Understory Vegetation Regulated the Soil Stoichiometry in Cold-Temperate Larch Forests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
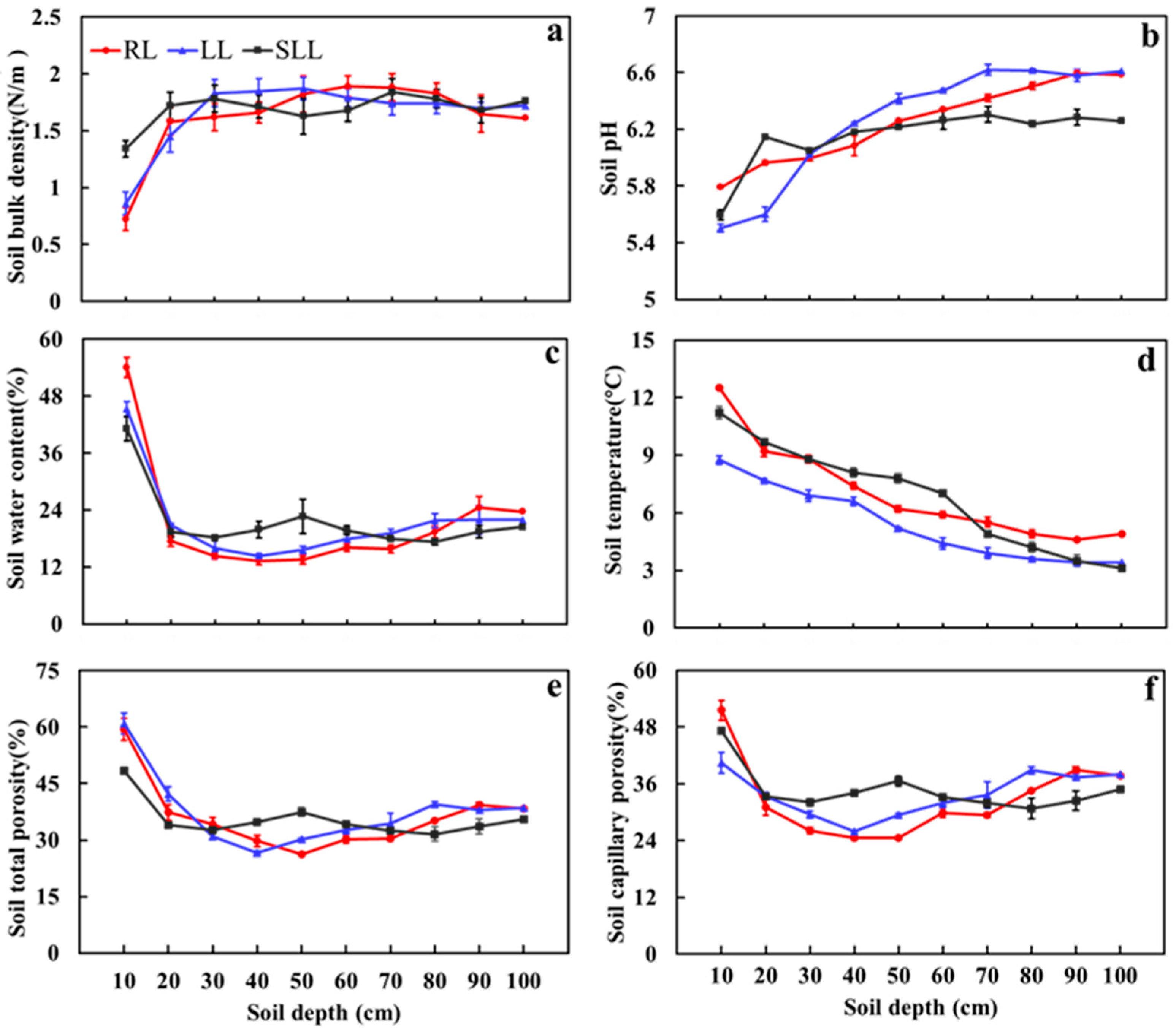
2.1. Soil Properties Among Different Forest Types
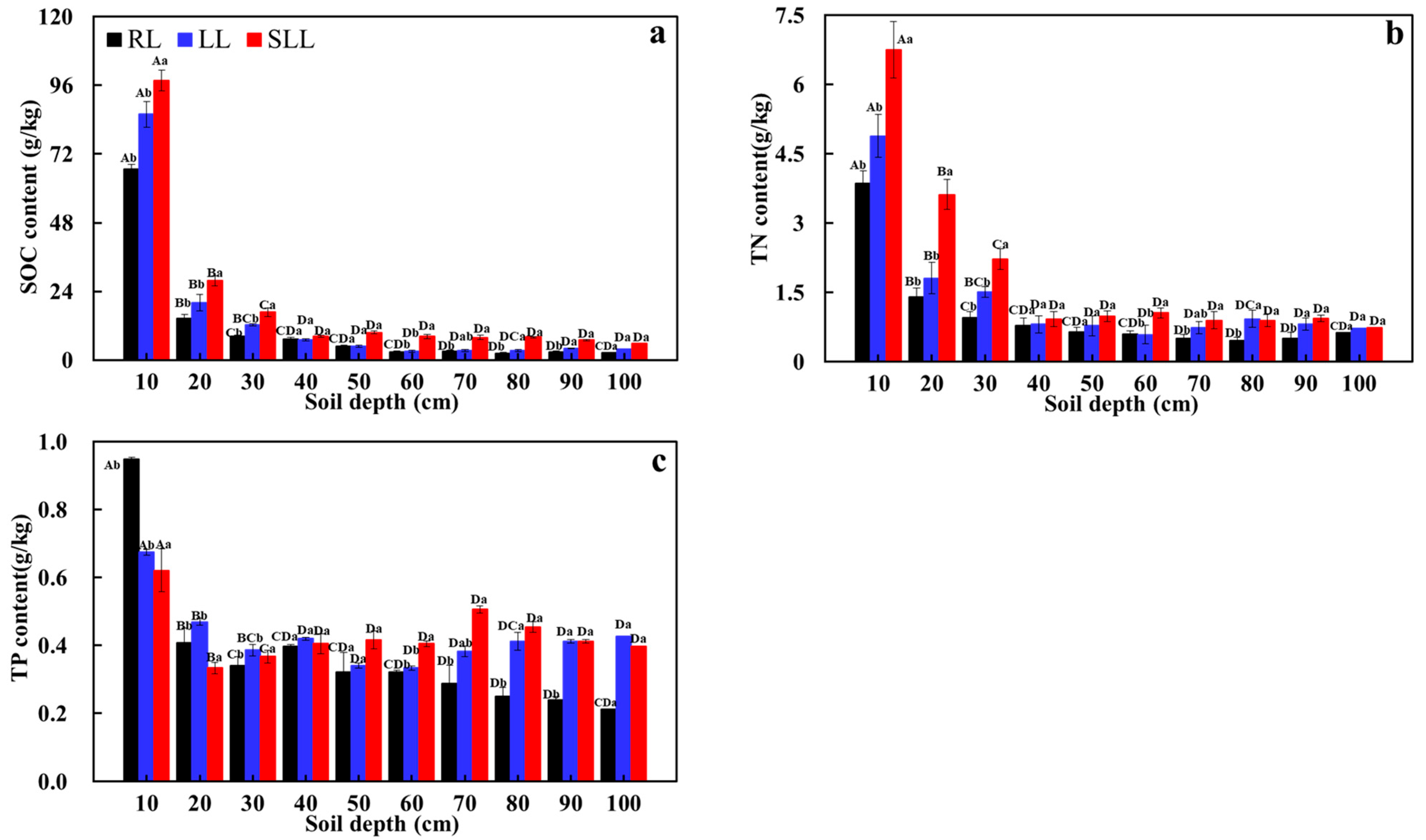
2.2. Soil Nutrient Content Among Different Forest Types
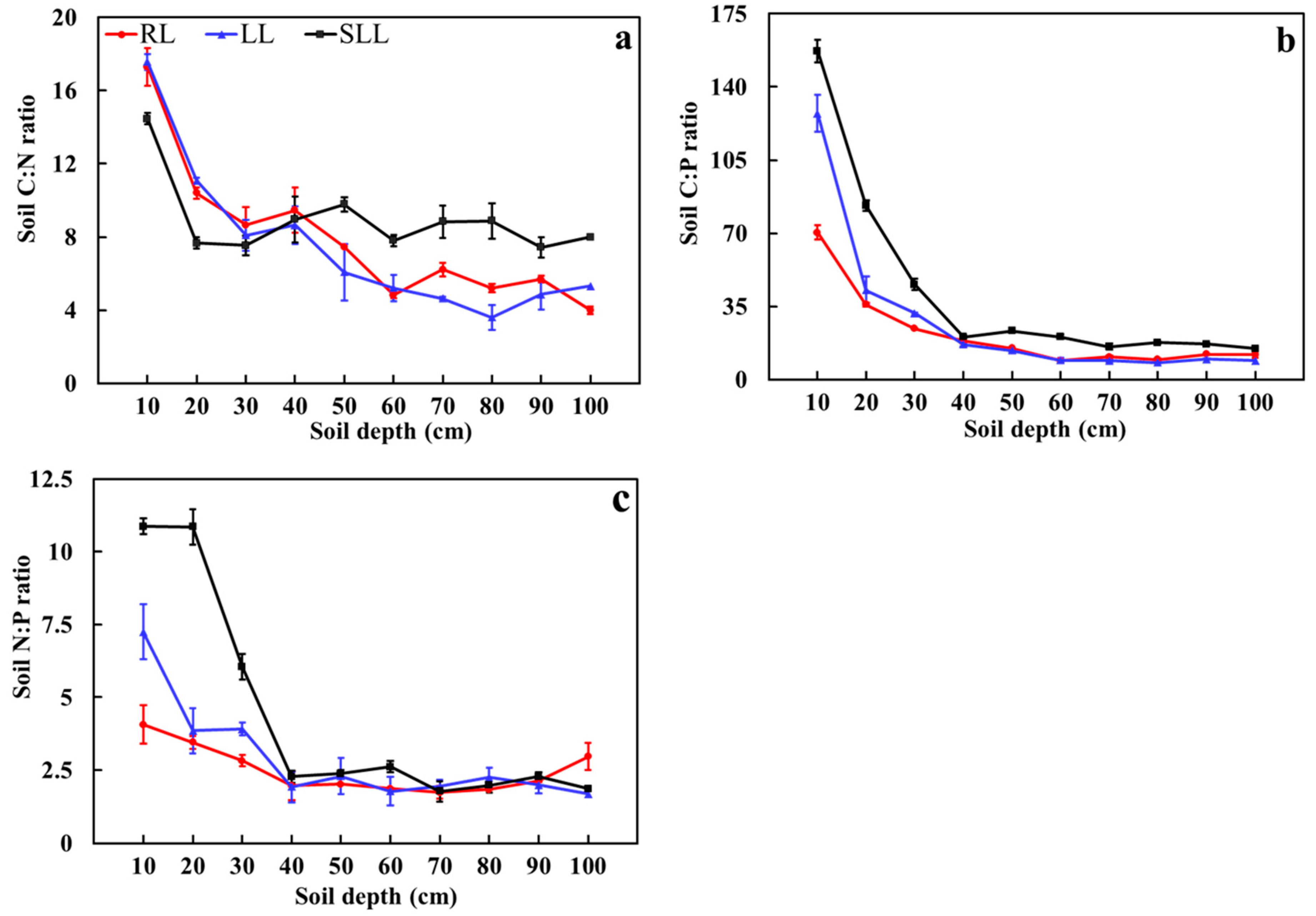
2.3. Soil Stoichiometric Ratios of Different Forest Types
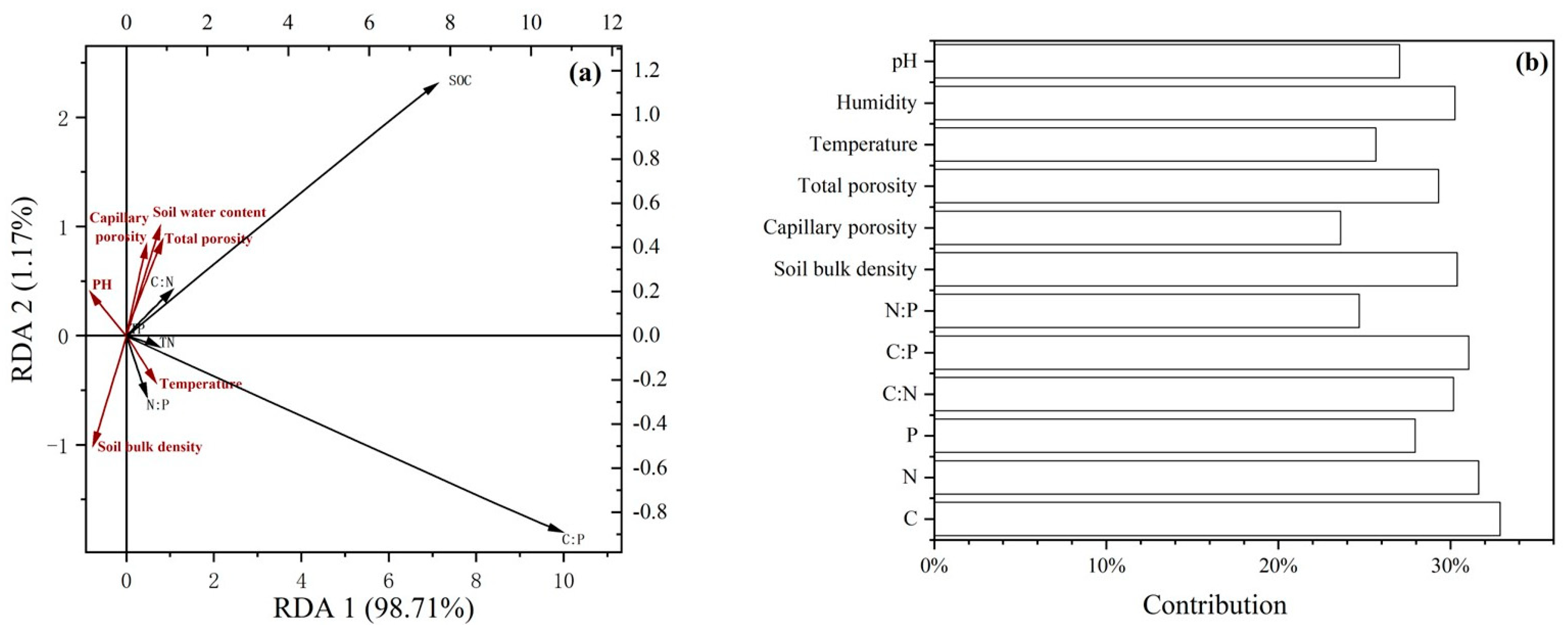
2.4. Effect of Environmental Factors on Soil Stoichiometric Ratios
3. Discussion
3.1. Influence of Understory Vegetation on Soil Nutrient Content
3.2. Influence of Understory Vegetation on Soil Stoichiometry
3.3. Relationship Between Soil Stoichiometric Characteristics and Environmental Factors
3.4. Insights
4. Materials and Methods
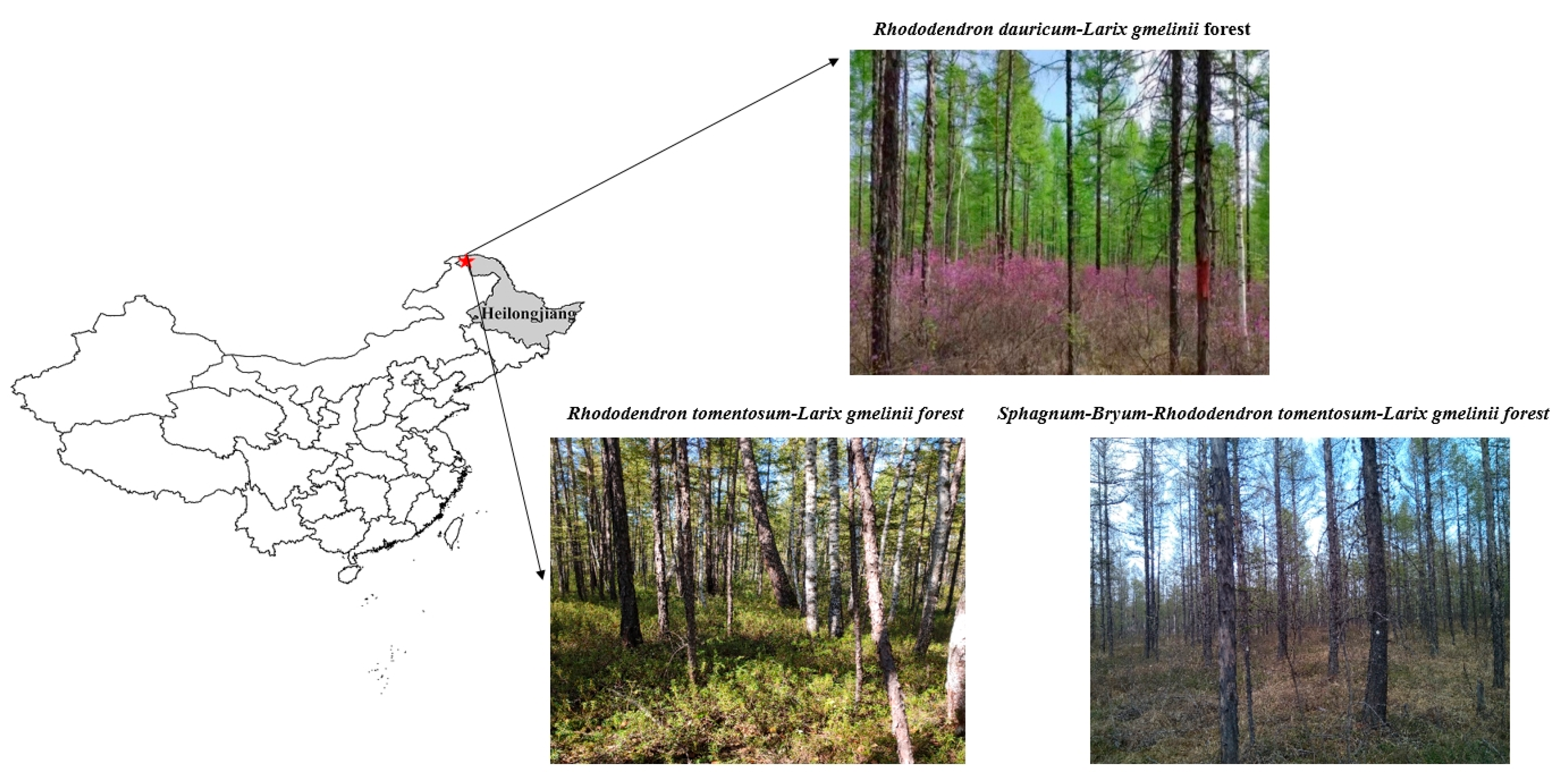
4.1. Study Area Description
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Soil Sampling
4.4. Soil Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Factors | RDA1 | RDA2 |
| Soil bulk density | −0.78243 | −0.46915 |
| Capillary porosity | 0.60729 | 0.41123 |
| Total porosity | 0.77187 | 0.41938 |
| Temperature | 0.76469 | −0.23741 |
| Water content | 0.81537 | 0.49641 |
| pH | −0.83584 | 0.19071 |
| C | 8.16872 | 1.23558 |
| N | 0.47731 | −0.00935 |
| P | 0.03728 | 0.01977 |
| C:N | 1.06701 | 0.17928 |
| C:P | 11.52941 | −0.87821 |
| N:P | 0.62899 | −0.24703 |
References
- Yang, Y.; Liu, B.-R.; An, S.-S. Ecological stoichiometry in leaves, roots, litters and soil among different plant communities in a desertified region of Northern China. Catena 2018, 166, 328–338. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Z.; Sheng, M.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Ecological stoichiometry of C, N, P and Si of Karst Masson pine forests: Insights for the forest management in southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169490. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Ma, C.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, J. Restoring Farmland to Forest Increases Phosphorus Limitation Based on Microbial and Soil C:N:P Stoichiometry—A Synthesis Across China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 556, 121745. [Google Scholar]
- Trogisch, S.; Liu, X.; Rutten, G.; Xue, K.; Bauhus, J.; Brose, U.; Bu, W.; Cesarz, S.; Chesters, D.; Connolly, J.; et al. The significance of tree-tree interactions for forest ecosystem functioning. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2021, 55, 33–52. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Mariotte, P.; Gu, J.; Song, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, G. Impacts of geography, climate, soil properties and vegetation characteristics on soil C:N:P stoichiometry across the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Pedosphere 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, B.; Cong, N.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, W.; Duan, X. Excessive climate warming exacerbates nitrogen limitation on microbial metabolism in an alpine meadow of the Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from soil ecoenzymatic stoichiometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172731. [Google Scholar]
- He, P.; Lu, J.; Ren, Y.; Li, J.; Hou, L.; Deng, X.; Gao, T.; Cheng, F. Altitude and slope aspects as the key factors affecting the change of C:N:P stoichiometry in the leaf-litter-soil system of alpine timberline ecotones of the Sygera Mountains in Southeast Tibet, China. Geoderma Reg. 2023, 32, e00602. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Q.; Tan, Y.; Yan, P.; Arif, M. Examining the stoichiometry of C:N:P:K in the dynamics of foliar-litter-soil within dominant tree species across different altitudes in southern China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 51, e02885. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Pu, L.; Li, B.; Xu, Y.; Kong, F. Coupling mechanism of C:N:P stoichiometry between plant and soil after long-term reclamation in the coastal area, eastern China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 68, 103178. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, N.B.; Singh, L.I.; Yadava, P.S.; Khan, M.R. Shift in microbial biomass, soil and microbial stoichiometry in different land uses of Northeast India. Microbe 2024, 3, 100085. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Zuo, X.; Zhao, X.; Qiao, J.; Ya, H.; Li, X.; Yue, P.; Chen, M.; Wang, S.; Medina-Roldán, E. Plant functional traits mediate the response magnitude of plant-litter-soil microbial C:N:P stoichiometry to nitrogen addition in a desert steppe. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 169915. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Y.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Ma, Y.; Song, Z.; Gao, P.; Ba, Y.; Wei, W. Soil moisture regulates soil-microbe-enzyme stoichiometries during recovery succession in patchily degraded alpine meadows on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 204, 107287. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wu, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Cui, Y.; Shangguan, Z.; Deng, L. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry in response to precipitation changes in terrestrial ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 191, 109321. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, D.; Yang, X.; Deng, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Ren, H. Soil C:N:P stoichiometry in tropical forests on Hainan Island of China: Spatial and vertical variations. Catena 2021, 201, 105228. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Man, X. Effects of understory vegetation on soil phosphorus forms and availability in cold temperate Larix gmelinii forests. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 2, 339–350+363. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, M. Effects of thinning on understory vegetation diversity and nutrient element stocks in Chinese fir plantations. J. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 1, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Duan, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Yao, C.; Chen, Y.; Cao, W.; Niu, Y. Patterns and driving factors of soil ecological stoichiometry in typical ecologically fragile areas of China. Catena 2022, 219, 106628. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, H.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.; Feng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, H. Characteristics of soil nutrients and salinization in semi-arid lake wetlands: A case study of Daihai Lake. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 1, 188–196. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, R.K.; Garkoti, S.C. Influence of vegetation types on soil physical and chemical properties, microbial biomass and stoichiometry in the central Himalaya. Catena 2023, 222, 106835. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Joshi, R.K.; Mishra, A.; Kumar, S.; Hansda, P.; Garkoti, S.C. Treeline ecotone drives the soil physical, biochemical and stoichiometry properties in alpine ecosystems of the western Himalaya, India. Catena 2024, 239, 107950. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Z.; Liu, D.; Li, G.; Wang, S.; Wu, X. Soil C, N, and P Contents and Their Stoichiometry as Impacted by Main Forest Vegetation Types in Xinglongshan, China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norby, R.J.; Jackson, R.B. Root Dynamics and Global Change: Seeking an Ecosystem Perspective. New Phytol. 2000, 147, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Clemmensen, K.E.; Bahr, A.; Ovaskainen, O.; Dahlberg, A.; Ekblad, A.; Wallander, H.; Stenlid, J.; Finlay, R.D.; Wardle, D.A.; Lindahl, B.D. Roots and Associated Fungi Drive Long-Term Carbon Sequestration in Boreal Forest. Science 2013, 339, 1615–1618. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C. Biomass allometric equations for 10 co-occurring tree species in Chinese temperate forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 222, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Cai, T. Changes in species diversity and influencing factors during secondary forest succession in northern Daxing’anling. J. Plant Ecol. 2024, 3, 349–363. [Google Scholar]
- Che, F.; Liu, M.; Zhou, G.; Wang, J.; Shan, J.; Duan, S. Current status of permafrost in northern Daxing’anling. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2020, 12, 107–111+115. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.; Man, X.; Duan, B.; Cai, T.; Ge, Z.; Li, X.; Vesala, T. Changes in soil bacterial communities and nitrogen mineralization with understory vegetation in boreal larch forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 166, 108572. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Qi, J.; Li, T.; Yu, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Hao, J. Effects of stand density on species diversity and biomass of Pinus massoniana plantations in Wenfeng Mountain, Xinjing. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 15, 5709–5717. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, J.; Kong, H.; Liu, H. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil C, N, P, and K in different forest types of Pinus massoniana. J. Northwest AF Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2016, 2, 68–76+82. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Cui, X. Response of soil C, N, P stoichiometry to forest type and altitude in cold temperate forests. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2022, 10, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, L. Effects of different forest types on soil nutrient content in Geqiugou Basin, Inner Mongolia. Soil Bull. 2023, 2, 328–335. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Guo, Q.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in three forest types in southeastern Guizhou. J. South Agric. 2022, 11, 3192–3200. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Teng, J.; Qin, J.; Liang, Z.; He, J.; Qin, L. Differential responses of soil C:N:P stoichiometry to mixed coniferous and broad-leaved plantations and their pure stands. West. For. Sci. 2024, 2, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.T.; Sun, Y.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Ruan, H. Effects of elevated CO2 on the C:N stoichiometry of plants, soils, and microorganisms in terrestrial ecosystems. Catena 2021, 201, 105219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.Q.; Chen, G.S.; Zhang, C.; Melillo, J.M.; Hall, C.A. Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 2010, 98, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Wang, W.; Deqiu, L.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y. Vertical variation of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus contents and ecological stoichiometry in typical vegetation of Qilian Mountains. Arid Zone Res. 2024, 3, 444–455. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Ma, J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, R.; Yan, C.; Ren, X.; Li, X. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of soil C, N, P in typical shrubs in Xishui Forest Area, Qilian Mountains, Gansu. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2022, 3, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Güsewell, S.; Koerselman, W.; Verhoeven, J.T.A. Biomass N:P ratios as indicators of nutrient limitation for plant populations in wetlands. Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, G. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus elements in ecosystems. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 8, 3937–3947. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Hao, Y.; Xin, Z.; Duan, R.; Li, X.; Liu, F. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus under four typical shrubs in Horqin Sandy Land. J. Northwest Bot. 2019, 1, 164–172. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Mao, R. Effects of Alnus sibirica expansion on plant and soil ecological stoichiometry in peatlands of Daxing’anling. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2025, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q. Changes in soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry with different forest ages of Larix principis-rupprechtii. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 1, 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, D.B.; Wang, G.Z.; Li, G.J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics of two typical plantations in the Karst ecosystem of southwestern China. Forests 2018, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Ouyang, M.; Liu, J.; Song, Q.; Fang, X.; Luan, F.; Yang, Q. Effects of Moso Bamboo Expansion on Soil and Nitrogen-Phosphorus Stoichiometry in Chinese Fir Forests. Ecol. Sci. 2024, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Elisabeth, N.B.; Brent, L.H. C:N:P Stoichiometry in Australian Soils with Respect to Vegetation and Environmental Factors. Plant Soil 2013, 373, 553–568. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Tuo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, R.; Wang, S.; Zhu, X.; He, X. Response of Soil Stoichiometric Characteristics, Microbes, and Their Seasonal Dynamics to Forest Stand Types in Liziping Nature Reserve. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 38, 285–295. [Google Scholar]
- Palati, Q.; Liu, D.; Mao, J.; Qiao, F.; Wang, C. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in alpine grasslands with different degradation levels. J. Ecol. 2024, 6, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, B.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil in Caragana korshinskii shrub dunes at different development stages. Chin. J. Grassl. 2023, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, F.; Yao, D.; Wang, W.; Zhao, F.; Cao, G.; Yu, K. Stoichiometric characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in jujube orchards around the Tarim Basin. China Fruits 2024, 3, 60–67+74. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Yan, P.; Jing, Y.; Wei, Y.; Ni, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Study on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Microbial Characteristics of Three Forest Types in the Eastern Liaoning Mountains. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2018, 49, 552–558. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Lv, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Ren, Q.; Feng, G. Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Stoichiometric Characteristics of Typical Forest Types in the Upper Reaches of Baiyangdian. Soil Bull. 2024, 55, 960–967. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.X.; Bai, Y.F.; Han, X.G. Application of N:P Stoichiometry to Ecology Studies. Acta Bot. Sin. 2003, 45, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.H.; Man, X.L.; Duan, B.X. Carbon and nitrogen stocks in three types of Larix gmelinii forests in Daxing’an mountains, northeast china. Forests 2020, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Chen, C.; Man, X.; Han, Z. The Foliar-soil Ecostoichiometric Characteristics of the Principal Arboreal Species in the Northern Region the Greater Hinggan Mountains. For. Eng. 2024, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Matsoukis, A.; Gasparatos, D.; Chronopoulou-Sereli, A. Micronutrient content in relation to specific leaf area, light regime and drenched-applied paclobutrazol in Lantana camara L. Curr. Agric. Res. J. 2015, 3, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, F.; Tang, X.; Fan, S.; Zhao, J.; Peng, C. Changes in Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Stocks Followed the Conversion from Secondary Forest to Chinese Fir and Moso Bamboo Plantations. Catena 2015, 133, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gong, X.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Dang, K.; Feng, B. Microbial Nutrient Limitation in Rhizosphere Soils of Different Food Crop Families: Evidence from Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Wang, K.; Chen, M.; Shangguan, Z.; Sweeney, S. Soil Organic Carbon Storage Capacity Positively Related to Forest Succession on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2013, 110, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Sharma, V.; Arya, V.M.; Sharma, K.R.; Rao, C.S. Total Organic and Inorganic Carbon in Soils under Different Land Use/Land Cover Systems in the Foothill Himalayas. Catena 2019, 182, 104104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Man, X.; Cai, T.; Xiao, R.; Ge, Z. Increasing Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Stocks Along with Secondary Forest Succession in Permafrost Region of the Daxing’an Mountains, Northeast China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Source of Difference | SOC | TN | TP | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | F | p | Mean Squares | df | F | p | Mean Squares | df | F | p | Mean Squares | |
| Understory vegetation type | 1 | 85.849 | <0.001 | 995.849 | 1 | 97.916 | <0.001 | 11.327 | 1 | 24.619 | <0.001 | 0.052 |
| Soil depth | 9 | 29.052 | <0.001 | 337.007 | 9 | 4.325 | <0.001 | 0.500 | 9 | 46.212 | <0.001 | 0.098 |
| Soil depth × Understory vegetation type | 9 | 9.679 | <0.001 | 112.272 | 9 | 11.853 | <0.001 | 1.371 | 9 | 19.498 | <0.001 | 0.041 |
| Source of Difference | Soil C:N | Soil C:P | Soil N:P | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | F | p | Mean Squares | df | F | p | Mean Squares | df | F | p | Mean Squares | |
| Understory vegetation type | 1 | 9.019 | 0.004 | 14.786 | 1 | 159.614 | <0.001 | 5861.774 | 1 | 88.527 | <0.001 | 49.232 |
| Soil depth | 9 | 24.792 | <0.001 | 40.645 | 9 | 2.590 | 0.012 | 95.131 | 9 | 3.344 | 0.002 | 1.859 |
| Soil depth × Understory vegetation type | 9 | 6.417 | <0.001 | 10.521 | 9 | 30.057 | <0.001 | 1103.821 | 9 | 24.324 | <0.001 | 13.527 |
| Forest Ecological Characteristics | Mean DBH (cm) | Stand Age | Mean Tree Height (m) | Slope/° | Stand Density (Trees·ha−1) | Elevation (m) | Understory Species Composition | Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RL | 13.78 ± 2.12 | 75–90 | 17.23 ± 1.54 | 3 | 1266 ± 126 | 324 | Vaccinium uliginosum L. | 30 |
| Ledum palustre L. | 20 | |||||||
| Vaccinium vitis-idaea L. | 10 | |||||||
| Rhododendron dauricum L. | 80 | |||||||
| LL | 13.14 ± 2.61 | 75–90 | 16.78 ± 1.94 | 4 | 1300 ± 100 | 326 | Pyrola incarnate H.Andr. | 40 |
| Vaccinium uliginosum L. | 20 | |||||||
| Rhododendron tomentosum L. | 70 | |||||||
| Vaccinium vitis-idaea L. | 50 | |||||||
| Fragaria orientalis Losinsk | 10 | |||||||
| SLL | 14.06 ± 2.23 | 75–90 | 17.47 ± 1.60 | 2 | 1117 ± 126 | 332 | Fragaria orientalis Losinsk | 5 |
| Vaccinium vitis-idaea L. | 30 | |||||||
| Pyrola incarnata H.Andr | 10 | |||||||
| Vaccinium uliginosum L. | 50 | |||||||
| Vaccinium macrocarpon L. | 20 | |||||||
| Rhododendron tomentosum L. | 70 | |||||||
| Bryum L. | 40 | |||||||
| Sphagnum palustre L. | 60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, R.; Liang, X.; Duan, B. Understory Vegetation Regulated the Soil Stoichiometry in Cold-Temperate Larch Forests. Plants 2025, 14, 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071088
Xiao R, Liang X, Duan B. Understory Vegetation Regulated the Soil Stoichiometry in Cold-Temperate Larch Forests. Plants. 2025; 14(7):1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071088
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Ruihan, Xinyuan Liang, and Beixing Duan. 2025. "Understory Vegetation Regulated the Soil Stoichiometry in Cold-Temperate Larch Forests" Plants 14, no. 7: 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071088
APA StyleXiao, R., Liang, X., & Duan, B. (2025). Understory Vegetation Regulated the Soil Stoichiometry in Cold-Temperate Larch Forests. Plants, 14(7), 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071088





