The Roles of Gibberellins in Regulating Leaf Development
Abstract
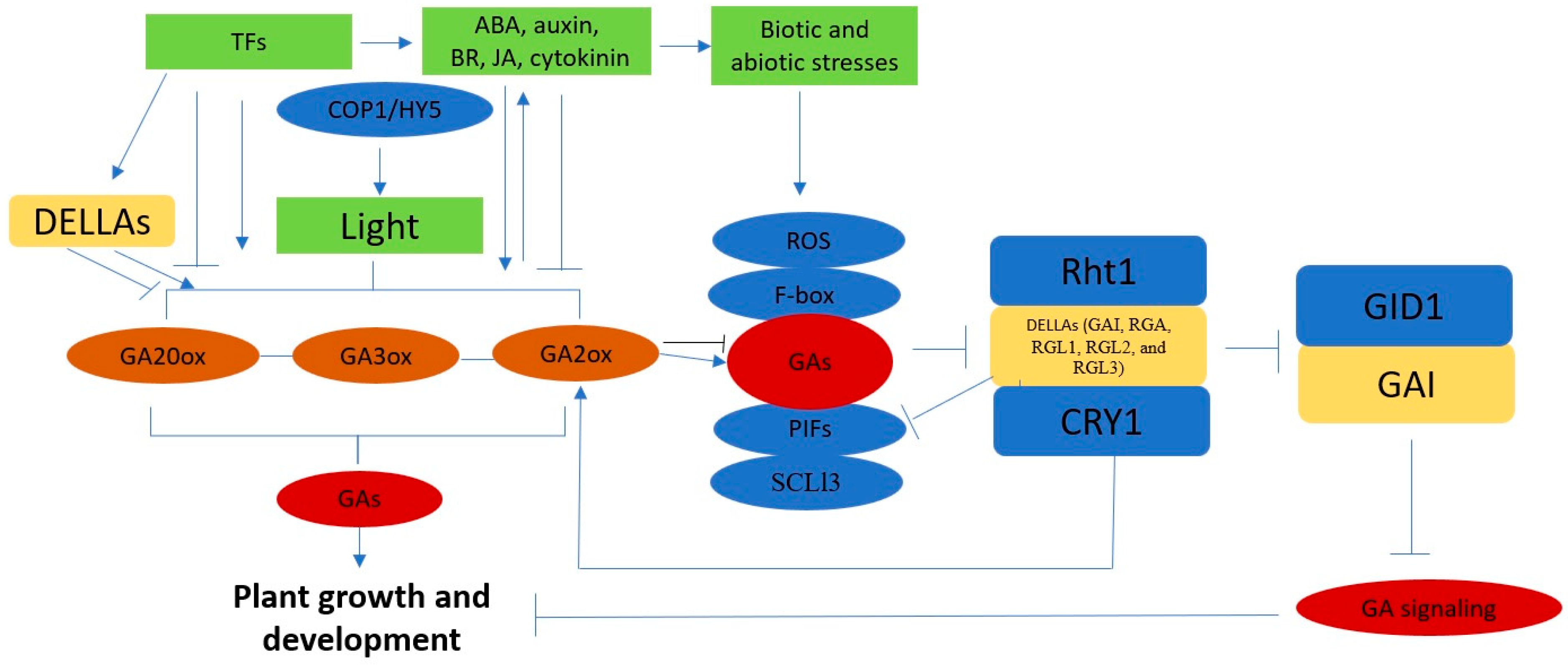
:1. Introduction
2. GA Level Affects Plant Phenotype
3. GAs Regulate Leaf Development
3.1. Leaf Size
3.2. Leaf Angle
3.3. Leafy Head Formation
3.4. Leaf Senescence
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitchell, J.W.; Skaggs, D.P.; Anderson, W.P. Plant growth-stimulating hormones in immature bean seeds. Science 1951, 114, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anterola, A.; Shanle, E. Genomic Insights in Moss Gibberellin Biosynthesis. Bryologist 2008, 111, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirk, W.A.; Tarkowská, D.; Gruz, J.; Strnad, M.; Ördög, V.; van Staden, J. Effect of gibberellins on growth and biochemical constituents in Chlorella minutissima (Trebouxiophyceae). S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 126, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Cerezo, S.; Martínez-Montiel, N.; García-Sánchez, J.; Pérez-y-Terrón, R.; Martínez-Contreras, R.D. Gibberellin biosynthesis and metabolism: A convergent route for plants, fungi and bacteria. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 208, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T. Gibberellin metabolism, perception and signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. Arab. Book/Am. Soc. Plant Biol. 2008, 6, e0103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Xin, P.; Ma, X.; Chu, J.; Wang, G. Gibberellin Metabolism in Flowering Plants: An Update and Perspectives. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gao, H.; Jiang, J.; Dzyubenko, N.; Chapurin, V.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X. Overexpression of the Galega orientalis gibberellin receptor improves biomass production in transgenic tobacco. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 73, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.-w.; Lyu, S.-w.; Tang, J.; Zhou, D.-y.; Bonnema, G.; Xiao, D.; Hou, X.-l.; Zhang, C.-w. Genome-wide analysis of auxin transport genes identifies the hormone responsive patterns associated with leafy head formation in Chinese cabbage. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Wu, P.; Lu, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhong, Z.; Shen, R.; Xie, Q. Synergistic Interaction of Phytohormones in Determining Leaf Angle in Crops. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Chen, Q.; Wu, X.; Chen, F.; Yuan, L.; Mi, G. Gibberellins synthesis is involved in the reduction of cell flux and elemental growth rate in maize leaf under low nitrogen supply. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 150, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Maodzeka, A.; Zhou, L.; Ali, E.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, L. Removal of DELLA repression promotes leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2014, 219–220, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miransari, M.; Smith, D. Plant hormones and seed germination. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 99, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaion, L.A.; Muniz, J.C.; Barreto, R.F.; D’Amico-Damião, V.; de Mello Prado, R.; Carvalho, R.F. Amplification of gibberellins response in tomato modulates calcium metabolism and blossom end rot occurrence. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 246, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.-w.; Lei, Y.-l.; Huang, X.-m.; Su, W.; Chen, R.-y.; Hao, Y.-w. Crosstalk of cold and gibberellin effects on bolting and flowering in flowering Chinese cabbage. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.-m.; Xu, Y.-m.; Zeng, Z.-x.; Tan, X.-l.; Liu, Z.-l.; Chen, J.-w.; Su, X.-g.; Chen, J.-y. Activation of the Transcription of BrGA20ox3 by a BrTCP21 Transcription Factor Is Associated with Gibberellin-Delayed Leaf Senescence in Chinese Flowering Cabbage during Storage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Sima, W.; Ouyang, B.; Wang, T.; Ziaf, K.; Luo, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Chen, M.; Huang, Y.; et al. Tomato SlDREB gene restricts leaf expansion and internode elongation by downregulating key genes for gibberellin biosynthesis. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 6407–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Gao, Y.; Xue, M.; Xu, J.; Liao, R.; Shang, S.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; et al. BrKAO2 mutations disrupt leafy head formation in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 2453–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieu, I.; Ruiz-Rivero, O.; Fernandez-Garcia, N.; Griffiths, J.; Powers, S.J.; Gong, F.; Linhartova, T.; Eriksson, S.; Nilsson, O.; Thomas, S.G.; et al. The gibberellin biosynthetic genes AtGA20ox1 and AtGA20ox2 act, partially redundantly, to promote growth and development throughout the Arabidopsis life cycle. Plant J. 2008, 53, 488–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesejo, C.; Yuste, R.; Reig, C.; Martínez-Fuentes, A.; Iglesias, D.J.; Muñoz-Fambuena, N.; Bermejo, A.; Germanà, M.A.; Primo-Millo, E.; Agustí, M. Gibberellin reactivates and maintains ovary-wall cell division causing fruit set in parthenocarpic Citrus species. Plant Sci. 2016, 247, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshome, S.; Kebede, M. Analysis of regulatory elements in GA2ox, GA3ox and GA20ox gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana: An important trait. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2021, 35, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ye, X.; Xiong, A.; Zhu, N.; Jiang, L.; Qu, S. The regulatory role of gibberellin related genes DKGA2ox1 and MIR171f_3 in persimmon dwarfism. Plant Sci. 2021, 310, 110958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Underhill, S.J.R. Breadfruit (Artocarpus altilis) gibberellin 2-oxidase genes in stem elongation and abiotic stress response. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Ali, S.S.; Gao, L.; Ni, X.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, J. Identification and expression analysis of Sorghum bicolor gibberellin oxidase genes with varied gibberellin levels involved in regulation of stem biomass. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 145, 111951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Gao, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Han, M.; An, N.; Ren, X. Effects of Brassinosteroid Associated with Auxin and Gibberellin on Apple Tree Growth and Gene Expression Patterns. Hortic. Plant J. 2019, 5, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, M.; You, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Small Grain and Dwarf 2, encoding an HD-Zip II family transcription factor, regulates plant development by modulating gibberellin biosynthesis in rice. Plant Sci. 2019, 288, 110208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Du, K.; Kang, X.; Wei, H. The diverse roles of cytokinins in regulating leaf development. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prerostova, S.; Zupkova, B.; Petrik, I.; Simura, J.; Nasinec, I.; Kopecky, D.; Knirsch, V.; Gaudinova, A.; Novak, O.; Vankova, R. Hormonal responses associated with acclimation to freezing stress in Lolium perenne. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 182, 104295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelissen, H.; Rymen, B.; Jikumaru, Y.; Demuynck, K.; Van Lijsebettens, M.; Kamiya, Y.; Inzé, D.; Beemster, G.T. A Local Maximum in Gibberellin Levels Regulates Maize Leaf Growth by Spatial Control of Cell Division. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1183–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavallali, V.; Karimi, S. Methyl jasmonate enhances salt tolerance of almond rootstocks by regulating endogenous phytohormones, antioxidant activity and gas-exchange. J. Plant Physiol. 2019, 234-235, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Li, J.; Lu, L.; Yi, X.; Yao, N.; Lai, Z.; Zhang, J. Comparative transcriptome study of the elongating internode in elephant grass (Cenchrus purpureus) seedlings in response to exogenous gibberellin applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 178, 114653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Tang, D.; Shen, Y.; Qin, B.; Hong, L.; You, A.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Gu, M.; et al. Activation of gibberellin 2-oxidase 6 decreases active gibberellin levels and creates a dominant semi-dwarf phenotype in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Genet. Genom. 2010, 37, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayano, M.; Kani, T.; Kojima, M.; Sakakibara, H.; Kitaoka, T.; Kuroha, T.; Angeles-Shim, R.B.; Kitano, H.; Nagai, K.; Ashikari, M. Gibberellin biosynthesis and signal transduction is essential for internode elongation in deepwater rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 2313–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Tang, J.; Yang, D.; Yang, T.; Liu, H.; Luo, W.; Wu, J.; Jianqiang, W.; Wang, L. Jasmonoyl-l-isoleucine and allene oxide cyclase-derived jasmonates differently regulate gibberellin metabolism in herbivory-induced inhibition of plant growth. Plant Sci. 2020, 300, 110627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, S.; Qu, G.; Fu, W.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Feng, H. The mutation of ent-kaurene synthase, a key enzyme involved in gibberellin biosynthesis, confers a non-heading phenotype to Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Neill, S.J.; Tang, Z.; Cai, W. Gibberellin-regulated XET is differentially induced by auxin in rice leaf sheath bases during gravitropic bending. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallego-Giraldo, L.; García-Martínez, J.L.; Moritz, T.; López-Díaz, I. Flowering in tobacco needs gibberellins but is not promoted by the levels of active GA1 and GA4 in the apical shoot. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007, 48, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choubane, D.; Rabot, A.; Mortreau, E.; Legourrierec, J.; Péron, T.; Foucher, F.; Ahcène, Y.; Pelleschi-Travier, S.; Leduc, N.; Hamama, L.; et al. Photocontrol of bud burst involves gibberellin biosynthesis in Rosa sp. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, L.; Fambrini, M.; Pugliesi, C.; Scartazza, A. The gibberellin-deficient dwarf2 mutant of sunflower shows a high constitutive level of jasmonic and salicylic acids and an elevated energy dissipation capacity in well-watered and drought conditions. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 194, 104697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Tarkowska, D.; Sedaghatmehr, M.; Welsch, M.; Gupta, S.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Balazadeh, S. The HB40-JUB1 transcriptional regulatory network controls gibberellin homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant. 2022, 15, 322–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcioni, R.; Moriwaki, T.; Bonato, C.M.; de Souza, L.A.; Nanni, M.R.; Antunes, W.C. Distinct growth light and gibberellin regimes alter leaf anatomy and reveal their influence on leaf optical properties. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2017, 140, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMason, D.A. Auxin-cytokinin and auxin-gibberellin interactions during morphogenesis of the compound leaves of pea (Pisum sativum). Planta 2005, 222, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, N.; Hammad, H. The effect of vernalization and sprayed gibberellins and humic acid on the growth and production of cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitat). J. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 3, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Xiang, F.; Su, Y.; Luo, Z.; Luo, W.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Xiao, L. Gibberellin Increases the Bud Yield and Theanine Accumulation in Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze. Molecules 2021, 26, 3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duclos, D.V.; Björkman, T. Gibberellin control of reproductive transitions in Brassica oleracea curd development. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2015, 140, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, W.; Wang, Y.; Qi, C.; Luo, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, W.; Qu, S. Fine mapping identified the gibberellin 2-oxidase gene CpDw leading to a dwarf phenotype in squash (Cucurbita pepo L.). Plant Sci. 2021, 306, 110857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, B.; Liu, H.; Song, S.; Hao, Y.; Chen, R. Identification of DELLA Genes and Key Stage for GA Sensitivity in Bolting and Flowering of Flowering Chinese Cabbage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, W.; Li, J.; Jiang, W.; Xiao, C.; Wei, D.; Yang, C.; Xu, R.; et al. Gibberellin disturbs the balance of endogenesis hormones and inhibits adventitious root development of Pseudostellaria heterophylla through regulating gene expression related to hormone synthesis. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, H.; De Bodt, S.; Inzé, D. Gibberellins and DELLAs: Central nodes in growth regulatory networks. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Hashemi, J.; Ahmadi, A.; Abbasi, A.; Pompeiano, A.; Tavarini, S.; Guglielminetti, L.; Angelini, L.G. Opposing Effects of External Gibberellin and Daminozide on Stevia Growth and Metabolites. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.O.; Omena-Garcia, R.P.; Oliveira, F.S.; Silva, W.A.; Hajirezaei, M.-R.; Vallarino, J.G.; Ribeiro, D.M.; Fernie, A.R.; Nunes-Nesi, A.; Araújo, W.L. Differential root and shoot responses in the metabolism of tomato plants exhibiting reduced levels of gibberellin. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 157, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Y.; An, C. Identification of gibberellin acid-responsive proteins in rice leaf sheath using proteomics. FBL 2010, 15, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shwartz, I.; Levy, M.; Ori, N.; Bar, M. Hormones in tomato leaf development. Dev. Biol. 2016, 419, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Wang, S.; Qi, L.; Yin, L.; Deng, X. Galactolipid remodeling is involved in drought-induced leaf senescence in maize. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 150, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Li, P.; Shang, B.; Liu, S.; Yang, A.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Z. Differential responses of peach (Prunus persica) seedlings to elevated ozone are related with leaf mass per area, antioxidant enzymes activity rather than stomatal conductance. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritonga, F.N.; Yan, S.; Chen, S.; Slamet, S.A.; Irmayanti, L.; Song, R.; Lin, X.; Jing, Y.; Farooq, U.; Khoso, M.A.; et al. Cold Acclimation Affects Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Betula platyphylla S. under Freezing Stress. Forests 2021, 12, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, D.; Li, C.; Ding, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Zheng, H.; Gao, J. Genetic and Transcriptome Analysis of Leaf Trichome Development in Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa L. subsp. pekinensis) and Molecular Marker Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrom, L.; Munné-Bosch, S. Hormonal regulation of leaf senescence in Lilium. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, N.; Vanhaeren, H.; Inzé, D. Leaf size control: Complex coordination of cell division and expansion. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukaya, H. Organ shape and size: A lesson from studies of leaf morphogenesis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozuka, T.; Horiguchi, G.; Kim, G.T.; Ohgishi, M.; Sakai, T.; Tsukaya, H. The different growth responses of the Arabidopsis thaliana leaf blade and the petiole during shade avoidance are regulated by photoreceptors and sugar. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelissen, H.; Gonzalez, N.; Inzé, D. Leaf growth in dicots and monocots: So different yet so alike. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2016, 33, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Pan, C.; Yang, N.; Sun, K.; He, C. Gibberellins are required for dimorphic flower development in Viola philippica. Plant Sci. 2021, 303, 110749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasetyaningrum, P.; Mariotti, L.; Valeri, M.C.; Novi, G.; Dhondt, S.; Inzé, D.; Perata, P.; van Veen, H. Nighttime gibberellin biosynthesis is influenced by fluctuating environmental conditions and contributes to growth adjustments of Arabidopsis leaves. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyaningrum, P.; Mariotti, L.; Valeri, M.C.; Novi, G.; Dhondt, S.; Inzé, D.; Perata, P.; van Veen, H. Nocturnal gibberellin biosynthesis is carbon dependent and adjusts leaf expansion rates to variable conditions. Plant Physiol. 2021, 185, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, F.; Inagaki, N.; Takano, M. Differences and similarities in the photoregulation of gibberellin metabolism between rice and dicots. Plant Signal Behav 2013, 8, e23424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Yu, C.; Zhao, T.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Liu, J. OsBIC1 Directly Interacts with OsCRYs to Regulate Leaf Sheath Length through Mediating GA-Responsive Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Cheng, Q.; Qin, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Ji, R.; Mu, R.; Li, H.; Zhao, T.; Liu, J.; et al. GmCRY1s modulate gibberellin metabolism to regulate soybean shade avoidance in response to reduced blue light. Mol. Plant. 2021, 14, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Yang, Z.; He, G.; Jing, Y.; Dong, H.; Ju, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, J. The blue light receptor CRY1 interacts with GID1 and DELLA proteins to repress gibberellin signaling and plant growth. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ye, D.; Xing, J.; Duan, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M. Ethephon-regulated maize internode elongation associated with modulating auxin and gibberellin signal to alter cell wall biosynthesis and modification. Plant Sci. 2020, 290, 110196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusmoto, T.; Yamada, K.; Yoshizawa, Y.; Oh, K. Comparison of Effect of Brassinosteroid and Gibberellin Biosynthesis Inhibitors on Growth of Rice Seedlings. Rice Sci. 2016, 23, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Yu, H.; Jiang, W.; Li, H.; Wu, T.; Chu, J.; Xin, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhou, T.; et al. Overexpression of ovate family protein 22 confers multiple morphological changes and represses gibberellin and brassinosteroid signalings in transgenic rice. Plant Sci. 2021, 304, 110734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yimer, H.Z.; Nahar, K.; Kyndt, T.; Haeck, A.; Van Meulebroek, L.; Vanhaecke, L.; Demeestere, K.; Höfte, M.; Gheysen, G. Gibberellin antagonizes jasmonate-induced defense against Meloidogyne graminicola in rice. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Luo, X.; Zhang, A.-Y.; Ma, C.-Y.; Sun, K.; Zhang, T.-T.; Dai, C.-C. Jasmonate signaling restricts root soluble sugar accumulation and drives root-fungus symbiosis loss at flowering by antagonizing gibberellin biosynthesis. Plant Sci. 2021, 309, 110940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.; Gao, X.; Nam, K.H.; Takahashi, K.; Matsuura, H.; Yoshihara, T. Theobroxide inhibits stem elongation in Pharbitis nil by regulating jasmonic acid and gibberellin biosynthesis. Plant Sci. 2005, 169, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.-H.; Shen, H.-L.; Cheng, W.-H. Genetic analyses of the interaction between abscisic acid and gibberellins in the control of leaf development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci. 2015, 236, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Lin, S.-J.; Han, M.-H.; Zhuang, J. Genomic analyses of the crosstalk between gibberellins and brassinosteroids metabolisms in tea plant (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). Sci. Hortic. 2020, 268, 109368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, D. Gibberellins, brassinolide, and ethylene signaling were involved in flower differentiation and development in Nelumbo nucifera. Hortic. Plant J. 2022, 8, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Han, Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Xu, X.; Lin, H.; Zhang, D. A HAT1-DELLA signaling module regulates trichome initiation and leaf growth by achieving gibberellin homeostasis. New Phytol. 2021, 231, 1220–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, N.; De Bodt, S.; Sulpice, R.; Jikumaru, Y.; Chae, E.; Dhondt, S.; Van Daele, T.; De Milde, L.; Weigel, D.; Kamiya, Y.; et al. Increased Leaf Size: Different Means to an End. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1261–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanai, O.; Shani, E.; Russ, D.; Ori, N. Gibberellin partly mediates LANCEOLATE activity in tomato. Plant J. 2011, 68, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, S.; Takasaki, H. Gibberellin-regulated gene in the basal region of rice leaf sheath encodes basic helix–loop–helix transcription factor. Amino Acids 2009, 37, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Krishnan, S.; Merewitz, E.; Xu, J.; Huang, B. Gibberellin-Regulation and Genetic Variations in Leaf Elongation for Tall Fescue in Association with Differential Gene Expression Controlling Cell Expansion. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Zheng, J.; Huang, R.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Fang, X. Phytohormones signaling and crosstalk regulating leaf angle in rice. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 2423–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, K.Y.; Khodaeiaminjan, M.; Yahya, G.; El-Tantawy, A.A.; Abdel El-Moneim, D.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Abd-Elaziz, M.A.A.; Nassrallah, A.A. Modulation of cell cycle progression and chromatin dynamic as tolerance mechanisms to salinity and drought stress in maize. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 172, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Zanten, M.; Pons, T.L.; Janssen, J.A.M.; Voesenek, L.A.C.J.; Peeters, A.J.M. On the Relevance and Control of Leaf Angle. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2010, 29, 300–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zanten, M.; Voesenek, L.A.C.J.; Peeters, A.J.M.; Millenaar, F.F. Hormone- and Light-Mediated Regulation of Heat-Induced Differential Petiole Growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 1446–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millenaar, F.F.; Van Zanten, M.; Cox, M.C.H.; Pierik, R.; Voesenek, L.; Peeters, A.J.M. Differential petiole growth in Arabidopsis thaliana: Photocontrol and hormonal regulation. New Phytol. 2009, 184, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benschop, J.J.; Jackson, M.B.; Gühl, K.; Vreeburg, R.A.; Croker, S.J.; Peeters, A.J.; Voesenek, L.A. Contrasting interactions between ethylene and abscisic acid in Rumex species differing in submergence tolerance. Plant J. 2005, 44, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cox, M.C.; Benschop, J.J.; Vreeburg, R.A.; Wagemaker, C.A.; Moritz, T.; Peeters, A.J.; Voesenek, L.A. The roles of ethylene, auxin, abscisic acid, and gibberellin in the hyponastic growth of submerged Rumex palustris petioles. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 2948–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimada, A.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Sazuka, T.; Ashikari, M.; Matsuoka, M. The rice SPINDLY gene functions as a negative regulator of gibberellin signaling by controlling the suppressive function of the DELLA protein, SLR1, and modulating brassinosteroid synthesis. Plant J. 2006, 48, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Fujisawa, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Ashikari, M.; Iwasaki, Y.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. Rice dwarf mutant d1, which is defective in the alpha subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein, affects gibberellin signal transduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11638–11643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Chong, K.; Xu, Y. OsmiR396d Affects Gibberellin and Brassinosteroid Signaling to Regulate Plant Architecture in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 946–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Qu, G.; Huang, S.; Liu, Z.; Fu, W.; Zhang, M.; Feng, H. BrCPS1 function in leafy head formation was verified by two allelic mutations in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 2426, 889798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, J.; Cai, X.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Lin, R.; Cheng, F.; Wang, X. Divergence of three BRX homoeologs in Brassica rapa and its effect on leaf morphology. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Liang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Lv, H.; Yin, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A cluster of transcripts identifies a transition stage initiating leafy head growth in heading morphotypes of Brassica. Plant J. 2022, 110, 688–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.K.; Xue, W.X.; Sun, Y.D.; Yu, X.H.; Liu, P.L. Leafy head formation of the progenies of transgenic plants of Chinese cabbage with exogenous auxin genes. Cell Res. 2000, 10, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardena, D.M.; Heckathorn, S.A.; Bista, D.R.; Boldt, J.K. Elevated carbon dioxide plus chronic warming causes dramatic increases in leaf angle in tomato, which correlates with reduced plant growth. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Su, T.; Xin, X.; Li, P.; Wang, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; et al. The Adaxial/Abaxial Patterning of Auxin and Auxin Gene in Leaf Veins Functions in Leafy Head Formation of Chinese Cabbage. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 918112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liang, J.; Lin, R.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. Series-Spatial Transcriptome Profiling of Leafy Head Reveals the Key Transition Leaves for Head Formation in Chinese Cabbage. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 787826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Hou, Z.; Gao, L.; Xiao, D.; Hou, X.; Zhang, C.; Yan, J.; Song, L. Conjunctive Analyses of BSA-Seq and BSR-Seq to Reveal the Molecular Pathway of Leafy Head Formation in Chinese Cabbage. Plants 2019, 8, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Lavelle, D.; Yu, C.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Michelmore, R.W.; Kuang, H. The upregulated LsKN1 gene transforms pinnately to palmately lobed leaves through auxin, gibberellin, and leaf dorsiventrality pathways in lettuce. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1756–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Yan, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Lavelle, D.; An, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Han, R.; et al. Upregulation of a KN1 homolog by transposon insertion promotes leafy head development in lettuce. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 33668–33678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemán-Báez, J.; Qin, J.; Cai, C.; Zou, C.; Bucher, J.; Paulo, M.-J.; Voorrips, R.E.; Bonnema, G. Genetic dissection of morphological variation in rosette leaves and leafy heads in cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 3611–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.J.; Herman, D.; Blomme, J.; Chae, E.; Kojima, M.; Coppens, F.; Storme, V.; Van Daele, T.; Dhondt, S.; Sakakibara, H.; et al. Natural Variation of Molecular and Morphological Gibberellin Responses. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, A.-Q.; Feng, K.; Liu, J.-X.; Que, F.; Xu, Z.-S.; Xiong, A.-S. Elevated gibberellin altered morphology, anatomical structure, and transcriptional regulatory networks of hormones in celery leaves. Protoplasma 2019, 256, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zegeye, W.A.; Chen, D.; Islam, M.; Wang, H.; Riaz, A.; Rani, M.H.; Hussain, K.; Liu, Q.; Zhan, X.; Cheng, S.; et al. OsFBK4, a novel GA insensitive gene positively regulates plant height in rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Ecol. Genet. Genom. 2022, 23, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Tan, C.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Huang, S.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Liu, Z.; Feng, H. BrAN contributes to leafy head formation by regulating leaf width in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhac167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Gao, L.; Liu, W.; Song, L.; Xiao, D.; Liu, T.; Hou, X.; Zhang, C. Transcription coactivator ANGUSTIFOLIA3 (AN3) regulates leafy head formation in Chinese cabbage. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhong, W.; Bai, J.; Liu, P.; He, Y. QTL mapping of leafy heads by genome resequencing in the RIL population of Brassica rapa. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.-M.; Kim, J.-T.; Hamayun, M.; Hwang, I.-C.; Khan, A.L.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, I.-J. Influence of prohexadione-calcium on growth and gibberellins content of Chinese cabbage grown in alpine region of South Korea. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 125, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Khan, A.L.; Hamayun, M.; Kim, J.T.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, I.C.; Yoon, C.S.; Lee, I.-J. Effects of Prohexadione Calcium on growth and gibberellins contents of Chrysanthemum morifolium R. cv Monalisa White. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 123, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.Q.; Feng, K.; Wang, G.L.; Liu, J.X.; Xu, Z.S.; Xiong, A.S. Elevated gibberellin enhances lignin accumulation in celery (Apium graveolens L.) leaves. Protoplasma 2019, 256, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ren, G.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Miao, Y.; Guo, H. Leaf senescence: Progression, regulation, and application. Molecular Horticulture 2021, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.R.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, P.O.; Nam, H.G. Leaf Senescence: Systems and Dynamics Aspects. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 347–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Gan, S. Leaf senescence: Signals, execution, and regulation. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2005, 71, 83–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Chai, Z.; Yao, W.; Chen, B.; Zhang, M. Interactions between ScNAC23 and ScGAI regulate GA-mediated flowering and senescence in sugarcane. Plant Sci. 2021, 304, 110806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Duan, X.; Chang, X.; Xian, L.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y. Molecular and metabolic insights into anthocyanin biosynthesis during leaf coloration in autumn. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 190, 104584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.-q.; Tan, X.-l.; Shan, W.; Kuang, J.-f.; Lu, W.-j.; Lin, H.-t.; Su, X.-g.; Lakshmanan, P.; Zhao, M.-l.; Chen, J.-y. Involvement of BrNAC041 in ABA-GA antagonism in the leaf senescence of Chinese flowering cabbage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 168, 111254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Li, Y.; Yao, X.; Qiao, K.; Wei, L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, D.; Lin, H. NAP is involved in GA-mediated chlorophyll degradation and leaf senescence by interacting with DELLAs in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2020, 39, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwat, M.; Naqvi, A.R.; Ahmad, P.; Ashraf, M.; Akram, N.A. Phytohormones and microRNAs as sensors and regulators of leaf senescence: Assigning macro roles to small molecules. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1153–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Wei, J.; Ma, Q.; Yu, D.; Li, J. Senescence of aerial parts is impeded by exogenous gibberellic acid in herbaceous perennial Paris polyphylla. J. Plant Physiol. 2009, 166, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.-Q.; Wei, W.; Tan, X.-L.; Shan, W.; Kuang, J.-F.; Lu, W.-J.; Su, X.-G.; Lakshmanan, P.; Lin, H.-T.; Chen, J.-Y. A NAC transcription factor BrNAC087 is involved in gibberellin-delayed leaf senescence in Chinese flowering cabbage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 181, 111673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritonga, F.N.; Chen, S. Physiological and Molecular Mechanism Involved in Cold Stress Tolerance in Plants. Plants 2020, 9, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritonga, F.N.; Ngatia, J.N.; Song, R.X.; Farooq, U.; Somadona, S.; Andi, T.L.; Chen, S. Abiotic stresses induced physiological, biochemical, and molecular changes in Betula platyphylla: A review. Silva Fenn. 2021, 55, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranwala, A.P.; Miller, W.B. Preventive mechanisms of gibberellin4+7 and light on low-temperature-induced leaf senescence in Lilium cv. Stargazer. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2000, 19, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.-Q.; Tan, X.-L.; Shan, W.; Kuang, J.-F.; Lu, W.-J.; Chen, J.-Y. Characterization of a Transcriptional Regulator, BrWRKY6, Associated with Gibberellin-Suppressed Leaf Senescence of Chinese Flowering Cabbage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.; Chen, Y.; Yu, D.; Chen, L. AtWRKY75 positively regulates age-triggered leaf senescence through gibberellin pathway. Plant Div. 2021, 43, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Yu, D. Arabidopsis WRKY45 Interacts with the DELLA Protein RGL1 to Positively Regulate Age-Triggered Leaf Senescence. Mol. Plant. 2017, 10, 1174–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| No | GA Biosynthesis Genes | Species | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | OsGA2ox6 | O. sativa | Dwarfism, flowering, and seed production | [31] |
| 2 | ZmGA20ox1 | Z. mays | Reduces dwarfism | [28] |
| 3 | RoGA20ox, RoGA3ox, and RoGA2ox | R. rubiginosa | Branching pattern and bud burst | [37] |
| 4 | AaGA2ox1–AaGA2ox3 | A. altilis | Internode elongation | [22] |
| 5 | OsCPS1, OsKO2, OsGA20ox1, and OsGA20ox3 | O. sativa | Leaf angle | [92] |
| 6 | BrKS1 | B. rapa | Leafy head | [34] |
| 7 | BrCPS1 | B. rapa | Leafy head | [93] |
| 8 | BrGASAs, BrGA2oxs, and BrGA20oxs | B. rapa | Leafy head | [100] |
| 9 | LsGA3ox1 and LsGA20ox1 | Lactuca serriola | Leafy head | [101,102] |
| 10 | BolGA20ox1 | B. oleracea | Leafy head | [103] |
| 11 | SbGA2ox1 | Sorghum bicolor | Stem biomass | [23] |
| 12 | GA20ox1 | Arabidopsis | Leaf size and shape | [104] |
| 13 | AgKO, AgKAO, AgGA20ox1, AgGA20ox2, AgGA3ox1, AgGA2ox1, AgGA2ox3, AgKS, and AgGA2ox2 | Apium graveolens | Leafy head | [105] |
| 14 | NtGA20ox1, NtGA20ox2, NtGA3ox1, and NtGA2ox1 | N. tabacum | Bolting and flowering | [36] |
| 15 | GA20ox4 | Z. mays | Elongation zone | [10] |
| 16 | GA20ox2 | Citrus unshiu | Fruit set | [19] |
| 17 | ZmGA2ox3, ZmGA2ox10, and ZmGA3ox1 | Z. mays | Promote fruit ripening, abscission, and flower induction | [69] |
| 18 | VpGA20ox and VpGA3ox | Viola philippica | Flower development | [62] |
| 19 | CsGA20ox1 | C. sinensis | All development stages | [76] |
| 20 | OsGA20ox2 | O. sativa | Internode | [90] |
| 21 | OsKAO, OsGA3ox2, and OsGA2ox2 | O. sativa | Semi-dwarf | [106] |
| 22 | BrKAO2 | B. rapa | Leafy head | [17] |
| No | TFs | TF Family | GA Biosynthesis Genes | Species | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HDZIP5, HDZIP8, HDZIP3, and HDZIP6 | HD-ZIP | GA2ox GID1 | C. purpureus | Improve internode elongation | [30] |
| 2 | SGD2/OsHOX3 | HD-ZIP | O. sativa | Improve height and grain size | [25] | |
| 3 | SlDREB | AP2/ERF | SlGA20ox1, SlGA20ox2, and SlGA20ox4 | S. lycopersicum | Leaf expansion and internode elongation | [16] |
| 4 | LANCEOLATE (LA) | CIN-TCP | SlGA20ox1 and SlGA2ox4 | S. lycopersicum | Leaf differentiation | [80] |
| 5 | bHLH | O. sativa | Leaf sheath elongation | [81] | ||
| 6 | HAT1 | HD-ZIP II | DELLAs (GAI and RGA) | Arabidopsis | Enlarges cotyledons and trichome initiation | [78] |
| 7 | BrNAC08 | NAC | BrPPH, BrRCCR, and BrGA2ox1 | B. rapa | Leaf senescence | [122] |
| 8 | BrWRKY6 | WRKY | BrKAO2 and BrGA20ox2 | B. rapa | Leaf senescence | [126] |
| 9 | WRKY75 | WRKY | SAG12 | Arabidopsis | Leaf senescence | [127] |
| 10 | BrTCP21 | TCP | BrGA20ox3 | B. rapa | Leaf senescence | [15] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ritonga, F.N.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Song, R.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Gao, J. The Roles of Gibberellins in Regulating Leaf Development. Plants 2023, 12, 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061243
Ritonga FN, Zhou D, Zhang Y, Song R, Li C, Li J, Gao J. The Roles of Gibberellins in Regulating Leaf Development. Plants. 2023; 12(6):1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061243
Chicago/Turabian StyleRitonga, Faujiah Nurhasanah, Dandan Zhou, Yihui Zhang, Runxian Song, Cheng Li, Jingjuan Li, and Jianwei Gao. 2023. "The Roles of Gibberellins in Regulating Leaf Development" Plants 12, no. 6: 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061243
APA StyleRitonga, F. N., Zhou, D., Zhang, Y., Song, R., Li, C., Li, J., & Gao, J. (2023). The Roles of Gibberellins in Regulating Leaf Development. Plants, 12(6), 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12061243






