Recent Advances in Sugarcane Leaf Scald Disease: Pathogenic Insights and Sustainable Management Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
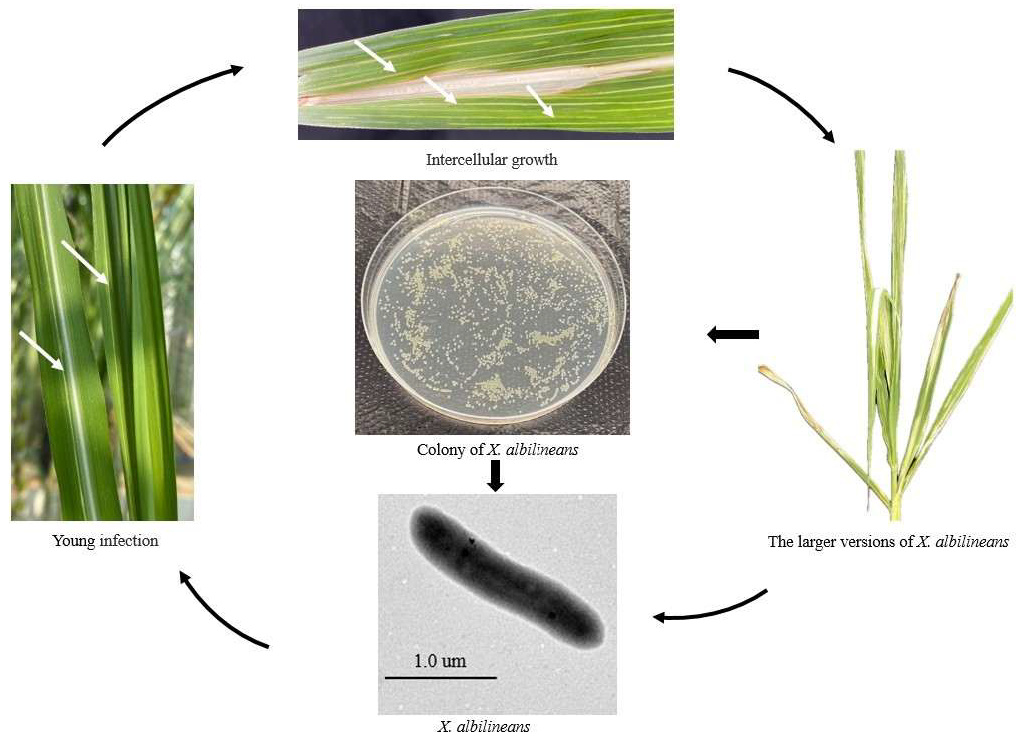
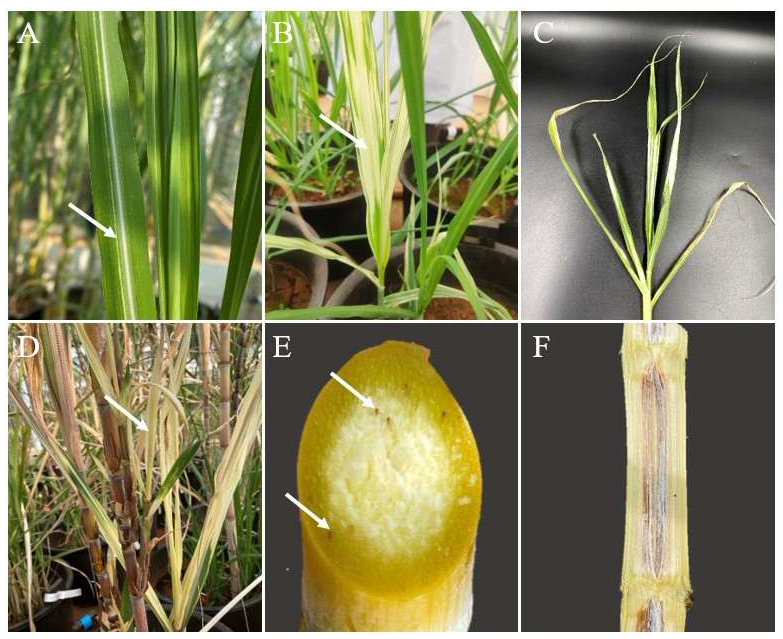
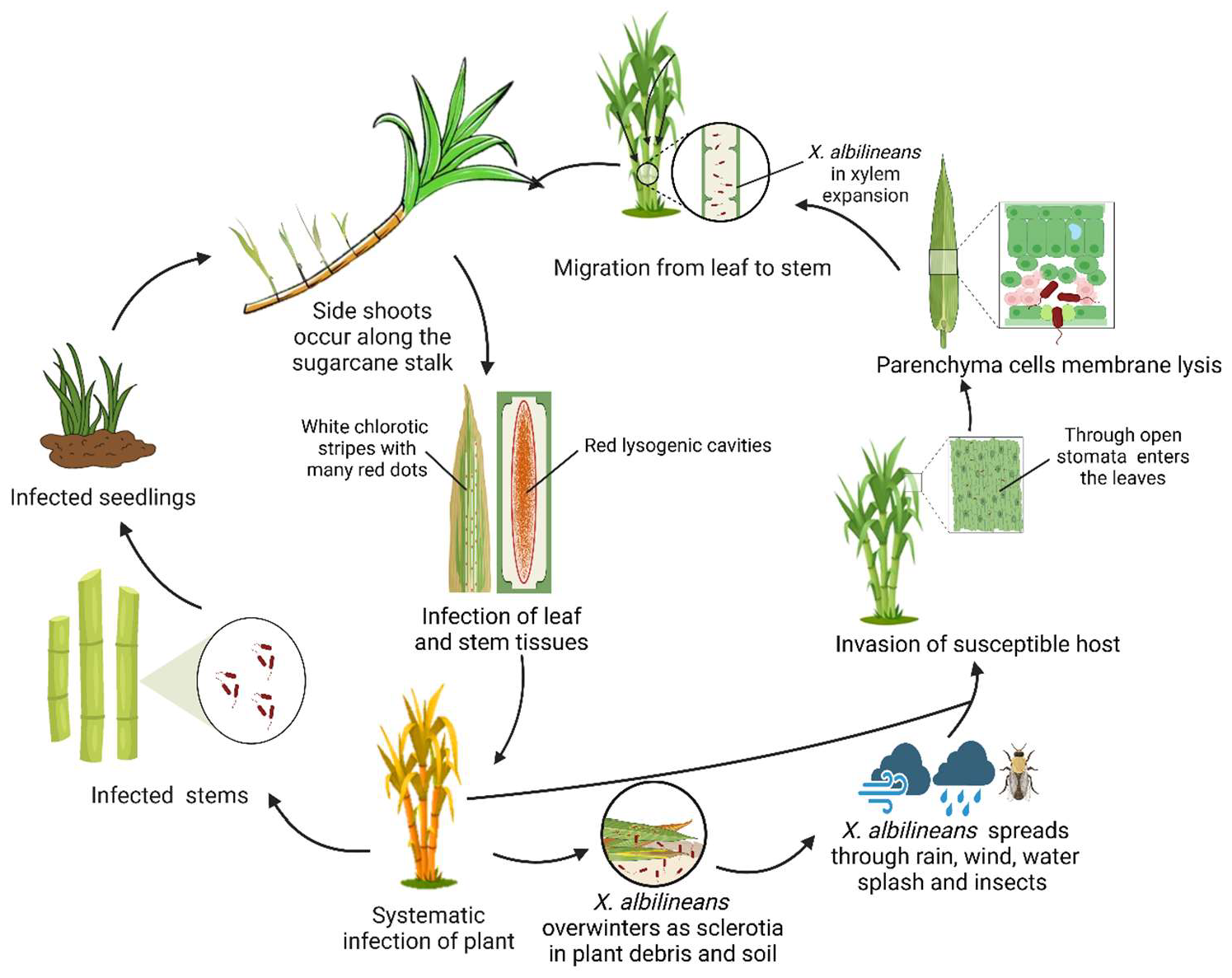
2. The Disease Cycle of Sugarcane Leaf Scald Disease
3. Influence of Environmental Factors on Sugarcane Leaf Scald
4. Research Progresses on Pathogenic Bacteria
4.1. Biological Properties of Sugarcane Leaf Scald Pathogens
4.2. Genomic Characterization of the Sugarcane Leaf Scald
4.3. Rapid Detection Methods of Pathogens
5. Host–Pathogen Interactions
5.1. Genetic Diversity and Pathogenic Variation in X. albilineans
5.2. Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
5.3. Sugarcane Immune Response Induced by Leaf Scald Pathogen
6. Integrated Disease Management (IDM) of Sugarcane Leaf Scald
6.1. Agricultural Practices for Sugarcane Leaf Scald Disease Control
6.1.1. Screening Methods and Breeding Materials for Resistance to Sugarcane Leaf Scald Disease
6.1.2. Agronomic Practices for the Integrated Management of Sugarcane Leaf Scald
6.2. Chemical Control of Sugarcane Leaf Scald Disease
6.3. Biological Control
7. Future Perspectives
7.1. Future Perspectives on Host–Pathogen Interactions
7.2. Precise Resistance Identification Method
7.3. Comprehensive Control of Leaf Scald in Sugarcane
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, T.; Wang, J.G.; Xu, C.H.; Lu, X.; Mao, J.; Lin, X.Q.; Kong, C.Y.; Li, C.J.; Li, X.J.; Tian, C.Y.; et al. Genetic engineering for enhancing sugarcane tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses. Plants 2024, 13, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.H.; Li, C.J.; Su, H.S.; Lu, X.; Li, X.J.; Liu, H.B.; Lin, X.Q.; Mao, J.; Zi, Q.Y.; Liu, X.L. Progress in the studies on abiotic stress resistance of sugarcane (Saccharum spp.). J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2017, 18, 483–493. [Google Scholar]
- Wickramasinghe, K.P.; Kong, C.Y.; Lin, X.Q.; Zhao, P.F.; Mehdi, F.; Li, X.J.; Liu, X.L.; Mao, J.; Lu, X. Photoperiodic and lighting treatments for flowering control and its genetic regulation in sugarcane breeding. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Zhu, P.J.; Lyu, P.; Tan, Q.L.; Pang, X.H.; Zhou, Q.G.; Lu, Y.F. Regulatory role of MicroRNAs in sugarcane. Biotechnology 2019, 29, 283–287+244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Muhammad, A.L. Leveraging the sugarcane CRISPR/Cas9 technique for genetic improvement of non-cultivated grasses. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1369416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrichs, R.; Otto, R.; Magalhães, A.; Meirelles, G.C. Importance of sugarcane in brazilian and world bioeconomy. In Knowledge-Driven Developments in the Bioeconomy; Economic Complexity and Evolution, Dabbert, S., Lewandowski, I., Weiss, J., Pyka, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresha, G.S.; Mahadevaiah, C.; Appunu, C. Biotechnological interventions for improving sucrose accumulation in sugarcane. In Sugarcane Biotechnology: Challenges and Prospects; Mohan, C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Lin, L.H.; Huang, H.Y.; Gao, S.J. Research advances in sugarcane leaf scald disease and its causal agent Xanthomonas albilineans. J. Plant Prot. 2019, 46, 257–265. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Xiong, L.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Khan, A.; Powell, C.A.; Chen, B.; Zhang, M. VirB11, a traffic ATPase, mediated flagella assembly and type IV pilus morphogenesis to control the motility and virulence of Xanthomonas albilineans. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 25, pe70001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Bao, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Du, J.; Khan, A.; Khan, M.T.; Powell, C.A.; Chen, B. Diffusible signal factor (DSF)-mediated quorum sensing modulates swarming in Xanthomonas albilineans. Phytopathology 2024, 115, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.T.; Zhang, T.J.; Fang, Y.; Pan, C.P.; Fu, H.Y.; Gao, S.J. Nano-selenium enhances sugarcane resistance to Xanthomonas albilineans infection and improvement of juice quality. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 254, 114759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La, O.; Hechavarría, M.; Puchades Izaguirre, Y.; Pérez Pérez, Y.; Michavila, G.; Casas González, M.A.; Pérez Pérez, J.; Carvajal Jaime, O.; Montalván Delgado, J.; Pena Malavera, A.; et al. Assessment of sugarcane cultivars with stable reaction to Xanthomonas albilineans under mechanical inoculation conditions. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2022, 47, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, P.; Bailey, R.A.; Comstock, J.C.; Croft, B.J.; Saumtally, A.S. A Guide to Sugarcane Diseases; International Society of Sugarcane Technologists: Montpellier, France, 2000; pp. 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ntambo, M.S.; Meng, J.Y.; Rott, P.C.; Royer, M.; Lin, L.H.; Zhang, H.L.; Gao, S.J. Identification and characterization of Xanthomonas albilineans causing sugarcane leaf scald in China using multilocus sequence analysis. Plant Pathol. 2019, 68, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M. Sugarcane Cultivation in China; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1985; pp. 431–443. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.N. Distribution and classification of sugarcane diseases and control of main diseases in Guangdong province. Sugarcane Cane Sugar 1987, 5, 50–52. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.D.; Li, C.C.; Pan, C.Z.; Zhang, X.B. Sugarcane diseases in China. Sugarcane 1997, 4, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G. People’s Republic of China imported plant quarantine pest list. Pest Mark. Inf. 2007, 13, 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Shan, H.L.; Li, W.F.; Cang, X.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Yin, J.; Luo, Z.M.; Huang, Y.K. First report of sugarcane leaf scald caused by Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Downson in the province of Guangxi, China. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Shan, H.L.; Li, J.; Li, W.F.; Cang, X.Y.; Luo, Z.M.; Yin, J.; Huang, Y.K. Identification and phylogenetic analysis of Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowson based on multiple gene sequences in Yunnan province, China. Sugar Tech 2019, 21, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Xu, Z.X.; Lin, Y.; Mao, L.R.; Wang, W.H.; Deng, Z.H.; Huang, M.T.; Gao, S.J. First report of Xanthomonas albilineans causing leaf scald on two chewing cane clones in Zhejiang province, China. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.H.; Zhao, J.Y.; Fu, H.Y.; Shi, Y.Y.; Su, J.B.; Liu, J.R. Molecular detection and identification of Xanthomonas albilineans causing leaf scald of sugarcane in Zhanjiang, Guangdong province of China. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2022, 23, 731–737. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.W.; Li, Y.H.; Lu, H.F.; Shan, H.L.; Li, J.; Wei, B.C.; Shi, H.D.; Zhang, R.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Huang, Y.K. Investigation and molecular detection of sugarcane leaf scald disease caused by Xanthomonas albilineans in Yizhou, Guangxi. Plant Quar. 2023, 37, 4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricaud, C.; Ryan, C.C. Leaf Scald; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 39–53. [Google Scholar]
- Rott, P.; Soupa, D.; Brunet, Y.; Feldmann, P.; Letourmy, P. Leaf scald (Xanthomonas albilineans) incidence and its effect on yield in seven sugarcane cultivars in Guadeloupe. Plant Pathol. 1995, 44, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhao, J.Y.; Zhou, J.R.; Ntambo, M.S.; Xu, P.Y.; Rott, P.C.; Gao, S.J. Molecular detection and quantification of Xanthomonas albilineans in juice from symptomless sugarcane stalks using a real-time quantitative PCR assay. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 3451–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, J.W.; Grisham, M.P. Sugarcane leaf scald distribution, symptomatology, and effect on yield in Louisiana. Plant Dis. 1994, 78, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klett, P.; Rott, P. Inoculum sources for the spread of leaf scald disease of sugarcane caused by Xanthomonas albilineans in Guadeloupe. J. Phytopathol. 1994, 142, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.Y.; Ntambo, M.S.; Rott, P.C.; Fu, H.Y.; Huang, M.T.; Zhang, H.L.; Gao, S.J. Identification of differentially expressed proteins in sugarcane in response to infection by Xanthomonas albilineans using iTRAQ quantitative proteomics. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitaitis, R.; Walcott, R. The epidemiology and management of seedborne bacterial diseases. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2007, 45, 371–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, R.P.; Vorhölter, F.J.; Potnis, N.; Jones, J.B.; Van Sluys, M.A.; Bogdanove, A.J.; Dow, J.M. Pathogenomics of Xanthomonas: Understanding bacterium–plant interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.Q.; Potnis, N.; Dow, M.; Vorhölter, F.J.; He, Y.Q.; Becker, A.; Teper, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, N.; Bleris, L.; et al. Mechanistic insights into host adaptation, virulence and epidemiology of the phytopathogen Xanthomonas. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugrois, J.H.; Boisne-Noc, R.; Champoiseau, P.; Rott, P. The revisited infection cycle of Xanthomonas albilineans, the causal agent of leaf scald of sugarcane. Funct. Plant Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 6, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, M.J.; Rott, P.; Baudin, P.; Dean, J.L. Evaluation of selective media and immunoassays for detection of Xanthomonas albilineans, the causal agent of sugarcane leaf scald disease. Plant Dis. 1994, 78, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.H.; Ntambo, M.S.; Rott, P.C.; Wang, Q.N.; Lin, Y.H.; Fu, H.Y.; Gao, S.J. Molecular detection and prevalence of Xanthomonas albilineans, the causal agent of sugarcane leaf scald, in China. Crop Prot. 2018, 109, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.Y.; Wei, J.J.; Zhang, X.Q.; Zhang, B.Q.; Song, X.P.; Li, D.W.; Qin, Z.Q.; Li, Y.R. Isolation and identification of the pathogens causing sugarcane leaf scald in Guangxi province, in China. Plant Quar. 2019, 33, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- de Almeida Ramos, E.T.; Meneses, C.H.S.G.; Vidal, M.S.; Baldani, J.I. Characterisation and action mode of Gluconacin, a bacteriocin with antimicrobial activity against Xanthomonas albilineans. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2022, 180, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S.; Li, M.L.; Du, J.X.; Zhang, M.Q. Ultrastructure of sugarcane leaves and stem tissue infected by Xanthomonas albilineans. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2022, 52, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.X.; Li, Y.S.; Li, M.L.; Chen, W.H.; Zhang, M.Q. Evaluation of resistance to leaf scald disease in different sugarcane genotypes. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2022, 55, 4118–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholthof, K.B.G. The disease triangle: Pathogens, the environment and society. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes-Romero, B.; Pérez-Rodríguez, P.; Rott, P.; Valdez-Balero, A.; Osnaya-González, M.; Robledo-Paz, A.; Hernández-Juárez, C.; Crossa, J.; Rosas-Saito, G.H.; Silva-Rojas, H.V. Distribution, phylogeny, and pathogenicity of Xanthomonas albilineans causing sugarcane leaf scald in Mexico. Crop Prot. 2021, 150, 105799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugrois, J.H.; Boisne, R.; Rott, P. Leaf surface colonization of sugarcane by Xanthomonas albilineans and subsequent disease progress vary according to the host cultivar. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champoiseau, P.; Rott, P.; Daugrois, J.H. Epiphytic populations of Xanthomonas albilineans and subsequent sugarcane stalk infection are linked to rainfall in Guadeloupe. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duttamajumder, S.K. Fluff transmission of Xanthomonas albilineans the incitant of leaf scald disease of sugarcane. Curr. Sci. 1990, 59, 744–745. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, R.G. Xanthomonas albilineans and the antipathogenesis approach to disease control. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2001, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielnichuk, N.; Bianco, M.I.; Yaryura, P.M.; Bertani, R.P.; Toum, L.; Daglio, Y.; Colonnella, M.A.; Lizarraga, L.; Castagnaro, A.P.; Vojnov, A.A. Virulence factors analysis of native isolates of Xanthomonas albilineans and Xanthomonas sacchari from Tucumán, Argentina, reveals differences in pathogenic strategies. Plant Pathol. 2021, 70, 1072–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, M.C.M.; Bini, A.P.; Prado, R.M.; Piccolo, M.C.; Gratão, P.L. Silicon induces resistance to leaf scald in sugarcane under water deficit. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, A.B.; Mary, L.T. Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 811–817. [Google Scholar]
- Saddler, G.S.; Bradbury, J.F. Xanthomonas. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic of Archaea and Bacteria; in association with Bergey’s Manual Trust; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieretti, I.; Royer, M.; Barbe, V.; Carrere, S.; Koebnik, R.; Cociancich, S.; Couloux, A.; Darrasse, A.; Gouzy, J.; Jacques, M.; et al. The complete genome sequence of Xanthomonas albilineans provides new insights into the reductive genome evolution of the xylemlimited Xanthomonadaceae. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.L.; Ntambo, M.S.; Rott, P.C.; Chen, G.; Chen, L.L.; Huang, M.T.; Gao, S.J. Complete genome sequence reveals evolutionary and comparative genomic features of Xanthomonas albilineans causing sugarcane leaf scald. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, R.P.; Turrini, P.C.G.; Bonadio, D.T.; Zerillo, M.M.; Berselli, A.P.; Creste, S.; Van Sluys, M.A. Genome organization of four Brazilian Xanthomonas albilineans strains does not correlate with aggressiveness. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e02802-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieretti, I.; Pesic, A.; Petras, D.; Royer, M.; Süssmuth, R.D.; Cociancich, S. What makes Xanthomonas albilineans unique amongst Xanthomonads? Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauben, L.; Vauterin, L.; Swings, J.; Moore, E.R. Comparison of 16S ribosomal DNA sequences of all Xanthomonas species. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, V.D.; Fernandez, E.; Cunha, M.G.; Pieretti, I.; Hincapie, M.; Roumagnac, P.; Comstock, J.C.; Rott, P. Comparison of loop-mediated isothermal amplification, polymerase chain reaction, and selective isolation assays for detection of Xanthomonas albilineans from sugarcane. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2018, 43, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.B.; Grisham, M.P.; Burner, D.M. A polymerase chain reaction protocol for the detection of Xanthomonas albilineans, the causal agent of sugarcane leaf scald disease. Plant Dis. 1997, 81, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.B.; Grisham, M.P.; Burner, D.M.; Legendre, B.L.; Wei, Q. Development of polymerase chain reaction primers highly specific for Xanthomonas albilineans, the causal bacterium of sugarcane leaf scald disease. Plant Dis. 1999, 83, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.K.; Comstock, J.C.; Hatziloukas, E.; Schaad, N.W. Comparison of PCR, BIO-PCR, DIA, ELISA and isolation on semi selective medium for detection of Xanthomonas albilineans, the causal agent of leaf scald of sugarcane. Plant Pathol. 1999, 48, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garces, F.F.; Gutierrez, A.; Hoy, J.W. Detection and quantification of Xanthomonas albilineans by qPCR and potential characterization of sugarcane resistance to leaf scald. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persley, G.J. Pathogenic variation in Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowson, the causal agent of leaf-scald disease of sugar cane. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 1973, 26, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champoiseau, P.; Daugrois, J.H.; Pieretti, I.; Cociancich, S.; Royer, M.; Rott, P. High variation in pathogenicity of genetically closely related strains of Xanthomonas albilineans, the sugarcane leaf scald pathogen, in Guadeloupe. Phytopathology 2006, 96, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta-Lara, M.; Rojas-Martinez, R.I.; Bautista-Calles, J.; Reyes-Lopez, D.; Becerril-Herrera, M.; Romero-Arenas, O.; Franco-Mora, O.; Jimenez-Garcia, D.; Aragon-Garcia, A.; Simon-Baez, A.; et al. Genetic and pathogenic diversity of Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowson, in Mexico. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 4, 312–319. [Google Scholar]
- Rott, P.; Arnaud, M.; Baudin, P. Serological and lysotypical variability of Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowson, causal agent of sugarcane leaf scald disease. J. Phytopathol. 1986, 116, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, P.; Davis, M.J.; Baudin, P. Serological variability in Xanthomonas albilineans, causal agent of leaf scald disease of sugarcane. Plant Pathol. 1994, 43, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.M.; Schenck, S.; Benedict, A.A. Differentiation of Xanthomonas albilineans strains with monoclonal antibody reaction patterns and DNA fingerprints. Plant Pathol. 1996, 45, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.J.; Rott, P.; Warmuth, C.J.; Chatenet, M.; Baudin, P. Intraspecific genomic variation within Xanthomonas albilineans, the sugarcane leaf scald pathogen. Phytopathology 1997, 87, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieretti, I.; Royer, M.; Barbe, V.; Carrere, S.; Koebnik, R.; Couloux, A.; Darrasse, A.; Gouzy, J.; Jacques, M.A.; Lauber, E.; et al. Genomic insights into strategies used by Xanthomonas albilineans with its reduced artillery to spread within sugarcane xylem vessels. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.Y.; Li, Y.S.; Li, M.L.; Zhang, G.Y.; Chen, B.S.; Zhang, M.Q. Identification and pathogenicity analysis of Xanthomonas albilineans causing sugarcane leaf scald in Guangxi. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2022, 52, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.T.; Ntambo, M.S.; Zhao, J.Y.; Talha, J.; Shi, Y.; Fu, H.Y.; Huang, M.T.; Gao, S.J. Genetic divergence and population structure of Xanthomonas albilineans strains infecting Saccharum spp. Hybrid and Saccharum officinarum. Plants 2023, 12, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L.; Huang, H.B.; Bian, Y.T.; Deng, Z.H.; Gao, S.J.; Zhang, H.L. Advances in albicidin. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 2738–2753. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Bao, Y.; Li, Y.; Akbar, S.; Wu, G.; Du, J.; Wen, R.; Chen, B.; Zhang, M. Comparative genome analysis unravels pathogenicity of Xanthomonas albilineans causing sugarcane leaf scald disease. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marguerettaz, M.; Pieretti, I.; Gayral, P.; Puig, J.; Brin, C.; Cociancich, S.; Poussier, S.; Rott, P.; Royer, M. Genomic and evolutionary features of the SPI-1 type III secretion system that is present in Xanthomonas albilineans but is not essential for xylem colonization and symptom development of sugarcane leaf scald. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, R.G.; Patil, S.S. The relation of blocked chloroplast differentiation to sugarcane leaf scald disease. Phytopathology 1983, 73, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, R.G.; Patil, S.S. Correlation between albicidin production and chlorosis induction by Xanthomonas albilineans, the sugarcane leaf scald pathogen. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1987, 30, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, P.C.; Costet, L.; Davis, M.J.; Frutos, R.; Gabriel, D.W. At least two separate gene clusters are involved in albicidin production by Xanthomonas albilineans. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royer, M.; Costet, L.; Vivien, E.; Bes, M.; Cousin, A.; Damais, A.; Pieretti, I.; Savin, A.; Megessier, S.; Viard, M.; et al. Albicidin pathotoxin produced by Xanthomonas albilineans is encoded by three large PKS and NRPS genes present in a gene cluster containing also several putative modifying, regulatory and resistance genes. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2004, 17, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortright, K.E.; Doss-Gollin, S.; Chan, B.K.; Turner, P.E. Evolution of bacterial cross-resistance to lytic phages and albicidin antibiotic. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 658374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, P.; Fleites, L.; Marlow, G.; Royer, M.; Gabriel, D.W. Identification of new candidate pathogenicity factors in the xylem-invading pathogen Xanthomonas albilineans by transposon mutagenesis. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieretti, I.; Cociancich, S.; Bolot, S.; Carrère, S.; Morisset, A.; Rott, P.; Royer, M. Full genome sequence analysis of two isolates reveals a novel Xanthomonas species close to the sugarcane pathogen Xanthomonas albilineans. Genes 2015, 6, 714–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.H.; Li, M.L.; Wu, D.; Du, J.X.; Xiong, L.Y.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, M.Q. Preliminary study on the phoq-mediated pathogenicity of Xanthomonas albilineans causing sugarcane leaf scald disease. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2024, 1–12, 2024–0403. [Google Scholar]
- Roper, M.C.; Greve, L.C.; Warren, J.G.; Labavitch, J.M.; Kirkpatrick, B.C. Xylella fastidiosa requires polygalacturonase for colonization and pathogenicity in Vitis vinifera grapevines. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, A.G.; Sun, Q.; Roper, M.C.; Greve, L.C.; Kirkpatrick, B.; Labavitch, J.M. Cell wall-degrading enzymes enlarge the pore size of intervessel pit membranes in healthy and Xylella fastidiosa-infected grapevines. Plant Physiol. 2012, 152, 1748–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Almeida, R.P.; Lindow, S. Living in two worlds: The plant and insect lifestyles of Xylella fastidiosa. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2008, 46, 243–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rott, P.; Fleites, L.A.; Mensi, I.; Sheppard, L.; Daugrois, J.H.; Dow, J.M.; Gabriel, D.W. The RpfCG two-component system negatively regulates the colonization of sugar cane stalks by Xanthomonas albilineans. Microbiology 2013, 159, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntambo, M.S.; Meng, J.Y.; Rott, P.C.; Henry, R.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Gao, S.J. Comparative transcriptome profiling of resistant and susceptible sugarcane cultivars in response to infection by Xanthomonas albilineans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Y.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.; Fu, H.Y.; Huang, M.T.; Rott, P.C.; Gao, S.J. Sugarcane responses to two strains of Xanthomonas albilineans differing in pathogenicity through a differential modulation of salicylic acid and reactive oxygen species. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1087525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhu, X.M.; Zhang, Y.R.; Cai, Y.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Liu, M.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Bao, J.D.; Lin, F.C. Research on the molecular interaction mechanism between plants and pathogenic fungi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaño-Pachón, D.M.; Mattiello, L. Draft genome sequencing of the sugarcane hybrid SP80-3280. F1000Res 2017, 6, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Hua, X.; Ma, X.; Zhu, F.; Jones, T.; Zhu, X.; Bowers, J.; et al. Allele-defined genome of the autopolyploid sugarcane Saccharum spontaneum L. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Feng, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, C.; Lu, H.; Fan, D.; Yan, J.; Lu, Y.; Tian, Q.; et al. Chromosome-scale assembly and analysis of biomass crop Miscanthus lutarioriparius genome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Ge, C.; Xu, P.; Wang, S.; Cheng, S.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Hou, X.; Yu, T.; et al. The reference genome of Miscanthus floridulus illuminates the evolution of Saccharinae. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qi, Y.; Pan, H.; Tang, H.; Wang, G.; Hua, X.; Wang, Y.; Lin, L.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Genomic insights into the recent chromosome reduction of autopolyploid sugarcane Saccharum spontaneum. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearman, J.R.; Pootakham, W.; Sonthirod, C.; Naktang, C.; Yoocha, T.; Sangsrakru, D.; Jomchai, N.; Tongsima, S.; Piriyapongsa, J.; Ngamphiw, C.; et al. A draft chromosome-scale genome assembly of a commercial sugarcane. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kui, L.; Majeed, A.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; He, L.; Di, Y.; Li, X.; Qian, Z.; Jiao, Y.; et al. A chromosome-level genome assembly for Erianthus fulvus provides insights into its biofuel potential and facilitates breeding for improvement of sugarcane. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, B.; Hua, X.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, R.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Yu, Z.; et al. A complete gap-free diploid genome in Saccharum complex and the genomic footprints of evolution in the highly polyploid Saccharum genus. Nat. Plants 2023, 9, 554–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, A.L.; Garsmeur, O.; Lovell, J.T.; Shengquiang, S.; Sreedasyam, A.; Jenkins, J.; Plott, C.B.; Piperidis, N.; Pompidor, N.; Llaca, V.; et al. The complex polyploid genome architecture of sugarcane. Nature 2024, 628, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yao, W.; Yu, Z.; Deng, Z.; Yu, J.; Kong, W.; Yu, X.; et al. A chromosomal-scale genome assembly of modern cultivated hybrid sugarcane provides insights into origination and evolution. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asnaghi, C.; D’Hont, A.; Glaszmann, J.; Rott, P. Resistance of sugarcane cultivar R570 to Puccinia melanocephala isolates from different geographic locations. Plant Dis. 2001, 85, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costet, L.; Cunff, L.L.; Royaert, S.; Raboin, L.M.; Hervouet, C.; Toubi, L.; Telismart, H.; Garsmeur, O.; Rousselle, Y.; Pauquet, J.; et al. Haplotype structure around Bru1 reveals a narrow genetic basis for brown rust resistance in modern sugarcane cultivars. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 825–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racedo, J.; Perera, M.F.; Bertani, R.; Funes, C.; González, V.; Cuenya, M.I.; D’Hont, A.; Welin, B.; Castagnaro, A.P. Bru 1 gene and potential alternative sources of resistance to sugarcane brown rust disease. Euphytica 2013, 191, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parco, A.S.; Avellaneda, M.C.; Hale, A.H.; Hoy, J.W.; Kimbeng, C.A.; Pontif, M.J.; Gravois, K.A.; Baisakh, N. Frequency and distribution of the brown rust resistance gene Bru 1 and implications for the Louisiana sugarcane breeding programme. Plant Breed. 2014, 133, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parco, A.S.; Hale, A.L.; Avellaneda, M.C.; Hoy, J.W.; Kimbeng, C.A.; Pontif, M.J.; McCord, P.H.; Ayala-Silva, T.; Todd, J.R.; Baisakh, N. Distribution and frequency of Bru 1, a major brown rust resistance gene, in the sugarcane world collection. Plant Breed. 2017, 136, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Xu, J.L.; Birch, R.G. Engineered detoxification confers resistance against a pathogenic bacterium. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, A.F.; Hoy, J.W.; Kimbeng, C.A.; Baisakh, N. Identification of genomic regions controlling leaf scald resistance in sugarcane using a bi-parental mapping population and selective genotyping by sequencing. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Lu, Y.J.; Gao, S.J.; Fatima, M.; Ming, R.; Yue, J. Transcriptome analysis of sugarcane reveals rapid defense response of SES208 to Xanthomonas albilineans in early infection. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, J.Y.; Shi, Y.; Fu, H.Y.; Huang, M.T.; Meng, J.Y.; Gao, S.J. Systematic and functional analysis of non-specific lipid transfer protein family genes in sugarcane under Xanthomonas albilineans infection and salicylic acid treatment. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1014266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, T.; Zhou, J.R.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.T.; Wang, Q.N.; Gao, S.J. Identification and expression profiling of WRKY family genes in sugarcane in response to bacterial pathogen infection and nitrogen implantation dosage. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 917953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.P.; Robinson, P.E. Leaf scald. In Sugarcane Diseases of the World; Martin, J.P., Abbott, E.V., Hughes, C.O., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publisher: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1961; Volume I, pp. 79–107. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, C.Y.; Mao, J.; Liu, X.L.; Lin, X.Q.; Wei, C.Y.; Xu, C.H.; Li, X.J.; Liu, H.B.; Li, C.J.; Lu, X. Concentration determination for pathogenic bacteria suspension of sugarcane leaf scald disease by spectrophotometry. Sugar Crops China 2022, 44, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Du, J.; Li, M.; Yao, W.; Zhang, M. Field Evaluation of Sugarcane Genotypes for Resistance to Leaf Scald Disease in China. Sugar Tech 2025, 27, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.Y.; Zhang, T.; Peng, W.J.; Duan, Y.Y.; Xu, Z.X.; Lin, Y.H.; Gao, S.J. Identification of resistance to leaf scald in newly released sugarcane varieties at seedling stage by artificial inoculation. Acta Agron. Sin. 2021, 47, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, H. The aluminum-cap method for testing sugarcane varieties against leaf scald disease. Phytopathology 1965, 55, 317–319. [Google Scholar]
- Rott, P.; Mohamed, I.S.; Klett, P.; Soupa, D.; Saint, A.; Feldmann, P.; Letourmy, P. Resistance to leaf scald disease is associated with limited colonization of sugarcane and wild relatives by Xanthomonas albilineans. Phytopathology 1997, 87, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro, T.S.S.K.; Rao, G.V.N. Reaction of sugarcane clones to leaf scald disease incited by Xanthomonas albilineans. J. Mycol. Plant Pathol. 2006, 36, 241–243. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, A.; Garces, F.F.; Hoy, J.W. Evaluation of resistance to leaf scald by quantitative PCR of Xanthomonas albilineans in sugarcane. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.S.; Zhao, J.Y.; Javed, T.; Ali, A.; Huang, M.T.; Fu, H.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Gao, S.J. Insights into reactive oxygen species production-scavenging system involved in sugarcane response to Xanthomonas albilineans infection under drought stress. Plants 2024, 13, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCord, P.; Zhao, D.; Abbott, T.; Comstock, J.C.; Singh, M.P.; Davidson, R.W.; Gordon, V.S.; Sandhu, H.S.; Sood, S.G.; Baltazar, M.; et al. Registration of ‘CP 09-2392’ sugarcane. J. Plant Regist. 2019, 13, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; McCord, P.; Sandhu, H.S.; Zhao, D.; Davidson, R.W.; Gordon, V.; Sood, S.; Comstock, J.C.; Singh, M.P.; Baltazar, M. Registration of ‘CP 10-2195’ sugarcane. J. Plant Regist. 2019, 13, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, J.R.; Hale, A.L.; Pan, Y.B.; Tew, T.L.; Milligan, S.B.; Dufrene, J.E.O.; Duet, J.M.J.; Verdun, D.L.; Landry, C.J.; Grisham, M.P.; et al. Registration of ‘HoCP 11-537’ sugarcane. J. Plant Regist. 2019, 13, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Comstock, J.C.; Glaz, B.; Edmé, S.J.; Davidson, R.W.; Gilbert, R.A.; Glynn, N.C.; Sood, S.; Sandhu, H.S.; McCorkle, K.; et al. Registration of ‘CP 05-1526’ sugarcane. J. Plant Regist. 2013, 7, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.W.; Sandhu, H.S.; McCord, P.; Comstock, J.C.; Edmé, S.J.; Zhao, D.; Glaz, B.; Sood, S.; Glynn, N.C.; Gilbert, R.A.; et al. Registration of ‘CP 06-2042’ Sugarcane. J. Plant Regist. 2017, 11, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravois, K.A.; Bischoff, K.P.; Hoy, J.W.; Reagan, T.E.; Pontif, M.J.; Kimbeng, C.A.; Hawkins, G.L.; Fontenot, D.P.; Sexton, D.R.; Orgeron, A.O. Registration of ‘L 03-371’sugarcane. J. Plant Regist. 2012, 6, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tew, T.L.; Dufrene, E.O.; Garrison, D.D.; White, W.H.; Grisham, M.P.; Pan, Y.B.; Richard, J.E.P.; Legendre, B.L.; Miller, J.D. Registration of ‘HoCP 00-950’ sugarcane. J. Plant Regist. 2009, 3, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.A.; Comstock, J.C.; Glaz, B.; Edmé, S.J.; Davidson, R.W.; Glynn, N.C.; Miller, J.D.; Tai, P.Y. Registration of ‘CP 00-1101’sugarcane. J. Plant Regist. 2008, 2, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, S.A.; Damann, K.E.; Hoy, J.W.; Grisham, M.P. Infectivity titration for assessing resistance to leaf scald among sugarcane cultivars. Plant Dis. 2001, 85, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andru, S.; Pan, Y.B.; Thongthawee, S.; Burner, D.M.; Kimbeng, C.A. Genetic analysis of the sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) cultivar ‘LCP 85-384’. I. Linkage mapping using AFLP, SSR, and TRAP markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 123, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.P.; Comstock, J.C.; Davidson, W.; Gordon, V.; Sandhu, H.S.; McCord, P.; Zhao, D.; Sood, S.; Baltazar, M.; McCorkle, K. Registration of ‘CP 06-2425’, ‘CP 06-2495’, ‘CP 06-2964’, ‘CP 06-3103’, and ‘CP 07-1313’ sugarcane for sand soils in Florida. J. Plant Regist. 2017, 11, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.W.; Gordon, V.S.; Sandhu, H.S.; McCord, P.; Zhao, D.; Comstock, J.C.; Singh, M.P.; Sood, S.; Baltazar, M.; McCorkle, K. Registration of ‘CP 09-1952’ Sugarcane. J. Plant Regist. 2018, 12, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, S.B.; Davidson, R.W.; Edmé, S.J.; Comstock, J.C.; Hu, C.J.; Holder, D.G.; Glaz, B.; Glynn, N.C.; Gilbert, R.A. Registration of ‘CPCL 97-2730’ sugarcane. J. Plant Regist. 2009, 3, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmé, S.J.; Davidson, R.W.; Gilbert, R.A.; Comstock, J.C.; Glynn, N.C.; Glaz, B.; del Blanco, I.A.; Miller, J.D.; Tai, P.Y. Registration of ‘CP 01-1372’ sugarcane. J. Plant Regist. 2009, 3, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.W.; Milligan, S.B.; Glaz, B.; Comstock, J.C.; Hu, C.J.; Glynn, N.C.; Edmé, S.J.; Holder, D.G.; Gilbert, R.A.; Sood, S.; et al. Registration of ‘CPCL 99-4455’ Sugarcane. J. Plant Regist. 2011, 5, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensi, I.; Girard, J.C.; Pieretti, I.; Larbre, F.; Roumagnac, P.; Royer, M.; Rott, P. First report of sugarcane leaf scald in Gabon caused by a highly virulent and aggressive strain of Xanthomonas albilineans. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 988–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, M.; José, S.S.; Cárdenas, E.; Rojas, R.I.; Flores, S.; Marín, M. Evaluación de resistencia de caña de azúcar (Saccharum officinarum L.) Co997 y MEX 64-1487, analizando colonización y dinámica poblacional de Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowson en tallos. Rev. Mex. Fitopatol. 2003, 21, 316–322. [Google Scholar]
- Huerta, M.; Ortega, L.D.; Landeros, C.; Fucikovsky, L.; Marín, M. Response of 10 sugarcane varieties to leaf scald [Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowson], in the central coast region of Veracruz. Agrociencia 2003, 37, 511–519. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.J.; Wei, C.Y.; Song, X.P.; Qin, Z.Q.; Tan, H.W.; Zhang, R.H.; Pang, T.; Wang, L.W.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.R. Sugarcane leaf scald disease in sugarcane planting areas of Beihai, Guangxi. J. South. Agric. 2018, 49, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.G. Varietal evaluation of sugarcane in Taiwan. Southwest. China J. Agric. Sci. 1996, 9, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.Y. Screening of Fungicides and Resistance Mechanism to Xanthomonas albilineans Causing Leaf Scald in Sugarcane. Master’s Thesis, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, China, 2023. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=1k070040j0410pm0sr5a0mw050768481&site=xueshu_se (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Li, M.R. Occurrence regulity and control of Xanthomonas albilineans in chewing cane. Fujian Agric. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, D.K.; Javed, T.; Yao, Y.; Zou, Z.Y.; Fu, H.Y.; Gao, S.J.; Xie, Y. Silicon enhancement for endorsement of Xanthomonas albilineans infection in sugarcane. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Chen, J.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Li, W.J.; Hang, C.Y.; Chen, J.W.; Hu, S.F.; Shen, W.K. Effect of ethylicin on prevention and control of sugarcane leaf scald and its promoting effect on growth. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2024, 1, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, L.R.; Lin, Y.; Wang, C.; Cai, M.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Lin, G.P.; Lin, Y. Effectiveness of several agents in the control of leaf scald of Guangdong yellow skin sugarcane. Bull. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 179–181. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Hong, D.K.; Chen, Y.H.; Gao, S.J.; Fu, H.Y.; Zheng, H.K.; Fang, Y.; Wang, J.D. Synergistic effects of organosilicon and Cu(OH)2 in controlling sugarcane leaf scald disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, Y.; Blanch, M.; Pinón, D.; Legaz, M.; Vicente, C. Antagonism of Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus (a sugarcane endosymbiont) against Xanthomonas albilineans (pathogen) studied in alginate—Immobilized sugarcane stalk tissues. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 99, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.M.; Zhang, T.J.; Shi, M.T.; Hong, D.K.; Gao, S.J.; Wang, J.D. Effects of exogenous spraying of jasmonic acid on the occurrence of sugarcane leaf scald. J. South. Agric. 2023, 7, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar]


| Strain | Size (Mb) | BioSample | %GC | Assembly | Scaffolds | CDS | Geographic Location | Collection | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xa04 | 3.78504 | SAMN24462201 | 62.98% | Complete | 1 | 3141 | Brazil: Sao Paulo | 2010 | [52] |
| Xa11 | 3.90843 | SAMN24462202 | 62.91% | Complete | 1 | 3255 | Brazil: Sao Paulo | 2010 | [52] |
| Xa21 | 3.95909 | SAMN24462203 | 62.88% | Complete | 1 | 3283 | Brazil: Sao Paulo | 2010 | [52] |
| Xa26 | 3.88559 | SAMN24462204 | 62.97% | Complete | 1 | 3283 | Brazil: Sao Paulo | 2010 | [52] |
| Xa-FJ1 | 3.75612 | SAMN12905433 | 62.97% | Complete | 2 | 2968 | China | 2015 | [51] |
| GPEPC73 | 3.85230 | SAMEA3138291 | 62.91% | Complete | 4 | 3105 | Guadeloupe | 2003 | [50] |
| HVO005 | 3.65265 | SAMN03262630 | 62.90% | Scaffold | 2 | 2912 | Burkina Faso | 1979 | [52] |
| HVO082 | 3.63602 | SAMN03262511 | 63.00% | Scaffold | 1 | 2878 | Burkina Faso | 1989 | [52] |
| CFBP2523 | 3.68418 | SAMN05526486 | 63.10% | Scaffold | 148 | 2996 | Fiji | 1961 | [52] |
| FIJ080 | 3.68125 | SAMN03257616 | 63.00% | Scaffold | 1 | 2929 | Fiji | 1961 | [52] |
| REU209 | 3.68727 | SAMN03262627 | 63.00% | Scaffold | 2 | 2921 | France | 1995 | [52] |
| REU174 | 3.86323 | SAMN03263614 | 62.80% | Scaffold | 29 | 3097 | France | 1995 | [52] |
| GAB266 | 3.79190 | SAMN03263609 | 62.90% | Scaffold | 4 | 3013 | Gabon | 2011 | [52] |
| GPEPC86 | 3.85143 | SAMN03262651 | 62.80% | Scaffold | 4 | 3158 | Guadeloupe | 2003 | [52] |
| GPEPC17 | 3.81135 | SAMN03262650 | 62.80% | Scaffold | 4 | 3122 | Guadeloupe | 2003 | [52] |
| MTQ032 | 3.80155 | SAMN03257639 | 62.90% | Scaffold | 4 | 3079 | Martinique | 1932 | [52] |
| PNG130 | 3.54265 | SAMN03262494 | 63.30% | Scaffold | 4 | 2868 | Papua New Guinea | 1993 | [52] |
| LKA070 | 3.66795 | SAMN03262508 | 63.10% | Scaffold | 2 | 2940 | Sri Lanka | 1962 | [52] |
| USA048 | 3.58204 | SAMN03262645 | 63.10% | Scaffold | 6 | 2828 | USA | 1986 | [52] |
| Xa23R1 | 3.54903 | SAMN03262642 | 63.10% | Scaffold | 4 | 2839 | USA | 1993 | [53] |
| XaFL07-1 | 3.79895 | SAMN03262647 | 62.90% | Scaffold | 6 | 3111 | USA | 2007 | [52] |
| Target Gene | Primer | Forward or Reverse Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) | Product Size/bp | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | Ala4/L1 | F | CCCGACTGGCTCCACCACTG | 360 bp | [56] |
| R | CAAGGCATCCACCGT | ||||
| ITS | PGBL1/PGBL2 | F | CTTTGGGTCTGTAGCTCAGG | 288 bp | [57] |
| R | GCCTCAAGGTCATATTCAGC | ||||
| ABC | XAF1/XAR1 | F | CCTGGTGATGACGCTGGGTT | 608 bp | [58] |
| R | CGATCAGCGATGCACGCAGT | ||||
| albicidin toxin biosynthesis gene | XaQf/XaQr | F | TTTGCGGTGTCGGTAAAGGAG | 148 bp | [59] |
| R | GCGATGGCACTAGGTACAGC |
| Grade | Symptom |
|---|---|
| Score 0 | Asymptomatic |
| Score 1 | One or two white pencil lines |
| Score 2 | More than two white pencil lines |
| Score 3 | Chlorotic or yellowing leaf |
| Score 4 | Leaf necrosis |
| Score 5 | Plant death |
| Resistance Evaluation | Disease Index (%) |
|---|---|
| High resistant | Disease index ≤ 5.0 |
| Resistant | 5.0 < Disease index ≤ 15.0 |
| Medium resistant | 15.0 < Disease index ≤ 30.0 |
| Susceptible | 30.0 < Disease index ≤ 50.0 |
| High susceptible | Disease index > 50.0 |
| No. | Resistance Materials | Source | LSD Resistance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | ||||
| 1 | CP09-2392 | Florida | Resistant | [117] |
| 2 | CP10-2195 | Florida | Resistant | [118] |
| 3 | HoCP00-950, L01-283, HoCP04-838 | Texas | Resistant | [119] |
| 4 | CP70-321, HoCP96-540, L07-57, Ho08-711, Ho08-717, HoCP08-726, L08-88, L08-92 | Gabrielle | Resistant | [115] |
| 5 | CP05-1526 | Florida | Resistant | [120] |
| 6 | CP72-2086 | Florida | Resistant | [121] |
| 7 | L99-233, L03-371 | Louisiana | Resistant | [122] |
| 8 | L97-128 | Florida | Resistant | [123] |
| 9 | CP00-1101 | Florida | Resistant | [124] |
| 10 | L88-63, CP79-318, CP65-357, LHo83-153 | Gabrielle | Resistant | [125] |
| 11 | LCP85-384 | Florida | Resistant | [126] |
| 12 | CP06-2425, CP06-2495, CP06-2964, CP06-3103, CP89-2143 | Florida | Resistant | [127] |
| 13 | CP78-1628 | Florida | Medium resistance | [117] |
| 14 | L99-226 | Texas | Medium resistance | [119] |
| 15 | CP09-1952 | Florida | Medium resistance | [128] |
| 16 | L01-299 | Louisiana | Medium resistance | [122] |
| 17 | CPCL97-2730 | Florida | Medium resistance | [129] |
| 18 | CP01-1372 | Florida | Medium resistance | [130] |
| 19 | CPCL99-4455 | Florida | Medium resistance | [131] |
| 20 | CP00-2180 | Florida | Medium resistance | [129] |
| 21 | CP07-1313, CL88-4730 | Florida | Medium resistance | [127] |
| France | ||||
| 22 | R570 | Guadeloupe | Resistant | [25] |
| 23 | FR95285, FR94129, FR88196 | Guadeloupe | Resistant | [42] |
| Gabon | ||||
| 24 | Co6415 | Franksville | High resistance | [132] |
| 25 | B8008 | Franksville | Resistant | [132] |
| México | ||||
| 26 | Co997 | Veracruz | Resistant | [133] |
| 27 | Q96, CP74-2005, RD75-11 | Veracruz | Resistant | [134] |
| Australia | ||||
| 28 | Co740, SP70-1423, Q84, Q90, Q110, Q115, Q117, Q120 | High resistance | [113] | |
| 29 | Q124 | Resistant | [113] | |
| Cuba | ||||
| 30 | C1051-73 | Jovellanos | Resistant | [12] |
| China | ||||
| 31 | Zhongzhe9,Zhongzhe2, GUC19, GUC8, Yunrui03-103, Yunrui05-649, Yunrui05-182, Yunrui05-367, Yunrui89-159, ROC22, Funong11601, Funong09-4059, Guitang02-467, Guitang08-297 | Guangxi | High resistance | [39] |
| 32 | Zhongzhe5, GUC13, GUC9, Yunrui03-394, ROC10, ROC23, ROC25, ROC1, Funong5, Funong07-3206, Guitang05-2605, Guitang00-245, GUC25, GUC35 | Guangxi | Resistant | [39] |
| 33 | Yuegan50, Funong09-7111, Zhongzhe10 | Fujian | Resistant | [111] |
| 34 | Zhongzhe13 | Fujian | Resistant | [116] |
| 35 | NCo310, F156, F160, F170, F173 | Taiwan | Resistant | [135] |
| 36 | Dezhe12-88, Funong11-2907Yuegan49, Zhongzhe1, Haizhe28, Yuegan51 | Guangxi, Guangdong | Medium resistance | [26] |
| 37 | Guitang40, Guitang08-120, Liucheng07-150, Yunzhe11-3898, Yuegan53, Mintang11-610, Yunzhe09-1601, Yuegan43 | Fujian | Medium resistance | [111] |
| 38 | Funong14-1854, Liucheng05-136, Yunzhe15-505 | Fujian | Medium resistance | [116] |
| 39 | Q42, Q50, Q98, Q813, POJ36, POJ2725, CP807, CP29-116, Co290, Co301, Co331, Co421, B4908 | Taiwan | Medium resistance | [135] |
| 40 | ROC19 | Taiwan | Medium resistance | [136] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, C.-Y.; Wickramasinghe, K.P.; Xu, C.-H.; Mao, J.; Liu, H.-B.; Kumar, T.; Lin, X.-Q.; Li, X.-J.; Tian, C.-Y.; Zhao, P.-F.; et al. Recent Advances in Sugarcane Leaf Scald Disease: Pathogenic Insights and Sustainable Management Approaches. Plants 2025, 14, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14040508
Kong C-Y, Wickramasinghe KP, Xu C-H, Mao J, Liu H-B, Kumar T, Lin X-Q, Li X-J, Tian C-Y, Zhao P-F, et al. Recent Advances in Sugarcane Leaf Scald Disease: Pathogenic Insights and Sustainable Management Approaches. Plants. 2025; 14(4):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14040508
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Chun-Yan, Kamal Priyananda Wickramasinghe, Chao-Hua Xu, Jun Mao, Hong-Bo Liu, Tanweer Kumar, Xiu-Qin Lin, Xu-Juan Li, Chun-Yan Tian, Pei-Fang Zhao, and et al. 2025. "Recent Advances in Sugarcane Leaf Scald Disease: Pathogenic Insights and Sustainable Management Approaches" Plants 14, no. 4: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14040508
APA StyleKong, C.-Y., Wickramasinghe, K. P., Xu, C.-H., Mao, J., Liu, H.-B., Kumar, T., Lin, X.-Q., Li, X.-J., Tian, C.-Y., Zhao, P.-F., & Lu, X. (2025). Recent Advances in Sugarcane Leaf Scald Disease: Pathogenic Insights and Sustainable Management Approaches. Plants, 14(4), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14040508






