Establishment of an Efficient Sugarcane Transformation System via Herbicide-Resistant CP4-EPSPS Gene Selection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
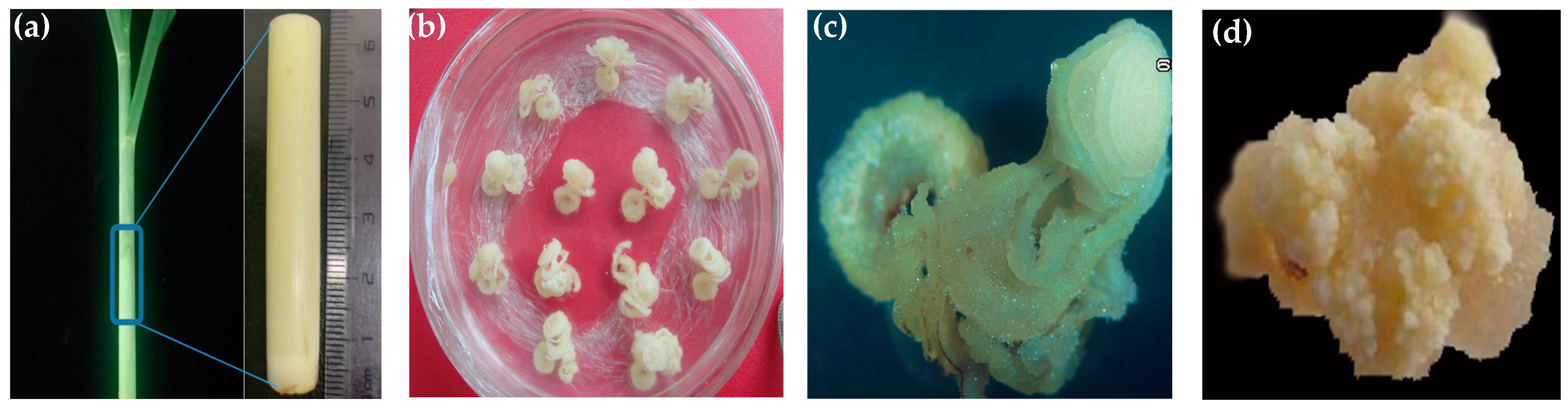
2.1. Establishment of Embryogenic Callus
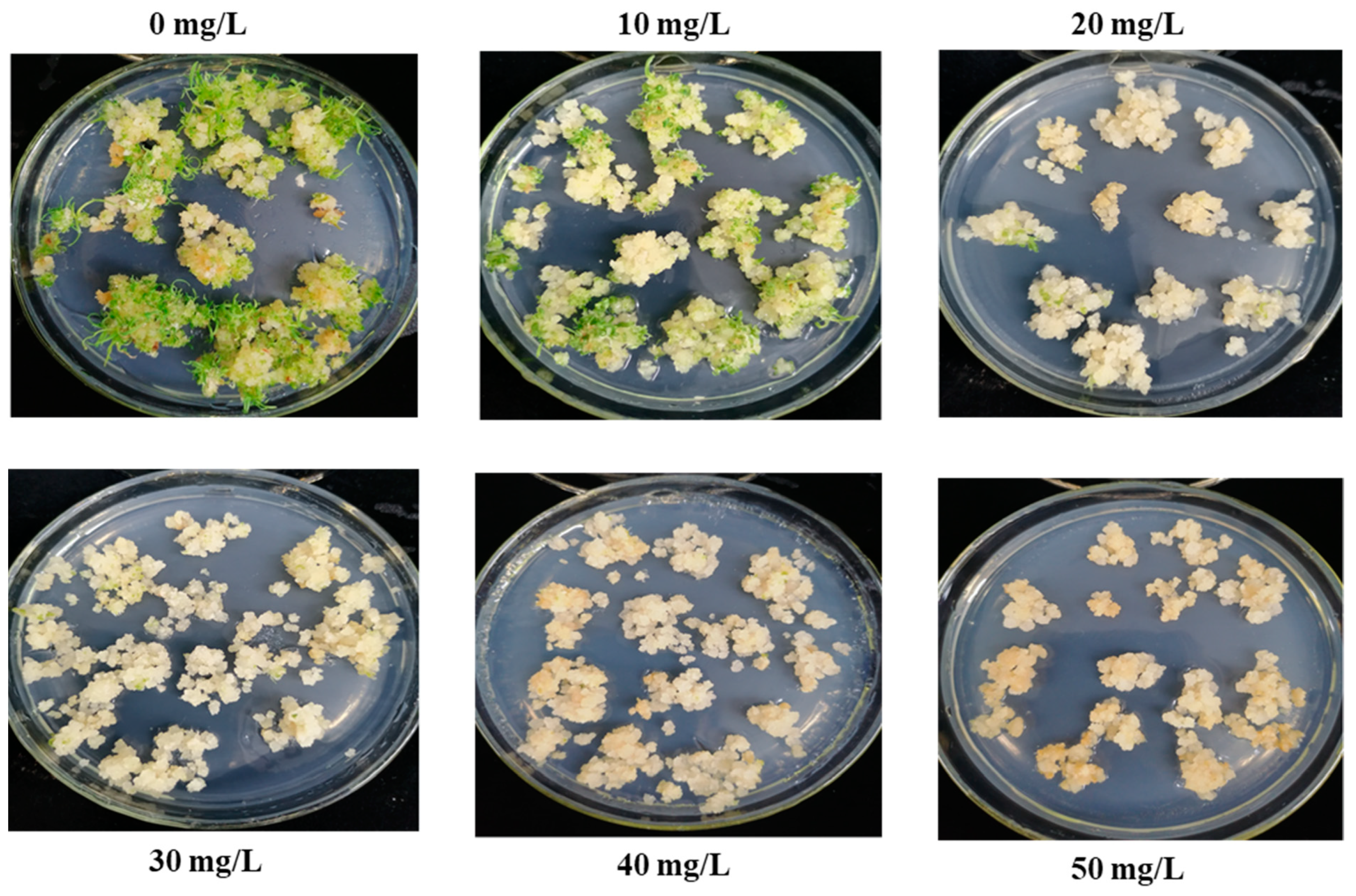
2.2. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Roundup
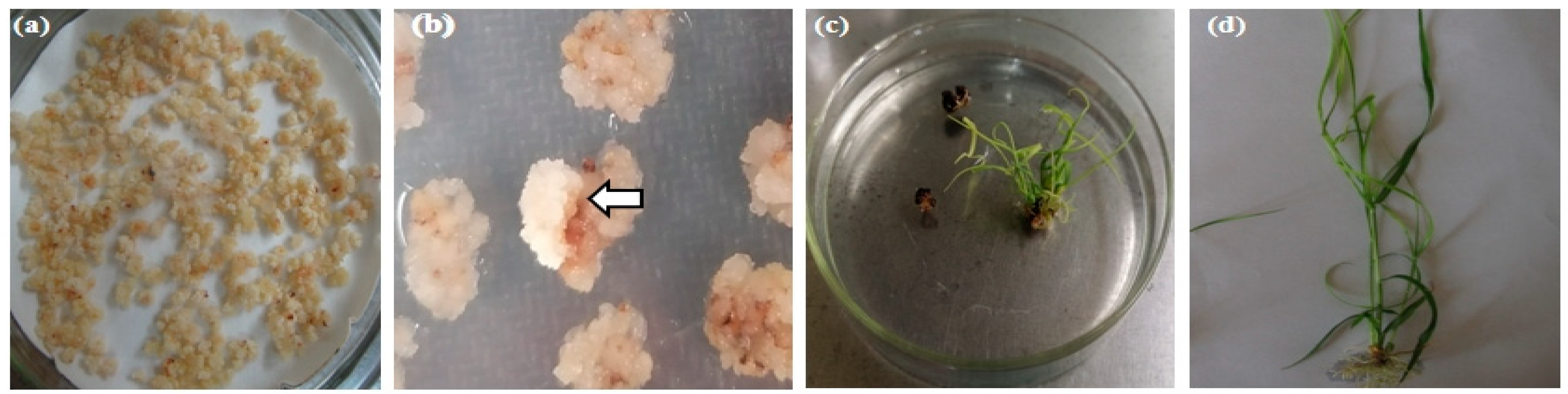
2.3. Selection of Resistant Shoots
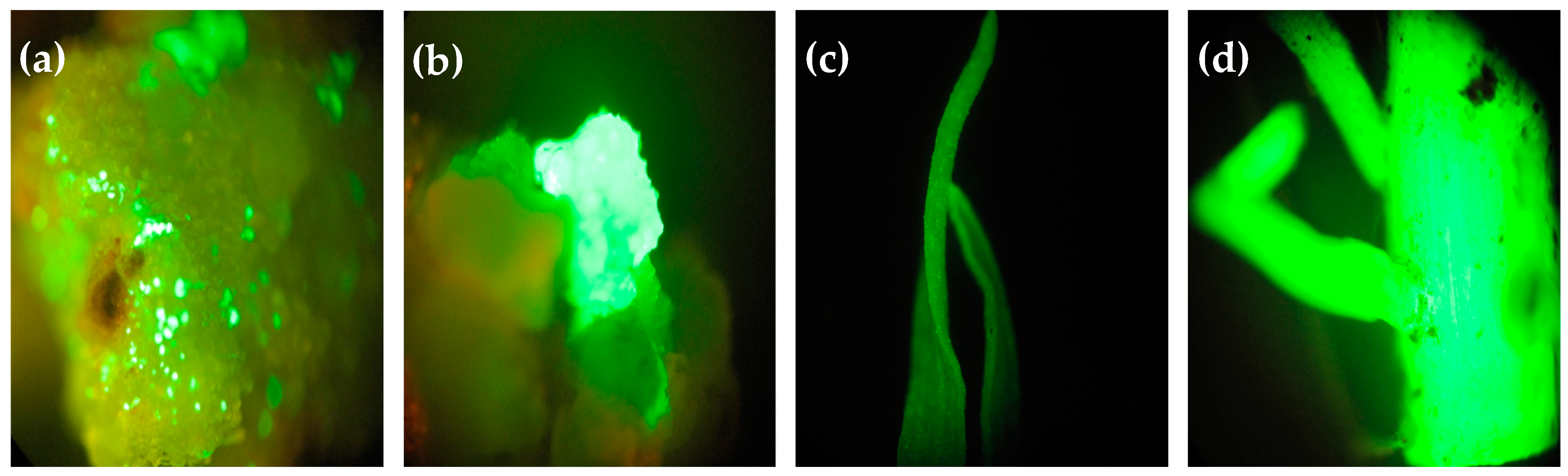
2.4. Green Fluorescent Protein Expression
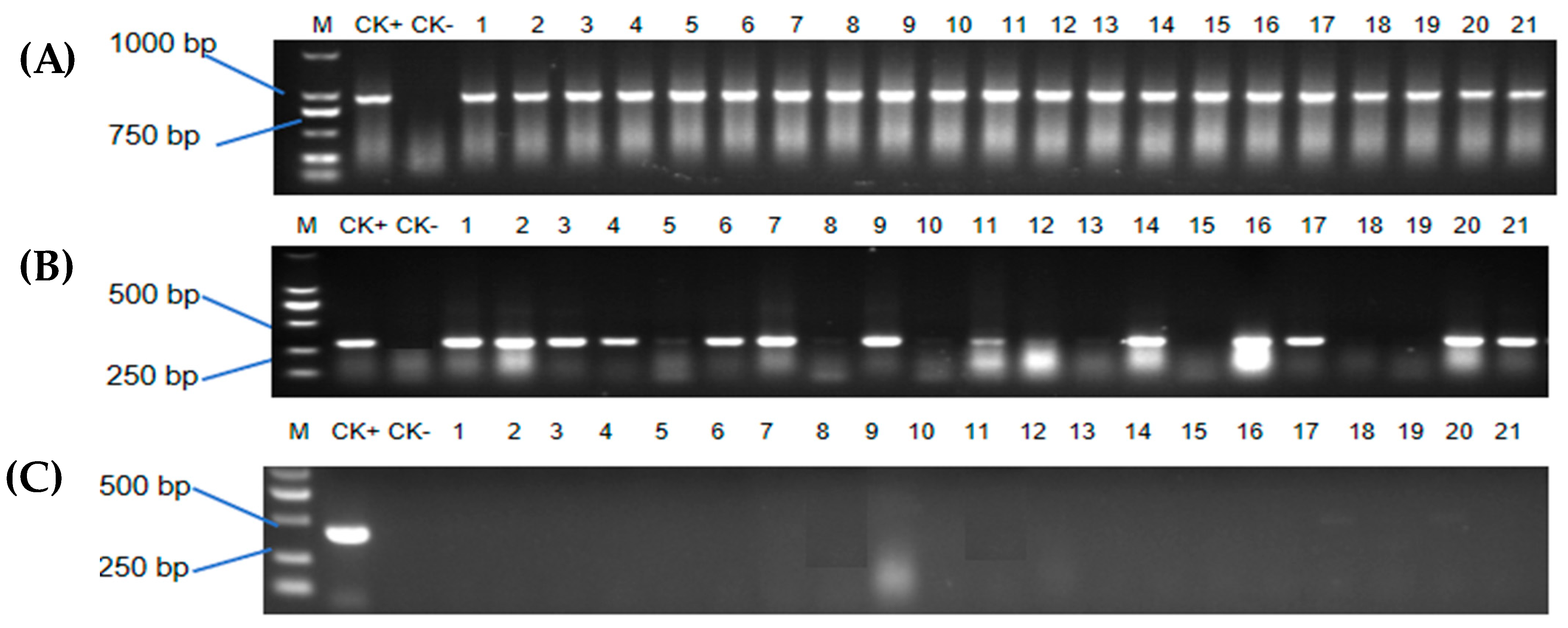
2.5. PCR Assay of Potential Transformed Shoots
2.6. Transformation Efficiency
2.7. Detection of CP4-EPSPS Gene Expression by Quick Stix Strips
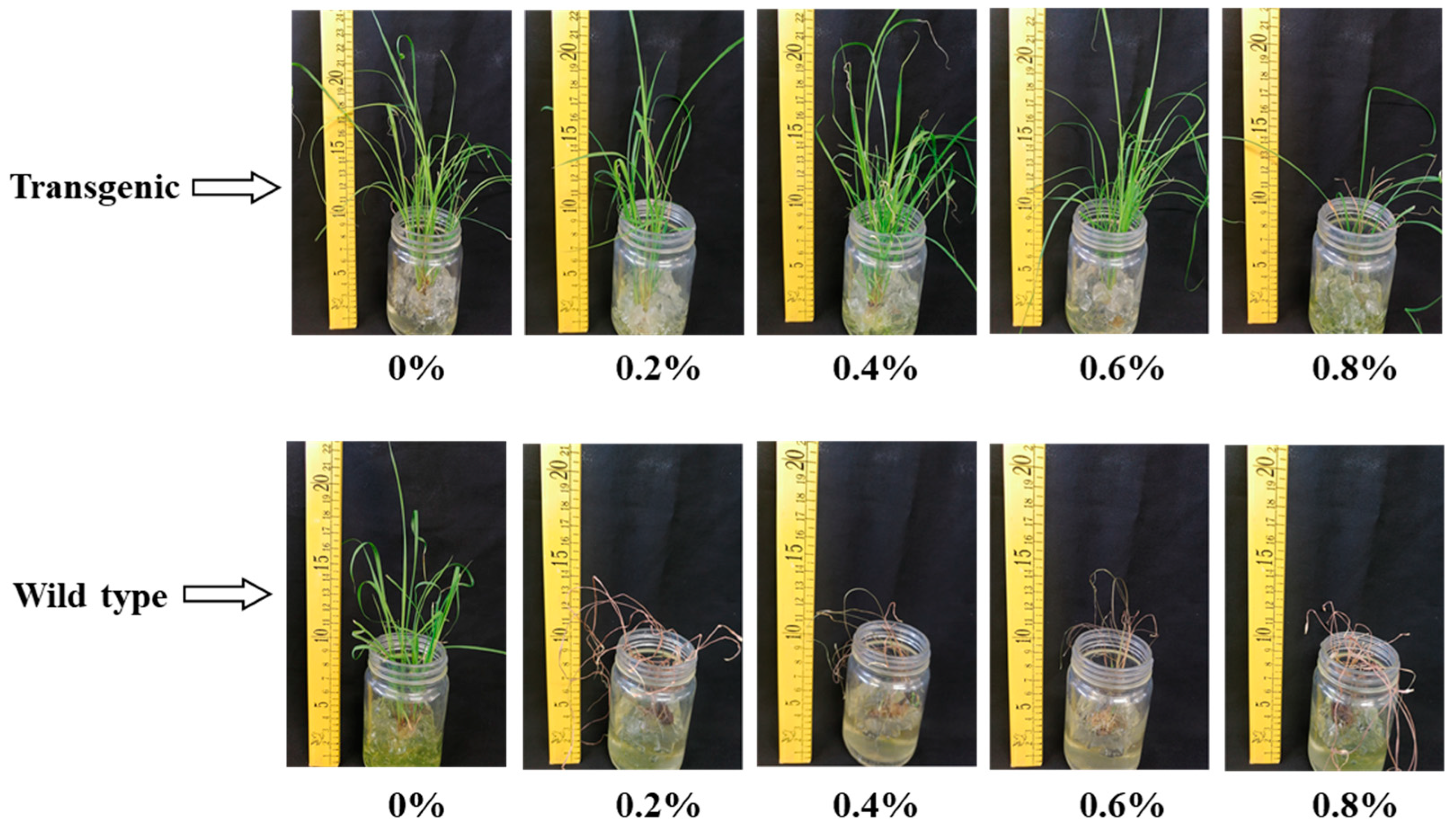
2.8. Herbicide Sensitivity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Media Compositions
4.2. Plant Material and Callus Induction
4.3. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Roundup
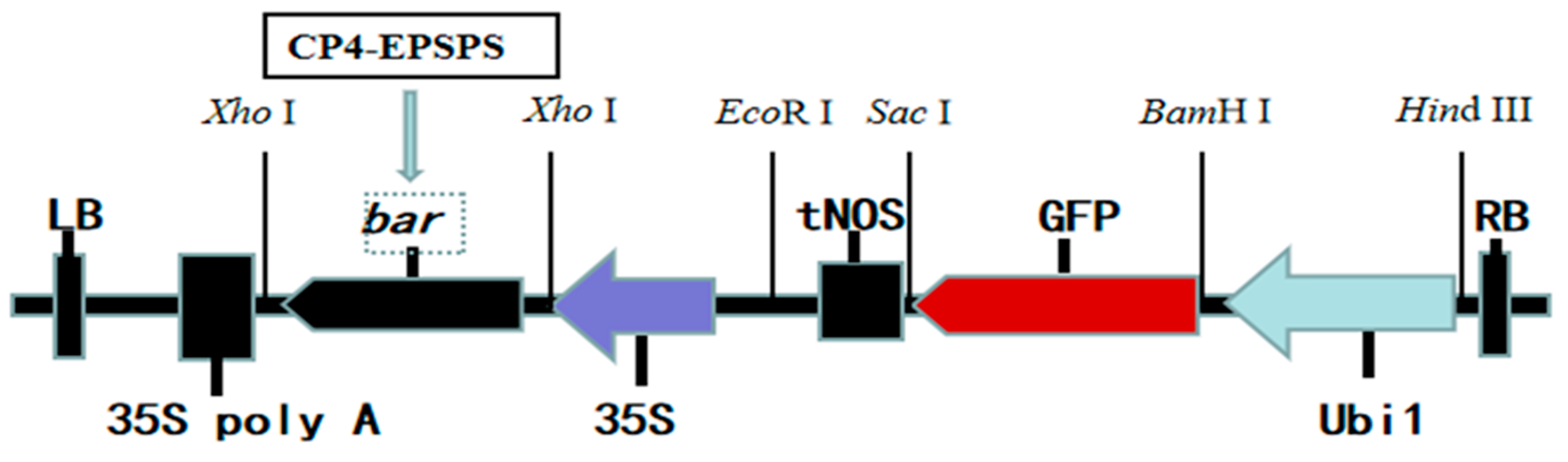
4.4. Binary Vector and Agrobacterium Strain
4.5. Agrobacterium Initiation
4.6. Infection and Co-Cultivation
4.7. Resistant Plant Screening
4.8. Visualization of Green Fluorescent Protein Expression
4.9. Total Genomic DNA Extraction and PCR Assay
4.10. Quick Stix Strips Assay
4.11. Herbicide Sensitivity Assay
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Javed, T.; Shabbir, R.; Ali, A.; Afzal, I.; Zaheer, U.; Gao, S.-J. Transcription Factors in Plant Stress Responses: Challenges and Potential for Sugarcane Improvement. Plants 2020, 9, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aono, H.; Pimenta, G.; Garcia, B.; Correr, H.; Hosaka, K.; Carrasco, M.; Cardoso-Silva, B.; Mancini, C.; Sforça, A.; Santos, B.; et al. The wild sugarcane and sorghum kinomes: Insights into expansion, diversification, and expression patterns. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 668623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Razzaq, A.; Mehmood, S.S.; Zou, X.; Zhang, X.; Lv, Y.; Xu, J. Impact of climate change on crops adaptation and strategies to tackle its outcome: A review. Plants 2019, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. John Warne, M.; Neale, P.A.; Macpherson, M.J. A pesticide decision support tool to guide the selection of less environmentally harmful pesticides for the sugar cane industry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 108036–108050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakdaman, S.B.; Mohammadi, G.E. Weeds, herbicides and plant disease management. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 31: Biocontrol; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 41–178. [Google Scholar]
- Schütte, G.; Eckerstorfer, M.; Rastelli, V.; Reichenbecher, W.; Restrepo-Vassalli, S.; Ruohonen-Lehto, M.; Saucy, A.G.W.; Mertens, M. Herbicide resistance and biodiversity: Agronomic and environmental aspects of genetically modified herbicide-resistant plants. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2017, 29, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Khaliq, A.; Mehmood, U.; Tauqeer, Q.; Muhammad, S.; Muhammad, A.I.; Saddam, H. Sugarcane production under changing climate: Effects of environmental vulnerabilities on sugarcane diseases, insects and weeds. In Climate Change and Agriculture; Intech Open: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018; pp. 137–151. [Google Scholar]
- Sanghera, G.S.; Malhotra, P.K.; Singh, H.; Bhatt, R. Climate change impact in sugarcane agriculture and mitigation strategies. In Harnessing Plant Biotechnology and Physiology to Stimulate Agricultural Growth; Agrobios: Jodhpur, India, 2019; pp. 99–115. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, T.; Liu, X.; Lakshmanan, P. A combined genomics and phenomics approach is needed to boost breeding in sugarcane. Plant Phenomics 2023, 5, 0074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Fang, J.; Zhang, J. Advances in sugarcane genomics and genetics. Sugar Tech 2022, 24, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M. Plant breeding advancements with “CRISPR-Cas” genome editing technologies will assist future food security. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1133036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolera, B.; Gedebo, A.; Tena, E. Variability, heritability and genetic advance in sugarcane (Saccharum spp. hybrid) genotypes. Cogent Food Agric. 2023, 9, 2194482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Z.; Yang, B.P.; Feng, C.L.; Wang, J.G.; Xiong, G.R.; Zhao, T.T.; Zhang, S.Z. Efficient sugarcane transformation via bar gene selection. Trop. Plant Biol. 2017, 10, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, M.F.; da Cunha, B.A.D.B.; Ribeiro, A.P.; Martins, P.K.; de Souza, W.R.; de Oliveira, N.G.; Nakayama, T.J.; Augusto das Chagas Noqueli Casari, R.; Santiago, T.R.; Vinecky, F.; et al. Improved genetic transformation of sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) embryogenic callus mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Curr. Protoc. Plant Biol. 2017, 2, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, G.M.; Cajacob, C.A.; Padgette, S.R. Glyphosate resistant crops: Adoption, use and future considerations. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Gambhir, G.; Dass, A.; Tripathi, A.K.; Singh, A.; Jha, A.K.; Yadava, P.; Choudhary, M.; Rakshit, S. Genetically modified crops: Current status and future prospects. Planta 2020, 251, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Xu, P. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. cv. Zhongmian 35) using glyphosate as a selectable marker. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossen, J.H.; van Arkel, G.; Bergervoet, M.; Jo, K.R.; Jacobsen, E.; Visser, R.G. The Solanum demissum R8 late blight resistance gene is an Sw-5 homologue that has been deployed worldwide in late blight resistant varieties. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 1785–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.Z.; Yang, B.P.; Feng, X.Y.; Cao, Z.Y.; Feng, C.L.; Wang, J.G.; Xiong, G.R.; Shen, L.B.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, T.T.; et al. Development and Characterization of Transgenic Sugarcane with Insect Resistance and Herbicide Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Fan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Dai, B.; Gao, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Yao, M.; Wen, H.; Yu, W. Ectopic expression of MNX gene from Arabidopsis thaliana involved in auxin biosynthesis confers male sterility in transgenic cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) plants. Mol. Breed. 2010, 26, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-W.; Kim, K.-Y.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, B.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Lee, S.-H. Development of antibiotic marker-free creeping bentgrass resistance against herbicides. Acta Biochim. Et Biophys. Sin. 2010, 43, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.-L.; Liu, C.; Piao, C.-L.; Liu, C.-L. A Stable Agrobacterium rhizogenes-Mediated Transformation of Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) and Plant Regeneration From Transformed Hairy Root via Embryogenesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 604255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.K.; Pothana, A.; Prasad, K.; Shah, D.; Kaur, J.; Bhatnagar, D.; Chen, Z.; Raruang, Y.; Cary, J.W.; Rajasekaran, K.; et al. Peanuts that keep aflatoxin at bay: A threshold that matters. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 16, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Delucca, P.; Geijskes, R.J.; Ke, J.; Mayo, K.; Mai, P.; Sainz, M.; Caffall, K.; Moser, T.; Yarnall, M.; et al. Advances in agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane transformation and stable transgene expression. Sugar Tech 2014, 16, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, R.; Brich, R.G. Transgenic sugarcane plants via microprojectile bombardment. Plant J. 1992, 2, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, B.; Cai, W.; Feng, C.; Wang, J.; Xiong, G.; Zhang, S. Establishment of Mannose Selection System in Sugarcane Transformation. Biotechnol. Bull. 2015, 31, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.P.; Biest, N.; Chen, G.; Cheng, M.; Feng, X.; Radionenko, M.; Lu, F.; Fry, J.; Hu, T.; Metz, S.; et al. Agrobacterium-mediated large-scale transformation of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using glyphosate selection. Plant Cell Rep. 2003, 21, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, A.; Rao, A.Q.; Khan, M.A.U.; Shahid, N.; Bajwa, K.S.; Ashraf, M.A.; Abbas, M.A.; Azam, M.; Shahid, A.A.; Nasir, I.A.; et al. Herbicide-resistant cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) plants: An alternative way of manual weed removal. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonny, S. Genetically modified glyphosate-tolerant soybean in the USA: Adoption factors, impacts and prospects. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-M.; Zhang, X.-J.; Gao, Y.; Shen, Z.-C.; Lin, C.-Y. Molecular characterization and efficacy evaluation of a transgenic corn event for insect resistance and glyphosate tolerance. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2018, 19, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.; Agapito-Tenfen, S.Z. Z. Unintended Genomic Outcomes in Current and Next Generation GM Techniques: A Systematic Review. Plants 2022, 11, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Glyphosate Concentration (mg/L) | Weight of Calli (g) | No. of Resistant Shoots (Line) | CP4-EPSPS Positive (Line) | SE (%) | GFP Positive (Line) | TE (Lines/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 3.5 | 31 | 29 | 93.4 | 26 | 7.4 |
| 30 | 3.5 | 19 | 19 | 100 | 17 | 4.9 |
| 40 | 3.5 | 21 | 21 | 100 | 15 | 4.2 |
| Medium | MS (g/L) | Sucrose (g/L) | Phytoblend (g/L) | 2,4-D (mg/L) | 6-BA (mg/L) | NAA (mg/L) | Glyphosate (mg/L) | Timentin (mg/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Callus Induction | 4.43 | 30 | 8 | 1–3 | 0–0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.8 |
| Recovery | 4.43 | 30 | 8 | 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 300 | 5.8 |
| Callus Screening | 4.43 | 30 | 8 | 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 20–40 | 300 | 5.8 |
| Regeneration Screening | 4.43 | 30 | 8 | 0 | 1–2 | 0 | 10 | 300 | 5.8 |
| Elongation Screening | 4.43 | 30 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 300 | 5.8 |
| Rooting Screening | 4.43 | 20 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1–2 | 10 | 300 | 5.8 |
| Gene | Product Size (bp) | TM | Primer Sequence | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP4-EPSPS | 969 | 58 °C | Forward | GGCGACAAGAGCATCAGTCA |
| Reverse | CCTCGAGACGTTCATCACGG | |||
| GFP | 249 | 58 °C | Forward | CTGGATGAAGTGCCAGTCGG |
| Reverse | TGCATGTACCACGAGTCCAA | |||
| VirG | 332 | 58 °C | Forward | TTCGTTCCGATGCTCTATGA |
| Reverse | AGGTCGTCTTTCTGCTTTCC | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Javed, T.; Shen, L.; Sun, T.; Yang, B.; Zhang, S. Establishment of an Efficient Sugarcane Transformation System via Herbicide-Resistant CP4-EPSPS Gene Selection. Plants 2024, 13, 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13060852
Wang W, Javed T, Shen L, Sun T, Yang B, Zhang S. Establishment of an Efficient Sugarcane Transformation System via Herbicide-Resistant CP4-EPSPS Gene Selection. Plants. 2024; 13(6):852. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13060852
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenzhi, Talha Javed, Linbo Shen, Tingting Sun, Benpeng Yang, and Shuzhen Zhang. 2024. "Establishment of an Efficient Sugarcane Transformation System via Herbicide-Resistant CP4-EPSPS Gene Selection" Plants 13, no. 6: 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13060852
APA StyleWang, W., Javed, T., Shen, L., Sun, T., Yang, B., & Zhang, S. (2024). Establishment of an Efficient Sugarcane Transformation System via Herbicide-Resistant CP4-EPSPS Gene Selection. Plants, 13(6), 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13060852






