvial soil. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denardin, L.G.D.O.; Carmona, F.D.C.; Veloso, M.G.; Martins, A.P.; Freitas, T.F.S.D.; Carlos, F.S.; Marcolin, É.; Camargo, F.A.D.O.; Anghinoni, I. No-tillage increases irrigated rice yield through soil quality improvement along time. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 186, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Yang, X.; Bouman, B.A.M.; Deng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, W.; Zhang, T.; Rouzi, A.; Wang, H. Optimizing yield, water requirements, and water productivity of aerobic rice for the North China. Plain Irrig Sci. 2008, 26, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhu, J.; Peng, H.; Li, C.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, X. Effects of Organic Fertilizer on the Risk of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss in Soil Surface Water. Res. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, K.K.; Swain, D.K.; Bohra, A.; Singh, S.S.; Kumar, N.; Nath, C.P. Organic rice: Potential production strategies, challenges and prospects. Org. Agric. 2018, 8, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshayb, O.M.; Nada, A.M.; Sadek, A.H.; Ismail, S.H.; Shami, A.; Alharbi, B.M.; Alhammad, B.A.; Seleiman, M.F. The Integrative Effects of Biochar and ZnO Nanoparticles for Enhancing Rice Productivity and Water Use Efficiency under Irrigation Deficit Conditions. Plants 2022, 11, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, U.; Raja, P.; Jayakumar, M.; Subramoniam, S.R. Use of efficient water saving techniques for production of rice in India under climate change scenario: A critical review. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 309, 127272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, H.; Sun, J.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Shen, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, K. The effects of nitrogen application rate on the grain physicochemical properties of japonica rice under controlled and flooding irrigation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 2428–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, A.; Valente, M.; Langasco, I.; Leardi, R.; Orlandoni, A.M.; Ciulu, M.; Deroma, M.A.; Spano, N.; Barracu, F.; Pilo, M.I.; et al. Effect of the irrigation method and genotype on the bioaccumulation of toxic and trace elements in rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 142484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanu, A.; Murtas, A.; Ledda, L.; Ballone, F. Innovative Agronomic Techniques for Rice Cultivation. Conference Proceedings of Challenger and Opportunities for Sustainable Rice Based Production Systems, Torino, Italy. 2004, pp. 207–216. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264874823_CHALLENGES_AND_OPPORTUNITIES_FOR_SUSTAINABLE_RICE-BASED_PRODUCTION_SYSTEMS (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- Okami, M.; Kato, Y.; Yamagishi, J. Role of early vigor in adaptation of rice to water-saving aerobic culture: Effects of nitrogen utilization and leaf growth. Field Crop. Res. 2011, 124, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadiyala, M.D.M.; Mylavarapu, R.S.; Li, Y.C.; Reddy, G.B.; Reddy, M.D. Impact of aerobic rice cultivation on growth, yield, and water productivity of rice-maize rotation in semiarid tropics. Agron. J. 2012, 104, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolak, Y.B. Comparison of aerobic rice cultivation using drip systems with conventional flooding. J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 159, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Nie, J.; Cao, W.; Gao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liao, Y. Long-term green manuring to substitute partial chemical fertilizer simultaneously improving crop productivity and soil quality in a double-rice cropping system. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 142, 126641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Das, D.; Hu, Q.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J. Alternate wetting and drying irrigation and phosphorus rates affect grain yield and quality and heavy metal accumulation in rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoli, M.; Paleari, L.; Confalonieri, R.; Bacenetti, J. Setting-up of different water managements as mitigation strategy of the environmental impact of paddy rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 14936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Jiménez, E.; Meharg, A.A.; Smolders, E.; Manzano, R.; Becerra, D.; Sánchez-Llerena, J.; Albarrán, A.; López-Piñero, A. Sprinkler irrigation of rice fields reduces grain arsenic but enhances cadmium. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485–486, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Powell, M.A.; Kumar Biswas, P.; Banik, P. The role of agronomic factors (rice cultivation practices and soil amendments) on Arsenic fractionation: A strategy to minimise Arsenic uptake by rice, with some observations related to cadmium. Catena 2021, 206, 105556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, J.; Liang, T.; Yan, X.; Zhong, L.; Shao, J.; El-Naggar, A.; Guan, C.-Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y. A combined management scheme to simultaneously mitigate As and Cd concentrations in rice cultivated in contaminated paddy soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, A.; Langasco, I.; Serra, M.; Deroma, M.A.; Spano, N.; Barracu, F.; Pilo, M.I.; Sanna, G. Sprinkler irrigation in the production of safe rice by soils heavily polluted by arsenic and cadmium. Chemosphere 2021, 277, 130351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, P.; Fernández-Rodríguez, D.; Abades, D.P.; Rato-Nunes, J.M.; Albarrán, Á.; López-Piñeiro, A. Combined use of olive mill waste compost and sprinkler irrigation to decrease the risk of As and Cd accumulation in rice grain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Gu, C.; Tao, T.; Chen, G.; Shan, Y. Straw incorporation increases solubility and uptake of cadmium by rice plants. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B-Soil Plant Sci. 2013, 63, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Kwong, R.W.M.; Tang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, H. Straw return enhances the risks of metals in soil? Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2021, 207, 111201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutrotsios, G.; Tagkouli, D.; Bekiaris, G.; Kaliora, A.; Tsiaka, T.; Tsiantas, K.; Chatzipavlidis, I.; Zoumpoulakis, P.; Kalogeropoulos, N.; Zervakis, G.I. Enhancing the nutritional and functional properties of Pleurotus citrinopileatus mushrooms through the exploitation of winery and olive mill wastes. Food Chem. 2021, 370, 131022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COM. Report from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social. Committee and the Committee of the Regions. On the Implementation of the Circular Economy Action Plan. 33 end; European Comission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aharonov-Nadborny, R.; Raviv, M.; Graber, E.R. Soil spreading of liquid olive mill processing wastes impacts leaching of adsorbed terbuthylazine. Chemosphere 2016, 156, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortosa, G.; Castellano-Hinojosa, A.; Correa-Galeote, D.; Bedmar, E.J. Evolution of bacterial diversity during two-phase olive mill waste (“alperujo”) composting by 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, D.; Fernández, D.; Albarrán, A.; Gómez, S.; Martín, C.; Sánchez-Terrón, J.; Vicente, L.; López-Piñeiro, A. Using olive mill waste compost with sprinkler irrigation as a strategy to achieve sustainable rice cropping under Mediterranean conditions. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Guidelines for Soil Description; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/a0541e/a0541e.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Mohammed, U.; Aimrun, W.; Amin, M.S.M.; Khalina, A.; Zubairu, U.B. Influence of soil cover on moisture content and weed suppression under system of rice intensification (SRI). Paddy Water Environ. 2016, 14, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, G.; Marí, A.; Aibar, J.; Cirujeda, A. Do Crop Rotations in Rice Reduce Weed and Echinochloa spp. Infestations? Recommendations for Integrated Weed Control. Agronomy 2021, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Piñeiro, A.; Martín-Franco, C.; Terrón-Sánchez, J.; Vicente, L.A.; Fernández-Rodríguez, D.; Albarrán, Á.; Nunes, J.M.R.; Peña, D. Environmental fate and efficiency of bispyribac-sodium in rice soils under conventional and alternative production systems affected by fresh and aged biochar amendment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, D.; Gómez, S.; Albarrán, Á.; Peña, D.; Rozas, M.Á.; Rato-Nunes, J.M.; López-Piñeiro, A. How the environmental fate of clomazone in rice fields is influenced by amendment with olive-mill waste under different regimes of irrigation and tillage. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, S.; Fernández-Rodríguez, D.; Peña, D.; Albarrán, Á.; Rozas, M.Á.; López-Piñeiro, A. Olive mill sludge may reduce water contamination by 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acid (MCPA) in non-flooding but enhance it in flooding rice cropping agroecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamara, B.S.; Marambe, B.; Kumar, V.; Ismail, A.M.; Septiningsih, E.M.; Chauhan, B.S. Optimizing sowing and flooding depth for anaerobic germination-tolerant genotypes to enhance crop establishment, early growth, and weed management in dry-seeded rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 871, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayanto, T.; Susanti, Y.; Rahni, N.M.; Tufaila, M.; Rembon, F.S. Seedling-stage screening method for tolerance of upland rice genotypes to low pH stress. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 782, 032030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girsang, S.S.; Quilty, J.R.; Correa, T.Q.; Sanchez, P.B.; Buresh, R.J. Rice yield and relationships to soil properties for production using overhead sprinkler irrigation without soil submergence. Geoderma 2019, 352, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanat, M.A.; Naeem, M.K.; Algwaiz, H.I.M.; Uzair, M.; Attia, K.A.; Alkathani, M.D.F.; Zaid, I.U.; Zafar, S.A.; Inam, S.; Fiaz, S.; et al. Evaluation of Green Super Rice Lines for Agronomic and Physiological Traits under Salinity Stress. Plants 2022, 11, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korres, N.E.; Loka, D.A.; Gitsopoulos, T.K.; Varanasi, V.K.; Chachalis, D.; Price, A.; Slaton, N.A. Salinity effects on rice, rice weeds, and strategies to secure crop productivity and effective weed control. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borin, J.B.M.; Carmona, F.D.C.; Anghinoni, I.; Martins, A.P.; Jaeger, I.R.; Marcolin, E.; Hernandes, G.C.; Camargo, E.S. Soil solution chemical attributes, rice response and water use efficiency under different flood irrigation management methods. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, R.N.; Iqbal, A.; Iqbal, M.A.; Ali, O.M.; Ahmed, R.; Ijaz, R.; Hadifa, A.; Bethune, B.J. Weed-free durations and fertilization regimes boost nutrient uptake and paddy yield of direct-seeded fine rice (Oryza sativa L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhukar, A.; Kumar, V.; Dashora, K. Spatial and Temporal Trends in the Yields of Three Major Crops: Wheat, Rice and Maize in India. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2020, 14, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitran, T.; Basak, N.; Mani, P.K.; Tamang, A.; Singh, D.K.; Biswas, S.; Mandal, B. Improving Crop Productivity and Soil Quality Through Soil Management Practices in Coastal Saline Agro-ecosystem. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 3514–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Muhammad, A.; Chattha, M.U.; Skalicky, M.; Bilal Chattha, M.; Ahsin Ayub, M.; Rizwan Anwar, M.; Soufan, W.; Hassan, M.U.; Rahman, M.A.; et al. Mitigation of Salinity-Induced Oxidative Damage, Growth, and Yield Reduction in Fine Rice by Sugarcane Press Mud Application. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 840900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bhattacharya, T.; Mukherjee, S.; Sarkar, B. A perspective on biochar for repairing damages in the soil–plant system caused by climate change-driven extreme weather events. Biochar 2022, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mboyerwa, P.A.; Kibret, K.; Mtakwa, P.W.; Aschalew, A. Evaluation of growth, yield, and water productivity of paddy rice with water-saving irrigation and optimization of nitrogen fertilization. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Ma, F.; Yang, R.; Chen, L.; Jia, B.; Cui, J.; Fan, H.; Wang, X.; Li, L. Rice performance and water use efficiency under plastic mulching with drip irrigation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, G.; Chen, T.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Reprint of “Morphological and physiological traits of roots and their relationships with water productivity in water-saving and drought-resistant rice”. Field Crop. Res. 2014, 165, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and in Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rokonuzzaman, M.D.; Ye, Z.; Wu, C.; Li, W. Arsenic accumulation in rice: Alternative irrigation regimes produce rice safe from arsenic contamination. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 310, 119829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Huang, B.; Zeng, H.; Wang, X.; Peng, B.; Yu, H.; Guo, W. Arsenic extraction from seriously contaminated paddy soils with ferrihydrite-loaded sand columns. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrijo, D.R.; LaHue, G.T.; Parikh, S.J.; Chaney, R.L.; Linquist, B.A. Mitigating the accumulation of arsenic and cadmium in rice grain: A quantitative review of the role of water management. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Bhattacharyya, K.; Mandal, J.; Bhattacharya, P.; Halder, S.; Pari, A. Deficit irrigation and organic amendments can reduce dietary arsenic risk from rice: Introducing machine learning-based prediction models from field data. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 319, 107516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.T.; Paniz, F.P.; Sanchez, F.E.S.; Pedron, T.; Torres, D.P.; da Rocha Concenço, F.I.G.; Barbat Parfitt, J.M.; Batista, B.L. Selected soil water tensions at phenological phases and mineral content of trace elements in rice grains—mitigating arsenic by water management. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Yang, Z.; Ji, J.; Yu, T.; Yuan, J. Effects of Soil pH and Mineral Nutrients on Cadmium Uptake by Rice Grain in the Pearl River Delta, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrasek, G.; Rengel, Z.; Romic, D. Humic acids decrease uptake and distribution of trace metals, but not the growth of radish exposed to cadmium toxicity. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2018, 151, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, D.; López-Piñeiro, A.; Albarrán, A.; Peña, D. Direct and residual effects on diuron behaviour and persistence following two-phase olive mill waste addition to soil: Field and laboratory experiments. Geoderma 2010, 157, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Piñeiro, A.; Albarrán, A.; Rato-Nunes, J.M.; Peña, D.; Cabrera, D. Long-term impacts of de-oiled two-phase olive mill waste on soil chemical properties, enzyme activities and productivity in an olive grove. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 114, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| GI (%) | RI (%) | Y (kg ha−1) | WP (g L−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | ||||
| SNT | 56.5cA | 87.0aB | 9 226abA | 1.07bA |
| SNT-C | 51.9bcA | 88.2aB | 9 183abA | 1.07bA |
| ST | 52.2cA | 88.6aB | 10 307bA | 1.20bA |
| ST-C | 52.7cA | 86.2aA | 10 212bA | 1.19bA |
| FT | 46.2abB | 88.4aB | 8 343aA | 0.513aA |
| FT-C | 43.8aB | 91.0aB | 7 780aA | 0.478aA |
| 2019 | ||||
| SNT | 62.7bA | 73.2aA | 7 070aA | 0.796bA |
| SNT-C | 59.4bA | 73.1aA | 8 436aA | 0.950bA |
| ST | 62.9bB | 82.3bA | 11 625bA | 1.31cA |
| ST-C | 58.4bA | 80.2bA | 10 872bA | 1.22cA |
| FT | 31.6aA | 74.7aA | 7 921aA | 0.516aA |
| FT-C | 31.6aA | 73.5aA | 7 654aA | 0.499aA |
| Y | NS | *** | NS | NS |
| T | *** | * | *** | *** |
| Y × T | * | NS | * | ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peña, D.; Martín, C.; Fernández-Rodríguez, D.; Terrón-Sánchez, J.; Vicente, L.A.; Albarrán, Á.; Rato-Nunes, J.M.; López-Piñeiro, A. Medium-Term Effects of Sprinkler Irrigation Combined with a Single Compost Application on Water and Rice Productivity and Food Safety. Plants 2023, 12, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12030456
Peña D, Martín C, Fernández-Rodríguez D, Terrón-Sánchez J, Vicente LA, Albarrán Á, Rato-Nunes JM, López-Piñeiro A. Medium-Term Effects of Sprinkler Irrigation Combined with a Single Compost Application on Water and Rice Productivity and Food Safety. Plants. 2023; 12(3):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12030456
Chicago/Turabian StylePeña, David, Carmen Martín, Damián Fernández-Rodríguez, Jaime Terrón-Sánchez, Luis Andrés Vicente, Ángel Albarrán, Jose Manuel Rato-Nunes, and Antonio López-Piñeiro. 2023. "Medium-Term Effects of Sprinkler Irrigation Combined with a Single Compost Application on Water and Rice Productivity and Food Safety" Plants 12, no. 3: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12030456
APA StylePeña, D., Martín, C., Fernández-Rodríguez, D., Terrón-Sánchez, J., Vicente, L. A., Albarrán, Á., Rato-Nunes, J. M., & López-Piñeiro, A. (2023). Medium-Term Effects of Sprinkler Irrigation Combined with a Single Compost Application on Water and Rice Productivity and Food Safety. Plants, 12(3), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12030456









