Biochar Organic Fertilizer Combined with Indigenous Microorganisms Enhances the Growth of Landscape Grass Cultivated in a Substrate Mixed with Iron Tailings and Mining Topsoil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Impact of Biochar Organic Fertilizer Combined with Indigenous Microorganisms on Plant Growth Indices
2.2. The Effects of Biochar Organic Fertilizer Combined with Indigenous Microorganisms on Plant Physiological Parameters
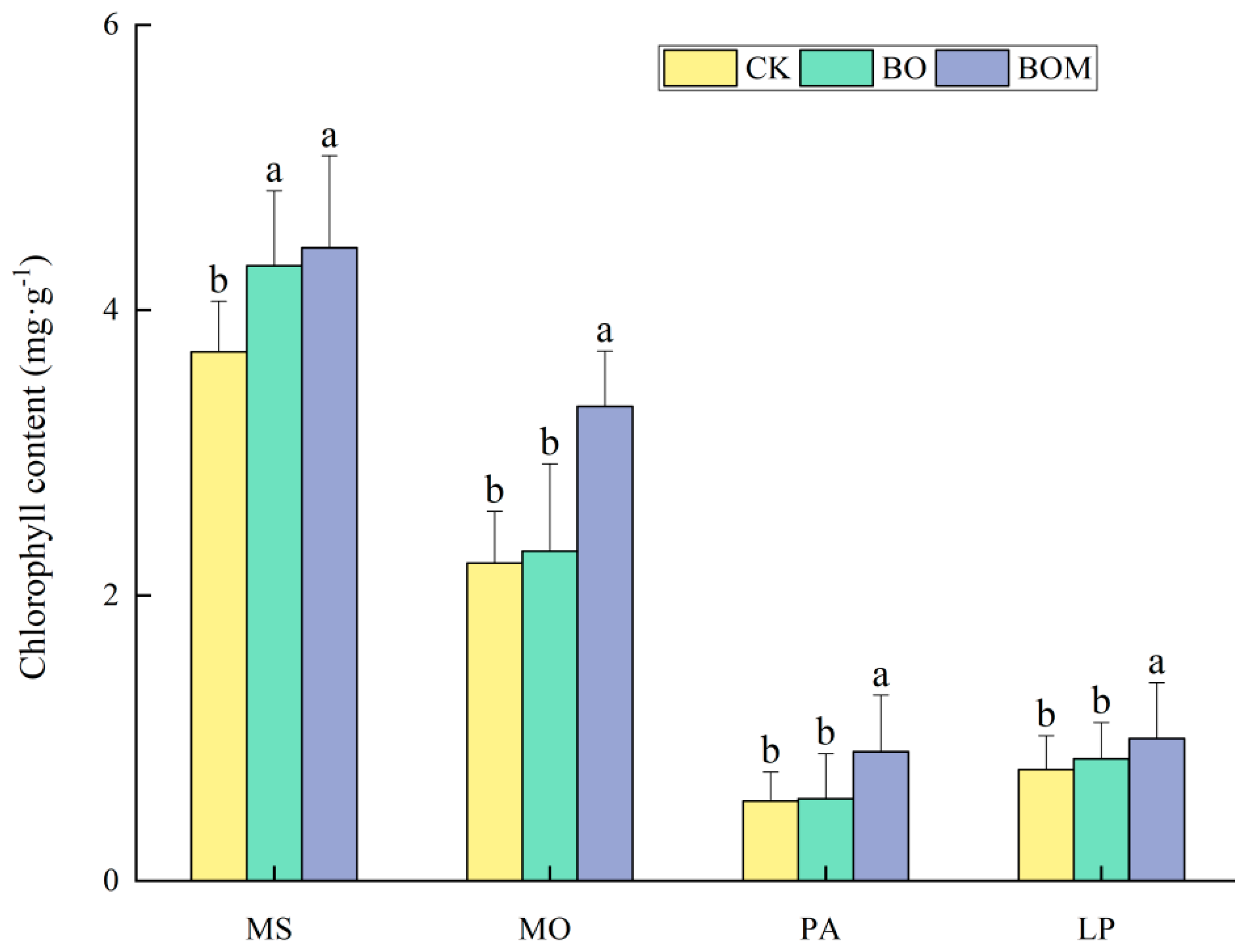
2.2.1. Chlorophyll Content
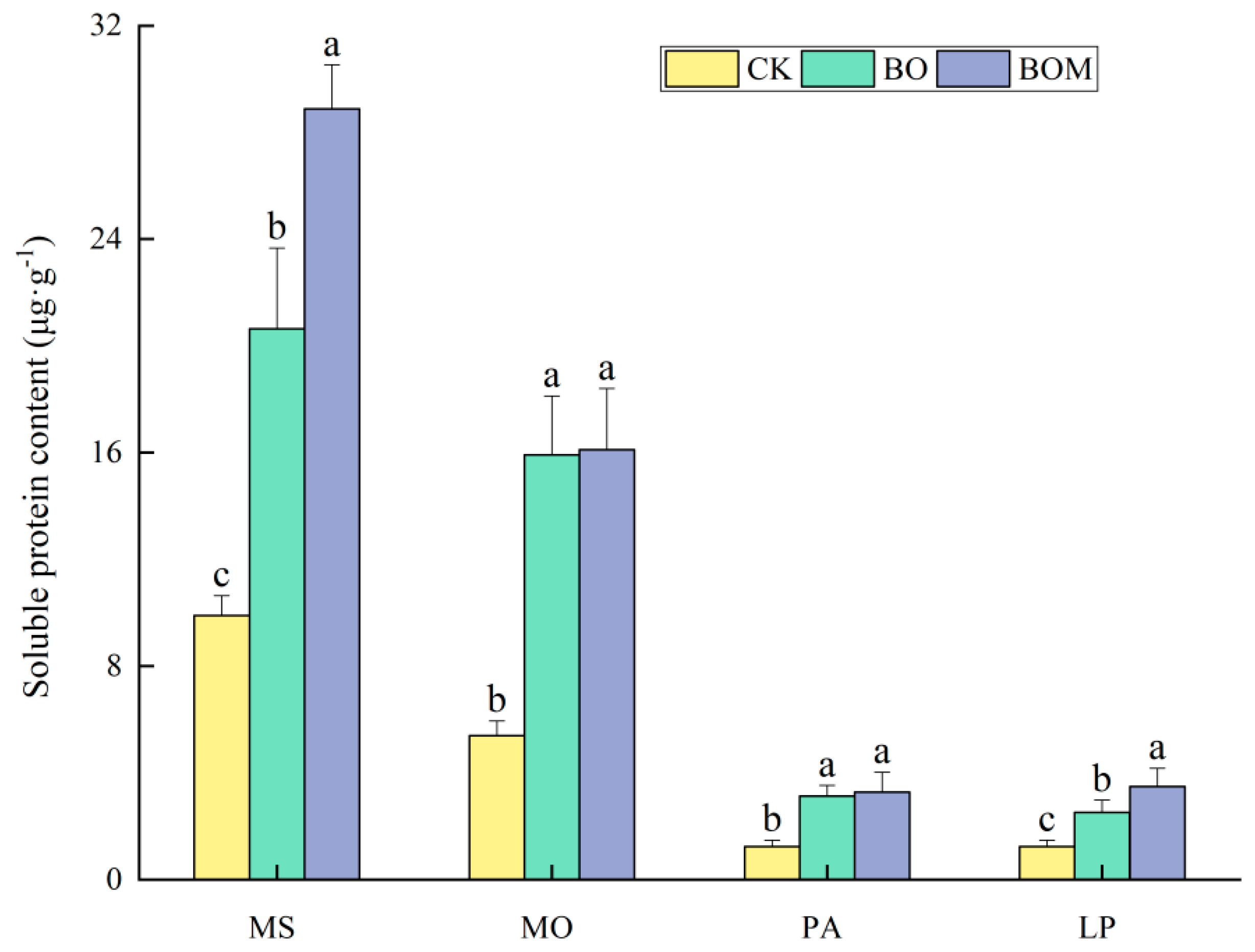
2.2.2. Soluble Protein Content
2.2.3. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
2.2.4. Essential Nutrient Elements in the Landscape Grasses
2.3. The Impact of Microorganisms and Biochar Organic Fertilizer on the Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Community of Plants
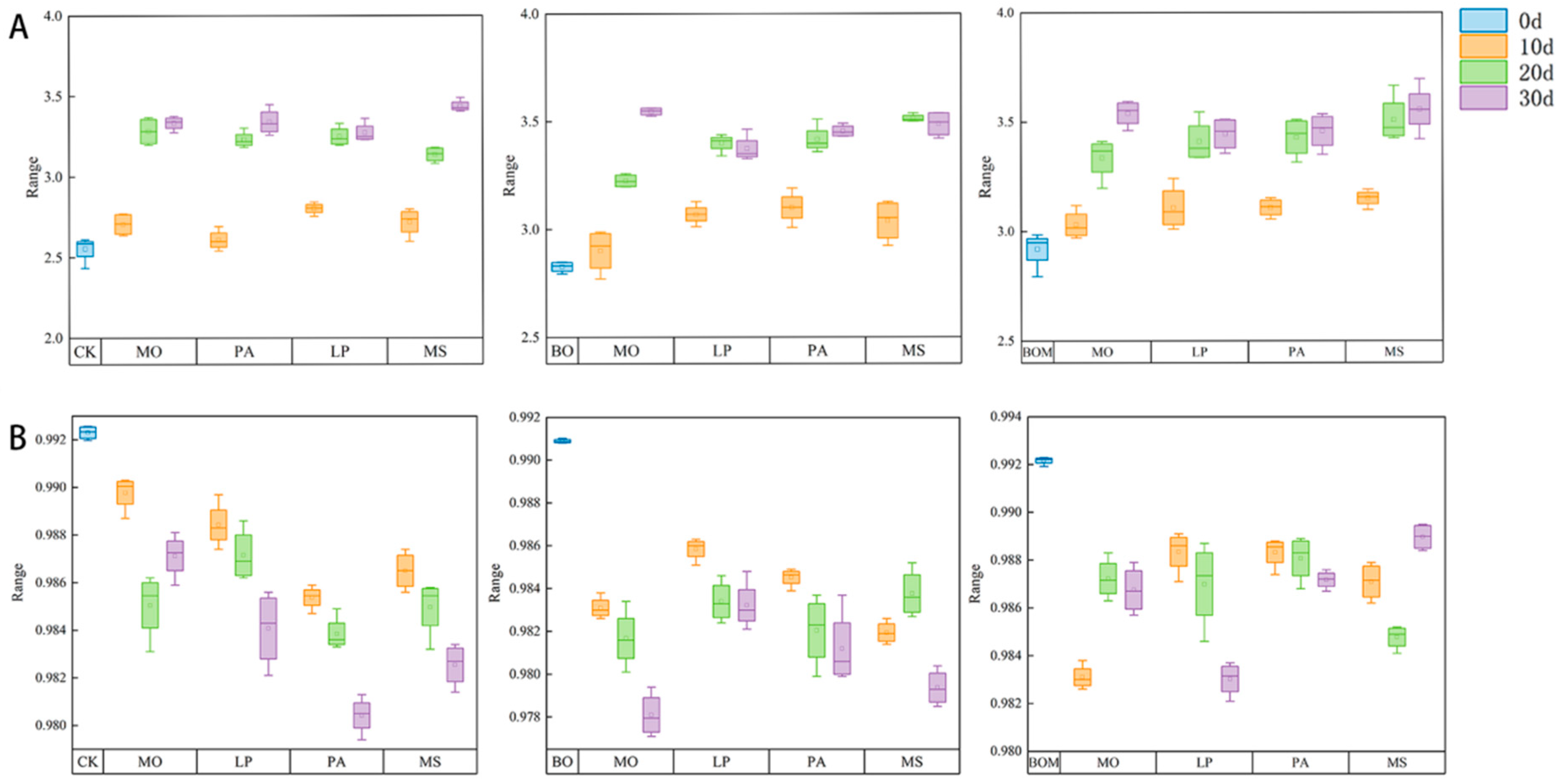
2.3.1. Diversity Index
2.3.2. Colony Similarity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Material
4.2. Method of Compounding Culture Substrate
4.3. Method for the Preparation of Indigenous Microbial Formulations from Plant Rhizosphere Soil
4.4. Pot Experiment
4.5. Methods for the Detection of Plant Growth and Development Indicators
4.6. Detection Methods for Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Content
4.7. Data Processing and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CK | control check |
| BO | biochar organic fertilizer |
| BOM | biochar organic fertilizer and indigenous microorganisms |
| PAL | phenylalanine ammonia-lyase |
| POD | peroxidase |
| L. perenne, LP | Lolium perenne L. |
| M. officinalis, MO | Melilotus officinalis (L.) Lam. |
| M. sativa, MS | Medicago sativa L. |
| P. alopecuroides, PA | Pennisetum alopecuroides (L.) Spreng. |
References
- Dong, Y.; Zan, J.; Lin, H. Bioleaching of heavy metals from metal tailings utilizing bacteria and fungi: Mechanisms, strengthen measures, and development prospect. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Han, Y.; Liu, X.; Shan, Y.; Li, Y. Effect of fluidized magnetizing roasting on iron recovery and transformation of weakly magnetic iron mineral phasein iron tailings. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2019, 55, 906–916. [Google Scholar]
- Benarchid, Y.; Taha, Y.; Argane, R.; Tagnit-Hamou, A.; Benzaazoua, M. Concrete containing low-sulphide waste rocks as fine and coarse aggregates: Preliminary assessment of materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 221, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Wang, W. Flexural behavior evaluation and energy dissipation mechanisms of modified iron tailings powder incorporating cement and fibers subjected to freeze-thaw cycles. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 351, 131527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, H.E. Geochemistry and mineralogy of solid mine waste: Essential knowledge for predicting environmental impact. Elements 2011, 7, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmignano, O.R.; Vieira, S.S.; Teixeira, A.P.C.; Lameiras, F.S.; Brandão, P.R.G.; Lago, R.M. Iron ore tailings: Characterization and applications. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2021, 32, 1895–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Xing, R.; Zheng, Z.; Qiu, J.; Yang, L. Bacterial community structure and diversity responses to the direct revegetation of an artisanal zinc smelting slag after 5 years. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14773–14788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarsjö, J.; Chalov, S.R.; Pietroń, J.; Alekseenko, A.V.; Thorslund, J. Patterns of soil contamination, erosion and river loading of metals in a gold mining region of northern Mongolia. Reg. Environ. Change 2017, 17, 1991–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarathchandra, S.S.; Rengel, Z.; Solaiman, Z.M. A review on remediation of Iron ore mine tailings via organic amendments coupled with phytoremediation. Plants 2023, 12, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, S.M.A.C.; Sousa, L.N.; Diniz, P.; Martins, M.E.; Assis, P.S. Steel slag and iron ore tailings to produce solid brick. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, T.; Hou, X.; Li, S. Co-utilization of iron ore tailings and coal fly ash for porous ceramsite preparation: Optimization, mechanism, and assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Tian, G.; Gong, L.; Tang, Q.; Meng, J.; Duan, X.; Liang, J. Mesoporous manganese silicate composite adsorbents synthesized from high-silicon iron ore tailing. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 159, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Wei, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Han, C.; Bian, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qian, F.; Liu, Y. Effects of constructing farmland with large amounts of iron tailings as soil reconstruction materials on soil properties and crop growth. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, P.H.D.C.; Silva, A.O.; Santos, J.V.D.; Carvalho, A.M.X.D.; Carneiro, M.A.C.; Siqueira, J.O. Soil conditioners improve the environment for grass growth in iron mining tailings of the Fundão dam failure. Ciência Agrotecnologia 2024, 48, e002724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, W.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.C.; Fan, Q.; Huang, M.; Fang, L. Enhancing soil ecological security through phytomanagement of tailings in erosion-prone areas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 462, 132730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Y.; Lv, X.; Yang, W. Is underground coal mining causing land degradation and significantly damaging ecosystems in semi-arid areas? A study from an Ecological Capital perspective. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1969–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burylo, M.; Hudek, C.; Rey, F. Soil reinforcement by the roots of six dominant species on eroded mountainous marly slopes (Southern Alps, France). Catena 2011, 84, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ji, B.; Hu, Y.; Liu, R.; Sun, W. A review on in situ phytoremediation of mine tailings. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; You, F.; Wu, S.; Lu, Z.; Hastwell, A.; Ferguson, B.; Huang, L. Nodule Formation and Nitrogen Fixation in Acacia holosericea Plants Grown in Soil Admixed with Iron Ore Tailings. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, S.; Kibort, K.; Mioduska, J.; Lieder, M.; Małachowska, A. Waste management in the mining industry of metals ores, coal, oil and natural gas-A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbano Barzallo, D.A. Ground Improvement for Tailing Dam Remediation and Design. Master’s Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Heiskanen, J.; Ruhanen, H.; Hagner, M. Effects of compost, biochar and ash mixed in till soil cover of mine tailings on plant growth and bioaccumulation of elements: A growing test in a greenhouse. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Chen, W.; Wei, L.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z. Biochar Blended with Alkaline Mineral Can Better Inhibit Lead and Cadmium Uptake and Promote the Growth of Vegetables. Plants 2024, 13, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayne, N.; Aula, L. Livestock manure and the impacts on soil health: A review. Soil Syst. 2020, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aini, N.; Yamika, W.S.D.; Ulum, B. Effect of nutrient concentration, PGPR and AMF on plant growth, yield, and nutrient uptake of hydroponic lettuce. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2019, 21, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Wu, S.-H.; Wen, M.-X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.-S. Effects of combined inoculation with Rhizophagus intraradices and Paenibacillus mucilaginosus on plant growth, root morphology, and physiological status of trifoliate orange (Poncirus trifoliata L. Raf.) seedlings under different levels of phosphorus. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 205, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoyo, G.; Guzmán-Guzmán, P.; Parra-Cota, F.I.; Santos-Villalobos, S.D.L.; Orozco-Mosqueda, M.D.C.; Glick, B.R. Plant growth stimulation by microbial consortia. Agronomy 2021, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALKahtani, M.D.; Attia, K.A.; Hafez, Y.M.; Khan, N.; Eid, A.M.; Ali, M.A.; Abdelaal, K.A. Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and antioxidant defense system can display salt tolerance of salt acclimated sweet pepper plants treated with chitosan and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siswanti, D.; Umah, N. Effect of biofertilizer and salinity on growth and chlorophyll content of Amaranthus tricolor L. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, H.; He, Z.; Ma, D.; Sun, W.; Xu, X.; Tian, Q. Effects of Drought Stress on Leaf Functional Traits and Biomass Characteristics of Atriplex canescens. Plants 2024, 13, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, R.; Nawaz, M.S.; Siddique, M.J.; Hakim, S.; Imran, A. Plant survival under drought stress: Implications, adaptive responses, and integrated rhizosphere management strategy for stress mitigation. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 242, 126626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, U.B.; Sahu, P.K.; Paul, S.; Kumar, A.; Malviya, D.; Singh, S.; Kuppusamy, P.; Singh, P.; Paul, D.; et al. Linking soil microbial diversity to modern agriculture practices: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Sisodia, A.; Sisodia, V.; Padhi, M. Role of microbes in restoration ecology and ecosystem services. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Maron, P.A.; Sarr, A.; Kaisermann, A.; Lévêque, J.; Mathieu, O.; Guigue, J.; Karimi, B.; Bernard, L.; Dequiedt, S.; Terrat, S.; et al. High microbial diversity promotes soil ecosystem functioning. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02738-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, P.; Enespa. Soil–microbes–plants: Interactions and ecological diversity. In Plant Microbe Interface; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 145–176. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z. Meta-analysis shows positive effects of plant diversity on microbial biomass and respiration. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Nesme, J.; Røder, H.L.; Li, X.; Zuo, Z.; Petersen, M.; Burmølle, M.; Sørensen, S.J. Emergent bacterial community properties induce enhanced drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, W.; Yan, J.; Zhou, M.; Yao, X.; Gao, A.; Ma, C.; Cheng, J.; Ruan, J. Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as a biocontrol agent in the control of plant diseases. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, A.; Malla, M.A.; Khan, F.; Chowdhary, K.; Yadav, S.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.; Khare, P.K.; Khan, M.L. Soil microbiome: A key player for conservation of soil health under changing climate. Biodivers. Conserv. 2019, 28, 2405–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Riaz, M.; Babar, S.; Eldesouki, Z.; Liu, B.; Xia, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, X.; Jiang, C. Alterations in the composition and metabolite profiles of the saline-alkali soil microbial community through biochar application. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 120033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Tang, Y.; Yang, H.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, G. Effects of Fertilization and Planting Modes on Soil Organic Carbon and Microbial Community Formation of Tree Seedlings. Plants 2024, 13, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, R.P. Biological control of soilborne diseases in organic potato production using hypovirulent strains of Rhizoctonia solani. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 2020, 36, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Lv, X.; Zhu, X.; Song, X. Beneficial effects of biochar application with nitrogen fertilizer on soil nitrogen retention, absorption and utilization in maize production. Agronomy 2022, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Li, L.; Ma, G.; Wei, Z. Halotolerant Microorganism-Based Soil Conditioner Application Improved the Soil Properties, Yield, Quality and Starch Characteristics of Hybrid Rice under Higher Saline Conditions. Plants 2024, 13, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tan, X.; Zheng, M.; Yu, D.; Lin, A.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Gao, Z.; Cui, J. Modified biochar/humic substance/fertiliser compound soil conditioner for highly efficient improvement of soil fertility and heavy metals remediation in acidic soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Shahzad, S.M.; Arif, M.S.; Yasmeen, T.; Ali, B.; Tanveer, A. Inoculation of potassium solubilizing bacteria with different potassium fertilization sources mediates maize growth and productivity. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 57, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar]
- Bargaz, A.; Lyamlouli, K.; Chtouki, M.; Zeroual, Y.; Dhiba, D. Soil microbial resources for improving fertilizers efficiency in an integrated plant nutrient management system. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addisu, B. Rhizobia Symbiosis in Legumes and Non-Legumes Crops. Adv. Crop Sci. Tech. 2023, 11, 559. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, K.; Biswas, D.R.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Das, D.; Suman, A.; Das, T.K.; Paul, R.K.; Ghosh, A.; Sarkar, A.; Kumar, R.; et al. Recycling of silicon-rich agro-wastes by their combined application with phosphate solubilizing microbe to solubilize the native soil phosphorus in a sub-tropical Alfisol. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, L.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Wu, Z. Exploring the Organic Acid Secretion Pathway and Potassium Solubilization Ability of Pantoea vagans ZHS-1 for Enhanced Rice Growth. Plants 2024, 13, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.; Hassan, H.M.; Ghazali, A.H.A.; Ahmad, M. Halotolerant potassium solubilizing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria may improve potassium availability under saline conditions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Urano, D.; Liao, K.L.; Hedrick, T.L.; Gao, Y.; Jones, A.M. A nondestructive method to estimate the chlorophyll content of Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Methods 2017, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Shen, F.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Ye, S. Preparation and functional characteristics of protein from Ginkgo endophytic Pseudomonas R6 and Ginkgo seed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rácz, A.; Hideg, É.; Czégény, G. Selective responses of class III plant peroxidase isoforms to environmentally relevant UV-B doses. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 221, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, M.J.; D’cunha, G.B. A modern view of phenylalanine ammonia lyase. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.; Flowers, T.H. Evaluation of Kjeldahl digestion method. J. Res. 2004, 15, 159–179. [Google Scholar]
- Heidari-Bafroui, H.; Charbaji, A.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Faghri, M. A colorimetric dip strip assay for detection of low concentrations of phosphate in seawater. Sensors 2021, 21, 3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Luo, Y.; Huang, J.; Hou, B.; Wang, B.; Ogino, K.; Zhao, J.; Si, H. The effect of biochar on the migration theory of nutrient ions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, R.S.; Evangelista, L.R.; Thomaz, S.M.; Agostinho, A.A.; Gomes, L.C. A unified index to measure ecological diversity and species rarity. Ecography 2008, 31, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-R.; Shin, J.; Guevarra, R.B.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Seol, K.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.B.; Isaacson, R.E. Deciphering diversity indices for a better understanding of microbial communities. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 2089–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Song, H.; An, J. Biochar Organic Fertilizer Combined with Indigenous Microorganisms Enhances the Growth of Landscape Grass Cultivated in a Substrate Mixed with Iron Tailings and Mining Topsoil. Plants 2024, 13, 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13213042
Li X, Zhang X, Wang J, Liu Z, Song H, An J. Biochar Organic Fertilizer Combined with Indigenous Microorganisms Enhances the Growth of Landscape Grass Cultivated in a Substrate Mixed with Iron Tailings and Mining Topsoil. Plants. 2024; 13(21):3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13213042
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinyue, Xun Zhang, Jiaoyue Wang, Zhouli Liu, Hewei Song, and Jing An. 2024. "Biochar Organic Fertilizer Combined with Indigenous Microorganisms Enhances the Growth of Landscape Grass Cultivated in a Substrate Mixed with Iron Tailings and Mining Topsoil" Plants 13, no. 21: 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13213042
APA StyleLi, X., Zhang, X., Wang, J., Liu, Z., Song, H., & An, J. (2024). Biochar Organic Fertilizer Combined with Indigenous Microorganisms Enhances the Growth of Landscape Grass Cultivated in a Substrate Mixed with Iron Tailings and Mining Topsoil. Plants, 13(21), 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13213042









