The Identification of a Single-Base Mutation in the Maize Dwarf 1 Gene Responsible for Reduced Plant Height in the Mutant 16N125
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phenotyping and Genetic Analysis of Dwarf Maize Plants
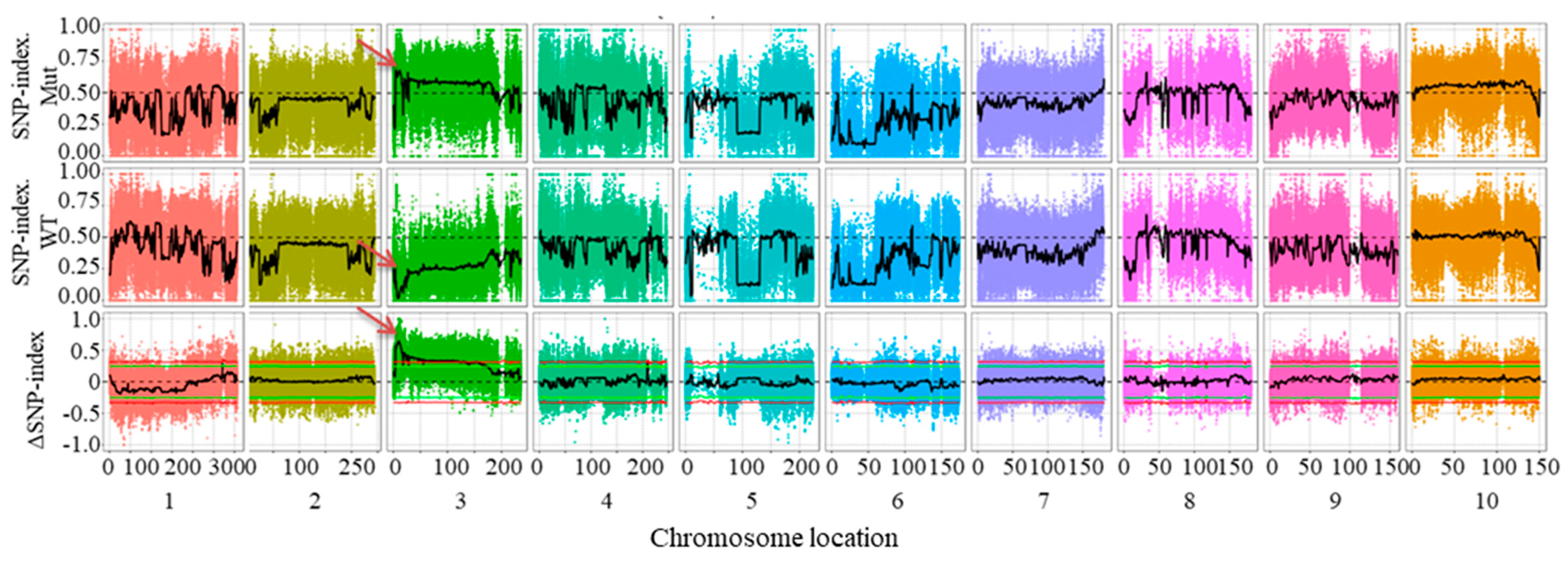
2.2. BSA-Seq Analysis and Mapping of Candidate Gene
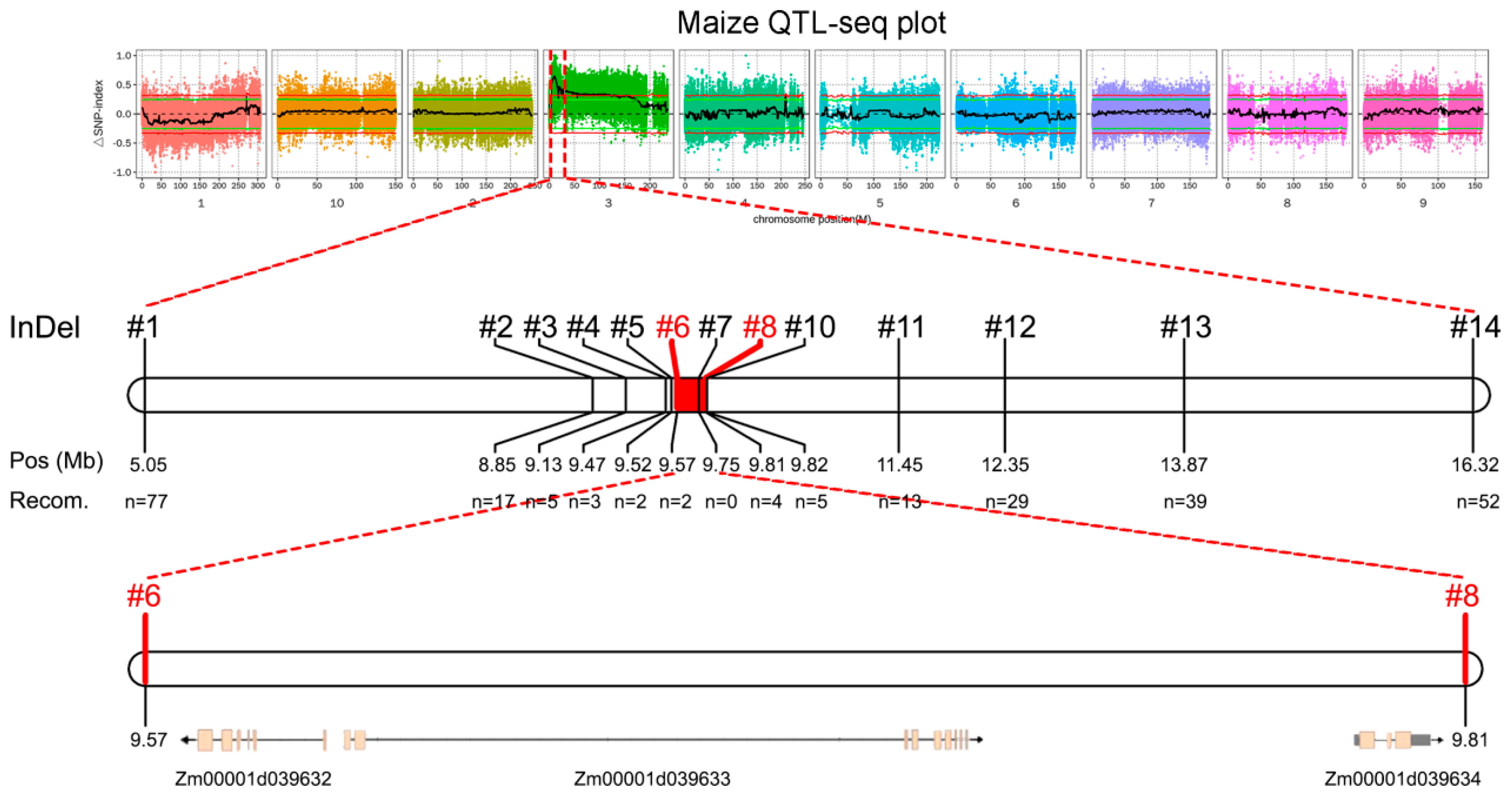
2.3. Fine Mapping of Candidate Gene
2.4. Identification of Candidate Gene Related to Plant Height in 16N125 Plants
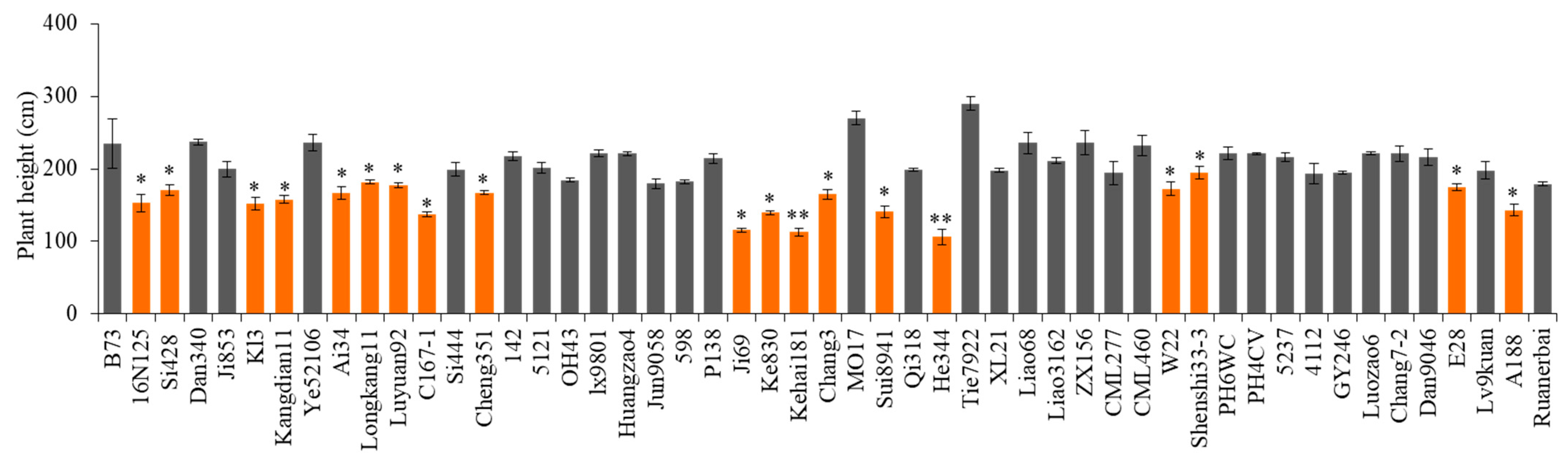
2.5. Investigation of D1 Mutant Genes in Widely Utilized Chinese Inbred Lines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials, DNA Extraction, and Sanger Sequencing
4.2. SNP Library Construction and High-Throughput Sequencing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, L.E.; Chen, S.; Smith, J.D. The role of maize in global food security and nutrition. Food Policy 2022, 108, 102241. [Google Scholar]
- Haley, C. A cornucopia of maize genes. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, R.; Qiao, F.; Ma, C.; Luo, J.; Li, W.; et al. The genetic mechanism of heterosis utilization in maize improvement. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Ge, F.; Qiang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Fu, Y. Maize ZmRPH1 encodes a microtubule-associated protein that controls plant and ear height. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1345–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.; Guo, W.; Du, D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, C.; Pu, L. A spatiotemporal transcriptomic network dynamically modulates stalk development in maize. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 2313–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.P.; Liu, X.H. Genetic analysis of agronomic traits associated with plant architecture by QTL mapping in maize. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, L.; Zhang, L.; Tian, Z.; Guo, S.; Su, H.; Ren, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Dissection of the genetic architecture underlying the plant density response by mapping plant height-related traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Mol. Genet. Genom. 2015, 290, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, R.d.C.M.; Araújo, W.L.; Nunes-Nesi, A.; Siqueira, J.A. Time-to-growth: Photoperiod and photosynthesis make the call. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 1159–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Guo, T.; Li, X.R.; Yu, J. Phenotypic plasticity in plant height shaped by interaction between genetic loci and diurnal temperature range. New Phytol. 2022, 233, 1768–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, A.K.; Hazra, K.K.; Lamichaney, A.; Singh, A.K.; Dixit, G.P. Delineating the role of plant stature towards heat stress tolerance in field pea (Pisum sativum L.). Heliyon 2023, 9, e13876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.M.; Wu, X.P.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.H. Quantitative trait locus analysis for ear height in maize based on a recombinant inbred line population. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Hao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, X.; Di, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, D.; Yong, H.; et al. Genetic dissection of maize plantarchitecture with an ultra-high density bin map based on recombinant inbred lines. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, D.A.; Gardiner, M.M.; van der Werf, W.; Swinton, S.M. Increasing Corn for Biofuel Production Reduces Biocontrol Services in Agricultural Landscapes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20552–20557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Richards, D.E.; Hartley, N.M.; Murphy, G.P.; Devos, K.M.; Flintham, J.E.; Beales, J.; Fish, L.J.; Worland, A.J.; Pelica, F.; et al. Green revolution genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators. Nature 1999, 400, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khush, G.S. Green revolution: The way forward. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, A.; Ashikari, M.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Itoh, H.; Nishimura, A.; Swapan, D.; Ishiyama, K.; Saito, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Khush, G.S.; et al. Green revolution: A mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice. Nature 2002, 416, 701–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.d.L.A.; de Souza, C.L.; Bento, D.A.V.; de Souza, A.P.; Carlini-Garcia, L.A. Mapping QTL for grain yield and plant traits in a tropical maize population. Mol. Breed. 2006, 17, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, R.G.; Helentjaris, T. The maize Dwarf3 gene encodes a cytochrome P450-mediated early step in gibberellin biosynthesis. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar]
- Multani, D.S.; Briggs, S.P.; Chamberlin, M.A.; Blakeslee, J.J.; Murphy, A.S.; Johal, G.S. Loss of an MDR transporter in compact stalks of maize br2 and sorghum dw3 mutants. Science 2003, 302, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J. Molecular basis of plant architecture. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 253–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawit, S.J.; Wych, H.M.; Xu, D.; Kundu, S.; Tomes, D.T. Maize DELLA proteins dwarf plant8 and dwarf plant9 as modulators of plant development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 1854–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinney, B.O. Growth response of single-gene dwarf mutants in maize to gibberellic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1956, 42, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spray, C.R.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Phinney, B.O.; Gaskin, P.; MacMillan, J. The dwarf-1 (dt) Mutant of Zea mays blocks three steps in the gibberellin biosynthetic pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 10515–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, F.; Zhai, L.; Liu, R.; Bai, W.; Wang, L.; Huo, D.; Tao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z. ZmGA3ox2, a candidate gene for a major QTL, qPH3.1 for plant height in maize. Plant J. 2013, 73, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hou, M.; Liu, L. The Maize DWARF1 Encodes a Gibberellin 3—Oxidase and is dual localized to the nucleus and cytosol. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Guo, J.; Liu, Q.; Yin, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xia, H.; Li, B.; Sun, X.; et al. Gene editing of ZmGA20ox3 improves plant architecture and drought tolerance in maize. Plant Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas Fernandez, M.G.; Becraft, P.W.; Yin, Y.; Lubberstedt, T. From dwarves to giants? Plant height manipulation for biomass yield. Trends. Plant Sci. 2014, 14, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andorf, C.M.; Lawrence, C.J.; Harper, L.C.; Schaeffer, M.L.; Campbell, D.A.; Sen, T.Z. The Locus Lookup tool at MaizeGDB: Identification of genomic regions in maize by integrating sequence information with physical and genetic maps. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelmore, R.W.; Paran, I.; Kesseli, R. Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: A rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 9828–9832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yuan, M.; Xia, H.; He, L.Q.; Ma, J.; Wang, M.X.; Zhao, H.L.; Hou, L.; Zhao, S.Z.; Li, P.C.; et al. BSA-seq and geneticmapping reveals AhRt2 as a candidate gene responsible for red testa of peanut. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, H.; Xiao, Y.G.; Conklin, P.A.; Govindarajulu, R.; Kelly, J.A.; Scanlon, M.J.; Whipple, C.J.; Bartlett, M. Bulked-segregant analysis coupled to whole genome sequencing (BSA-Seq) for rapid gene cloning in maize. G3-Genes Genomes Genet. 2018, 8, 3583–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, G.; Laplant, K.E.; Mazourek, M.; Gore, M.A.; Smart, C.D. A combined BSA-Seq and linkage map approach identifies genomic regions associated with Phytophthora root and crown rot resistance in squash. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, D.F.; Xu, M.L. A sequential quantitative trait locus fine-mapping strategy using recombinant-derived progeny. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2012, 54, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, W.L.; Chao, Q.; Zhang, N.; Ye, J.R.; Tan, G.Q.; Li, B.L.; Xing, Y.X.; Zhang, B.Q.; Liu, H.J.; Fengler, K.A.; et al. A maize wall-associated kinase confers quantitative resistance to head smut. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Zhang, J.; Cao, J. QTL analysis of low temperature tolerance in maize germination by SLAF-seq and BSA technique. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 70, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Deng, M.; Lv, D. Combined BSA-Seq and RNA-Seq reveal genes associated with the visual stay-green of maize (Zea mays L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Tan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, T.; Zhou, S.; Hao, J.; Yu, X.; Zang, Z.; Zhang, D. Research on the genetic improvement effects of lodging resistance-related traits in maize core germplasm. Agronomy. 2025, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F. Agriculture. In Science and Civilisation in China; Needham, J., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1984; Volume 6, Part 2; p. 451. [Google Scholar]
- Mathan, J.; Bhattacharya, J.; Ranjan, A. Enhancing crop yield by optimizing plant developmental features. Development 2016, 143, 3283–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.H.; Yan, S.; Zhai, G.W.; Zhang, Z.P.; Zou, J.Q.; Tao, Y.Z. Genetic variability and correlation of stalk yield related traits and sugar concentration of stalk juice in a sweet sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) population. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2011, 5, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.W.; Liu, D.Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Li, W.B.; Liu, H.; Hong, W.G.; Jiang, C.B.; Guan, N.; Ma, C.X.; Zeng, H.P.; et al. SLAF-seq: An efficient method of large-scale De novo SNP discovery and genotyping using high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, W.J. BLAT—The BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Qi, X.; Gong, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, M. High-resolution map reveals a Ht3-like locus against northern corn leaf blight. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 968924. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, A.; McMillan, L.; Wang, W.; Parker, J.; Rusyn, I.; Threadgill, D. Inferring missing genotypes in large SNP panels using fast nearest-neighbor searches over sliding windows. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Generation | Total Plants | Tall | Dwarf | a Expected Ratio | b χ2 | c p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F2 | 825 | 609 | 216 | 3:1 | 0.62 | 0.43 |
| Sample | Clean Reads | Clean Bases | GC (%) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A101 | 168,863,930 | 25,329,589,500 | 0.4631 | 0.9741 | 0.9296 |
| 16N125 | 172,965,252 | 25,944,787,800 | 0.4695 | 0.9699 | 0.9201 |
| Dwarf | 913,765,764 | 137,064,864,600 | 0.4653 | 0.9762 | 0.9337 |
| Tall | 945,640,034 | 141,846,005,100 | 0.4657 | 0.9732 | 0.9274 |
| Sum | 2,201,234,980 | 330,185,247,000 | 0.4659 | 0.9733 | 0.9277 |
| Chromosome ID | Start | End | Size (Mb) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 3,800,000 | 17,900,000 | 14.1 |
| 3 | 18,400,000 | 28,000,000 | 9.6 |
| 3 | 28,700,000 | 55,300,000 | 26.6 |
| 3 | 55,800,000 | 122,100,000 | 66.3 |
| 3 | 126,300,000 | 131,500,000 | 5.2 |
| 3 | 132,300,000 | 134,200,000 | 1.9 |
| 3 | 151,300,000 | 152,200,000 | 0.9 |
| 3 | 152,500,000 | 153,200,000 | 0.7 |
| 3 | 154,200,000 | 154,300,000 | 0.1 |
| Gene Number | Annotation |
|---|---|
| Zm00001d039632 | Putative polyol transporter 1, Arabidopsis thaliana (mouse-ear cress) |
| Zm00001d039633 | Pleiotropic drug resistance protein 15, Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (rice) |
| Zm00001d039634 | Gibberellin 3-beta-dioxygenase 2-2, Triticum aestivum (wheat) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Liang, B.; Li, Z.; Dong, H.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X. The Identification of a Single-Base Mutation in the Maize Dwarf 1 Gene Responsible for Reduced Plant Height in the Mutant 16N125. Plants 2025, 14, 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14081217
Wang P, Liang B, Li Z, Dong H, Zhang L, Lu X. The Identification of a Single-Base Mutation in the Maize Dwarf 1 Gene Responsible for Reduced Plant Height in the Mutant 16N125. Plants. 2025; 14(8):1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14081217
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ping, Bingbing Liang, Zhengjun Li, Huaiyu Dong, Lixia Zhang, and Xiaochun Lu. 2025. "The Identification of a Single-Base Mutation in the Maize Dwarf 1 Gene Responsible for Reduced Plant Height in the Mutant 16N125" Plants 14, no. 8: 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14081217
APA StyleWang, P., Liang, B., Li, Z., Dong, H., Zhang, L., & Lu, X. (2025). The Identification of a Single-Base Mutation in the Maize Dwarf 1 Gene Responsible for Reduced Plant Height in the Mutant 16N125. Plants, 14(8), 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14081217






