Assessment of the Restoration Potential of Forest Vegetation Coverage in the Alxa Desert Region of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
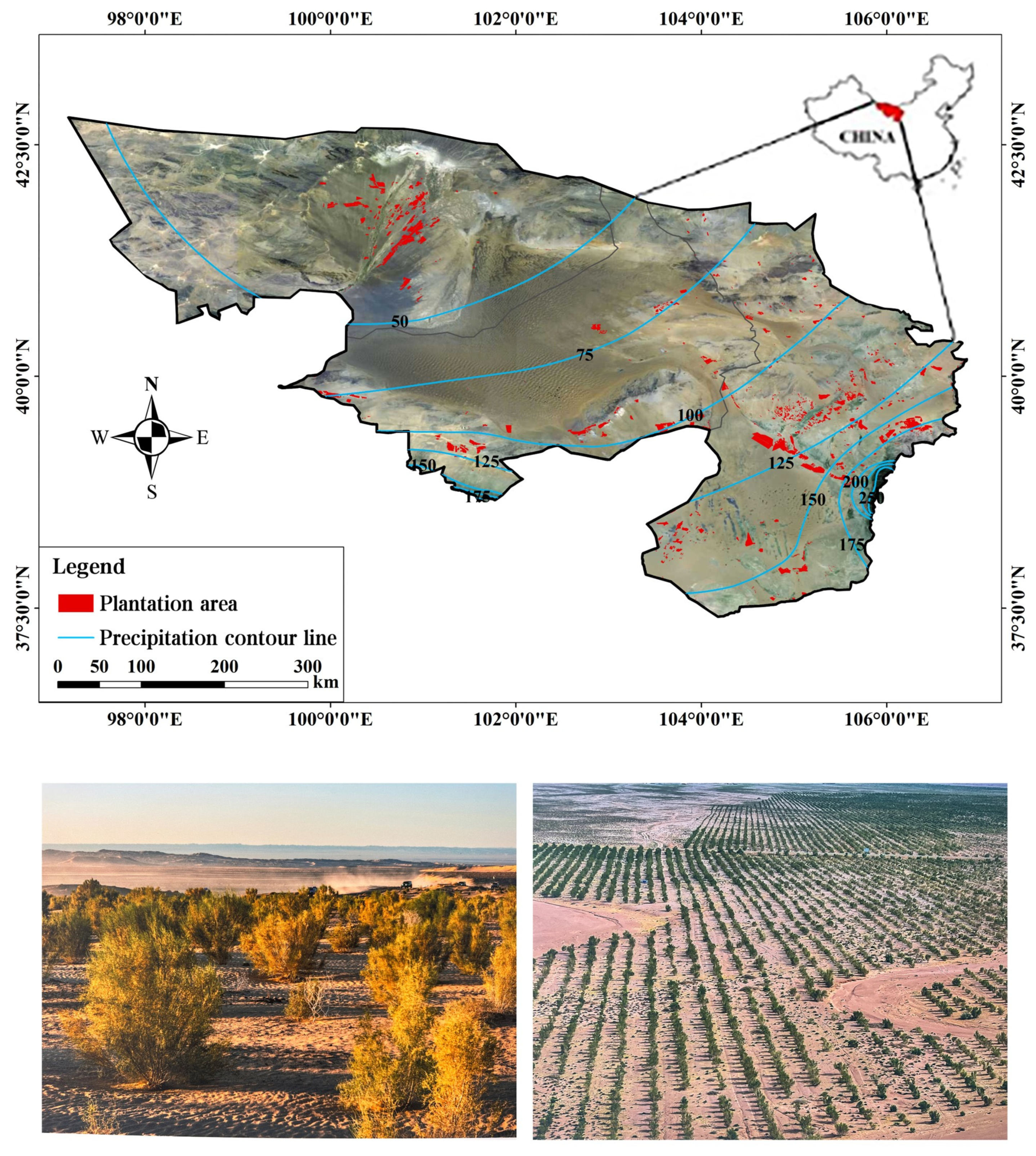
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Research Methods
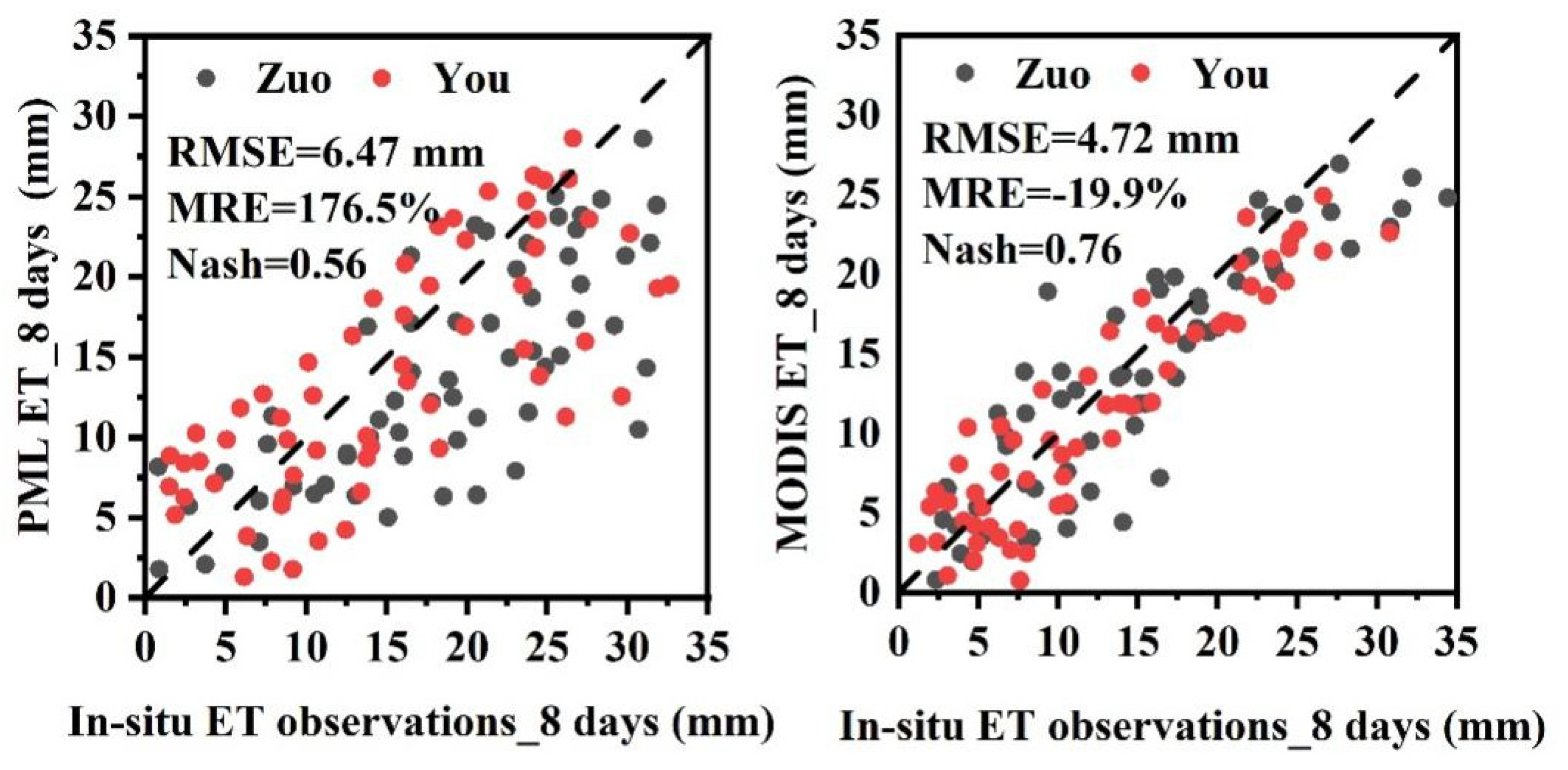
2.2.1. Evaluation Method for ET Product Accuracy
2.2.2. Trend Slope Analysis Method
2.2.3. Construction of Response Relationships between ET and Meteorological Elements and EVI
2.2.4. Classification of Wet, Normal, and Dry Years
2.2.5. Estimation of Vegetation Cover Recovery Potential under Different Scenarios
3. Results and Analysis
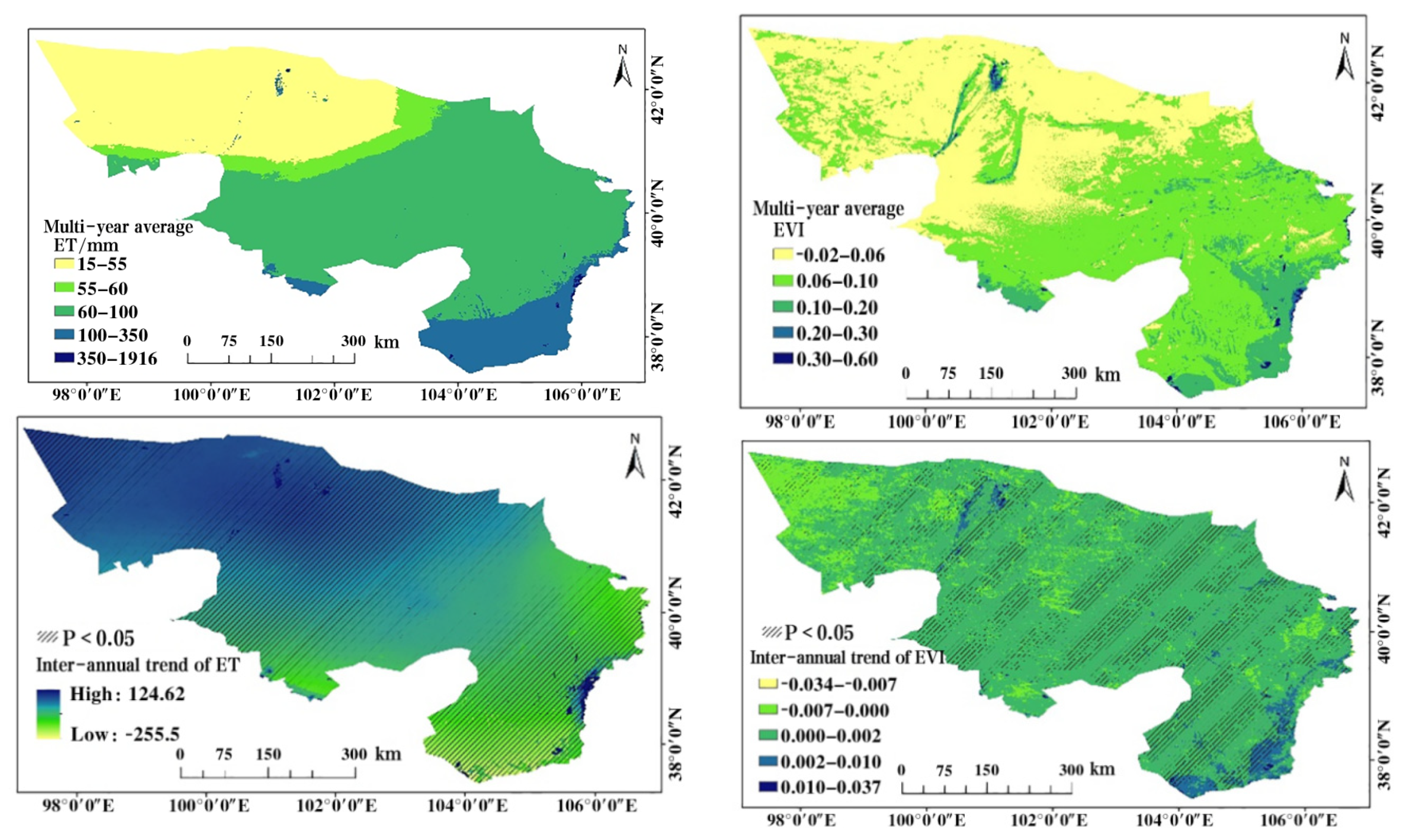
3.1. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of ET and EVI in the Alxa Desert Region
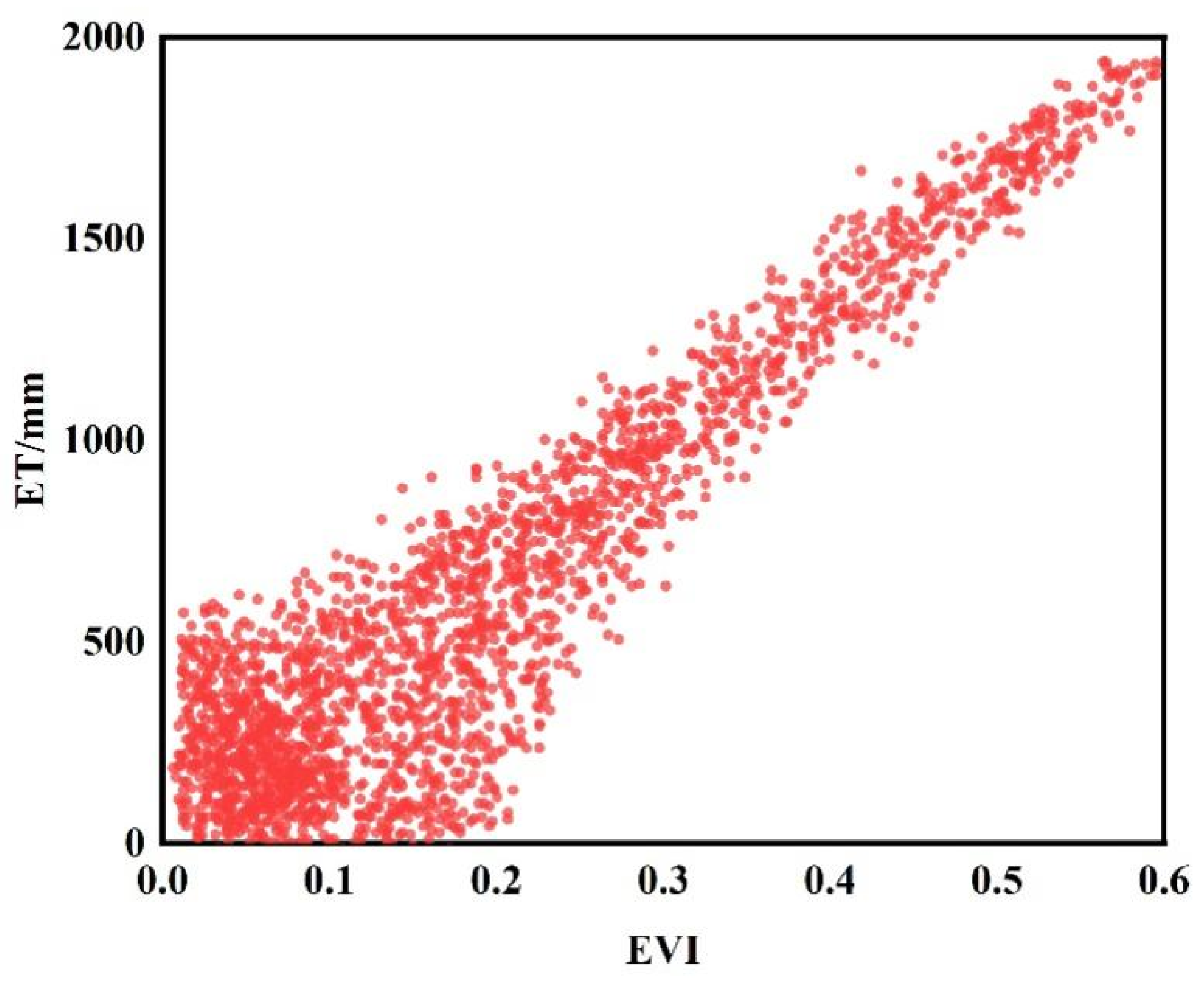
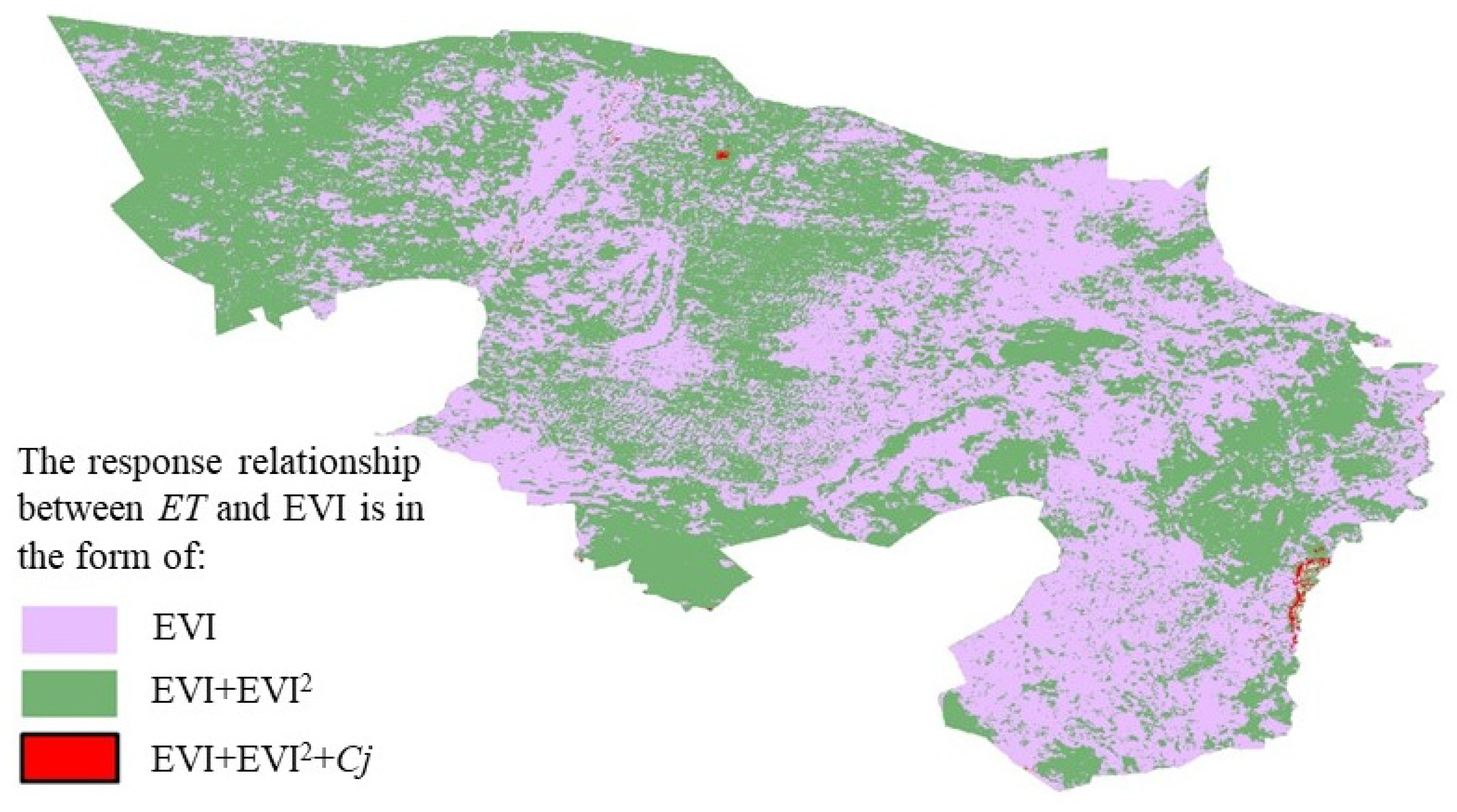
3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of the Response Relationship between ET and EVI
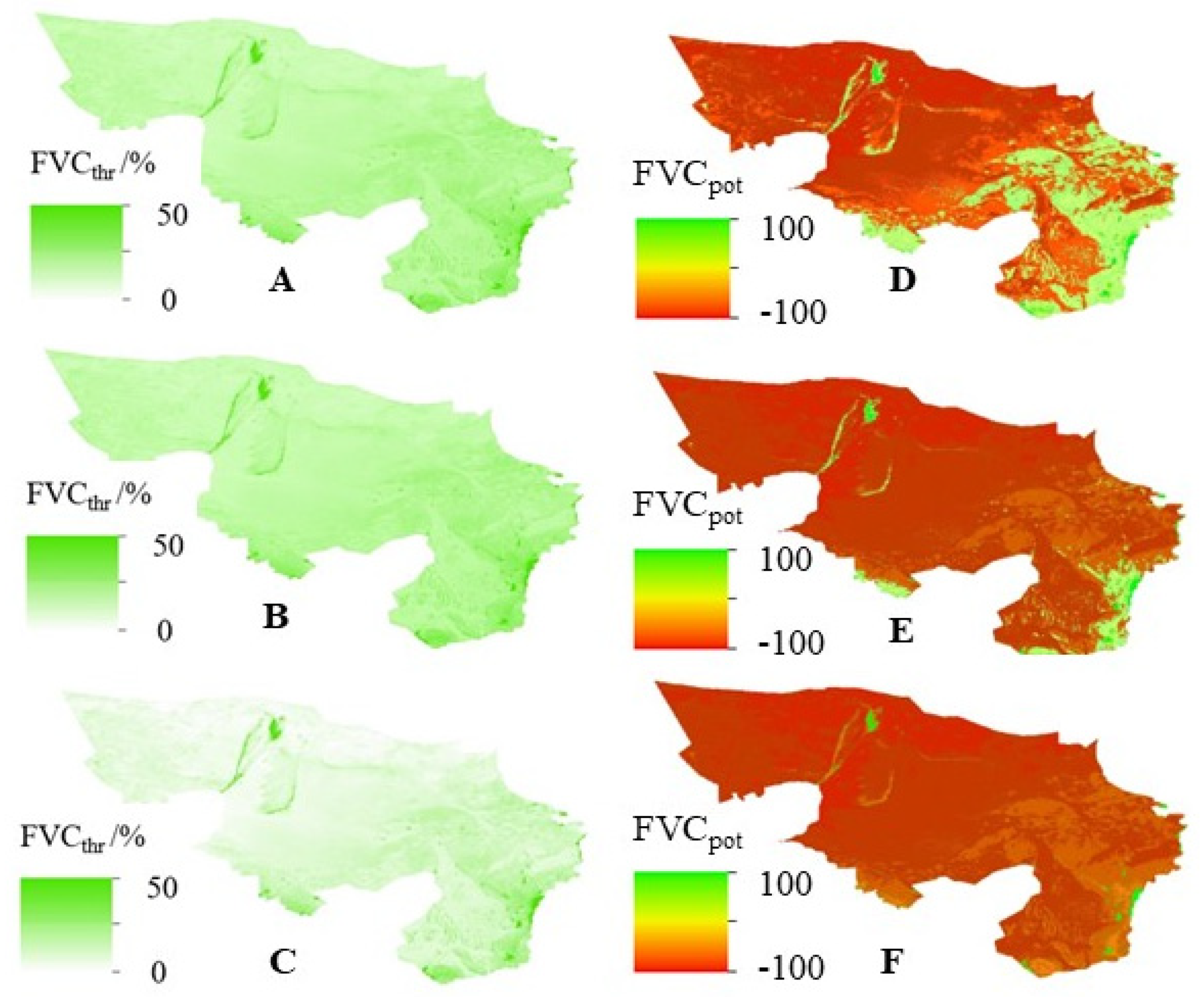
3.3. Recovery Potential of Forest and Grassland Vegetation Cover under Scenarios of High, Normal, and Low Water Years
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion on the Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of ET and EVI in the Alxa Desert Region
4.2. The Spatial Distribution Characteristics of ET and EVI Response Relationships
4.3. Potential for Vegetation Cover Recovery of Forests and Grasslands under Scenarios of Wet, Normal, and Dry Years
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Evapotranspiration (ET) in the Alxa Desert region shows an increasing trend in 84.17% of the area, with a significant increase in 61.53% of the area, mainly concentrated in the key implementation areas of the Three-North Shelterbelt Forest Program, indicating that the implementation of the program has achieved positive results. However, ET in the southeastern plain area shows a decreasing trend, which is closely related to human activities such as urbanization.
- (2)
- This study uses a stepwise multiple regression method to construct response relationship models between ET and meteorological elements and EVI, with linear relationship areas accounting for 47.52% and nonlinear relationship areas accounting for 45.51%. The overall model R2 value is 0.69, indicating good performance, and 75.32% of the regional models are significant. The average RMSE of the model is 25.3 mm, with high prediction accuracy, and the average RMSE of the ET simulation value is 49.5 mm, providing a quantitative assessment of model prediction error.
- (3)
- Through the analysis of forest and grassland cover under different hydrological year scenarios in the Alxa Desert region, the average RMSE of the restoration thresholds and recovery potential is calculated to be 5.4% using quantitative calculation methods. Under high water year scenarios, the forest and grassland vegetation cover shows a significant recovery trend, with an average restoration threshold of (75.4 ± 12.5)% and an average recovery potential of (8.5 ± 3.6)%. The forest and grassland vegetation cover in 31.25% of the area has exceeded the restoration threshold, mainly distributed in the central and western parts where the Three-North Shelterbelt Forest Program is intensively implemented; while 68.75% of the area has not reached the threshold but has recovery potential, mainly distributed near the Helan Mountains.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, W.Y.; He, L.; Zhao, C.Y. Desertification dynamics in Alxa League over the period of 2000–2012. J. Lanzhou Univ. Nat. Sci. 2015, 51, 55–60+71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Si, J.; He, X.; Jia, B.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Qin, J.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Z. Simulation of the soil water-carrying capacity of Haloxylon ammodendron plantations in the Alxa Desert, China: Implications for afforestation. Catena 2024, 235, 107637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.L.; Yan, C.Z.; Li, S.; Li, B. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Oasis Spatial-temporal Changes in Alxa during Recent 35 Years. J. Desert Res. 2012, 32, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Na, W.; Gao, Y.; Gao, Z. Response of soil water in deep dry soil layers to monthly precipitation, plant species, and surface mulch in a semi-arid hilly loess region of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 291, 108612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Wang, G.; Duan, R. Impacts of long-term climate change on the groundwater flow dynamics in a regional groundwater system: Case modeling study in Alashan, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Guo, X.; Feng, C.; Xiao, C. Soil seed bank responses to anthropogenic disturbances and its vegetation restoration potential in the arid mining area. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shao, M. Vegetation soil water carrying capacity of artificial pasture in loess region in Northern Shaanxi, China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Huang, M.; Gallichand, J.; Shao, M. Optimization of plant coverage in relation to water balance in the Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 2012, 173, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Shao, M.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Binley, A. Spatial variations in soil-water carrying capacity of three typical revegetation species on the Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 273, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Ning, Z.; Fu, B.; Sivapalan, M. Spatio-temporal patterns of the effects of precipitation variability and land use/cover changes on long-term changes in sediment yield in the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 4363–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, X.; Yao, S.; Zhang, J.; Hou, X.; Yin, R. A novel similar habitat potential model based on sliding-window technique for vegetation restoration potential mapping. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, S.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.; Lü, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Jin, Z.; Feng, X.; Yan, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S. Quantification of the ecosystem carrying capacity on China’s Loess Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, D.; Yang, Y.; Piao, S.; Yang, H.; Lei, H.; Fu, B. Excessive afforestation and soil drying on China’s Loess Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2018, 123, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W. Spatiotemporal variations of evapotranspiration and influence factors in Qilian Mountain from 2000 to 2018. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.N.; Wang, G.X.; Wu, W.; Xu, Y. Medium and long term forecast of reservoir inflow in upper reaches of the Yangtze River. Water Resour. Protect. 2022, 38, 131–136+165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.H.; Shen, B.; Zhang, X.W.; Li, Z.B. Synchronous-Asynchronous encounter probability of rich-poor runoff based on copula function. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2009, 37, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Z.H. Evaluation of MODIS MOD16 evaportranspiration product in Chinese river basins. J. Nat. Resour. 2017, 32, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Zhu, Q.K.; Shi, R.Y.; Gou, Q.P. Spatial and temporal changes of vegetation cover and its influencing factors in the Loess Plateau from 2000 to 2018. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 19, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, H.; Yu, F.; Chen, W.; Xie, Z. Effects of artificial vegetation construction on soil physical properties in the northeastern edge of Tengger Desert. Arid Zone Res. 2022, 39, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.H.; Long, X.J. Study on prediction model of water resources carrying capacity. Water Resour. Hydrop. Eng. 2018, 49, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Z.; Xia, J.; Tan, G. Measurement and evaluation of water resources carrying capacity of northwest china. Resour. Sci. 2003, 25, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Luo, M.; Chen, K.; Sun, J.; Wu, Y. Intra-annual vegetation changes and spatial variation in China over the past two decades based on remote sensing and time-series clustering. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.H.; Ren, Z.G.; Wei, H.T. Driving Mechanism of the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Vegetation in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2020. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.Z.; Liu, X.F.; Zhu, X.F.; Pan, Y.Z.; Chen, S.C. Spatiotemporal analyses and associated driving forces of vegetation coverage change in the Loess Plateau. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 1568–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.A.; Fu, B.J.; Piao, S.L.; Lu, Y.H.; Ciaia, P.; Feng, X.M.; Wang, Y.F. Reduced sediment transport in the Yellow River due to anthropogenic changes. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | VIF | 1/VIF |
|---|---|---|
| EVI | 1.17 | 0.85 |
| × EVI | 1.09 | 0.92 |
| EVI2 | 1.23 | 0.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.; Zhou, D.; Si, J.; Jia, B. Assessment of the Restoration Potential of Forest Vegetation Coverage in the Alxa Desert Region of China. Plants 2024, 13, 2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172536
Pan Y, Zhou D, Si J, Jia B. Assessment of the Restoration Potential of Forest Vegetation Coverage in the Alxa Desert Region of China. Plants. 2024; 13(17):2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172536
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Yanlin, Dongmeng Zhou, Jianhua Si, and Bing Jia. 2024. "Assessment of the Restoration Potential of Forest Vegetation Coverage in the Alxa Desert Region of China" Plants 13, no. 17: 2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172536
APA StylePan, Y., Zhou, D., Si, J., & Jia, B. (2024). Assessment of the Restoration Potential of Forest Vegetation Coverage in the Alxa Desert Region of China. Plants, 13(17), 2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172536





