Control Efficacy of the Bt Maize Event DBN3601T Expressing Cry1Ab and Vip3Aa Proteins against Beet Armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Hübner), in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Insecticidal Protein Expression in DBN3601T Maize Tissues
2.2. Susceptibility of Spodoptera exigua to Both Cry1Ab and Vip3Aa Proteins
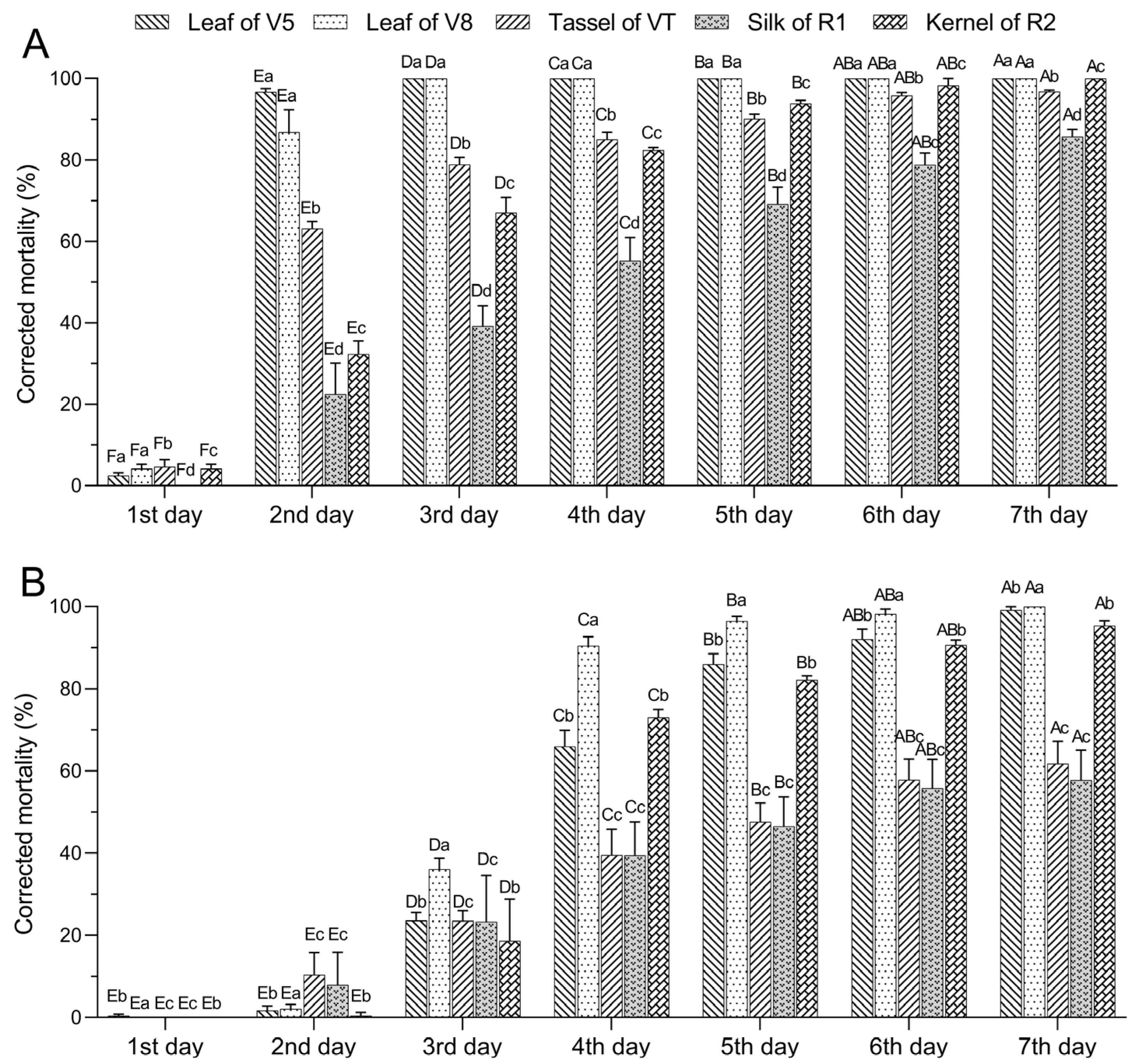
2.3. Lethal Effects of Various Tissues of DBN3601T Maize on Spodoptera exigua Larvae
2.4. Field Control Efficacy of DBN3601T Maize on Spodoptera exigua Larvae by the Cage Trial
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insects and Maize Materials
4.2. Insecticidal Protein Expression in DBN3601T Maize Tissues
4.3. Susceptibility of Spodoptera exigua to Cry1Ab and Vip3Aa Proteins
4.4. Bioassay of DBN3601T Maize Tissue’s Resistance to Spodoptera exigua
4.5. Field Control Efficacy of DBN3601T Maize on Spodoptera exigua Larvae by Cage Trial
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.L.; Cong, X.P.; Wang, X.P.; Lei, C.L. A review of geographic distribution, overwintering and migration in Spodoptera exigua Hübner (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Entomol. Res. Soc. 2011, 13, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Smits, P.H.; Velden, M.C.; Vrie, M.; Vlak, J.M. Feeding and dispersion of Spodoptera exigua larvae and its relevance for control with a nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1987, 43, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia-Meseguer, A.; Alves, T.J.; Budia, F.; Ortiz, A.; Medina, P. Insecticidal toxicity of thirteen commercial plant essential oils against Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Phytoparasitica 2018, 46, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrkhou, F.; Talebi, A.A.; Moharramipour, S.; Naveh, V.H. Demographic parameters of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on different soybean cultivars. Environ. Entomol. 2012, 41, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.Z.; Cao, Y.Z.; Jiang, X.F. Occurrence characteristics and trend analysis of beet armyworm. Plant Prot. 2000, 26, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.F.; Luo, Z.L. Outbreak characteristic and management of Spodoptera exigua in China. J. Changjiang Veg. 2010, 18, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Shelton, A.; Ye, G.Y. Insect-resistant genetically modified rice in China: From research to commercialization. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.J.; Huang, J.K.; Qiao, F.B. Farmers’ knowledge on pest management and pesticide use in Bt cotton production in China. China Econ. Rev. 2013, 27, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Xang, X.; Yu, H.L.; Liu, S.H.; Yin, Y.; Cui, P.; Wu, Y.Q.; Yang, J.; Jiang, C.X.; Yang, Q.F. Monitoring and biochemical characterization of beta-cypermethrin resistance in Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Sichuan Province, China. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 146, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, W.N.; Shi, T.; Wu, Y.D.; Yang, Y.H. Insecticide resistance status of field populations of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) from China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, B.D.; Hellmich, R.L. Understanding successful resistance management: The European corn borer and Bt corn in the United States. GM Crops Food 2012, 3, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkness, E.C.; Dively, G.; Patton, T.; Morey, A.C.; Hutchison, W.D. Novel Vip3A Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) maize approaches high-dose efficacy against Helicoverpa zea (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) under field conditions: Implications for resistance management. GM Crops 2010, 1, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.N.; Leonard, B.R.; Gable, R.H. Comparative susceptibility of European corn borer, southwestern corn borer, and sugarcane borer (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) to Cry1Ab protein in a commercial Bacillus thuringiensis corn hybrid. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 99, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimi, D.A.; Parody, B.; Ramos, M.L.; Machado, M.; Ocampo, F.; Willse, A.; Martinelli, A.; Head, G. Field-evolved resistance to Bt maize in sugarcane borer (Diatraea saccharalis) in Argentina. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissle, M.; Romeis, J.; Bigler, F. Bt maize and integrated pest management-a European perspective. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botha, A.S.; Erasmus, A.; Plessis, H.; Berg, J.V. Efficacy of Bt maize for control of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in South Africa. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchison, W.D.; Burkness, E.C.; Mitchell, P.D.; Moon, R.D.; Leslie, T.W.; Fleischer, S.J.; Abrahamson, M.; Hamilton, K.L.; Steffey, K.L.; Gray, M.E.; et al. Areawide suppression of European corn borer with Bt maize reaps savings to non-Bt maize growers. Science 2010, 330, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassmann, A.J.; Reisig, D.D. Management of insect pests with Bt crops in the United States. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2023, 68, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, Q.L.; Wang, Y.H. Global genetically modified crop industrialization trends in 2022. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 25, 6–16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.P.; Wu, K.M. Commercial strategy of transgenic insect-resistant maize in China. J. Plant Prot. 2022, 49, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Naranjo, S.E. Impacts of Bt transgenic cotton on integrated pest management. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5842–5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.L.; Li, Y.H.; Li, X.J.; Romeis, J.; Wu, K.M. Expression of Cry1Ac in transgenic Bt soybean lines and their efficiency in controlling lepidopteran pests. Pest Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.H.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhao, S.Y.; Wu, K.M. Susceptibilities of the Invasive Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) to the Insecticidal Proteins of Bt maize in China. Toxins 2022, 14, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wang, W.H.; Kang, G.D.; Yang, X.M.; Wu, K.M. Toxic effects of Bt-(Cry1Ab+Vip3Aa) maize on storage pest Paralipsa gularis (Zeller). Toxins 2024, 16, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Yang, X.M.; Wang, W.H.; Wu, K.M. Insecticidal effects of transgenic maize Bt-Cry1Ab, Bt-Vip3Aa, and Bt-Cry1Ab+Vip3Aa against the Oriental Armyworm, Mythimna separata (Walker) in southwest China. Toxins 2024, 16, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.G.; Zhang, D.D.; Li, D.Y.; Zhao, S.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Xiao, Y.T.; Xu, D.; Yang, Y.Z.; Li, G.P.; Wang, L.L.; et al. Expression profiles of Cry1Ab protein and its insecticidal efficacy against the invasive fall armyworm for Chinese domestic GM maize DBN9936. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Y.; Yang, X.M.; Liu, D.Z.; Sun, X.X.; Li, G.P.; Wu, K.M. Performance of the domestic Bt corn event expressing pyramided Cry1Ab and Vip3Aa19 against the invasive Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) in China. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.P.; Ji, T.J.; Zhao, S.Y.; Feng, H.Q.; Wu, K.M. High-dose assessment of transgenic insect-resistant maize events against major lepidopteran pests in China. Plants 2022, 11, 3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.D.; Quan, Y.D.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L. Resistance of transgenic Bt maize (Ruifeng 125, DBN9936 & DBN9978) to Asian corn borer. Plant Prot. 2021, 47, 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Carriere, Y. Surge in insect resistance to transgenic crops and prospects for sustainability. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassmann, A.J. Resistance to Bt maize by western corn rootworm: Effects of pest biology, the pest-crop interaction and the agricultural landscape on resistance. Insects 2021, 5, 12–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storer, N.P.; Kubiszak, M.E.; Ed King, J.; Thompson, G.D.; Santos, A.C. Status of resistance to Bt maize in Spodoptera frugiperda: Lessons from Puerto Rico. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhao, W.L.; Han, S.; Wang, L.X.; Chang, X.; Liu, K.Q.; Quan, Y.D.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L. Seven years of monitoring susceptibility to Cry1Ab and Cry1F in Asian corn borer. Toxins 2023, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.B.; Liu, S.; Long, Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhao, W.L.; Shwe, S.M.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L.; Bai, S.X. Baseline susceptibility and resistance allele frequency in Ostrinia furnacalis in relation to Cry1Ab toxins in China. Toxins 2022, 14, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y.H.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, Y.H.; Carrière, Y.; Wu, Y.D. Susceptibility and diagnostic concentration for Bacillus thuringiensis toxins and newer chemical insecticides in Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) from China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 116, 1830–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnepf, E.; Crickmore, N.; Van Rie, J.; Lereclus, D.; Baum, J.; Feitelson, J.; Zeigler, D.R.; Dean, D.H. Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 775–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Martínez, P.; Ferré, J.; Escriche, B. Susceptibility of Spodoptera exigua to 9 toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2008, 97, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tindall, K.V.; Siebert, M.W.; Leonard, B.R.; All, J.; Haile, F.J. Efficacy of Cry1Ac: Cry1F proteins in cotton leaf tissue against fall armyworm, beet armyworm, and soybean looper (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.; Banks, D.; Adang, M.J. Toxicity, binding, and permeability analyses of four Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1 delta-endotoxins using brush border membrane vesicles of Spodoptera exigua and Spodoptera frugiperda. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.T.; Wang, Y.Q.; Hu, F.; Bi, S.J.; Hu, B.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xu, L.N. Susceptibility of different geographical populations of fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda in Anhui Province to Bt proteins. J. Plant Prot. 2022, 49, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar]
- Bilbo, T.R.; Reay-Jones, F.P.F.; Reisig, D.D.; Greene, J.K.; Turnbull, M.W. Development, survival, and feeding behavior of Helicoverpa zea (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) relative to Bt protein concentrations in corn ear tissues. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Jehle, J.A. Expression of Cry3Bb1 in transgenic corn MON88017. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9990–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Székács, A.; Lauber, É.; Juracsek, J.; Darvas, B. Cry1Ab toxin production of MON 810 transgenic maize. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naegeli, H.; Birch, A.N.; Casacuberta, J.; De Schrijver, A.; Gralak, M.A.; Guerche, P.; Jones, H.; Manachini, B.; Messean, A.; Nielsen, E.E.; et al. Risk assessment of information on the subcombination Bt11×MIR162, related to the application of Syngenta (EFSA-GMO-DE-2009-66) for authorization of food and feed containing, consisting and produced from genetically modified maize Bt11×MIR162×MIR604×GA 21. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04745. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trtikova, M.; Wikmark, O.G.; Zemp, N.; Widmer, A.; Hilbeck, A. Transgene expression and Bt protein content in transgenic Bt maize (MON810) under optimal and stressful environmental conditions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, M.W.; Nolting, S.P.; Hendrix, W.; Dhavala, S.; Craig, C.; Leonard, B.R.; Stewart, S.D.; All, J.; Musser, F.R.; Buntin, G.D.; et al. Evaluation of corn hybrids expressing Cry1F, cry1A.105, Cry2Ab2, Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1, and Cry3Bb1 against southern United States insect pests. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, D.Y.; He, K.L.; Bai, S.X.; Liu, H.; Cong, B. Effects of transgenic corn hybrids expressing Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab toxin on survival and growth of the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Hübner). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2005, 48, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chen, L.; Shang, H.W.; Zhu, C.Y. Research advances and nutrition analysis of the artificial diets for Tephritid fruit flies. Plant Quar. 2013, 27, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Sekhar, J.C.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, R.K. Avoidable losses due to Spodoptera exigua Hübner in grain yield of maize sown in Rabi season. Indian J. Entomol. 2008, 70, 402–403. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.P.; Wang, Y.N.; Li, H.; Huang, J.R.; Huang, Y.Z.; Feng, H.Q. Larval identification of Spodoptera frugiperda and other common species occurring at seedling stage maize in Henan Province. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2019, 25, 747–754. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, E.J.G.; Storer, N.P.; Seigfreid, S.D. Inheritance of Cry1F resistance in laboratory-selected European corn borer and its survival on transgenic corn expressing the Cry1F toxin. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2008, 98, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Biopesticide Registration Action Document Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1F Corn. Available online: http://bch.cbd.int/database/attachment/?id=10711 (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Quan, Y.D.; Wu, K.M. Managing practical resistance of Lepidopteran pests to Bt cotton in China. Insects 2023, 14, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Brévault, T.; Carrière, Y. Insect resistance to Bt crops: Lessons from the first billion acres. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.; García-Benítez, C.; Ortego, F.; Farinós, G.P. Monitoring insect resistance to Bt maize in the European Union: Update, challenges, and future prospects. J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 116, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency. White Paper on Resistance in Lepidopteran Pests of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) Plant-Incorporated Protectants in the United States. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2018-07/documents/position_paper_07132018.pdf (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Bourguet, D.; Desquilbet, M.; Lemarié, S. Regulating insect resistance management: The case of non-Bt corn refuges in the US. J. Environ. Manag. 2005, 76, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.F.; Jing, D.P.; Tai, H.K.; Zhang, A.H.; He, K.L.; Wang, Z.Y. Morphological characteristics of Spodoptera frugiperda in comparison with three other lepidopteran species with similar injury characteristics and morphology in cornfields. Plant Prot. 2019, 45, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.L.; Farhan, Y.; Schaafsma, A.W. Practical Resistance of Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) to Cry1F Bacillus thuringiensis maize discovered in Nova Scotia, Canada. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.Z.; An, X.F. Indoor feeding method for Spodoptera exigua. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2014, 31, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Nleya, T.; Chungu, C.; Kleinjan, J. Corn growth and development. In Best Management Practices; South Dakota University: Brookings, SD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenheim, J.A.; Hoy, M.A. Confidence intervals for the Abbott’s formula correction of bioassay data for control response. J. Econ. Entomol. 1989, 82, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, W.P.; Buckley, P.M.; Daves, C.A. Identifying resistance in corn to southwestern corn borer (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), and corn earworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Agric. Urban Entomol. 2006, 23, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Carriere, Y.; Ellers-Kirk, C.; Sisterson, M.; Antilla, L.; Whitlow, M.; Dennehy, T.J.; Tabashnik, B.E. Long-term regional suppression of pink bollworm by Bacillus thuringiensis cotton. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1519–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Liesner, L.R.; Ellsworth, P.C.; Unnithan, G.C.; Fabrick, J.A.; Naranjo, S.E.; Li, X.C.; Dennehy, T.J.; Antilla, L.; Staten, R.T.; et al. Transgenic cotton and sterile insect releases synergize eradication of pink bollworm a century after it invaded the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2019115118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeez, M.; Ullah, F.; Khan, M.M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shah, S.; Imran, M.; Assiri, M.A.; Fernández-Grandon, G.M.; Desneux, N.; et al. Metabolic-based insecticide resistance mechanism and ecofriendly approaches for controlling of beet armyworm Spodoptera exigua: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 1746–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Growth Stage | Tissue | Cry1Ab (µg/g) | Vip3Aa (µg/g) | Total Bt Proteins (µg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V5 | Leaf | 78.93 ± 0.89 a | 29.27 ± 0.22 a | 108.20 ± 0.98 a |
| V8 | Leaf | 76.33 ± 0.11 b | 28.88 ± 0.09 a | 105.21 ± 0.15 b |
| VT | Tassel | 11.47 ± 0.19 c | 4.83 ± 0.09 b | 16.30 ± 0.22 c |
| R1 | Silk | 1.71 ± 0.19 e | 0.68 ± 0.06 d | 2.39 ± 0.17 e |
| R2 | Kernel | 4.43 ± 0.41 d | 3.45 ± 0.04 c | 7.88 ± 0.41 d |
| Bt Protein | N | Lethal Concentration | Growth Inhibitory Concentration | df | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC50 (95%FL) ng/cm2 | LC95 (95%FL) ng/cm2 | Slope ± SE | χ2 | GIC50 (95%FL) ng/cm2 | GIC95 (95%FL) ng/cm2 | Slope ± SE | χ2 | |||
| Cry1Ab | 960 | 11.66 (8.67~15.18) | 510.61 (332.41~879.81) | 1.00 ± 0.07 | 21.57 | 1.59 (1.20~2.02) | 144.14 (112.89~191.26) | 0.84 ± 0.04 | 23.30 | 34 |
| Vip3Aa | 960 | 27.74 (20.86~35.83) | 756.59 (500.61~1286.09) | 1.15 ± 0.07 | 18.92 | 7.93 (7.01~8.90) | 195.42 (162.02~241.02) | 1.18 ± 0.04 | 13.40 | 34 |
| Grade | Definition of Damage |
|---|---|
| 0 | No visible damage to leaves |
| 1 | Only pin-hole damage to leaves |
| 2 | Pin-hole and shot-hole damage to leaves |
| 3 | Small elongated lesions (5–10 mm) on 1–3 leaves |
| 4 | Midsized, elongated lesions (10–30 mm) on 4–7 leaves |
| 5 | Large, elongated lesions (>30 mm) or small portions eaten on 3–5 leaves |
| 6 | Large, elongated lesions (>30 mm) and large portions eaten on 3–5 leaves |
| 7 | Large, elongated lesions (>30 mm) and large portions eaten on 50% of leaves |
| 8 | Large, elongated lesions (>30 mm) and large portions eaten on 70% of leaves |
| 9 | Leaves destroyed on 70% of leaves |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, C.; Yang, X.; He, L.; Wang, W.; Wu, K. Control Efficacy of the Bt Maize Event DBN3601T Expressing Cry1Ab and Vip3Aa Proteins against Beet Armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Hübner), in China. Plants 2024, 13, 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141933
Song C, Yang X, He L, Wang W, Wu K. Control Efficacy of the Bt Maize Event DBN3601T Expressing Cry1Ab and Vip3Aa Proteins against Beet Armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Hübner), in China. Plants. 2024; 13(14):1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141933
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Cheng, Xianming Yang, Limei He, Wenhui Wang, and Kongming Wu. 2024. "Control Efficacy of the Bt Maize Event DBN3601T Expressing Cry1Ab and Vip3Aa Proteins against Beet Armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Hübner), in China" Plants 13, no. 14: 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141933
APA StyleSong, C., Yang, X., He, L., Wang, W., & Wu, K. (2024). Control Efficacy of the Bt Maize Event DBN3601T Expressing Cry1Ab and Vip3Aa Proteins against Beet Armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Hübner), in China. Plants, 13(14), 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141933






