Effect of Phosphorus Fertilization on the Growth, Photosynthesis, Nitrogen Fixation, Mineral Accumulation, Seed Yield, and Seed Quality of a Soybean Low-Phytate Line
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Biomass Production at the Flowering Stage
2.2. Photosynthesis and Dinitrogen Fixation Activity at the Flowering Stage
2.3. Seed Yield and Yield Components
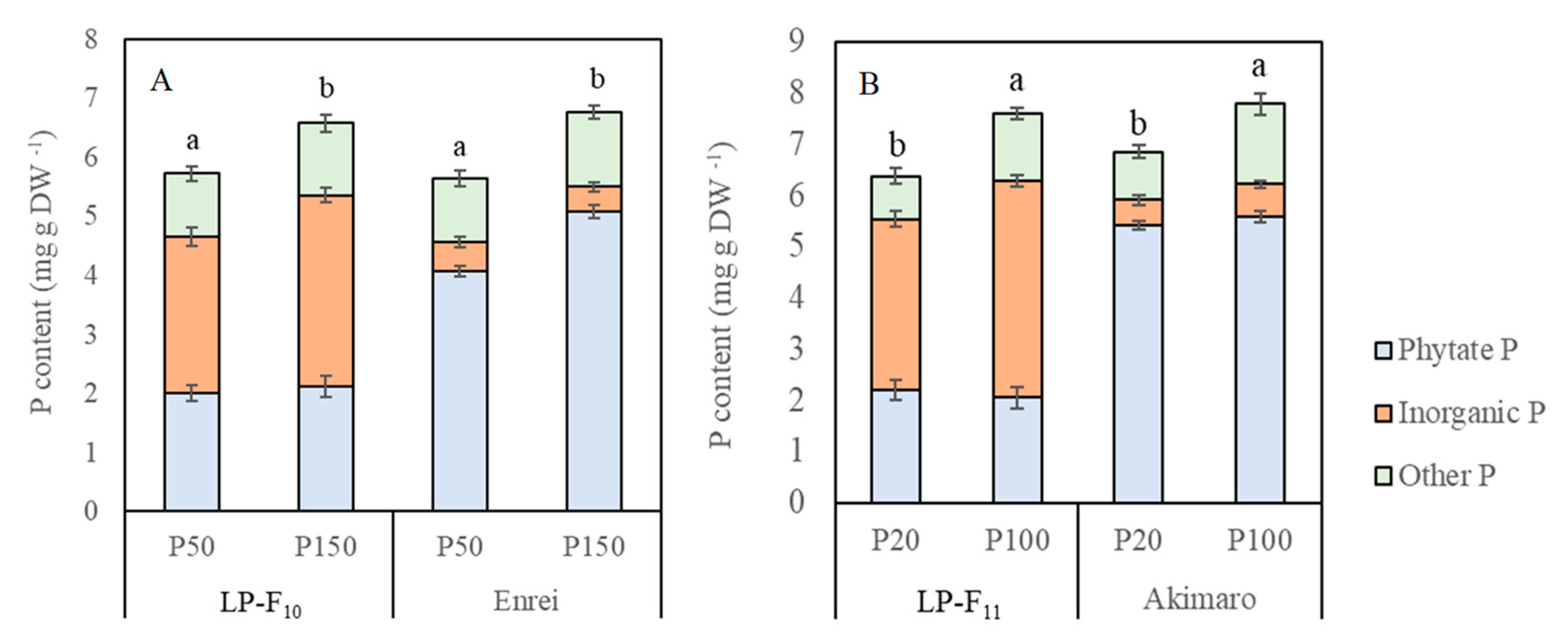
2.4. Seed Total P, Phytate P and Inorganic P Concentration
2.5. Seed Crude Protein, Lipid and Mineral Concentrations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Growing Condition
4.2. Determination of Leaf Photosynthesis and Dinitrogen Fixation
4.3. Determination of Seed Mineral Concentration
4.4. Determination of Phytate P and Inorganic P Concentration
4.5. Determination of Zn, Fe and Mn Concentration
4.6. Determination of Lipid Concentration
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raboy, V. Seeds for a better future: ‘low phytate’ seeds help to overcome malnutrition and reduce pollution. Trends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, P.; Bhattacharyya, M.; Banerjee, U. Use of phytases (myo-inositol hexakisphosphstate phosphohydrolases) for combatting environmental pollution: A biological approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 35, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, J.N.A.; Ockenden, I.; Raboy, V.; Batten, G.D. Phytic acid and phosphorus in crop and fruits: A global estimate. Seed Sci. Res. 2000, 10, 11–33. [Google Scholar]
- Urbano, G.; López-Jurado, M.; Aranda, P.; Vidal-Valverde, C.; Porres, T.J. The role of phytic acid in legumes: Antinutrient or beneficial function? J. Physiol. Biochem. 2000, 56, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raboy, V. Approaches and challenges to engineering seed phytate and total phosphorus. Plant Sci. 2009, 177, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdman, J. Bioavailability of trace minerals from cereals and legumes. Cereal Chem. 1981, 58, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, H.; Türk, M.; Nyman, M.; Sandberg, A.S. Binding of Cu2+, Zn2+, and Cd2+ to inositol tri-, tera-, penta-, and hexaphosphates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3194–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, P.B.; Kristiansen, K.N.; Pedersen, H.B. Transgenic approaches in commonly consumed cereals to improve iron and zinc concentration and bioavailability. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 514S–516S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, S.R.; Young, K.A.; Cook, A.; Blake, T.K.; Raboy, V. Linkage mapping of two mutations that reduce phytic acid concentration of barley seed. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1998, 97, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raboy, V.; Cichy, K.; Peterson, K.; Reichman, S.; Sompong, U.; Srinives, P.; Saneoka, H. Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Low phytic acid 1-1: An endosperm-specific, filial determinant of seed total phosphorus. J. Hered. 2014, 105, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, S.R.; Rutger, J.N.; Young, K.A.; Raboy, V. Isolation and genetic mapping of a non-lethal rice (Oryza sativa L.) low phytic acid 1 mutation. Crop. Sci. 2000, 40, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raboy, V.; Gerbasi, P.F.; Young, K.A.; Stoneberg, S.D.; Pickett, S.G.; Bauman, A.T.; Murthy, P.P.; Sheridan, W.F.; Ertl, D.S. Origin and seed phenotype of maize low phytic acid 1-1 and low phytic acid 2-1. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttieri, M.; Bowen, D.; Dorsch, J.A.; Raboy, V.; Souza, E. Identification and characterization of low phytic acid wheat. Crop. Sci. 2004, 44, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, J.R.; Premachandra, G.S.; Young, K.A.; Raboy, V. Isolation of high seed inorganic P, low-phytate soybean mutants. Crop. Sci. 2000, 40, 1601–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campion, B.; Sparvoli, F.; Doria, E.; Tagliabue, G.; Galasso, I.; Fileppi, M.; Bollini, R.; Nielsen, E. Isolation and characterisation of an lpa (low phytic acid) mutant in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cominelli, E.; Confalonieri, M.; Carlessi, M.; Cortinovis, G.; Daminati, M.G.; Porch, T.G.; Losa, A.; Sparvoli, F. Phytic acid transport in Phaseolus vulgaris: A new low phytic acid mutant in the PvMRP1 gene and study of the PvMRPs promoters in two different plant systems. Plant Sci. 2018, 270, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raboy, V.; Dickinson, D.B. Phytic acid levels in seeds of Glycine max and G. soja as influenced by phosphorus status. Crop. Sci. 1993, 33, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.A.; Youngs, V.L.; Oplinger, E.S. Effect of available soil-phosphorus and environment on the phytic acid concentration in oats. Cereal Chem. 1980, 57, 192–194. [Google Scholar]
- Saneoka, H.; Koba, T. Plant growth and phytic acid accumulation in seed as affected by phosphorus application in maize (Zea maize L.). Grassl. Sci. 2003, 48, 485–489. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, T.R.; Hada, A.; Jolly, M.; Ganapathi, A.; Sachdev, A. Probing phosphorus efficient low phytic acid concentration soybean genotypes with phosphorus starvation in hydroponics growth system. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2015, 177, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, Y.; Tatsukawa, E.; Saneoka, H.; Hoshina, T.; Uefuji, M.; Raboy, V. Growth characteristics, phytate concentrations, and coagulation properties of soymilk from a low-phytate Japanese soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) line. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2011, 57, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.S.; Simpson, R.J.; Sands, R. Nitrogenase activity of two genotypes of Acacia mangium as affected by phosphorus nutrition. Plant Soil 1992, 144, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Aslam, M.; Lodhi, A. Improved potassium nutrition retrieves phosphorus-induced decrease in zinc uptake and seed zinc concentration of wheat. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4351–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, X.; Guo, X.H.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Ma, Z.H.; Han, X.R.; Zhao, M.H.; Xie, F.T. Effect of phosphorus fertilization to P uptake and dry matter accumulation in soybean with different P efficiencies. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Reddy, V.R.; Fleisher, D.H.; Timlin, D.J. Phosphorus nutrition affects temperature response of soybean growth and canopy photosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.S.; Khan, A. Leaf gas exchange, phosphorus uptake, growth and yield responses of cotton cultivars to different phosphorus rate. Photosynthetica 2018, 56, 1414–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, D.; Young, K.A.; Raboy, V. Plant genetic approaches to phosphorus management in agricultural production. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raboy, V.; Young, K.A.; Dorsch, J.A.; Cook, A. Genetics and breeding of seed phosphorus and phytic acid. J. Plant Physiol. 2001, 158, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meis, S.J.; Fehr, W.R.; Schnebly, S.R. Seed source effect on field emergence of soybean lines with reduced phytate and raffinose saccharides. Crop. Sci. 2003, 43, 1336–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltmans, S.E.; Fehr, W.R.; Welke, G.A.; Raboy, V.; Peterson, K.L. Agronomic and seed traits of soybean lines with low–phytate phosphorus. Crop. Sci. 2005, 45, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggins, S.J.; Smallwood, C.J.; West, D.R.; Kopsell, D.A.; Sams, C.E.; Pantalone, V.R. Agronomic Performance and Seed Inorganic Phosphorus Stability of Low-Phytate Soybean Line TN09-239. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2018, 95, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Reddy, V.R. Methods of mesophyll conductance estimation: Its impact on key biochemical parameters and photosynthetic limitations in phosphorus-stressed soybean across CO2. Physiol. Plant 2016, 157, 234–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillman, J.D.; Pantalone, V.R.; Bilyeu, K. The low phytic acid phenotype in soybean line CX1834 is due to mutations in two homologs of the maize low phytic acid gene. Plant Genome 2009, 2, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzeri, D.; Cassani, E.; Doria, E.; Tagliabue, G.; Forti, L.; Campion, B.; Bollini, R.; Brearley, C.A.; Pilu, R.; Nielsen, E.; et al. A defective ABC transporter of the MRP family, responsible for the bean lpa1 mutation, affects the regulation of the phytic acid pathway, reduces seed myo-inositol and alters ABA sensitivity. New Phytol. 2011, 191, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raboy, V.; Dickinson, D.B. The timing and rate of phytic acid accumulation in developing soybean seeds. Plant Physiol. 1987, 85, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oltmans, S.E.; Fehr, W.R.; Welke, G.A.; Raboy, V.; Peterson, K.L.; Peeler, H.T. Biological availability of nutrients in feeds: Availability of major mineral ions. J. Anim. Sci. 1972, 35, 695–712. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, M.K.; Tahir, M.M.; Abbas, W.A.; Rahim, N. Soybean yield and chemical composition in response to phosphorus-potassium nutrition in Kashmir. Agron. J. 2012, 104, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Bellaloui, N.; MaClure, A.M.; Tyler, D.D.; Mengistu, A. Phosphorus fertilization differentially influences fatty acids, protein, and oil in soybean. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1975–1992. [Google Scholar]
- Krueger, K.; Goggi, A.S.; Mallarino, A.P.; Mullen, R.E. Phosphorus and potassium fertilization effects on soybean seed quality and composition. Crop. Sci. 2013, 53, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethlenfalvay, G.J.; Schreiner, R.P.; Mihara, K.L. Mycorrhizal fungi effects on nutrient composition and yield of soybean seeds. J. Plant Nutr. 1997, 20, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, K.; Takahashi, K.; Ono, T.; Kitamura, K.; Nakamura, Y. Variation in the phytic acid concentration of soybeans and its effect on consistency of tofu made from soybean cultivars with high protein concentration. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Rodríguez, A.R.; del Campillo, M.C.; Torrent, J. Phosphorus reduces the zinc concentration in cereals pot-grown on calcareous vertisols from southern Spain. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 3427–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Deng, Y.; Chen, R.Y.; Cui, Z.L.; Chen, X.P.; Yost, R.; Zhang, F.S.; Zou, C.Q. The reduction in zinc concentration of wheat seed upon increased phosphorus-fertilization and its mitigation by foliar zinc application. Plant Soil 2012, 361, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, D.Y.; Li, C.; Chen, X.P.; Zou, C.Q. Accumulation, partitioning, and bioavailability of micronutrients in summer maize as affected by phosphorus supply. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 86, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.S.J.; Toribara, T.Y.; Warner, H. Microdetermination of phosphorus. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 1756–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, F.; Tomé, D.; Mirand, P.P. Converting nitrogen into protein-beyond 6.25 and Jones’ factors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raboy, V.; Dickinson, D.B.; Below, F.E. Variation in seed total phosphorus, phytic acid, zinc, calcium, magnesium, and protein among lines of Glycine max and G. soja L. Crop. Sci. 1984, 24, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raboy, V.; Dickinson, D.B. Effect of phosphorus and zinc nutrition on soybean seed phytic acid and zinc. Plant Physiol. 1984, 75, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar]


| Line or Cultivar | Treatment | Photosynthetic Rate | Nitrogen Fixation | Nodule Number | Specific Nodule Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (μmol CO2 m−2 s−1) | (μmol C2H4 plant−1 h−1) | (number plant−1) | (μmol g−1 nodule weight h−1) | ||
| LP-F10 | P50 | 14b ± 1 | 158b ± 9 | 119b ± 6 | 310a ± 12 |
| P150 | 18a ± 1 | 227a ± 8 | 146a ± 5 | 236b ± 15 | |
| Enrei | P50 | 13b ± 2 | 151b ± 6 | 102c ± 3 | 336a ± 14 |
| P150 | 18a ± 2 | 203a ± 10 | 138a ± 4 | 246b ± 16 |
| Line or Cultivar | Treatment | Yield | Pod Number | 100 Seed Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g plant−1) | (number plant−1) | (g) | ||
| LP-F11 | P20 | 42c ± 4 | 75c ± 2 | 24a ± 1 |
| P100 | 99a ± 4 | 156a ± 3 | 26a ± 1 | |
| Akimaro | P20 | 33d ± 4. | 53c ± 2 | 15b ± <1 |
| P100 | 74b ± 4. | 122b ± 5 | 16b ± 1 |
| Seed Quality | LP-F11 | Akimaro | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P20 | P100 | P20 | P100 | |
| Protein (%) | 33b ± 2 | 38.9a ± 1.9 | 31.9b ± 1.3 | 34.8b ± 1.5 |
| Lipid (%) | 19c ± < 1 | 23a ± <1 | 22b ± <1 | 24a ± <1 |
| K (mg g−1) | 203b ± 16 | 229a ± 17 | 174c ± 15 | 238a ± 14 |
| Ca (mg g−1) | 0.97b ± 0.1 | 1.35a ± 0.2 | 1.13b ± 0.1 | 1.49a ± 0.1 |
| Mg (mg g−1) | 2.2a ± 0.2 | 2.2a ± 0.3 | 2.5a ± 0.3 | 2.9a ± 0.3 |
| Zn (μg g−1) | 48a ± 3 | 39b ± 3 | 39b ± 3 | 35c ± 3 |
| Fe (μg g−1) | 51a ± 7 | 49a ± 6 | 41b ± 6 | 49a ± 7 |
| Mn (μg g−1) | 63a ± 6 | 50b ± 4 | 44bc ± 4 | 38c ± 4 |
| Cu (μg g−1) | 7.3a ± 0.7 | 4.1b ± 0.4 | 6.4a ± 0.6 | 3.8b ± 0.4 |
| Phytic acid (mg g−1) | 7.8b ± 04 | 7.4b ± 0.2 | 19.2a ± 1 | 19.8a ± 1 |
| Phytic acid:Zn (Molar ratio) | 18.4c ± 0.7 | 18.0c ± 0.9 | 45.3b ± 4.2 | 56.3a ± 3.4 |
| Phytic acid:Fe (Molar ratio) | 12.9b ± 0.6 | 12.8b ± 0.8 | 39.7a ± 4.2 | 34.4a ± 3.3 |
| Phytic acid:Mn (Molar ratio) | 10.3c ± 0.8 | 12.4c ± 0.6 | 36.1b ± 1.6 | 43.7a ± 2.5 |
| Phytic acid:Cu (Molar ratio) | 103.9d ± 6.8 | 174.5c ± 8.7 | 291.0b ± 20.5 | 503.6a ± 18 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taliman, N.A.; Dong, Q.; Echigo, K.; Raboy, V.; Saneoka, H. Effect of Phosphorus Fertilization on the Growth, Photosynthesis, Nitrogen Fixation, Mineral Accumulation, Seed Yield, and Seed Quality of a Soybean Low-Phytate Line. Plants 2019, 8, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8050119
Taliman NA, Dong Q, Echigo K, Raboy V, Saneoka H. Effect of Phosphorus Fertilization on the Growth, Photosynthesis, Nitrogen Fixation, Mineral Accumulation, Seed Yield, and Seed Quality of a Soybean Low-Phytate Line. Plants. 2019; 8(5):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8050119
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaliman, Nisar Ahmad, Qin Dong, Kohei Echigo, Victor Raboy, and Hirofumi Saneoka. 2019. "Effect of Phosphorus Fertilization on the Growth, Photosynthesis, Nitrogen Fixation, Mineral Accumulation, Seed Yield, and Seed Quality of a Soybean Low-Phytate Line" Plants 8, no. 5: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8050119
APA StyleTaliman, N. A., Dong, Q., Echigo, K., Raboy, V., & Saneoka, H. (2019). Effect of Phosphorus Fertilization on the Growth, Photosynthesis, Nitrogen Fixation, Mineral Accumulation, Seed Yield, and Seed Quality of a Soybean Low-Phytate Line. Plants, 8(5), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8050119




