Candidate Gene for Kernel-Related Traits in Maize Revealed by a Combination of GWAS and Meta-QTL Analyses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phenotypic Analysis of Kernel-Related Traits
2.2. GWAS Analysis
2.3. Screening and Functional Analysis of Candidate Genes
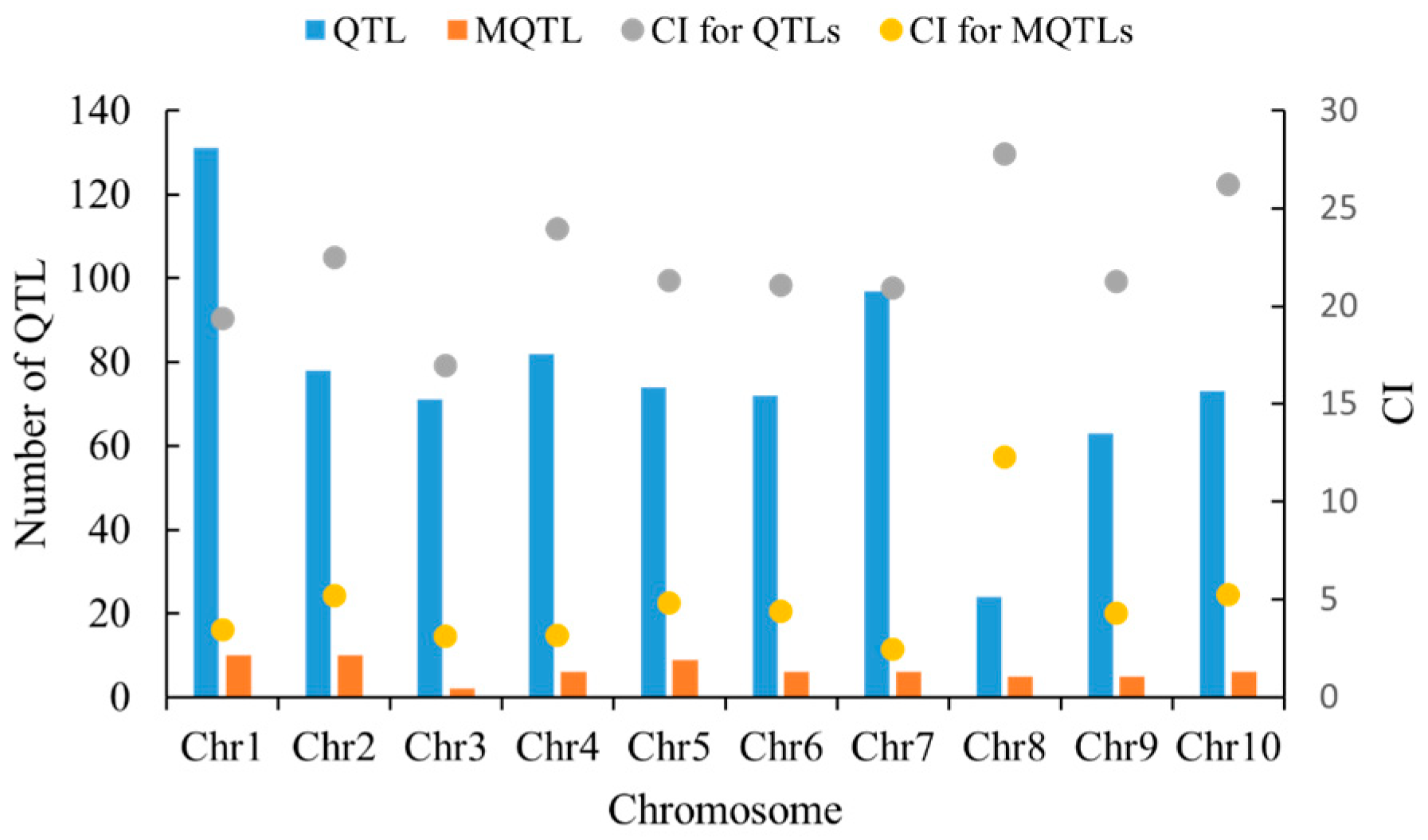
2.4. Basic Characteristics of QTLs Related to Maize Kernel Traits
2.5. Meta-QTL Analysis
2.6. Homologous Gene Mining
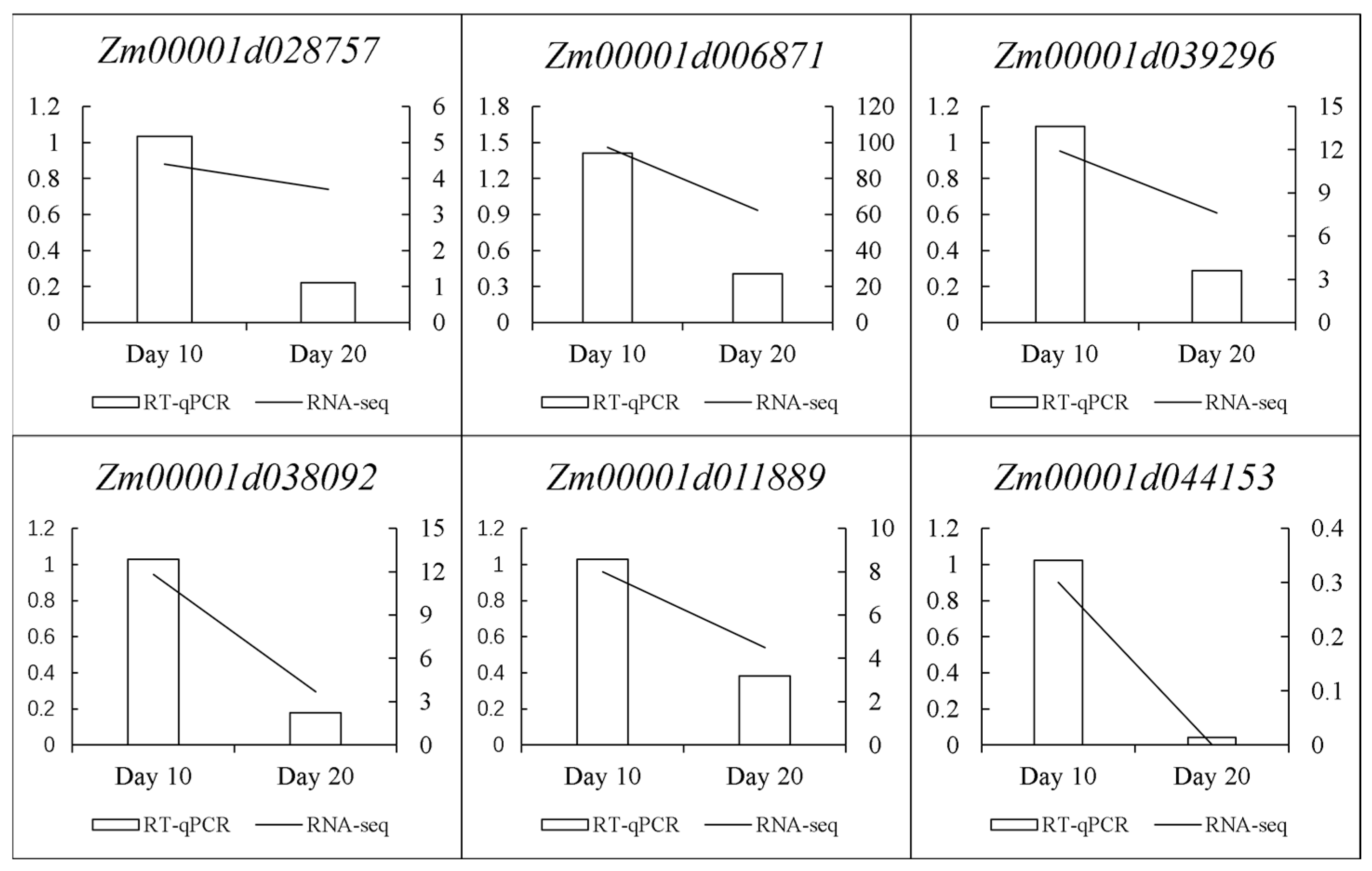
2.7. RT-qPCR Verification
3. Discussion
3.1. Genetic Mechanisms of Kernel Size-Related Traits in Maize
3.2. Predictive Analysis of Candidate Gene Function
3.3. Analysis of the Genetic Basis of Maize Kernel Traits
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Material Planting, Experimental Design, and Phenotypic Trait Determination
4.2. Phenotypic Data Analysis
4.3. GWAS
4.4. Collection of Initial QTL Information
4.5. Candidate Gene Mining and Functional Analysis
4.6. Mining of Homologous Genes
4.7. Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) Verification of Candidate Genes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, T.; Meng, Z.; Yue, R.; Lu, S.; Li, W.; Li, W.; Meng, H.; Sun, Q. Genome wide association analysis for yield related traits in maize. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ren, Z.; Li, L.; Du, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Yi, F.; Duan, L. Meta-QTL analysis explores the key genes, especially hormone related genes, involved in the regulation of grain water content and grain dehydration rate in maize. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; An, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Shi, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, T.; Li, Y. Candidate Loci for Yield-Related Traits in Maize Revealed by a Combination of MetaQTL Analysis and Regional Association Mapping. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doebley, J.; Gaut, B.; Smith, B. The Molecular Genetics of Crop Domestication. Cell 2006, 127, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Jia, A.; Rong, T. Identification of QTL for maize grain yield and kernel-related traits. J. Genet. 2016, 95, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Wu, L.; Dong, Q.; Yan, G.; Qu, J.; Wang, P. Genome-wide association analysis of maize kernel length. J. Northwest A F Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2018, 46, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Z. Genetic Dissection of Major QTL Associated with Kernel Width and Kernel Weight in Maize. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, J.; Feng, W.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S.; Xue, J. Dissecting the genetic architecture of maize kernel size based on genome-wide association study. Acta Agron. Sin. 2022, 48, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, G.; Li, K.; Yu, Y.; Li, G.; Li, W.; Gao, Y.; Hu, J. Genome-wide association study of kernel volume and weight in sweet corn. J. China Agric. Univ. 2022, 27, 12–25. [Google Scholar]
- Veldboom, L.; Lee, M.; Woodman, W. Molecular marker-facilitated studies in an elite maize population: I. Linkage analysis and determination of QTL for morphological traits. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1994, 88, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L. QTL Mapping for Plant Type, Ear Traits and Genetic Analysis of a Male Sterile Line in Maize (Zea mays L.). Ph.D. Thesis, Agricultural University of Hebei, Baoding, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Yan, J.; Ma, X.; Teng, W.; Meng, Y.; Dai, J.; Li, J. Genetic Dissection for Grain Yield and Its Components Using an “Immortalized F2 Population” in Maize. Acta Agron. Sin. 2007, 33, 1299–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T. Genome Sequencing Analysis of Maize Inbred Line KA105 and QTL Mapping of Grain Yield Traits. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Nie, L.; Guo, S.; Wang, D.; Tu, L.; Liu, P.; Guo, X.; Wang, A.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. QTL Mapping and Candidate Gene Analysis of Kernel Related Traits by Using Maize F2:3 Family Lines. Seed 2024, 43, 119–124+156. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, P.; Zhang, H.; Lu, X.; Hao, Z.; Li, B.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Ci, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; et al. Analysis of Meta-QTL and Candidate Genes Related to Yield Components in Maize. Acta Agron. Sin. 2013, 39, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veyrieras, J.; Goffinet, B.; Charcosset, A. MetaQTL: A package of new computational methods for the meta-analysis of QTL mapping experiments. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Mullan, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, A.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yan, G. Major genomic regions responsible for wheat yield and its components as revealed by meta-QTL and genotype–phenotype association analyses. Planta 2020, 252, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anilkumar, C.; Sah, R.; Muhammed Azharudheen, T.; Behera, S.; Singh, N.; Prakash, N.; Sunitha, N.; Devanna, B.; Marndi, B.; Patra, B.; et al. Understanding complex genetic architecture of rice grain weight through QTL-meta analysis and candidate gene identification. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truntzler, M.; Barrière, Y.; Sawkins, M.C.; Lespinasse, D.; Betran, J.; Charcosset, A.; Moreau, L. Meta-analysis of QTL involved in silage quality of maize and comparison with the position of candidate genes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 121, 1465–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Zhuang, Z.; Bian, J.; Ren, Z.; Ta, W.; Peng, Y. GWAS and Meta-QTL Analysis of Kernel Quality-Related Traits in Maize. Plants 2024, 13, 2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Luo, J.; Qiao, F.; Yang, W.; Zhang, R.; Meng, Y.; Sun, J.; Yan, S.; et al. CUBIC: An atlas of genetic architecture promises directed maize improvement. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudi, S.; Saini, D.; Singh, G.; Halladakeri, P.; Kumar, P.; Shamshad, M.; Tanin, M.; Singh, S.; Sharma, A. Unravelling consensus genomic regions associated with quality traits in wheat using meta-analysis of quantitative trait loci. Planta 2022, 255, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Tang, Y.; Luo, W.; Zhang, J.; Chong, K.; Xu, Y. A cyclophilin OsCYP20–2 Interacts with OsSYF2 to regulate Grain Length by Pre-mRNA splicing. Rice 2020, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, S.; Cai, M.; Cui, S.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, T.; Zhou, C.; Jin, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. ESCRT-III component OsSNF7.2 modulates leaf rolling by trafficking and endosomal degradation of auxin biosynthetic enzyme OsYUC8 in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 1408–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Cho, L.; Kim, S.; Tun, W.; Peng, X.; Pasriga, R.; Moon, S.; Hong, W.; Ji, H.; Jung, K.; et al. CTP synthase is essential for early endosperm development by regulating nuclei spacing. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2177–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, M.; Li, W.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Genetic variation in ZmKW1 contributes to kernel weight and size in dent corn and popcorn. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2024, 22, 1453–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zheng, H.; Jin, L.; Xing, L.; Zou, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Chu, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, L. miR169o and ZmNF-YA13 act in concert to coordinate the expression of ZmYUC1 that determines seed size and weight in maize kernels. New Phytol. 2022, 235, 2270–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Ding, L.; Feng, W.; Cao, Y.; Lu, F.; Yang, Q.; Li, W.; Lu, Y.; Shabek, N.; Fu, F.; et al. Maize transcription factor ZmBES1/BZR1-5 positively regulates kernel size. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 1714–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Tian, Y.; Li, H.; Lv, X.; Wang, Y.; Duanmu, H. Research Progress of Plant bHLH Transcription Factor. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2019, 35, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Fu, Y.; Lee, Y.; Chern, M.; Li, M.; Cheng, M.; Dong, H.; Yuan, Z.; Gui, L.; Yin, J.; et al. The PGS1 basic helix-loop-helix protein regulates Fl3 to impact seed growth and grain yield in cereals. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1311–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heang, D.; Sassa, H. An atypical bHLH protein encoded by POSITIVE REGULATOR OF GRAIN LENGTH 2 is involved in controlling grain length and weight of rice through interaction with a typical bHLH protein APG. Breed. Sci. 2012, 62, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Wu, Q.; Tang, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, Q.; Guan, S.; Wang, C. Cloning Expression Analysis and Expression Vectors Construction of 60S Ribosomal Protein L29-1(RPL29-1) Gene from Peanut. Mol. Plant Breed. 2016, 14, 1730–1736. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, L.; Liu, M.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.; Xue, W. Data-independent acquisition-based global phosphoproteomics reveal the diverse roles of casein kinase 1 in plant development. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 2077–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Li, W. Cloning and Expression Analysis of A RING/U-box Protein of Glyma. 13G115900 from Soybean under Abiotic Stress. Soybean Sci. 2017, 36, 851–856. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S. Identification and Functional Analysis of the U-Box Gene Family in Tea Plant. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.; Li, N.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Y. The ubiquitin receptor DA1 regulates seed and organ size by modulating the stability of the ubiquitin-specific protease UBP15/SOD2 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Dong, C.; Sun, D.; Hu, Y.; Xie, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of U-Box E3 Ubiquitin-Protein Ligase Gene Family in Banana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, H.; Ding, L.; Wei, J. Isolation, structural analysis, and expression characteristics of the maize (Zea mays L.) hexokinase gene family. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 6157–6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, P.; Li, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, P.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; et al. OsHXK3 encodes a hexokinase-like protein that positively regulates grain size in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 3417–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, M.; Ohta, D. Diversification of P450 genes during land plant evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Wei, X.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, X.; Ma, S.; Lin, S.; Li, F.; Bu, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, H.; et al. GW10, a member of P450 subfamily regulates grain size and grain number in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 3941–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, D.; Amand, P.; Bernardo, A.; Li, W.; He, F.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Yuan, X.; et al. High-resolution genome-wide association study identifies genomic regions and candidate genes for important agronomic traits in wheat. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1311–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halladakeri, P.; Gudi, S.; Akhtar, S.; Singh, G.; Saini, D.; Hilli, H.; Sakure, A.; Macwana, S.; Mir, R. Meta-analysis of the quantitative trait loci associated with agronomic traits, fertility restoration, disease resistance, and seed quality traits in pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan L.). Plant Genome 2023, 16, e20342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ju, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Ma, Q.; Su, J. Pinpointing MQTLs and candidate genes related to early maturity in upland cotton through the integration of meta-analysis, RNA-seq, and VIGS approaches. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 223, 120195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Li, Y. Signaling pathways of seed size control in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2016, 33, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Guo, H.; Lan, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, W.; Tong, H.; Xiao, Y.; et al. The conserved and unique genetic architecture of kernel size and weight in maize and rice. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Jing, F.; Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, T.; Che, Z.; Yang, D. Major Genomic Regions for Wheat Grain Weight as Revealed by QTL Linkage Mapping and Meta-Analysis. Front. Plant. Sci. 2022, 13, 802310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, P.; Jing, W.; Cao, C.; Sun, M.; Chi, W.; Zhao, S.; Dai, J.; Shi, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, B.; et al. Transcriptional repressor RST1 controls salt tolerance and grain yield in rice by regulating gene expression of asparagine synthetase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2210338119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Tang, L.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Tong, X.; Wei, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, J. Serine carboxypeptidase 46 regulates grain filling and seed germination in rice (Oryza sativa L.). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xiang, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mao, D.; Luan, S.; Chen, L. bHLH57 confers chilling tolerance and grain yield improvement in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2023, 46, 1402–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Qian, Q.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, G.; Gao, T.; Xie, Q.; Xue, Y. The U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase TUD1 functions with a heterotrimeric G α subunit to regulate brassinosteroid-mediated growth in rice. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CN 114581507 A; Seed Size Calibration Method and System Based on Image Seed Examination, Devices and Storage Media. Zhejiang Topu Yunnong Technology Co., Ltd.: Hangzhou, China, 2022.
- Gómez-Rubio, V. ggplot2-elegant graphics for data analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 77, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipka, A.E.; Tian, F.; Wang, Q.; Peiffer, J.; Li, M.; Bradbury, P.J.; Gore, M.A.; Buckler, E.S.; Zhang, Z. GAPIT: Genome association and prediction integrated tool. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2397–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvasi, A.; Soller, M. A simple method to calculate resolving power and confidence interval of QTL map location. Behav. Genet. 1997, 27, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Sleper, D.; Lu, P.; Shannon, J.; Nguyen, H.; Arelli, P. QTLs associated with resistance to soybean cyst nematode in soybean: Meta-analysis of QTL locations. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Wu, J.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Wang, Q. Detection of consensus genomic regions and candidate genes for quality traits in barley using QTL meta-analysis. Front. Plant. Sci. 2024, 14, 1319889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goffinet, B.; Gerber, S. Quantitative trait loci: A meta-analysis. Genetics 2000, 155, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshitha, R.; Arunraj, D. Real-time quantitative PCR: A tool for absolute and relative quantification. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2021, 49, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X. Identification of QTL for Kernel Oil Content and Analysis of Related Treits in Maize. Ph.D. Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Tang, H.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, J. Quantitative trait loci mapping and epistatic analysis for grain yield and yield components using molecular markers with an elite maize hybrid. Euphytica 2006, 149, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Tang, J.; Yan, J.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Ma, J.; Liu, Z.; E, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Quantitative Trait Loci Mapping of Maize Yield and Its Components Under Different Water Treatments at Flowering Time. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2006, 48, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tang, J.; Wei, X.; Wang, C.; Tian, G.; Hu, Y.; Chen, W. QTL Mapping of Ear Traits under Low and High Nitrogen Conditions in Maize. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2007, 11, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Niu, S.; Dong, Y.; Cui, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wei, M. Identification of trait-improving quantitative trait loci for grain yield components from a dent corn inbred line in an advanced backcross BC2F2 population and comparison with its F2:3 population in popcorn. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 115, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) and Genetic Effect for Important Traits with an Elite Maize Hybrid. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumchi, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Feng, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Hu, Y. QTL Analysis for Ear Traits in Maize Using Molecular Markers. J. Henan Agric. Univ. 2008, 2, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Improtant Inbred lines and QTLs Identification on Yield-Related Traits in Maize. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Wu, A.; Zheng, C.; Wang, Y.; Cai, R.; Shen, X.; Xu, R.; Liu, P.; Kong, L.; Dong, S. QTL mapping of maize (Zea mays) stay-green traits and their relationship to yield. Plant Breed. 2009, 128, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, M. Dent corn genetic background influences QTL detection for grain yield and yield components in high-oil maize. Euphytica 2009, 169, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Gao, H.; Zhao, Y. QTL mapping for ear traits under different densities using DH population of maize. J. Hebei Agric. Univ. 2009, 32, 1–6+17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, Y. Correlation Analysis and QTL Mapping for Traits of Kernel Structure and Yield Components in Maize. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2009, 42, 408–418. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Analysis of QTL for Ear-Kernel Characters and the Genetic Correlation Between Grain Weight and Kernel Nutritional Characters Using Two Connected F2:3 Populations in Maize. Master’s Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. QTL Mapping and Analysis on Plant Architectures and Yield Related Traits in Maize. Master’s Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T. Phenotype Analysis and QTL Location of Yield Related Characters in RILs Population of Maize. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, D.; Tan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, B.; Shi, Y.; et al. QTL Analysis for Yield Components and Kernel-Related Traits in Maize under Different Water Regimes. Acta Agron. Sin. 2010, 36, 1832–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Song, Z.; Cheng, J. QTL Analysis of Ear Traits Based on BC2F2 Population in Maize (Zea may L.). Acta Agric. Bor Sin. 2010, 25, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Guo, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Z. Mapping QTLs for grain yield and yield components under high and low phosphorus treatments in maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Sci. 2010, 178, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Tan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Shi, Y.; Sun, B.; et al. QTL analysis for yield components and kernel-related traits in maize across multi-environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 122, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Liu, R.; Li, C.; Xing, X.; Cao, X.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, Z. QTL Mapping for Grain Yield Associated Traits Using Ye478 Introgression Lines in Maize. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2011, 44, 3508–3519. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G. Construction of Genetic Map and QTL Analysis for Main Traits Using Two Connected RIL Populations in Maize. Ph.D. Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Ji, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, J. Correlation Analysis and QTL Mapping for Kernel Traits and Zinc, Iron Content in Maize. Acta Agric. Bor Sin. 2011, 26, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y. QTL consistency and meta-analysis for grain yield components in three generations in maize. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 122, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B.; Song, W.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Dai, J.; Lai, J. Identification of genetic factors affecting plant density response through QTL mapping of yield component traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Euphytica 2011, 182, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, E.; Rocheford, T. Genetic and QTL analysis of pericarp thickness and ear architecture traits of Korean waxy corn germplasm. Euphytica 2012, 183, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mi, G.; Cheng, F. QTL Mapping of Ear Traits in Maize Grown under Two Nitrogen Applications. J. Maize Sci. 2011, 19, 17–20+25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z. QTL Mapping for Flowering Time, Plant-Type and Yield Components Using Two Related Populations in Maize. Ph.D. Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Shen, B.; Zhang, F.; Liang, X. Detection and integration of quantitative trait loci for grain yield components and oil content in two connected recombinant inbred line populations of high-oil maize. Mol. Breeding. 2012, 29, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhai, L.; Liu, R.; Tao, y.; Zhang, Z. QTL mapping of eight yield-relative traits in maize. J. Hebei Agric. Univ. 2012, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R. QTL Mapping of Kernel Shape Related Traits Using a Four-Way Cross Population in Maize. Master’s Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, P. Evaluation for Seeding Drought Resistance of Different Maize Inbred Lines and QTLs Identification on Yield-Related Traits in Maize. Master’s Thesis, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P. QTL Mapping of Density Tolerance and Related Traits Based on Four-Way Cross Populationin Maize (Zea mays L.). Ph.D. Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. QTL Mapping and Genetic Analysis of Kernel Size and Yield Components in Maize. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T. Construction of Genetic Linkage Map and Identification of QTLs for Important Agronomic Trait in Maize (Zea mays L.). Master’s Thesis, Yanbian University, Yanji, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Li, W.; Fu, Z.; Ding, D.; Li, H.; Qiao, M.; Tang, J. QTL analysis of kernel-related traits in maize using an immortalized F2 population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Qiu, F. Genetic analysis and major QTL detection for maize kernel size and weight in multi-environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1019–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, G. Methods of Kernel Traits Measurement and QTL Mapping and Analysis of Association. Ph.D. Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumchi, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C. Genetic Analysis and Identification of QTL Responsible for Ear Row Number and Related Traits in Maize. Ph.D. Thesis, Sichuan Agricultural University, Yaan, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Su, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Luo, B.; Liu, D.; Wu, L.; Rong, T.; Gao, S. Characterization and QTL Mapping of Yield Trait under Two Phosphorus Regimes in Maize. Acta Agric. Bor Sin. 2015, 30, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z. Correlation Analysis and QTL Mapping for Kernel Traits and Leaves Zinc, Iron, Copper and Manganese Content in Maize. Master’s Thesis, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Li, G.; Yang, Z.; Hu, J.; Zheng, J.; Qi, X. Identification of a major quantitative trait locus for ear size induced by space flight in sweet corn. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 3069–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Rong, T. Detection of quantitative trait loci for ear row number in F2 populations of maize. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 14229–14238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Huang, R.; Li, Y.; Cheng, H.; Li, X.; Zhou, B.; Wu, S.; et al. The genetic basis of natural variation in kernel size and related traits using a four-way cross population in maize. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, R. QTL Mapping of Grain Test Weight Related Traits in Maize. Master’s Thesis, Sichuan Agricultural University, Yaan, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. QTL Analyses for Main Agronomy Traits Using Segregation Populations Derived from Different Maize Hybrids in China. Ph.D. Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Yin, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, J. QTL for maize grain yield identified by QTL mapping in six environments and consensus loci for grain weight detected by meta-analysis. Plant Breed. 2017, 136, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Song, W.; Xing, J.; Duan, M.; Wang, F.; Tian, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, S.; Su, A.; Li, C.; et al. Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci for three kernel-related traits in maize using a double haploid population. Mol. Breed. 2017, 37, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; He, K.; Chang, L.; Cui, T.; Zhao, Z.; Xue, J.; Liu, J. QTL mapping and genetic analysis for maize kernel size and weight in multi-environments. Euphytica 2018, 214, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramekar, R.; Sa, K.; Park, K.; Roy, N.; Kim, N.; Lee, J. Construction of genetic linkage map and identification of QTLs related to agronomic traits in maize using DNA transposon-based markers. Breed. Sci. 2018, 68, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B. QTL Mapping for Maize Ear and Kernel Traits under Different Environments and Confirmation of a Major QTLs for Maize Kernel Row Number. Ph.D. Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q. QTL Mapping and Candidate Gene Analysis of Yield-Related Traits by Using Two Maize F2:3 Families. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, B.; Yang, Q.; Dai, Z.; Hao, J. QTLs Mapping for Traits Related with Kernel in Maize. J. Henan Agric. Univ. 2021, 50, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, M.; Qiu, H. QTL mapping of maize (Zea mays L.) kernel traits under low-phosphorus stress. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2023, 29, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, D.; Qiu, F. Mapping of QTL for ear-related traits and prediction of key candidate genes in maize. Acta Agron. Sin. 2024, 50, 1435–1450. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, H.; Long, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Wei, X.; Wan, X. A systemic investigation of genetic architecture and gene resources controlling kernel size-related traits in maize. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Tian, R.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. DEK219 and HSF17 Collaboratively Regulate the Kernel Length in Maize. Plants 2024, 13, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiu, Z.; Yang, H.; Ma, Z.; Yang, D.; Wang, H.; Tan, B. Maize Shrek1 encodes a WD40 protein that regulates pre-rRNA processing in ribosome biogenesis. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 4028–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Huo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Chang, S.; Cai, P.; Song, K.; Galbraith, D.; Zhang, W.; et al. Decoding the gene regulatory network of endosperm differentiation in maize. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zou, Q. Genome-Wide Analysis of the MADS-Box Gene Family in Maize: Gene Structure, Evolution, and Relationships. Genes 2021, 12, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Song, G.; Guo, W.; Le, L.; Xu, F.; Wang, T.; Wang, F.; Wu, Y.; Gu, X.; Pu, L. ZmBELL10 interacts with other ZmBELLs and recognizes specific motifs for transcriptional activation to modulate internode patterning in maize. New Phytol. 2023, 240, 577–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Yu, J.; Zhu, D.; Zhao, Q. Maize GSK3-like kinase ZmSK2 is involved in embryonic development. Plant Sci. 2022, 318, 111221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Hu, D.; Li, T.; Liang, H.; Ye, F.; Xue, J.; Xu, S. Genome-wide association analysis for candidate genes contributing to kernel-related traits in maize. Front. Plant. Sci. 2022, 13, 872292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Feng, F.; Zhang, K.; He, Y.; Qi, W.; Ma, Z.; Song, R. ZmICE1a regulates the defence–storage trade-off in maize endosperm. Nat. Plants 2024, 10, 1999–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, P.; Wang, P.; Sidhu, G.; Yennawar, N.; Hsieh, J.; Chen, P.; Song, R.; Meyers, B.; et al. Maize unstable factor for orange1 encodes a nuclear protein that affects redox accumulation during kernel development. Plant Cell 2025, 37, koae301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Yu, H.; He, J.; Peng, D.; Zhu, P.; Pan, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Ji, C.; Chao, Z.; et al. The transcription factors ZmNAC128 and ZmNAC130 coordinate with Opaque2 to promote endosperm filling in maize. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 4066–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, M.; Saini, D.; Devi, V.; Kaur, C.; Singh, M.; Singh, J.; Pruthi, G.; Kaur, A.; Singh, A.; Chaudhary, D. Unravelling the genetic framework associated with grain quality and yield-related traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1248697. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Dai, Q.; Ajayo, B.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Insights into ZmWAKL in maize kernel development: Genome-wide investigation and GA-mediated transcription. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Wang, J.; Dong, R.; Guan, H.; Liu, T.; Liu, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L. Overexpression of an antisense RNA of maize receptor-like kinase gene ZmRLK7 enlarges the organ and seed size of transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Front. Plant. Sci. 2020, 11, 579120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Guo, L.; Ji, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, Q.; Wu, Y. The B3 domain-containing transcription factor ZmABI19 coordinates expression of key factors required for maize seed development and grain filling. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 104–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Pu, A.; Dong, Z.; Wei, X.; Wan, X. Molecular mechanisms controlling grain size and weight and their biotechnological breeding applications in maize and other cereal crops. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 62, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gu, W.; Sun, S.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Song, W.; Zhao, H.; Lai, J. Defective Kernel 39 encodes a PPR protein required for seed development in maize. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, B.; Shao, D.; Yan, R.; Wu, J.; Zheng, G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X. Defective kernel 66 encodes a GTPase essential for kernel development in maize. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 5694–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Liu, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhou, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, R.; Wang, L. Genome-wide analysis of sugar transporter genes in maize (Zea mays L.): Identification, characterization and their expression profiles during kernel development. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, S.; Shu, H.; Wang, Y.; Lai, J.; Du, J.; Yang, C. OsAGSW1, an ABC1-like kinase gene, is involved in the regulation of grain size and weight in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 5691–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, C.; Liu, Y.; Chang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Ding, C. Cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase family genes exhibit functional divergence and overlap in rice growth and development, especially in control of tillering. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 3552–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kereamy, A.; Bi, Y.; Mahmood, K.; Ranathunge, K.; Yaish, M.; Nambara, E.; Rothstein, S. Overexpression of the CC-type glutaredoxin, OsGRX6 affects hormone and nitrogen status in rice plants. Front. Plant. Sci. 2015, 6, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Tanaka, A.; Tanabata, T.; Ohtake, M.; Fujioka, S.; Nakamura, H.; Ichikawa, H.; Mori, M. Short grain1 decreases organ elongation and brassinosteroid response in rice. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 1208–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, D.; Lu, S.; Chen, Z.; Lin, Y.; Yu, D.; Yang, X. Molecular characterization reveals that OsSAPK3 improves drought tolerance and grain yield in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Wu, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C.; et al. The OsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rice yield and grain quality. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Lan, H.; Wang, C.; Yin, C.; Wu, Y.; Tang, H.; Qian, Q.; Li, J.; et al. Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21534–21539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, R.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, Y. Retention of OsNMD3 in the cytoplasm disturbs protein synthesis efficiency and affects plant development in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3055–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, B.; Shang, L.; Zhang, B.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhang, A.; Liu, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, L.; et al. Natural variation in the promoter of TGW2 determines grain width and weight in rice. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Tan, W.; You, A.; Wu, S.; Tao, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; et al. OsPP2C09, a negative regulatory factor in abscisic acid signalling, plays an essential role in balancing plant growth and drought tolerance in rice. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 1417–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Qu, J.; He, W.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, J.; Ma, Y.; Lin, Q.; et al. Roles of FERONIA-like receptor genes in regulating grain size and quality in rice. Sci. China Life Sci. 2021, 64, 294–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, R.; Hu, B.; Wang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, D.; Yin, W.; Tong, H.; Chu, C. POLLEN STERILITY, a novel suppressor of cell division, is required for timely tapetal programmed cell death in rice. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 1235–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Cui, Y.; Huang, L.; Ge, L.; Xu, X.; Xue, D.; Tang, M.; Zheng, J.; Yi, Y.; Chen, L. The RNA binding protein OsLa influences grain and anther development in rice. Plant J. 2022, 110, 1397–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, E.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Geng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Geng, H.; Qian, Y.; Ma, S. Rice co-expression network analysis identifies gene modules associated with agronomic traits. Plant Physiol. 2022, 190, 1526–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Luo, Y.; Li, F.; Tan, J.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; et al. Rice OsUBR7 modulates plant height by regulating histone H2B monoubiquitination and cell proliferation. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 100412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, K.; Xiong, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Fan, X.; Huang, L.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q. Glucan, Water-Dikinase 1 (GWD1), an ideal biotechnological target for potential improving yield and quality in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2606–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Trait | Mean | Range | CV/% | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | 9.50 ± 0.78 | 7.05–13.1 | 8 | 0.26 | 0.53 |
| KW | 7.90 ± 0.66 | 5.58–10.81 | 8 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| HKW | 26.62 ± 4.86 | 9.84–53.78 | 18 | 0.33 | 0.88 |
| Trait | SNPs | Gene | Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| HKW | 1_45747417 | Zm00001d028757 | transcription factor bHLH140 |
| HKW | 2_218329593 | Zm00001d006871 | 40S ribosomal protein SA-1 |
| HKW | 3_1222238 | Zm00001d039296 | Casein Kinase I |
| HKW | 6_147537023 | Zm00001d038092 | RING/U-box superfamily protein |
| HKW | 8_164076212 | Zm00001d011889 | hex9—hexokinase9 |
| KW | 3_220626790 | Zm00001d044153 | cyp10—cytochrome P450 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Bian, J.; Tang, R.; Ren, Z.; Peng, Y. Candidate Gene for Kernel-Related Traits in Maize Revealed by a Combination of GWAS and Meta-QTL Analyses. Plants 2025, 14, 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060959
Dong H, Zhuang Z, Bian J, Tang R, Ren Z, Peng Y. Candidate Gene for Kernel-Related Traits in Maize Revealed by a Combination of GWAS and Meta-QTL Analyses. Plants. 2025; 14(6):959. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060959
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Hanlong, Zelong Zhuang, Jianwen Bian, Rui Tang, Zhenping Ren, and Yunling Peng. 2025. "Candidate Gene for Kernel-Related Traits in Maize Revealed by a Combination of GWAS and Meta-QTL Analyses" Plants 14, no. 6: 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060959
APA StyleDong, H., Zhuang, Z., Bian, J., Tang, R., Ren, Z., & Peng, Y. (2025). Candidate Gene for Kernel-Related Traits in Maize Revealed by a Combination of GWAS and Meta-QTL Analyses. Plants, 14(6), 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060959





