Vacuolar Sorting Receptor-Mediated Trafficking of Soluble Vacuolar Proteins in Plant Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Involvement of VSRs in Trafficking of Soluble Vacuolar Proteins to Lytic Vacuoles and PSVs
3. Vacuolar Sorting Signals and Their Interactions with VSRs
4. Molecular Mechanisms of VSR-Mediated Vacuolar Trafficking
4.1. Model I: VSR-Mediated Trafficking from the TGN to the PVC
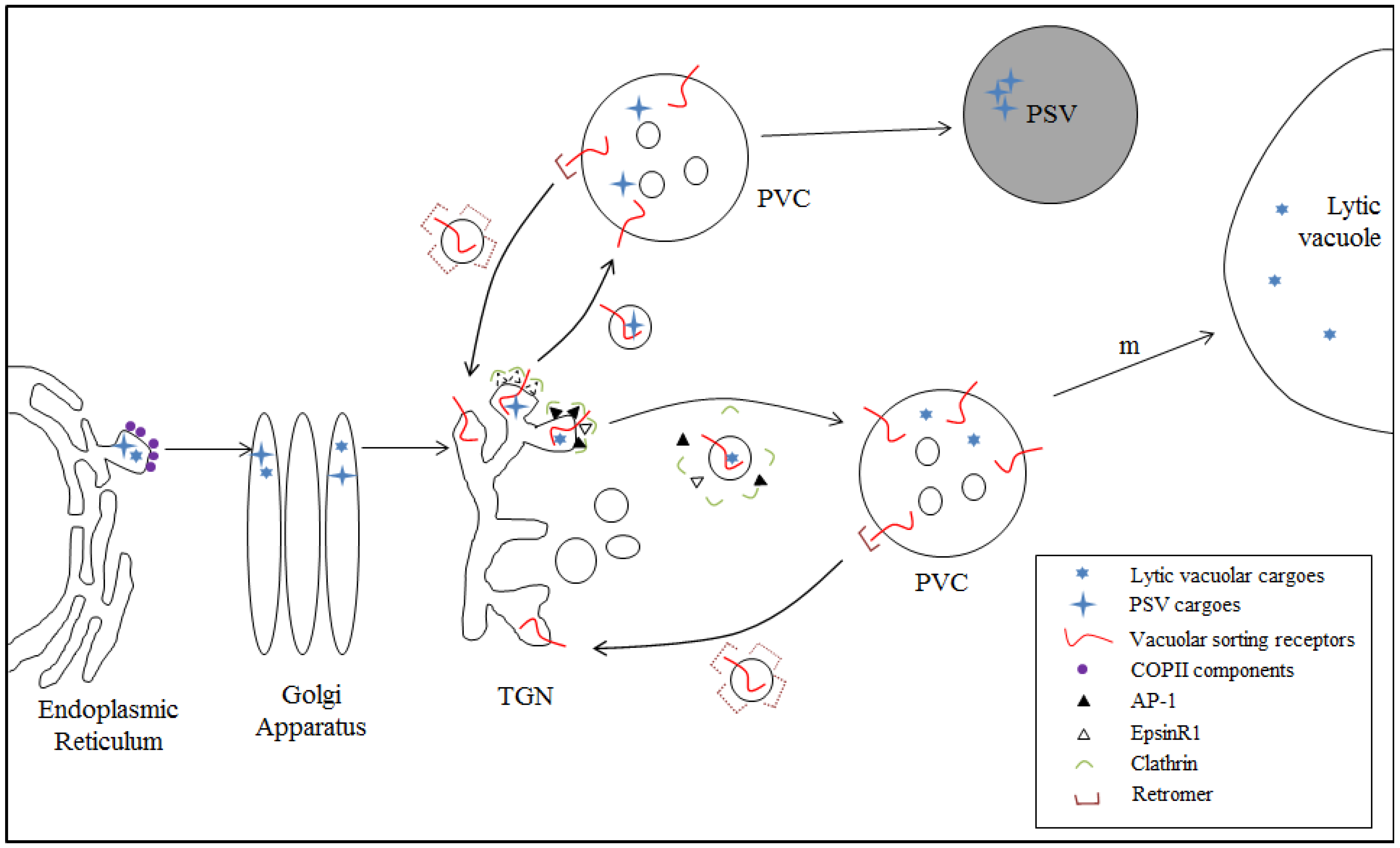
4.2. VSR-Mediated Transport from the ER to the TGN: Model II

5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paris, N.; Stanley, C.M.; Jones, R.L.; Rogers, J.C. Plant cells contain two functionally distinct vacuolar compartments. Cell 1996, 85, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müntz, K. Deposition of storage proteins. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 38, 77–99. [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens, G. Membrane trafficking in plants. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 20, 481–504. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.L.; Wang, Y.; Ong, Y.S.; Hong, W. COPII and exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1744, 293–303. [Google Scholar]
- Traub, L.M. Common principles in clathrin-mediated sorting at the Golgi and the plasma membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1744, 415–437. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, I. Sorting and anterograde trafficking at the Golgi apparatus. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, S.; Voß, U.; Jürgens, G. Post-Golgi traffic in plants. Traffic 2009, 10, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foresti, O.; Gershlick, D.C.; Bottanelli, F.; Hummel, E.; Hawes, C.; Denecke, J. A recycling-defective vacuolar sorting receptor reveals an intermediate compartment situated between prevacuoles and vacuoles in tobacco. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 3992–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.; Lee, G.J.; Jang, M.; Lee, M.; Lee, J.; Kang, H.; Sohn, E.J.; Hwang, I. Identification of sorting motifs of AtβFruct4 for trafficking from the ER to the vacuole through the Golgi and PVC. Traffic 2011, 12, 1774–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, T.; Paris, N.; Butler, J.M.; Beevers, L.; Rogers, J.C. Purification and initial characterization of a potential plant vacuolar targeting receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3403–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, T.; Kuroyanagi, M.; Nishimura, M.; Hara-Nishimura, I. A pumpkin 72-kDa membrane protein of precursor-accumulating vesicles has characteristics of vacuolar sorting receptor. Plant Cell Physiol. 1997, 38, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, N.; Rogers, S.W.; Jiang, L.; Kirsch, T.; Beevers, L.; Phillips, T.E.; Rogers, J.C. Molecular cloning and further characterization of a probable plant vacuolar sorting receptor. Plant Physiol. 1997, 115, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouhar, J.; Muñoz, A.; Rojo, E. Functional specialization within the vacuolar sorting receptor family: VSR1, VSR3 and VSR4 sort vacuolar storage cargo in seeds and vegetative tissues. Plant J. 2010, 64, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marcos Lousa, C.; Gershlick, D.C.; Denecke, J. Mechanisms and concepts paving the way towards a complete transport cycle of plant vacuolar sorting receptors. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 1714–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Paris, N.; Neuhaus, J.M. BP-80 as a vacuolar sorting receptor. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 50, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, T.; Saalbach, G.; Raikhel, N.V.; Beevers, L. Interaction of a potential vacuolar targeting receptor with amino- and carboxyl-terminal targeting determinants. Plant Physiol. 1996, 111, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, G.J.; Yoo, C.M.; Hwang, I. Arabidopsis EPSIN1 plays an important role in vacuolar trafficking of soluble cargo proteins in plant cells via interactions with clathrin, AP-1, VTI11, and VSR1. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 2258–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DaSilva, L.L.; Foresti, O.; Denecke, J. Targeting of the plant vacuolar sorting receptor BP80 is dependent on multiple sorting signals in the cytosolic tail. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 1477–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kang, H.; Jang, M.; Chang, J.H.; Miao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Hwang, I. Homomeric interaction of AtVSR1 is essential for its function as a vacuolar sorting receptor. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershlick, D.C.; de Marcos Lousa, C.; Foresti, O.; Lee, A.J.; Pereira, E.A.; DaSilva, L.L.; Bottanelli, F.; Denecke, J. Golgi-dependent transport of vacuolar sorting receptors is regulated by COPII, AP1, and AP4 protein complexes in tobacco. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1308–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Rogers, J.C. Integral membrane protein sorting to vacuoles in plant cells: Evidence for two pathways. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 1183–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottanelli, F.; Foresti, O.; Hanton, S.; Denecke, J. Vacuolar transport in tobacco leaf epidermis cells involves a single route for soluble cargo and multiple routes for membrane cargo. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 3007–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viotti, C.; Krüger, F.; Krebs, M.; Neubert, C.; Fink, F.; Lupanga, U.; Scheuring, D.; Bouttè, Y.; Frescatada-Rosa, M.; Wolfenstetter, S.; et al. The endoplasmic reticulum is the main membrane source for biogenesis of the lytic vacuole in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 3434–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Kim, S.J.; Vitale, A.; Hwang, I. Identification of the protein storage vacuole and protein targeting to the vacuole in leaf cells of three plant species. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isayenkov, S.; Isner, J.C.; Maathuis, F.J. Rice two-pore K+ channels are expressed in different types of vacuoles. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuko, H.N.; Shimada, T.; Hatano, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Nishimura, M. Transport of storage proteins to protein storage vacuoles is mediated by large precursor-accumulating vesicles. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfenstetter, S.; Wirsching, P.; Dotzauer, D.; Schneider, S.; Sauer, N. Routes to the tonoplast: The sorting of tonoplast transporters in Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marty, F. Plant vacuoles. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrazzini, E.; Komarova, N.Y.; Rentsch, D.; Vitale, A. Traffic routes and signals for the tonoplast. Traffic 2013, 14, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Pierce, M. Targeting of tonoplast proteins to the vacuole. Plant Sci. 2013, 211, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Viotti, C. ER and vacuoles: Never been closer. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, e20. [Google Scholar]
- Laval, V.; Masclaux, F.; Serin, A.; Carrière, M.; Roldan, C.; Devic, M.; Pont-Lezica, R.F.; Galaud, J.P. Seed germination is blocked in Arabidopsis putative vacuolar sorting receptor (atbp80) antisense transformants. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, T.; Fuji, K.; Tamura, K.; Kondo, M.; Nishimura, M.; Hara-Nishimura, I. Vacuolar sorting receptor for seed storage proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 16095–16100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DaSilva, L.L.; Taylor, J.P.; Hadlington, J.L.; Hanton, S.L.; Snowden, C.J.; Fox, S.J.; Foresti, O.; Brandizzi, F.; Denecke, J. Receptor salvage from the prevacuolar compartment is essential for efficient vacuolar protein targeting. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Jang, M.; Song, K.; Kang, H.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, D.W.; Zouhar, J.; Rojo, E.; Sohn, E.J.; Hwang, I. Functional identification of sorting receptors involved in trafficking of soluble lytic vacuolar proteins in vegetative cells of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, E.; Shimada, T.; Tamura, K.; Matsushima, R.; Koumoto, Y.; Nishimura, M.; Hara-Nishimura, I. An ER-localized form of PV72, a seed-specific vacuolar sorting receptor, interferes the transport of an NPIR-containing proteinase in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Suen, P.K.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Lo, S.W.; Rojo, E.; Jiang, L. An in vivo expression system for the identification of cargo proteins of vacuolar sorting receptors in Arabidopsis culture cells. Plant J. 2013, 75, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Yan, P.K.; Kim, H.; Hwang, I.; Jiang, L. Localization of green fluorescent protein fusions with the seven Arabidopsis vacuolar sorting receptors to prevacuolar compartments in tobacco BY-2 cells. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 945–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, A.; Hinz, G. Sorting of proteins to storage vacuoles: How many mechanisms? Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holwerda, B.C.; Padgett, H.S.; Rogers, J.C. Proaleurain vacuolar targeting is mediated by short contiguous peptide interactions. Plant Cell 1992, 4, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koide, Y.; Matsuoka, K.; Ohto, M.; Nakamura, K. The N-terminal propeptide and the C-terminus of the precursor to 20-kilo-dalton potato tuber protein can function as different types of vacuolar sorting signals. Plant Cell Physiol. 1999, 40, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Dong, T.; Jeong, J.C.; Jin, J.B.; Kanno, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Seo, M.; Bressan, R.A.; et al. A vacuolar β-glucosidase homolog that possesses glucose-conjugated abscisic acid hydrolyzing activity plays an important role in osmotic stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2184–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, T.; Watanabe, E.; Tamura, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Nishimura, M.; Hara-Nishimura, I. A vacuolar sorting receptor PV72 on the membrane of vesicles that accumulate precursors of seed storage proteins (PAC vesicles). Plant Cell Physiol. 2002, 43, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, E.; Shimada, T.; Kuroyanagi, M.; Nishimura, M.; Hara-Nishimura, I. Calcium-mediated association of a putative vacuolar sorting receptor PV72 with a propeptide of 2S albumin. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8708–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suen, P.K.; Shen, J.; Sun, S.S.M.; Jiang, L. Expression and characterization of two functional vacuolar sorting receptor (VSR) proteins, BP-80 and AtVSR4 from culture media of transgenic tobacco BY-2 cells. Plant Sci. 2010, 179, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selander-Sunnerhagen, M.; Ullner, M.; Persson, E.; Eleman, O.; Stenflo, J.; Drakenberg, T. How an epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain binds calcium. High resuolution NMR structure of the calcium form of the NH2-terminal EGF-like domain in coagulation factor X. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 19642–19649. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Rogers, S.W.; Butler, J.; Beevers, L.; Rogers, J.C. Structural requirements for ligand binding by a probable plant vacuolar sorting receptor. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornfeld, S. Structure and function of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulinlike growth factor II receptors. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1992, 61, 307–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, J.R.; Grinstein, S.; Orlowski, J. Sensors and regulators of intracellular pH. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinière, A.; Bassil, E.; Jublanc, E.; Alcon, C.; Reguera, M.; Sentenac, H.; Blumwald, E.; Paris, N. In vivo intracellular pH measurements in tobacco and Arabidopsis reveals an unexpected pH gradient in the endomembrane system. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 4028–4043. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Zeng, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Sun, L.; Yao, X.; Pimpl, P.; Jiang, L. Organelle pH in the Arabidopsis endomembrane system. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1419–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderfoot, A.A.; Ahmed, S.U.; Marty-Mazars, D.; Rapoport, I.; Kirchhausen, T.; Marty, F.; Raikhel, N.V. A putative vacuolar cargo receptor partially colocalizes with AtPEP12p on a prevacuolar compartment in Arabidopsis roots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9920–9925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.B.; Rogers, S.W.; Tse, Y.C.; Lo, S.W.; Sun, S.S.; Jauh, G.Y.; Jiang, L. BP-80 and homologs are concentrated on post-Golgi: Probable lytic prevacuolar compartments. Plant Cell Physiol. 2002, 43, 726–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, Y.C.; Mo, B.; Hillmer, S.; Zhao, M.; Lo, S.W.; Robinson, D.G.; Jiang, L. Identification of multivesicular bodies as prevacuolar compartments in Nicotiana tabacum BY-2 cells. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 672–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Park, M.; Kim, S.J.; Hwang, I. Actin filaments play a critical role in vacuolar trafficking at the Golgi complex in plant cells. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 888–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabel, C.A.; Goldberg, D.E.; Kornfeld, S. Lysosomal enzyme oligosaccharide phosphorylation in mouse lymphoma cells: Specificity and kinetics of binding to the mannose 6-phosphate receptor in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 1982, 95, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcusson, E.G.; Horazdovsky, B.F.; Cereghino, J.L.; Gharakhanian, E.; Emr, S.D. The sorting receptor for yeast vacuolar carboxypeptidase Y is encoded by the VPS10 gene. Cell 1994, 77, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arighi, C.N.; Hartnell, L.M.; Aguilar, R.C.; Haft, C.R.; Bonifacino, J.S. Role of the mammalian retromer in sorting of the cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 165, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifacino, J.S.; Rojas, R. Retrograde transport from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Song, K.; Sohn, E.J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, D.W.; Hara-Nishimura, I.; Hwang, I. Trafficking of vacuolar proteins: The crucial role of Arabidopsis vacuolar protein sorting 29 in recycling vacuolar sorting receptor. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 5058–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Song, K.; Reichardt, I.; Kim, H.; Mayer, U.; Stierhof, Y.D.; Hwang, I.; Jürgens, G. Arabidopsis μ-adaptin subunit AP1M of adaptor protein complex 1 mediates late secretory and vacuolar traffic and is required for growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10318–10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, P.; Dahms, N.M.; Kornfeld, S. Mannose 6-phosphate receptors: New twists in the tale. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happel, N.; Höning, S.; Neuhaus, J.M.; Paris, N.; Robinson, D.G.; Holstein, S.E. Arabidopsis mu A-adaptin interacts with the tyrosine motif of the vacuolar sorting receptor VSR-PS1. Plant J. 2004, 37, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saint-Jean, B.; Seveno-Carpentier, E.; Alcon, C.; Neuhaus, J.M.; Paris, N. The cytosolic tail dipeptide Ile-Met of the pea receptor BP80 is required for recycling from the prevacuole and for endocytosis. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2825–2837. [Google Scholar]
- Seaman, M.N. Cargo-selective endosomal sorting for retrieval to the Golgi requires retromer. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 165, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaman, M.N.; Marcusson, E.G.; Cereghino, J.L.; Emr, S.D. Endosome to Golgi retrieval of the vacuolar protein sorting receptor, Vps10p, requires the function of the VPS29, VPS30, and VPS35 gene products. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 137, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaman, M.N.; McCaffery, J.M.; Emr, S.D. A membrane coat complex essential for endosome-to-Golgi retrograde transport in yeast. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 142, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nothwehr, S.F.; Ha, S.A.; Bruinsma, P. Sorting of yeast membrane proteins into an endosome-to-Golgi pathway involves direct interaction of their cytosolic domains with Vps35p. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 151, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliviusson, P.; Heinzerling, O.; Hillmer, S.; Hinz, G.; Tse, Y.C.; Jiang, L.; Robinson, D.G. Plant retromer, localized to the prevacuolar compartment and microvesicles in Arabidopsis, may interact with vacuolar sorting receptors. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 1239–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaillais, Y.; Fobis-Loisy, I.; Miège, C.; Rollin, C.; Gaude, T. AtSNX1 defines an endosome for auxin-carrier trafficking in Arabidopsis. Nature 2006, 443, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaillais, Y.; Santambrogio, M.; Rozier, F.; Fobis-Loisy, I.; Miège, C.; Gaude, T. The retromer protein VPS29 links cell polarity and organ initiation in plants. Cell 2007, 130, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, N.Q.; Kim, S.J.; Bassham, D.C. Overexpression of Arabidopsis sorting nexin AtSNX2b inhibits endocytic trafficking to the vacuole. Mol. Plant 2008, 1, 961–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourcher, M.; Santambrogio, M.; Thazar, N.; Thierry, A.M.; Fobis-Loisy, I.; Miège, C.; Jaillais, Y.; Gaude, T. Analyses of sorting nexins reveal distinct retromer-subcomplex functions in development and protein sorting in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 3980–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemes, S.; Langhans, M.; Viotti, C.; Scheuring, D.; San Wan Yan, M.; Jiang, L.; Hillmer, S.; Robinson, D.G.; Pimpl, P. Retromer recycles vacuolar sorting receptors from the trans-Golgi network. Plant J. 2010, 61, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierhof, Y.D.; Viotti, C.; Scheuring, D.; Sturm, S.; Robinson, D.G. Sorting nexins 1 and 2a locate mainly to the TGN. Protoplasma 2013, 250, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGough, I.J.; Cullen, P.J. Recent advances in retromer biology. Traffic 2011, 12, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, T.; Koumoto, Y.; Li, L.; Yamazaki, M.; Kondo, M.; Nishimura, M.; Hara-Nishimura, I. AtVPS29, a putative component of a retromer complex, is required for the efficient sorting of seed storage proteins. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A.A.; Stevens, T.H. Vps10p cycles between the late-Golgi and prevacuolar compartments in its function as the sorting receptor for multiple yeast vacuolar hydrolases. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 133, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, T.; Ueda, T.; Ohniwa, R.L.; Nakano, A.; Takeyasu, K.; Sato, M.H. Systematic analysis of SNARE molecules in Arabidopsis: Dissection of the post-Golgi network in plant cells. Cell Struct. Funct. 2004, 29, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordenes, V.R.; Moreno, I.; Maturana, D.; Norambuena, L.; Trewavas, A.J.; Orellana, A. In vivo analysis of the calcium signature in the plant Golgi apparatus reveals unique dynamics. Cell Calcium 2012, 52, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stael, S.; Wurzinger, B.; Mair, A.; Mehlmer, N.; Vothknecht, U.C.; Teige, M. Plant organellar calcium signaling: An emerging field. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 1525–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemes, S.; Labs, M.; Scheuring, D.; Krueger, F.; Langhans, M.; Jesenofsky, B.; Robinson, D.G.; Pimpl, P. Sorting of plant vacuolar proteins is initiated in the ER. Plant J. 2010, 62, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheuring, D.; Viotti, C.; Krüger, F.; Künzl, F.; Sturm, S.; Bubeck, J.; Hillmer, S.; Frigerio, L.; Robinson, D.G.; Pimpl, P.; et al. Multivesicular bodies mature from the trans-Golgi network/early endosome in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 3463–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Gao, C.; Ding, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Ueda, T.; Nakano, A.; Jiang, L. Activation of the Rab7 GTPase by the MON1-CCZ1 complex is essential for PVC-to-vacuole trafficking and plant growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 2080–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebine, K.; Inoue, T.; Ito, J.; Ito, E.; Uemura, T.; Goh, T.; Abe, H.; Sato, K.; Nakano, A.; Ueda, T. Plant vacuolar trafficking occurs through distinctly regulated pathways. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.K.; Krüger, F.; Beckmann, H.; Brumm, S.; Vermeer, J.E.; Munnik, T.; Mayer, U.; Stierhof, Y.D.; Grefen, C.; Schumacher, K.; Jürgens, G. Protein delivery to vacuole requires SAND protein-dependent Rab GTPase conversion for MVB-vacuole fusion. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Blume, J.; Duran, J.M.; Forlanelli, E.; Alleaume, A.M.; Egorov, M.; Polishchuk, R.; Molina, H.; Malhotra, V. Actin remodeling by ADF/cofilin is required for cargo sorting at the trans-Golgi network. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 187, 1055–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Scherer, P.E.; Lederkremer, G.Z.; Williams, S.; Fogliano, M.; Baldini, G.; Lodish, H.F. Cab45, a novel (Ca2+)-binding protein localized to the Golgi lumen. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 133, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Blume, J.; Alleaume, A.M.; Cantero-Recasens, G.; Curwin, A.; Carreras-Sureda, A.; Zimmermann, T.; van Galen, J.; Wakana, Y.; Valverde, M.A.; Malhotra, V. ADF/cofilin regulates secretory cargo sorting at the TGN via the Ca2+ ATPase SPCA1. Dev. Cell 2011, 20, 652–662. [Google Scholar]
- Von Blume, J.; Alleaume, A.M.; Kienzle, C.; Carreras-Sureda, A.; Valverde, M.; Malhotra, V. Cab45 is required for Ca(2+)-dependent secretory cargo sorting at the trans-Golgi network. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 199, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Curwin, A.J.; von Blume, J.; Malhotra, V. Cofilin-mediated sorting and export of specific cargo from the Golgi apparatus in yeast. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 2327–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chanroj, S.; Wu, Z.; Romanowsky, S.M.; Harper, J.F.; Sze, H. A distinct endosomal Ca2+/Mn2+ pump affects root growth through the secretory process. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 1675–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, R.F.; Doherty, M.L.; Lopez-Marques, R.L.; Weimar, T.; Dupree, P.; Palmgren, M.G.; Pittman, J.K.; Williams, L.E. ECA3, a Golgi-localized P2A-type ATPase, plays a crucial role in manganese nutrition in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.H.; Nielsen, E.; Preuss, M.L.; Mastronarde, D.; Staehelin, L.A. Electron tomography of RabA4b- and PI-4Kbeta1-labeled trans Golgi network compartments in Arabidopsis. Traffic 2011, 12, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.G.; Pimpl, P. Receptor-mediated transport of vacuolar proteins: A critical analysis and a new model. Protoplasma 2014, 251, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, K.; Bassham, D.C.; Raikhel, N.V.; Nakamura, K. Different sensitivity to wortmannin of two vacuolar sorting signals indicates the presence of distinct sorting machineries in tobacco cells. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 130, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batoko, H.; Zheng, H.Q.; Hawes, C.; Moore, I. A rab1 GTPase is required for transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus and for normal golgi movement in plants. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 2201–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, H.; Hwang, I. Vacuolar Sorting Receptor-Mediated Trafficking of Soluble Vacuolar Proteins in Plant Cells. Plants 2014, 3, 392-408. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants3030392
Kang H, Hwang I. Vacuolar Sorting Receptor-Mediated Trafficking of Soluble Vacuolar Proteins in Plant Cells. Plants. 2014; 3(3):392-408. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants3030392
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Hyangju, and Inhwan Hwang. 2014. "Vacuolar Sorting Receptor-Mediated Trafficking of Soluble Vacuolar Proteins in Plant Cells" Plants 3, no. 3: 392-408. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants3030392
APA StyleKang, H., & Hwang, I. (2014). Vacuolar Sorting Receptor-Mediated Trafficking of Soluble Vacuolar Proteins in Plant Cells. Plants, 3(3), 392-408. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants3030392




