The Combined Application of Biofertilizer Alleviates the Continuous Cropping Obstacles of Replanted Zanthoxylum bungeanum: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
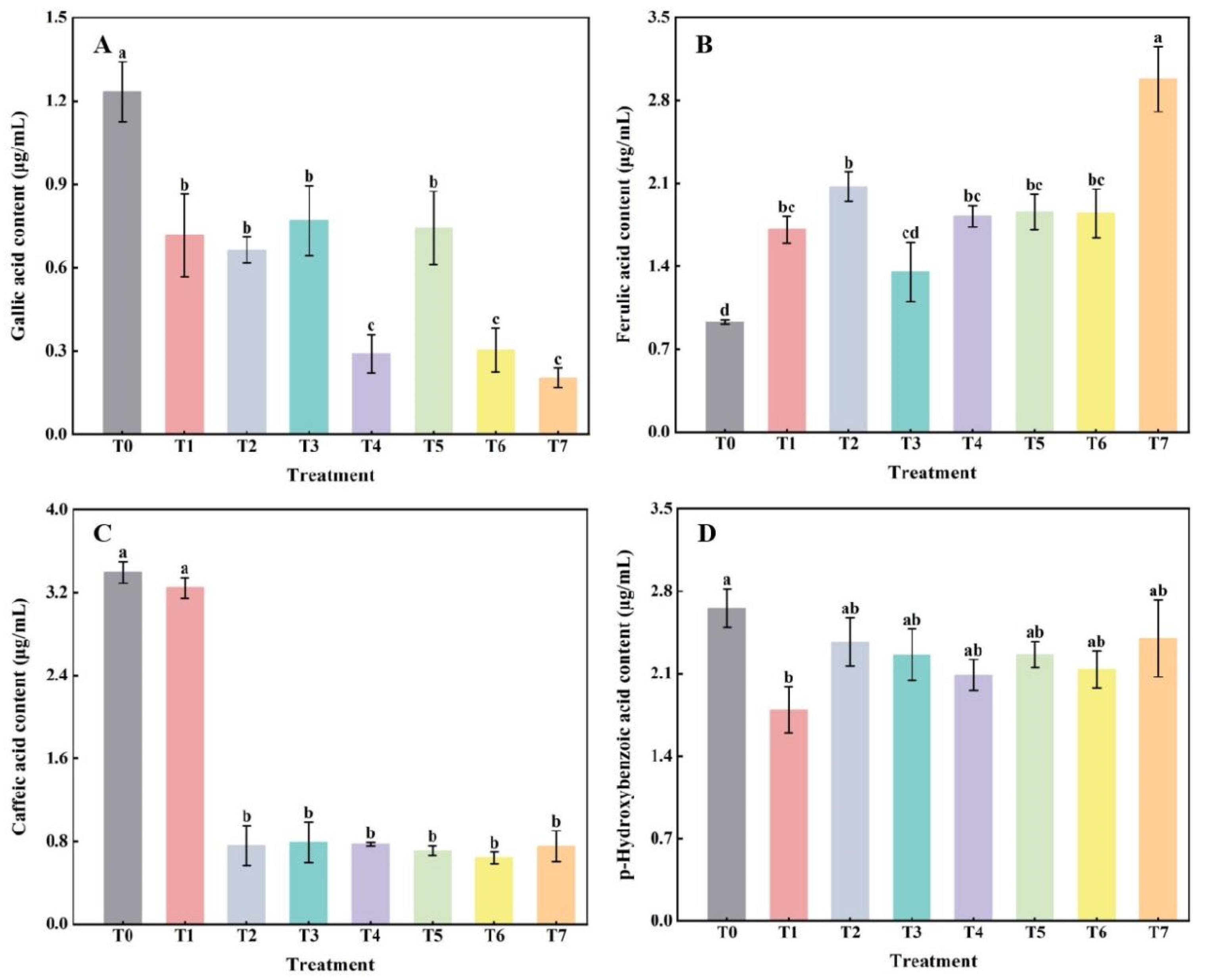
2.1. The Effect of Combined Application of Biofertilizers on the Content of Phenolic Acids in Replanted Z. bungeanum Soil
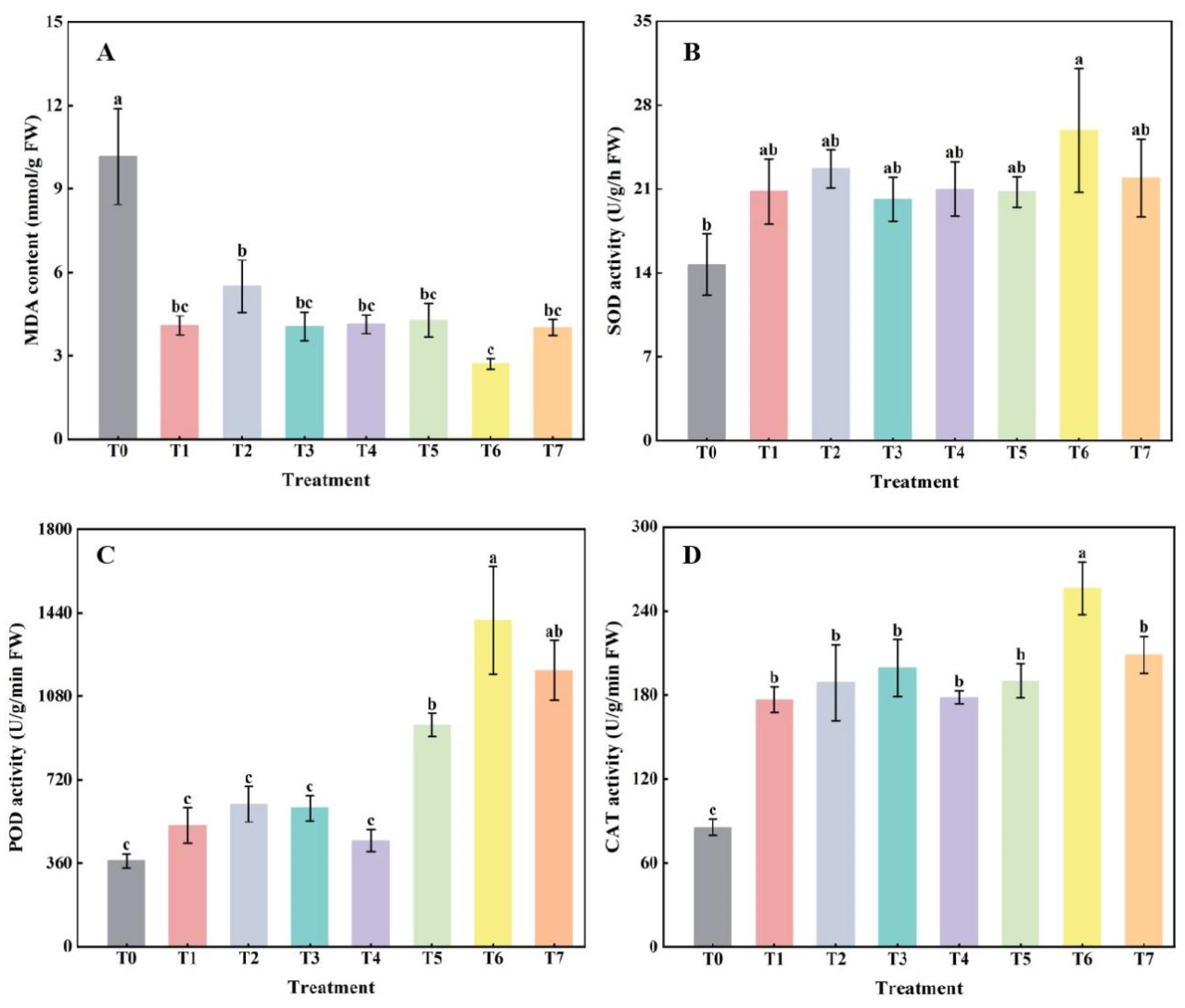
2.2. The Effect of Combined Application of Biofertilizers on Membrane Peroxidation Products and Defense Enzyme Activities in Replanted Z. bungeanum
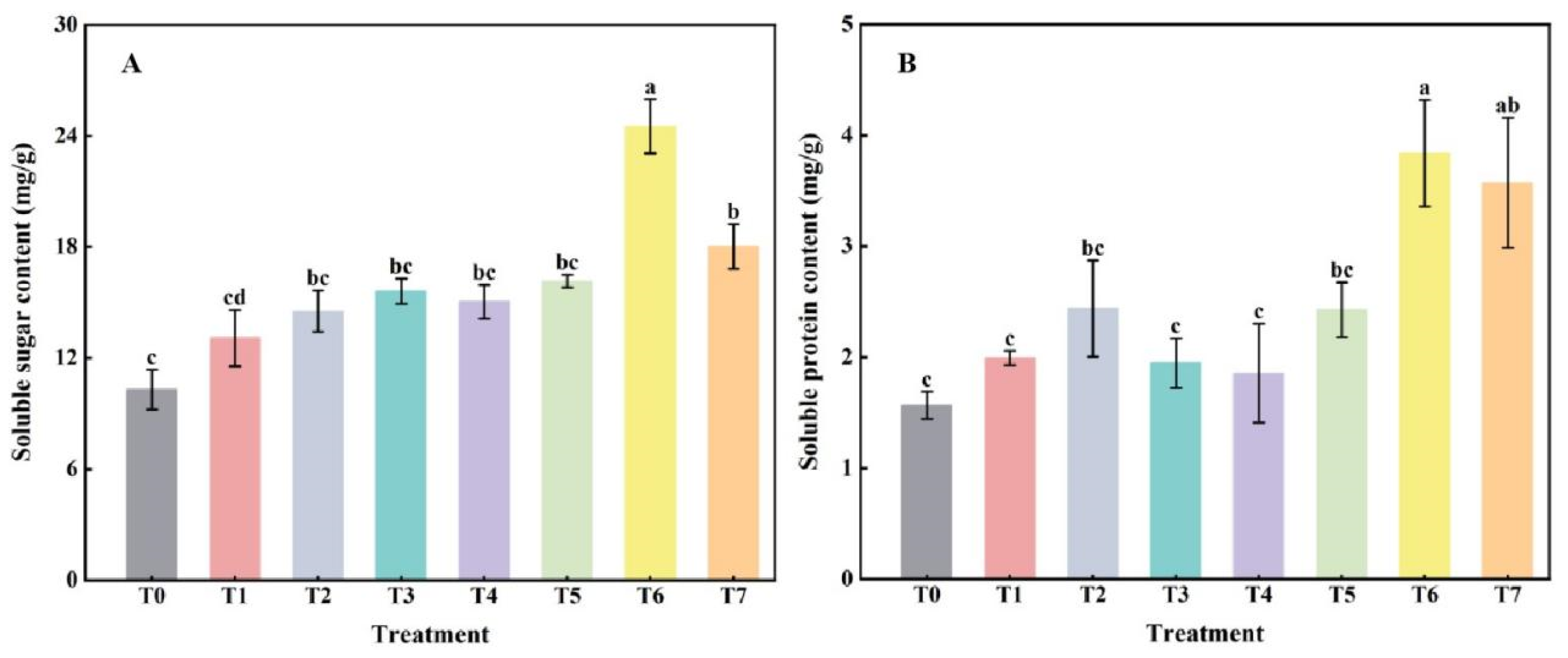
2.3. The Effect of Combined Application of Biofertilizers on the Accumulation of Osmoregulatory Substances in Replanted Z. bungeanum
2.4. The Effect of Combined Application of Biofertilizers on NR Activity in Replanted Z. bungeanum
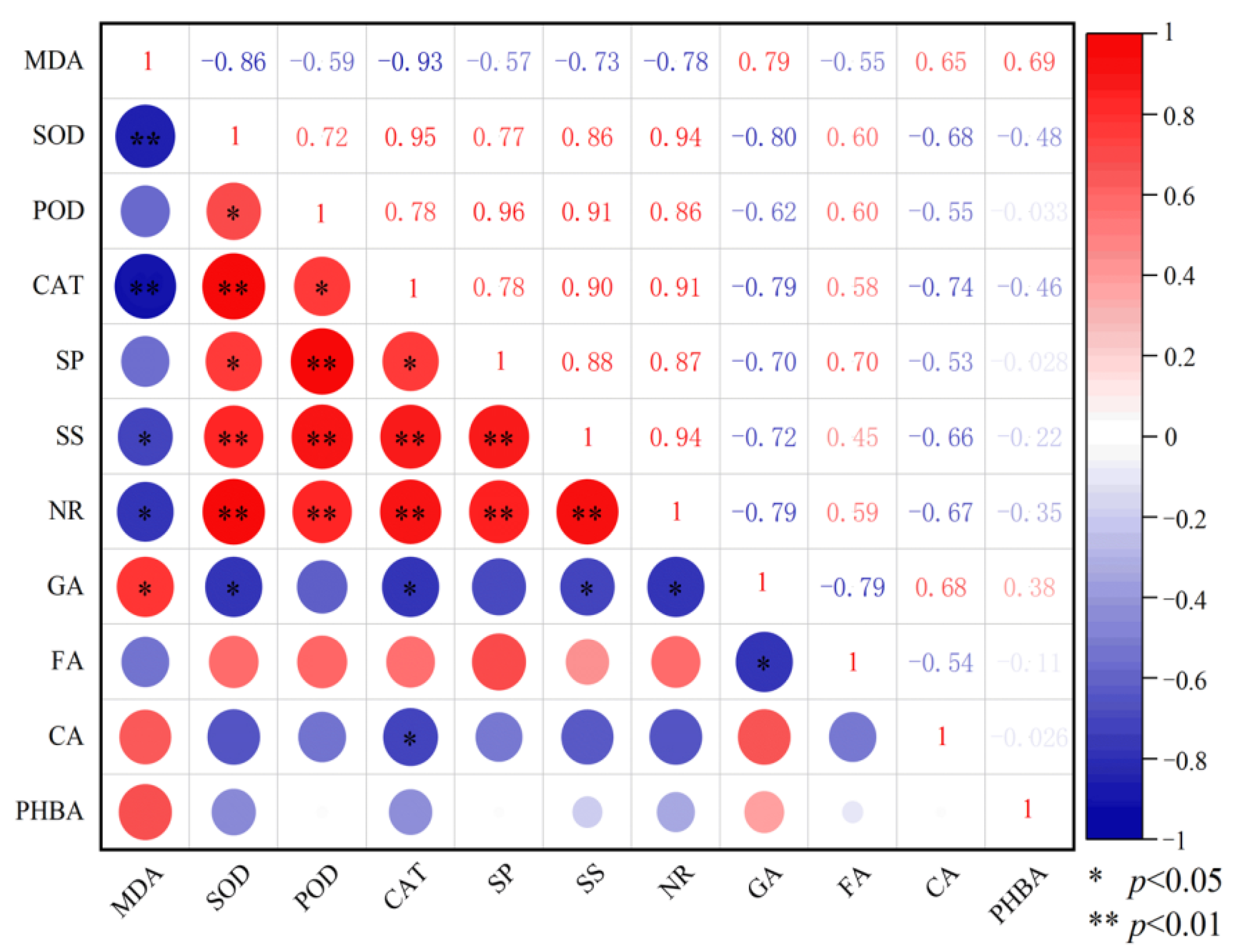
2.5. Correlation Analysis Between Physiological and Biochemical Indicators of Replanted Z. bungeanum and Soil Phenolic Acids
2.6. Principal Component Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. The Effect of Combined Application of Biofertilizers on Phenolic Acids in Replanted Z. bungeanum Soil
3.2. The Effect of Combined Application of Biofertilizers on Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Replanted Z. bungeanum
3.3. Research Prospects
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Overview of the Study Area
4.2. Test Materials
4.3. Experimental Design
4.4. Test Methods
4.4.1. Determination of Phenolic Acids in Soil
4.4.2. Determination of Physiological and Biochemical Indexes of Seedlings
4.5. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jing, N.; Wang, M.; Gao, M.; Zhong, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wei, A. Color sensory characteristics, nutritional components and antioxidant capacity of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. as affected by different drying methods. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 160, 113167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Yang, H.; Lei, H.; Xiang, Z.; Duan, Y.; Xin, H.; Han, T.; Su, J. Phytochemistry and health functions of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim and Zanthoxylum schinifolium Sieb. et Zucc as pharma-foods: A systematic review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 143, 104225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ye, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Guan, F.; Zhang, T.; Huang, J.; Min, X.; Zhang, T. Fractionation and antioxidation activities of polysaccharides from Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. Food Chem. 2024, 439, 138050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Shen, Q.; Sun, Y. Effects of continuous cropping of Zanthoxylum bungeanum on soil chemical properties and enzyme activities. Mol. Plant Breed. 2019, 17, 7545–7550. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, K.; Xiong, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Cai, L. Effects of Zanthoxylum bungeanum planting on soil hydraulic properties and soil moisture in a karst area. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 257, 107125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ding, D.; He, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, D.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, X. Effect of two biofertilizer mixtures on growth and photosynthetic characteristic of replanted Zanthoxylum bungeanum. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2021, 30, 1355–1364. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Yang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Tao, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, P.; Cai, H.; Yin, H. Response of soil bacterial community structure and co-occurrence network topology properties to soil physicochemical properties in long-term continuous cropping farmland. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2022, 62, 2403–2416. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartini, N.L.; Saifulloh, M.; Trigunasih, N.M.; Sukmawati, N.M.S.; Mega, I.M. Impact of long-term continuous cropping on soil nutrient depletion. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2024, 25, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Zhou, D.; Wei, H.; Wu, S.; Xie, B. Alleviating soil degradation caused by watermelon continuous cropping obstacle: Application of urban waste compost. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Liu, Y.; Peng, S.; Yin, H.; Meng, D.; Tao, J.; Gu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Xiao, N.; et al. Soil potentials to resist continuous cropping obstacle: Three field cases. Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, C.; Lu, D.; Wu, Y.; Ye, Z.; Xia, L.; Sun, Y.; Bao, E.; Ye, L.; Tang, Y.; et al. Variation of soil microbial community and sterilization to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. niveum play roles in slightly acidic electrolyzed water-alleviated watermelon continuous cropping obstacle. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 837121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Chai, D.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Yu, X.; Shuai, Z.; Liu, H.; et al. The cropping obstacle of garlic was associated with changes in soil physicochemical properties, enzymatic activities and bacterial and fungal communities. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 828196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, Q.; Xia, R.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Ye, X.; Yu, L.; Qi, Y.; Yang, S.; Xue, Z.; et al. Effects of biochar fertilizer on rhizosphere flora and physicochemical properties of flue-cured tobacco susceptible to root knot nematode. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 26, 206–214. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Zhang, C.; Deng, S.; Niu, C.; Li, Q.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. Pseudomonas chlororaphis ZH2: Evaluation of the biocontrol potential of continuous cropping obstacles on the basis of genome analysis, autotoxic substance degradation and in vitro antifungal activity. Curr. Microbiol. 2025, 82, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, X.F.; Shen, X.; Chen, X.S.; Mao, Z.Q. Effect of residual roots on the biomass of Malus hupehensis seedlings, phenolic acids and microbiology in the soil of continuous cropping. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2015, 42, 131–139. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Liu, H.; Zhao, F.Y.; Zhang, G.X.; Li, M.J.; Yang, L.J. Regulation of various fertilization measures on soil microbial functional diversity and phenolic acid contents under tomato continuous cropping in greenhouse. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 48, 887–894. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavo, A.; Abbate, C.; Mauromicale, G. Plant allelochemicals: Agronomic, nutritional and ecological relevance in the soil system. Plant Soil 2019, 442, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Wang, Q.; Ruan, X.; Pan, C.D.; Jiang, D.A. Phenolics and plant allelopathy. Molecules 2010, 15, 8933–8952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Ding, W. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria alleviate aluminum toxicity and ginger bacterial wilt in acidic continuous cropping soil. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 569512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.R.; Jiang, S.T.; Xie, X.Y.; Xu, Y.C.; Dong, C.X.; Shen, Q.R. Effects of reducing chemical fertilizers combined with organic fertilizers on soil microbial community in litchi orchards. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 1099–1108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Liu, X.; Ding, W.; Song, X.; Li, S.; Wu, X. Positive effects of crop rotation on soil aggregation and associated organic carbon are mainly controlled by climate and initial soil carbon content: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 355, 108600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Song, B.; Wang, C. Progress of research on alleviating obstacles of continuous cropping by soil sterilization and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 26, 158–167. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Li, P.; Wu, W.Q.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, L.; Gao, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.R. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer and microbial agent on the growth of tea chrysanthemum and soil fertility under continuous cropping cultivation system in the mountainous area of Beijing. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2023, 12, 107–113. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, P.; Hou, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L. Progress in microbial fertilizer regulation of crop growth and soil remediation Research. Plants 2024, 13, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.C.; Chen, X.M.; Zhang, Z.L.; Lv, J.Y.; Ji, C.; Zhang, J. Mechanism of bio-organic fertilizer on improving soil productivity for continuous cucumber in greenhouse. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2019, 25, 814–823. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Q.S.; Xie, C.Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, C.; Zhang, A.K.; Sun, C.M. Effects of combined application of bio-organic fertilizer and biomass ash on the growth of continuous cropping muskmelon and soil properties. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2024, 55, 1386–1394. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Cao, J.D.; Zheng, Y.X.; Wang, J.M.; Xu, Y.L.; Tong, W.J.; Lin, Z.L.; Yang, M.; Wei, W.; Huang, F.Y.; et al. Regulation of microbial agent on soil phenolic acid contents and microbial population. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 33, 2037–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, T.; Tian, P.C.; Gao, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y.Q. Effects of microbial agent and microbial fertilizer input on soil microbial community structure and diversity in a peanut continuous cropping system. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 64, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hou, C.; Zhang, C. Effects of microbial organic fertilizer, microbial inoculant, and quicklime on soil microbial community composition in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) continuous cropping system. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, L.; Han, N.; Wang, D. Characterization of phenolic chemotypes, anatomy, and histochemistry of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 193, 116149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, Z.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y. Biodiversity, phylogeny, and antifungal functions of endophytic fungi associated with Zanthoxylum bungeanum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Improving physicochemical properties and bacterial communities of peach-heavy soils using biofertilizers and organic fertilizers. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2024, 51, 2089–2104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, L.; Duan, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yin, C.; Mao, Z. Effects of Bacillus velezensis XC1 on phenolic acid content and the growth of Malus hupehensis seedlings under replant condition. Plant Physiol. J. 2021, 57, 1974–1982. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Lu, C.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Cai, B. AMF inhibit the production of phenolic acid autotoxins at the seed-filling stage in soybeans with continuous monocropping. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, G.X.; Daniel, A.J.; Liu, Z.H.; Ding, C.Q.; Tang, S.; Li, G.H.; Wang, S.H.; Ding, Y.F. Determination of phenolic acids in rice by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 48, 1718–1726. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.A.; Wegner, C.J.; Gaussoin, R.E.; Zbasnik, R.; Sarath, G.; Schlegel, V.L. Phenolic content and profile alterations during seedling growth in supina bluegrass and bermudagrass. Crop Sci. 2018, 58, 2010–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Chen, Y.; Bu, Y.; Dai, C. A review of allelopathic researches on phenolic acids. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 6417–6428. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiradate, S.; Morita, S.; Furubayashi, A.; Fujii, Y.; Harada, J. Plant growth inhibition by cis-cinnamoyl glucosides and cis-cinnamic acid. J. Chem. Ecol. 2005, 31, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, K.; Hirt, H. Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.M.; Li, C.L.; Ye, S.P.; Wang, H.; Pan, K.W.; Wu, N.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, W.; Zhang, L. Autotoxic effects of aqueous extracts of ginger on growth of ginger seedlings and on antioxidant enzymes, membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation in leaves. Allelopath. J. 2012, 30, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Roach, T.; Neuner, G.; Kranner, I.; Buchner, O. Heat acclimation under drought stress induces antioxidant enzyme activity in the alpine plant Primula minima. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Yang, A.; Wang, J.; Ke, L.; Chen, S.; Li, W. Effects of the synergistic treatments of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and trehalose on adaptability to salt stress in tomato seedlings. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e03404-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Xin, L.; Gao, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, X. Effects of foliar selenium application on oxidative damage and photosynthetic properties of greenhouse tomato under drought stress. Plants 2024, 13, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anli, M.; Baslam, M.; Tahiri, A.; Raklami, A.; Symanczik, S.; Boutasknit, A.; Ait-El-Mokhtar, M.; Ben-Laouane, R.; Toubali, S.; Rahou, Y.A.; et al. Biofertilizers as strategies to improve photosynthetic apparatus, growth, and drought stress tolerance in the date palm. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 516818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Sun, B.; Song, M.; Yan, G.; Hu, Q.; Bai, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhuang, X. Improvement of saline soil properties and Brassica rapa L. growth using biofertilizers. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Mou, X.; Meng, P.; Chen, J.; Tang, X.; Meng, G.; Xin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus inoculation on the growth and nitrogen metabolism of Catalpa bungei C.A.Mey. under different nitrogen levels. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1138184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro EC, N.; Mógor, Á.F.; Amatussi, J.O.; Mógor, G.; Marques HM, C.; de Lara, G.B. Microalga biofertilizer improves potato growth and yield, stimulating amino acid metabolism. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J. Effects of different LED spectra on the antioxidant capacity and nitrogen metabolism of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. Pekinensis). Plants 2024, 13, 2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.L.; Yan, T.T.; Bi, Y.M.; Sun, Z.J.; Zhang, L.S. Effects of continuous cropping soil sterilization and applying of different fertilizer on phenolic acids in rhizosphere soil of the strawberry plants and soil enzyme activities. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2015, 42, 2039–2048. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhou, C.; Xie, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhou, C.; Li, X.; Du, Y.; Lu, F. A new method for simultaneous determination of 14 phenolic acids in agricultural soils by multiwavelength HPLC-PDA analysis. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 14939–14944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.F. Experimental Guidance for Plant Physiology; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006; ISBN 978-7-04-019170-7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.S. Principles and Techniques of plant Physiological Biochemical Experiment; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2005; ISBN 978-7-04-008076-1. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

| Extracted Ingredients | Eigenvalue | Proportion of Variance (%) | Cumulative Variance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 7.663 | 69.660 | 69.660 |
| PC2 | 1.439 | 13.080 | 82.740 |
| Treatments | PC1 | PC2 | Comprehensive Score | Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | −1.41 | −0.22 | −1.01 | 8 |
| T1 | −0.13 | −1.54 | −0.29 | 7 |
| T2 | −0.13 | 0.38 | −0.04 | 4 |
| T3 | −0.29 | −0.31 | −0.24 | 6 |
| T4 | −0.01 | −0.97 | −0.14 | 5 |
| T5 | −0.16 | 0.08 | −0.10 | 3 |
| T6 | 2.07 | 1.60 | 1.65 | 1 |
| T7 | 0.06 | 0.98 | 0.17 | 2 |
| pH | Organic Matter (g·kg−1) | Total Nitrogen (g·kg−1) | Total Phosphorus (g·kg−1) | Total Potassium (g·kg−1) | Available Nitrogen (mg·kg−1) | Available Phosphorus (mg·kg−1) | Available Potassium (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.29 | 16.21 | 0.79 | 0.61 | 7.85 | 45.00 | 4.36 | 75.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, M.; Ding, D.; He, J. The Combined Application of Biofertilizer Alleviates the Continuous Cropping Obstacles of Replanted Zanthoxylum bungeanum: A Preliminary Study. Plants 2025, 14, 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060854
Chen W, Zhang S, Wang B, Zhang M, Ding D, He J. The Combined Application of Biofertilizer Alleviates the Continuous Cropping Obstacles of Replanted Zanthoxylum bungeanum: A Preliminary Study. Plants. 2025; 14(6):854. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060854
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wei, Shuheng Zhang, Bin Wang, Mengyang Zhang, Dedong Ding, and Jing He. 2025. "The Combined Application of Biofertilizer Alleviates the Continuous Cropping Obstacles of Replanted Zanthoxylum bungeanum: A Preliminary Study" Plants 14, no. 6: 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060854
APA StyleChen, W., Zhang, S., Wang, B., Zhang, M., Ding, D., & He, J. (2025). The Combined Application of Biofertilizer Alleviates the Continuous Cropping Obstacles of Replanted Zanthoxylum bungeanum: A Preliminary Study. Plants, 14(6), 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060854






