Abstract
The prevalence of kidney-related diseases has been increasing and has emerged globally as a leading cause of mortality, especially in developing countries where they are considered a neglected public health problem. Renal diseases are commonly progressive and may cause irreversible loss of organ function, eventually necessitating renal replacement therapy. Although different pharmaceuticals are considered for the treatment of these pathologies, the uncertain effectiveness and presence of adverse effects have generated a growing need for the development of novel nephroprotective compounds. Because many medicinal herbs are typically used in Brazilian folk medicine to prevent and cure kidney ailments, ethnomedicine may play a promising and strategic role in identifying and adding new potential molecules to the pharmacological arsenal. This review focuses on the use of plants and secondary metabolites belonging to different classes to treat renal diseases, associating the screened plant extracts with the bioactive components present in each species. Flavonoids and triterpenes are notable metabolites that have therapeutic potential. The putative pharmacological mechanisms related to nephroprotective properties are also discussed in in vitro and in vivo models, when available.
1. Introduction
Renal diseases are common global causes of morbidity and mortality that cause an increasing socioeconomic burden on public health programs, particularly in low- and middle-income countries [1]. These conditions may impair both kidney structure and function and are associated with significant adverse clinical outcomes [2]. In addition to their high prevalence, kidney diseases are typically associated with comorbidities, including diabetes, hypertension, and coronary heart disease [3,4]. Currently, the management of renal diseases remains a challenge because of their multifold impact, with more than two million people globally receiving renal replacement therapy in the form of continuous dialysis methods or, eventually, kidney transplantation [5]. Based on the cause, duration, and severity, abnormalities in kidney function can be classified as acute kidney disease (AKD) or chronic kidney disease (CKD) [6,7].
AKD is a life-threatening decline in kidney function that affects the glomerular filtration rate and is more reversible than CKD [8]. Glomerular or tubular injury, trauma, and exposure to nephrotoxic compounds, including medicines and mycotoxins, are associated with this condition [9]. Importantly, persistent and unresolved episodes of acute renal injury are implicated in the progression to CKD and end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), particularly in the elderly [10]. Serum creatine, proteinuria, and microalbuminuria are the current clinical markers for the detection of kidney disease progression; however, these markers are neither specific nor sensitive [8]. Repeated renal injuries may result in glomerulosclerosis, vascular rarefaction, and fibrosis, all of which are associated with CKD and ESRD [11].
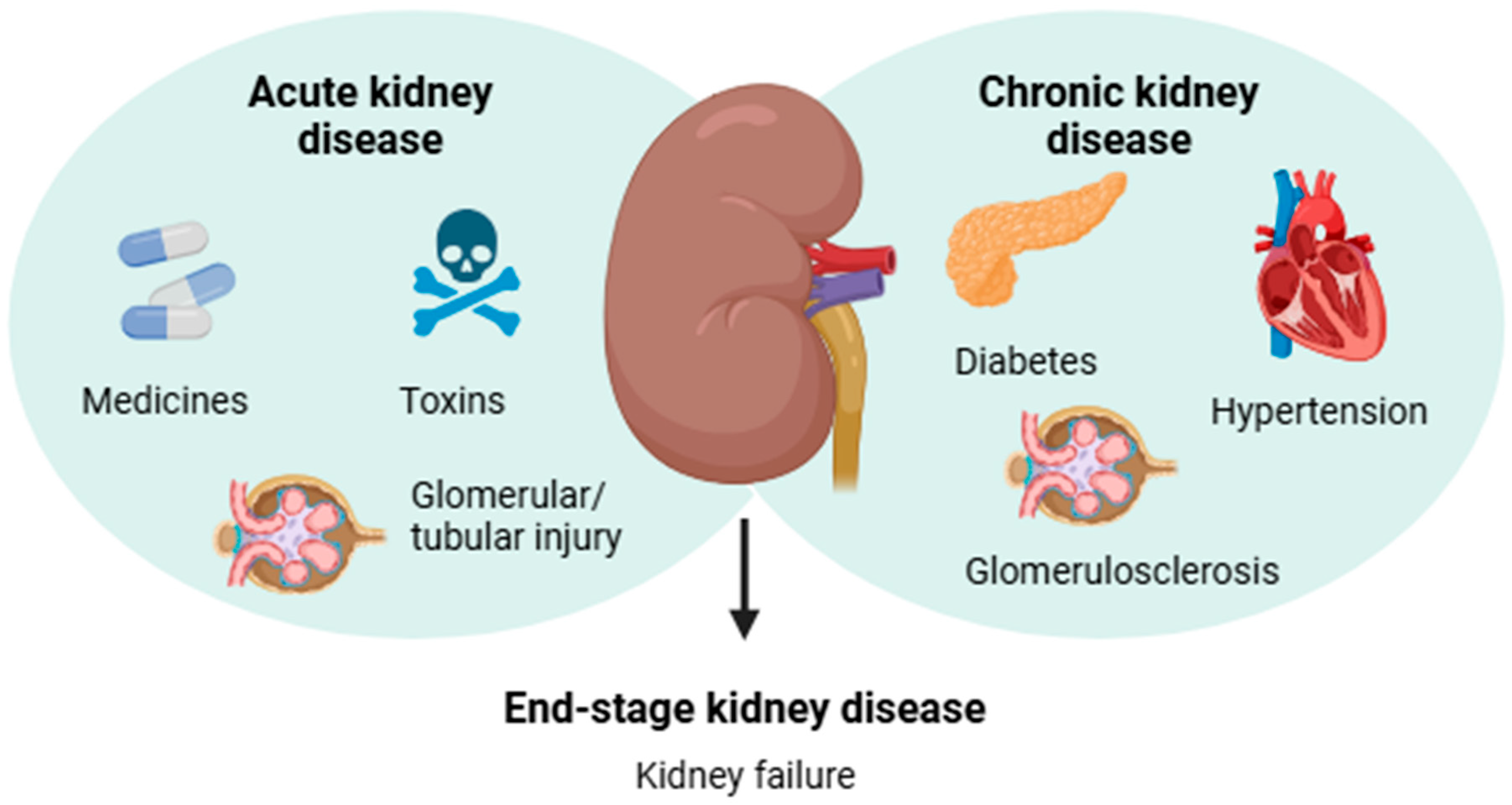
In contrast, CKD gradually develops as a systemic kidney disorder associated with renal pathological features or secondary complications of chronic diseases including diabetes and hypertension [3,4]. The diagnosis of CKD is mainly based on the presence of albuminuria for a period or a glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 for ≥3 months, which indicates decreased kidney function [12]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates, approximately 850 million people worldwide are affected by some form of kidney disease, and CKD is projected to become the 5th most common chronic disease by 2040 [6]. Notably, deterioration of renal function is a silent process due to the lack of physical signs, and most affected individuals are asymptomatic until CKD advances to kidney failure [4,13]. The main causes related to the development of AKD and CKD are shown in Figure 1.
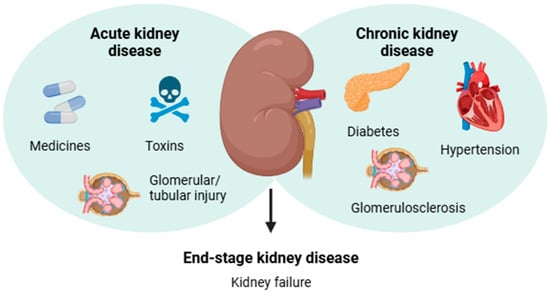
Figure 1.
Infographic summarizing the main causes related to the etiology of acute and chronic kidney diseases, which may lead to end-stage kidney disease.
Patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension are more closely affected and experience a substantial reduction in the quality of life with progressive loss of renal function, resulting in kidney failure and high mortality rates. Some non-pharmacological approaches, including a range of lifestyle and dietary strategies (weight loss, protein restriction, blood pressure, and glucose control), can adequately preserve kidney function [14,15]. Traditionally available pharmacological interventions are rarely curative and are classified into three main targets: (i) agents that slow the progression of the disease (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, and sodium-glucose transport protein inhibitors, known as SGLT-2 inhibitors or gliflozins); (ii) agents that reduce cardiovascular risk (lipid, glucose, and blood pressure-lowering drugs); and (iii) agents that manage uremia and associated symptoms (veverimer, loop or thiazide diuretics, and uric acid-lowering drugs) [16,17]. Further clinical evidence shows that newer nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists play an important role in preventing and managing AKD-CKD transition, acting as antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory agents [18].
In addition to the limited number of nephroprotective therapies available in current clinics, studies have associated an increased risk of adverse outcomes with the use of some agents, including hyperkalemia or uncertain effectiveness of multi-agent renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system blockade and euglycemic ketoacidosis for SGLT-2 inhibitors [16]. Some drug combinations have not shown additional benefits and may induce serious adverse effects including acute kidney injury and renal dysfunction [19]. Moreover, current pharmacological approaches have been shown to mitigate the risk of CKD progression, particularly in patients with diabetes type 2, but are unlikely to slow disease progression, prevent the development of ESRD and cardiovascular disease, or ensure a better health-related quality of life for these patients [20].
Therefore, we considered the research of plant species that may have nephroprotective activity because many of these plants are widely used as folk medicines in Brazil. In this review, we discuss how plants and their active compounds are used to treat conditions (in vitro and in vivo effects) that are consistent with kidney-related diseases. Furthermore, we review and summarize the empirical use of medicinal plants for the treatment of renal symptoms and provide scientific evidence obtained from preclinical studies.
2. Plant Species Used in Brazilian Ethnomedicine with Nephroprotective and Kidney-Related Properties
The primary source of human healthcare has been linked to the millennial use of medicinal plants. The World Health Organization has estimated that four billion people worldwide still rely on traditional remedies, representing 80% of the world’s population [21,22]. Ethnomedicine plays a pivotal role as a validated strategy to identify new natural chemical entities with important pharmacological activities [23,24]. Plant-derived metabolites are often regarded as chemically complex molecules with outstanding and versatile scaffold diversity compared with typical synthetic compounds [25,26]. Screening and identification of novel therapeutic leads are routinely performed using analytical and computational techniques, including high-throughput screening, medicinal chemistry, molecular docking, and omics [27]. The importance of plants in discovering new drug entities is still growing, as approximately half of the new therapeutic agents approved between 1981 and 2019 are recognized as natural products or their synthetic variants based on natural pharmacophoric groups [28].
Brazil contains approximately 45,000 plant species, corresponding to 20–22% of the global flora, many of which are used for medicinal purposes [29]. Various bioactive molecules have been isolated from native Brazilian plants; however, few studies have investigated their mechanisms of action [30]. Global estimates show that only a small percentage of higher plants on the planet have been chemically (15%) or pharmacologically (6%) investigated [31]. In Brazil, a significant number of plant species have historically been used to normalize kidney function, including medicinal allegations as nephroprotective and diuretic agents, stone elimination, and blood depuration. The properties of plant species used in traditional medicine for these purposes compiled from books about medicinal plants and folk medicine published in Brazil (Table 1) are listed in Table 2.

Table 1.
List of books consulted in the process of survey and of the main Brazilian biomes involved (Amazon Forest, Cerrado, Atlantic Forest, Caatinga, Pantanal, and Pampa).

Table 2.
Plant species used in Brazilian ethnomedicine as nephroprotective agents.
3. Methodology
A comprehensive review of the medicinal plants used in Brazilian traditional medicine as remedies against kidney-related disorders and their associated bioactive compounds was conducted. To perform bibliographic research, ethnobotanical books containing primary surveys and compilations conducted by authors linked to the national scientific academy were searched (Table 1). The literature used in the review covered plants native or exotic to the Brazilian flora present in all biomes in the country using specific keywords in Portuguese such as “diuretic”, “kidney stones”, “blood purifier”, and “kidney disease”, among others. The following information was collected: plant species, vernacular names, parts of the plant used, and related folk medicinal uses (Table 2). All valid scientific names of species, authors, botanical families, and origins were checked using The World Flora Online “http://www.worldfloraonline.org (accessed on 12 October 2024)” and Flora e Funga do Brasil “http://floradobrasil.jbrj.gov.br (accessed on 15 October 2024)”.
The review process was continued by consulting peer-reviewed journal articles available in electronic databases such as Scopus, PubMed, SciFinder, and SciELO and using keywords associated with the scientific names of plants with in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo nephroprotective activities. Next, the secondary metabolites present in related plant species used in folk medicine were reviewed using the databases mentioned above, and a comprehensive review was further refined by combining keywords related to the in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo nephroprotective activities of each compound, resulting in a list of bioactive metabolites useful for treating kidney-related disorders (Tables S1 and S2 of the Supporting Information). For all searches, the inclusion criteria were based on the credibility of the sources from which data were collected. No specific restrictions were considered, and all preclinical studies were included and investigated.
The inclusion criteria for the ethnobotanical compilation were as follows: (i) plants species traditionally used in traditional Brazilian medicine specifically for the treatment of kidney-related diseases, (ii) books edited in Brazil based on ethnobotanical studies or compilations of folk medicinal reports published by scientists, and (iii) reports containing the specific botanical epithet. The inclusion criteria for pharmacological evidence were as follows: (i) Brazilian species with traditional reports of nephroprotection, (ii) well-designed studies of pharmacological evaluation (in vitro, in vivo, or in silico), and (iii) bioactive components present in the organs of the species traditionally used for renal diseases. The exclusion criteria applied for medicinal plants were if they were (i) identified only to the genus level, (ii) cited only by their popular names, and (iii) exotic, non-acclimatized plants were excluded, resulting in a complete database final list.
4. Nephroprotective Strategies in Acute Kidney Disease and Chronic Kidney Disease
One potential reason for plant-derived phytochemicals being suggested as promising strategies to prevent or treat kidney-related diseases is their complex pleiotropic effects based on potential interactions with different pharmacological sites. Considering that kidney-related diseases involve multiple pathological pathways, the presence of different nephroprotective natural compounds in plant extracts represents a multitarget approach, as they can act synergistically, thus modulating important proteins involved in renal pathogenesis [52].
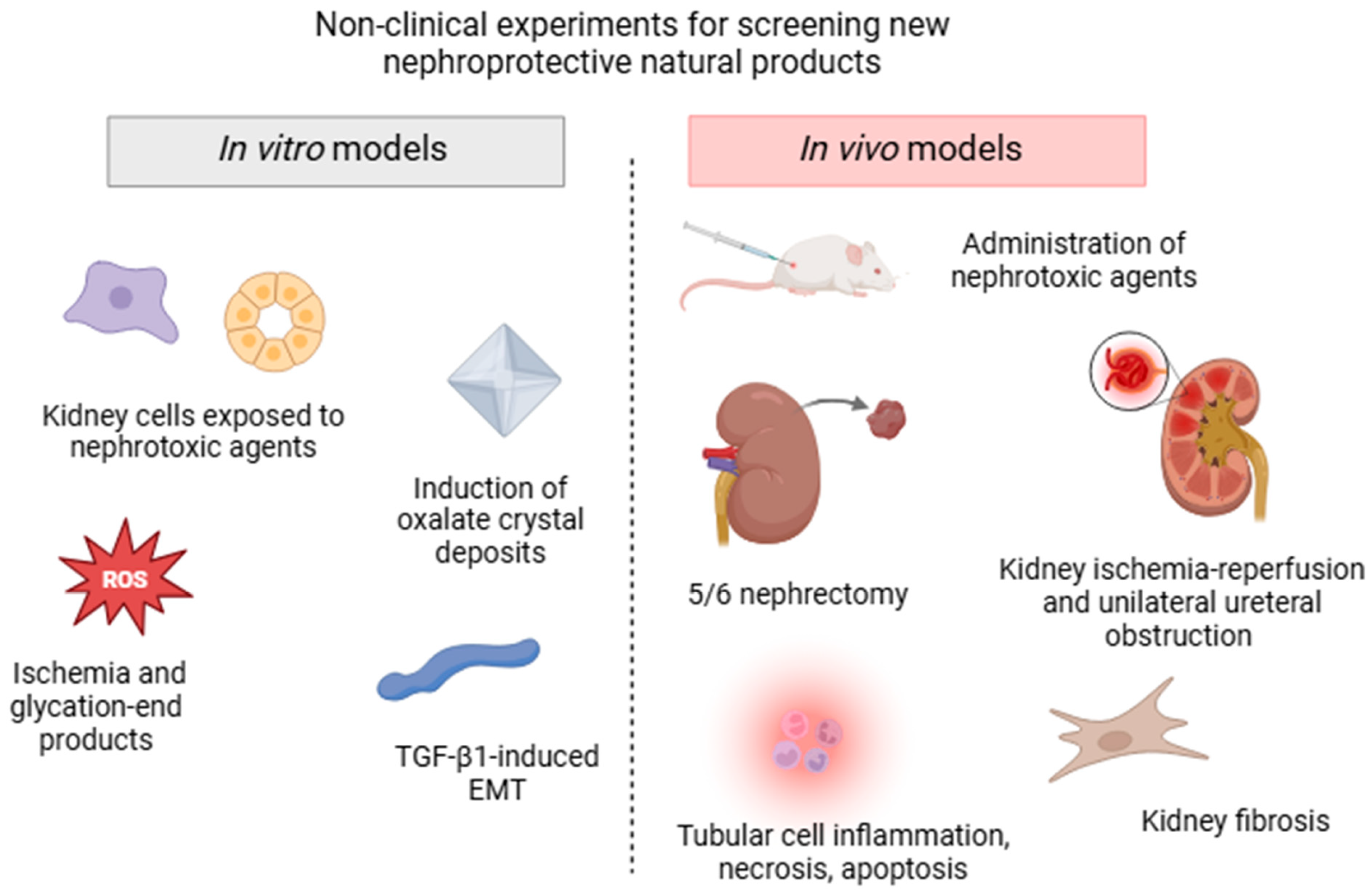
Diverse experimental non-clinical approaches are currently used to screen the bioactive components of plants traditionally used for their pharmacological activity in kidney disorders, all of which mimic the different processes involved in AKD and CKD (summarized in Figure 2). In vitro models can be quickly performed in batteries and often use human, rat, porcine, or canine renal cell lines, such as glomerular mesangial cells, tubular epithelial cells, interstitial fibroblast cells, podocytes, or renal structures exposed to drug-induced nephrotoxicity. Strategies to target the pharmacological mechanisms in these cells also include incubation with high glucose and glycation end products, chemical ischemia, transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1)-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition, and induction of kidney oxalate crystal deposits [53,54,55,56].
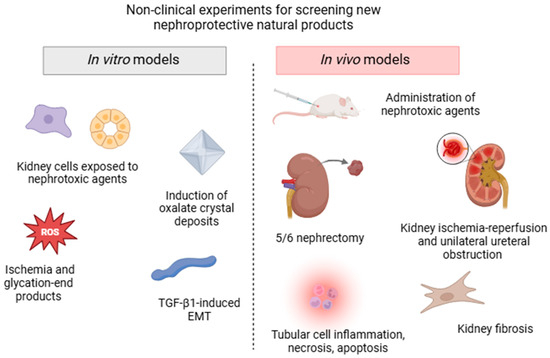
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the main non-clinical models (in vitro and in vivo assays) commonly used for screening nephroprotective plant extracts and/or isolated compounds.
However, in vivo experimental models that expose rats or mice to different etiological factors and conditions are more extensively used to assay molecules or extracts that can potentially block or reverse the progression of kidney diseases. Classically, AKI is induced by the administration of various noxious stimuli including antibiotics, chemotherapeutic agents, aristolochic acid, heavy metals, pesticides, and endogenous toxins (sepsis-induced AKD) [52]. Surgical strategies, such as kidney ischemia-reperfusion and unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) models, are low-cost and often used to affect specific physiological components, triggering tubular cell necrosis, apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress damage. Some CKD models include diabetic nephropathy, hypertension-induced renal damage, glomerular injury, and renal mass reduction (5/6 nephrectomy) [57]. Although these models do not fully reproduce human clinical features, they share some common specific cell-signaling pathways and are usually accompanied by a decline in renal function, represented by elevated serum creatinine and urea levels, decreased glomerular filtration rate, tubular lesions, proteinuria, and fibrosis [52].
Considering that CKD may ultimately result in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), renal fibrosis, and nephron loss, novel pharmacological targets focus on the modulation of molecular and cellular cascades related to the deposition of extracellular matrix proteins or fibrinogenesis [58]. Most of these studies have suggested that classical oxidative stress and inflammation biomarkers as well as the activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), regulation of cell differentiation and migration pathways (such as Notch, Wnt, Hedgehog, and SOX9), myofibroblast-targeting strategies, TGFβ1 signaling blockers, and inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway are promising therapeutic approaches [59,60,61].
5. Plant Extracts Characterized in In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
According to the collected data, 398 plant species were identified as folk nephroprotective agents, most of which were native to Brazilian flora, resulting in 741 citations. Table 2 provides an overview of their taxonomic distribution, morphological structures, and folk indications. Among them, 235 genera belonging to 91 botanical families were identified. The most cited families with traditional use were Fabaceae, followed by Asteraceae and Rubiaceae (65, 50, and 33 citations, respectively). As for the number of species, the most common families were Fabaceae, followed by Asteraceae and Bignoniaceae (42, 25, and 18 plant species, respectively). These results agree with previous studies indicating that Fabaceae and Asteraceae are among the largest botanical families found in Brazilian territory, thus reinforcing their importance for medicinal use in the country [62].
Roots were the predominant morphological structure of nephroprotective drugs used in household remedies (28.7%), followed by leaves (28.2%), and whole plants (9.6%). The species most commonly cited as useful for the treatment of renal complaints in the context of Brazilian traditional medicine were Persea americana (13 citations), Phyllanthus niruri, and Casearia sylvestris (both with 10 citations). Among these, P. niruri appears to be the most widely investigated plant for kidney diseases, sharing scientific evidence of its biological and pharmacological efficacy attributed to lignans, which are regarded as putative bioactive components (Table 3, Table 4 and Tables S1 and S2). Extracts obtained from P. americana have demonstrated important effects, particularly after in vivo assays. However, pharmacological studies to confirm the nephroprotective therapeutic properties of C. sylvestris are lacking. Notably, P. americana is a plant that shares the highest number of use reports, but is an exotic (non-native) species. This fact is consistent with the higher availability of some species that are cultivated in domestic gardens and also points to the fact that the Brazilian population tends to fill the medicinal gaps not met by native species [63,64].
A detailed list of plant extracts with nephroprotective activity in vitro and in vivo is provided in Table 3 and Table 4. Although these studies reported the effectiveness of the extracts using distinct models, the minimal concentration at which significant effects were achieved, and the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) were the measurements presented. The most potent extract (Table 3) was the aqueous leaf extract of Guazuma ulmifolia, which displayed an in vitro protective effect at a concentration of 3.125 μg/mL in mouse mesangial cells (SV40MES13) exposed to high glucose concentrations, simulating diabetic glomerulosclerosis [65]. G. ulmifolia is a Brazilian native tree widely found in the country, with edible fruits and known locally as “mutamba”. Decoctions of the leaves, fruits, and stem bark are traditionally used to treat kidney stones and digestive and cardiovascular disorders [66]. Polar extracts obtained from the bark of G. ulmifolia are especially rich in procyanidin oligomers, consisting mainly of [4β → 8]-(−)-epicatechin units, including procyanidin B1 (epicatechin-(4β → 8)-catechin), procyanidin B2 (epicatechin-(4β → 8)-epicatechin), procyanidin B5 (epicatechin-(4β → 6)-epicatechin), procyanidin C1 ([epicatechin-(4β → 8)]2-epicatechin), cinnamtannin A2 ([epicatechin-(4β → 8)]3-epicatechin), and epiphyllocoumarin derivatives [67,68]. The cardioprotective and antihypertensive activities of this species have been demonstrated both in vitro and in vivo and are mainly attributed to the presence of proanthocyanidins and flavonoids [69]. Bioassay-guided fractionation was conducted with a G. ulmifolia bark acetone extract to inhibit angiotensin II binding to the hAT1 receptor, leading to the isolation of a number of bioactive condensed tannins; the most promising compounds are highly polymerized pentamer and hexamer proanthocyanidins [70].
Other potent extracts include P. niruri, a medicinal herb known in Brazil as “stone-breaker” and widely used in household remedies to eliminate renal and urinary calculi, and as diuretic [71]. A hot aqueous plant extract at 5 µg/mL significantly inhibited the endocytic response observed in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells (MDCK) exposed to calcium oxalate (CaOx) crystals without impairing cell viability [53]. Another study demonstrated that the infusion of P. niruri extract inhibited the in vitro growth of CaOx crystals and reduced their aggregation in human urine, which could be useful for the treatment of urolithiasis [72]. Oral administration of an aqueous plant extract (1.25 mg/mL/day) over 42 days in rats induced relaxation, elimination, and dissolution of bladder CaOx stones, possibly by preventing crystal aggregation and promoting glycosaminoglycan adsorption [73]. An important dose-dependent reversion of plasma uric acid in hyperuricemic rats was displayed by the extract and apolar fractions of P. niruri leaves at 50 mg/kg, leading to the isolation of phyllanthin (42), a lignan with anti-hyperuricemic properties comparable to that of allopurinol at a dose of 23.9 µmol/kg [74]. A mechanistic investigation showed that the anti-hyperuricemic activity of the P. niruri methanol extract in animals was associated with the induction of uric acid excretion and in vitro (IC50 = 39.4 µg/mL) and in vivo inhibition of xanthine oxidase activity after intraperitoneal administration.
Studies have also shown that an ethanolic fraction of Phyllanthus amarus decoction induces urinary excretion and produces natriuretic effects at doses ranging from 5 to 80 mg/kg in rats, with evidence that the prostaglandin E2 pathway mediates the diuretic response [75]. The main active constituents of P. amarus are lignans such as phyllanthin and hypophyllanthin (28), which are also related to the pharmacological and biological activities of this species [76].
The hydroethanolic extract of Costus spiralis leaves, traditionally used in Brazilian folk medicine to treat pyelonephritis and kidney stones, significantly reversed renal function after cisplatin-induced nephrotoxic damage in rats at an oral dose of 5 mg/kg [77]. These effects were related to the presence of flavonoids, mainly apigenin glycosides, which partially validated the popular use of this plant. The infusion of Euphorbia serpens aerial parts increased urine volume in rats concomitantly with the loss of electrolytes in a dose-dependent manner, similar to that of the standard drug furosemide. D-mannitol was found to be the main constituent of the plant extract and was primarily associated with its diuretic activity [78]. Bredemeyera floribunda is a medicinal liana used as a remedy to control nephrolithiasis symptoms. A series of in vivo studies have been conducted using the root ethanolic extract, which resulted in a hypotensive response and a direct effect on the glomerular filtration rate after intravenous administration in antidiuretic or water diuretic rats [79,80]. The diuretic and saluretic responses of the extract were suggested to possibly occur via detergent-like interactions with Na+/K+-ATPase in proximal tubular cells, attributed to its triterpenoid saponins known as bredemeyerosides [81].

Table 3.
Nephroprotective activities of extracts from Brazilian plants evaluated through in vitro and ex vivo assays.
Table 3.
Nephroprotective activities of extracts from Brazilian plants evaluated through in vitro and ex vivo assays.
| Family | Specie | Morph. Struc. | Extract | Model | Effective Concentration(s) | Effects/Mechanisms | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asteraceae | Ageratum conyzoides | Leaf | EtOH | CaOx crystallization | 10 mg | Antilithiatic effect | [82] |
| Lychnophora pinaster | Aerial part | EtOH | Enzymatic activity | IC50 = 73.9 µg/mL | Inhibition of xanthine oxidase activity | [83] | |
| Hex | |||||||
| EtOAc | IC50 = 43.2 µg/mL | ||||||
| EtOH | |||||||
| Bignoniaceae | Sparattosperma leucanthum | Leaf | EtOAc | Enzymatic activity | IC50 = 107 µg/mL | Inhibition of xanthine oxidase activity | [84] |
| MeOH | |||||||
| AQ | |||||||
| Costaceae | Costus arabicus | Whole plant | AQ | CaOx crystallization-induced MDCK-I cells | 10, 100 µg/mL | Antilithiatic effect | [85] |
| Euphorbiaceae | Euphorbia hirta | Leaf | AQ, EtOAc, HEX, MeOH | CaOx crystallization | 1 mg/mL | Antilithiatic effect | [86] |
| Fabaceae | Copaifera langsdorffii | Leaf | HA | CaOx crystallization | 0.3, 0.7, 1 mg/mL | Antilithiatic effect | [87] |
| Lauraceae | Persea americana | Fruit, seed | Oil | Rotenone-induced VERO cells | 1, 3, 10, 30, 100, 300, 600, 1000 µg/mL | Cytoprotective effect | [88] |
| Leaf | Extract (n.d.) | ||||||
| Malvaceae | Guazuma ulmifolia | Leaf | AQ | Glu-induced glomerulosclerosis in HRM cells | 3.25, 6.25 μg/mL | Reduction in fibronectin levels | [65] |
| Theobroma grandiflorum | Fruit | Pulp | High glucose-induced mouse immortalized mesangial cells | 10, 50, 100 μg/mL | Antiproliferative and anti-inflammatory effects | [89] | |
| Phyllanthaceae | Phyllanthus niruri | Whole plant | AQ | CaOx crystallization | 0.0625, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1 mg/mL | Inhibition of CaOx crystals growth and aggregation | [72] |
| Whole plant | AQ | CaOx crystallization-induced MDCK | 5, 10, 50, 100, 500, 1000 μg/mL | Inhibitory effect on the CaOx crystal internalization | [53] | ||
| Leaf | MeOH | Enzymatic activity | IC50 = 39.4 µg/mL | Inhibition of xanthine oxidase activity | [90] | ||
| F1 | IC50 = 427.7 µg/mL | ||||||
| F2 | IC50 = 86.9 µg/mL | ||||||
| F3 | IC50 = 28.6 µg/mL | ||||||
| F4 | IC50 = 22.7 µg/mL | ||||||
| Leaf | MeOH | CaOx crystallization | 50 mg/mL | Antilithiatic effect | [91] | ||
| AQ | 50 mg/mL |
AQ, Aqueous, CaOx, Calcium oxalate, EtOAc, Ethyl acetate, EtOH, Ethanol, F, Fraction, Glu, Glucose, HEX, Hexane, HRM, Human renal mesangial cells, MDCK, Madin-Darby canine kidney cells, MeOH, Methanol, Morph. Struc., Morphological structure, n.d., not described, VERO, Monkey kidney epithelial cells line.

Table 4.
Nephroprotective activities of extracts obtained from Brazilian plants evaluated through in vivo assays.
Table 4.
Nephroprotective activities of extracts obtained from Brazilian plants evaluated through in vivo assays.
| Family | Species | Morph. Struc. | Extract | Experimental Model | Route of Administration | Effective Dose (s) | Pharmacological Activities | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alismataceae | Aquarius grandiflorus | Leaf | AQ (EtOH-F) | Male Wistar rats | p.o. | 300 mg/kg | Diuretic and hypotensive effects | [92] |
| Aquarius macrophyllus | Leaf | HA | Gentamicin- induced kidney injury in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 30 mg/kg | Antidiuretic and nephroprotective effects | [93] | |
| Apiaceae | Centella asiatica | Leaf | EtOH | STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 400 mg/kg | Reduction in glomerular and vascular injuries | [94] |
| Leaf | EtOH | Subtotal nephrectomy-induced nephropathy in male Swiss mice | p.o. | 840 mg/kg | Reduction in kidney fibrosis and renal injury | [95] | ||
| Aquifoliaceae | Ilex paraguariensis | Leaf and stem | AQ | K2Cr2O7-induced nephropathy in Wistar rats | p.o. | 540 to 600 mg | Improvement of glomerular filtration rate and nephroprotective effect | [96] |
| Araceae | Pistia stratiotes | Leaf | EtOH | Male Wistar rats | p.o. | 200, 400 mg/kg | Diuretic effect | [97] |
| Whole plant | HA | Renal ischemia and reperfusion-induced damage in diabetic male Sprague Dawley rats | p.o. | 100 mg/kg | Nephroprotective, antiapoptotic, and anti-inflammatory effects | [98] | ||
| Arecaceae | Acrocomia aculeata | Ripe fruit | Pulp oil | Male Wistar rats | p.o. | 300, 700 mg/kg | Diuretic effect | [99] |
| Asteraceae | Acanthospermum hispidum | Aerial part | AQ (EtOH-F) | Male Wistar rats | p.o., i.d. | 30, 100, 300 mg/kg | Acute hypotensive and absence of diuretic effect | [100] |
| Aerial part | AQ (EtOH-F) | Female ovariectomized Wistar rats | p.o. | 30, 100, 300 mg/kg | Reduction in renovascular hypertension. Saluretic effect | [101] | ||
| Ageratum conyzoides | Leaf | AQ | Gentamicin and diet-induced hyperoxaluria and CaOx deposition in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 400 mg/kg | Antiurolithiatic effect | [102] | |
| Baccharis trimera | Aerial parts | AQ (EtOH-F) | Female Wistar rats exposed to cholesterol, diabetes and tobacco cigarettes | p.o., | 30, 100, 300 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect in glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and vessels | [103] | |
| Aerial parts | AQ (EtOH-F) | Male Wistar rats exposed to hookah, alcohol, and energy drink | p.o. | 30, 100, 300 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [104] | ||
| Aerial parts | AQ (EtOH-F) | Male Wistar rats exposed to cholesterol, diabetes and tobacco cigarettes | p.o. | 30, 100, 300 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [105] | ||
| Eclipta prostrata | Leaf | HA | Cisplatin-induced kidney injury in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 400, 600 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [106] | |
| Leaf | MeOH | Gentamicin- induced kidney injury in female Sprague Dawley rats | p.o. | 300, 600 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [107] | ||
| Leaf | HA | Male Sprague Dawley rats | p.o. | 14, 28 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect. Increase in renal 11β- hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity | [108] | ||
| Lychnophora pinaster | Aerial part | EtOH | Oxonate-induced hyperuricemia in male Swiss mice | p.o. | 40, 125, 375 mg/kg | Hypouricemic and anti-inflammatory effects | [109] | |
| Sonchus oleraceus | Aerial part | EtOH | Renal ischemia and reperfusion-induced damage in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 300 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [110] | |
| Bignoniaceae | Bignonia binata | Leaf | EtOH | CCl4-induced nephrotoxicity in male albino rats | p.o. | 300 mg/kg | n.e. | [111] |
| PE | n.e. | |||||||
| EtOAc | Nephroprotective effect | |||||||
| AQ | Nephroprotective effect | |||||||
| Sparattosperma leucanthum | Leaf | EtOAc | Oxonate-induced hyperuricemia in male Swiss mice | p.o. | 125, 250, 500 mg/kg | Hypouricemic and anti-inflammatory effects | [84] | |
| MeOH | ||||||||
| AQ | ||||||||
| Bromeliaceae | Ananas comosus | Ripe fruit | EtOH | Oxalate-induced urolithiasis in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 500, 750, 1000 mg/kg | Antilithiatic and diuretic effects | [112] |
| Celastraceae | Monteverdia ilicifolia | Leaf | EtOAc-F | Male Wistar rats | p.o. | 30, 100 mg/kg | Diuretic effect. Increase in urinary excretion of Na+ and sparing effect of K+ and Cl− | [113] |
| Costaceae | Costus spiralis | Leaf | HA | Cisplatin-induced kidney injury in Wistar rats | p.o. | 5, 15, 30 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [77] |
| Equisetaceae | Equisetum giganteum | Whole plant | CHCl3 | CD1 strain mice | p.o. | 50 mg/kg | Diuretic effect. Increase in urinary excretion of Na+, Cl− and K+ | [114] |
| Euphorbiaceae | Euphorbia hirta | Whole plant | EtOH | Nitrobenzene- induced nephrotoxicity in female Wistar rats | p.o. | 400 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [115] |
| Euphorbia serpens | Aerial parts | AQ | Male Wistar rats | p.o. | 5, 10, 20 mg/mL | Diuretic activity, increase in urinary excretion of Na+ | [78] | |
| Euphorbia thymifolia | Whole plant | EtOH | Ethylene glycol- induced urolithiasis in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 250, 500 mg/kg | Antilithiatic and diuretic effects | [116] | |
| Fabaceae | Abrus precatorius | Stem bark | MeOH | Gentamicin- induced kidney injury in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 100, 200 mg/kg | Nephroprotective, antiapoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects | [117] |
| Bauhinia forficata | Leaf | AQ | Normotensive male Wistar rats | p.o. | 300 mg/kg | Diuretic, anti-natriuretic, and antikaliuretic effects | [118] | |
| MeOH | 100, 300 mg/kg | Diuretic effect | ||||||
| EtOAc- BuOH-F | 30, 100 mg/kg | Diuretic, anti-natriuretic, and antikaliuretic effects | ||||||
| CHCl3-F | 100 mg/kg | Diuretic, anti-natriuretic, and antikaliuretic effects | ||||||
| Copaifera langsdorffii | Leaf | HA | Ethylene glycol- induced nephrolithiasis in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 40, 80, 160 mg/kg | Nephroprotective and antilithiatic effects | [87] | |
| Mucuna pruriens | Leaf | HA | CCl4 and rifampicin-induced nephrotoxicity in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 50, 100 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [119] | |
| Seed | AQ | Arsenic-induced nephrotoxicity in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 350, 530, 700 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [120] | ||
| Senna alata | Leaf | AQ | Acetaminophen- induced nephrotoxicity in male Sprague Dawley rats | p.o. | 200 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [121] | |
| Leaf | HA | STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy in Wistar rats | p.o. | 400 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [122] | ||
| Senna occidentalis | Leaf | AQ | Male and female Wistar rats | p.o. | 240, 320, 400 mg/kg | Diuretic and saluretic effects | [123] | |
| Lamiaceae | Vitex megapotamica | Leaf | MeOH: H2O (7:3) | High fat diet- induced nephropathy in C57BL/6 LDLr-null mice | p.o. | 300 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [124] |
| Lauraceae | Persea americana | Seed | AQ | Cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 400 mg/kg | Nephroprotective, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects | [125] |
| Leaf | AQ | Nicotinamide and STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 100 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [126] | ||
| MeOH | ||||||||
| EtOH | ||||||||
| Fruit pulp | Oil | Male diabetic Goto- Kakizaki rats | p.o. | 1 mL/250 g | Modulation of the redox state of kidney mitochondrial glutathione | [127] | ||
| Fruit pulp | AQ | Cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 10% of the diet | Nephroprotective effect. Restoration of memory and learning disabilities caused by cadmium | [128] | ||
| Leaf | HA | Ethylene glycol and NH4Cl-induced urolithiasis in male Sprague Dawley rats | p.o. | 100, 300 mg/kg | Antiurolithic and nephroprotective effects | [129] | ||
| Lythraceae | Cuphea carthagenensis | Leaf | AQ (EtOH-F) | Ovariectomized hypertensive female Wistar rats | p.o. | 30, 100, 300 mg/kg | Cardiorenal protective effect, preservation of renal function | [130] |
| Malvaceae | Ceiba pentandra | Aerial part | EtOAc-F | Methotrexate- induced kidney injury in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 400 mg/kg | Nephroprotective, antiapoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects | [131] |
| Sida rhombifolia | Aerial part | HA | STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy in male Wistar rats | n.d. | 100, 200 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [132] | |
| Theobroma cacao | Polyphenol -F | CCl4-induced nephrotoxicity in male F344 rats | p.o. | 500 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [133] | ||
| Theobroma grandiflorum | Fruit | Pulp | STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 1 g/mL | Nephroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects | [89] | |
| Menispermaceae | Cissampelos pareira | Root | AQ | Ethylene glycol and NH4Cl-induced urolithiasis in male albino rats | p.o. | 100, 200, 400 mg/kg | Antiurolithic and nephroprotective effects | [134] |
| Whole plant | HA | Acetaminophen- induced nephrotoxicity in male albino rats | p.o. | 200, 400 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [135] | ||
| Myrtaceae | Eugenia uniflora | Leaf | HA | Renal ischemia and reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 200 mg/kg | Stabilization of glomerular filtration rate, renal blood flow and renal vascular resistance parameters | [136] |
| Leaf | AQ | Normotensive male Wistar rats | p.o. | 120 mg d.L./kg | Diuretic effect. Reduction in Na+ excretion. | [137] | ||
| Passifloraceae | Passiflora edulis | Fruit peel | AQ | STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 400 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [138] |
| Fruit peel | EtOH | Gentamicin- induced kidney injury in male albino rats | p.o. | 250, 500 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [139] | ||
| Phyllanthaceae | Phyllanthus amarus | Whole plant | EtOH | High salt diet- induced renal metabolic derangement in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 75, 100, 150 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [140] |
| Leaf | HA | Rifampicin-induced nephrotoxicity in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 50, 100 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [141] | ||
| Leaf | AQ | Glycolate-induced hyperoxaluria in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 3.5 mg | Diuretic effect. Reduction in oxalate crystal deposition of Ca2+ kidney content | [142] | ||
| Aerial part | AQ | Gentamicin and acetaminophen- induced kidney injury in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 100, 200, 400 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [143] | ||
| Whole plant | AQ (EtOH-F) | Male Wistar rats | i.p. | 5, 10, 20, 40, 80 mg/kg | Diuretic and natriuretic effects | [75] | ||
| Phyllanthus niruri | Whole plant | AQ | CaOx-induced urolithiasis in male albino rats | p.o. | 1.25 mg/mL | Inhibitory effect of crystal growth | [73] | |
| Whole plant | AQ | CaOx-induced urolithiasis in male albino rats | p.o. | 5 mg | Inhibitory effect of crystal deposition | [144] | ||
| Leaf | MeOH | Oxonate and uric acid-induced hyperuricemia in male Sprague Dawley rats | i.p. | 50 mg/kg | Uricosuric effect, inhibition of xanthine oxidase activity | [90] | ||
| F 1 | n.e. | |||||||
| F 2 | ||||||||
| F 3 | Inhibition of xanthine oxidase activity | |||||||
| F 4 | Inhibition of xanthine oxidase activity | |||||||
| Leaf | MeOH | Oxonate and uric acid-induced hyperuricemia in male Sprague Dawley rats | i.p. | 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000 mg/kg | Antihyperuricemic effect | [74] | ||
| F 1 | 50 mg/kg | n.e. | ||||||
| F 2 | 50 mg/kg | |||||||
| F 3 | 50 mg/kg | |||||||
| F 4 | 50 mg/kg | Antihyperuricemic effect | ||||||
| Leaf | AQ | STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 200, 400 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [145] | ||
| Leaf | AQ | STZ/nicotinamide-induced diabetic nephropathy in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 200, 400 mg/kg | Nephroprotective, anti-inflammatory, antiapoptotic and antifibrotic effects | [146] | ||
| Phyllanthus sellowianus | Stem bark | AQ | Female Sprague Dawley rats | p.o. | 400 mg/kg | Diuretic effect | [147] | |
| Phyllanthus tenellus | Aerial parts | AQ (EtOH-F) | Male Sprague Dawley rats | p.o. | 30, 100, 300 mg/kg | Absence of diuretic effect | [148] | |
| Piperaceae | Piper peltatum | Root | HA | Female albino rats | p.o. | 25, 100, 200 mg/kg | Diuretic and saluretic effect | [149] |
| Piper umbellatum | Leaf | MeOH | Atherogenic diet- induced renal injury in male Syrian Golden hamsters | p.o. | 0.25 and 1 g/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [150] | |
| Polygalaceae | Bredemeyera floribunda | Root | EtOH | Male Wistar rats | i.v. | 15, 30 mg/kg | Diuretic, natriuretic, and kaliuretic effects | [79] |
| 0.05 mg/100 g | Increase in glomerular filtration rate, fractional water and sodium excretion and solute clearance | [80] | ||||||
| Portulacaceae | Portulaca pilosa | Leaf, stem | HA | Male Wistar rats | p.o. | 400 mg/kg | Kaliuretic effects | [151] |
| Pteridaceae | Adiantum capillus-veneris | Aerial part | HA | Ethylene glycol and NH4Cl-induced urolithiasis in male Sprague Dawley rats | p.o. | 127.6, 255.2 mg/kg | Antiurolithic and nephroprotective effects | [152] |
| Rhamnaceae | Ampelozizyphus amazonicus | Root | HA (n-BuOH- F) | Furosemide-induced diuresis in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 50 mg/kg | Antidiuretic effect | [153] |
| Root | EtOH | Male Wistar rats | p.o. | 100 mg/kg | Diuretic effect | [154] | ||
| Saponin-F | 50, 100, 200, 1000 mg/kg | Antidiuretic effect | ||||||
| Saponin- free F | 50, 100, 200 mg/kg | Diuretic effect | ||||||
| Rubiaceae | Alibertia edulis | Leaf | AQ | Male Wistar rats | i.d. | 200 mg/kg | Diuretic effect. Increased excretion of Na+, Cl−, K+, Ca2+ | [155] |
| Palicourea coriacea | Aerial part | HA | Male Wistar rats | p.o. | 20, 40, 80 mg/kg | Diuretic, natriuretic, and kaliuretic effects | [156] | |
| Rudgea viburnoides | Leaf | AQ | 2K1C-hypertensive male Wistar rats | p.o. | 30, 100, 300 mg/kg | Preservation of urine excretion and electrolyte levels. Reduction in the progression of cardiorenal disease | [157] | |
| Leaf | HA | Gentamicin- induced kidney injury in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 50, 200 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [158] | ||
| Sapindaceae | Cardiospermum halicacabum | Whole plant | MeOH, PE | Acetaminophen- induced nephrotoxicity in Wistar rats | p.o. | 400 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [159] |
| Whole plant | AQ | Gentamicin- induced kidney injury in albino rats | p.o. | 200, 400 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [160] | ||
| Talinaceae | Talinum paniculatum | Leaf, stem | AQ (EtOH-F) | Male Wistar rats | p.o. | 30, 100, 300 mg/kg | Diuretic and saluretic effect | [161] |
| Leaf | HA | 2K1C-hypertensive male Wistar rats | p.o. | 100, 300 mg/kg | Diuretic and nephroprotective effects | [162] | ||
| Urticaceae | Cecropia pachystachya | Leaf | EtOH (AQ-F) | Subtotal nephrectomy- induced nephropathy in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 0.5 g/kg | Nephroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects | [163] |
| Leaf | AQ | Subtotal nephrectomy- induced nephropathy in male Wistar rats | p.o. | 0.6 g/kg | Reduction in glomerulosclerosis and of the urinary excretion of MCP-1 and TGF-β | [164] | ||
| Laportea aestuans | Leaf | MeOH | Arsenite and STZ-induced nephrotoxicity in Wistar rats | p.o. | 200 mg/kg | Nephroprotective effect | [165] | |
| Urera baccifera | Root, leaf, stem | AQ | Male Wistar rats | p.o. | 400 mg/kg | Diuretic effect | [166] | |
| Violaceae | Anchietea pyrifolia | Leaf | AQ (EtOH-F) | Male Wistar rats | p.o. | 30, 100, 300 mg/kg | Absence of diuretic effect. Decreased urine excretion of Na+, K+, and Cl− | [167] |
2K1C 2-Kidney, 1-clip surgery, AQ aqueous, CaOx calcium oxalate, CCl4 carbon tetrachloride, CHCl3 chloroform, EtOAc ethyl acetate, EtOH ethanol, F fraction, HA hydroalcoholic, i.d. intraduodenal administration, i.v. intravenous, K2Cr2O7 potassium dichromate, MeOH methanol, n-BuOH n-butanol, n.e. no effect, NH4Cl ammonium chloride, PE petroleum ether, STZ streptozotocin, mg/kg milligram/kilogram, Morph. Struc. morphological structure, n.d. not described, n.e. no effect, p.o. oral administration.
6. In Vitro and In Vivo Studies with Plant Secondary Metabolites
Although successful, natural product-based drug discovery for kidney-related diseases has some drawbacks. It is not uncommon to observe a reduction or loss of biological activity throughout the bioactivity-guided fractionation process, possibly because of synergistic interactions among the compounds in unrefined phytocomplex mixtures [168]. Nevertheless, in contrast to extracts and synthetic compounds, single nephroprotective molecules may offer some special features to the limited available therapeutic arsenal, including their diverse chemical diversity and reduction in active doses/concentrations due to the purification of extracts [169]. Tables S1 and S2 of Supporting Information show 74 secondary metabolites belonging to the classes of alkaloids, anthraquinones, coumarins, flavonoids, lignans, phenylpropanoids, saponins, and triterpenes with in vitro and in vivo nephroprotective activities, respectively. The structures of bioactive secondary metabolites are shown in Figure S1. Likewise, as the studies reported the effectiveness of the isolated compounds using distinct models, the minimal concentration at which significant effects were achieved, and the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) were the measurements presented.
Surprisingly, phytochemical studies of some plant species based on ethnomedical information have resulted in the identification of potent nephrotoxins. For example, aristolochic acid, a compound commonly found in the roots of Aristolochia species and used medicinally for kidney ailments, is associated with nephropathy, renal interstitial fibrosis, and urothelial cancer [170]. Aristolochic acid is currently used in models to induce CKD and screen for new nephroprotective drugs [171]. Controversially, five species from the Aristolochia genus are used as folk blood depuratives and diuretics in Brazil, as shown in Table 2. This fact points to the relevant risks associated with their use of self-care as home remedies.
Polyphenols are among the most potent nephroprotective compounds that have been assayed in vitro. For example, scopoletin (51), a coumarin found in a number of medicinal plants, such as Persea americana and Sida rhombifolia, displayed significant protection in a model of diabetic glomerulosclerosis in rat glomerular mesangial cells exposed to high glucose [172]. At a concentration of 0.1 µM, this compound reduced cell proliferation, inhibited the overexpression of ECM proteins, and reduced connective tissue growth factor and TGF-ꞵ expression, proving that scopoletin could be a potential antifibrotic agent against diabetes-induced nephropathy. Another highlight is that the anthraquinone emodin (16), which is found in Handroanthus impetiginosus and Senna occidentalis, displayed an in vitro protective effect at 0.5 µM against cisplatin-induced damage in human kidney (HEK 293) cells, mostly because of its antioxidant properties [173]. Delphinidin (14), an anthocyanidin commonly found in medicinal edible fruit trees such as Euterpe precatoria and Plinia peruviana, reduced the oxidative injury caused by antimycin a, patulin and insulin in epithelial rat kidney (NRK) cells at 1 µM [174]. Ferulic acid (20), quercetin (48), kaempferol (32), epicatechin (17), and wedelolactone (57) all displayed significant protective effects against nephrotoxic agents at a concentration of 1 µM in renal cell lines [175,176,177,178,179]. The triterpenes betulinic acid (6) and ursolic acid (55) were also effective in mitigating the damage induced by different toxins at concentrations of 0.25 and 1 µM, respectively [180,181].
Several secondary metabolites present in the selected medicinal plants have undergone in vitro to in vivo tests, and their nephroprotective properties have been characterized. For example, it has been suggested that the beneficial properties against nephrolithiasis symptoms described for P. niruri preparations can be attributed to lignans, a class of compounds that are particularly found in other medicinal herbs used to treat kidney-related disorders belonging to the Phyllanthus genus, such as P. amarus, P. tenellus, and P. sellowianus [182]. As previously mentioned, bio-guided fractionation of P. niruri methanol extract and fractions that displayed potent anti-hyperuricemic oral effects in animals afforded three lignans, of which phyllanthin (42) at 10 mg/kg displayed significant and dose-dependent uricosuric action [74]. Although phyllanthin, hypophyllanthine (28), and phyltetralin (43) alone showed no appreciable effect owing to possible synergistic interactions, the first significantly induced changes in urine output and uric acid content in hyperuricemic rats [90]. Therefore, the uricosuric and antiurolithic properties of lignans from Phyllanthus spp. may provide attractive therapeutic alternatives for the management of hyperuricemia and urinary stones.
The flavonoids afzelin (1) and kaempferitrin (31), both kaempferol glucosides isolated from the medicinal plant Bauhinia forficata, demonstrated significant diuretic and saluretic effects after oral administration to rats at low concentrations (0.1 mg/kg) [118,183]. Moreover, afzelin presented acute and subchronic Ca2+-sparing and renoprotective effects in normotensive and hypertensive rats, as well as antiurolithiatic effects in synthetic and rat urine [183], which may support the ethnopharmacological use of this herb for kidney ailments. In a type-1 diabetic model, subcutaneous administration of 0.78 mg/kg/day of apigenin (4) for 10 days attenuated nephropathy features in rats by decreasing the overexpression of dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) in kidney tissues [184]. Similarly, epicatechin (17) counteracted the progression of renal damage in rats subjected to a subtotal nephrectomy at a dose of 0.01 mg/kg administered orally for 14 days, preserving renal function and systolic blood pressure [185].
In addition to the in vitro results, oral in vivo pretreatment with betulinic acid (6) mitigated the damage induced by nephrotoxic T-2 mycotoxins in mice [186]. At 0.25 mg/kg, this triterpene reduced the inflammatory response and renal oxidative damage via Nrf2 signaling pathway activation. These results suggest the possibility of conducting clinical trials using betulinic acid to limit the progression of renal disease in humans.
7. Conclusions
According to the literature review, there is a great diversity of medicinal plants popularly used for the treatment of kidney disorders in Brazil, but only a few of them have been preclinically tested for their potential nephroprotective effects. In contrast, the number of isolated secondary metabolites found in the aforementioned plants was higher, which demonstrates a greater interest in validating the pharmacological potential of single molecules, particularly polyphenols and triterpenes. New nephroprotective agents are needed for the therapeutic arsenal because the drugs currently available are not entirely satisfactory. Flavonoids appeared to be the leading class of compounds investigated for renal disorders, highlighting quercetin, rutin, kaempferol, apigenin, fisetin, and luteolin. Phenylpropanoids, including caffeic, chlorogenic, ellagic, gallic and rosmarinic acids, also shared a large number of scientific reports. Finally, asiatic acid, betulinic acid, lupeol, and ursolic acid were identified as important bioactive nephroprotective triterpenes in this study. Considering that many of these molecules may occur concomitantly in the compiled folk medicinal species, more vigorous efforts directed towards isolation (bioguided assay), as well as clinical assays for potent extracts and/or isolated compounds, are required to establish effectiveness and toxicological data and to ensure their potential use.
8. Future Prospects
A significant number of medicinal plants are commonly used in traditional Brazilian medicine to relieve the symptoms associated with renal diseases. Additionally, available biological and pharmacological reports suggest that several species have their use examined and pre-validated and are considered safe in toxicological studies. This study provides a comprehensive overview of the diverse secondary metabolites belonging to different chemical classes found in the most cited plants, in vitro and in vivo investigations, and their efficacy, presenting the most common mechanisms and active doses/concentrations required to reduce kidney damage. Future research efforts should be directed towards the identification of active compounds for plant species, given the still limited data available on isolated nephroprotective phytochemicals. Complementary information on revealing and comparing the pharmacological potencies of extracts and their derived isolated molecules and clinical trials are also relevant future challenges for the development of new drugs. Experimental findings published over the last few years have confirmed their high potency, offering unique and safe multitarget approaches for the modulation of different signaling pathways involved in kidney diseases. Based on the search conducted, alkaloids, anthraquinones, coumarins, flavonoids, lignans, phenylpropanoids, saponins, and triterpenes provided satisfactory preclinical efficacy and could be recommended for use alone or concomitantly with available nephroprotective synthetic drugs. A drug discovery program to provide nephroprotective products in biodiverse regions is essential for expediting the development of novel products for the benefit of humanity, which has an important impact in underdeveloped countries.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/plants14050648/s1, Table S1: Nephroprotective activities of secondary metabolites found in Brazilian plants evaluated through in vitro assays; Table S2: Nephroprotective activities of secondary metabolites found in native Brazilian plants extracts evaluated through in vivo assays; Figure S1: Molecular structures of secondary metabolites with nephroprotective activity evaluated in vitro and in vivo, shown in Tables S1 and S2 of the supporting information.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.M.C., M.R.R. and E.L.K.; writing—original draft preparation, R.M.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.L.R.C., A.d.C.P., E.S.R. and E.L.K.; software, T.d.S.C.; supervision, D.D.B., T.d.S.C. and E.L.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to FAPERGS, CNPq, and CAPES.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ene-Iordache, B.; Perico, N.; Bikbov, B.; Carminati, S.; Remuzzi, A.; Perna, A.; Islam, N.; Bravo, R.F.; Aleckovic-Halilovic, M.; Zou, H.; et al. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk in six regions of the world (ISN-KDDC): A cross-sectional study. Lancet Glob. Health 2016, 4, e307–e319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Bowe, B.; Mokdad, A.H.; Xian, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, T.; Maddukuri, G.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Floyd, T.; Al-Aly, Z. Analysis of the global burden of disease study highlights the global, regional, and national trends of chronic kidney disease epidemiology from 1990 to 2016. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, R.; Carlson, N.; Søndergaard, J.; Persson, F. The growing challenge of chronic kidney disease: An overview of current knowledge. Int. J. Nephrol. 2023, 2023, 9609266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Mulatu, K.; Feleke, S.F.; Wassie, G.T. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and associated factors among patients with underlying chronic disease at Dessie Referral Hospital, East Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Front. Epidemiol. 2023, 3, 1154522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Kidney Foundation. World Kidney Day. Chronic Kidney Disease. Available online: http://www.worldkidneyday.org/faqs/chronic-kidney-disease (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- International Society of Nephrology. ISN Framework for Developing Dialysis Programs in Low-Resource Settings, Brussels, Belgium. 2021. Available online: http://www.theisn.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/ISN-Framework-Dialysis-Report-HIRES.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2024).
- Lameire, N.H.; Levin, A.; Kellum, J.A.; Cheung, M.; Jadoul, M.; Winkelmayer, W.C.; Stevens, P.E. Harmonizing acute and chronic kidney disease definition and classification: Report of a kidney disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) consensus conference. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.L.; Yap, J.Q.; Qian, Q. Acute kidney injury: Tubular markers and risk for chronic kidney disease and end-stage kidney failure. Blood Purif. 2016, 41, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazella, M.A.; Rosner, M.H. Drug-induced acute kidney injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 1220–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palant, C.E.; Amdur, R.L.; Chawla, L.S. The acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease transition: A potential opportunity to improve care in acute kidney injury. Contrib. Nephrol. 2016, 187, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Langenberg, C.; Bagshaw, S.M.; May, C.N.; Bellomo, R. The histopathology of septic acute kidney injury: A systematic review. Crit. Care 2008, 12, R38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2012, 379, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.P.; Parving, H.H.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Ravid, M.; Remuzzi, G.; Lewis, J.B. Renal dysfunction in the presence of normoalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes: Results from the DEMAND study. Cardiorenal Med. 2012, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.T.; Su, G.; Zhang, L.; Qin, X.; Marshall, S.; González-Ortiz, A.; Clase, C.M.; Campbell, K.L.; Xu, H.; Carrero, J.J. Modifiable lifestyle factors for primary prevention of CKD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.C.; Maggo, J.K.; Campbell, K.L.; Craig, J.C.; Johnson, D.W.; Sutanto, B.; Ruospo, M.; Tong, A.; Strippoli, G.F. Dietary interventions for adults with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 4, CD011998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Jafar, T.H.; Nitsch, D.; Neuen, B.L.; Perkovic, V. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2021, 398, 786–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Adachi, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Katsuyama, H. Molecular biological and clinical understanding of the pathophysiology and treatments of hyperuricemia and its association with metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular diseases and chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Chimal, J.; Girerd, S.; Jaisser, F. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists and kidney diseases: Pathophysiological basis. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, L.F.; Emanuele, N.; Zhang, J.H.; Brophy, M.; Conner, T.A.; Duckworth, W.; Leehey, D.J.; McCullough, P.A.; O’Connor, T.; Palevsky, P.M.; et al. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1892–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mende, C.W. Chronic kidney disease and SGLT2 inhibitors: A review of the evolving treatment landscape. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekor, M. The growing use of herbal medicines: Issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO (World Health Organization). WHO Traditional Medicine Strategy 2002–2005, Geneva. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-EDM-TRM-2002.1 (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Natural products: A continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 21830, 3670–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusotti, G.; Cesari, I.; Dentamaro, A.; Caccialanza, G.; Massolini, G. Isolation and characterization of bioactive compounds from plant resources: The role of analysis in the ethnopharmacological approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 87, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Lou, H.X. Strategies to diversify natural products for drug discovery. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 1255–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; Supuran, C.T. Natural products in drug discovery: Advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomford, N.E.; Senthebane, D.A.; Rowe, A.; Munro, D.; Seele, P.; Maroyi, A.; Dzobo, K. Natural products for drug discovery in the 21st Century: Innovations for novel drug discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministério do Meio Ambiente e Mudança do Clima, Biodiversidade e Biomas, Brazil. 2024. Available online: https://www.gov.br/mma/pt-br/assuntos/biodiversidade-e-biomas (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Dutra, R.C.; Campos, M.M.; Santos, A.R.; Calixto, J.B. Medicinal plants in Brazil: Pharmacological studies, drug discovery, challenges and perspectives. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 112, 4–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.C. Brazilian traditional medicine: Historical basis, features and potentialities for pharmaceutical development. J. Trad. Chin. Med. Sci. 2021, 8, S44–S50. [Google Scholar]
- Di Stasi, L.C.; Hiruma-Lima, C.A. Plantas Medicinais na Amazônia e Mata Atlântica, 2nd ed.; Editora UNESP: São Paulo, Brazil, 2002; pp. 1–595. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzi, H.; Matos, F.J. Plantas Medicinais No Brasil: Nativas e Exóticas, 2nd ed.; Instituto Plantarum: São Paulo, Brazil, 2008; pp. 1–544. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, G.L. Dicionário das Plantas Úteis do Brasil, 2nd ed.; Editora Civilização Brasileira: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1979; pp. 1–599. [Google Scholar]
- Balbach, A. Flora Nacional na Medicina Doméstica, 2nd ed.; Edel: São Paulo, Brazil, 1974; pp. 1–915. [Google Scholar]
- La Cruz, M.G. Plantas Medicinais de Mato Grosso: A Farmacopéia Popular dos Raizeiros, 1st ed.; Carlini & Caniato: Cuiabá, Brazil, 2008; pp. 1–224. [Google Scholar]
- Guarim Neto, G. Plantas Utilizadas na Medicina Popular do Estado de Mato Grosso, 1st ed.; CNPq: Brasília, Brazil, 1987; pp. 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Teske, M.; Trentini, A.M. Compêndio de Fitoterapia: Herbarium, 4th ed.; Herbarium Laboratório Botânico: Curitiba, Brazil, 1995; pp. 1–317. [Google Scholar]
- Silva Araújo, J.E.; Lucas, V. Catálogo de Extratos Fluidos; Silva Araújo e Cia. Ltda: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1930; pp. 1–185. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, E.R. Plantas Medicinais Brasileiras: Conhecimentos Populares e Científicos; Hemus Editora: São Paulo, Brazil, 1993; pp. 1–342. [Google Scholar]
- Borrás, M.R.L. Plantas da Amazônia: Medicinais ou Mágicas? Plantas Comercializadas no Mercado Municipal Adolpho Lisboa; Valer Editora: Manaus, Brazil, 2003; pp. 1–322. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo, M.T.L.A. Plantas Medicinais e de Rituais Afro-Brasileiros II: Estudo Etnofarmacobotânico; Ícone: São Paulo, Brazil, 1998; pp. 1–232. [Google Scholar]
- Villas Bôas, G.K.; Galvão, M.; Machado, M.N.; Fraga, S.A.P.M. Conhecimento Popular de Plantas Medicinais do Extremo Sul da Bahia, 1st ed.; Outras Expressões: São Paulo, Brazil, 2018; pp. 1–174. [Google Scholar]
- Grandi, T.S.M. Tratado das Plantas Medicinais: Mineiras, Nativas e Cultivadas, Adaequatio, 1st ed.; Estúdio: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2014; pp. 1–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Coletto, L.M.M.; Pereira, B.M.R.; Cardozo Junior, E.L.; Zardinello, A.; Souza, H.A.S.; Lawich, M.C. Plantas Medicinais: Nativas dos Remanescentes Florestais do Oeste do Paraná, 1st ed.; Itaipu Binacional: Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, 2010; pp. 1–107. [Google Scholar]
- Alice, C.B.; Siqueira, N.C.S.; Mentz, L.A.; Silva, G.A.A.B.; José, K.F.D. Plantas Medicinais de Uso Popular—Atlas Farmacognóstico, 1st ed.; Editora da ULBRA: Canoas, Brazil, 1995; pp. 1–205. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, R. Plantas do Nordeste, Especialmente do Ceará, 3rd ed.; Fundação Vingt-Un Rosado: Mossoró, Brazil, 2001; pp. 1–526. [Google Scholar]
- Magalhães, K.N.; Bandeira, M.A.M.; Monteiro, M.P. Plantas Medicinais da Caatinga do Nordeste Brasileiro: Etnofarmacopeia do Professor Francisco José de Abreu Matos, 1st ed.; Imprensa Universitária: Fortaleza, Brazil, 2020; pp. 1–250. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, S.P.; Proença, C.E.B.; Sano, S.M.; Ribeiro, J.F. Cerrado: Espécies Vegetais Úteis, 1st ed.; Embrapa-CPAC: Planaltina, Brazil, 1998; pp. 1–464. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, V.E.G.; Carvalho, D.A. Plantas Medicinais No Domínio dos Cerrados; Imprenta UFLA: Lavras, Brazil, 2001; pp. 1–180. [Google Scholar]
- Pott, A.; Pott, V.J. Plantas do Pantanal, 1st ed.; EMBRAPA-SPI: Brasília, Brazil, 1994; pp. 1–320. [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda, R.; Cáceres, A.; Cruz, S.M.; Aceituno, J.A.; Marroquín, E.S.; Barrios Sosa, A.C.; Strangman, W.K.; Williamson, R.T. Nephroprotective plant species used in traditional Mayan Medicine for renal-associated diseases. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 301, 115755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.H.; Schor, N. Phyllanthus niruri inhibits calcium oxalate endocytosis by renal tubular cells: Its role in urolithiasis. Nephron 1999, 81, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.L.; Wang, L.T.; Huang, K.H.; Wang, C.C.; Chiang, C.K.; Liu, S.H. Quercetin attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via an activation of AMP-activated protein kinase-regulated autophagy pathway. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, G.Y.; Nam, M.H.; Lee, K.W. Inhibitory effect of caffeic acid on advanced glycation end product-induced renal fibrosis in vitro: A potential therapeutic target. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.B.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.Y. Quercetin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by reducing the expressions of transforming growth factor-β1 and connective tissue growth factor in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Ren. Fail. 2012, 34, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.W.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, J.H.; Lin, W.Q. Kidney disease models: Tools to identify mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Zool. Res. 2018, 39, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Rayego-Mateos, S.; Lamas, S.; Ortiz, A.; Rodrigues-Diez, R.R. Targeting the progression of chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, K.; Yokoi, H.; Mori, K.; Kasahara, M.; Kuwabara, T.; Imamaki, H.; Ishii, A.; Mori, K.P.; Kato, Y.; Ohno, S.; et al. MicroRNA-26a inhibits TGF-β-induced extracellular matrix protein expression in podocytes by targeting CTGF and is downregulated in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2169–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edeling, M.; Ragi, G.; Huang, S.; Pavenstadt, H.; Susztak, K. Developmental signalling pathways in renal fibrosis: The roles of Notch, Wnt and Hedgehog. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, D.; Tan, R.J.; Liu, Y. Loss of klotho contributes to kidney injury by derepression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giulietti, A.M.; Harley, R.M.; De Queiroz, L.P.; Wanderley, M.G.L.; Van den Berg, C. Biodiversity and conservation of plants in Brazil. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, F.; Leitão, S.G.; Fonseca-Kruel, V.S.; Silva, I.M.; Martins, K.S. Medicinal plants traded in the open-air markets in the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: An overview on their botanical diversity and toxicological potential. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2014, 24, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, L.N.B.; Boeing, T.; da Silva, R.C.V.; da Silva, L.M.; Gasparotto-Júnior, A.; Cechinel-Filho, V.; de Souza, P. Exotic medicinal plants used in Brazil with diuretic properties: A review. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202200258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahastuti, S.; Hidayat, M.; Hasiana, S.T.; Widowati, W.; Amalia, A.; Qodariah, R.L.; Rizal, R.; Kusuma, H.S.; Khoiriyah, Z. Ethanol extract of jati belanda (Guazuma ulmifolia L.) as therapy for chronic kidney disease in in vitro model. J. Rep. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 8, 229. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, G.A.; Peixoto Araujo, N.M.; Arruda, H.S.; Farias, D.P.; Molina, G.; Pastore, G.M. Phytochemicals and biological activities of mutamba (Guazuma ulmifolia Lam.): A review. Food Res. Int. 2019, 126, 108713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldini, M.; Di Micco, S.; Montoro, P.; Darra, E.; Mariotto, S.; Bifulco, G.; Pizza, C.; Piacente, S. Flavanocoumarins from Guazuma ulmifolia bark and evaluation of their affinity for STAT1. Phytochem. 2013, 86, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.C.; Pedrochi, F.; Hernandes, L.; de Mello, J.C.; Baesso, M.L. Ex vivo evaluation of the percutaneous penetration of proanthocyanidin extracts from Guazuma ulmifolia using photoacoustic spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 587, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, J.M.; Alfredo, T.M.; Antunes, K.Á.; da Cunha, J.D.S.M.; Costa, E.M.A.; Lima, E.S.; Silva, D.B.; Carollo, C.A.; Schmitz, W.O.; Boleti, A.P.A.; et al. Guazuma ulmifolia Lam. decreases oxidative stress in blood cells and prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 2935051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero-George, C.; Vanderheyden, P.M.; De Bruyne, T.; Shahat, A.A.; Van den Heuvel, H.; Solis, P.N.; Gupta, M.P.; Claeys, M.; Pieters, L.; Vauquelin, G.; et al. In vitro inhibition of [3H]-angiotensin II binding on the human AT1 receptor by proanthocyanidins from Guazuma ulmifolia bark. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.Y.; Khoo, W.K.; Adnan, M.A.; Mahalingam, T.P.; Fernandez, A.R.; Jeevaratnam, K. The pharmacological potential of Phyllanthus niruri. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 953–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, M.E.; Schor, N.; Boim, M.A. Effects of an aqueous extract from Phyllanthus niruri on calcium oxalate crystallization in vitro. J. Urol. Res. 2003, 30, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, A.M.; Schor, N.; Boim, M.A. The effect of Phyllanthus niruri on urinary inhibitors of calcium oxalate crystallization and other factors associated with renal stone formation. BJU Int. 2002, 89, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugaiyah, V.; Chan, K.L. Antihyperuricemic lignans from the leaves of Phyllanthus niruri. Planta Med. 2006, 72, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, A.; Kamagate, M.; Amonkan, A.K.; Chabert, P.; Kpahé, F.; Koffi, C.; Kouame, M.; Auger, C.; Kati-Coulibaly, S.; Schini-Kerth, V.; et al. The acute diuretic effect of an ethanolic fraction of Phyllanthus amarus (Euphorbiaceae) in rats involves prostaglandins. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.R.; Tripathi, P.; Sharma, V.; Chauhan, N.S.; Dixit, V.K. Phyllanthus amarus: Ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 286–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, J.M.; Ribeiro de Souza, L.C.; Lemos de Souza, R.A.; da Silva Filha, R.; de Oliveira Silva, J.; de Almeida Araújo, S.; Tagliti, C.A.; Simões e Silva, A.C.; Castilho, R.O. Costus spiralis extract restores kidney function in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity model: Ethnopharmacological use, chemical and toxicological investigation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 299, 115510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garro, M.F.; Gil, R.A.; Leporati, J.; Garro, H.A. Diuretic activity of Euphorbia serpens extracts in Wistar rats. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 38, 2140–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevevino, L.H.; Vieira, F.S.; Cassola, A.C.; Sanioto, S.M. Effect of crude extract of roots of Bredemeyera floribunda Willd. I, Effect on arterial blood pressure and renal excretion in the rat. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1994, 43, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevevino, L.H.; Aires, M.M. Effect of crude extract of roots of Bredemeyera floribunda Willd. II, Effect on glomerular filtration rate and renal tubular function of rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1994, 43, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Daros, M.D.; Matos, F.J.; Parente, J.P. A new triterpenoid saponin, bredemeyeroside B. from the roots of Bredemeyera floribunda. Planta Med. 1996, 62, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tailor, C.; Goyal, A. In vitro antilithiatic activity of alcoholic leaf extract of Ageratum conyzoides L. World J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 2, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar]
- Filha, Z.S.; Vitolo, I.F.; Fietto, L.G.; Lombardi, J.A.; Saúde-Guimarães, D.A. Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of Lychnophora species from Brazil (“Arnica”). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 107, 200679–200682. [Google Scholar]
- Lemos Lima, R.C.; Ferrari, F.C.; Souza, M.R.; Sá Pereira, B.M.; Paula, C.A.; Saúde-Guimarães, D.A. Effects of extracts of leaves from Sparattosperma leucanthum on hyperuricemia and gouty arthritis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 161, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cógáin, M.R.; Linnes, M.P.; Lee, H.J.; Krambeck, A.E.; Mendonça Uchôa, J.C.; Kim, S.H.; Lieske, J.C. Aqueous extract of Costus arabicus inhibits calcium oxalate crystal growth and adhesion to renal epithelial cells. Urolithiasis 2015, 43, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauzi, A.N.; Muhammad, N.; Sairi, N.H.; Tuan Putra, T.N.M.; Gul, M.T.; Rahim, N.F.A.; Marzuki, N.A.S.; Abu Bakar, M.F.; Talip, B.A.; Abdullah, N. The effect of different solvent extraction towards antiurolithiatic properties of Euphorbia hirta and Orthosiphon stamineus. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 269, 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.B.; Coelho, E.B.; Rodrigues, M.R.; Costa-Machado, A.R.; Sousa, J.P.; Berretta, A.A.; Bastos, J.K. Effect of the Copaifera langsdorffii Desf. leaf extract on the ethylene glycol-induced nephrolithiasis in rats. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 131372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz Junior, N.F.; Steffani, J.A.; Machado, L.; Longhi, P.J.H.; Montano, M.A.E.; Martins, M.; Machado, S.A.; Machado, A.K.; Cadoná, F.C. Antioxidant and cytoprotective effects of avocado oil and extract (Persea americana Mill) against rotenone using monkey kidney epithelial cells (Vero). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2021, 84, 875–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punaro, G.R.; Lima, D.Y.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Pugliero, S.; Mouro, M.G.; Rogero, M.M.; Higa, E.M.S. Cupuaçu extract reduces nitrosative stress and modulates inflammatory mediators in the kidneys of experimental diabetes. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugaiyah, V.; Chan, K.L. Mechanisms of antihyperuricemic effect of Phyllanthus niruri and its lignin constituents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 124, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, P.; Mishra, V.K.; Arun, K.; Bais, N.; Singh, R. Study on in vitro anti-lithiatic activity of Phyllanthus niruri Linn. leaves by homogeneous precipitation and turbiditory method. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Prando, T.B.; Barboza, L.N.; Araújo, V.O.; Gasparotto, F.M.; Souza, L.M.; Lourenço, E.L.; Gasparotto Junior, A. Involvement of bradykinin B2 and muscarinic receptors in the prolonged diuretic and antihypertensive properties of Echinodorus grandiflorus (Cham. & Schltdl.) Micheli. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Portella, V.G.; Cosenza, G.P.; Diniz, L.R.; Pacheco, L.F.; Cassali, G.D.; Caliari, M.V.; Brandão, M.G.; Vieira, M.A. Nephroprotective effect of Echinodorus macrophyllus Micheli on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Nephron Extra 2012, 2, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setyaningsih, W.A.W.; Arfian, N.; Fitriawan, A.S.; Yuniartha, R.; Sari, D.C.R. Ethanolic extract of Centella asiatica treatment in the early stage of hyperglycemia condition inhibits glomerular injury and vascular remodeling in diabetic rat model. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2021, 6, 6671130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfian, N.; Setyaningsih, W.A.W.; Anggorowati, N.; Romi, M.M.; Sari, D.C.R. Ethanol extract of Centella asiatica (Gotu Kola) attenuates tubular injury through inhibition of inflammatory cytokines and enhancement of anti-fibrotic factor in mice with 5/6 subtotal nephrectomy. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 26, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muccillo-Baisch, A.L.; Moura, F.R.; Penteado, J.O.; Fernandes, C.L.F.; Costa Bueno, E.; Menestrino Garcia, E. Silva Júnior, F.M.R. Beneficial effects of mate-herb, Ilex paraguariensis St. Hil. against potassium dichromate-induced oxidative stress and nephrotoxicity. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2023, 86, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.K.; Roy, A.; Jha, A.K.; Sharma, U. Diuretic activity of Pistia stratioides leaf extract in rats. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2009, 2, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Bhavsar, V.P.; Patel, A.; Vaghasiya, J.D.; Padhiyar, S.; Patel, T.B. Pistia stratiotes has renoprotective potentials in ischemia reperfusion injury in normal and diabetic rats. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2023, 55, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescano, C.H.; Iwamoto, R.D.; Sanjinez-Argandoña, E.J.; Kassuya, C.A. Diuretic and anti-inflammatory activities of the microencapsulated Acrocomia aculeata (Arecaceae) oil on Wistar rats. J. Med. Food. 2015, 18, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirloni, C.A.S.; Lívero, F.A.D.R.; Palozi, R.A.C.; Silveira, R.C.A.; Vasconcelos, P.C.P.; Souza, R.I.C.; Dos Santos, A.C.; Almeida, V.P.; Manfron Budel, J.; Souza, L.M.; et al. Ethnopharmacological investigations of the cardio-renal properties of a native species from the region of Pantanal, state of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 206, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palozi, R.A.C.; Schaedler, M.I.; Tirloni, C.A.S.; Silva, A.O.; Lívero, F.A.D.R.; Souza, R.I.C.; Dos Santos, A.C.; Prando, T.B.L.; Souza, L.M.; Gasparotto Junior, A. Roles of nitric oxide and prostaglandins in the sustained antihypertensive effects of Acanthospermum hispidum DC. on ovariectomized rats with renovascular hypertension. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2017, 2017, 2492483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindhi, S.; Methra, T.; Chandu, B.R.; Boyina, R.; Dasari, V. Antiurolithiatic and in vitro antioxidant activity of leaves of Ageratum conyzoides in rat. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 2, 636–649. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, T.C.; Silva, G.R.D.; Silva, A.O.; Schaedler, M.I.; Guarnier, L.P.; Palozi, R.A.C.; Signor, C.T.; Bosco, J.D.D.; Auth, P.A.; Amaral, E.C.; et al. Hepato- and cardioprotective effects of Baccharis trimera (Less.) DC. against multiple risk factors for chronic noncommunicable diseases. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2021, 93, e20200899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, E.C.; Silva, G.R.; Abreu Braga, F.; Palozi, R.A.; Lorençone, B.R.; Marques, A.A.M.; Moreno, K.T.; Leite, P.R.T.; Barboza, L.N.; Souza, R.I.; et al. Cardioprotective effects of Baccharis trimera (Less.) DC in a rodent model of hookah, alcohol, and energy drink exposure. Bol. Latinoam. Caribe Plant Med. Aromat. 2023, 22, 377–392. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, M.M.Q.; Silva, G.R.D.; Cola, I.M.; Silva, A.O.; Schaedler, M.I.; Guarnier, L.P.; Palozi, R.A.C.; Barboza, L.N.; Menetrier, J.V.; Froelich, D.L.; et al. Baccharis trimera (Less.) DC: An innovative cardioprotective herbal medicine against multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease. J. Med. Food. 2020, 23, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.O.; Sial, A.S.; Akhtar, I.; Naeem, M.; Hazafa, A.; Ansari, R.A.; Rizvi, S.A.A. The nephroprotective effects of Daucus carota and Eclipta prostrata against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 12702–12721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dungca, N.T.P. Protective effect of the methanolic leaf extract of Eclipta alba (L.) Hassk. (Asteraceae) against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in Sprague Dawley rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 184, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wei, B.; Fu, X.; Luo, M.; Liu, S.; Li, R.; Ren, B.; Tang, L. Effect of Eclipta prostrata on 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in rat liver and kidney. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014, 2014, 651053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins de Sá Müller, C.; Coelho, G.B.; Paula Michel Araújo, M.C.; Saúde-Guimarães, D.A. Lychnophora pinaster ethanolic extract and its chemical constituents ameliorate hyperuricemia and related inflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 242, 112040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-González, L.; Cienfuegos-Pecina, E.; Perales-Quintana, M.M.; Alarcon-Galvan, G.; Muñoz-Espinosa, L.E.; Pérez-Rodríguez, E.; Cordero-Pérez, P. Nephroprotective effect of Sonchus oleraceus extract against kidney injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in Wistar rats. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 9572803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, M.N.; Hamed, A.N.E.; Mahmoud, B.K.; Attia, E.Z.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Fawzy, M.A.; Attya, M.E.; Kamel, M.S. LC-MS-based identification of bioactive compounds and hepatoprotective and nephroprotective activities of Bignonia binata leaves against carbon tetrachloride-induced injury in rats. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, A.A.; Fahmy, S.R.; Soliman, A.M.; Mohamed, D.M. Antinephrolithiatic activity of Ananas comosus extract against experimentally induced renal calculi in rats. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 33, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar]
- Leme, T.S.; Prando, T.B.; Gasparotto, F.M.; Souza, P.; Crestani, S.; Souza, L.M.; Cipriani, T.R.; Lourenço, E.L.; Gasparotto, A., Jr. Role of prostaglandin/cAMP pathway in the diuretic and hypotensive effects of purified fraction of Maytenus ilicifolia Mart ex Reissek (Celastraceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Gutiérrez, R.M.; Laguna, G.Y.; Walkowski, A. Diuretic activity of Mexican Equisetum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1985, 14, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganya, S.; Sophia, D.; Raj, C.A.; Rathi, M.A.; Thirumoorthi, L.; Meenakshi, P.; Kumar, D.G.; Gopalakrishnan, V.K. Amelioration of nitrobenzene-induced nephrotoxicity by the ethanol extract of the herb Euphorbia hirta. Pharmacognosy Res. 2011, 3, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siva Jyothi, C.H.; Babu, P.; Karimulla, S.K.; Gobinath, M. Preventive effect of Euphorbia thymifolia Linn against ethylene glycol-induced urolithiasis in male Wistar albino rats. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 8, 590–595. [Google Scholar]
- Falayi, O.O.; Oyagbemi, A.A.; Omobowale, T.O.; Ayodele, E.A.; Adedapo, A.D.; Yakubu, M.A.; Adedapo, A.A. Nephroprotective properties of the methanol stem extract of Abrus precatorius on gentamicin-induced renal damage in rats. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2018, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, P.; Silva, L.M.; Boeing, T.; Somensi, L.B.; Cechinel-Zanchett, C.C.; Campos, A.; Krueger, C.M.A.; Bastos, J.K.; Cechinel-Filho, V.; Andrade, S.F. Influence of prostanoids in the diuretic and natriuretic effects of extracts and kaempferitrin from Bauhinia forficata Link leaves in rats. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunmoyole, T.; Ola-Awe, A.M.; Fatile, O.G. Ethanolic extract of Mucuna pruriens leaves ameliorates carbon tetrachloride and rifampicin-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in Wistar albino rat. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concessao, P.; Bairy, L.K.; Raghavendra, A.P. Protective effect of Mucuna pruriens against arsenic-induced liver and kidney dysfunction and neurobehavioral alterations in rats. Vet. World. 2020, 13, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu, I.; Fazel, M.F. Alleviation of renal oxidative stress by Cassia alata in acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxic rats. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 9, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sugumar, M.; Doss, D.V.A.; Maddisetty, P.N.P. Hepato-renal protective effects of hydroethanolic extract of Senna alata on enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidant systems in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Integr. Med. Res. 2016, 5, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntchapda, F.; Barama, J.; Kemeta Azambou, D.R.; Etet, P.F.; Dimo, T. Diuretic and antioxidant activities of the aqueous extract of leaves of Cassia occidentalis (Linn.) in rats. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2015, 8, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, V.O.; Gasparotto, F.M.; Pires, V.A.; Maciel, A.A.; Ortmann, C.F.; Cardozo Junior, E.L.; Lourenço, E.L.; Gasparotto Junior, A. Renoprotective effects of Vitex megapotamica (Spreng.) Moldenke in C57BL/6 LDLr-null mice undergoing high fat diet. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 475380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osukoya, O.A.; Oyinloye, B.E.; Ajiboye, B.O.; Olokode, K.A.; Adeola, H.A. Nephroprotective and anti-inflammatory potential of aqueous extract from Persea americana seeds against cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity in Wistar rats. Biometals 2021, 34, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouamé, N.M.; Koffi, C.; N’Zoué, K.S.; Yao, N.A.R.; Doukouré, B.; Kamagaté, M. Comparative antidiabetic activity of aqueous, ethanol, and methanol leaf extracts of Persea americana and their effectiveness in type 2 diabetic rats. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2019, 16, 5984570. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Avila, O.; Figueroa-García, M.D.; García-Berumen, C.I.; Calderón-Cortés, E.; Mejía-Barajas, J.A.; Rodriguez-Orozco, A.R.; Mejía-Zepeda, R.; Saavedra-Molina, A.; Cortés-Rojo, C. Avocado oil induces long-term alleviation of oxidative damage in kidney mitochondria from type 2 diabetic rats by improving glutathione status. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2017, 49, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, S.; Ali, H.; Naseer, F.; Abduh, M.S.; Qadir, H.; Kakar, S.; Waheed, Y.; Ahmad, T. Antioxidant activity of Carica papaya & Persea americana fruits against cadmium induced neurotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and hepatotoxicity in rats with a computational approach. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 81, 127324. [Google Scholar]
- Wientarsih, I.; Purwono, R.; Prasetyo, B.; Aldobrata, A. Anti-lithiasis activity of avocado (Persea americana Mill) leaves extract in white male rats. Hayati J. Biosci. 2012, 19, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaedler, M.I.; Palozi, R.A.C.; Tirloni, C.A.S.; Silva, A.O.; Araújo, V.O.; Lourenço, E.L.B.; Souza, L.M.; Lívero, F.A.D.R.; Gasparotto Junior, A. Redox regulation and NO/cGMP plus K+ channel activation contributes to cardiorenal protection induced by Cuphea carthagenensis (Jacq.) J.F. Macbr. in ovariectomized hypertensive rats. Phytomedicine 2018, 51, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouelela, M.E.; Orabi, M.A.A.; Abdelhamid, R.A.; Abdelkader, M.S.; Madkor, H.R.; Darwish, F.M.M.; Hatano, T.; Elsadek, B.E.M. Ethyl acetate extract of Ceiba pentandra (L.) Gaertn. reduces methotrexate-induced renal damage in rats via antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic actions. J. Tradit. Complement. 2019, 10, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Robert, S.M.J.; Sharma, M.; Aeri, V. Evaluation of Sida cordifolia and Sida rhombifolia extracts in a rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. Polim. Med. 2023, 53, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Miyazawa, T.; Kimura, F.; Kamei, M.; Miyazawa, T. Carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic and renal damages in rat: Inhibitory effects of cacao polyphenol. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayana, S.; Khanwelkar, C.; Venkat, R.; Nimmagadda, C.; Chavan, V.; Sambu Naveen, N. Diuretic activity of aqueous extract of roots of Cissampelos pareira in albino rats. Int. J. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 3, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.C.; Swamy, B.M.; Swamy, P. Protective effect of Cissampelos pareira Linn. on paracetamol induced nephrotoxicity in male albino rats. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 695–705. [Google Scholar]
- Meira, E.; Oliveira, N.; Mariani, N.; Porto, M.; Severi, J.; Siman, F.; Meyrelles, S.; Vasquez, E.; Gava, A. Eugenia uniflora (pitanga) leaf extract prevents the progression of experimental acute kidney injury. J. Func. Foods. 2020, 66, 103818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consolini, A.E.; Baldini, O.A.; Amat, A.G. Pharmacological basis for the empirical use of Eugenia uniflora L. (Myrtaceae) as antihypertensive. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 66, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo Galdino, O.; Souza Gomes, I.; Ferreira de Almeida Júnior, R.; Conceição Ferreira de Carvalho, M.I.; Abreu, B.J.; Abbott Galvão Ururahy, M.; Cabral, B.; Zucolotto Langassner, S.M.; Costa de Souza, K.S.; Augusto de Rezende, A. The nephroprotective action of Passiflora edulis in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerdy, N.; Ritarwan, K. Hepatoprotective activity and nephroprotective activity of peel extract from three varieties of the passion fruit (Passiflora sp.) in the albino rat. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olorunnisola, O.S.; Fadahunsi, O.S.; Adegbola, P.I.; Ajilore, B.S.; Ajayi, F.A.; Olaniyan, L.W.B. Phyllanthus amarus attenuated derangement in renal-cardiac function, redox status, lipid profile and reduced TNF-α, interleukins-2, 6 and 8 in high salt diet fed rats. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunmoyole, T.; Awodooju, M.; Idowu, S.; Daramola, O. Phyllanthus amarus extract restored deranged biochemical parameters in rat model of hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woottisin, S.; Hossain, R.Z.; Yachantha, C.; Sriboonlue, P.; Ogawa, Y.; Saito, S. Effects of Orthosiphon grandiflorus, Hibiscus sabdariffa and Phyllanthus amarus extracts on risk factors for urinary calcium oxalate stones in rats. J. Urol. 2011, 185, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeneye, A.A.; Benebo, A.S. Protective effect of the aqueous leaf and seed extract of Phyllanthus amarus on gentamicin and acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 118, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, M.E.; Lima, R.; Mercuri, L.P.; Matos, J.R.; Schor, N.; Boim, M.A. Effect of extract of Phyllanthus niruri on crystal deposition in experimental urolithiasis. Urol. Res. 2006, 34, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giribabu, N.; Rao, P.V.; Kumar, K.P.; Muniandy, S.; Swapna Rekha, S.; Salleh, N. Aqueous extract of Phyllanthus niruri leaves displays in vitro antioxidant activity and prevents the elevation of oxidative stress in the kidney of streptozotocin-induced diabetic male rats. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014, 2014, 834815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giribabu, N.; Karim, K.; Kilari, E.K.; Salleh, N. Phyllanthus niruri leaves aqueous extract improves kidney functions, ameliorates kidney oxidative stress, inflammation, fibrosis and apoptosis and enhances kidney cell proliferation in adult male rats with diabetes mellitus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 205, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnatyszyn, O.; Miño, J.; Gorzalczany, S.; Opezzo, J.; Ferraro, G.; Coussio, J.; Acevedo, C. Diuretic activity of an aqueous extract of Phyllanthus sellowianus. Phytomedicine 1999, 6, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Prando, T.B.; Barboza, L.N.; Gasparotto, F.M.; Araújo, V.O.; Slgnor Tirloni, C.A.; Souza, L.M.; Lourenço, E.L.; Gasparotto Junior, A. Ethnopharmacological investigation of the diuretic and hemodynamic properties of native species of the Brazilian biodiversity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 174, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta León, K.L.; Moyano Aguay, M.B.; Vinueza Tapia, D.R. Diuretic activity of Piper peltatum L. (Piperaceae) from Ecuador on Rattus norvegicus. Pharmacologyonline 2020, 1, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Agbor, G.A.; Akinfiresoye, L.; Sortino, J.; Johnson, R.; Vinson, J.A. Piper species protect cardiac, hepatic and renal antioxidant status of atherogenic diet fed hamsters. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.J.; Fulgencio, S.F.; Rabetti, A.C.; Nicolau, M.; Poli, A.; Simões, C.M.; Ribeiro-do-Valle, R.M. Effects of hydroalcoholic extracts of Portulaca pilosa and Achyrocline satureioides on urinary sodium and potassium excretion. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1994, 43, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Wadud, A.; Jahan, N.; Bilal, A.; Hajera, S. Efficacy of Adiantum capillus veneris Linn in chemically induced urolithiasis in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 146, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, L.R.; Portella, V.G.; Cardoso, F.M.; Souza, A.M.; Caruso-Neves, C.; Cassali, G.D.; Reis, A.M.; Brandão, M.; Vieira, M.A. The effect of saponins from Ampelozizyphus amazonicus Ducke on the renal Na+ pumps’ activities and urinary excretion of natriuretic peptides. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, L.R.; Santana, P.C.; Ribeiro, A.P.; Portella, V.G.; Pacheco, L.F.; Meyer, N.B.; César, I.C.; Cosenza, G.P.; Brandão, M.; Vieira, M.A. Effect of triterpene saponins from roots of Ampelozizyphus amazonicus Ducke on diuresis in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 123, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana Aquino, D.F.; Signor Tirloni, C.A.; Tolouei Menegati, S.E.; Lima Cardoso, C.A.; Heredia Vieira, S.C.; Carmo Vieira, M.D.; Simonet, A.M.; Macías, F.A.; Gasparotto Junior, A. Alibertia edulis (L.C. Rich.) A.C. Rich—A potent diuretic arising from Brazilian indigenous species. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 196, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, P.C.; Pucci, L.L.; Vieira, M.S.; Lino, R.S., Jr.; Oliveira, C.M.; Cunha, L.C.; Paula, J.R.; Valadares, M.C. Diuretic activity and acute oral toxicity of Palicourea coriacea (Cham.) K Schum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulin, F.V.; Palozi, R.A.C.; Lorençone, B.R.; Macedo, A.L.; Guarnier, L.P.; Tirloni, C.A.S.; Romão, P.V.M.; Gasparotto Junior, A.; Silva, D.B. Prolonged administration of Rudgea viburnoides (Cham.) Benth. prevents impairment of redox status, renal dysfunction, and cardiovascular damage in 2K1C-hypertensive rats by inhibiting ACE activity and NO-GMPC pathway activation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdino, P.M.; Alexandre, L.N.; Pacheco, L.F.; Souza Lino Junior, R.; Paula, J.R.; Pedrino, G.R.; Xavier, C.H.; Ferreira, P.M. Nephroprotective effect of Rudgea viburnoides (Cham.) Benth leaves on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 92, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parameshappa, B.; Ali Basha, M.S.; Sen, S.; Chakraborty, R.; Kumar, G.V.; Sagar, G.V.; Sowmya, L.; Raju, K.K.; Sesh Kumar, P.K.; Lakshmi, A.V. Acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: Protective role of Cardiospermum halicacabum. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameshappa, B.; Venkata, R.N.; Mounika, M.A.; Srilatha, D. Protective effect of aqueous extract of Cardiospermum helicacabum Linn against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. Der Pharm. Lett. 2011, 3, 351–357. [Google Scholar]
- Tolouei, S.E.L.; Palozi, R.A.C.; Tirloni, C.A.S.; Marques, A.A.M.; Schaedler, M.I.; Guarnier, L.P.; Silva, A.O.; Almeida, V.P.; Manfron Budel, J.; Souza, R.I.C.; et al. Ethnopharmacological approaches to Talinum paniculatum (Jacq.) Gaertn.—Exploring cardiorenal effects from the Brazilian Cerrado. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 238, 111873. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Souto, C.G.R.G.; Lorençone, B.R.; Marques, A.A.M.; Palozi, R.A.C.; Romão, P.V.M.; Guarnier, L.P.; Tirloni, C.A.S.; Dos Santos, A.C.; Souza, R.I.C.; Zago, P.M.J.J.; et al. Cardioprotective effects of Talinum paniculatum (Jacq.) Gaertn. in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in hypertensive rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 281, 114568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maquiaveli, C.C.; Silva, E.R.; Rosa, L.C.; Francescato, H.D.; Lucon Júnior, J.F.; Silva, C.G.; Casarini, D.E.; Ronchi, F.A.; Coimbra, T.M. Cecropia pachystachya extract attenuated the renal lesion in 5/6 nephrectomized rats by reducing inflammation and renal arginase activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 158, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maquiaveli, C.C.; Silva, E.R.; Francescato, H.D.; Costa, R.S.; Silva, C.G.; Casarini, D.E.; Ronchi, F.A.; Coimbra, T.M. Brazilian embauba (Cecropia pachystachya) extract reduces renal lesions in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. J. Renin. Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2014, 15, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, O.A.; Olugbami, J.O.; Adegoke, A.M.; Gbadegesin, M.A.; Odunola, O.A. Reno-hepatoprotective and antidiabetic properties of methanol leaf extract of Laportea aestuans in Wistar rats. J. Evid. Based Integr. Med. 2021, 26, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaitén, Y.I.G.; Lizama, R.S.; González, A.F.; Moreno, M.D.F.; Orta, R.M.C.; Galarza, L.M. Physicochemical characterization and preliminary diuretic activity of Urera baccifera (L.) watery extracts. Rev. Cub. Farm. 2020, 53, e431. [Google Scholar]
- Tolouei, S.E.L.; Palozi, R.A.C.; Tirloni, C.A.S.; Marques, A.A.M.; Schaedler, M.I.; Guarnier, L.P.; Silva, A.O.; Almeida, V.P.; Budel, J.M.; Souza, R.I.C.; et al. Anchietea pyrifolia A. St.-Hil. as a cardiovascular-endowed species: A whole-biological investigation. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.C.; Rates, S.M.K.; Simões, C.M.O. Avaliação da eficácia e segurança de produtos naturais candidatos a fármacos e medicamentos. In Farmacognosia: Do Produto Natural ao Medicamento; Simões, C.M.O., Schenckel, E.P., Mello, J.C.P., Mentz, L.A., Petrovick, P.R., Eds.; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2017; pp. 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiró, M.; Ilha, J.; Pochmann, D.; Porciúncula, L.O.; Xavier, L.L.; Achaval, M.; Nunes, D.S.; Elisabetsky, E. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition in cognition-relevant brain areas of mice treated with a nootropic Amazonian herbal (Marapuama). Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michl, J.; Jennings, H.M.; Kite, G.C.; Ingrouille, M.J.; Simmonds, M.S.; Heinrich, M. Is aristolochic acid nephropathy a widespread problem in developing countries? A case study of Aristolochia indica L. in Bangladesh using an ethnobotanical-phytochemical approach. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudoux, T.; Jadot, I.; Declèves, A.E.; Antoine, M.H.; Colet, J.M.; Botton, O.; De Prez, E.; Pozdzik, A.; Husson, C.; Caron, N.; et al. Experimental aristolochic acid nephropathy: A relevant model to study AKI-to-CKD transition. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 822870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Guo, J.; Liu, H.; He, B.; Lai, R.; Zhu, Q.; Zheng, Z. Scopoletin and umbelliferone from Cortex Mori as protective agents in high glucose-induced mesangial cell as in vitro model of diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Chin. J. Physiol. 2021, 64, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waly, M.I.; Ali, B.H.; Al-Lawati, I.; Nemmar, A. Protective effects of emodin against cisplatin-induced oxidative stress in cultured human kidney (HEK 293) cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankoglu, E.E.; Broscheit, J.; Arnaudov, T.; Roewer, N.; Stopper, H. Protective effects of tricetinidin against oxidative stress inducers in rat kidney cells: A comparison with delphinidin and standard antioxidants. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 121, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunel, V.; Antoine, M.H.; Nortier, J.; Duez, P.; Stévigny, C. Nephroprotective effects of ferulic acid, Z-ligustilide and E-ligustilide isolated from Angelica sinensis against cisplatin toxicity in vitro. Toxicol. Vitro 2015, 29, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, K.; Tamura, Y.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Miyazaki, M.; Suzuki, N.; Sato, W.; Maeshima, Y.; Schreiner, G.F.; Villarreal, F.J.; Johnson, R.J.; et al. Epicatechin limits renal injury by mitochondrial protection in cisplatin nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2012, 303, F1264–F1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, S.Q.; He, Y.L.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z.Y. Protective effects of quercetin on cadmium-induced cytotoxicity in primary cultures of rat proximal tubular cells. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2013, 26, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zhao, S.; Hong, J.; Li, W.; Wang, X. Protective Effects of kaempferol on D-ribose-induced mesangial cell injury. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 7564207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Bi, Y.; Xiong, H.; Bo, T.; Han, L.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Wedelolactone protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice via inhibition of organic cation transporter 2. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, S447–S459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, R. Betulinic acid attenuates T-2 toxin-induced cytotoxicity in porcine kidney cells by blocking oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 249, 109124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, W.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, B.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Sha, J.; et al. Ameliorative effect of ursolic acid on ochratoxin A-induced renal cytotoxicity mediated by Lonp1/Aco2/Hsp75. Toxicon 2019, 168, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawfetrias, W.; Devy, L.; Esyanti, R.R.; Faizal, A. Phyllanthus lignans: A review of biological activity and elicitation. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cechinel-Zanchett, C.C.; Bolda Mariano, L.N.; Boeing, T.; da Costa, J.C.; da Silva, L.M.; Bastos, J.K.; Cechinel-Filho, V.; de Souza, P. Diuretic and renal protective effect of kaempferol 3-O-alpha-L-rhamnoside (afzelin) in normotensive and hypertensive rats. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1980–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, M.; Salama, R.A.M.; Aboughalia, A.; Tarek, M.; Mohamed Fawzy, N. Apigenin ameliorates genitourinary dysfunction in a type 1 diabetic rat model via Drp1 modulation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes-Rivera, J.; Arellano-Mendoza, M.; Nájera, N.; Del Valle-Mondragón, L.; Villarreal, F.; Rubio-Gayosso, I.; Perez-Duran, J.; Meaney, E.; Ceballos, G. Effect of (−)-epicatechin on the modulation of progression markers of chronic renal damage in a 5/6 nephrectomy experimental model. Heliyon 2019, 16, e01512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhu, L.; Ou, Z.; Ma, C.; Kong, L.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wen, L.; Wu, J.; et al. Betulinic acid protects against renal damage by attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammation via Nrf2 signaling pathway in T-2 toxin-induced mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101 Pt B, 108210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).