Effect of Seed Hydropriming on the Elongation of Plumule and Radicle During the Germination Process and Changes in Enzyme Activity Under Water-Deficient Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Germination
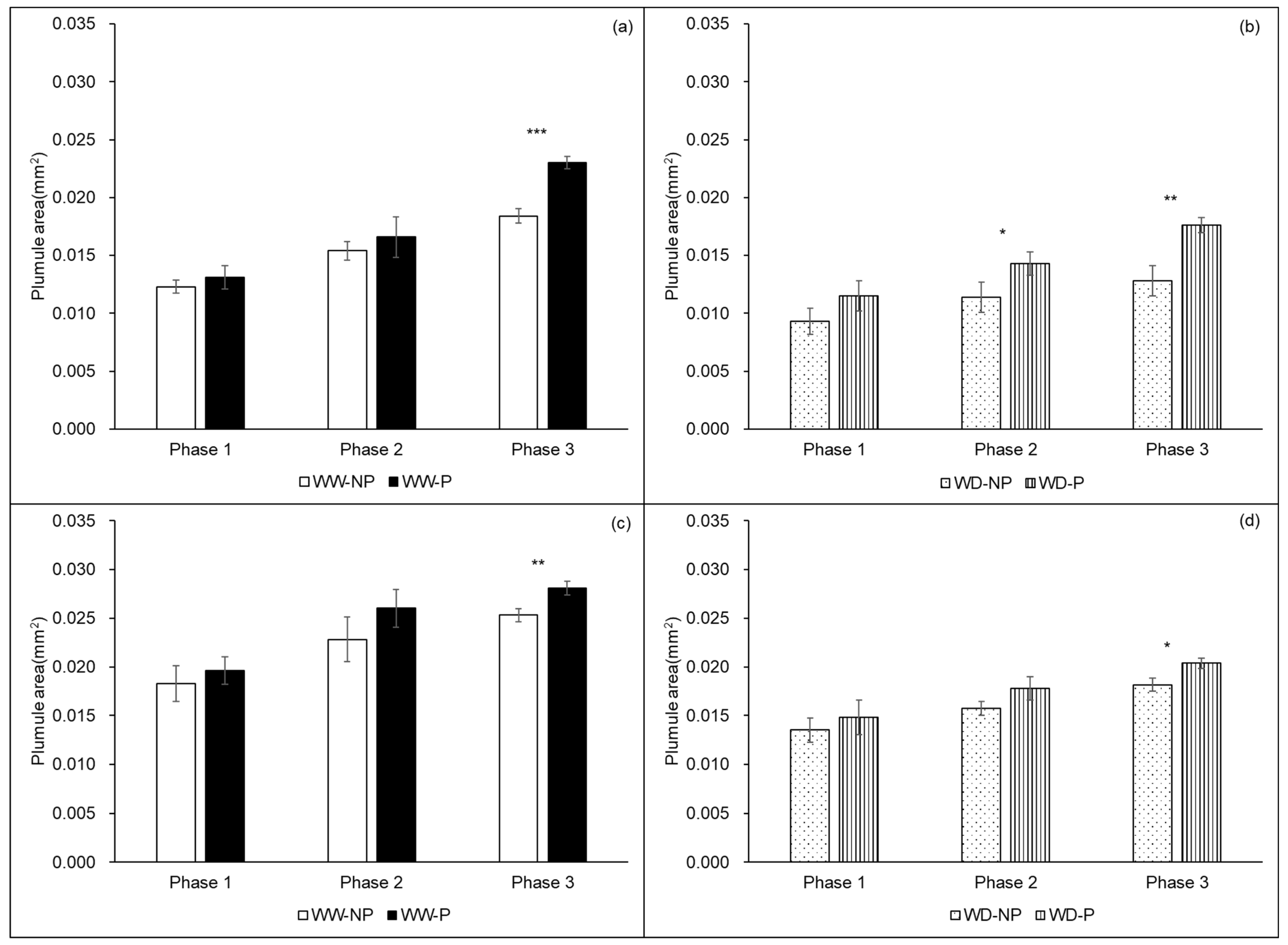
2.2. Morpho-Physiological Changes Without and with Hydropriming of Seeds of Two Rice Varieties
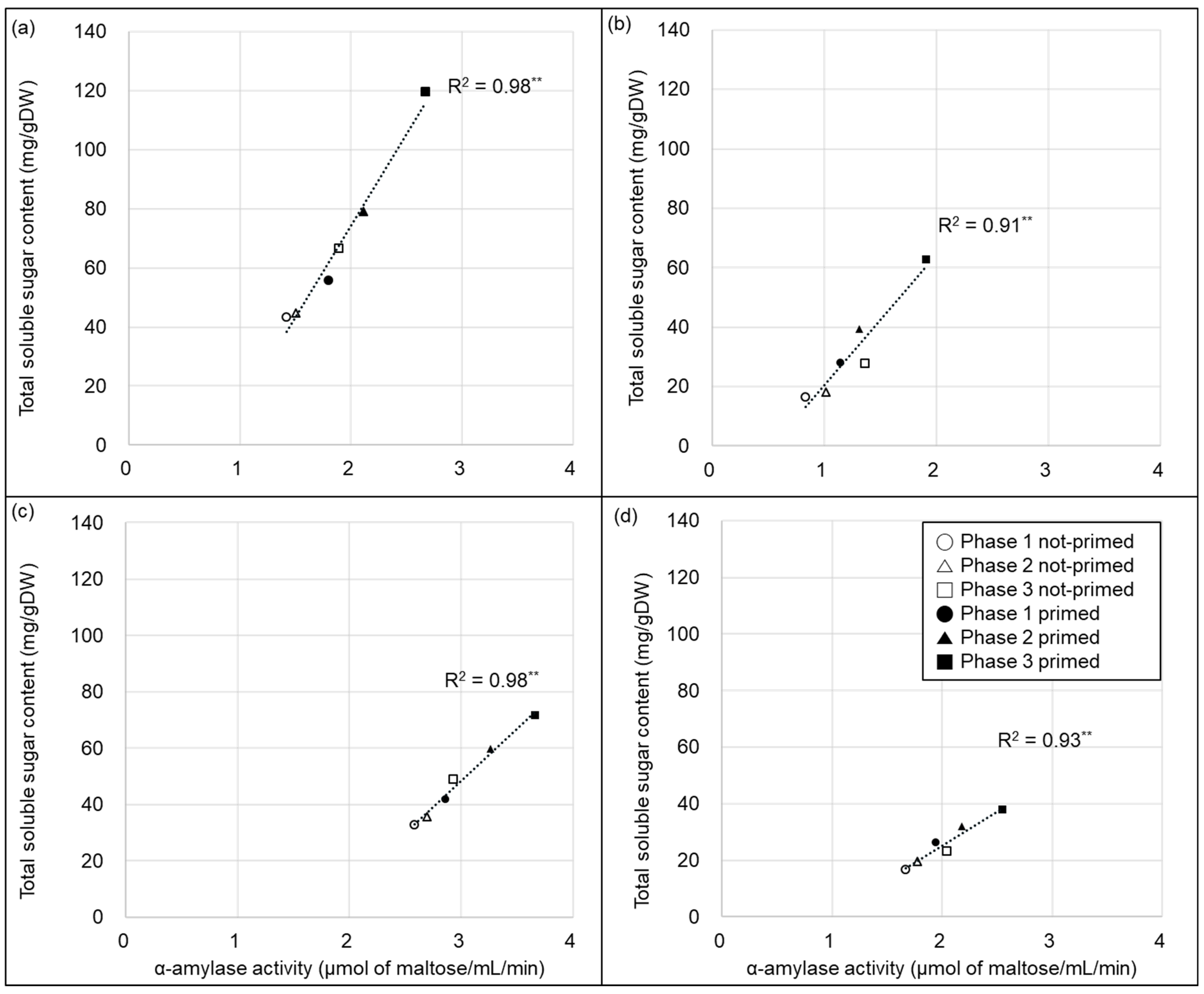
2.3. Changes in Total Starch Content, α-Amylase Activity, and Total Soluble Sugar Content
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Seed Sources
4.2. Seed Priming Treatment
4.3. Experimental Design
4.3.1. Germination Assay and Germination Test
4.3.2. Anatomical Analysis
4.3.3. Total Starch Content
4.3.4. α-Amylase Activity
4.3.5. Total Soluble Sugar Content
4.3.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.; Sun, F. Integrated drought vulnerability and risk assessment for future scenarios: An indicator based analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyasulu, M.; Zhong, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; He, H.; Bian, J. Uncovering novel genes for drought stress in rice at germination stage using genome wide association study. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1421267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; Ali, N.; Akmal, M.; Alotaibi, M.; Refay, Y.; Dindaroglu, T.; Abdul-Wajid, H.H.; Battaglia, M.L. Drought stress impacts on plants and different approaches to alleviate its adverse effects. Plants 2021, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; He, Y.; Li, X.; Weng, X.; Feng, D.; Ying, J.; Wang, Z. An integrated RNA-Seq and physiological study reveals gene responses involving in the initial imbibition of seed germination in rice. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 90, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Kim, J.H. Total sugars, alpha-amylase activity, and germination after priming of normal and aged rice seeds. Korean J. Crop Sci. 2000, 45, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G. Analysis of gene expression in early seed germination of rice: Landscape and genetic regulation. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.F.; Peterson, M.L. Relations between alpha-amylase activity and growth of rice seedlings 1. Crop Sci. 1973, 13, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damaris, R.N.; Lin, Z.; Yang, P.; He, D. The rice alpha-amylase, conserved regulator of seed maturation and germination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, L.; Song, S.; Yin, Q.; Zhao, T.; Liu, H.; He, A.; Wang, W. Enhancement in seed priming-induced starch degradation of rice seed under chilling stress via GA-mediated α-amylase expression. Rice 2022, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.M. Amylase synthesis and stability in crested wheatgrass seeds at low water potentials. Plant Physiol. 1971, 48, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Khan, F.; Hussain, H.A.; Nie, L. Physiological and biochemical mechanisms of seed priming-induced chilling tolerance in rice cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumpa, T.; Phetcharaburanin, J.; Suksawat, M.; Pattanagul, K.; Pattanagu, W. Metabolic profiles and some physiological traits of three rice cultivars differing in salinity tolerance under salinity stress at the germination stage. Asian J. Agric. Biol. 2024, 1, 2023088. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Arora, R. Priming memory invokes seed stress-tolerance. Cond. Exp. Bot. 2013, 94, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marthandan, V.; Geetha, R.; Kumutha, K.; Renganathan, V.G.; Karthikeyan, A.; Ramalingam, J. Seed priming: A feasible strategy to enhance drought tolerance in crop plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, Y.; Asea, G.; Yoshino, M.; Kojima, N.; Hanada, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Yabuta, S.; Kamioka, R.; Sakagami, J.I. Development of hydropriming techniques for sowing seeds of upland rice in Uganda. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 2170–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devika, O.S.; Singh, S.; Sarkar, D.; Barnwal, P.; Suman, J.; Rakshit, A. Seed priming: A potential supplement in integrated resource management under fragile intensive ecosystems. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 654001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskow, A.; Howling, A.; Furno, I. Mechanisms of plasma-seed treatments as a potential seed processing technology. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 617345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Pérez, C.A.; Gómez-Merino, F.C.; Spinoso-Castillo, J.L.; Bello-Bello, J.J. In vitro screening of sugarcane cultivars (Saccharum spp. hybrids) for tolerance to polyethylene glycol-induced water stress. Agronomy 2021, 11, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellal, F.A.; El-Shabrawi, H.M.; Abd El-Hady, M.; Khatab, I.A.; El-Sayed, S.A.A.; Abdelly, C. Influence of PEG induced drought stress on molecular and biochemical constituents and seedling growth of Egyptian barley cultivars. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, J.A.O.; Casas, D.E.; Gandia, J.L.; Parducho, M.J.L.; Renovalles, E.M.; Quilloy, E.P.; Delfin, E.F. Polyethylene glycol-induced drought stress screening of selected Philippine high-yielding sugarcane varieties. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, A.; Sidari, M.; Anastasi, U.; Santonoceto, C.; Maggio, A. Effect of PEG-induced drought stress on seed germination of four lentil genotypes. J. Plant Interact. 2014, 9, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatpathy, P.; Kar, M.; Dwibedi, S.K.; Dash, A. Seed priming with salicylic acid improves germination and seedling growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under PEG-6000 induced water stress. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano-Nakata, M.; Tatsumi, J.; Inukai, Y.; Asanuma, S.; Yamauchi, A. Effect of various intensities of drought stress on δ 13 C variation among plant organs in rice: Comparison of two cultivars. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.; Kano-Nakata, M.; Takeda, M.; Menge, D.; Mitsuya, S.; Inukai, Y.; Yamauchi, A. Nitrogen application enhanced the expression of developmental plasticity of root systems triggered by mild drought stress in rice. Plant Soil. 2014, 378, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, B.; Ali, A.; Rangappa, K.; Choudhury, B.U.; Mishra, V.K. A detailed study on genetic diversity, antioxidant machinery, and expression profile of drought-responsive genes in rice genotypes exposed to artificial osmotic stress. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolny, E.; Betekhtin, A.; Rojek, M.; Braszewska-Zalewska, A.; Lusinska, J.; Hasterok, R. Germination and the early stages of seedling development in Brachypodium distachyon. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, Y.; Sone, C.; Sakagami, J.I. Genetic diversity of hydro priming effects on rice seed emergence and subsequent growth under different moisture conditions. Genes 2020, 11, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaik, S.S.; Carciofi, M.; Martens, H.J.; Hebelstrup, K.H.; Blennow, A. Starch bioengineering affects cereal grain germination and seedling establishment. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2257–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.; Wahid, A.; Ahmad, N.; Asad, S.A. Comparative efficacy of surface drying and re-drying seed priming in rice: Changes in emergence, seedling growth and associated metabolic events. Paddy Water Cond. 2010, 8, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambona, C.M.; Koua, P.A.; Léon, J.; Ballvora, A. Stress memory and its regulation in plants experiencing recurrent drought conditions. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2023, 136, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmens, E.; Deleu, L.J.; De Brier, N.; De Man, W.L.; De Proft, M.; Prinsen, E.; Delcour, J.A. The impact of hydro-priming and osmo-priming on seedling characteristics, plant hormone concentrations, activity of selected hydrolytic enzymes, and cell wall and phytate hydrolysis in sprouted wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). ACS Omega 2019, 4, 22089–22100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, Y.; Sugiyama, M.; Sakagami, J.I.; Fukuda, A.; Ohe, M.; Watanabe, H. Seed germination and coleoptile growth of new rice lines adapted to hypoxic conditions. Plant Prod. Sci. 2015, 18, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Tan, B.; Xu, J.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Tang, Q.; Wang, W. Priming methods affected deterioration speed of primed rice seeds by regulating reactive oxygen species accumulation, seed respiration and starch degradation. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1267103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purbajanti, E.D.; Kusmiyati, F.; Fuskhah, E.; Rosyida, R.; Adinurani, P.G.; Vincēviča-Gaile, Z. Selection for drought-resistant rice (Oryza sativa L.) using polyethylene glycol. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Conditional Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 293, p. 012014. [Google Scholar]
- Bernfeld, B. Amylases α and α. Methods Enzymol. 1955, 1, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Libron, J.A.; Putri, H.H.; Bore, E.K.; Chepkoech, R.; Akagi, I.; Odama, E.; Goto, K.; Tamaru, S.; Yabuta, S.; Sakagami, J.I. Halopriming in the submergence-tolerant rice variety improved the resilience to salinity and combined salinity-submergence at the seedling stage. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 208, 108494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
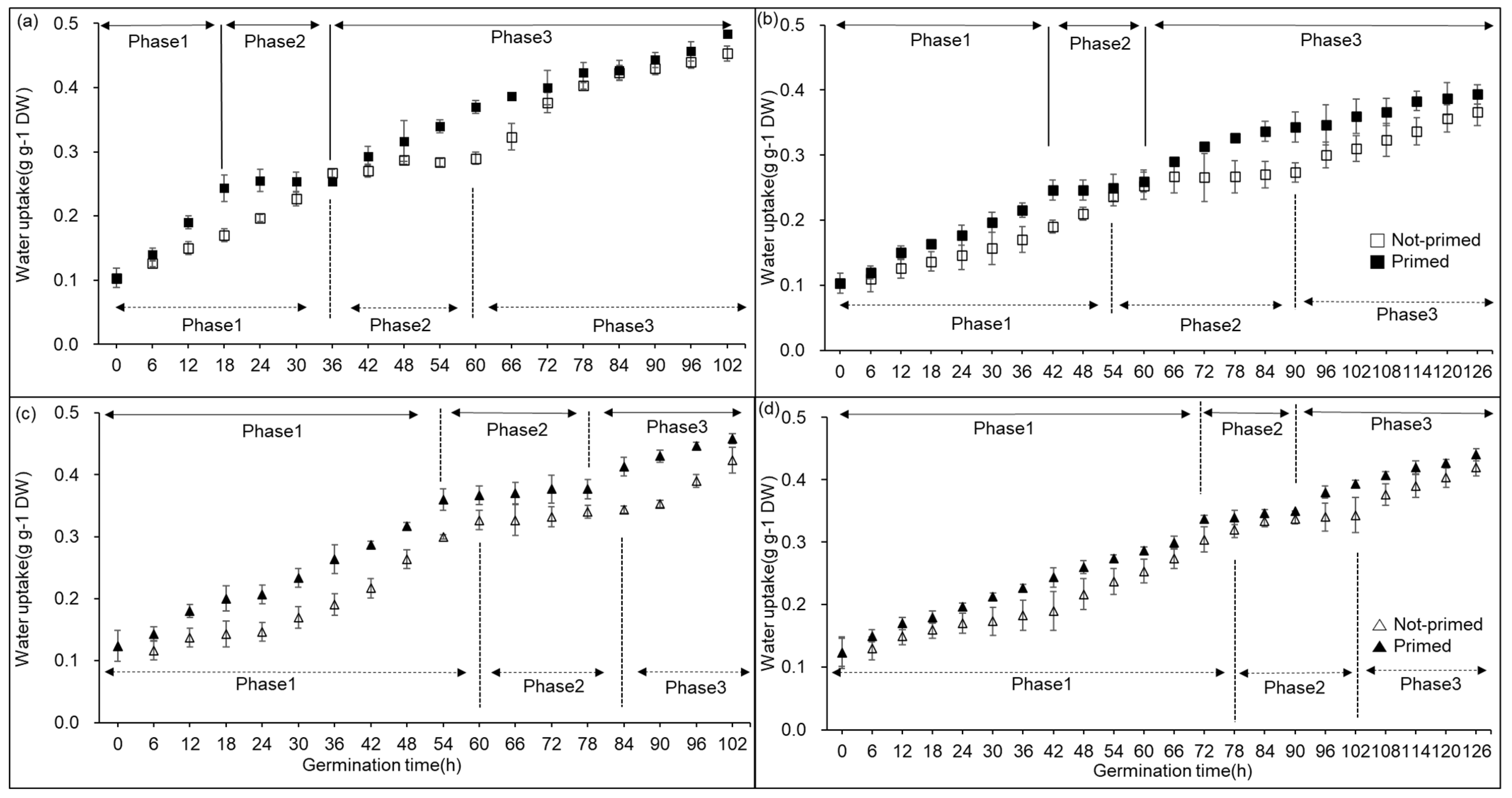


| Variety | Water Status | ST | T50 (h) | MGT (h) | GU | GP (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kasalath | Well-watered | NP | 38.38 | ± | 1.61 | 40.48 | ± | 1.41 | 11.45 | ± | 6.04 | 93.00 | ± | 2.74 |
| P | 29.82 | ± | 3.34 ** | 34.32 | ± | 1.96 ** | 8.94 | ± | 1.00 ns | 99.20 | ± | 1.10 ** | ||
| 15% of PEG6000 | NP | 80.15 | ± | 2.13 | 78.96 | ± | 1.24 | 14.95 | ± | 1.04 | 72.60 | ± | 2.51 | |
| P | 60.24 | ± | 1.96 ** | 61.44 | ± | 0.68 ** | 9.63 | ± | 1.5 ** | 94.00 | ± | 4.18 ** | ||
| Nipponbare | Well-watered | NP | 69.60 | ± | 3.92 | 71.40 | ± | 2.55 | 9.74 | ± | 0.57 | 92.80 | ± | 2.59 |
| P | 61.25 | ± | 3.56 ** | 64.08 | ± | 2.10 * | 8.29 | ± | 1.05 * | 98.40 | ± | 2.04 ** | ||
| 15% of PEG6000 | NP | 95.49 | ± | 2.88 | 95.16 | ± | 2.02 | 13.29 | ± | 0.90 | 62.80 | ± | 3.03 | |
| P | 76.06 | ± | 4.1 ** | 78.96 | ± | 0.91 ** | 11.29 | ± | 1.12 * | 88.00 | ± | 5.70 ** | ||
| Source | ||||||||||||||
| Variety (V) | *** | *** | ns | *** | ||||||||||
| Priming (P) | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||||||||||
| Drought (D) | *** | *** | ** | *** | ||||||||||
| V × P | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||||||||||
| V × D | *** | *** | ns | ** | ||||||||||
| P × D | *** | *** | ns | *** | ||||||||||
| V × P × D | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||||||||||
| Variety | E | ST | Coleoptile (mm2) | Radicle (mm2) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Kasalath | WW | NP | 0.059 | ± | 0.003 d | 0.076 | ± | 0.003 bc | 0.084 | ± | 0.005 bc | 0.026 | ± | 0.002 cd | 0.034 | ± | 0.002 b | 0.043 | ± | 0.003 bc |
| P | 0.070 | ± | 0.005 bc | 0.086 | ± | 0.004 ab | 0.095 | ± | 0.004 ab | 0.035 | ± | 0.004 a | 0.051 | ± | 0.002 a | 0.063 | ± | 0.003 a | ||
| WD | NP | 0.045 | ± | 0.005 e | 0.054 | ± | 0.005 e | 0.063 | ± | 0.005 d | 0.017 | ± | 0.001 f | 0.021 | ± | 0.002 d | 0.028 | ± | 0.005 e | |
| P | 0.055 | ± | 0.003 de | 0.067 | ± | 0.004 cd | 0.081 | ± | 0.001 c | 0.023 | ± | 0.001 de | 0.029 | ± | 0.004 bc | 0.041 | ± | 0.003 bc | ||
| Nipponbare | WW | NP | 0.079 | ± | 0.006 ab | 0.092 | ± | 0.003 a | 0.096 | ± | 0.006 ab | 0.029 | ± | 0.001 bc | 0.032 | ± | 0.001 b | 0.040 | ± | 0.001 bc |
| P | 0.087 | ± | 0.001 a | 0.096 | ± | 0.004 a | 0.105 | ± | 0.006 a | 0.032 | ± | 0.002 ab | 0.037 | ± | 0.002 b | 0.048 | ± | 0.002 b | ||
| WD | NP | 0.053 | ± | 0.003 de | 0.062 | ± | 0.003 de | 0.067 | ± | 0.005 d | 0.019 | ± | 0.002 ef | 0.024 | ± | 0.005 cd | 0.032 | ± | 0.003 de | |
| P | 0.061 | ± | 0.003 cd | 0.069 | ± | 0.003 cd | 0.080 | ± | 0.001 c | 0.024 | ± | 0.001 cde | 0.030 | ± | 0.002 bc | 0.038 | ± | 0.003 cd | ||
| Source | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Variety (V) | *** | *** | *** | ns | * | *** | ||||||||||||||
| Priming (P) | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||||||||||||||
| Environment (E) | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | ** | ||||||||||||||
| V × P | ns | ns | ns | ns | ** | ns | ||||||||||||||
| V × E | ** | * | ns | ns | *** | ** | ||||||||||||||
| P × E | ns | ns | * | ns | ns | ** | ||||||||||||||
| V × P × E | ns | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ||||||||||||||
| Variety | E | ST | Total Starch Content (%) | α-Amylase Activity (µmol Maltose/mL/min) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Kasalath | WW | NP | 48.9 | ± | 1.0 ab | 47.9 | ± | 0.4 a | 44.7 | ± | 0.2 ab | 1.42 | ± | 0.08 cd | 1.51 | ± | 0.08 de | 1.90 | ± | 0.05 d |
| P | 48.3 | ± | 1.0 abc | 43.9 | ± | 0.9 cd | 38.1 | ± | 0.5 e | 1.80 | ± | 0.07 b | 2.11 | ± | 0.08 c | 2.68 | ± | 0.08 bc | ||
| WD | NP | 43.3 | ± | 0.4 d | 41.8 | ± | 0.3 d | 40.1 | ± | 0.2 de | 0.84 | ± | 0.06 e | 1.02 | ± | 0.04 f | 1.37 | ± | 0.15 e | |
| P | 45.9 | ± | 0.9 bcd | 43.0 | ± | 0.5 d | 38.5 | ± | 0.9 e | 1.15 | ± | 0.05 de | 1.32 | ± | 0.02 ef | 1.91 | ± | 0.04 d | ||
| Nipponbare | WW | NP | 48.8 | ± | 1.0 ab | 46.9 | ± | 0.7 ab | 46.7 | ± | 1.3 a | 2.58 | ± | 0.08 a | 2.70 | ± | 0.06 b | 2.93 | ± | 0.00 b |
| P | 49.8 | ± | 0.5 a | 46.1 | ± | 0.2 abc | 43.9 | ± | 0.5 abc | 2.86 | ± | 0.06 a | 3.27 | ± | 0.06 a | 3.66 | ± | 0.07 a | ||
| WD | NP | 44.9 | ± | 0.1 cd | 44.0 | ± | 0.8 bcd | 43.0 | ± | 0.4 bcd | 1.67 | ± | 0.11 bc | 1.78 | ± | 0.11 d | 2.05 | ± | 0.05 d | |
| P | 46.0 | ± | 0.6 bcd | 43.5 | ± | 0.5 cd | 40.9 | ± | 0.7 cde | 1.95 | ± | 0.05 b | 2.19 | ± | 0.05 c | 2.55 | ± | 0.07 c | ||
| Source | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Variety (V) | ns | * | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||||||||||||||
| Priming (P) | ns | * | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||||||||||||||
| Environment (E) | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||||||||||||||
| V × P | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||||||||||||||
| V × E | ns | ns | ns | ** | ** | ** | ||||||||||||||
| P × E | ns | ** | ** | ns | * | * | ||||||||||||||
| V × P × E | ns | ** | * | ns | ns | ns | ||||||||||||||
| Variety | E | ST | Total Soluble Sugar Content (mg·g−1 DW) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | |||||||||
| Kasalath | WW | NP | 43.40 | ± | 4.01 ab | 44.64 | ± | 6.53 bc | 66.43 | ± | 5.73 bc |
| P | 55.72 | ± | 7.17 a | 78.92 | ± | 11.94 a | 119.50 | ± | 13.05 a | ||
| WD | NP | 16.37 | ± | 5.49 d | 17.92 | ± | 2.95 d | 27.54 | ± | 2.30 e | |
| P | 28.04 | ± | 0.32 cd | 39.29 | ± | 2.38 c | 62.56 | ± | 0.84 bc | ||
| Nipponbare | WW | NP | 32.64 | ± | 1.16 bc | 35.64 | ± | 4.54 c | 48.88 | ± | 7.96 cd |
| P | 41.67 | ± | 8.11 b | 59.53 | ± | 1.52 b | 71.57 | ± | 5.86 b | ||
| WD | NP | 16.69 | ± | 0.92 d | 19.40 | ± | 1.48 d | 23.07 | ± | 2.18 e | |
| P | 26.37 | ± | 1.63 cd | 31.83 | ± | 1.35 cd | 37.81 | ± | 1.45 de | ||
| Source | |||||||||||
| Variety (V) | ** | ** | *** | ||||||||
| Priming (P) | *** | *** | *** | ||||||||
| Environment (E) | *** | *** | *** | ||||||||
| V × P | ns | * | *** | ||||||||
| V × E | ** | * | ** | ||||||||
| P × E | ns | * | * | ||||||||
| V × P × E | ns | ns | ns | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, J.-Y.; Ju, Y.-H.; Nakamichi, A.; Cho, S.-W.; Woo, S.-H.; Sakagami, J.-I. Effect of Seed Hydropriming on the Elongation of Plumule and Radicle During the Germination Process and Changes in Enzyme Activity Under Water-Deficient Conditions. Plants 2024, 13, 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13243537
Choi J-Y, Ju Y-H, Nakamichi A, Cho S-W, Woo S-H, Sakagami J-I. Effect of Seed Hydropriming on the Elongation of Plumule and Radicle During the Germination Process and Changes in Enzyme Activity Under Water-Deficient Conditions. Plants. 2024; 13(24):3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13243537
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Ju-Young, Young-Hwan Ju, Ayaka Nakamichi, Seong-Woo Cho, Sun-Hee Woo, and Jun-Ichi Sakagami. 2024. "Effect of Seed Hydropriming on the Elongation of Plumule and Radicle During the Germination Process and Changes in Enzyme Activity Under Water-Deficient Conditions" Plants 13, no. 24: 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13243537
APA StyleChoi, J.-Y., Ju, Y.-H., Nakamichi, A., Cho, S.-W., Woo, S.-H., & Sakagami, J.-I. (2024). Effect of Seed Hydropriming on the Elongation of Plumule and Radicle During the Germination Process and Changes in Enzyme Activity Under Water-Deficient Conditions. Plants, 13(24), 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13243537







