Taxonomy and Identification of Principal Foliar Nematode Species (Aphelenchoides and Litylenchus)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. General Techniques
3. Genus Aphelenchoides Fischer, 1894
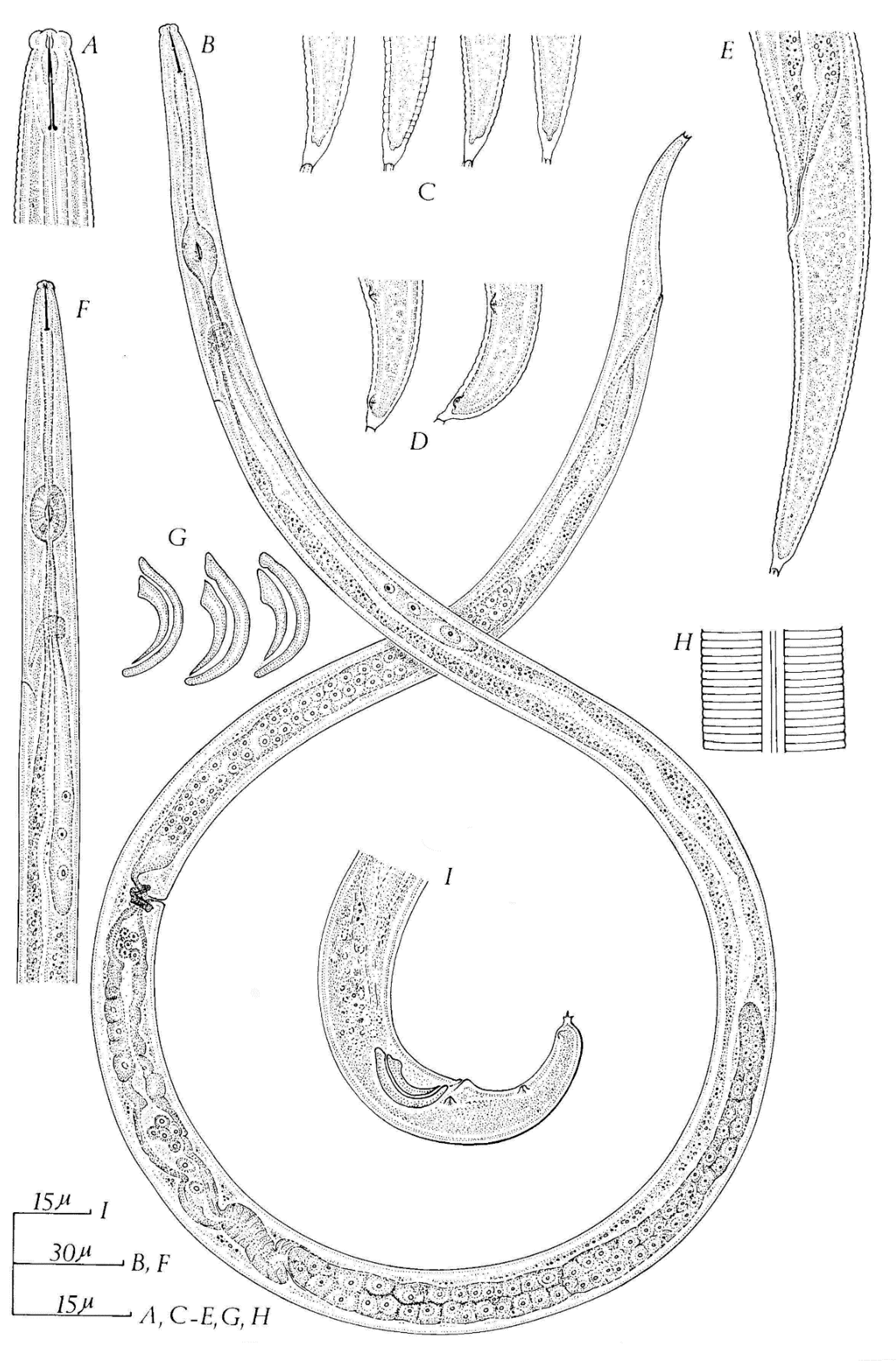
- Six fused, non-annulated, similar lips, slightly offset from body;
- Male tail without bursa, with one pair of approximately adanal and two pairs of postanal, ventro-submedian, caudal papillae;
- Spicules paired and shaped like rose thorns;
- Tails of both sexes never elongate filiform but short, tapering, conical, and frequently ending in one or more mucrones.
- The length of the post-vulval sac;
- The shape of the tail terminus and tail;
- Body length;
- Ratios ‘a’ and ‘c’.
- Cuticle marked by fine transverse striae;
- Lateral field marked as longitudinal incisures;
- Lip region set off from body;
- Six lips supported by six radial internal sclerotization;
- Lips not annulated;
- Stylet with or without basal knobs;
- Medial esophageal bulb well developed;
- Intestine joining esophagus immediately behind bulb;
- Nerve ring encircling anterior ends of intestine and the esophageal glands;
- Esophageal glands free in the body cavity;
- Single anteriorly directed ovary, oocytes on tandem or multiple;
- Male tail without bursa or gubernaculum;
- Three pairs of ventro-submedian papillae usually present on male tail;
- Spicules paired, ventrally arcuate.
- Stylet with small basal knobs;
- Males are common;
- Vulva located near 2/3 the body length from the anterior;
- Prodelphic (anteriorly outstretched) ovary and a post-uterine sac;
- Males have prominent, thorn-shaped spicules (paired, cuticularized copulatory structures).
- Body length between 0.4 to 1.2 mm (commonly from 0.4 to 0.8 mm);
- Females become straight to ventrally arcuate when heat relaxed while males assume a “walking-stick shape”;
- Cuticle finely annulated, two to four (rarely six) incisures in the lateral field;
- Stylet slender with basal knobs (sometimes indistinct), length between 10–12 μm;
- Long and slender procorpus; well-developed spherical to rounded-rectangular shaped metacorpus, with central valve plates; esophageal gland lobe long, with dorsal overlap of the intestine;
- Vulva usually between 60 and 75% of the body length;
- Ovary monoprodelphic, typically outstretched, but may reflex;
- Post-vulval sac present most of the times;
- Oocytes in one or more rows;
- Post-uterine sac present (sometimes absent) and most of the times contains spermatozoa;
- Tail shape is conoid to variable; males have a tail more strongly curved ventrally and papillae variable;
- Tail terminus with one or more mucros or without mucros;
- Spicules well-developed, thorn-shaped, paired and separate without bursa.
4. Genus Aphelenchoides Fischer, 1894
- Tail without any outgrowth or mucro;
- Tail with one or sometimes two mucronate structures on tail end;
- Star shaped tail with four mucronate structures;
- Tail end with outgrowth other than spine or star.
5. Systematic Position
6. Diagnostic Characters
- Slender body, length variable;
- Lips often slightly offset;
- Stylet with basal knobs;
- Oocytes in one or more rows;
- Post-uterine sac usually well-developed, with variable length;
- Spicules paired, rose thorn-shaped, not fused, rostrum usually prominent;
- Male tail without caudal alae or gubernaculum; with three pairs of ventro-submedian papillae;
- Tails of both sexes never elongate-filiform, but usually more or less tapering, conical, and frequently ending in one or more mucrons.
7. Genus Synonyms
- A. kuehnii Fischer, 1894 = A. (Aphelenchoides) kuehnii Fischer, 1894 (Filipjev, 1934)
- A. absari Husain and Khan, 1967
- A. abyssinicus (Filipjev, 1931) Filipjev, 1934 = Aphelenchus abyssinicus Filipjev, 1931
- A. aerialis Chanu, Mohilal, Victoria and Shah, 2015
- A. africanus Dassonville and Heyns, 1984
- A. agarici Seth and Sharma, 1986
- A. aligahriensis Siddiqi, Hussain and Khan, 1967
- A. andrassyi Husain and Khan, 1967
- A. angusticaudatus Eroshenko, 1968
- A. appendurus Singh, 1967
- A. arachidis = Robustodorus arachidis Bos, 1977
- A. arcticus Sanwal, 1965
- A. asterocaudatus Das, 1960
- A. asteromucronatus Eroshenko, 1967
- A. baguei Maslen, 1979
- A. besseyi Christie, 1942 = Aphelenchoides oryzae Yokoo, 1948 Asteroaphelenchoides besseyi (Christie 1942) Drozdovski, 1967
- A. bicaudatus (Imamura, 1931) Filipjev and Schuurmans Stekhoven, 1941 = Aphelenchus bicaudatus (Imamura, 1931)
- A. bimucronatus Nesterov, 1985
- A. blastophthorus Franklin, 1952
- A. brassicae Edward and Misra, 1969
- A. brevicaudatus Das, 1960
- A. brevionchus Das, 1960
- A. breviuteralis Eroshenko, 1967
- A. brushimucronatusBajaj and Walia, 1999
- A. capsuloplanus = Paraphelenchoides capsuloplanus Haque, 1967
- A. centralis Thorne and Malek, 1968
- A. chalonus Chawla and Khan, 1979
- A. chamelocephalus (Steiner, 1926) Filipjev, 1934
- A. chauhani Tandon and Singh, 1974
- A. chinensis Husain and Khan, 1967
- A. cibolensis Riffle, 2011
- A. citri Andrássy, 1957
- A. clarolineatus Baranovskaya, 1958
- A. clarus Thorne and Malek, 1968
- A. composticola Franklin, 1957
- A. confusus Thorne and Malek, 1968
- A. conimucronatus Bessarabova, 1966
- A. conophthori Massey, 1974
- A. curiolis Gritsenko, 1971
- A. cyrtus Paesler, 1957
- A. dactylocercus Hooper, 1958
- A. dalianensis Cheng, Hou and Lin, 2009
- A. daubichaensis Eroshenko, 1968
- A. delhiensis Cwala, Bhamburkar, Khan and Prasad, 1968
- A. dhanachandhi Chanu, Mohilal and Shaw, 2012
- A. dubitus Ebsary, 1991
- A. echinocaudatus Haque, 1968
- A. eldaricus Esmaeili, Heydari, Golhasan and Kanzaki, 2017
- A. editocaputis Shavrov, 1967
- A. eltayebi Zeidan and Geraert, 1991
- A. emiliae Romaniko, 1966
- A. ensete Swart, Bogale and Tiedt, 2000
- A. eradicitus Eroshenko, 1968
- A. fluviatilis Andrassy, 1960
- A. fragariae (Ritzema Bos, 1891) Christie, 1932 = Aphelenchoides olesistus (Ritzema Bos, 1893) Steiner, 1932 Aphelenchoides olesistus var. longicollis (Schwartz, 1911) Goodey, 1933 Aphelenchoides pseudolesistus (Goodey, 1928) Goodey, 1933 Aphelenchus fragariae Ritzema Bos, 1891 Aphelenchus olesistus Ritzema Bos, 1893 Aphelenchus olesistus var. longicollis Schwartz, 1911 Aphelenchus pseudolesistus Goodey, 1928
- A. franklini Singh, 1969
- A. fuchsi Esmaeili, Heydari, Ziaie and Gu, 2016
- A. fujianensis Zhuo, Cui, Ye, Luo, Wang, Hu, and Liao, 2010
- A. giblindavisi Aliramaji, Pourjam, Alvarez-Ortega, Afshar and Pedram, 2017
- A. goeldii (Steiner, 1914) Filipjev, 1934 = Aphelenchus goeldii Steiner, 1914 Aphelenchoides (A.) goeldii (Steiner, 1914) Filipjev, 1934
- A. goldeni Suryawanshi, 1971
- A. goodeyi Siddiqi and Franklin, 1967
- A. gorganensis Miraeiz, Heydari and Bert, 2017
- A. graminis Baranovskaya and Haque, 1968
- A. gynotylurus Timm and Franklin, 1969
- A. haguei Maslen, 1978
- A. hamatus Thorne and Malek, 1968
- A. heidelbergi Carta, Li, Skantar, and Newcombe, 2016 = Laimaphelenchus heidelbergi Zhao, Davies, Riley, and Nobbs, 2007
- A. helicosoma Maslen, 1978
- A. helicus Heyns, 1964
- A. helophilus (de Man, 1880) Goodey, 1933 = Aphelenchus helophilus le Man, 1880 Aparietinus var. helophilus de Man, 1880 Aphelenchoides (A.) helophilus (de Man, 1880) Goodey, 1933 Aphelenchus elegans Micoletzky, 1913
- A. heterophallus Steiner, 1934
- A. huntensis Esmaeili, Fang, Li and Heydari, 2016
- A. hunti Steiner, 1935
- A. hylurgi Massey, 1974
- A. indicus Chawla, Bhamburkar, Khan and Prasad, 1968
- A. involutus Minegawa, 1992
- A. iranicus Golhasan, Heydari, Alvarez-Ortega and Palomares-Rius, 2016
- A. jacobi Husain and Khan, 1967
- A. jodhpurensis Tikyani, Khera and Bhatnagar, 1970
- A. jonesi Singh, 1977
- A. kheirii Golhasan, Heydari, Esmaeili and Kanzaki, 2018
- A. kungradensis Karimova, 1957
- A. lanceolatus Tandon and Singh, 1974
- A. lagenoferrus Baranovskaya, 1963
- A. lanceolatus Tandon and Singh, 1974
- A. lichenicola Siddiqi and Hawksworth, 1982
- A. lilium Yokoo, 1964
- A. limberi Steiner, 1936 = Paraphelenchoides limberi (Steiner, 1936) Hague, 1967
- A. longiurus Das, 1960
- A. longiuteralis Eroshenko, 1967
- A. loofi Kumar, 1982
- A. lucknowensis Tandon and Singh, 1973
- A. macromucrons Slankis, 1967
- A. macronucleatus Baranovskaya, 1963
- A. macrospica Golhasan, Heydari, Esmaeili and Miraeiz, 2017
- A. marinus Timm and Franklin, 1969
- A. martinii Ruhm, 1955
- A. medicagus Wang, Bert, Gu, Couvrer and Li, 2019
- A. meghalayensis Bina and Mohilal, 2017
- A. menthae Lisetzkaya, 1971
- A. microsylus Kaisa, 2000
- A. minor Seth and Sharma, 1986
- A. myceliophagus Seth and Sharma, 1986
- A. nechaleos Hooper and Ibrahim, 1994
- A. neocomposticola Seth and Sharma, 1986
- A. neoechinocaudatus Chanu, Mohilal and Shah, 2012
- A. nonveilleri Andrassy, 1959
- A. obtusicaudatus Eroshenko, 1967
- A. obtusus Thorne and Malek, 1968
- A. orientalis Eroshenko, 1968
- A. pannocaudus Massey, 1966
- A. paradalianensis Cui, Zhuo, Wang and Liao, 2011
- A. paramonovi Eroshenko and Kruglik, 2004
- A. paranechaleos Hooper and Ibrahim, 1994
- A. parasaprophilus Sanwal, 1965
- A. parasexalineatus Kalinich, 1984
- A. montanus Singh, 1967
- A. panaxi Skarbilovich and Potekhina, 1959
- A. parabicaudatus, Shavrov, 1967
- A. parascalacaudatus Chawla, Bhamburkar, Khan and Prasad, 1968
- A. parasubtenuis Shavrov, 1967
- A. paraxui Esmaeili, Heydari, Fang and Li, 2017
- A. parietinus (Bastian, 1865) Steiner, 1932
- A. petersi Tandon and Singh, 1970
- A. pinusi Bajaj and Walia, 1999
- A. pityokteini Massey, 1974
- A. platycephalus Eroshenko, 1968
- A. polygraphi Massey, 1974
- A. primadentus Esmaeili, Heydari, Golhasan and Kanzaki, 2018
- A. pseudogoodeyi Oliveira, Subbotin, Alvarez-Ortega, Desaeger, Brito, Xavier, Freitas, Vau and Inserra, 2019
- A. pusillus (Thorne, 1929) Filipjev, 1934
- A. rarus Eroshenko, 1968
- A. rhytium Massey, 1971
- Aphelenchoides ritzemabosi (Schwartz, 1911) Steiner and Buhrer = Aphelenchoides ribes (Taylor, 1917) Goodey, 1933; Aphelenchus phyllophagus Stewart, 1921; Aphelenchus ribes (Taylor, 1917) Goodey, 1923; Aphelenchus ritzemabosi (Schwartz, 1911); Pathoaphelenchus ritzemabosi (Schwartz, 1911) Steiner, 1932; Pseudaphelenchoides ritzemabosi (Schwartz, 1911) Drozdovski, 1967; Tylenchus ribes Taylor, 1917
- A. rosei Dmitrenko, 1966
- A. rotundicaudatus Fang, Wang, Gu and Li, 2014
- A. rutgersi Hooper and Myers, 1971
- A. sacchari Hooper, 1958
- A. sanwali Chaturvedi and Khera, 1979
- A. saprophilus Franklin, 1957
- A. salixae Esmaeili, Heydari, Tahmoures and Ye, 2017
- A. scalacaudatus Sudakova, 1958
- A. seiachicus Nesterov, 1973
- A. sexlineatus Eroshenko, 1967
- A. shamimi Khera, 1970
- A. siddiqii Fortuner, 1970
- A. silvester Andrassy, 1968
- A. sinensis (Wu and Hoeppli, 1929) Andrassy, 1960
- A. singhi Das, 1960
- A. sinodendroni Ruhn, 1957
- A. smolae Cai, Gu, Wang, Fang and Li, 2020
- A. solani Steiner, 1935
- A. spasskii Eroshenko, 1968
- A. sphaerocephalus Goodey, 1953
- A. spicomucronatus Truskova, 1973
- A. spinosus Paesler, 1957
- A. spinohamatus Bajaj and Walia, 1999
- A. spinosus Paesler, 1957
- A. stammeti Korner, 1954
- A. steineri Ruhm, 1956
- A. stellatus Fang, Gu, Wang and Li, 2014
- A. submersus Truskova, 1973
- A. subparietinus Sanwal, 1961
- A. subtenuis = Robustodorus subtenuis (Cobb, 1926) Steiner and Buhrer, 1932
- A. suipingensis Feng and Li, 1986
- A. swarupi Seth and Sharma, 1986
- A. tabarestanensis Golhasan, Fang, Li, Maadi and Heydari, 2019
- A. tagetae Steiner, 1941
- A. taraii Edward and Misra, 1969
- A. tsalolikhini Ryss, 1993
- A. trivialis Franklin and Siddiqi, 1963
- A. tumulicaudatus Truskova, 1973
- A. turnipi Israr, Shahina and Nasira, 2017
- A. tuzeti B’Chir, 1978
- A. unisexus Jain and Singh, 1984
- A. varicaudatus Ibrahim and Hooper, 1994
- A. vaughani Maslen, 1978
- A. vigor Thorne and Malek, 1968
- A. wallacei Singh, 1977
- A. xui Wang, Wang, Gu, Wang and Li, 2013
- A. zeravschanicus Tulaganov, 1948
8. Principal Species
- Aphelenchoides besseyi Christie, 1942;
- Aphelenchoides bicaudatus (Imamura, 1931) Filipjev and Schuurmans Stekhoven;
- Aphelenchoides fragariae (Ritzema Bos, 1891) Christie, 1932;
- Aphelenchoides ritzemabosi (Schwartz, 1911) Steiner and Buhrer, 1941.
9. Rice White-Tip Nematode (Aphelenchoides besseyi Christie, 1942)
10. Strawberry Crimp Nematode (Aphelenchoides fragariae (Ritzema Bos, 1891) Christie, 1932)
11. Chrysanthemum Nematode (Aphelenchoides ritzemabosi (Schwartz, 1911) Steiner and Buhrer)
12. Genus Litylenchus Zhao, Davies, Alexander and Riley, 2011
- Adults and juveniles of Litylenchus gen. from within leaves not forming galls;
- Lacking obese females with a spiral form;
- Slender to semi-obese, cylindrical nematodes, barely curved around ventral axis;
- Lack of sexual dimorphism in head, pharyngeal, and tail characters;
- Cuticle with fine annulations, head offset;
- Stylet short (9–12 μm), robust, with rounded knobs;
- Pharynx with non-muscular fusiform median bulb, valve may be present;
- Pharyngeal glands contained in a large terminal bulb abutting intestine and three large nuclei present;
- Secretory/excretory pore opening 1–1.5 body diameter posterior to nerve ring;
- Female with mono-prodelphic gonad with quadricolumella and post-uterine sac;
- Male with arcuate spicules and simple gubernaculum;
- Bursa arising 1–2 cloacal body diameter anterior to cloacal aperture, extending nearly to tail tiptail medium, conoid, tip shape variable, usually bluntly rounded in male, more variable in female.
13. Systematic Position
- Litylenchus genus. does not induce typical galls like Anguina and Nothanguina;
- Lack of obese females with a spiral form in Anguina and Nothanguina and lack of semi-obese females in Ditylenchus;
- Stylet of Litylenchus genus is more robust and the stylet knobs are rounded compared to Ditylenchus;
- Excretory pore situated posterior to nerve ring;
- Tails of Litylenchus genus are conoid rather than elongate conoid to filiform in Ditylenchus, and elongate conoid in Nothotylenchus gen.;
- Males have a shorter bursa compared to those of Nothotylenchus gen.
- Litylenchus coprosma
- Litylenchus crenatae
- Litylenchus crenatae mccannii
14. Litylenchus coprosma Zhao, Davies, Alexander and Riley, 2011
15. Litylenchus crenatae Kanzaki, Ichihara, Aikawa, Ekino, and Masuya, 2019
16. Litylenchus crenatae Kanzaki et al., 2019 mccannii ssp. Carta, Handoo, Li, Kantor, Bauchan, McCann, Gabriel, Yu, Reed, Koch, Martin, Burke 2020
- Having longer stylet 9.7 ± 0.9 µm (8.6–11.2) vs. 8.0 ± 0.4 (7.4–8.5) and longer stylet conus 4.6 µm (3.6–5.2) vs. 3.1 ± 0.2 (2.8–3.5);
- The post- uterine sac in mature females was shorter (36.9 ± 9.4 vs. 68 ± 7.4);
- Tail was shorter in the fixed immature female populations (48.3 ± 6.2 vs. 55 ± 3.8) but it was longer in the mature populations (43.7 ± 11.3 vs 33 ± 2.3) which was also reflected in different c (16.8 ± 1.4 vs 24.5 ± 1.9) and c’ (5.3 ± 1.2 vs. 2.9 ± 0.3) ratios;
- The body width in mature females was narrower in all populations (16.2 ± 2.4 vs. 22.9 ± 2.6).
- Longer stylet (11.2 (10.6–12) vs. 10.2 (9.9–11)) μm and stylet conus (4.8 (4.4–5.3) vs. 3.6 (3.5–4.3)) μm;
- A wider body (16.7 (13.5–20.3)) μm than the fixed type population from Japan.
17. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kohl, L.M. Foliar nematodes: A summary of biology and control with a compilation of host range. Plant Health Prog. 2011, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez Monge, G.A.; Flores, L.; Salazar, L.; Hockland, S.; Bert, W. An updated list of the plants associated with plant-parasitic Aphelenchoides (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) and its implications for plant-parasitism within this genus. Zootaxa 2015, 4013, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nickle, W.R. A taxonomic review of the genera of the Aphelenchoidea (Fuchs, 1937) thorne, 1949 (Nematoda: Tylenchida). J. Nematol. 1970, 2, 375. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, S.; Togashi, K. A simple method for determining Aphelenchoides besseyi infestation level of Oryza sativa seeds. J. Nematol. 1999, 31, 641. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Golden, A.M. Preparation and mounting nematodes for microscopic observations. In B. Plant Nematology Laboratory Manual; Zuckerman, M., Mai, W.F., Krusberg, L.R., Amherst, M.A., Eds.; University of Massachusetts Agricultural Experiment Station: Amherst, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 197–205. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, D.J. Handling, fixing, staining, and mounting nematodes. In Laboratory Methods for Work with Plant and Soil Nematodes, 5th ed.; Southey, J.F., Ed.; Her Majesty’s Stationery Office: London, UK, 1970; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ryss, A.Y.; McClure, M.A.; Nischwitz, C.; Dhiman, C.; Subbotin, S.A. Redescription of Robustodorus megadorus with molecular characterization and analysis of its phylogenetic position within the family Aphelenchoididae. J. Nematol. 2013, 45, 237. [Google Scholar]
- McClure, M.A.; Stowell, L.J. A simple method of processing nematodes for electron microscopy. J. Nematol. 1978, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kantor, M.; Handoo, Z.A.; Skantar, A.M.; Hult, M.N.; Ingham, R.E.; Wade, N.M.; Ye, W.; Bauchan, G.R.; Mowery, J.D. Morphological and molecular characterisation of Punctodera mulveyi n. sp. (Nematoda: Punctoderidae) from a golf course green in Oregon, USA, with a key to species of Punctodera. Nematology 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Carta, L.K.; Bauchan, G.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Yuceer, C. Description of Parasitorhabditis frontali n. sp. (Nemata: Rhabditida) from Dendroctonus frontalis Zimmermann (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). J. Nematol. 2010, 42, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Carta, L.K.; Handoo, Z.A.; Li, S.; Kantor, M.R.; Bauchan, G.; McCann, D.; Gabriel, C.K.; Yu, Q.; Reed, S.E.; Koch, J.; et al. Beech leaf disease symptoms caused by newly recognized nematode subspecies Litylenchus crenatae mccannii (Anguinata) described from Fagus grandifolia in North America. For. Path. 2020, 50, e12580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, L.K.; Li, S. PCR amplification of a long rDNA segment with one primer pair in agriculturally important nematodes. J. Nematol. 2019, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rybarczyk-Mydłowska, K.; Mooyman, P.; van Megen, H.; van den Elsen, S.; Vervoort, M.; Veenhuizen, P.; van Doorn, J.; Dees, R.; Karssen, G.; Bakker, J.; et al. Small subunit ribosomal DNA-based phylogenetic analysis of foliar nematodes (Aphelenchoides spp.) and their quantitative detection in complex DNA backgrounds. Phytopathology 2012, 102, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Monge, A.; Janssen, T.; Fang, Y.; Couvreur, M.; Karssen, G.; Bert, W. mtCOI successfully diagnoses the four main plant-parasitic Aphelenchoides species (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) and supports a multiple origin of plant-parasitism in this paraphyletic genus. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 148, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holterman, M.; Van Der Wurff, A.; Van Den Elsen, S.; Van Megen, H.; Bongers, T.; Holovachov, O.; Bakker, J.; Helder, J. Phylum-wide analysis of SSU rDNA reveals deep phylogenetic relationships among nematodes and accelerated evolution toward crown clades. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunn, G.B. Nematode Molecular Evolution. An Investigation of Evolutionary Patterns among Nematodes Based upon DNA Sequences. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Goodey, J.B. The classification of the Aphelenchoidea Fuchs, 1937. Nematologica 1960, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagdale, G.B.; Grewal, P.S. Infection behavior and overwintering survival of foliar nematodes, Aphelenchoides fragariae, on Hosta. J. Nematol. 2006, 38, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, M.W. Taxonomic status of the bud and leaf nematodes related to Aphelenchoides fragariae (Ritzema Bos, 1891). Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1952, 19, 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, L.; Crow, W.T. Foliar Nematode, Aphelenchoides (spp.). Available online: http://entnemdept.ufl.edu/creatures/NEMATODE/foliar_nematode.html (accessed on 28 July 2020).
- Hunt, D.J. Aphelenchida, Longidoridae and Trichodoridae: Their Systematics and Bionomics; CABI International: Wallingford, UK, 1993; p. 352. [Google Scholar]
- Shahina, F. A diagnostic compendium of the genus Aphelenchoides Fischer, 1894 (Nematoda: Aphelenchida) with some new records of the group from Pakistan. Pak. J. Nematol. 1996, 14, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, D.J. A checklist of the Aphelenchoidea Nematoda:Tylenchina). J. Nematode Morphol. Syst. 2008, 10, 99–135. [Google Scholar]
- Christie, J.R. A description of Aphelenchoides besseyi n.sp., the summer- dwarf nematode of strawberries, with comments on the identity of Aphelenchoides subtenuis (Cobb, 1929) and Aphelenchoides hodsoni Goodey, 1935. Proc. Helminth Soc. Wash. 1942, 9, 82–84. [Google Scholar]
- De Jesus, D.S.; Oliveira, C.M.G.; Roberts, D.; Blok, V.; Neilson, R.; Prior, T.; de Lima Oliveira, R.D.A. Morphological and molecular characterisation of Aphelenchoides besseyi and A. fujianensis (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) from rice and forage grass seeds in Brazil. Nematology 2016, 18, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.M.; Li, D.; Alexander, B.J.; Zhao, Z.Q. First report of Litylenchus coprosma on Coprosma robusta. Australas. Plant Dis. Notes 2017, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, M.T.; Siddiqi, M.R. Aphelenchoides besseyi. In CIH Descriptions of Plant-Parasitic Nematodes; Commonwealth Institute of Helminthology: St. Albans, UK, 1972; 3p. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, I.A. Aphelenchoides bicaudatus. In CIH Descriptions of Plant-Parasitic Nematodes; Commonwealth Institute of Helminthology: St. Albans, UK, 1976; 3p. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, M.R. Aphelenchoides fragariae. In CIH Description of Plant-Parasitic Nematodes; Commonwealth Institute of Helminthology: St. Albans, UK, 1975; 4p. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, M.R. Aphelenchoides ritzemabosi. In CIH Description of Plant-Parasitic Nematodes; Commonwealth Institute of Helminthology: St. Albans, UK, 1974; 4p. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, I.A.; Taylor, D.P. A Redescription of Aphelenchoides bicaudatus (Imamura, 1931) Filipjev & Schuurmans Stekhoven, 1941 (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae), with a description of the previously undescribed male. Nematologica 1967, 13, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, F.Y.; Tsay, T.T.; Chen, P. Aphelenchoides bicaudatus from ornamental nurseries in Taiwan and its relationship with some agricultural crops. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 1763–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, Z.; Son, S.H.; Moon, H.S.; Kim, S.G.; Shin, H.D.; Jeon, Y.H. Description of a foliar nematode, Aphelenchoides fragariae (Nematoda: Aphelenchida) with additional characteristics from Korea. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2007, 10, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizhov, V.N.; Subbotin, S.A.; Chumakova, O.A.; Baldwin, J.G. Morphological and molecular characterization of foliar nematodes of the genus Aphelenchoides: A. fragariae and A. ritzemabosi (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) from the main botanical garden of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow. Russ. J. Nematol. 2006, 14, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Davies, K.; Alexander, B.; Riley, I.T. Litylenchus coprosma gen. n., sp. n. (Tylenchida: Anguinata), from Leaves of Coprosma repens (Rubiaceae) in New Zealand. Nematology 2011, 13, 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.R.; Handoo, Z.A.; Rao, U.; Rao, S.B.; Prasad, J.S. Observations on the foliar nematode, Aphelenchoides besseyi, infecting tuberose and rice in India. J. Nematol. 2012, 44, 391. [Google Scholar]
- Kanzaki, N.; Ichihara, Y.; Aikawa, T.; Ekino, T.; Masuya, H. Litylenchus crenatae n. sp. (Tylenchomorpha: Anguinidae), a laf gall nematode parasitizing Fagus crenata Blume. Nematology 2019, 21, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughtrey, M.L.; Wick, R.L.; Peterson, J.L. Compendium of Flowering Potted Plant Diseases; American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kepenekci, I. Rice white tip nematode (Aphelenchoides besseyi) in rice growing areas of Turkey. Nematropica 2013, 43, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, C.M.G.; Kubo, R.K. Foliar nematodes (Aphelenchoides spp.) on Begonia in Brazil. Rev. Bras. Hortic. Ornam. 2006, 12, 134–137. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, A.; Fernandez, E. New hosts of Aphelenchoides besseyi (Christie, 1942) in Cuba. Fitosanidad 2004, 8, 45–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hockland, S. A Pragmatic Approach to Identifying Aphelenchoides Species for Plant Health Quarantine and Pest Management Programmes; University of Reading: Reading, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.L.; Kuo, T.H.; Tsay, T.T.; Tsai, I.J.; Chen, P.J. Glycoside hydrolase (GH) 45 and 5 Candidate Cellulases in Aphelenchoides besseyi Isolated from Bird’s-Nest Fern. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Qing, X.; Xie, J.L.; Yang, F.; Peng, Y.L.; Ji, H.L. Population structure and species delimitation of rice white tip nematode, Aphelenchoides besseyi (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae), in China. Plant Pathol. 2020, 69, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuner, R. On the morphology of Aphelenchoides besseyi christie, 1942 and A. siddiqii n. sp. (Nematoda, Aphelenchoidea). J. Helminthol. 1970, 44, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devran, Z.; Tülek, A.; Mıstanoğlu, İ.; Çiftçiğil, T.H.; Özalp, T. A rapid molecular detection method for Aphelenchoides besseyi from rice tissues. Australas. Plant Path. 2017, 46, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Agudelo, P.; Wells, C.E. Detoxification-related gene expression accompanies anhydrobiosis in the foliar nematode (Aphelenchoides fragariae). J. Nematol. 2020, 52, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, T.T. Quarantine of plant-parasitic nematodes. Plant Pathol. Bull. 1995, 4, 43–59. [Google Scholar]
- Imamura, S. Nematodes in the paddy field, with notes on their population before and after irrigation. J. Coll. Agric. Imp. Univ. Tokyo 1931, 11, 193–240. [Google Scholar]
- Israr, M.; Shahina, F.; Nasira, K. Description of Aphelenchoides turnipi n. sp. and Redescription of A. siddiqii with Notes on A. bicaudatus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) from Pakistan. Pak. J. Nematol. 2017, 35, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanwal, K.C. A key to the species of the nematode genus Aphelenchoides fischer, 1894. Can. J. Zool. 1961, 3S, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, T.; Park, J.K. First report of Aphelenchoides bicaudatus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) from South Korea. Anim. Syst. Evol. Divers. 2016, 32, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunn, R.A. Foliar Nematodes as Pests of Ornamental Plants; Institute of Food and Agricultural Science, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2005; 3p. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, M.T. Two species of Aphelenchoides associated with strawberry bud disease in Britain. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1950, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CABI. Invasive Species Compendium. Available online: https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/6378 (accessed on 28 July 2020).
- Reed, S.E.; Greifenhagen, S.; Yu, Q.; Hoke, A.; Burke, D.J.; Carta, L.K.; Handoo, Z.A.; Kantor, M.R.; Koch, J.L. Foliar nematode, Litylenchus crenatae ssp. mccannii, population dynamics in leaves and buds of beech leaf disease-affected trees in Canada and the US. For. Path. 2020, 50, e12599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, R.E.; LaMondia, J. First Report of beech leaf disease, caused by the foliar nematode, Litylenchus crenatae mccannii, on American Beech (Fagus grandifolia) in Connecticut. Plant Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanzaki, N.; Futai, K. A PCR primer set for determination of phylogenetic relationships of Bursaphelenchus species within the xylophilus group. Nematology 2002, 4, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]












Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Handoo, Z.; Kantor, M.; Carta, L. Taxonomy and Identification of Principal Foliar Nematode Species (Aphelenchoides and Litylenchus). Plants 2020, 9, 1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111490
Handoo Z, Kantor M, Carta L. Taxonomy and Identification of Principal Foliar Nematode Species (Aphelenchoides and Litylenchus). Plants. 2020; 9(11):1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111490
Chicago/Turabian StyleHandoo, Zafar, Mihail Kantor, and Lynn Carta. 2020. "Taxonomy and Identification of Principal Foliar Nematode Species (Aphelenchoides and Litylenchus)" Plants 9, no. 11: 1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111490
APA StyleHandoo, Z., Kantor, M., & Carta, L. (2020). Taxonomy and Identification of Principal Foliar Nematode Species (Aphelenchoides and Litylenchus). Plants, 9(11), 1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111490





