Phenotypic Traits, Hormonal Distribution, and Metabolite Profiling of Isatis indigotica Seeds from 21 Samples in China: A Traditional Chinese Medicinal Herb
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phenotype of I. indigotica Seeds Under Different Regional Conditions
2.2. Metabolite Detection in I. indigotica Seeds from Different Regions
2.3. Analysis of Hormone Content in the I. indigotica Seed from Different Regions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
4.2. Measurement of Seed Phenotypic Parameters
4.3. Sample Extraction and Metabolite Profiling of I. indigotica Seed from 21 Origins in China
4.4. Analysis of Endogenous Hormones in I. indigotica Seed from 21 Origins in China
4.5. Seed Germination Experiment
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Han, Y.; Yao, Z.; Chen, W.; Yang, S.; Wu, X. Research Progress on Radix isatidis. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xiao, S. Studies of the flowering habits and pollination for diploid Isatis indigotica. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2019, 28, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivarathri, B.S.; Kodadinne Narayana, N.; Bryant, C.J.; Dhillon, J.; Reddy, K.R.; Bheemanahalli, R. Influence of seed-applied biostimulants on soybean germination and early seedling growth under low and high temperature stress. Plant Physiol. Rep. 2024, 30, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicek, E.; Tilki, F. Seed Size Effects on Germination, Survival and Seedling Growth of Castanea sativa Mill. J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 7, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khidrapure, G.; Lakshmana, D.; Hanumanthappa, M.; Rekha, B.; Chandana, B.C. Seed quality enhancement techniques in medicinal and aromatic crops: A review. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ambika, S.; Manonmani, V.; Somasundaram, G. Review on Effect of Seed Size on Seedling Vigour and Seed Yield. Res. J. Seed Sci. 2014, 7, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.S.; Hamid, A.; Miah, M.G.; Hashem, A. Seed Size Variation and its Effects on Germination and Seedling Vigour in Rice. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 1996, 176, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, S.; Pang, S.; Piao, X.; Wang, Y. Effect of seed size on seedling performance, yield and ginsenoside content of Panax Ginseng. Seed Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, F.; Baena-Gonzalez, E.; Sheen, J. Sugar Sensing And Signaling In Plants: Conserved and Novel Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 675–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Rafiq, R.; Zaib-un-Nisa; Wijaya, L.; Ahmad, A.; Kaushik, P. Exogenous citric acid improves growth and yield by concerted modulation of antioxidant defense system in brinjal (Solanum melongena L.) under salt-stress. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2024, 36, 103012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, P.T.; Sutariya, J.A.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Pandya, D.K.; Rathore, M.S. Non-targeted metabolomic evaluations during seed germination and seedling growth in Salicornia brachiata (Roxb.) under saline conditions. Aquat. Bot. 2024, 190, 103712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.S.; Elozeiri, A.A.; Ali, A.S.; Elozeiri, A.A. Metabolic Processes During Seed Germination. In Advances in Seed Biology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, M.; Brütting, C.; Meza-Canales, I.D.; Großkinsky, D.K.; Vankova, R.; Baldwin, I.T.; Meldau, S. The role of cis -zeatin-type cytokinins in plant growth regulation and mediating responses to environmental interactions. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 4873–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhu, Q.S.; Liu, L.J. Involvement of abscisic acid and cytokinins in the senescence and remobilization of carbon reserves in wheat subjected to water stress during grain filling. Plant Cell. Environ. 2003, 26, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frydman, V.M.; MacMillan, J. The metabolism of gibberellins A9, A20 and A29 in immature seeds of Pisum sativum cv. Progress No. 9. Planta 1975, 125, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.; Qi, Y.; Chen, F.; Meng, Y.; Luo, X.; Shuai, H.; Zhou, W.; Ding, J.; Du, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Salt Stress Represses Soybean Seed Germination by Negatively Regulating GA Biosynthesis While Positively Mediating ABA Biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Qanmber, G.; Li, F.; Wang, Z. Updated role of ABA in seed maturation, dormancy, and germination. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 35, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Marsolais, F.; Bernards, M.A.; Sumarah, M.W.; Bykova, N.V.; Igamberdiev, A.U. Glyoxylate cycle and metabolism of organic acids in the scutellum of barley seeds during germination. Plant Sci. 2016, 248, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Van Dijck, P. How Do Sugars Regulate Plant Growth? Front. Plant Sci. 2011, 2, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.; Prado, C.; Podazza, G.; Interdonato, R.; González, J.A.; Hilal, M.; Prado, F.E. Soluble sugars: Metabolism, sensing and abiotic stress: A complex network in the life of plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sińska, I.; Lewak, S. Is the gibberellin A4 biosynthesis involved in the removal of dormancy in apple seeds? Plant Sci. Lett. 1977, 9, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javeed, A.; Sarfraz, M.; Bhutta, N.K.; Han, B. Alkaloids as natural anti-allergy agents: A mini review. Allergy Med. 2024, 2, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Luo, J.; Sheng, Z.; Fang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Wang, N.; Yang, B.; Xu, B. Latest research progress on anti-microbial effects, mechanisms of action, and product developments of dietary flavonoids: A systematic literature review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 156, 104839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.-H.; Yu, X.; Cao, F.; Cai, X.; Chen, P.; Li, M.; Feng, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Pharmacokinetics of Anthraquinones from Medicinal Plants. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 638993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Bi, J.; He, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, X.; Xu, H. The indole alkaloids from the roots of Isatidis Radix. Fitoterapia 2021, 153, 104950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-D.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.-Y.; Ruan, D.-Q.; Chen, K.-X.; Li, Y.-M.; Wang, R. Chemical constitutes from alcohol extract of Isatidis Radix and their nitric oxide inhibitory activities. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2022, 53, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-T.; Yu, S.; Yuan, M.; Guo, Q.-S.; Gong, C.; Xu, X. Determination of Epigoitrin in Radix Isatidis by Solid Phase Extraction-Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Q.-H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Xing, N.; Kuang, H.-X. Analysis on Isatidis Radix Protein in Different Areas by SDS-PAGE. Chin. J. Inf. TCM 2015, 22, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Bi, K.; Sun, Y. Identification of Chemical Constituents in the Root of Isatis Indigotica Fort. by LC/DAD/ESI/MS/MS. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2007, 30, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Zhou, L.; Wan, H.; Fu, X.; Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Guo, W.; Guo, X.; Sui, C.; Wei, J. A comprehensive comparison on root yield and content of polysaccharides and alkaloids from ten germplasms of Isatis indigotica Fort. in two growing areas. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 187, 115254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domrös, M.; Gongbing, P. The Climate of China; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Yi, Z.; Dong, S. Effects of seed size on soybean performance: Germination, growth, stress resistance, photosynthesis, and yield. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moles, A.T.; Westoby, M. Seedling survival and seed size: A synthesis of the literature. J. Ecol. 2004, 92, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, S.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Fan, K.; Pan, Y.; Ping, J. An integrated plant glucose monitoring system based on microneedle-enabled electrochemical sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 248, 115964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, L.M.O.; Del Cerro, C.; Kijpornyongpan, T.; Yaguchi, A.; Bennett, A.; Donohoe, B.S.; Ramirez, K.J.; Benson, A.F.; Mitchell, H.D.; Purvine, S.O.; et al. Metabolic profiling of two white-rot fungi during 4-hydroxybenzoate conversion reveals biotechnologically relevant biosynthetic pathways. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Shi, X.; Wen, S.; Chen, J.; Luo, K.; Chen, Y.; Yue, S.; Yang, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y. The varying responses of leaves and roots and the link between sugar metabolic genes and the SWEET family in Dendrobium officinale under salt stress. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ľuptáková, E.; Vigouroux, A.; Končitíková, R.; Kopečná, M.; Zalabák, D.; Novák, O.; Salcedo Sarmiento, S.; Ćavar Zeljković, S.; Kopečný, D.J.; Von Schwartzenberg, K.; et al. Plant nucleoside N-ribohydrolases: Riboside binding and role in nitrogen storage mobilization. Plant J. 2024, 117, 1432–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Chen, Y.; Huang, H.; Pu, X.; Liang, H.; Kuang, Y.; Liu, Y. Structural characteristics, sugar metabolizing enzyme activity and biological activity of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides at different growth stages. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Qin, H.; Xin, Y.; Li, Q.; Kang, H.; Han, L.; Hua, W.; Cao, X. Characterization of 4-coumarate CoA ligase (4CL) gene family and functional study of Sm4CL2/3/7/9 in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2025, 25, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, C.; Li, L.; Lei, P.; Shen, W.; Xu, H.; Gao, N. Effect of n-hexadecanoic acid on N2O emissions from vegetable soil and its synergism with Pseudomonas stutzeri NRCB010. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 199, 105410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouni, C.; Theodosis-Nobelos, P.; Rekka, E.A. Antioxidant and Hypolipidemic Activities of Cinnamic Acid Derivatives. Molecules 2023, 28, 6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonel, E.A.; Vendruscolo, E.; Araújo, T.; Seron, C.d.C.; Sant’Ana, G.R.; Bortolheiro, F.; Martins, M.; de Lima, S.F.; Lafleur, L.; Silva Ribeiro, F. Niacin as a Biostimulant in Carrot Production in a Minimum Soil Tillage System in Brazil. Int. J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2025, 12, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Yadav, P.; Sharma, A.; Kumar Thukral, A.; Kumar, V.; Kaur Kohli, S.; Bhardwaj, R. Castasterone and citric acid treatment restores photosynthetic attributes in Brassica juncea L. under Cd(II) toxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-C.; Zhang, S.-L.; Wu, K.-J.; Li, R.; He, X.-R.; He, D.-N.; Huang, C.; Wei, H. The effects of exogenous organic acids on the growth, photosynthesis and cellular ultrastructure of Salix variegata Franch. Under Cd stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 187, 109790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-Q.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.-W.; Zhao, B.; Ren, B.-Z. Endogenous Hormones Inhibit Differentiation of Young Ears in Maize (Zea mays L.) Under Heat Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 533046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Kim, S.H.; Bahk, S.; Ali, A.; Nguyen, X.C.; Yun, D.-J.; Chung, W.S. The Auxin Signaling Repressor IAA8 Promotes Seed Germination Through Down-Regulation of ABI3 Transcription in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Guo, W.; Lv, G.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Histological and transcriptomic analysis reveals the cell number and plant hormone related to fruit size in Litchi chinensis Sonn. Sci. Hortic. 2025, 341, 114007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-H.; Liu, Y.-B.; Zhang, X.-S. Auxin–Cytokinin Interaction Regulates Meristem Development. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xiong, J.; Chen, X.-y. Advances in the research of physiological significances and genetic regulation of lignin metabolism. Acta Bot. Boreall-Occident. Sin. 2003, 23, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.-H.; Wu, J.-C.; Dong, B.; Li, D.-H.; Gu, H.-N. Two-way effect of pesticides on zeatin riboside content in both rice leaves and roots. Crop Prot. 2004, 23, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werle, R.; Nunes, J.J.; Arneson, N.J.; Mobli, A. Waterhemp emergence response to exogenous application of gibberellic and abscisic acids. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Wang, X.; Cui, N.; Xu, H.; Tian, T.; Wei, B. Enhancing germination and growth in Malania oleifera Chun & S. K. Lee seeds through gibberellic acid priming. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2025, 45, 100629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Mitchum, M.G.; Barnaby, N.; Ayele, B.T.; Ogawa, M.; Nam, E.; Lai, W.-C.; Hanada, A.; Alonso, J.M.; Ecker, J.R.; et al. Potential Sites of Bioactive Gibberellin Production during Reproductive Growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 320–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedden, P.; Phillips, A.L. Gibberellin metabolism: New insights revealed by the genes. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yu, Q.-X.; Yau, L.-F.; Huang, G.-K.; Lu, J.-G.; Liu, X.-X.; Jiang, Z.-H.; Wang, J.-R. Discrimination of Baphicacanthis Cusiae Rhizoma et radix and its adulterant species and establishment of an assay method for quality control. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
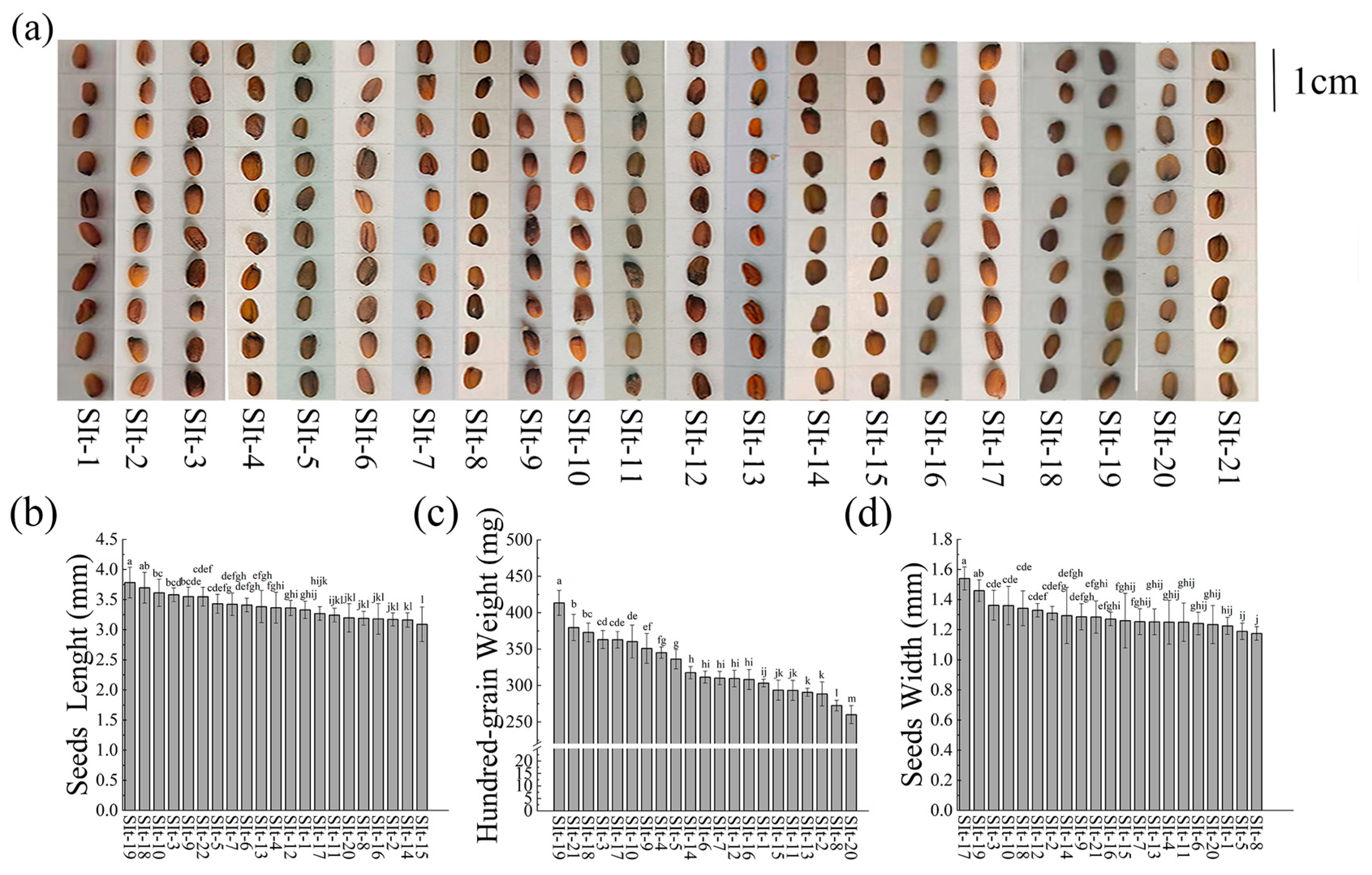
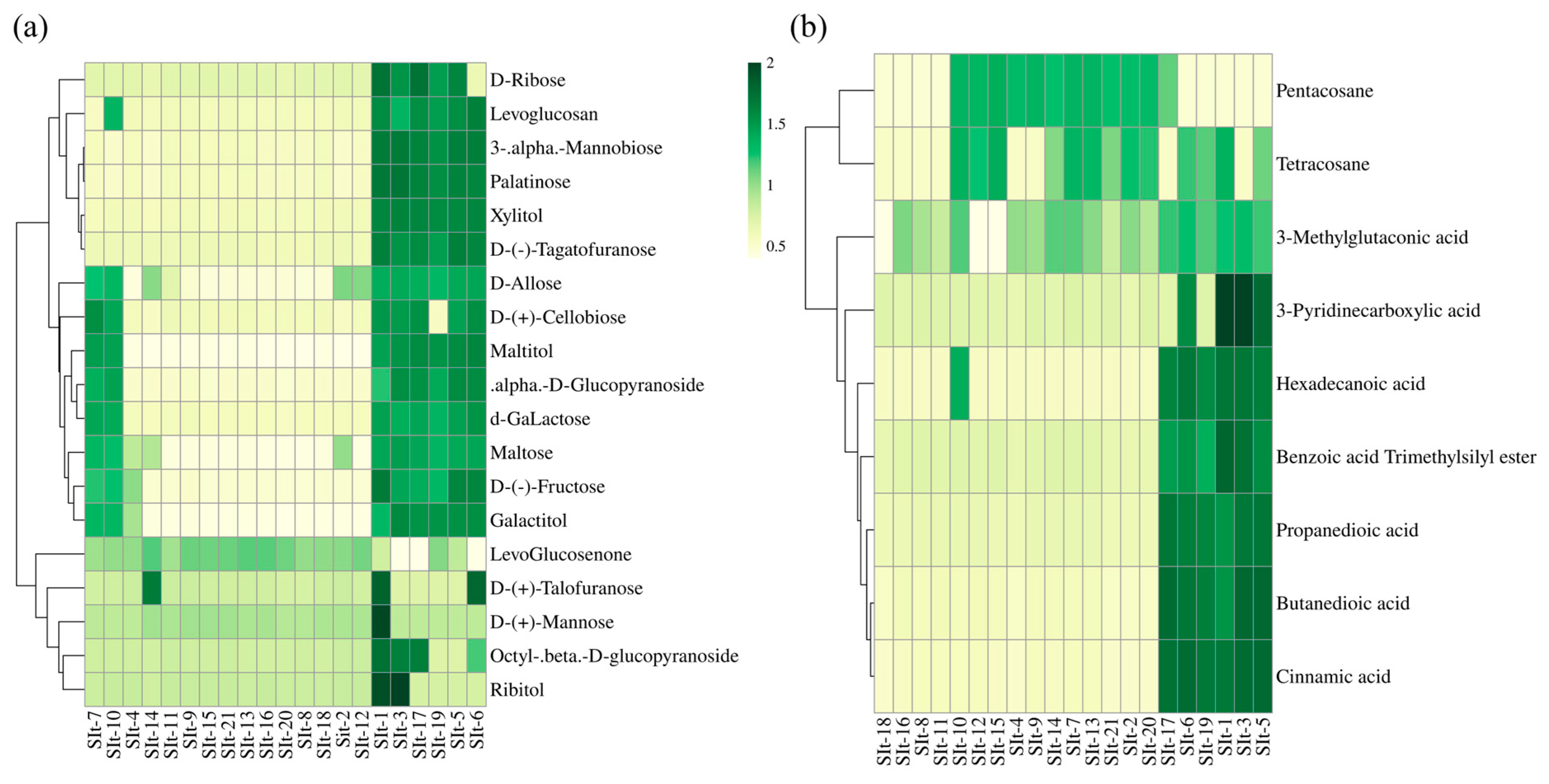

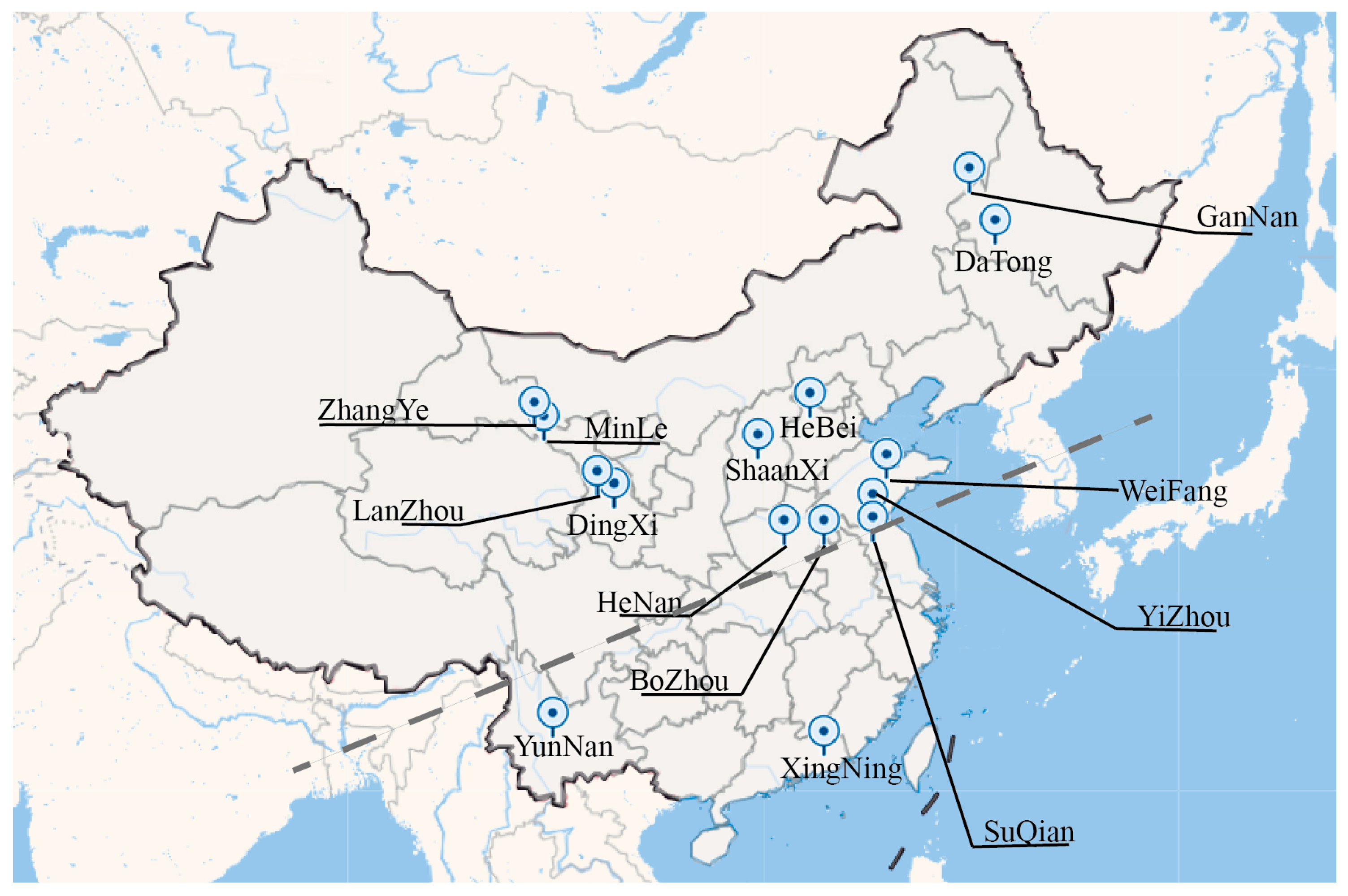
| No. | Collection Name | Serial Number | Province | GPS Coordinates | Category | Voucher Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SuQian | SIt-1 | JiangSu | N 118.28° E 33.96° | Isatidis Radix | NAS NAS00113843 |
| 2 | HeBei B.leaves | SIt-2 | HeBei | N 116.57° E 39.92° | Isatidis Radix | IBSC 0137007 |
| 3 | HeNan | SIt-3 | HeNan | N 113.75° E 34.77° | Isatidis Radix | PE 01055155 |
| 4 | BoZhou | SIt-4 | AnHui | N 115.78° E 33.85° | Isatidis Radix | WUK 0004816 |
| 5 | MinLe | SIt-5 | GanSu | N 100.81° E 38.43° | Isatidis Radix | WUK 0069675 |
| 6 | HeBei S.leaves | SIt-6 | HeBei | N 114.53° E 38.04° | Isatidis Radix | PE 01055154 |
| 7 | YunNan B.Leaves | SIt-7 | YunNan | N 102.71° E 25.05° | Isatidis Radix | KUN 0498901 |
| 8 | YunNan S.leaves | SIt-8 | YunNan | N 102.71° E 25.05° | Isatidis Radix | KUN 0498903 |
| 9 | GanNan | SIt-9 | GanSu | N 123.51° E 47.92° | Isatidis Radix | KUN 0498912 |
| 10 | LanZhou | SIt-10 | GanSu | N 103.83° E 36.06° | Isatidis Radix | WUK 0081682 |
| 11 | DingXi S.leaves | SIt-11 | GanSu | N 104.59° E 35.61° | Isatidis Radix | QYTC QYTC0003047 |
| 12 | DingXi B.leaves | SIt-12 | GanSu | N 104.59° E 35.61° | Isatidis Radix | QYTC QYTC0005994 |
| 13 | WeiFang | SIt-13 | ShanDong | N 119.16° E 36.71° | Isatidis Radix | GXMG GXMG0009684 |
| 14 | DaTong B.leaves | SIt-14 | ShanXi | N 124.92° E 46.11° | Isatidis Radix | SXTCM SXTCM0004019 |
| 15 | XingNing | SIt-15 | GuangDong | N 115.73° E 24.14° | Isatidis Radix | SZG SZG00028974 |
| 16 | ZhangYe B.leaves | SIt-16 | GanSu | N 100.45° E 38.92° | Isatidis Radix | PE 01055158 |
| 17 | ShanXi S.leaves | SIt-17 | ShanXi | N 112.58° E 37.81° | Isatidis Radix | WUK 0321714 |
| 18 | ZhangYe S.leaves | SIt-18 | GanSu | N 100.45° E 38.92° | Isatidis Radix | QYTC QYTC0003048 |
| 19 | DaTong S.leaves | SIt-19 | ShanXi | N 124.92° E 46.11° | Isatidis Radix | WUK 0324249 |
| 20 | YiZhou B.leaves | SIt-20 | ShanDong | N 118.36° E 35.10° | Isatidis Radix | NAS NAS00113877 |
| 21 | YiZhou S.leaves | SIt-21 | ShanDong | N 118.36° E 35.10° | Isatidis Radix | NAS NAS00113884 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xing, X.; Cong, T.; Meng, L.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Lemiasheuski, V.; et al. Phenotypic Traits, Hormonal Distribution, and Metabolite Profiling of Isatis indigotica Seeds from 21 Samples in China: A Traditional Chinese Medicinal Herb. Plants 2025, 14, 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071096
Wang L, Liu J, Dong Y, Gao Y, Xing X, Cong T, Meng L, Li W, Li X, Lemiasheuski V, et al. Phenotypic Traits, Hormonal Distribution, and Metabolite Profiling of Isatis indigotica Seeds from 21 Samples in China: A Traditional Chinese Medicinal Herb. Plants. 2025; 14(7):1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071096
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lunyan, Jia Liu, Yilun Dong, Yanan Gao, Xiangyu Xing, Tianyue Cong, Li Meng, Wanru Li, Xinyu Li, Viktar Lemiasheuski, and et al. 2025. "Phenotypic Traits, Hormonal Distribution, and Metabolite Profiling of Isatis indigotica Seeds from 21 Samples in China: A Traditional Chinese Medicinal Herb" Plants 14, no. 7: 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071096
APA StyleWang, L., Liu, J., Dong, Y., Gao, Y., Xing, X., Cong, T., Meng, L., Li, W., Li, X., Lemiasheuski, V., Zheng, C., & Liu, Y. (2025). Phenotypic Traits, Hormonal Distribution, and Metabolite Profiling of Isatis indigotica Seeds from 21 Samples in China: A Traditional Chinese Medicinal Herb. Plants, 14(7), 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071096






