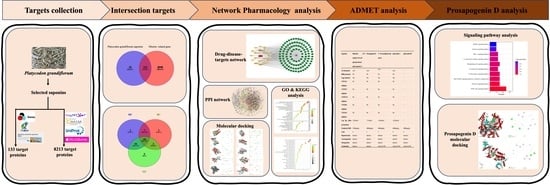
Revealing Molecular Mechanisms of the Bioactive Saponins from Edible Root of Platycodon grandiflorum in Combating Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Active Saponins of PG
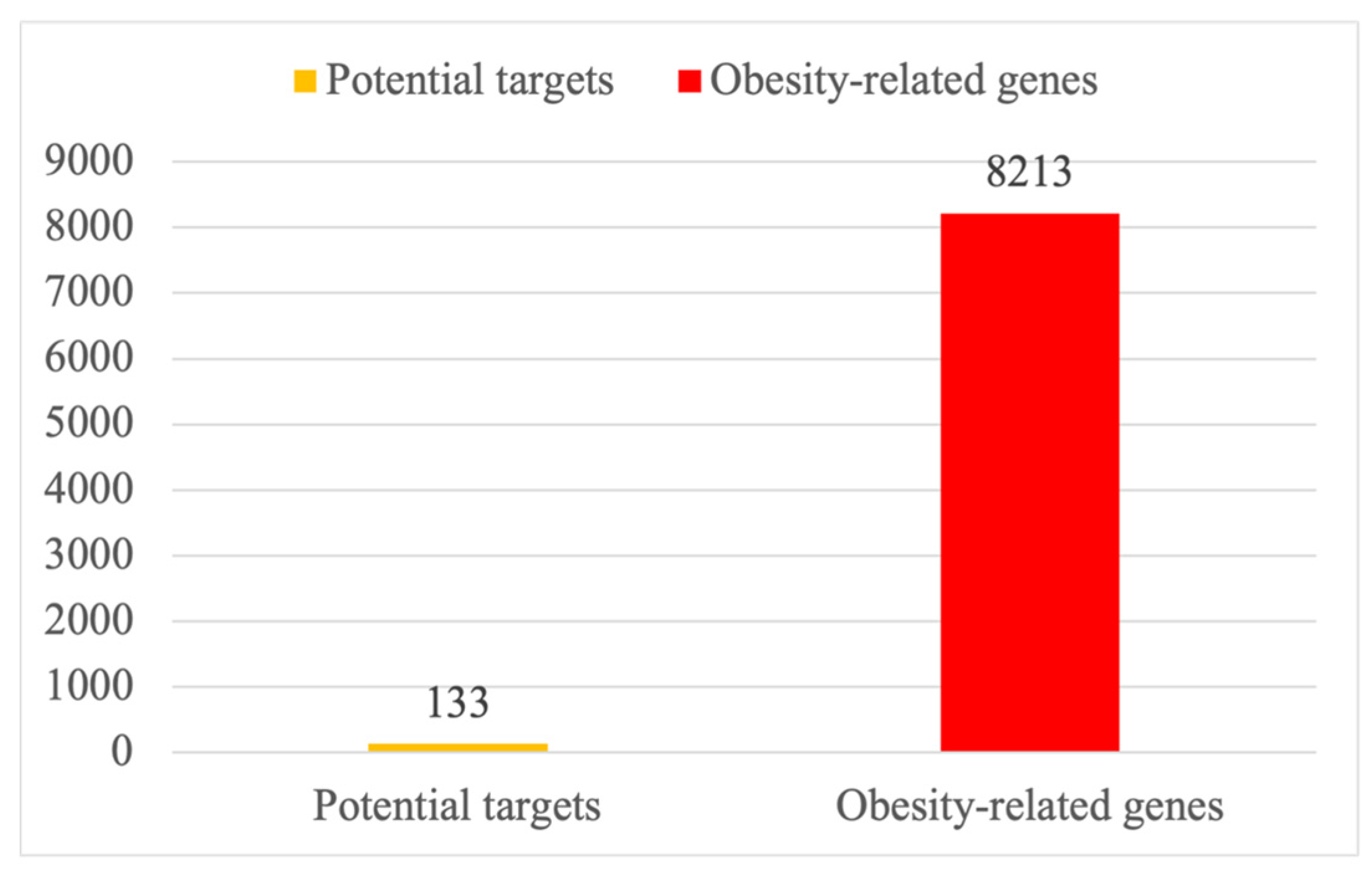
2.2. Targets and Statistics on Obesity-Related Genes of PG Saponins
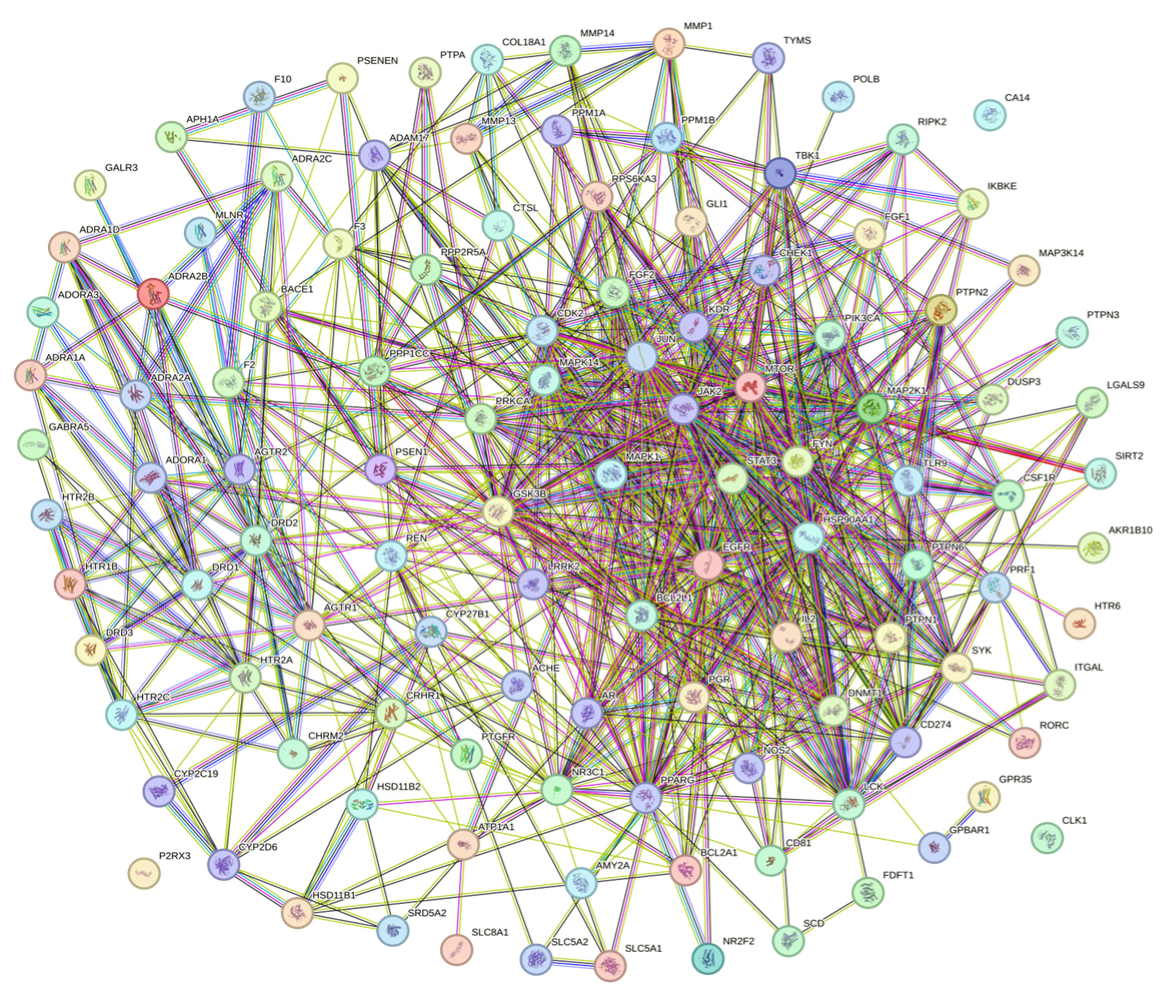
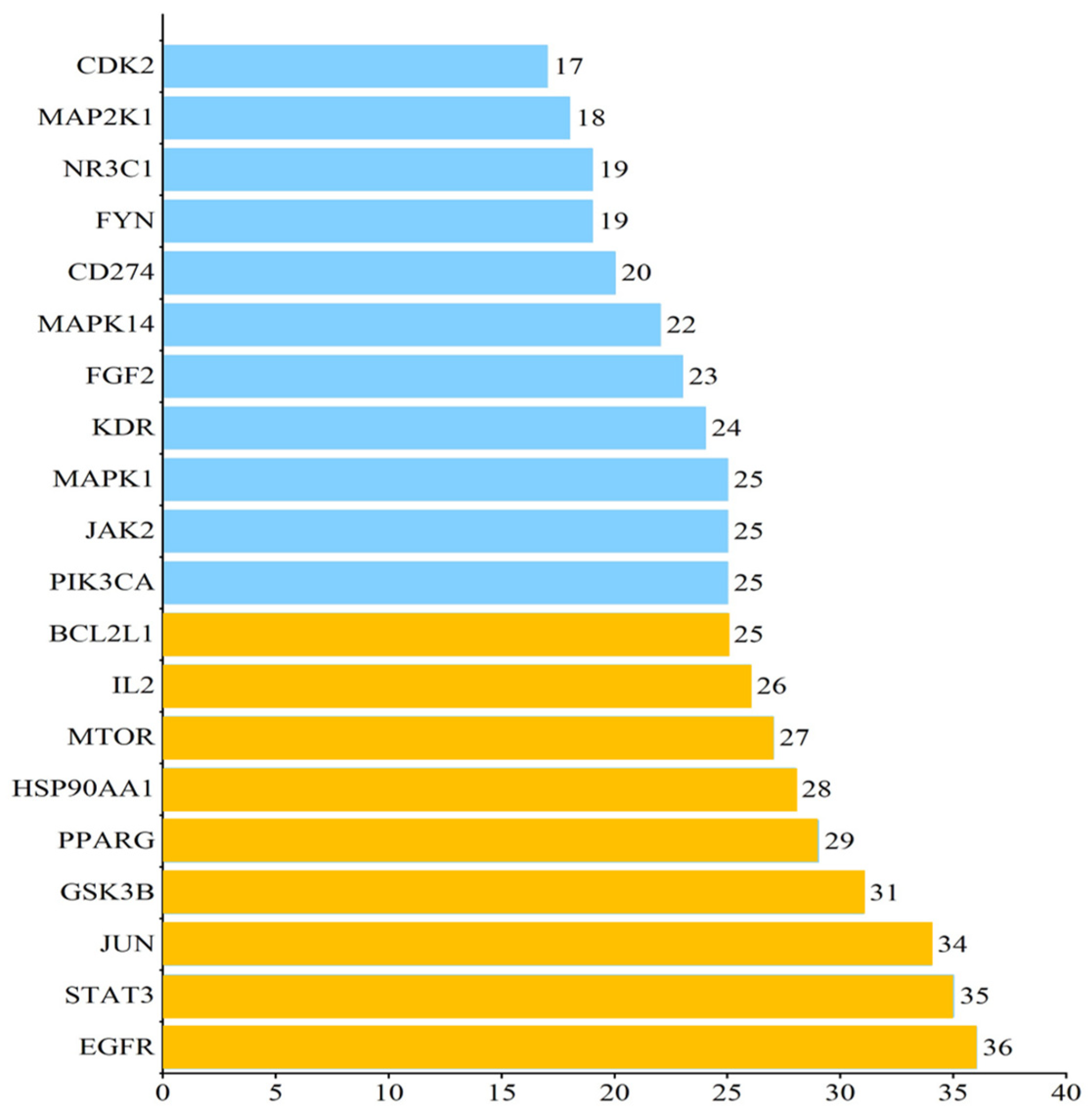
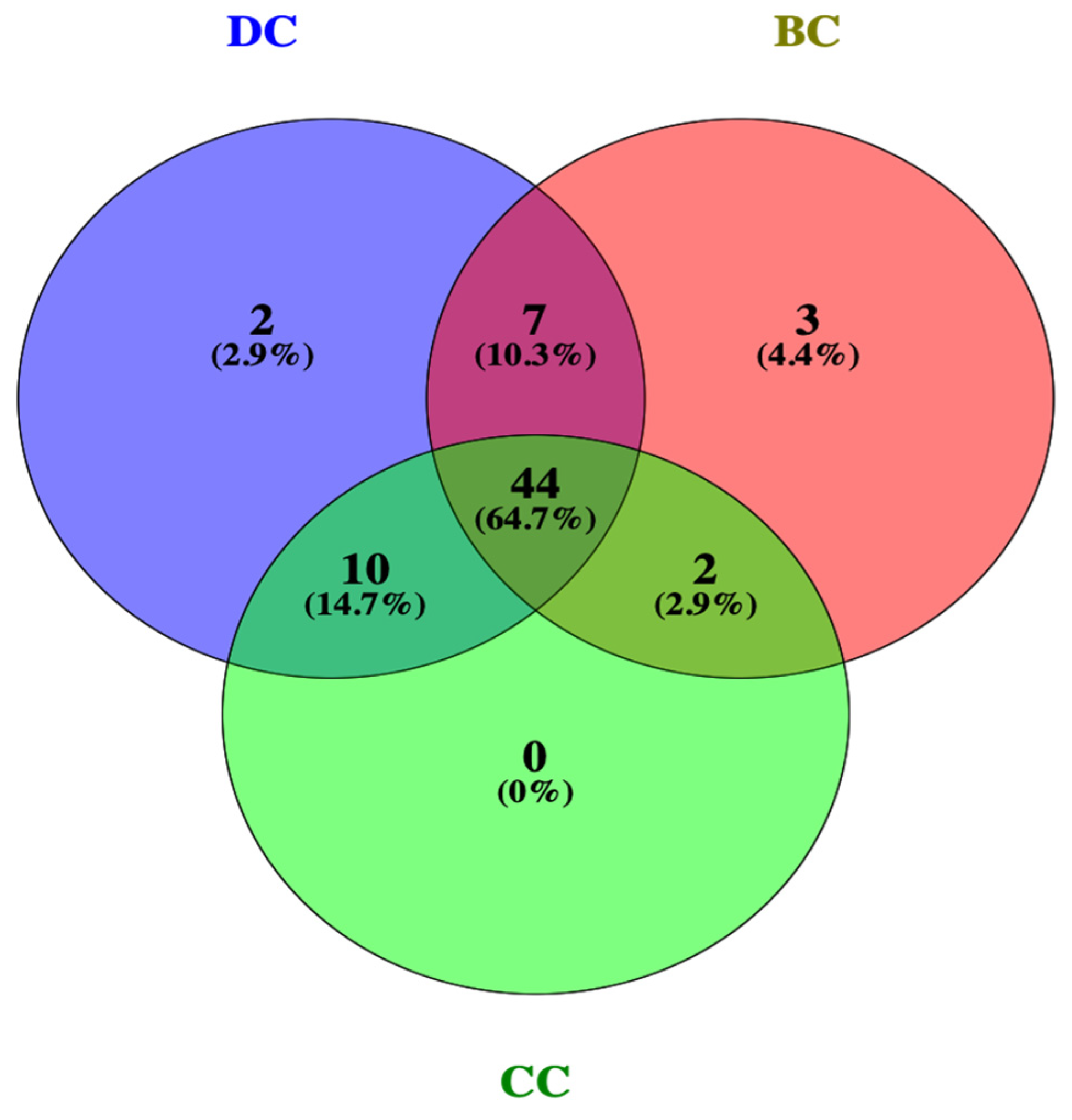
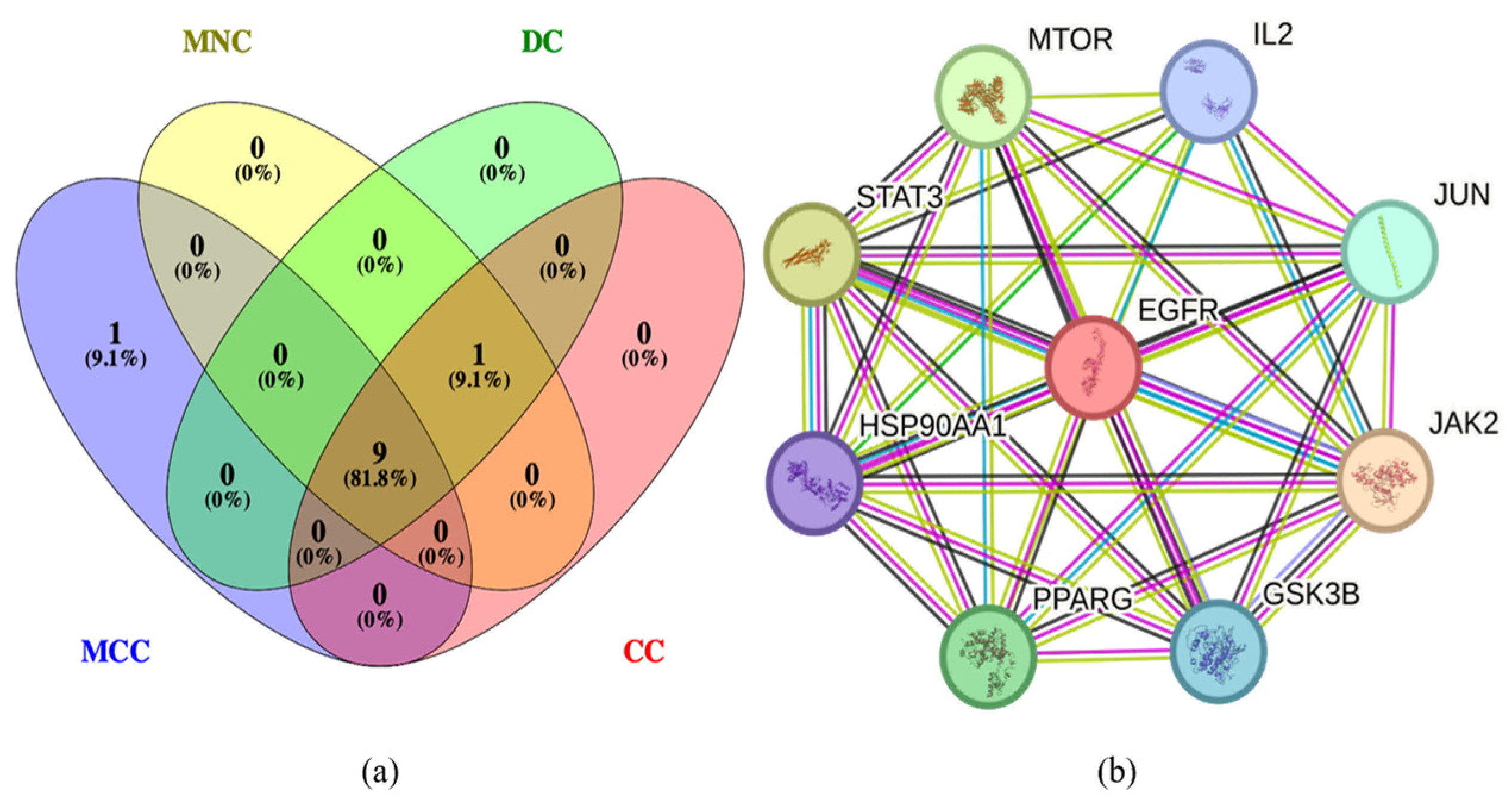
2.3. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Analysis of PG Saponins
2.4. The Network of Active Saponins and Anti-Obesity Targets of PG Saponins
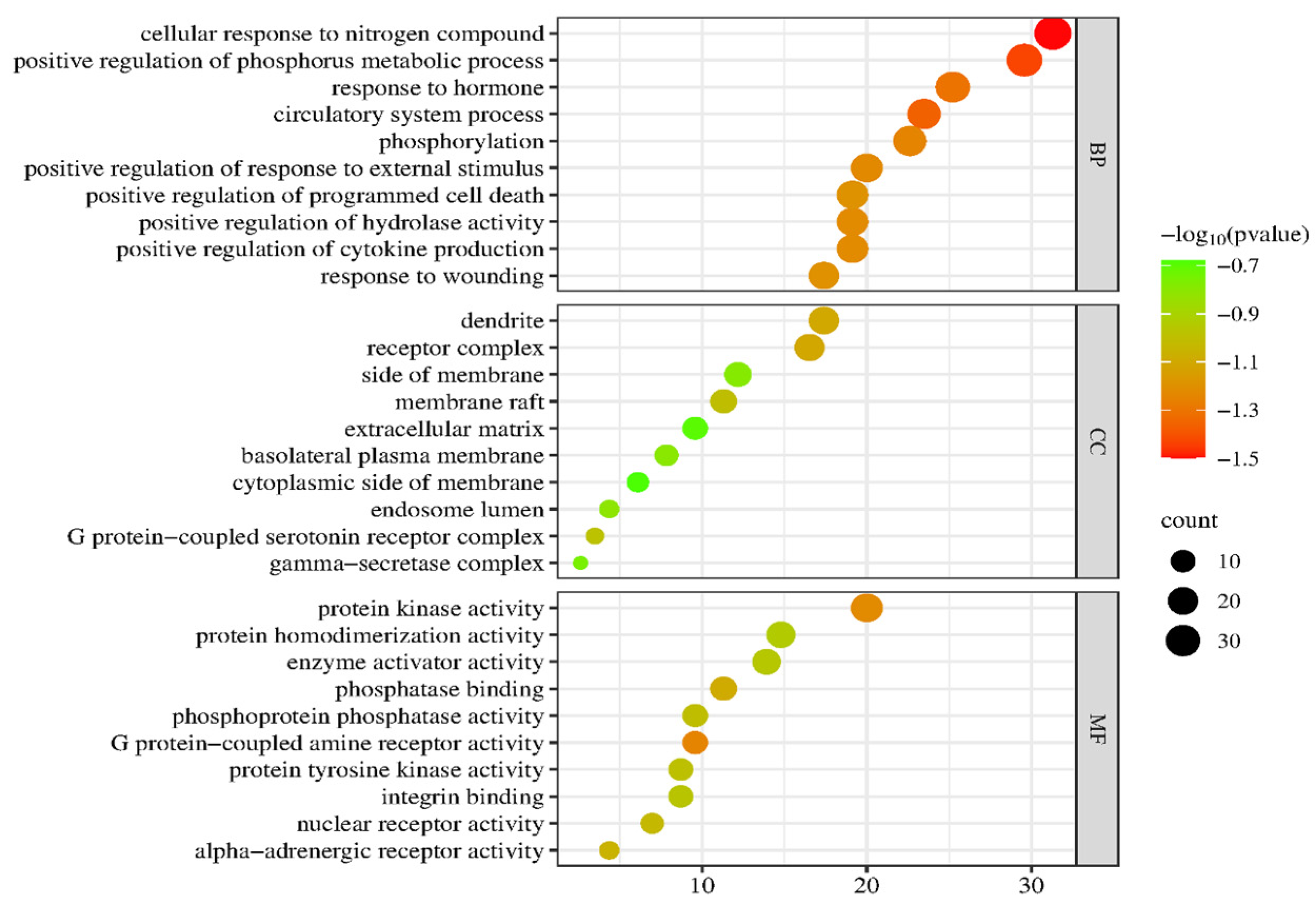
2.5. GO Enrichment and KEGG Signaling Pathway Analysis of PG Saponins
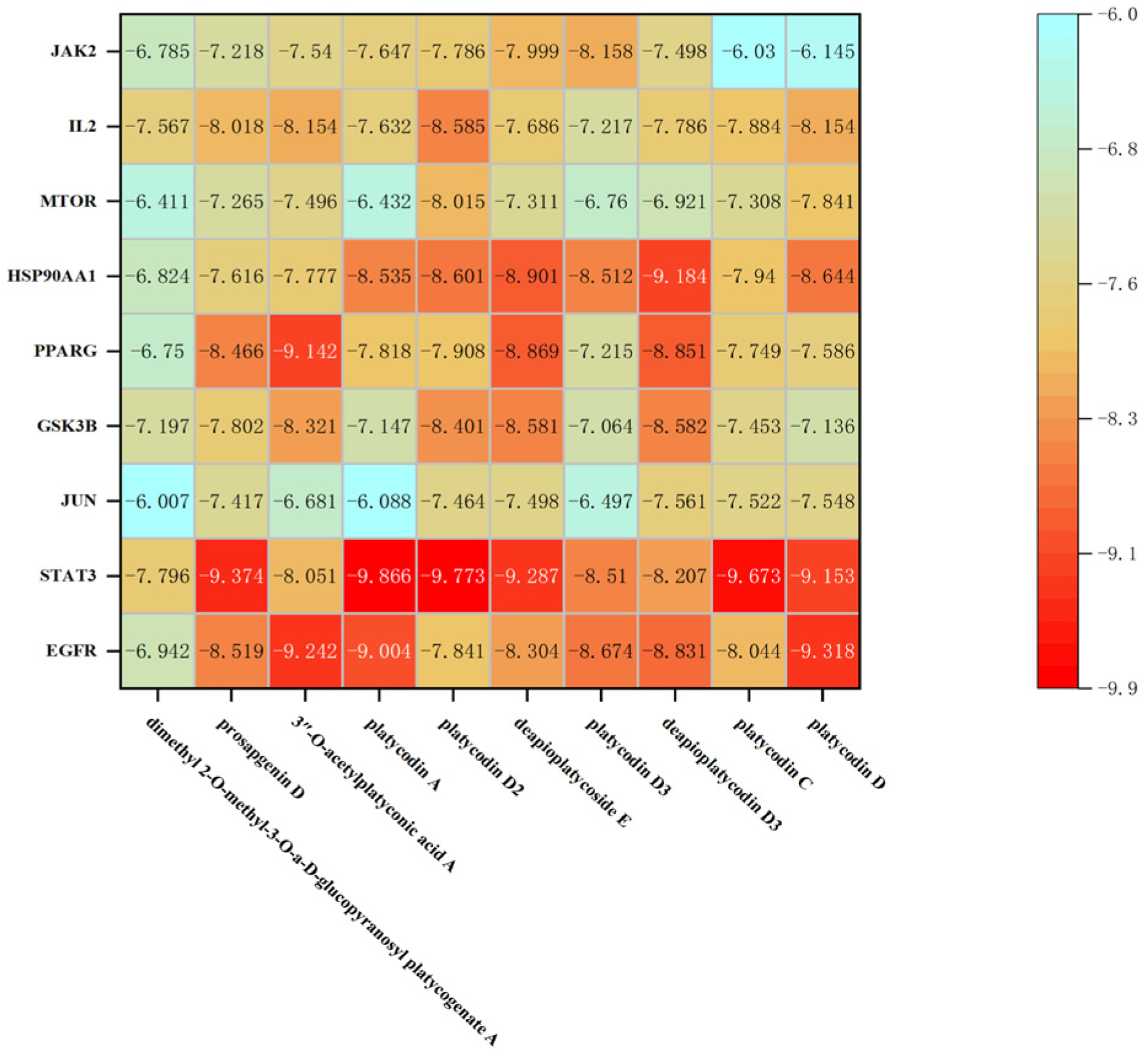
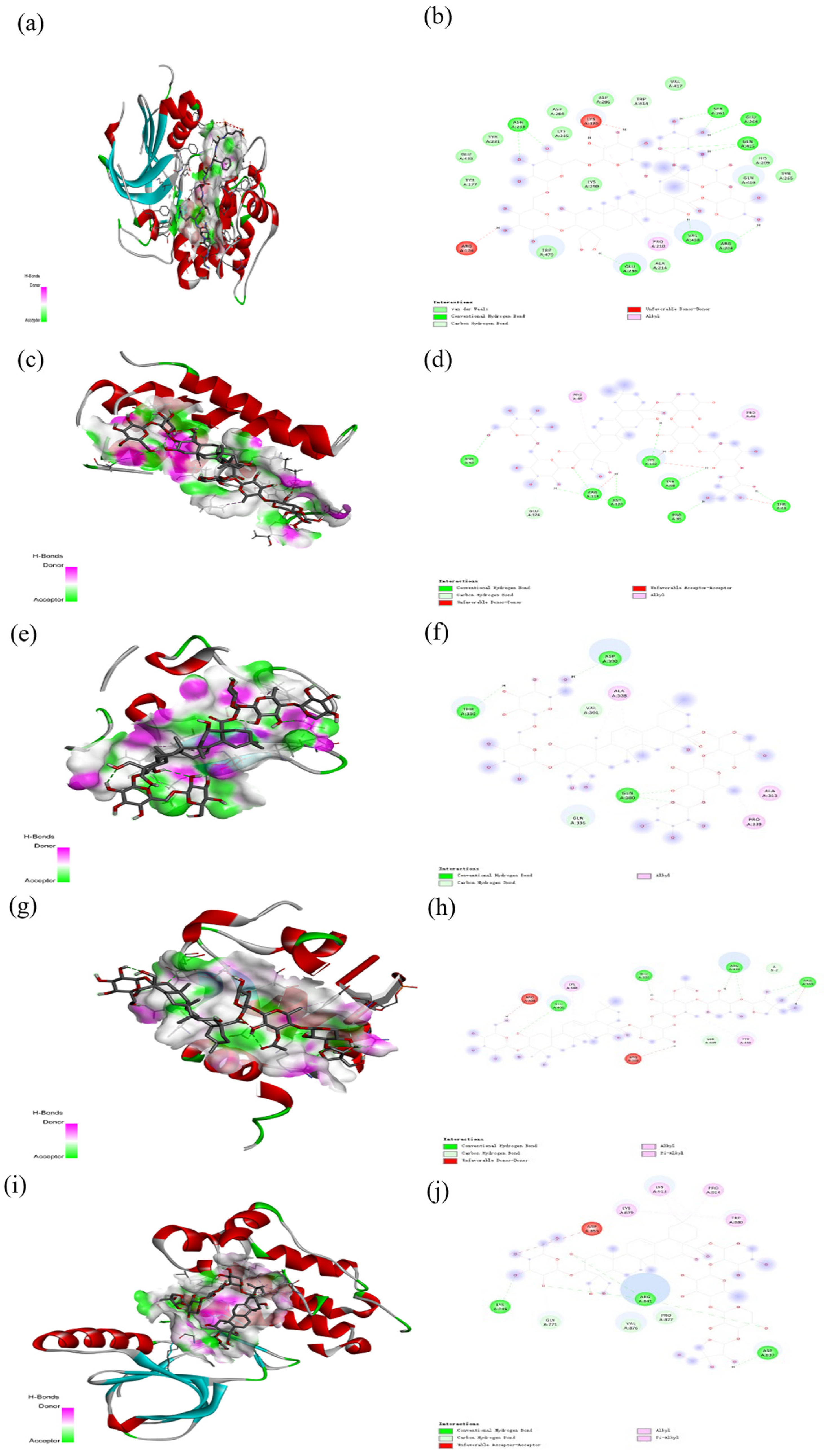
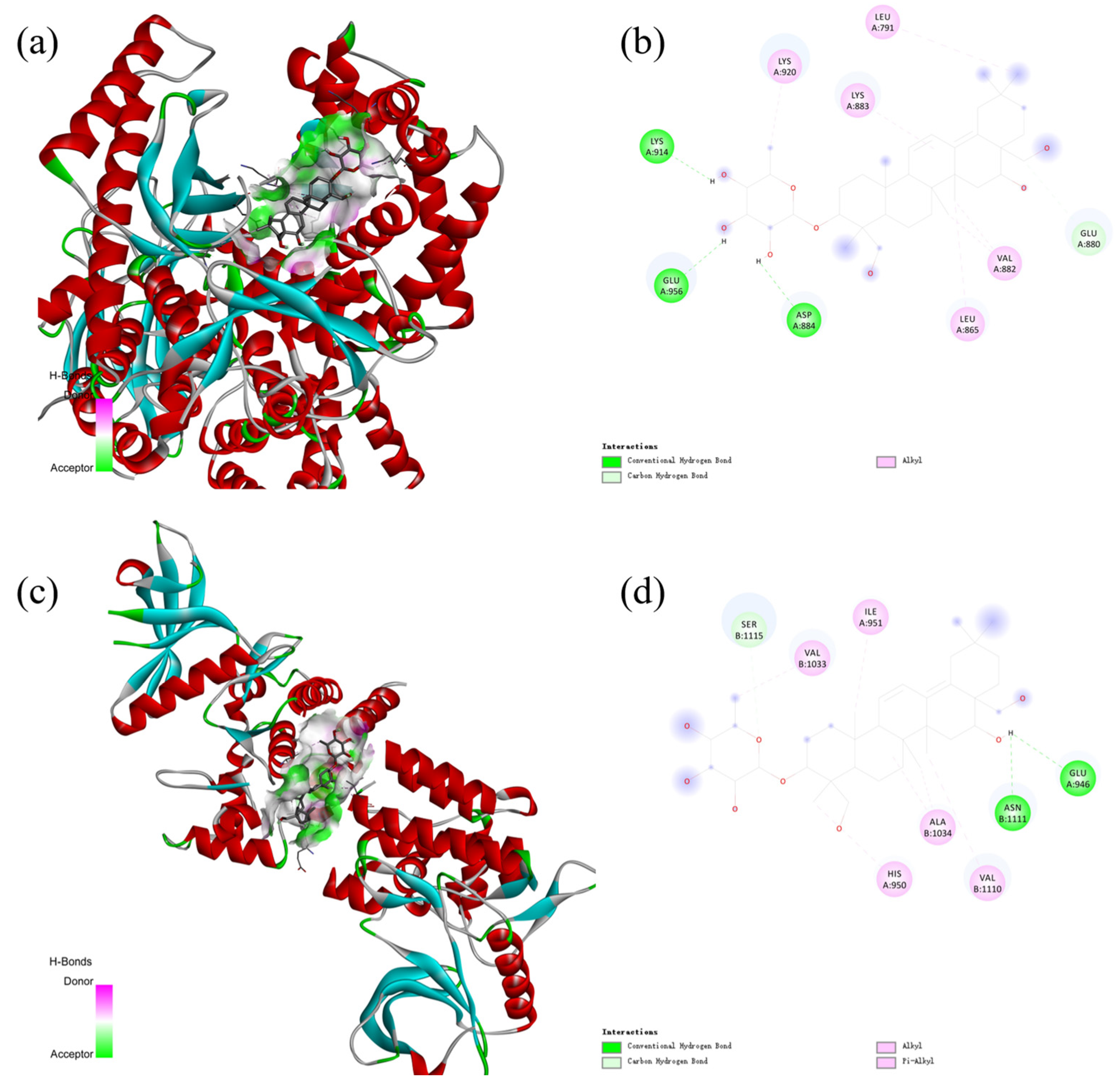
2.6. Molecular Docking
2.7. ADMET Analysis
2.8. The KEGG Analysis of Prosapogenin D
2.9. The Active Saponins of PG
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Using Databases to Collect Active Compounds of PG Saponins
4.2. The Intersection of PG Saponins and Obesity-Related Targets
4.3. Screening of Key Components and Targets of PG Saponins for Anti-Obesity
4.4. Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis
4.5. Enrichment Analyses of Potential Anti-Obesity Targets
4.6. Saponin Compound-Anti-Obesity Target Network Construction
4.7. Enrichment Analysis
4.8. Molecular Docking of PG Saponins and Potential Anti-Obesity Targets
4.9. ADMET Analysis of PG Saponins
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Beydoun, M.A.; Min, J.; Xue, H.; Kaminsky, L.A.; Cheskin, L.J. Has the prevalence of overweight, obesity and central obesity levelled off in the United States? Trends, patterns, disparities, and future projections for the obesity epidemic. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 810–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.C.; O’Neill, S.; Beck, B.R.; Forwood, M.R.; Khoo, S.K. Comparison of obesity and metabolic syndrome prevalence using fat mass index, body mass index and percentage body fat. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, T. The causes of obesity: An in-depth review. Adv. Obes. Weight Manag. Control 2020, 10, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, L.M.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Emanuele, E.; Lucia, A.; Gálvez, B.G. Adipaging’: Ageing and obesity share biological hallmarks related to a dysfunctional adipose tissue. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 3187–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piché, M.E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.P. Obesity phenotypes, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronne, L.J. Classification of obesity and assessment of obesity-related health risks. Obes. Res. 2002, 10, 105S–115S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.; Sockalingam, S.; Dash, S. Obesity as a multisystem disease: Trends in obesity rates and obesity-related complications. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meixner, L.; Cohrdes, C.; Schienkiewitz, A.; Mensink, G.B. Health-related quality of life in children and adolescents with overweight and obesity: Results from the German KIGGS survey. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorena, K.; Jachimowicz-Duda, O.; Ślęzak, D.; Robakowska, M.; Mrugacz, M. Adipokines and obesity. Potential link to metabolic disorders and chronic complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, K.; Abrams, G.A. Metabolic liver disease of obesity and role of adipose tissue in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morigny, P.; Boucher, J.; Arner, P.; Langin, D. Lipid and glucose metabolism in white adipocytes: Pathways, dysfunction and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 276–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chi, X.; Wang, Y.; Setrerrahmane, S.; Xie, W.; Xu, H. Trends in insulin resistance: Insights into mechanisms and therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.G.; Park, C.Y. Anti-obesity drugs: A review about their effects and safety. Diabetes Metab. J. 2012, 36, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chy, M.N.U.; Adnan, M.; Chowdhury, M.R.; Pagano, E.; Kamal, A.M.; Oh, K.K. Central and peripheral pain intervention by Ophiorrhiza rugosa leaves: Potential underlying mechanisms and insight into the role of pain modulators. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 276, 114182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, A.K.; Sharma, P.; Singh, A.; Kalita, K.J.; Saha, S.; Borah, J.C. Adipose and non-adipose perspectives of plant derived natural compounds for mitigation of obesity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021; 280, 114410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.L.; Harding, S.V.; Marinangeli, C.P.F.; Kim, Y.S.; Jones, P.J.H. Hypocholesterolemic and anti-obesity effects of saponins from Platycodon grandiflorum in hamsters fed atherogenic diets. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, H195–H200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yang, T.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Distribution, biotransformation, pharmacological effects, metabolic mechanism and safety evaluation of platycodin D: A comprehensive review. Curr. Drug Metab. 2022, 23, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.A.; Lee, J.; Hyun, T.K. Histone deacetylase inhibitor, sodium butyrate-induced metabolic modulation in Platycodon grandiflorus roots enhances anti-melanogenic properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyakudya, E.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, N.K.; Jeong, Y.S. Platycosides from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorum and their health benefits. PNF Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Jin, S.W.; Choi, C.Y.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.S.; Chung, Y.C.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, Y.C.; Jeong, H.G. Saponins from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorum ameliorate high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 86, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrelli, M.; Conforti, F.; Araniti, F.; Statti, G.A. Effects of saponins on lipid metabolism: A review of potential health benefits in the treatment of obesity. Molecules 2016, 21, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, N.; Li, M. Platycodon grandiflorus–An ethnopharmacological, phytochemical and pharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 164, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.O.; Choi, J.; Kang, H.J.; Che, D.N.; Shin, J.Y.; Kim, J.S. Anti-obesity effects of a mixed extract containing Platycodon grandiflorum, Apium graveolens and green tea in high fat diet induced obese mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 2783–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, A.L. Network pharmacology: The next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogales, C.; Mamdouh, Z.M.; List, M.; Kiel, C.; Casas, A.I.; Schmidt, H.H. Network pharmacology: Curing causal mechanisms instead of treating symptoms. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Wu, Y.; Li, A.S.M.; Fu, X.Q.; Yu, Z.L. Network pharmacology and molecular docking-based prediction of active compounds and mechanisms of action of Cnidii Fructus in treating atopic dermatitis. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.J.; Han, L.K.; Zheng, Y.N.; Lee, J.H.; Sung, C.K. In vitro inhibitory effect of triterpenoidal saponins from Platycodi Radix on pancreatic lipase. Arch Pharm. Res. 2005, 28, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Ryu, R.; Lee, J.; Cho, S.J.; Kwon, E.Y. Platycodon grandiflorus root extract attenuates body fat mass, hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance through the interplay between the liver and adipose tissue. Nutrients 2016, 8, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.L.; Sim, J.S.; Shim, S.H.; Ha, Y.W.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, Y.S. Antiobese and hypolipidemic effects of saponins in diet-induced obese rats: Evidences for lipase inhibition and calorie intake restriction. Int. J. Obesity 2005, 29, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keiser, M.J.; Roth, B.L.; Armbruster, B.N.; Ernsberger, P.; Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. Relating protein pharmacology by ligand chemistry. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C. TCMSP: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: Updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W357–W364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safran, M.; Dalah, I.; Alexander, J.; Rosen, N.; Iny Stein, T.; Shmoish, M. GeneCards Version 3: The human gene integrator. Database 2010, 2010, baq020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveros, J.C. VENNY. An Interactive Tool for Comparing Lists with Venn Diagrams. 2007. Available online: https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index.html (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R. The STRING database in 2023: Protein–protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Chen, B.; Zhan, X.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, H.; Dong, Y. Network pharmacology and molecular docking study on the mechanism of colorectal cancer treatment using Xiao-Chai-Hu-Tang. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, B.; Xiao, H.; Li, Z.; Li, R. Signaling pathways in obesity: Mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.J.; Wang, J.Z.; Deng, W.Q.; Zou, K. Induced-fit docking and binding free energy calculation on furostanol saponins from Tupistra chinensis as epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 4970–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ji, J.; Zhang, J.; Hou, X.; Fu, X.; Luo, Y.; Mei, Z.; Feng, Z. Anti-inflammatory and osteoprotective effects of Chikusetsusaponin Ⅳon rheumatoid arthritis via the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2021, 93, 153801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Q.; Xia, L.; Du, Q.; Shao, Y.; He, J.; Wu, P.; Liang, L.; Shen, X. The therapeutic role and potential mechanism of EGCG in obesity-related precocious puberty as determined by integrated metabolomics and network pharmacology. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1159657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.L.; Andricopulo, A.D. ADMET modeling approaches in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, Y.B.; Mazumder, P.B.; Talukdar, A.D. Hibiscus sabdariffa anthocyanins are potential modulators of estrogen receptor alpha activity with favourable toxicology: A computational analysis using molecular docking, ADME/Tox prediction, 2D/3D QSAR and molecular dynamics simulation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 611–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanabria-Chanaga, E.E.; Betancourt-Conde, I.; Hernández-Campos, A.; Téllez-Valencia, A.; Castillo, R. In silico hit optimization toward AKT inhibition: Fragment-based approach, molecular docking and molecular dynamics study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 37, 4301–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattan, S.W.; Nafie, M.S.; Elmgeed, G.A.; Alelwani, W.; Badar, M.; Tantawy, M.A. Molecular docking, anti-proliferative activity and induction of apoptosis in human liver cancer cells treated with androstane derivatives: Implication of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 198, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultze, S.M.; Hemmings, B.A.; Niessen, M.; Tschopp, O. PI3K/AKT, MAPK and AMPK signalling: Protein kinases in glucose homeostasis. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2012, 14, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savova, M.S.; Mihaylova, L.V.; Tews, D.; Wabitsch, M.; Georgiev, M.I. Targeting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in obesity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 159, 114244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuffer, M. Integrative health and medicine: Dietary supplements and modalities for the treatment of obesity. In Nutrition in the Prevention and Treatment of Abdominal Obesity; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabio, G.; Kennedy, N.J.; Cavanagh-Kyros, J.; Jung, D.Y.; Ko, H.J.; Ong, H. Role of muscle c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1 in obesity-induced insulin resistance. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priceman, S.J.; Kujawski, M.; Shen, S.; Cherryholmes, G.A.; Lee, H.; Zhang, C. Regulation of adipose tissue T cell subsets by Stat3 is crucial for diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13079–13084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Meng, Y.; Dou, M. Inhibiting glycogen synthase kinase 3 reverses obesity-induced white adipose tissue inflammation by regulating apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage/CD5L-mediated macrophage migration. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 2103–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Pan, Y.; Tang, J.; Terker, A.S.; Arroyo Ornelas, J.P.; Jin, G.N. EGFR-mediated activation of adipose tissue macrophages promotes obesity and insulin resistance. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, L.; Peng, L.; Xiong, J.; Yang, W. hPER3 promotes adipogenesis via hHSP90AA1-mediated inhibition of Notch1 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, N.M.; Gouda, W.; Almutairi, S.M.; Elshikh, M.S.; Morcos, G.N. PPARG expression patterns and correlations in obesity. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 102116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, A.; Mancini, M.C. Treatment of obesity: An update on anti-obesity medications. Obes. Rev. 2003, 4, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kola, B.; Grossman, A.B.; Korbonits, M. The role of AMP-activated protein kinase in obesity. Obes. Metab. 2008, 36, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulyaningsih, E.; Zhang, L.; Herzog, H.; Sainsbury, A. NPY receptors as potential targets for anti-obesity drug development. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1170–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assan, D.; Mustapha, U.F.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Peng, Y.; Li, G. The roles of neuropeptide Y (Npy) and peptide YY (Pyy) in teleost food intake: A mini review. Life 2021, 11, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Han, H.K.; Choi, C.I. Saikosaponin A and D inhibit adipogenesis via the AMPK and MAPK signaling pathways in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkovska, K.; Samsonov, S.A.; Paszkowski-Rogacz, M.; Pisabarro, M.T. Multipose binding in molecular docking. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 2622–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Wu, Z.; Yi, J.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z.; Hsieh, C. ADMETlab 2.0: An integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMET properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W5–W14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Gao, L.; Liang, H.; Chen, S.D. In silico screening of potential anti–COVID-19 bioactive natural constituents from food sources by molecular docking. Nutrition 2021, 82, 111049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zheng, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, A.; Yang, L. Systems pharmacology in drug discovery and therapeutic insight for herbal medicines. Brief. Bioinform. 2014, 15, 710–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apweiler, R.; Bairoch, A.; Wu, C.H.; Barker, W.C.; Boeckmann, B.; Ferro, S. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32 (Suppl. S1), D115–D119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamosh, A.; Scott, A.F.; Amberger, J.S.; Bocchini, C.A.; McKusick, V.A. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), a knowledgebase of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33 (Suppl. S1), D514–D517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R. DrugBank 5.0: A major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñero, J.; Ramírez-Anguita, J.M.; Saüch-Pitarch, J.; Ronzano, F.; Centeno, E.; Sanz, F. The DisGeNET knowledge platform for disease genomics: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D845–D855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, G.; Sherman, B.T.; Hosack, D.A.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Lane, H.C. DAVID: Database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Yang, J.Y.; Wu, R.X.; Fang, C.; Lu, H.; Li, H.C. Network pharmacology–based identification of key mechanisms of xihuang pill in the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer stem cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 714628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, W.; Cheng, G.; Wu, J.; Guo, S. A bioinformatics investigation into molecular mechanism of Yinzhihuang granules for treating hepatitis B by network pharmacology and molecular docking verification. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA. Discovery Studio; Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Limongelli, V. Ligand binding free energy and kinetics calculation in 2020. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2020, 10, e1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, P.; Eckert, A.O.; Schrey, A.K.; Preissner, R. ProTox-II: A webserver for the prediction of toxicity of chemicals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W257–W263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| PubChem ID | Saponins | Molecular Formula | Structure | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 46173910 | Platycodin A | C59H94O29 | 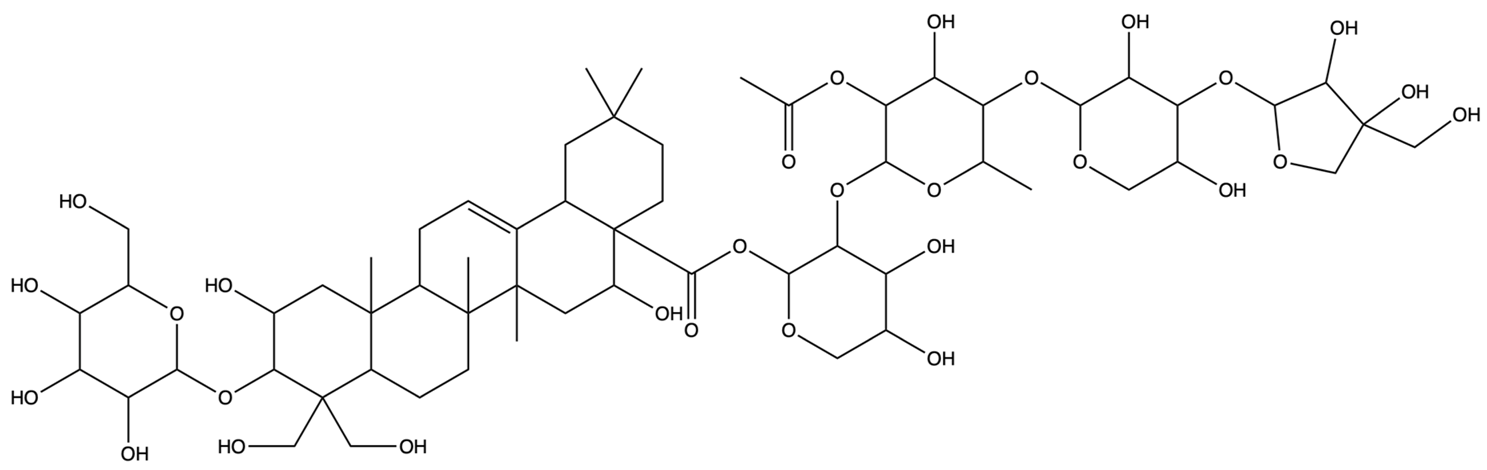 | [27] |
| 46173919 | Platycodin C | C59H94O29 |  | [27] |
| 162859 | Platycodin D | C57H92O28 | 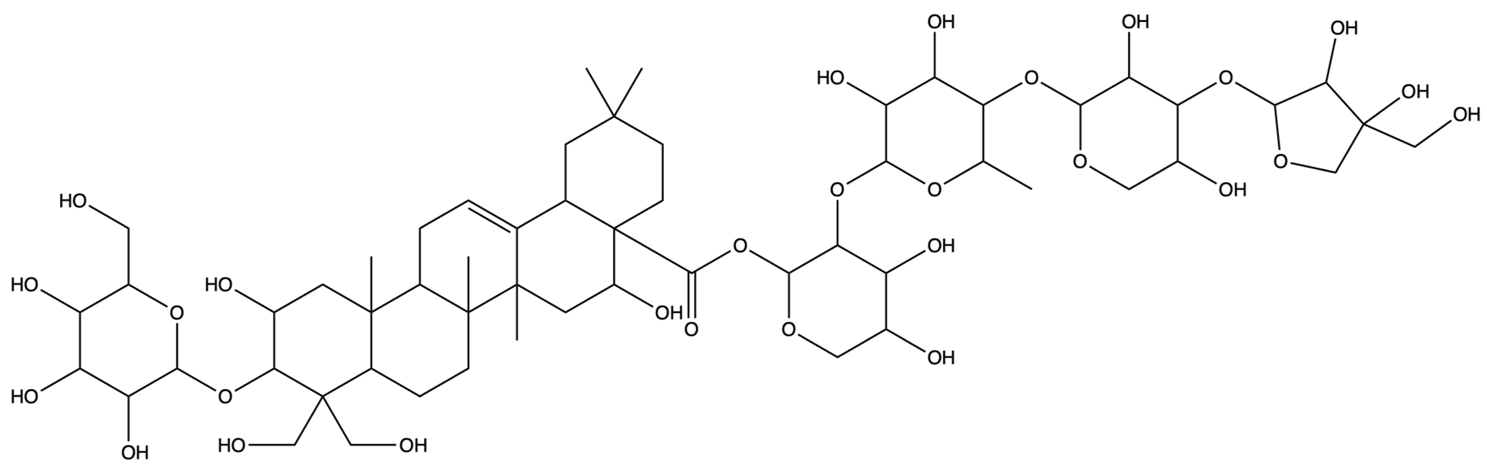 | [27] |
| 70698266 | Deapioplatycodin D | C52H84O24 | 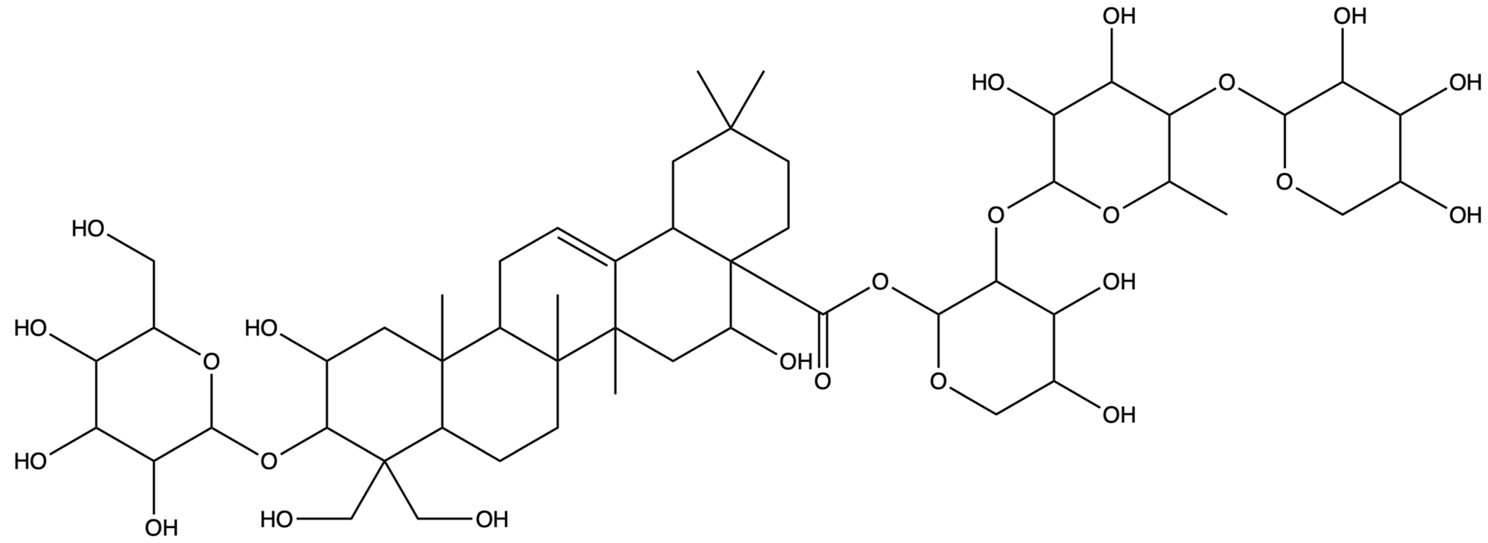 | [27] |
| 53317652 | Platycodin D2 | C63H102O33 | 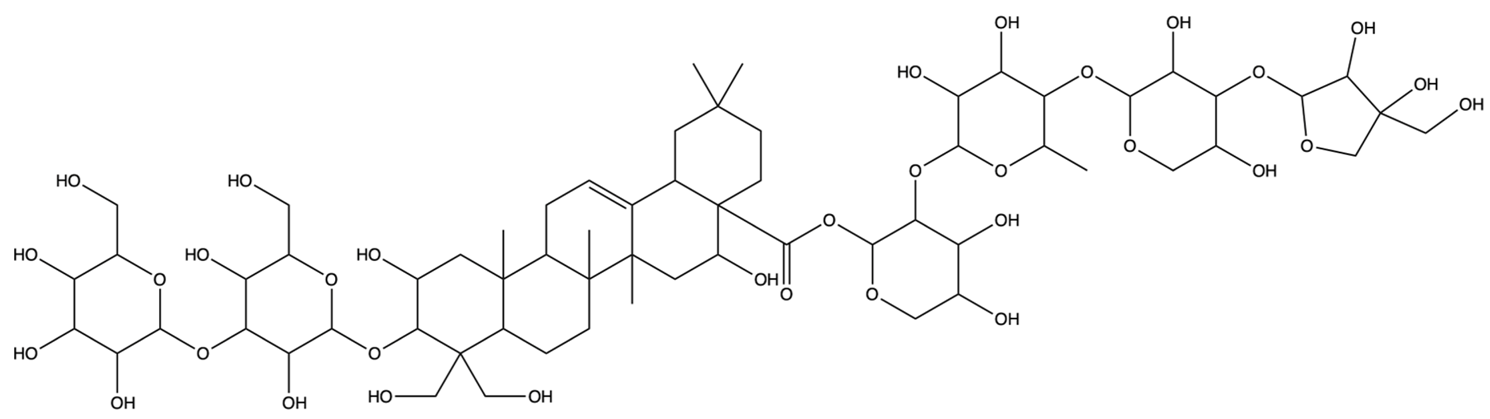 | [27] |
| 75251137 | Platycodin D3 | C63H102O33 | 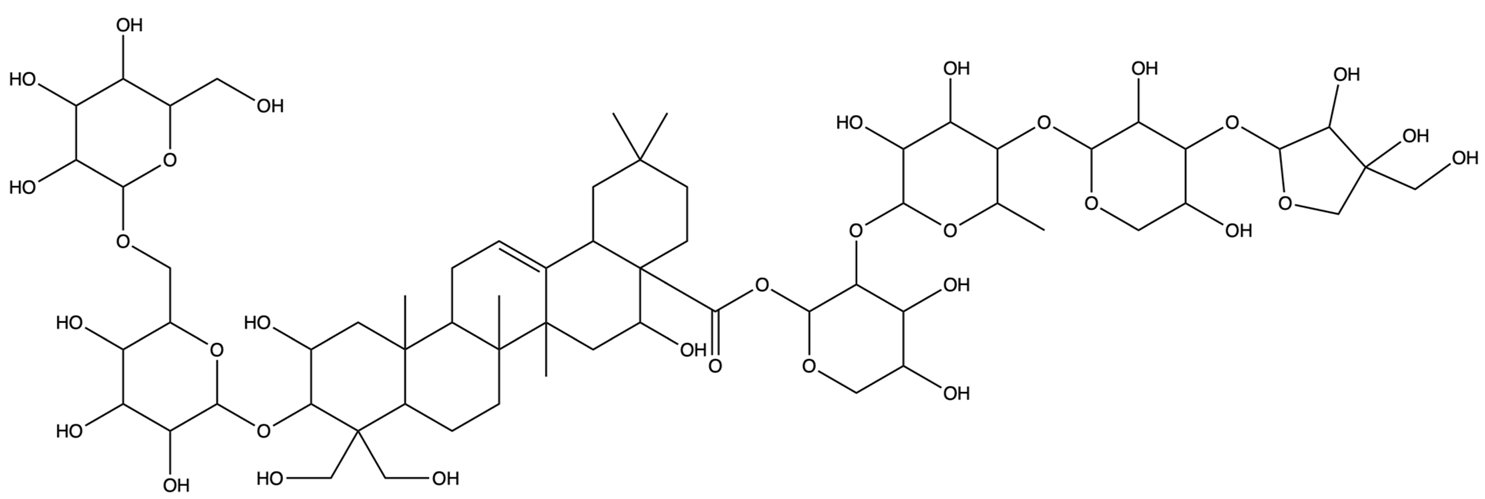 | [27] |
| / | Deapioplatycodin D3 | C58H94O29 |  | [27] |
| 70698289 | Deapioplatycoside E | C64H104O34 |  | [28] |
| 50900852 | Platyconic acid B lactone | C63H98O33 | 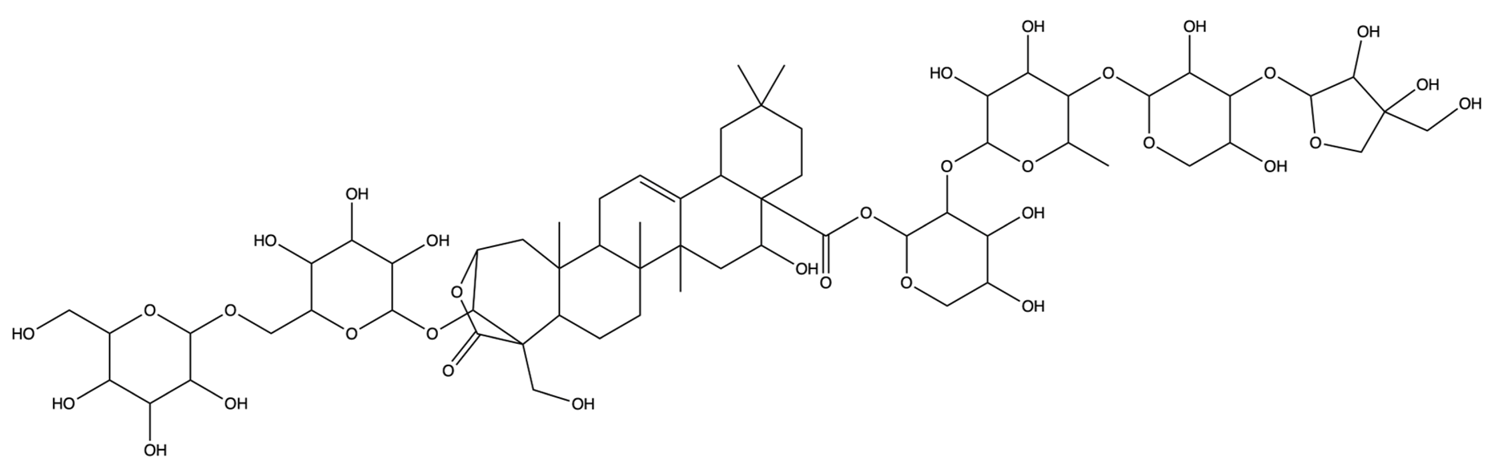 | [28] |
| / | 3″-O-acetylplatyconic acid A | C59H92O30 | 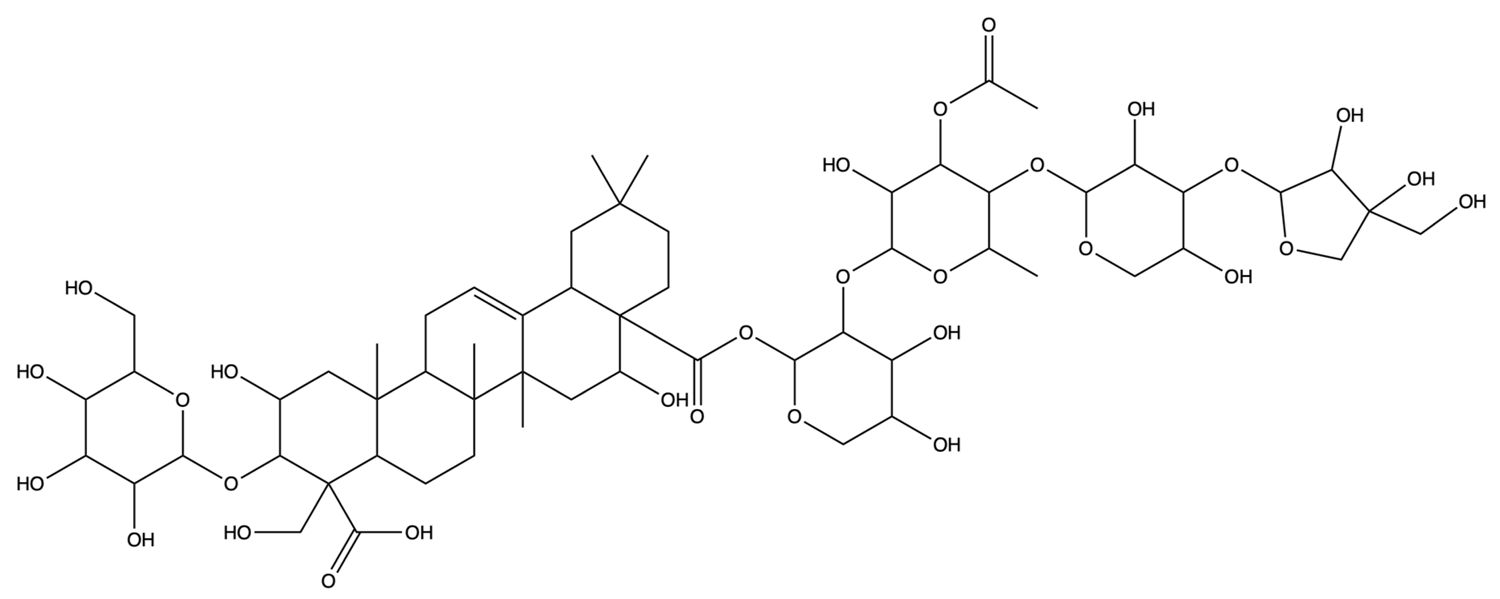 | [28] |
| / | Prosapogenin D | C36H58O8 | 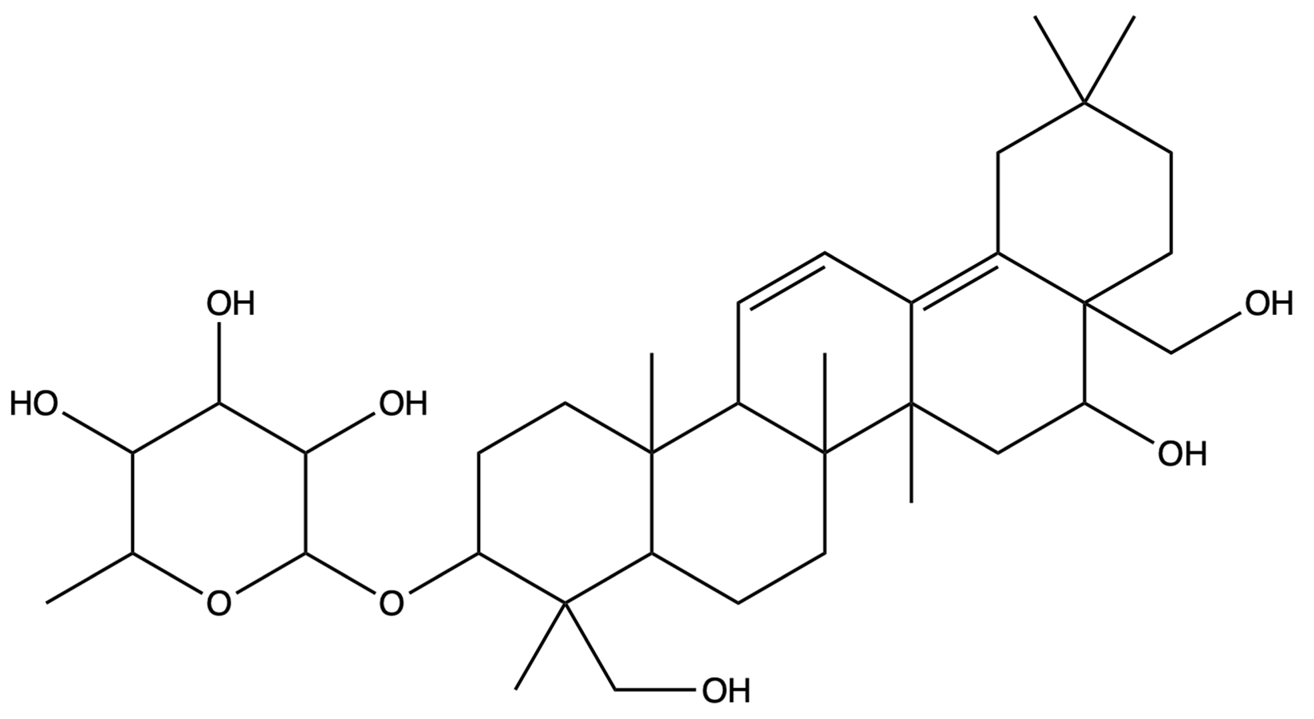 | [29] |
| 96023791 | Polygalacin D | C57H92O27 | 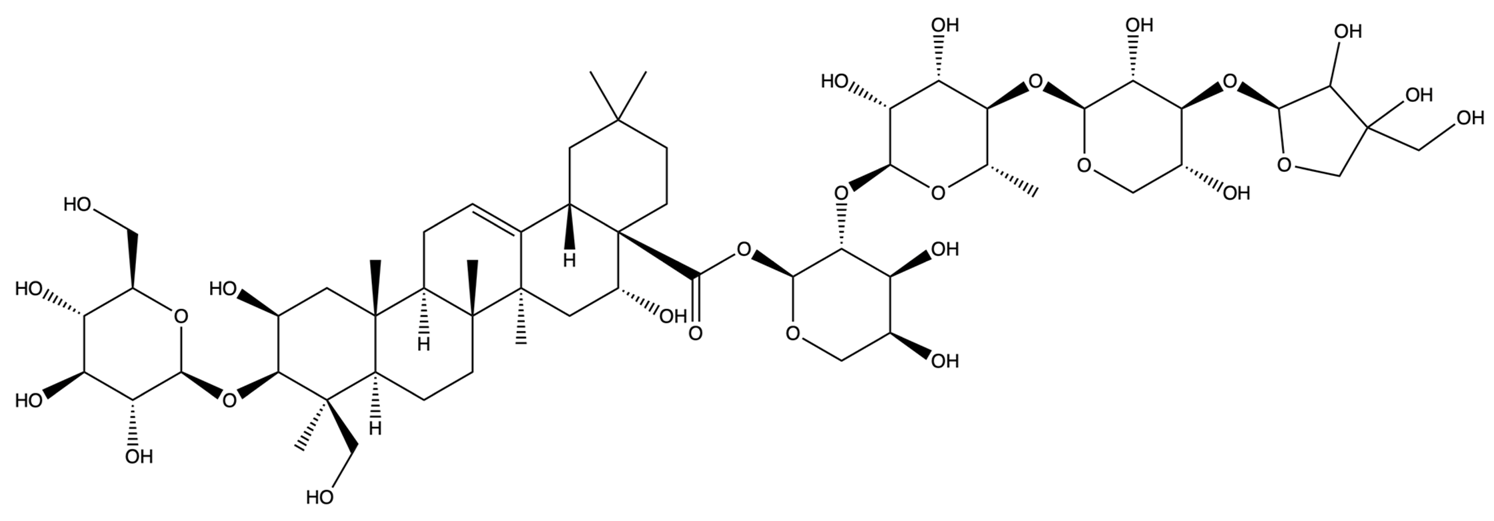 | [28] |
| 385678073 | Polygalacin D3 | C63H102O32 | 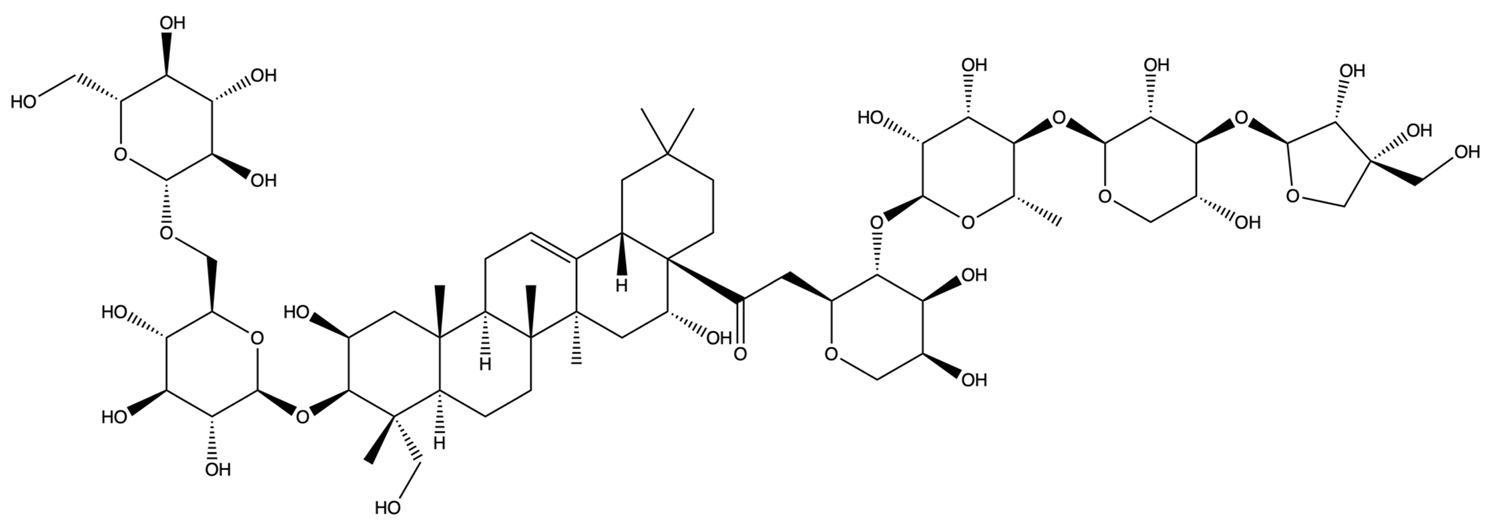 | [28] |
| 70698202 | Platycoside E | C69H112O38 | 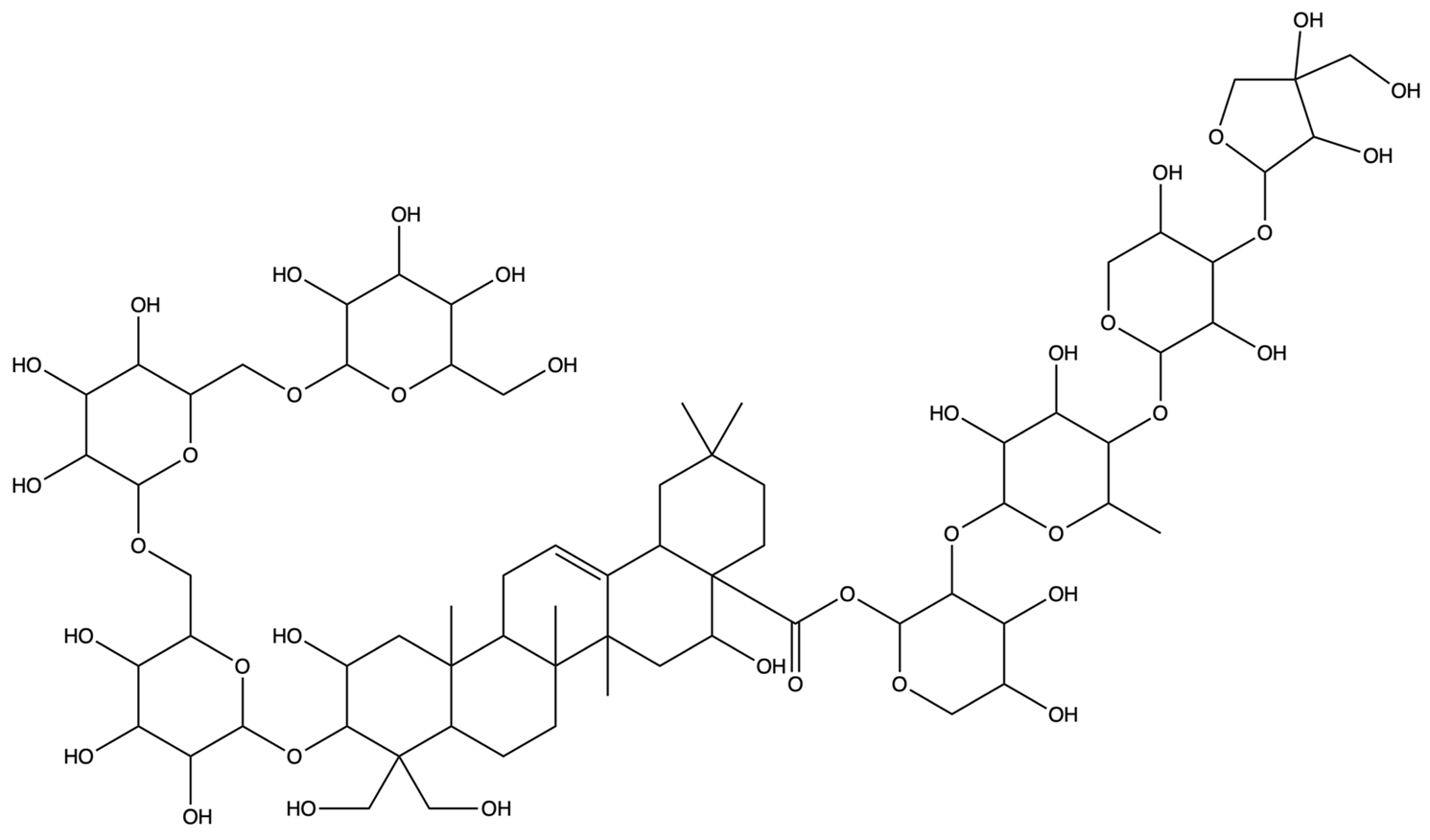 | [28] |
| 385678065 | Polygalacin D2 | C63H102O32 | 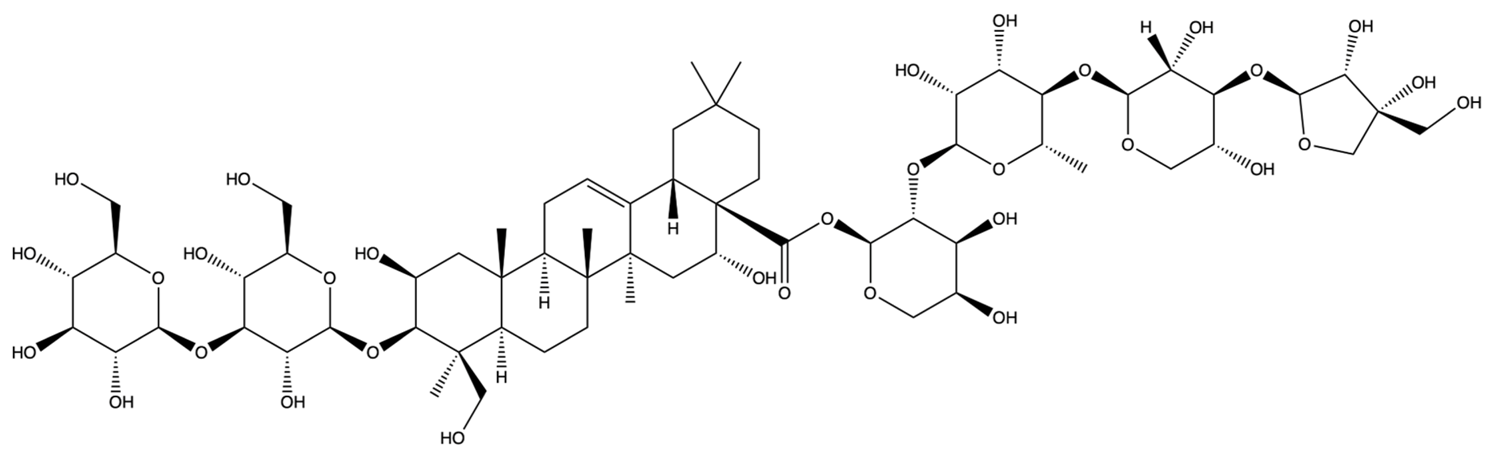 | [28] |
| / | Dimethyl 2-O-methyl-3-O-a-D-glucopyranosyl platycogenate A | / | 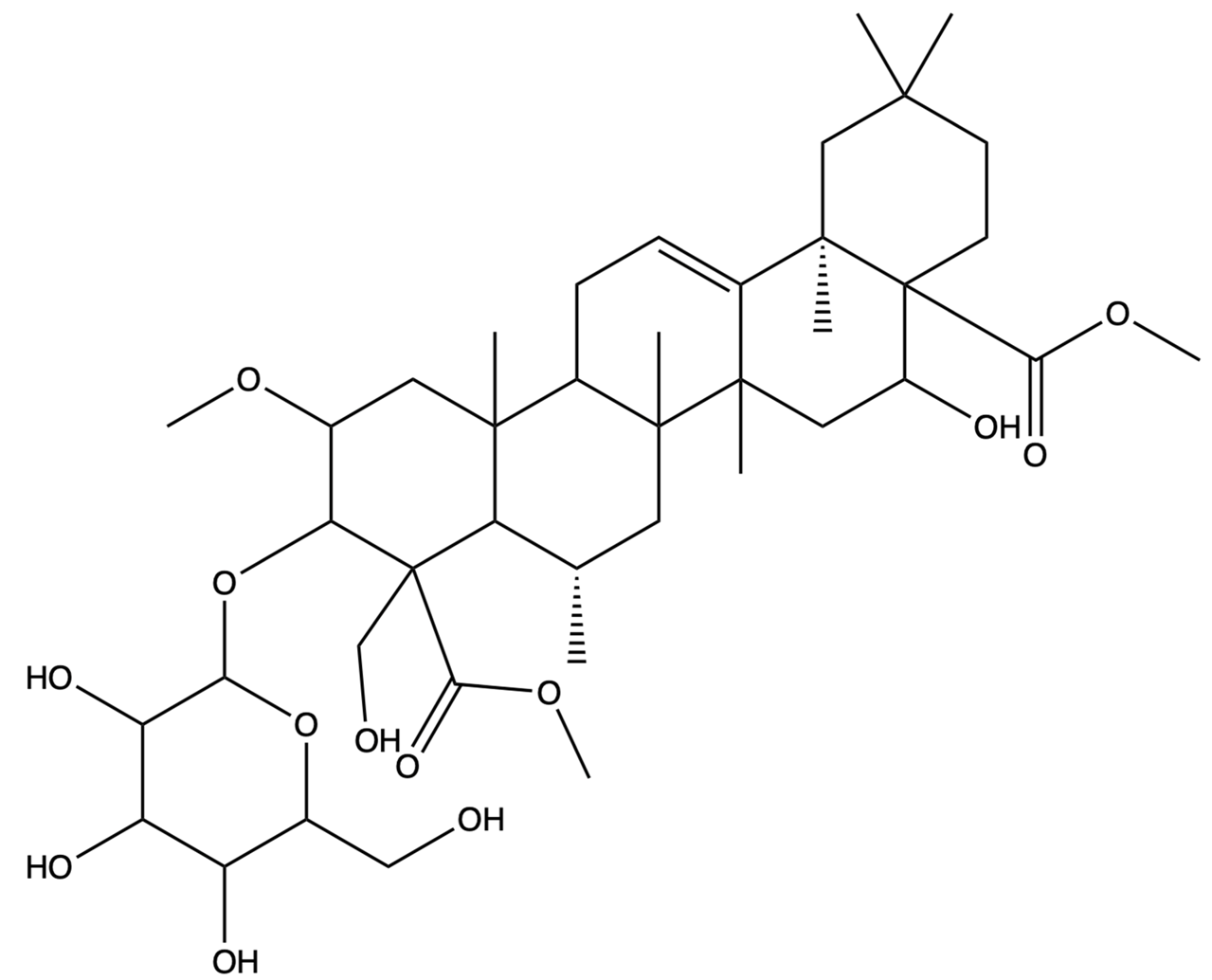 | TCMSP |
| / | Platycodin V | / |  | [27] |
| Saponins | Dimethyl 2-O-methyl-3-O-a-D-glucopyranosyl Platycogenate A | Prosapogenin D | 3″-O-acetylplatyconic Acid A | Platycodin A | Platycodin D2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GI absorption | Low | Low | Low | Low | / |
| BBB permeant | No | No | No | No | / |
| P-gp substrate | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | / |
| CYP1A2 inhibitor | No | No | No | No | / |
| CYP2C9 inhibitor | No | No | No | No | / |
| CYP2C19 inhibitor | No | No | No | No | / |
| CYP2D6 inhibitor | No | No | No | No | / |
| CYP3A4 inhibitor | No | No | No | No | / |
| Log Kp (Skin permeation) | −8.29 cm/s | −7.14 cm/s | −16.40 cm/s | −16.26 cm/s | / |
| Predicted LD50 | 1500 mg/kg | 4000 mg/kg | 4000 mg/kg | 4000 mg/kg | 4000 mg/kg |
| Class | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Hepatotoxicity | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
| Carcinogenicity | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
| Mutagenicity | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
| Cytotoxicity | Inactive | Inactive | Active (0.70) | Active (0.70) | Active (0.70) |
| Protein | PDB ID | Binding Energy | Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| PI3K | 4FA6 | −8.139 | Conventional Hydrogen Bond Carbon Hydrogen Bond Alkyl |
| AKT | 4GV1 | −8.494 | Conventional Hydrogen Bond Carbon Hydrogen Bond Alkyl Pi-Alkyl |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, B.; Luo, J.; Xu, B. Revealing Molecular Mechanisms of the Bioactive Saponins from Edible Root of Platycodon grandiflorum in Combating Obesity. Plants 2024, 13, 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13081123
Han B, Luo J, Xu B. Revealing Molecular Mechanisms of the Bioactive Saponins from Edible Root of Platycodon grandiflorum in Combating Obesity. Plants. 2024; 13(8):1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13081123
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Bincheng, Jinhai Luo, and Baojun Xu. 2024. "Revealing Molecular Mechanisms of the Bioactive Saponins from Edible Root of Platycodon grandiflorum in Combating Obesity" Plants 13, no. 8: 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13081123
APA StyleHan, B., Luo, J., & Xu, B. (2024). Revealing Molecular Mechanisms of the Bioactive Saponins from Edible Root of Platycodon grandiflorum in Combating Obesity. Plants, 13(8), 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13081123