The Influence of Nitrogen Application Level on Eating Quality of the Two Indica-Japonica Hybrid Rice Cultivars
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
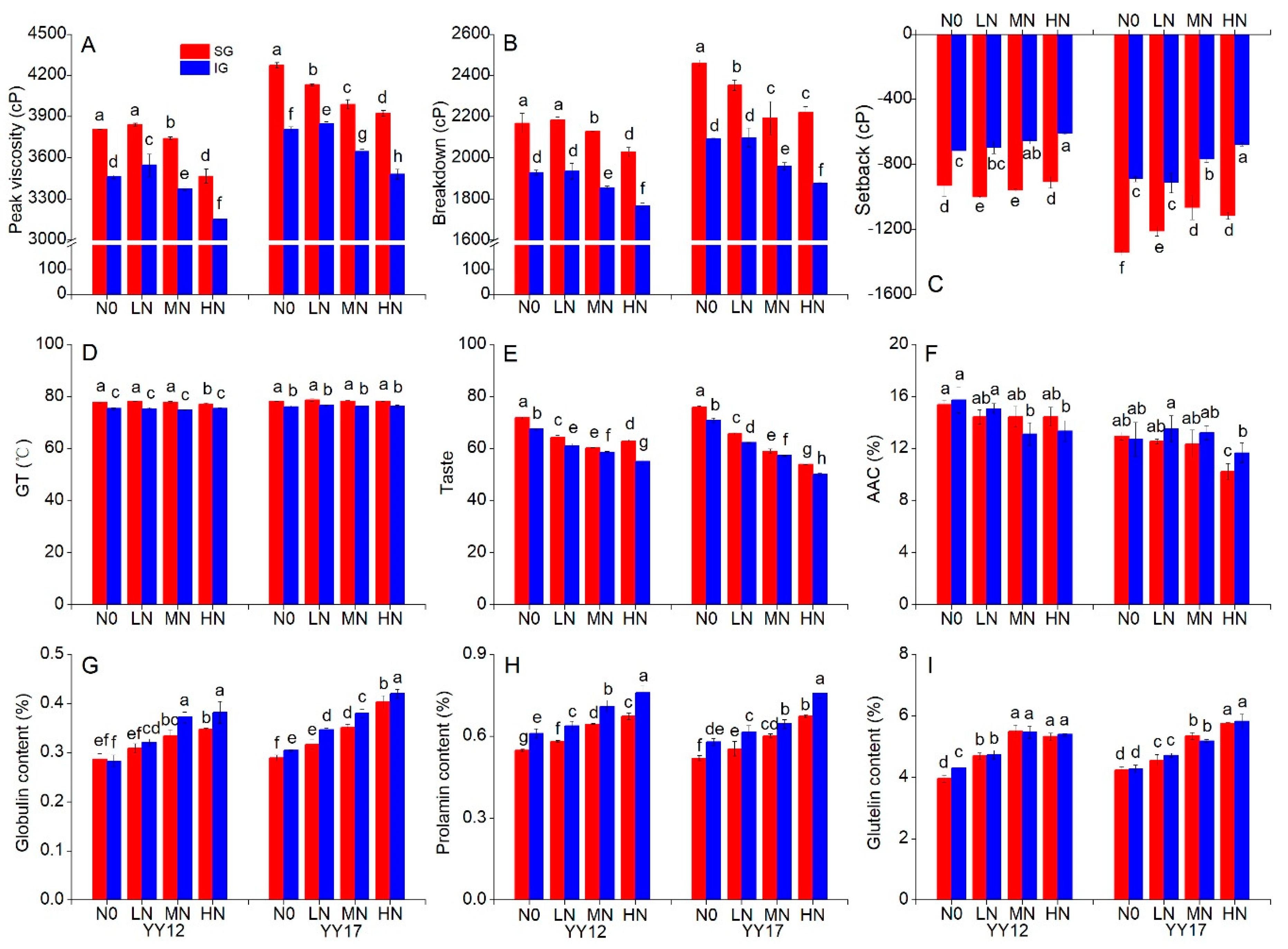
2.1. Effects of N Treatments on the Eating Quality
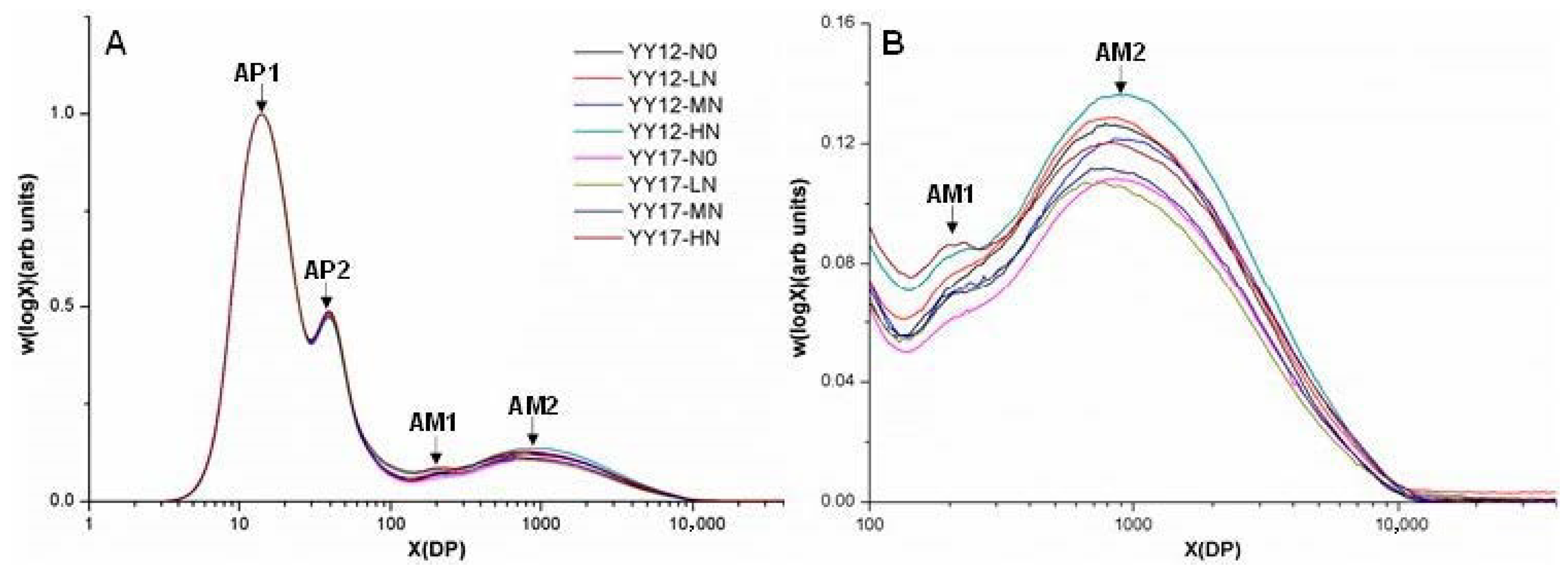
2.2. Effects of N Treatments on Endosperm Compositions
2.3. The Influence of N Level on the Grain Appearance of SG and IG
3. Discussion
3.1. High N Level Deteriorates the Eating Quality of Rice
3.2. The Deterioration of Rice-Eating Quality under a High N Level Is Attributed to an Increased Protein Content and Ratios of Amylose Chains
3.3. Inferior Grains Become Worse in the Eating Quality under a High N Level
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Experimental Design
4.2. Sampling
4.3. Grain Shape and Appearance Observation
4.4. Taste Measurement of Cooked Rice
4.5. Measurement of RVA
4.6. Starch Extraction and Measurement
4.7. Apparent Amylose and Protein Contents and Gel Consistency
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bao, J.S.; Kong, X.L.; Xie, J.K.; Xu, L.J. Analysis of genotypic and environmental effects on rice starch: I. Apparent amylose content, pasting viscosity, and gel texture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6010–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Wei, H.H.; Zhang, H.C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J.M.; Li, C.; Lu, H.B.; Yang, J.W.; Ma, R.R.; Xu, Q.F.; et al. Population characteristics for super-high yielding hybrid rice Yongyou 12 (>13.5 t/ha). Acta Agron. Sin. 2014, 40, 2149–2159, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.L.; Ren, G.L.; Han, C.; Xu, F.F.; Qiu, S.; Tang, J.H.; Zhang, H.C.; Wei, H.Y.; Gao, H. Comparative analysis on grain quality and yield of different panicle weight indica-japonica hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.S. Rice: Eating quality. Encyclopedia of Food Grains, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 3, pp. 166–175. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Sakai, H.; Usui, Y.; Tokida, T.; Nakamura, H.; Zhu, C.; Fukuoka, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Hasegawa, T. Grain growth of different rice cultivars under elevated CO2 concentrations affects yield and quality. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 179, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Tang, S.; Chen, W.Z.; Zhang, H.X.; Li, G.H.; Liu, Z.H.; Ding, C.Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.H.; Zhang, H.C.; et al. Effects of open-field warming during grain-filling stage on grain quality of two japonica rice cultivars in lower reaches of Yangtze River delta. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 81, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J. Grain quality changes and responses to nitrogen fertilizer of japonica rice cultivars released in the Yangtze River Basin from the 1950s to 2000s. Crop J. 2015, 3, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Bi, J.G.; Gilbert, R.G.; Li, G.H.; Liu, Z.H.; Wang, S.H.; Ding, Y.F. Amylopectin chain length distribution in grains of japonica rice as affected by nitrogen fertilizer and genotype. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 71, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.M.; Sun, H.Y.; Wang, C.G.; Ren, X.J.; Liu, H.F.; Zhang, Z.J. Effects of late-stage nitrogen fertilizer application on the starch structure and cooking quality of rice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2332–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Pal, N.; Mahajan, G.; Singh, S.; Shevkani, K. Rice grain and starch properties: Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Fu, L.; Ju, C.; Liu, L.; Yang, J. Effects of application of nitrogen as panicle-promoting fertilizer on seed setting and grain quality of rice under high temperature stress. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2013, 27, 591–602. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, H.X.; Liu, W.Z.; Zhi, D.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Chen, W.Z.; Wang, S.H.; Ding, Y.F. Nitrogen fertilizer at heading stage effectively compensates for the deterioration of rice quality by affecting the starch-related properties under elevated temperatures. Food Chem. 2019, 227, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.L.; Wei, Y.Z.; Yang, X.E.; Feng, Y.; Wu, C.Y. Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer levels on Fe, Mn, Cu and Zn concentrations in shoot and grain quality in rice (Oryza sativa). Rice Sci. 2007, 14, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, T.; Matsuda, T.; Ohsugi, R.; Yamagishi, T. Morphological development of rice caryopses located at the different positions in a panicle from early to middle stage of grain filling. Funct. Plant Biol. 2003, 30, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsue, Y.; Odahara, K.; Hirramatsu, M. Differences in protein content, amylose content and palatability in relation to location of grains within rice panicle. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 1994, 63, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Cheng, H.T.; Nitta, Y.; Aoki, N.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.X.; Ohsugi, R.; Lyu, W.Y. Differences in viscosity of superior and inferior spikelets of japonica rice with varying percentage apparent amylose content. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4237–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.H.; Chen, H.X.; Lyu, W.Y.; Cheng, H.T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.B. Comparison of the chemical and textural properties of germ remaining soft rice grains from different spikelet positions. Cereal Chem. 2019, 00, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, K.; Suzuki, K.; Iijima, K.; Ebana, K. Variation in cooking and eating quality traits in Japanese rice germplasm accessions. Breeding Sci. 2016, 66, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.W.; Zhang, H.C.; Guo, B.W.; Xu, K.; Dai, Q.G.; Wei, H.Y.; Gao, H.; Hu, Y.J.; Cui, P.Y.; Huo, Z.Y. Effects of nitrogen level on yield and quality of japonica soft super rice. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.W.; Zhang, H.C.; Guo, B.W.; Xu, K.; Dai, Q.G.; Wei, C.X.; Zhou, G.S.; Huo, Z.Y. Physicochemical properties of indica-japonica hybrid rice starch from Chinese varieties. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Prakash, S.; Nicholson, T.M.; Fitzgerald, M.A.; Gilbert, R.G. The importance of amylose and amylopectin fine structure for textural properties of cooked rice grains. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Fitzgerald, M.A. Proteins in rice grains influence cooking properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 36, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, G.; Zhao, J.; Blanchard, C. Albumin significantly affects pasting and textural characteristics of rice flour. Cereal Chem. 2010, 87, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, G.; Blanchard, C.; Zhao, J. Effects of glutelin and globulin on the physicochemical properties of rice starch and flour. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, G.; Blanchard, C.; Zhao, J. Effects of prolamin on the textural and pasting properties of rice flour and starch. J. Cereal Sci. 2004, 40, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balindong, J.L.; Ward, R.M.; Liu, L.; Rose, T.J.; Pallas, L.A.; Ovenden, B.W.; Snell, P.J.; Waters, D.L.E. Rice grain protein composition influences instrumental measures of rice cooking and eating quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Zhang, J.H. Grain flling problem in “super” rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.F.; Liu, Z.H.; Deng, S.Y.; Ning, H.F.; Yang, X.Y.; Lin, Z.M.; Li, G.H.; Wang, Q.S.; Wang, S.H.; Ding, Y.F. Occurrence of perfect and imperfect grains of six japonica rice cultivars as affected by nitrogen fertilization. Plant Soil 2011, 349, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Lei, J.C.; Zheng, D.Y.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, G.H.; Wang, S.H.; Ding, Y.F. Amino acid composition of leaf, grain and bracts of japonica rice (Oryza Sativa ssp. japonica) and its response to nitrogen fertilization. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 82, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaplana, F.; Gilbert, R.G. Two-dimensional size/branch length distributions of a branched polymer. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 7321–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hasjim, J.; Wu, A.C.; Henry, R.J.; Gilbert, R.G. Variation in amylose fine structure of starches from different botanical sources. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 4443–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagampang, G.O.; Perez, C.M.; Juliano, B.O. A gel consistency rest for eating quality of rice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1973, 24, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, H.F.; Qiao, J.F.; Liu, Z.H.; Lin, Z.M.; Li, G.H.; Wang, Q.S.; Wang, S.H.; Ding, Y.F. Distribution of proteins and amino acids in milled and brown rice as affected by nitrogen fertilization and genotype. J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 52, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cultivar | Treatment | RVA Characteristics (cP) | Taste Traits | GC (mm) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PV | HPV | CPV | BD | SB | GT (°C) | PT (min) | Appearance | Hardness | Viscosity | Balance | Taste | |||
| YY12 | N0 | 3502cd | 1605a | 2924a | 1897c | −578bc | 76.3bc | 5.91a | 5.70c | 6.88f | 6.12b | 5.83c | 65.08c | 55.3d |
| LN | 3434d | 1524bcd | 2832bc | 1910c | −602c | 76.7abc | 5.84a | 5.23d | 7.12e | 5.67c | 5.37d | 62.07d | 48.2e | |
| MN | 3302e | 1505cd | 2782cd | 1797d | −520ab | 76.6abc | 5.87a | 4.38g | 7.52c | 4.82e | 4.45f | 56.58f | 46.8e | |
| HN | 3225f | 1471d | 2731d | 1754d | −494a | 76.1c | 5.82a | 3.53h | 7.92a | 3.97g | 3.57h | 51.07h | 44.0f | |
| Average | 3366 | 1527 | 2817 | 1839 | −548 | 76.4 | 5.86 | 4.71 | 7.36 | 5.14 | 4.8 | 58.7 | 48.6 | |
| YY17 | N0 | 3769a | 1595ab | 2893ab | 2174a | −876e | 76.6abc | 5.76a | 7.22a | 6.23g | 7.57a | 7.32a | 74.47a | 77.5b |
| LN | 3738a | 1578ab | 2817bc | 2160a | −921e | 76.9ab | 5.76a | 5.97b | 6.78f | 6.32b | 6.07b | 66.55b | 84.8a | |
| MN | 3639b | 1630a | 2857abc | 2009b | −782d | 76.9ab | 5.82a | 4.98f | 7.23d | 5.20d | 5.02e | 59.93e | 68.2c | |
| HN | 3551c | 1569abc | 2801cd | 1982b | −751d | 77.1a | 5.76a | 4.03g | 7.65b | 4.23f | 4.02g | 53.82g | 57.0d | |
| Average | 3674 | 1593 | 2841 | 2081 | −832 | 76.89 | 5.77 | 5.55 | 6.98 | 5.83 | 5.6 | 63.69 | 71.9 | |
| Cultivar | Treatment | AAC | Albumin | Globulin | Prolamin | Glutelin | Total Protein | Pro/Pro+Glu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YY12 | N0 | 14.04a | 0.28b | 0.27d | 0.57cd | 3.96e | 5.08e | 0.127a |
| LN | 13.52ab | 0.29ab | 0.31bc | 0.61c | 4.26d | 5.47d | 0.125a | |
| MN | 13.54ab | 0.29ab | 0.32b | 0.65b | 4.63c | 5.89c | 0.123ab | |
| HN | 12.28bc | 0.31a | 0.37a | 0.69a | 4.93b | 6.30b | 0.123ab | |
| Average | 13.34 | 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.63 | 4.44 | 5.69 | 0.13 | |
| YY17 | N0 | 13.34ab | 0.28b | 0.29cd | 0.52e | 4.03de | 5.11e | 0.114cd |
| LN | 12.83abc | 0.27b | 0.29cd | 0.55de | 4.17de | 5.28de | 0.116bc | |
| MN | 11.43c | 0.28b | 0.32b | 0.60c | 4.62c | 5.81c | 0.115cd | |
| HN | 11.19c | 0.31a | 0.38a | 0.65b | 5.46a | 6.80a | 0.106d | |
| Average | 12.20 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.58 | 4.57 | 5.70 | 0.114 |
| Cultivar | Treatment | AC | XAP1 | XAP2 | XAM1 | XAM2 | hAP2/AP1 | hAM1/AP1 | hAM2/AP1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YY12 | N0 | 20.89abc | 14.1a | 38.9abc | ud | 787.8bc | 0.475bc | ud | 0.127ab |
| LN | 21.57ab | 14.1a | 38.9abc | 248.4ab | 862.0abc | 0.481abc | 0.080abc | 0.129ab | |
| MN | 20.74bcd | 14.0a | 38.9abc | 254.1a | 904.2a | 0.472c | 0.076abcd | 0.122bc | |
| HN | 22.79a | 14.0a | 38.6c | 237.9abc | 923.3a | 0.473c | 0.085ab | 0.136a | |
| Average | 21.5 | 14.1 | 38.9 | 246.8 | 869.332 | 0.475 | 0.081 | 0.128 | |
| YY17 | N0 | 18.52d | 14.0a | 39.0ab | 233.9abc | 868.2ab | 0.484ab | 0.064d | 0.109d |
| LN | 18.58d | 14.0a | 39.2a | 237.9abc | 773.9c | 0.488a | 0.072bcd | 0.107d | |
| MN | 19.25cd | 14.2a | 39.1ab | 218.8c | 781.4bc | 0.486a | 0.070bc | 0.112cd | |
| HN | 21.39ab | 14.1a | 38.8bc | 228.3bc | 843.2abc | 0.488a | 0.087a | 0.121bc | |
| Average | 19.43 | 14.1 | 39.1 | 229.7 | 816.7 | 0.487 | 0.073 | 0.112 |
| Cultivar | Treatment | Ratio of Whole Panicle (%) | Grain Length (mm) | Grain Width (mm) | Grain Thickness (mm) | Length/Width | Grain Weight (g) | GRK (%) | DRK (%) | NRK (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YY12 | N0-SG | 23.05c | 5.86a | 2.80a | 1.83b | 2.09d | 22.38a | ud | ud | 100.00a |
| LN-SG | 20.88d | 5.84a | 2.78ab | 1.83b | 2.10cd | 21.72b | ud | ud | 100.00a | |
| MN-SG | 20.70d | 5.69b | 2.78ab | 1.85a | 2.04e | 21.53b | 0.17e | ud | 99.83a | |
| HN-SG | 21.26d | 5.65b | 2.77b | 1.85a | 2.04e | 21.24b | 0.67e | ud | 99.33a | |
| Average | 21.47 | 5.76 | 2.79 | 1.84 | 2.07 | 21.72 | 0.21 | ud | 99.79 | |
| N0-IG | 42.10b | 5.47c | 2.57c | 1.62d | 2.13bc | 18.01c | 24.17d | 5.83d | 70.00b | |
| LN-IG | 44.14a | 5.49c | 2.53d | 1.65c | 2.17a | 17.60c | 28.83c | 10.83c | 60.33c | |
| MN-IG | 45.93a | 5.49c | 2.54cd | 1.62d | 2.16ab | 17.10c | 36.17b | 14.00b | 49.83d | |
| HN-IG | 44.05a | 5.32d | 2.52d | 1.55e | 2.11cd | 16.74d | 42.17a | 16.00a | 41.83e | |
| Average | 44.06 | 5.44 | 2.54 | 1.61 | 2.14 | 17.36 | 32.83 | 11.71 | 55.46 | |
| YY17 | N0-SG | 21.09d | 6.26a | 2.65a | 1.81a | 2.36b | 23.05a | ud | ud | 100.00a |
| LN-SG | 17.76e | 6.26a | 2.65a | 1.80b | 2.36b | 22.54b | ud | ud | 100.00a | |
| MN-SG | 17.64e | 6.24a | 2.65a | 1.81a | 2.35b | 22.33b | ud | 0.17e | 99.83a | |
| HN-SG | 16.00e | 6.15b | 2.61b | 1.81a | 2.35b | 22.34b | ud | 0.17e | 99.83a | |
| Average | 18.12 | 6.23 | 2.64 | 1.81 | 2.36 | 22.56 | ud | 0.08 | 99.92 | |
| N0-IG | 42.91c | 5.92c | 2.47c | 1.69c | 2.39a | 19.71b | 10.00c | 9.17c | 80.83b | |
| LN-IG | 44.49c | 5.85d | 2.47c | 1.66d | 2.37ab | 19.03c | 17.17b | 6.33d | 76.50c | |
| MN-IG | 46.73b | 5.94c | 2.49c | 1.66d | 2.38ab | 18.50d | 16.33b | 11.00b | 72.67d | |
| HN-IG | 51.38a | 5.84d | 2.46c | 1.63e | 2.38ab | 18.13e | 41.83a | 12.33a | 45.83e | |
| Average | 46.38 | 5.89 | 2.46 | 1.66 | 2.38 | 18.84 | 21.33 | 9.71 | 68.96 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Fu, L.; Tu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Kuang, L.; Zhang, G. The Influence of Nitrogen Application Level on Eating Quality of the Two Indica-Japonica Hybrid Rice Cultivars. Plants 2020, 9, 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9121663
Zhang X, Fu L, Tu Y, Zhao H, Kuang L, Zhang G. The Influence of Nitrogen Application Level on Eating Quality of the Two Indica-Japonica Hybrid Rice Cultivars. Plants. 2020; 9(12):1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9121663
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xincheng, Liangbo Fu, Yishan Tu, Huifang Zhao, Liuhui Kuang, and Guoping Zhang. 2020. "The Influence of Nitrogen Application Level on Eating Quality of the Two Indica-Japonica Hybrid Rice Cultivars" Plants 9, no. 12: 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9121663
APA StyleZhang, X., Fu, L., Tu, Y., Zhao, H., Kuang, L., & Zhang, G. (2020). The Influence of Nitrogen Application Level on Eating Quality of the Two Indica-Japonica Hybrid Rice Cultivars. Plants, 9(12), 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9121663







