Root Influences Rhizosphere Hydraulic Properties through Soil Organic Carbon and Microbial Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i).
- The aggregates from the rhizosphere (RZS) of annual ryegrass present higher organic carbon content and microbial activity than aggregates from the soil between plant rows (SBP) (i.e., bulk soil);
- (ii).
- Organic carbon input and microbial activity lead to higher aggregate stability in the RZS than in SBP;
- (iii).
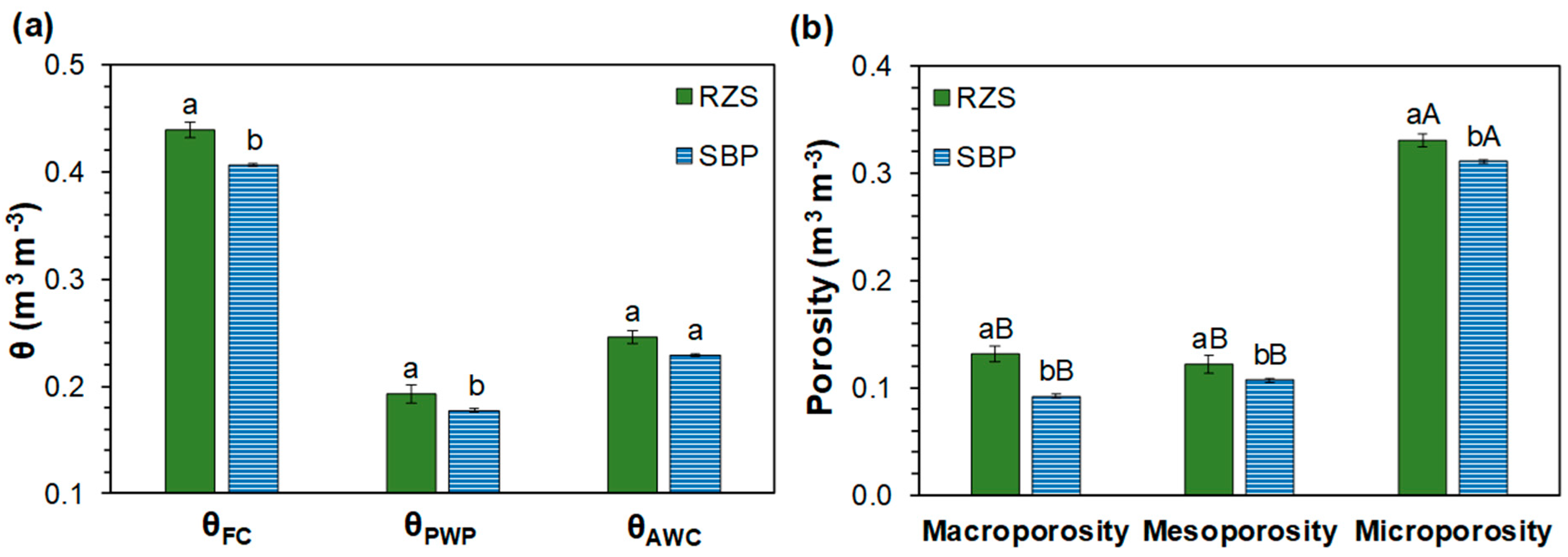
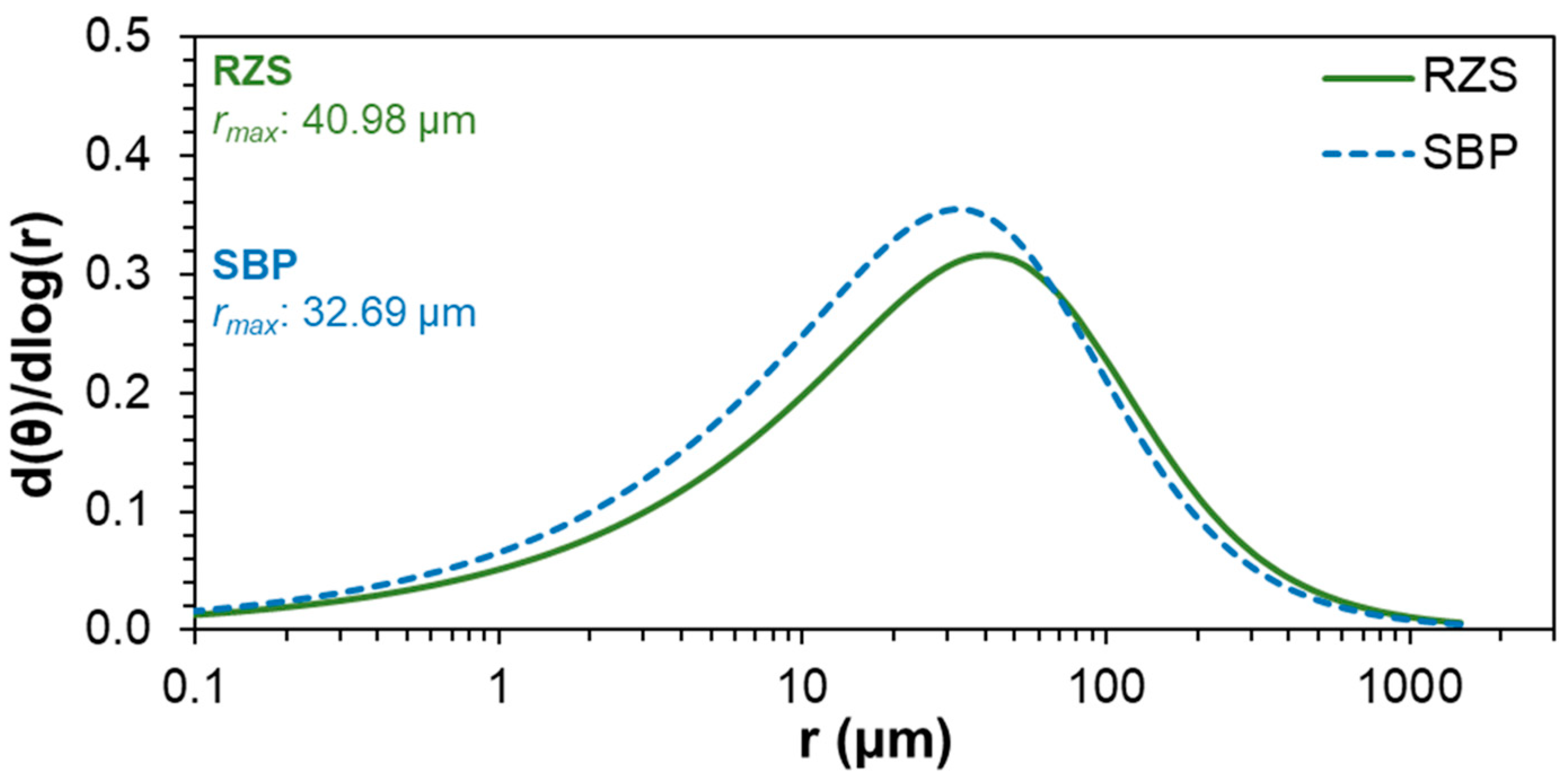
- Organic carbon input, microbial activity and aggregate stability in the RZS increase the RZS porosity, particularly micropores;
- (iv).
- The increase in micropores and aggregate stability, supported by the effect of organic carbon input and microbial activity, enhances the water retention capacity in the RZS;
- (v).
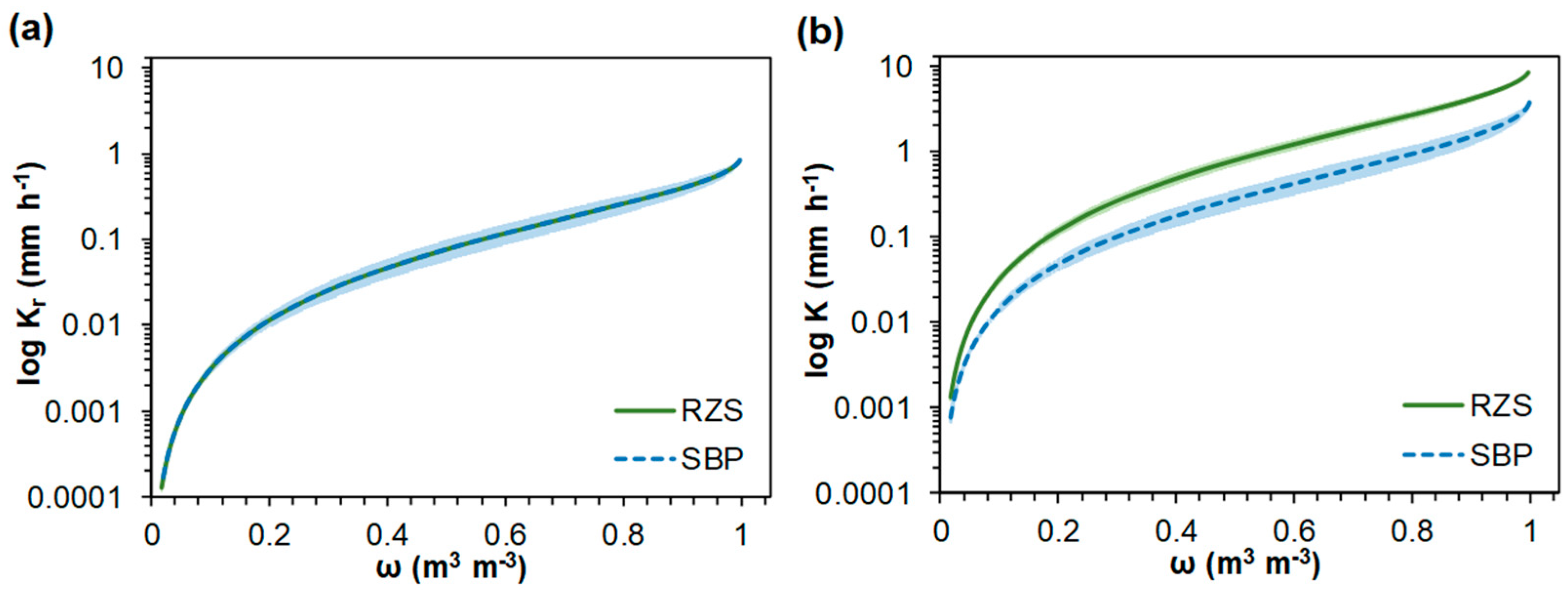
- Due to the residual effect of the mucilage, Ksat is lower in the RZS than in the SBP;
- (vi).
- K reflects soil quality and is higher in the RZS than in the SBP.
- (i).
- The SOC content and microbial parameters [microbial biomass carbon (MBC), β-glucosidase (BG), dehydrogenase (DH), easily extractable glomalin-related soil protein (EE-GRSP)] were determined;
- (ii).
- The aggregate stability was assessed by readily dispersible clay (RDC);
- (iii).
- The frequency and percentage of pores were obtained from the soil water retention curves (SWRCs);
- (iv).
- The water retention capacity was also obtained from the SWRCs;
- (v).
- Ksat was determined by a constant head permeameter method;
- (vi).
- K was derived from the water retention characteristics, with Ksat as the relative hydraulic conductivity, (Kr) as a function of the effective relative saturation (ω), and K as a function of the ω.
2. Results
2.1. Soil Parameters Related to Soil Aggregation
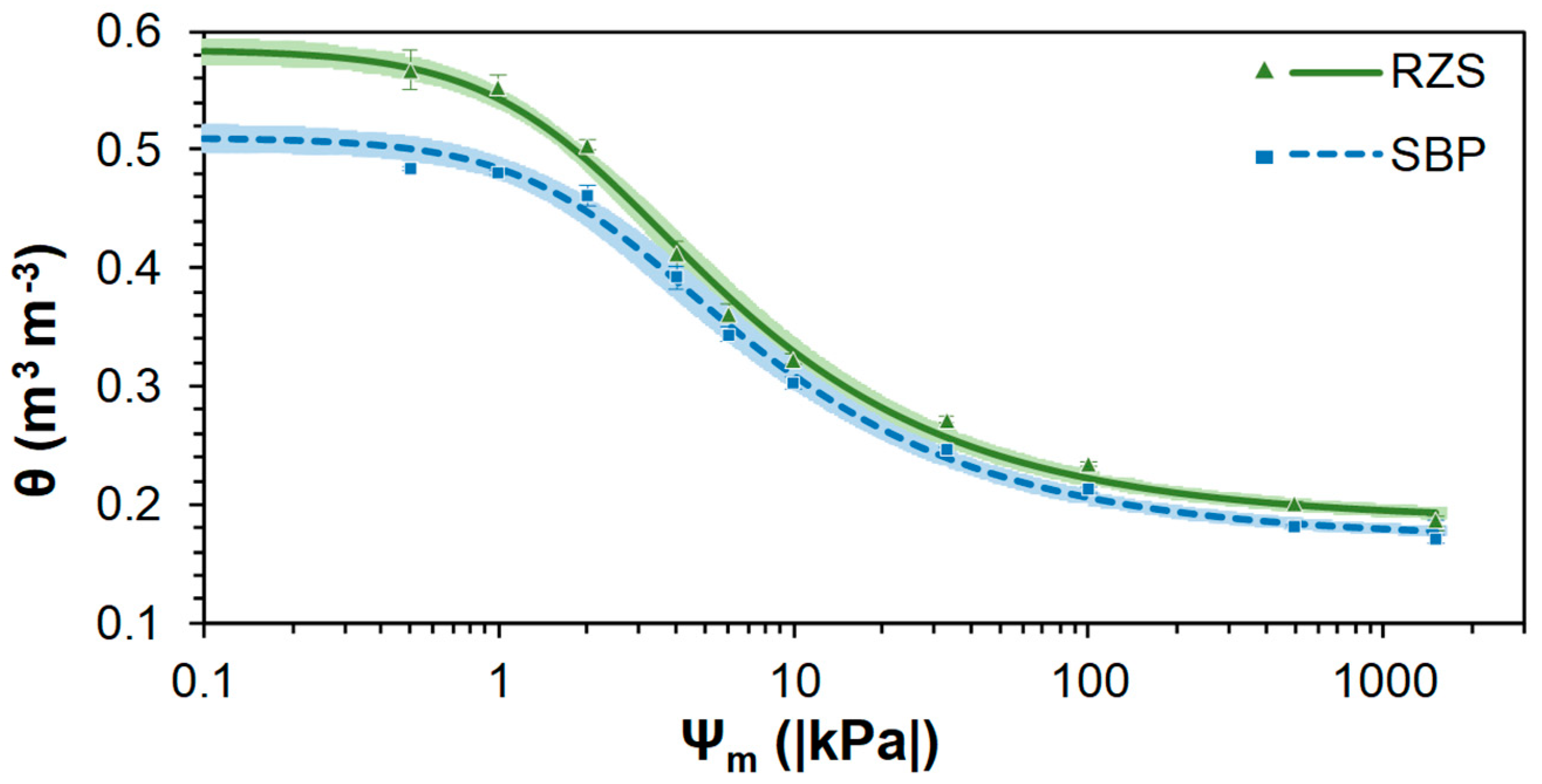
2.2. Soil Hydraulic Properties
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Field Experiment and Soil Sampling
4.2. Soil Aspects Related to Soil Aggregation
4.2.1. Readily Dispersible Clay in Water
4.2.2. Microbial Parameters
4.2.3. Soil Organic Carbon
4.3. Soil Hydraulic Properties
4.3.1. Soil–Water Retention Curve
4.3.2. Pore Size Classification and Pore Size Frequency
4.3.3. Hydraulic Conductivity
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hinsinger, P.; Bengough, A.G.; Vetterlein, D.; Young, I.M. Rhizosphere: Biophysics, Biogeochemistry and Ecological Relevance. Plant Soil 2009, 321, 117–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnes, S.; Dexter, A.R.; Bartoli, F. Wetting and Drying Cycles in the Maize Rhizosphere under Controlled Conditions. Mechanics of the Root-Adhering Soil. Plant Soil 2000, 221, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, P.J. Roots, Rhizosphere and Soil: The Route to a Better Understanding of Soil Science? Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 57, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helliwell, J.R.; Sturrock, C.J.; Miller, A.J.; Whalley, W.R.; Mooney, S.J. The Role of Plant Species and Soil Condition in the Structural Development of the Rhizosphere. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 1974–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Zarebanadkouki, M.; Ahmadi, K.; Kroener, E.; Kostka, S.; Kaestner, A.; Carminati, A. Engineering Rhizosphere Hydraulics: Pathways to Improve Plant Adaptation to Drought. Vadose Zone J. 2017, 17, 160090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Veelen, A.; Tourell, M.C.; Koebernick, N.; Pileio, G.; Roose, T. Correlative Visualization of Root Mucilage Degradation Using X-Ray CT and MRI. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarebanadkouki, M.; Ahmed, M.; Hedwig, C.; Benard, P.; Kostka, S.J.; Kastner, A.; Carminati, A. Rhizosphere Hydrophobicity Limits Root Water Uptake after Drying and Subsequent Rewetting. Plant Soil 2018, 428, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.W.; Baumert, V.; Carminati, A.; Germon, A.; Holz, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Peth, S.; Schlüter, S.; Uteau, D.; Vetterlein, D.; et al. From Rhizosphere to Detritusphere—Soil Structure Formation Driven by Plant Roots and the Interactions with Soil Biota. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 193, 109396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroener, E.; Holz, M.; Zarebanadkouki, M.; Ahmed, M.; Carminati, A. Effects of Mucilage on Rhizosphere Hydraulic Functions Depend on Soil Particle Size. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 170056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalley, W.R.; Riseley, B.; Leeds-Harrison, P.B.; Bird, N.R.A.; Leech, P.K.; Adderley, W.P. Structural Differences between Bulk and Rhizosphere Soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2005, 56, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassmann, C.S.; Mariano, E.; Rocha, K.F.; Gilli, B.R.; Rosolem, C.A. Effect of Tropical Grass and Nitrogen Fertilization on Nitrous Oxide, Methane, and Ammonia Emissions of Maize-Based Rotation Systems. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 234, 117571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, T.N.; Libardi, P.L. Physical-Hydric Properties of Oxisols as Influenced by Soil Structure and Clay Mineralogy. Catena 2022, 211, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwetha, P.; Varija, K. Soil Water Retention Curve from Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity for Sandy Loam and Loamy Sand Textured Soils. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengough, A.G. Water Dynamics of the Root Zone: Rhizosphere Biophysics and Its Control on Soil Hydrology. Vadose Zone J. 2012, 11, vzj2011.0111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gao, Y.; Li, M.; Sturrock, C.J.; Gregory, A.S.; Zhang, X. Change in Hydraulic Properties of the Rhizosphere of Maize under Different Abiotic Stresses. Plant Soil 2020, 452, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carminati, A. Rhizosphere Wettability Decreases with Root Age: A Problem or a Strategy to Increase Water Uptake of Young Roots? Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Kroener, E.; Holz, M.; Zarebanadkouki, M.; Carminati, A. Mucilage Exudation Facilitates Root Water Uptake in Dry Soils. Funct. Plant Biol. 2014, 41, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroener, E.; Zarebanadkouki, M.; Kaestner, A.; Carminati, A. Non-Equilibrium Dynamics of Rhizosphere. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 6479–6495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benard, P.; Zarebanadkouki, M.; Carminati, A. Physics and Hydraulics of the Rhizosphere Network. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2019, 182, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Passioura, J.; Carminat, A. Hydraulic Processes in Roots and the Rhizosphere Pertinent to Increasing Yield of Water-Limited Grain Crops: A Critical Review. Plant Soil 2018, 69, 3255–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carminati, A.; Moradi, A.B.; Vetterlein, D.; Vontobel, P.; Lehmann, E.; Weller, U.; Vogel, H.J.; Oswald, S.E. Dynamics of Soil Water Content in the Rhizosphere. Plant Soil 2010, 332, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Kroener, E.; Benard, P.; Zarebanadkouki, M.; Kaestner, A.; Carminati, A. Drying of Mucilage Causes Water Repellency in the Rhizosphere of Maize: Measurements and Modelling. Plant Soil 2016, 407, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarebanadkouki, M.; Kroener, E.; Kaestner, A.; Carminati, A. Visualization of Root Water Uptake: Quantification of Deuterated Water Transport in Roots Using Neutron Radiography and Numerical Modeling. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wu, L.; Harbottle, M. Influence of Biopolymer Gel-Coated Fibres on Sand Reinforcement as a Model of Plant Root Behaviour. Plant Soil 2019, 438, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, B.C.; Furrer, J.M.; Guo, Y.-S.; Dougherty, D.; Hinestroza, H.F.; Hernandez, J.S.; Gage, D.J.; Cho, Y.K.; Shor, L.M. Pore-Scale Water Dynamics during Drying and the Impacts of Structure and Surface Wettability. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 5585–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarebanadkouki, M.; Ahmed, M.A.; Carminati, A. Hydraulic Conductivity of the Root-Soil Interface of Lupin in Sandy Soil after Drying and Rewetting. Plant Soil 2016, 398, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.M.; Libardi, P.L.; Giarola, N.F.B. Evaluation of the Soil Aggregation Induced by the Plant Roots in an Oxisol by Turbidimetry and Water Percolation. Rhizosphere 2020, 16, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Brown, L.K.; Raffan, A.C.; George, T.S.; Bengough, A.G.; Roose, T.; Sinclair, I.; Koebernick, N.; Cooper, L.; Hackett, C.A.; et al. Plant Exudates May Stabilize or Weaken Soil Depending on Species, Origin and Time. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Li, P.; Fei, W.; Wang, J. Effects of Vegetation Roots on the Structure and Hydraulic Properties of Soils: A Perspective Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmuganathan, R.T.; Oades, J.M. Modification of Soil Physical Properties by Addition of Calcium Compounds. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1983, 21, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, T.R.D.; Machado, W.; Filho, J.T. Charge Sparsity: An Index to Quantify Cation Effects on Clay Dispersion in Soils. Sci. Agric. 2020, 77, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmans, J.W.; van Genuchten, M. Vadose Zone: Hydrological Processes. In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment; Hillel, D., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Tötzke, C.; Kardjilov, N.; Manke, I.; Oswald, S.E. Capturing 3D Water Flow in Rooted Soil by Ultra-Fast Neutron Tomography. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualem, Y. A New Model for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Porous Media. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A Closed-Form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettmann, U.; Bechtold, M.; Frahm, E.; Tiemeyer, B. On the Applicability of Unimodal and Bimodal van Genuchten-Mualem Based Models to Peat and Other Organic Soils under Evaporation Conditions. J. Hydrol. 2014, 515, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Kong, J.; Shen, C.; Lu, C.; Hua, G.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, L. Evaluation and Application of the Modified van Genuchten Function for Unsaturated Porous Media. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Chen, P.; Li, Z.G.; Li, L.Y.; Zhang, R.Q.; Hu, W.; Liu, Y. Soil Aggregate-Associated Organic Carbon Mineralization and Its Driving Factors in Rhizosphere Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 186, 109182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; He, M.; Jiang, C.; Li, C.; Liu, F. Microbial Community Structure in Rhizosphere Soil Rather than That in Bulk Soil Characterizes Aggregate-Associated Organic Carbon under Long-Term Forest Conversion in Subtropical Region. Rhizosphere 2021, 20, 100438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyż, E.A.; Dexter, A.R. Mechanical Dispersion of Clay from Soil into Water: Readily-Dispersed and Spontaneously-Dispersed Clay. Int. Agrophys. 2015, 29, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdall, J.M.; Oades, J.M. Organic Matter and Water-Stable Aggregates in Soils. J. Soil Sci. 1982, 33, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ali, A.; Dang, A.; Wandel, A.P.; Bennett, J.M.L. Re-Examining the Flocculating Power of Sodium, Potassium, Magnesium and Calcium for a Broad Range of Soils. Geoderma 2019, 352, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, L.; Pauletto, E.A.; Costa de-Castro, R.C.; Spinelli-Pinto, L.F.; Fontana-Fernandes, F.; Stumpf da-Silva, T.S.; Vaz-Ambus, J.; Furtado-Garcia, G.; Rodrigues de-Lima, C.L.R.; Nunes, M.R. Capability of Grass in Recovery of a Degraded Area after Coal Mining. Agrociencia 2014, 48, 477–487. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.; Ma, B.L.; Bomke, A.A. Effects of Cover Crops on Soil Aggregate Stability, Total Organic Carbon, and Polysaccharides. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matocha, C.J.; Karathanasis, T.D.; Murdock, L.W.; Grove, J.H.; Goodman, J.; Call, D. Influence of Ryegrass on Physico-Chemical Properties of a Fragipan Soil. Geoderma 2018, 317, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdall, J.M.; Oades, J.M. Stabilization of Soil Aggregates by the Root Systems of Ryegrass. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1979, 17, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Xiao, C. Root Exudates Mediate the Processes of Soil Organic Carbon Input and Efflux. Plants 2023, 12, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilling, A.; Keiluweit, M.; Contosta, A.R.; Frey, S.; Schimel, J.; Schnecker, J.; Smith, R.G.; Tiemann, L.; Grandy, A.S. Minerals in the Rhizosphere: Overlooked Mediators of Soil Nitrogen Availability to Plants and Microbes. Biogeochemistry 2018, 139, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.W.; Carminati, A.; Kaiser, C.; Subke, J.A.; Gutjahr, C. Editorial: Rhizosphere Functioning and Structural Development as Complex Interplay between Plants, Microorganisms and Soil Minerals. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, R.P.; Breakwell, D.P.; Turco, R.F. Soil Enzyme Activities and Biodiversity Measurements as Integrative Microbiological Indicators. Methods Assess. Soil Qual. 1997, 49, 247–271. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, B.L.; Hopkins, D.W.; Haygarth, P.M.; Ostle, N. Β-Glucosidase Activity in Pasture Soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2002, 20, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotaniya, M.L.; Kushwah, S.K.; Rajendiran, S.; Coumar, M.V.; Kundu, S.; Subba Rao, A. Rhizosphere Effect of Kharif Crops on Phosphatases and Dehydrogenase Activities in a Typic Haplustert. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2014, 37, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Hill, P.W.; Jones, D.L. Root Exudate Components Change Litter Decomposition in a Simulated Rhizosphere Depending on Temperature. Plant Soil 2007, 290, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dorodnikov, M.; Splettstößer, T.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Pausch, J. Effects of Maize Roots on Aggregate Stability and Enzyme Activities in Soil. Geoderma 2017, 306, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.S.; Bais, H.P.; Grotewold, E.; Vivanco, J.M. Root Exudation and Rhizosphere Biology. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demenois, J.; Carriconde, F.; Bonaventure, P.; Maeght, J.L.; Stokes, A.; Rey, F. Impact of Plant Root Functional Traits and Associated Mycorrhizas on the Aggregate Stability of a Tropical Ferralsol. Geoderma 2018, 312, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, F.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Hajabbasi, M.A.; Sabzalian, M.R. Influence of Tall Fescue Endophyte Infection on Structural Stability as Quantified by High Energy Moisture Characteristic in a Range of Soils. Geoderma 2015, 249–250, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Razavi, B.S. Rhizosphere Size and Shape: Temporal Dynamics and Spatial Stationarity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, D.; Chenu, C.; Le Bissonnais, Y. Aggregate Stability and Microbial Community Dynamics under Drying-Wetting Cycles in a Silt Loam Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2053–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, G.; Sarkar, S.K.; Singh, R.P. Improving Soil Microbiology under Rice-Wheat Crop Rotation in Indo-Gangetic Plains by Optimized Resource Management. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumert, V.L.; Forstner, S.J.; Zethof, J.H.T.; Vogel, C.; Heitkötter, J.; Schulz, S.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Mueller, C.W. Root-Induced Fungal Growth Triggers Macroaggregation in Forest Subsoils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 157, 108244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.M.; Feiler, H.P.; Qi, X.; de Araújo, V.L.V.P.; Lacerda-Júnior, G.V.; Fernandes-Júnior, P.I.; Cardoso, E.J.B.N. Impact of Water Shortage on Soil and Plant Attributes in the Presence of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi from a Harsh Environment. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wu, Q.S.; He, X.H. Exogenous Easily Extractable Glomalin-Related Soil Protein Promotes Soil Aggregation, Relevant Soil Enzyme Activities and Plant Growth in Trifoliate Orange. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.F.; Franke-Snyder, M.; Morton, J.B.; Upadhyaya, A. Time-Course Study and Partial Characterization of a Protein on Hyphae of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi during Active Colonization of Roots. Plant Soil 1996, 181, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, F.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Zarebanadkouki, M. Enhancing Rhizosphere Soil Water Retention in Wheat through Colonization with Endophytic Fungus Serendipita Indica. Rhizosphere 2023, 26, 100709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil Organic Matter and Water Retention. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 3265–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankenbauer, K.J.; Loheide, S.P. The Effects of Soil Organic Matter on Soil Water Retention and Plant Water Use in a Meadow of the Sierra Nevada, CA. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 31, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzehei, T.A.; Albalasmeh, A.A. Spatial Distribution of Rhizodeposits Provides Built-in Water Potential Gradient in the Rhizosphere. Ecol. Modell. 2015, 298, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr-Hersey, J.E.; Ritz, K.; Bengough, G.A.; Mooney, S.J. Reorganisation of Rhizosphere Soil Pore Structure by Wild Plant Species in Compacted Soils. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 6107–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helliwell, J.R.; Sturrock, C.J.; Mairhofer, S.; Craigon, J.; Ashton, R.W.; Miller, A.J.; Whalley, W.R.; Mooney, S.J. The Emergent Rhizosphere: Imaging the Development of the Porous Architecture at the Root-Soil Interface. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney, D.S.; Crawford, J.W.; Daniell, T.; Hallett, P.D.; Nunan, N.; Ritz, K.; Rivers, M.; Young, I.M. Three-Dimensional Microorganization of the Soil-Root-Microbe System. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbi, S.M.F.; Tighe, M.K.; Flavel, R.J.; Kaiser, B.N.; Guppy, C.N.; Zhang, X.; Young, I.M. Plant Roots Redesign the Rhizosphere to Alter the Three-Dimensional Physical Architecture and Water Dynamics. New Phytol. 2018, 219, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, L.P.; de Jong van Lier, Q.; Correa, M.M.; de Miranda, J.H.; de Oliveira, L.A. Retention and Solute Transport Properties in Disturbed and Undisturbed Soil Samples. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2016, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durner, W. Hydraulic Conductivity Estimation for Soils with Heterogeneous Pore Structure. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.L.D.N.; Libardi, P.L.; Gimenes, F.H.S. Soil Water Retention Curve as Affected by Sample Height. Rev. Bras. Ciência Solo 2018, 42, e0180058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyż, E.A.; Dexter, A.R. Soil Physical Properties under Winter Wheat Grown with Different Tillage Systems at Selected Locations. Int. Agrophys. 2008, 22, 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, M.R.; Silva, A.P.; Denardin, J.E.; Giarola, N.F.B.; Vaz, C.M.P.; van Es, H.M.; Silva, A.R. Soil Chemical Management Drives Structural Degradation of Oxisols under a No-till Cropping System. Soil Res. 2017, 55, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carminati, A.; Schneider, C.L.; Moradi, A.B.; Zarebanadkouki, M.; Vetterlein, D.; Vogel, H.-J.; Hildebrandt, A.; Weller, U.; Schüler, L.; Oswald, S.E. How the Rhizosphere May Favor Water Availability to Roots. Vadose Zone J. 2011, 10, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Qin, T.; Yan, D.; Tian, F.; Wang, H. A Meta-Analysis on Effects of Root Development on Soil Hydraulic Properties. Geoderma 2021, 403, 115363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.; Vidal-Torrado, P.; Lepsch, I. Stratigraphical Discontinuities, Tropical Landscape Evolution and Soil Distribution Relationships in a Case Study in SE-Brazil. Rev. Bras. Ciência Solo 2002, 26, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 12th ed.; USDA-NRCS: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, H.B.; Alvares, C.A.; Sentelhas, P.C. Um Século de Dados Meteorológicos Em Piracicaba, SP: Mudanças Do Clima Pela Classificação de Köppen. In Proceedings of the XX Congresso Brasileiro de Agrometeorologia, V Simpósio de Mudanças Climáticas e Desertificação do Semiárido Brasileiro, Juazeiro, BA, Brazil, 14–18 August 2017; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Dexter, A.R.; Richard, G.; Davy, J.; Hardy, M.; Duval, O. Clay Dispersion from Soil as a Function of Antecedent Water Potential. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.M.; Nunes, M.R.; Pessoa, T.N.; Libardi, P.L. Seasonal Variation of the Rhizosphere Soil Aggregation in an Oxisol. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 231, 105741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.M.; Libardi, P.L.; Alves, M.E.; Prataviera, F.; Giarola, N.F.B. Electrochemical Effects on Clay Dispersion in Rhizo- and Non-Rhizospheric Soils. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 3518–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An Extraction Method for Measuring Soil Microbial Biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A. Soil Enzymes. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Microbiological and Biochemical Properties; Weaver, R.W., Scott, A., Bottomeley, P., Bezdicek, D., Smith, S., Tabatabai, A., Wollum, A., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; pp. 775–833. ISBN 9780891188650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casida, L.E.; Klein, D.A.; Santoro, T. Soil Dehydrogenase Activity. Soil Sci. 1964, 98, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.F.; Upadhyaya, A. A Survey of Soils for Aggregate Stability and Glomalin, a Glycoprotein Produced by Hyphae of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi. Plant Soil 1998, 198, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An Examination of the Degtjareff Method for Determining Organic Carbon in Soils: Effect of Variation in Digestion Conditions and of Inorganic Soil Constituents. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klute, A.; Dirksen, C. Hydraulic Conductivity and Diffusivity: Laboratory Methods. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1 Physical and Mineralogical Methods; Klute, A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 687–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koorevaar, P.; Menelik, G.; Dirksen, C. Elements of Soil Physics, 1st ed.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; ISBN 0444422420. [Google Scholar]
- Klute, A. Laboratory Measurement of Hydraulic Conductitivy of Saturated Soil. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1 Physical and Mineralogical Properties, Including Statistics of Measurement and Sampling; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T.; Leij, F.J.; Yates, S.R. The RETC Code for Quantifying the Hydraulic Functions of Unsaturated Soils, Version 1.0; Environmental Protection Agency: Riverside, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Betioli Júnior, E.; Moreira, W.H.; Tormena, C.A.; Ferreira, C.J.B.; da Silva, Á.P.; Giarola, N.F.B. Intervalo Hídrico Ótimo e Grau de Compactação de Um Latossolo Vermelho Após 30 Anos Sob Plantio Direto. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2012, 36, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, Version 4.2.3. 2023. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 16 July 2024).

| Parameters | Unit | RZS | SPB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDC | NTU/(g L−1) | 0.41 | ±0.77 | b | 0.82 | ±1.49 | a |
| MBC | mg g−1 | 0.98 | ±0.04 | a | 0.76 | ±0.06 | b |
| BG | mg PNF kg−1 soil h−1 | 175.50 | ±7.55 | a | 100.54 | ±6.15 | b |
| DH | µg TPF g−1 soil 24 h−1 | 3.27 | ±0.03 | a | 3.14 | ±0.05 | a |
| EE-GRSP | mg g−1 | 46.69 | ±2.07 | a | 35.79 | ±3.24 | b |
| SOC | g kg−1 | 42.16 | ±0.86 | a | 35.84 | ±0.60 | b |
| Parameters | Unit | RZS | SPB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θs | m3 m−3 | 0.584 | ±0.0058 | a | 0.510 | ±0.0062 | b |
| θr | m3 m−3 | 0.186 | ±0.0023 | a | 0.171 | ±0.0015 | b |
| m | 0.381 | ±0.0021 | a | 0.381 | ±0.0084 | a | |
| n | 1.614 | ±0.0054 | a | 1.615 | ±0.0223 | a | |
| α | m−1 | 5.081 | ±0.2827 | a | 4.107 | ±0.4106 | a |
| R2 | 0.995 | ±0.0007 | 0.995 | ±0.0007 | |||
| RMSE | 0.010 | ±0.0010 | 0.009 | ±0.0008 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batista, A.M.; Pessoa, T.N.; Putti, F.F.; Andreote, F.D.; Libardi, P.L. Root Influences Rhizosphere Hydraulic Properties through Soil Organic Carbon and Microbial Activity. Plants 2024, 13, 1981. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141981
Batista AM, Pessoa TN, Putti FF, Andreote FD, Libardi PL. Root Influences Rhizosphere Hydraulic Properties through Soil Organic Carbon and Microbial Activity. Plants. 2024; 13(14):1981. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141981
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatista, Aline Martineli, Thaís Nascimento Pessoa, Fernando Ferrari Putti, Fernando Dini Andreote, and Paulo Leonel Libardi. 2024. "Root Influences Rhizosphere Hydraulic Properties through Soil Organic Carbon and Microbial Activity" Plants 13, no. 14: 1981. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141981
APA StyleBatista, A. M., Pessoa, T. N., Putti, F. F., Andreote, F. D., & Libardi, P. L. (2024). Root Influences Rhizosphere Hydraulic Properties through Soil Organic Carbon and Microbial Activity. Plants, 13(14), 1981. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141981








