Phytoremediation of Oil-Contaminated Soil by Tagetes erecta L. Combined with Biochar and Microbial Agent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons (TPH) Degradation Efficiency Under Different Remediation Methods
2.2. Soil Petroleum n-Alkane Components Under Different Remediation Methods
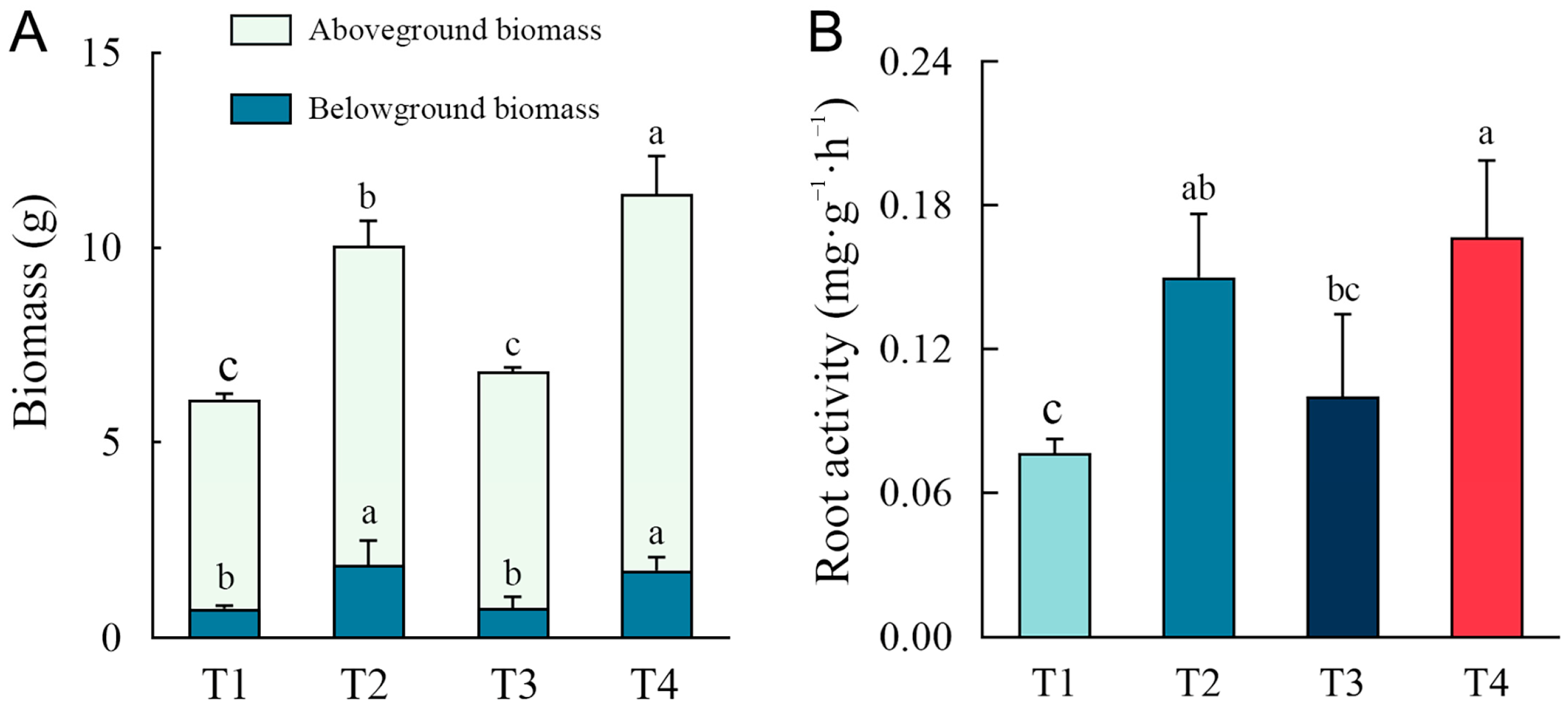
2.3. Plant Growth Under Different Remediation Methods
2.4. Soil Enzyme Activity Under Different Remediation Methods
2.5. Plant Antioxidant Enzyme Activity Under Different Remediation Methods
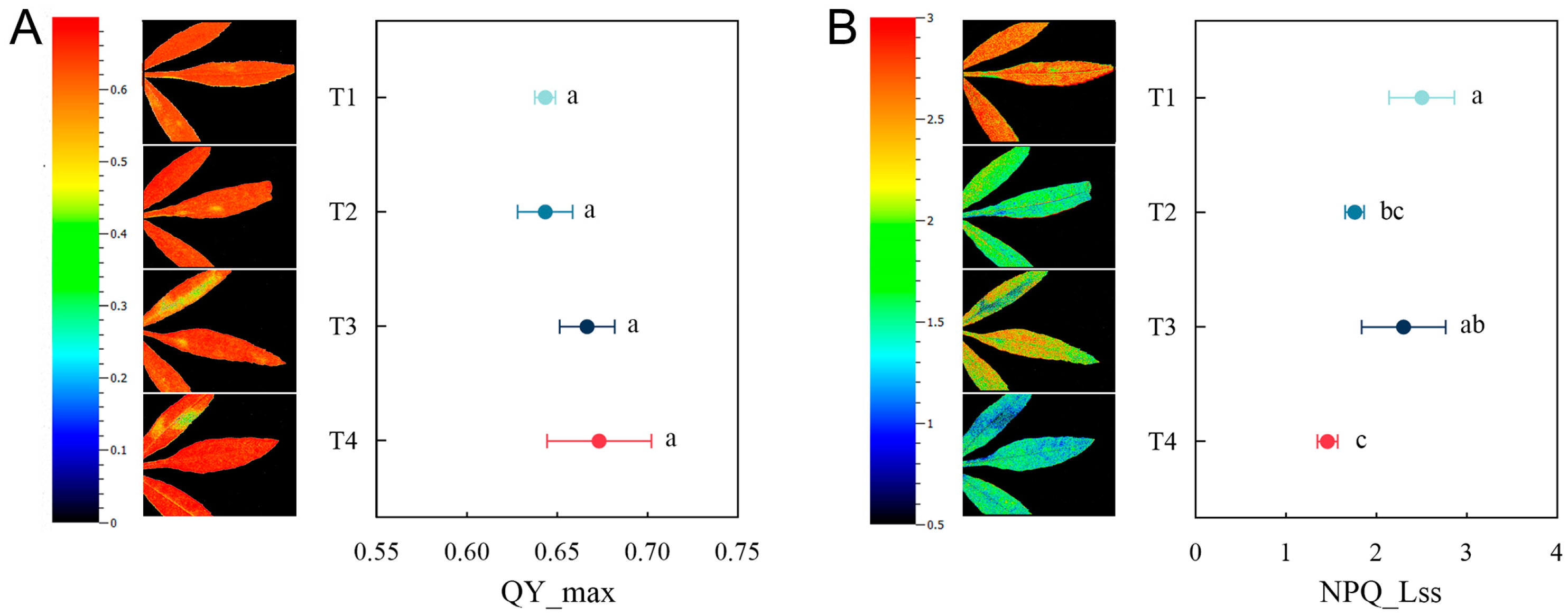
2.6. Plant Chlorophyll Fluorescence Under Different Remediation Methods
2.7. Correlation Analysis Between Remediation Methods and Physiological Indicators
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experiment Treatments and Design
4.2. Detection of Soil Total Petroleum Hydrocarbon
4.3. Analysis of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Components
4.4. Analysis of Plant Growth Performance
4.5. Analysis of Enzyme Activity
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Renegar, D.A.; Schuler, P.A.; Knap, A.H.; Dodge, R.E. TRopical oil pollution investigations in coastal systems [tropics]: A synopsis of impacts and recovery. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, M.W.; Von Lau, E.; Poh, P.E. A comprehensive guide of remediation technologies for oil contaminated soil—Present works and future directions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 14–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.C.; Wang, M.; Wang, F.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, Q.X. Eco-toxicity of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentati, O.; Lachhab, R.; Ayadi, M.; Ksibi, M. Toxicity assessment for petroleum contaminated soil using terrestrial invertebrates and plant bioassays. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 2989–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, I.I.; Nawawi, M.G.M.; Mohd, Z.J.; Farah, B.S. Environmental effects from petroleum product transportation spillage in Nigeria: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2023, 31, 1719–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoff, R.Z. Bioremediation: An overview of its development and use for oil spill cleanup. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1993, 26, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghio, M.; Aulenta, F.; Vaiopoulou, E.; Franzetti, A.; Arends, J.B.A.; Sherry, A.; Suárez-Suárez, A.; Head, I.M.; Bestetti, G.; Rabaey, K. Electrobioremediation of oil spills. Water Res. 2017, 114, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, L.A.; Reynolds, C.M. Phytodegradation of organic compounds. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2004, 15, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlik, M.; Plociniczak, T.; Thijs, S.; Pintelon, I.; Vangronsveld, J.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Comparison of two inoculation methods of endophytic bacteria to enhance phytodegradation efficacy of an aged petroleum hydrocarbons polluted soil. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante-Badu, B.; Kgorutla, L.E.; Li, S.S.; Danso, P.O.; Xue, Z.; Qiang, G. Phytoremediation of organic and inorganic compounds in a natural and an agricultural environment: A review. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 6875–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.H.A.; Kiyani, A.; Mirza, C.R.; Butt, T.A.; Barros, R.; Ali, B.; Iqbal, M.; Yousaf, S. Ornamental plants for the phytoremediation of heavy metals: Present knowledge and future perspectives. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambhu, A.; Satapanajaru, T.; Somsamak, P.; Pengthamkeerati, P.; Chokejaroenrat, C.; Muangkaew, K.; Nonthamit, K. Green cleanup of styrene-contaminated soil by carbon-based nanoscale zero-valent iron and phytoremediation: Sunn hemp (Crotalaria juncea), zinnia (Zinnia violacea Cav.), and marigold (Tagetes erecta L.). Heliyon 2024, 10, e27499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, M.; Wang, Y.J.; Yu, J.Y.; Xiao, M.; Jiang, L.F.; Yang, J.; Fang, C.M.; Chen, J.A.; Li, B. Understanding plant-microbe interactions for phytoremediation of petroleum-polluted soil. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.Y.; Liu, W.X.; Wang, B.B.; Wang, Q.L.; Luo, Y.M.; Franks, A.E. PGPR enhanced phytoremediation of petroleum contaminated soil and rhizosphere microbial community response. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.X.; Johnson, D.W.; Fu, S.L. Rhizosphere effects on decomposition: Controls of plant species, phenology, and fertilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Wei, S.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Masek, O.; Khan, M.A.; Li, D.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lu, W.K.; Su, X.S.; et al. Rhizosphere effect on the relationship between dissolved organic matter and functional genes in contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.Y.; Zhang, L.H.; Zhang, J.C.; Ren, L.H.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.L.; Chen, A.W. Physicochemical features, metal availability and enzyme activity in heavy metal-polluted soil remediated by biochar and compost. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Niazi, N.K.; Hassan, N.E.E.; Bibi, I.; Wang, H.L.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ok, Y.S.; Bolan, N.; Rinklebe, J. Wood-based biochar for the removal of potentially toxic elements in water and wastewater: A critical review. Int. Mater. Rev. 2019, 64, 216–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Hoang, S.A.; Beiyuan, J.Z.; Gupta, S.; Hou, D.Y.; Karakoti, A.; Joseph, S.; Jung, S.; Kim, K.H.; Kirkham, M.B.; et al. Multifunctional applications of biochar beyond carbon storage. Int. Mater. Rev. 2022, 67, 150–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.; Li, Y.E.; Saba, T.; Wu, J.S.; Bashir, S.; Gatasheh, M.K.; Diao, Z.H.; Chen, Z.B. Temperature responsiveness of soil carbon fractions, microbes, extracellular enzymes and CO2 emission: Mitigating role of texture. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Liang, D.L.; Liu, J.J.; Xie, J.Y. Ecotoxicological effects of copper and selenium combined pollution on soil enzyme activities in planted and unplanted soils. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, A.T.; Lewu, F.B.; Mulidzi, R.; Ncube, B. The biological activities of β-glucosidase, phosphatase and urease as soil quality indicators: A review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2017, 17, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.W.; Wu, Y.; Chen, W.J.; Sun, W.; Wang, Z.H.; Liu, G.B.; Xue, S. Soil enzyme kinetics and thermodynamics in response to long-term vegetation succession. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safinowski, M.; Griebler, C.; Meckenstock, R.U. Anaerobic cometabolic transformation of polycyclic and heterocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Evidence from laboratory and field studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4165–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Zoppini, A. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, S.O. Use of soil enzymes as indicators for contaminated soil monitoring and sustainable management. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Jung, J.; Hyun, S.; Park, H.; Park, W. Effects of nutritional input and diesel contamination on soil enzyme activities and microbial communities in antarctic soils. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.H.; Huang, Y.; Su, J.Q.; Gao, Z.; Li, S.Q.; Nan, Z.R. Temporal changes of metal bioavailability and extracellular enzyme activities in relation to afforestation of highly contaminated calcareous soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Annibale, A.; Ricci, M.; Quaratino, D.; Federici, F.; Fenice, M. Panus tigrinus efficiently removes phenols, color and organic load from olive-mill wastewater. Res. Microbiol. 2004, 155, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Dangi, A.K.; Shukla, P. Contemporary enzyme based technologies for bioremediation: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 210, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.L.; Zhang, Q.J.; Li, D.Y.; Du, J.; Wang, C.; Qin, J.Y. Rapid degradation of long-chain crude oil in soil by indigenous bacteria using fermented food waste supernatant. Waste Manag. 2019, 85, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbaspour, A.; Zohrabi, F.; Dorostkar, V.; Faz, A.; Acosta, J.A. Remediation of an oil-contaminated soil by two native plants treated with biochar and mycorrhizae. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 254, 109755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prematuri, R.; Mardatin, N.F.; Irdiastuti, R.; Turjaman, M.; Wagatsuma, T.; Tawaraya, K. Petroleum hydrocarbons degradation in contaminated soil using the plants of the Aster family. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2020, 27, 4460–4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, P.F.; Wang, H.M.; Wang, K.F.; Lv, J.; Shi, F.C. Biochar-bacteria-plant combined potential for remediation of oil-contaminated soil. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1343366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Rajput, V.D.; Sharma, R.; Ghazaryan, K.; Minkina, T. Salinity stress and nanoparticles: Insights into antioxidative enzymatic resistance, signaling, and defense mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2023, 235, 116585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, V.; Qadir, S.U.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P. Impact of drought and heat stress individually and in combination on physio-biochemical parameters, antioxidant responses, and gene expression in Solanum lycopersicum. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.Y.; Chen, P.A.; Zhuang, B.W. The stomatal conductance and Fv/Fm as the indicators of stress tolerance of avocado seedlings under short-term waterlogging. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.B.; Gao, S.; Wang, G.C. High salt stress in the upper part of floating mats of Ulva prolifera, a species that causes green tides, enhances non–photochemical quenching. J. Phycol. 2019, 55, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bano, H.; Athar, H.U.R.; Zafar, Z.U.; Ogbaga, C.C.; Ashraf, M. Peroxidase activity and operation of photo-protective component of NPQ play key roles in drought tolerance of mung bean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilcziek]. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 172, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xun, F.F.; Xie, B.M.; Liu, S.S.; Guo, C.H. Effect of plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPR) and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) inoculation on oats in saline-alkali soil contaminated by petroleum to enhance phytoremediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2015, 22, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Wyszkowski, M. Activity of soil dehydrogenases, urease, and acid and alkaline phosphatases in soil polluted with petroleum. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2010, 73, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claassens, S.; Van Rensburg, L.; Riedel, K.J.; Bezuidenhout, J.J.; Van Rensburg, P.J.J. Evaluation of the efficiency of various commercial products for the bioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminated soil. Environmentalist 2006, 26, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.P.; Hatton, B.J.; Singh, B.; Cowie, A.L.; Kathuria, A. Influence of biochars on nitrous oxide emission and nitrogen leaching from two contrasting soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, J.; Ahmad, W.; Munsif, F.; Khan, A.; Zou, Z.Y. Advances and prospects of biochar in improving soil fertility, biochemical quality, and environmental applications. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1114752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilliam, R.S.; Glanville, H.C.; Wade, S.C.; Jones, D.L. Life in the ’charosphere’—Does biochar in agricultural soil provide a significant habitat for microorganisms? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Zhao, Z.P.; Bartlam, M.; Wang, Y.Y. Combination of biochar amendment and phytoremediation for hydrocarbon removal in petroleum-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2016, 23, 21219–21228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issaka, E.; Fapohunda, F.O.; Amu-Darko, J.N.O.; Yeboah, L.; Yakubu, S.; Varjani, S.; Ali, N.; Bilal, M. Biochar-based composites for remediation of polluted wastewater and soil environments: Challenges and prospects. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dike, C.C.; Hakeem, I.G.; Rani, A.; Surapaneni, A.; Khudur, L.; Shah, K.; Ball, A.S. The co-application of biochar with bioremediation for the removal of petroleum hydrocarbons from contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Sun, S.; Tang, F.; Chen, H.X.; Chen, S.Q.; Zhao, C.C.; Li, L. A novel chitosan-biochar immobilized microorganism strategy to enhance bioremediation of crude oil in soil. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, W.F.; Hufbauer, R.A.; Agrawal, A.A.; Bever, J.D.; Borowicz, V.A.; Gilbert, G.S.; Maron, J.L.; Mitchell, C.E.; Parker, I.M.; Power, A.G.; et al. Direct and interactive effects of enemies and mutualists on plant performance: A meta-analysis. Ecology 2007, 88, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atai, E.; Jumbo, R.B.; Cowley, T.; Azuazu, I.; Coulon, F.; Pawlett, M. Efficacy of bioadmendments in reducing the influence of salinity on the bioremediation of oil-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruf, M.; Brunner, I. Vitality of tree fine roots: Reevaluation of the tetrazolium test. Tree Physiol. 2003, 23, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rossum, M.W.; Alberda, M.; van der Plas, L.H. Role of oxidative damage in tulip bulb scale micropropagation. Plant Sci. 1997, 130, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maehly, A.C.; Chance, B. The assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods Biochem. Anal. 1954, 1, 357–424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.S.; Yang, F.L.; Yang, Y.; Xing, G.L.; Deng, C.P.; Shen, Y.T.; Luo, L.Q.; Li, B.Z.; Yuan, H.L. A proposal of “core enzyme” bioindicator in long-term Pb–Zn ore pollution areas based on topsoil property analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz–Ferreiro, J.; Gascó, G.; Gutiérrez, B.; Méndez, A. Soil biochemical activities and the geometric mean of enzyme activities after application of sewage sludge and sewage sludge biochar to soil. Biol. Fert. Soils 2012, 48, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, X.; Zheng, P.; Wang, H.; Wang, K.; Shi, C.; Shi, F. Phytoremediation of Oil-Contaminated Soil by Tagetes erecta L. Combined with Biochar and Microbial Agent. Plants 2025, 14, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14020243
Fang X, Zheng P, Wang H, Wang K, Shi C, Shi F. Phytoremediation of Oil-Contaminated Soil by Tagetes erecta L. Combined with Biochar and Microbial Agent. Plants. 2025; 14(2):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14020243
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Xin, Pufan Zheng, Haomin Wang, Kefan Wang, Cong Shi, and Fuchen Shi. 2025. "Phytoremediation of Oil-Contaminated Soil by Tagetes erecta L. Combined with Biochar and Microbial Agent" Plants 14, no. 2: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14020243
APA StyleFang, X., Zheng, P., Wang, H., Wang, K., Shi, C., & Shi, F. (2025). Phytoremediation of Oil-Contaminated Soil by Tagetes erecta L. Combined with Biochar and Microbial Agent. Plants, 14(2), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14020243





