The Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Cell-Protective Properties of Bioactive Compounds Extracted from Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) Fruits In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Quantitative Determination of Total Polyphenols, Flavonoids and Carotenoids of Sorbus aucuparia L. Fruit Extracts
2.2. HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS Characterization of Phenolic Compounds of Sorbus aucuparia L. Fruit Extract
2.3. The Antioxidant Activity of Sorbus aucuparia L. Fruit Extract
2.4. The Antibacterial Capacity of Sorbus aucuparia L. Fruit Extract
2.4.1. Antibacterial Activity by Agar-Well Diffusion Method
2.4.2. Antibacterial Activity by Broth Microdilution Method
2.5. The Effect of Sorbus aucuparia L. Fruit Extract on Gentamicin-Stressed Primary Mice Renal Cells In Vitro
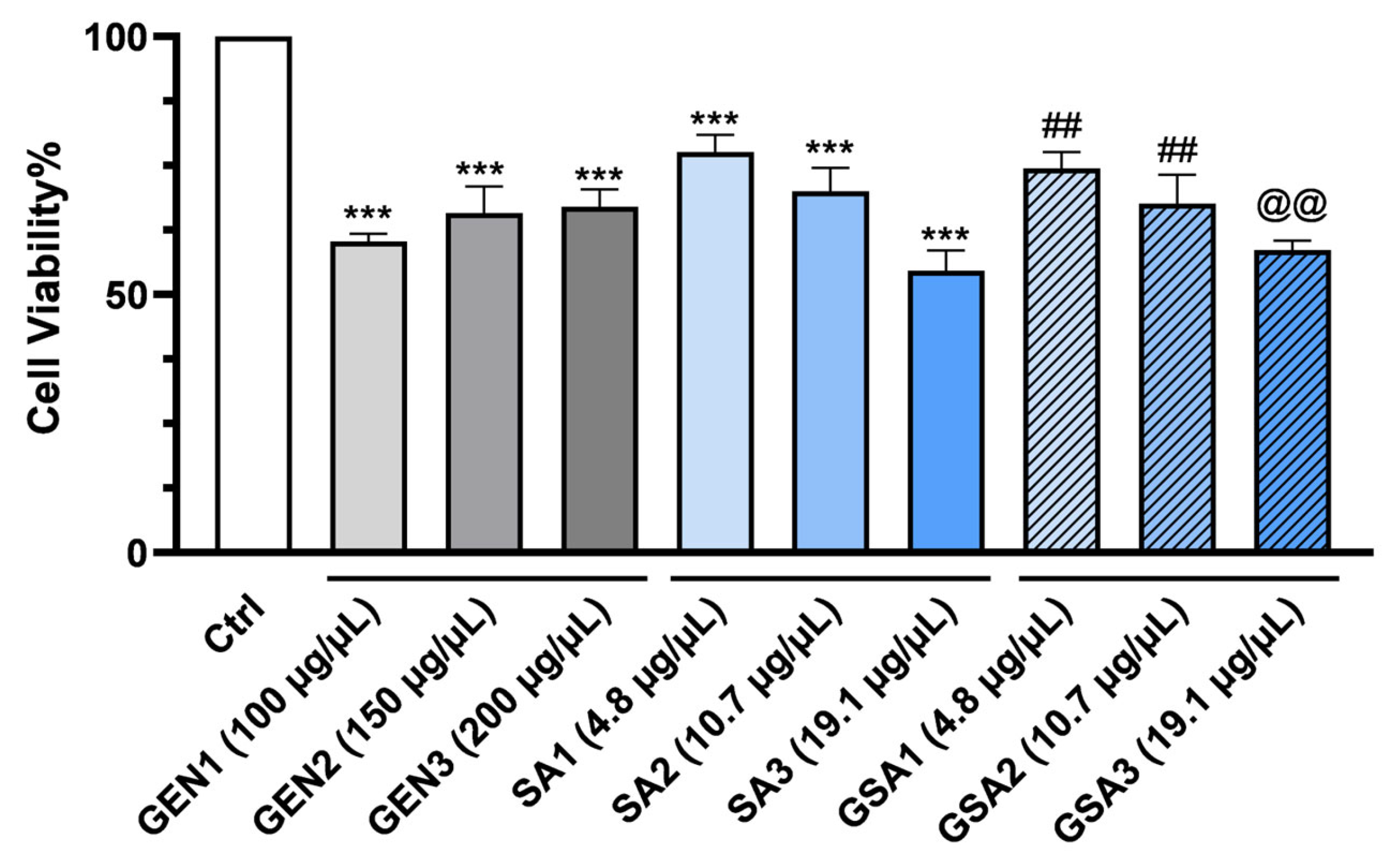
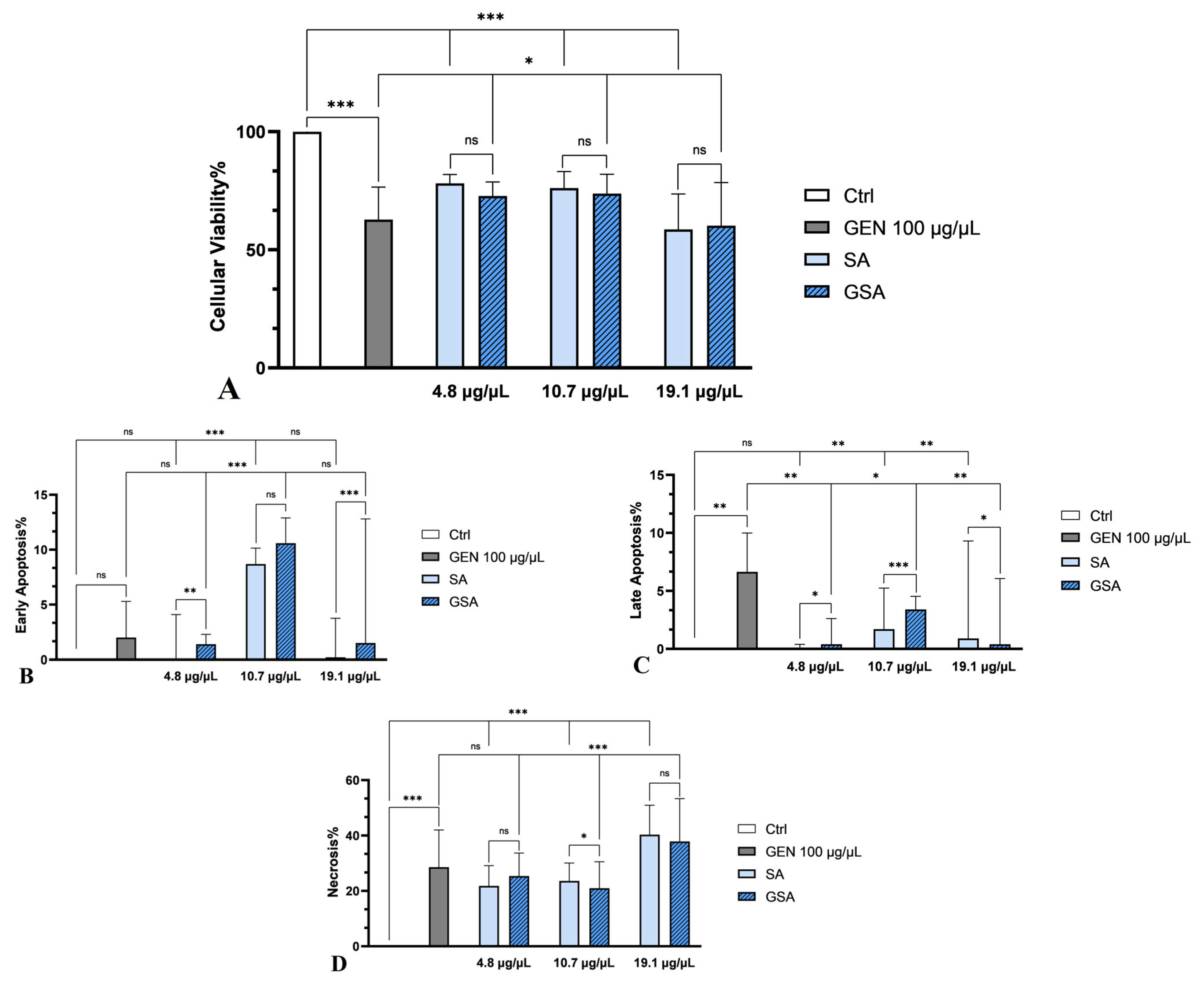
2.5.1. Cell Viability Analysis by MTT Assay
- Control (Ctrl) group, which included non-treated cells;
- Gentamicin (GEN) group, which was given antibiotic therapy in 3 separate doses, namely GEN1 = 100 μg/μL, GEN2 = 150 μg/μL and GEN3 = 200 μg/μL;
- Sorbus aucuparia (SA) group, which received herbal therapy in 3 different concentrations, particularly SA1 = 4.8 μg/μL, SA2 = 10.7 μg/μL and SA3 = 19.1 μg/μL;
- Gentamicin + Sorbus aucuparia (GSA) group, which received treatment with a mixture of both, namely GSA1 = 100 μg/μL gentamicin + 4.8 μg/μL Sorbus aucuparia L. extract, GSA2 = 100 μg/μL gentamicin + 10.7 μg/μL Sorbus aucuparia L. extract and GSA3 = 100 μg/μL gentamicin + 19.1 μg/μL Sorbus aucuparia L. extract.
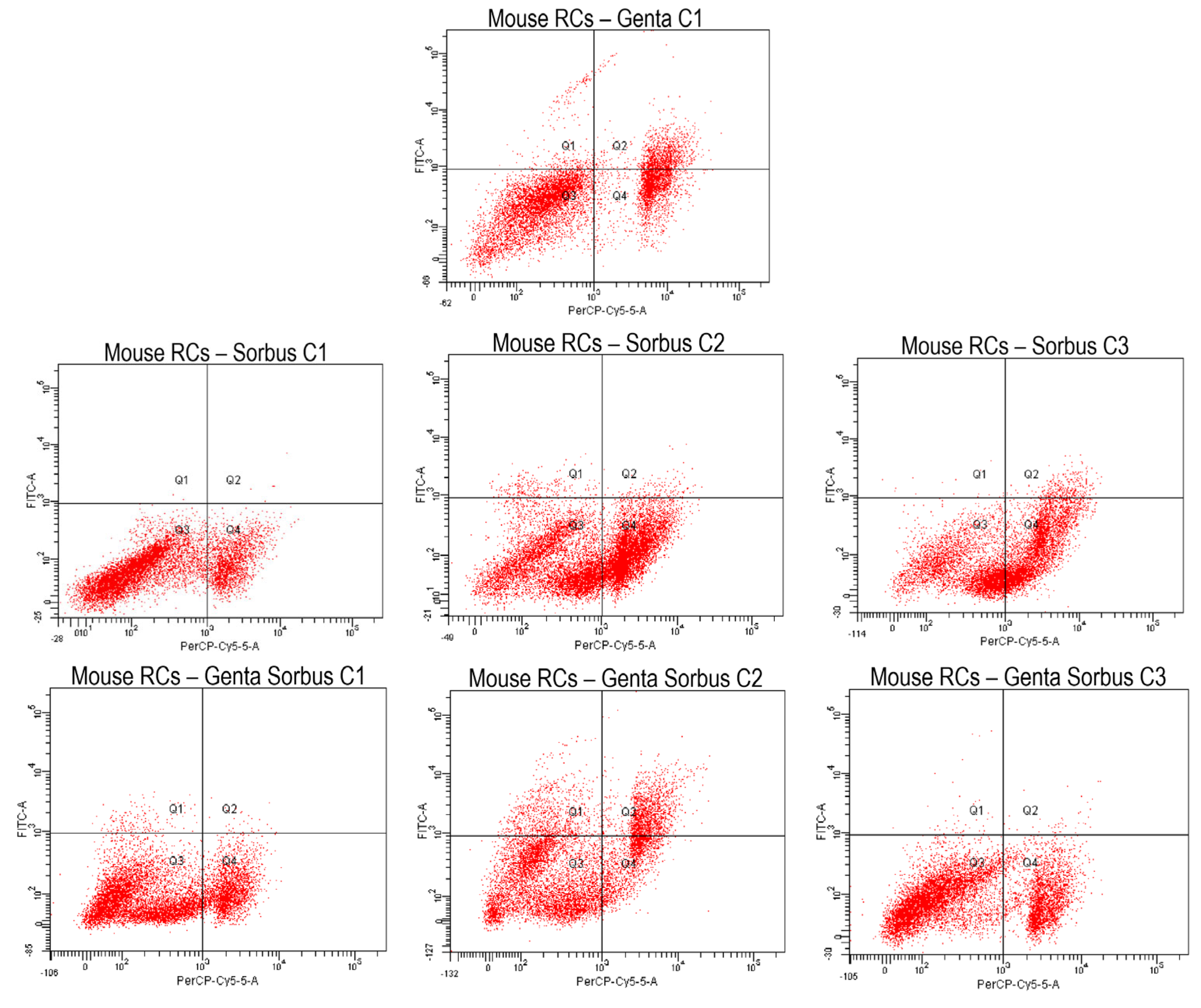
2.5.2. Cell Apoptosis Measurement by Annexin V-FITC Staining
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Agents, Bacterial Strains and Cell Culture
4.2. Fruit Collection and Extraction
4.3. Determination of Total Polyphenols, Flavonoids and Carotenoids
4.4. Identification of Phenolic Compounds by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS Analysis
4.5. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity
4.6. In Vitro Antibacterial Capacity
4.7. Experimental Procedures, Laboratory Rodents and Primary Renal Epithelial Cell Cultures
4.8. In Vitro Cell Viability Assay
4.9. In Vitro Cell Apoptosis Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paredes-López, O.; Cervantes-Ceja, M.L.; Vigna-Pérez, M.; Hernández-Pérez, T. Berries: Improving Human Health and Healthy Aging, and Promoting Quality Life—A Review. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2010, 65, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golovinskaia, O.; Wang, C.-K. Review of Functional and Pharmacological Activities of Berries. Molecules 2021, 26, 3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarv, V.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Bhat, R. The Sorbus spp.—Underutilised Plants for Foods and Nutraceuticals: Review on Polyphenolic Phytochemicals and Antioxidant Potential. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefzadeh, H.; Raeisi, S.; Esmailzadeh, O.; Jalali, G.; Nasiri, M.; Walas, Ł.; Kozlowski, G. Genetic Diversity and Structure of Rear Edge Populations of Sorbus aucuparia (Rosaceae) in the Hyrcanian Forest. Plants 2021, 10, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvinte, O.M.; Senila, L.; Becze, A.; Amariei, S. Rowanberry—A Source of Bioactive Compounds and Their Biopharmaceutical Properties. Plants 2023, 12, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raspe, O.; Findlay, C.; Jacquemart, A.-L. Sorbus aucuparia L. J. Ecol. 2000, 88, 910–930. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/2648347 (accessed on 20 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Räty, M.; Caudullo, G.; de Rigo, D. Sorbus aucuparia in Europe: Distribution, habitat, usage and threats. In European Atlas of Forest Tree Species; San-Miguel-Ayanz, J., de Rigo, D., Caudullo, G., Houston Durrant, T., Mauri, A., Eds.; European Commission: Luxembourg, 2016; pp. 176–177. [Google Scholar]
- Bobinaitė, R.; Kraujalis, P.; Tamkutė, L.; Urbonavičienė, D.; Viškelis, P.; Venskutonis, P.R. Recovery of bioactive substances from rowanberry pomace by consecutive extraction with supercritical carbon dioxide and pressurized solvents. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 85, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobinaitė, R.; Grootaert, C.; Van Camp, J.; Šarkinas, A.; Liaudanskas, M.; Žvikas, V.; Viškelis, P.; Rimantas Venskutonis, P. Chemical composition, antioxidant, antimicrobial and antiproliferative activities of the extracts isolated from the pomace of rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.). Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarv, V.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Rätsep, R.; Aluvee, A.; Kazernavičiūtė, R.; Bhat, R. Antioxidants Characterization of the Fruit, Juice, and Pomace of Sweet Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) Cultivated in Estonia. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Mijakovic, I. Rowan Berries: A Potential Source for Green Synthesis of Extremely Monodisperse Gold and Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antimicrobial Property. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zymone, K.; Raudone, L.; Žvikas, V.; Jakštas, V.; Janulis, V. Phytoprofiling of Sorbus L. Inflorescences: A Valuable and Promising Resource for Phenolics. Plants 2022, 11, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaikina, N.V.; Kalinkina, G.I.; Razina, T.G.; Zueva, E.P.; Rybalkina, O.Y.; Ulirich, A.V.; Fedorova, E.P.; Shilova, A.B. Sorbus aucuparia L. Fruit Is a Source of the Drug for Increasing the Efficiency of Tumor Chemotherapy. Russ. J. Bioorganic Chem. 2018, 44, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sołtys, A.; Galanty, A.; Podolak, I. Ethnopharmacologically important but underestimated genus Sorbus: A comprehensive review. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 491–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M.; Kolodziejczyk-Czepas, J.; Owczarek, A.; Zakrzewska, A.; Magiera, A.; Olszewska, M.A. Novel insight into biological activity and phytochemical composition of Sorbus aucuparia L. fruits: Fractionated extracts as inhibitors of protein glycation and oxidative/nitrative damage of human plasma components. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsavová, J.; Juríková, T.; Bednaříková, R.; Mlček, J. Total Phenolic and Total Flavonoid Content, Individual Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Sweet Rowanberry Cultivars. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristea, E.; Ghendov-Mosanu, A.; Patras, A.; Socaciu, C.; Pintea, A.; Tudor, C.; Sturza, R. The Influence of Temperature, Storage Conditions, pH, and Ionic Strength on the Antioxidant Activity and Color Parameters of Rowan Berry Extracts. Molecules 2021, 26, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampuss, K.; Kampuse, S.; Berņa, E.; Krūma, Z.; Krasnova, I.; Drudze, I. Biochemical composition and antiradical activity of rowanberry (Sorbus L.) cultivars and hybrids with different Rosaceae L. cultivars. Latv. J. Agron. 2009, 12, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Liepiņa, I.; Nikolajeva, V.; Jākobsone, I. Antimicrobial activity of extracts from fruits of Aronia melanocarpa and Sorbus aucuparia. Environ. Exp. Biol. 2013, 11, 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Boath, A.S.; Stewart, D.; McDougall, G.J. Berry components inhibit α-glucosidase in vitro: Synergies between acarbose and polyphenols from black currant and rowanberry. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grussu, D.; Stewart, D.; McDougall, G.J. Berry Polyphenols Inhibit α-Amylase in Vitro: Identifying Active Components in Rowanberry and Raspberry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2324–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Gao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, J. Polyphenols from Sorbus Aucuparia Ameliorate Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Disorders in Diabetic Mice. Curr. Top. Nutraceutical Res. 2016, 14, 227–233. [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny, K.; Jung, T.; Höhn, A.; Weber, D.; Grune, T. Advanced Glycation End Products and Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 194–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blahova, J.; Martiniakova, M.; Babikova, M.; Kovacova, V.; Mondockova, V.; Omelka, R. Pharmaceutical Drugs and Natural Therapeutic Products for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranasinghe, R.; Mathai, M.; Zulli, A. Cytoprotective remedies for ameliorating nephrotoxicity induced by renal oxidative stress. Life Sci. 2023, 318, 121466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrek, L. A Synopsis of Current Theories on Drug-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Life 2023, 13, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donate-Correa, J.; Martín-Carro, B.; Cannata-Andía, J.B.; Mora-Fernández, C.; Navarro-González, J.F. Klotho, Oxidative Stress, and Mitochondrial Damage in Kidney Disease. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarv, V. Valorisation of Fruits of Rowan (Sorbus spp.) Genotypes for Functional Food Ingredients. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Estonian University of Life Sciences, Tartu, Estonia, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasko, P. South Siberian fruits: Their selected chemical constituents, biological activity, and traditional use in folk medicine and daily nutrition. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 4698–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhuyuk, M.R.; Ercisli, S.; Ayed, R.B.; Jurikova, T.; Fidan, H.; Ilhan, G.; Ozkan, G.; Sagbas, H.I. Compositional diversity in fruits of rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) genotypes originating from seeds. Genetika 2020, 52, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykholat, Y.L.; Didur, O.O.; Khromykh, N.O.; Davydov, V.R.; Borodai, Y.S.; Kravchuk, K.V.; Lykholat, T.Y. Comparative analysis of the antioxidant capacity and secondary metabolites accumulation in the fruits of rowan (Sorbus aucuparia L.) and some closely related species. Ecol. Noospherol. 2021, 32, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewska, M.A.; Michel, P. Antioxidant activity of inflorescences, leaves and fruits of three Sorbus species in relation to their polyphenolic composition. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 1507–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewska, M.A.; Presler, A.; Michel, P. Profiling of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Dry Extracts from the Selected Sorbus Species. Molecules 2012, 17, 3093–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M.; Owczarek-Januszkiewicz, A.; Magiera, A.; Gieleta, M.; Olszewska, M.A. Chemometrics-Driven Variability Evaluation of Phenolic Composition, Antioxidant Capacity, and α-Glucosidase Inhibition of Sorbus aucuparia L. Fruits from Poland: Identification of Variability Markers for Plant Material Valorization. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šavikin, K.P.; Zdunić, G.M.; Krstić-Milošević, D.B.; Šircelj, H.J.; Stešević, D.D.; Pljevljakušić, D.S. Sorbus aucuparia and Sorbus aria as a Source of Antioxidant Phenolics, Tocopherols, and Pigments. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1700329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrkonjić, Z.; Nadpal, J.D.; Beara, I.; Aleksić-Sabo, V.S.; Cetojević-Simin, D.D.; Mimica-Dukić, N.; Lesjak, M. Phenolic profiling and bioactivities of fresh fruits and jam of Sorbus species. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2017, 82, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laczkó-Zöld, E.; Szabó, D.; Fogarasi, E.; Tömösközi-Farkas, R.; Ştefănescu, R.; Varga, E.; Eşianu, S. Contribution to the phytochemical evaluation of rowanberry fruits (Sorbus aucuparia L.). Acta Medica Marisiensis 2018, 64, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Mattila, P.; Hellström, J.; Törrönen, R. Phenolic Acids in Berries, Fruits, and Beverages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 7193–7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raudonis, R.; Raudonė, L.; Gaivelytė, K.; Viškelis, P.; Janulis, V. Phenolic and antioxidant profiles of rowan (Sorbus L.) fruits. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulic-Petkovsek, M.; Krska, B.; Kiprovski, B.; Veberic, R. Bioactive Components and Antioxidant Capacity of Fruits from Nine Sorbus Genotypes. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladedunye, F.; Matthäus, B. Phenolic extracts from Sorbus aucuparia (L.) and Malus baccata (L.) berries: Antioxidant activity and performance in rapeseed oil during frying and storage. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhuyuk, M.R. Morphological and Biochemical Diversity in Fruits of Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) Genotypes. Erwerbs-Obstbau 2021, 63, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turumtay, H.; Midilli, A.; Turumtay, E.A.; Demir, A.; Selvi, E.K.; Budak, E.E.; Er, H.; Kocaimamoglu, F.; Baykal, H.; Belduz, A.O.; et al. Gram (−) microorganisms DNA polymerase inhibition, antibacterial and chemical properties of fruit and leaf extracts of Sorbus acuparia and Sorbus caucasica var. yaltirikii. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31, e3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krisch, J.; Galgóczy, L.; Tölgyesì, M.; Papp, T.; Vágvölgyi, C. Effect of Fruit Juices and Pomace Extracts on the Growth of Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. Acta Biol. Szeged. 2008, 52, 267–270. [Google Scholar]
- Erbil, N. Potential Antibacterial Effect and L-Ascorbic Acid and Phenolic Content Profiles of Wild Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.). Erwerbs-Obstbau. 2022, 64, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, M.U.; Mustafa, S.; Hamza, A.; Almutairi, B.O.; Almutairi, M.H.; Riaz, M.N. Evaluation of possible protective role of glabridin against gentamicin-instigated nephrotoxicity via attenuation of oxidative stress. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2023, 35, 102692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randjelovic, P.; Veljkovic, S.; Stojiljkovic, N.; Sokolovic, D.; Ilic, I. Gentamicin nephrotoxicity in animals: Current knowledge andfuture perspectives. Excli J. 2017, 16, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bencheikh, N.; Bouhrim, M.; Kharchoufa, L.; Al Kamaly, O.M.; Mechchate, H.; Es-safi, I.; Dahmani, A.; Ouahhoud, S.; El Assri, S.; Eto, B.; et al. The Nephroprotective Effect of Zizyphus lotus L. (Desf.) Fruits in a Gentamicin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model in Rats: A Biochemical and Histopathological Investigation. Molecules 2021, 26, 4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiros, Y.; Vicente-Vicente, L.; Morales, A.I.; López-Novoa, J.M.; López-Hernández, F.J. An Integrative Overview on the Mechanisms Underlying the Renal Tubular Cytotoxicity of Gentamicin. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 119, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Fan, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, F. Protective effect of Cistanche deserticola on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Chin. Herb. Med. 2023, 15, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanth, D.; Reddy, L.S.S.; Dasari, T.; Bhavanam, P.R.; Ahmad, S.F.; Nalluri, R.; Pasala, P.K. LC/MS-Based Profiling of Hedyotis aspera Whole-Plant Methanolic Extract and Evaluation of Its Nephroprotective Potential against Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats Supported by In Silico Studies. Separations 2023, 10, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althobaiti, S.A.; Almalki, D.A.; Qahl, S.H.; Elsigar, L.; Gurafi, L.M.A.; Kanani, Z.; Nasir, O. Effect of Artemisia annua on kidney in gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice through regulation of the COX-2, NF-κB pathway. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2023, 35, 102813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.J.; Lowe, G.L. Carotenoids—Antioxidant Properties. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guru, A.; Sudhakaran, G.; Velayutham, M.; Murugan, R.; Pachaiappan, R.; Mothana, R.A.; Noman, O.M.; Juliet, A.; Arockiaraj, J. Daidzein normalized gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity and associated pro-inflammatory cytokines in MDCK and zebrafish: Possible mechanism of nephroprotection. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 258, 109364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasti, D.; Bhikshapathi, D.V.R. Nephroprotective Effect Of Ethanolic Extract Of Cissus Quadrangularis Linn Fruits In Gentamicin Induced Nephrotoxicity: In Vitro Cell Viability And In Vivo Models. Nveo-Nat. Volatiles Essent. Oils J. Nveo 2021, 8, 16704–16716. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, L.; Yang, Y.-R.; Ma, W.-X.; Wang, H.-Y.; Fan, Q.-W.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.-M.; Wang, X.-F.; et al. Epigallocatechin Gallate Attenuates Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity by Suppressing Apoptosis and Ferroptosis. Molecules 2022, 27, 8564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Jin, W.W.; Huang, M.; Ji, H.; Capen, D.E.; Xia, Y.; Yuan, J.; Păunescu, T.G.; Lu, H.A.J. Gentamicin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in an Animal Model Involves Programmed Necrosis of the Collecting Duct. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 2097–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morana, O.; Wood, W.; Gregory, C.D. The Apoptosis Paradox in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messner, B.; Frotschnig, S.; Steinacher-Nigisch, A.; Winter, B.; Eichmair, E.; Gebetsberger, J.; Schwaiger, S.; Ploner, C.; Laufer, G.; Bernhard, D. Apoptosis and necrosis: Two different outcomes of cigarette smoke condensate-induced endothelial cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havasi, A.; Borkan, S.C. Apoptosis and acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Yousif, A.; Chesnokov, M.; Hong, L.; Chefetz, I. A decade of cell death studies: Breathing new life into necroptosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 220, 107717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepand, M.R.; Soodi, M.; Keshavarz, H. Protective role of ellagic acid as an antioxidant on gentamicin-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis and nephrotoxicity in rats. Nutr. Food Sci. Res. 2014, 1, 237. [Google Scholar]
- Aurori, M.; Niculae, M.; Hanganu, D.; Pall, E.; Cenariu, M.; Vodnar, D.C.; Bunea, A.; Fiţ, N.; Andrei, S. Phytochemical Profile, Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Cytoprotective Effects of Cornelian Cherry (Cornus mas L.) Fruit Extracts. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitraş, D.-A.; Bunea, A.; Vodnar, D.C.; Hanganu, D.; Pall, E.; Cenariu, M.; Gal, A.F.; Andrei, S. Phytochemical Characterization of Taxus baccata L. Aril with Emphasis on Evaluation of the Antiproliferative and Pro-Apoptotic Activity of Rhodoxanthin. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculae, M.; Hanganu, D.; Oniga, I.; Benedec, D.; Ielciu, I.; Giupana, R.; Sandru, C.D.; Ciocârlan, N.; Spinu, M. Phytochemical Profile and Antimicrobial Potential of Extracts Obtained from Thymus marschallianus Willd. Molecules 2019, 24, 3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing EUCAST Disk Diffusion Method; EUCAST: Seongnam-si, Republic of Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Niculae, M.; Spînu, M.; Şandru, C.D.; Brudaşcă, F.; Cadar, D.; Szakacs, B.; Scurtu, I.; Bolfă, P.; Mateş, C. Antimicrobial potential of some Lamiaceae essential oils against animal multiresistant bacteria. Lucr. Stiint. Med. Vet. 2009, 42, 170–175. [Google Scholar]
- Benedec, D.; Oniga, I.; Hanganu, D.; Tiperciuc, B.; Nistor, A.; Vlase, A.-M.; Vlase, L.; Pușcaș, C.; Duma, M.; Login, C.C.; et al. Stachys Species: Comparative Evaluation of Phenolic Profile and Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Potential. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10993-6; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 2: Animal Welfare Requirements. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
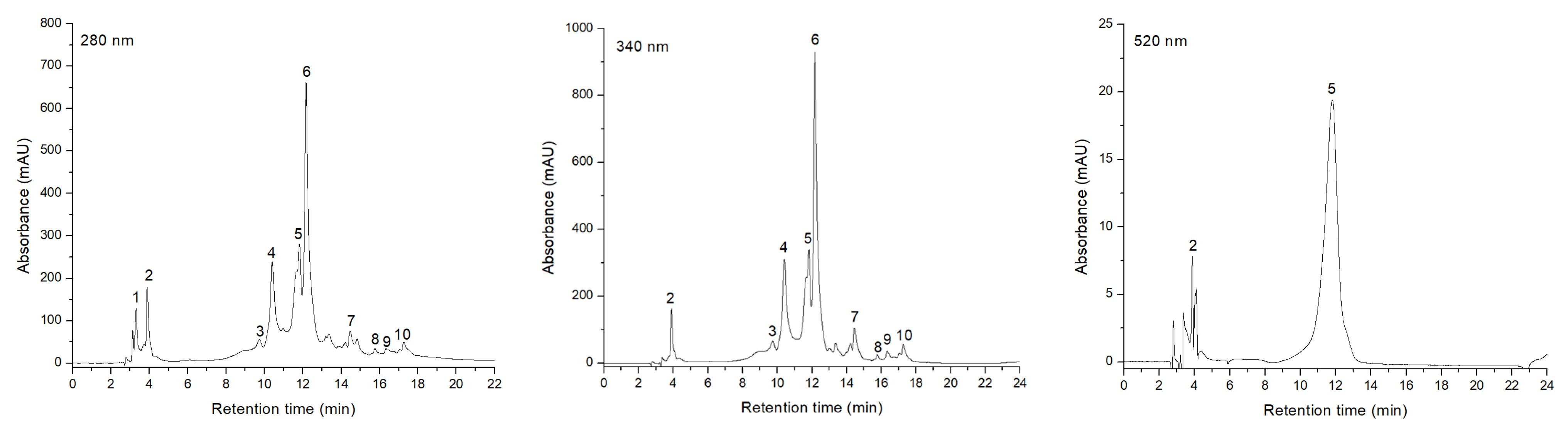

| Peak No. | Retention Time Rt (min) | UV λmax (nm) | [M+H]+ (m/z) | Compound | Subclass | Concentration (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.31 | 270 | 333, 171 | Gallic acid-glucoside | Hydroxybenzoic acid | 61.799 |
| 2 | 3.89 | 520, 322, 280 | 611, 449 | Cy 3-O-(caffeoyl-glucoside) | Anthocyanin | 3.212 |
| 3 | 9.74 | 330 | 355, 163 | 4-Caffeoylquinic acid (Cryptochlorogenic acid) | Hydroxycinnamic acid | 91.199 |
| 4 | 10.39 | 330 | 355, 163 | 3-Caffeoylquinic acid (Neochlorogenic acid) | Hydroxycinnamic acid | 376.610 |
| 5 | 11.82 | 520, 280 | 449, 287 | Cy 3-O-glucoside | Anthocyanin | 19.237 |
| 6 | 12.16 | 330 | 355, 163 | 5-Caffeoylquinic acid (Chlorogenic acid) | Hydroxycinnamic acid | 704.792 |
| 7 | 14.45 | 360, 255 | 627, 303 | Q 3,4′-O -diglucoside | Flavonol | 70.310 |
| 8 | 15.76 | 360, 255 | 611, 303 | Q 3-O-rutinoside (Rutin) | Flavonol | 12.198 |
| 9 | 16.32 | 361, 251 | 465, 303 | Q 3-O-glucoside | Flavonol | 24.139 |
| 10 | 17.26 | 322 | 195 | Ferulic acid | Hydroxycinnamic acid | 45.018 |
| Tested Products | Diameters of Inhibition Zone (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSSA | MRSA | Bacillus cereus | Enterococcus faecalis | Escherichia coli | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | |
| Sorbus aucuparia L. | 27.33 ± 0.47 a,d | 24.00 ± 0.00 a,c | 18 ± 0.00 a,d | 25.67 ± 0.94 a,c | 25.67 ± 0.47 a,c | 17.67 ± 0.47 b,c |
| Gentamicin | 20 ± 0.00 | 17 ± 0.00 | 26 ± 0.00 | 0 | 19 ± 0.00 | 19 ± 0.00 |
| Amoxicillin- clavulanic acid | 29 ± 0.00 | 28 ± 0.00 | 20 ± 0.00 | 17 ± 0.00 | 19 ± 0.00 | 0 |
| Tested Products | MIC Index MBC/MIC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSSA | MRSA | Bacillus cereus | Enterococcus faecalis | Escherichia coli | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | |
| Sorbus aucuparia L. | 1 D7/D7 | 1 D7/D7 | 1 D6/D6 | 1 D7/D7 | 1 D5/D5 | 1 D4/D4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aurori, M.; Niculae, M.; Hanganu, D.; Pall, E.; Cenariu, M.; Vodnar, D.C.; Fiţ, N.; Andrei, S. The Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Cell-Protective Properties of Bioactive Compounds Extracted from Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) Fruits In Vitro. Plants 2024, 13, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13040538
Aurori M, Niculae M, Hanganu D, Pall E, Cenariu M, Vodnar DC, Fiţ N, Andrei S. The Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Cell-Protective Properties of Bioactive Compounds Extracted from Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) Fruits In Vitro. Plants. 2024; 13(4):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13040538
Chicago/Turabian StyleAurori, Mara, Mihaela Niculae, Daniela Hanganu, Emoke Pall, Mihai Cenariu, Dan Cristian Vodnar, Nicodim Fiţ, and Sanda Andrei. 2024. "The Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Cell-Protective Properties of Bioactive Compounds Extracted from Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) Fruits In Vitro" Plants 13, no. 4: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13040538
APA StyleAurori, M., Niculae, M., Hanganu, D., Pall, E., Cenariu, M., Vodnar, D. C., Fiţ, N., & Andrei, S. (2024). The Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Cell-Protective Properties of Bioactive Compounds Extracted from Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) Fruits In Vitro. Plants, 13(4), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13040538













