Hybrid Breeding for MLN Resistance: Heterosis, Combining Ability, and Hybrid Prediction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phenotypic Variation
2.2. Heterosis and the Genetic Distance among Parental Lines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Selection of Parents, Hybrid Formation, and Trial Design
4.2. Viral Inoculum and Artificial Inoculation
4.3. Phenotypic Data Analysis
4.4. Molecular Data Analysis
4.5. Heterosis and Correlations
4.6. Genomic Prediction
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mudde, B.; Olubayo, F.; Miano, D.; Asea, G.; Kilalo, D.; Kiggundu, A.; Kwemoi, D.; Adriko, J. Distribution, Incidence and Severity of Maize Lethal Necrosis Disease in Major Maize Growing Agro-ecological Zones of Uganda. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redinbaugh, M.; Stewart, L. Maize Lethal Necrosis: An Emerging, Synergistic Viral Disease. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2018, 5, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miedaner, T.; Schulthess, A.; Gowda, M.; Reif, J.; Longin, F. High accuracy of predicting hybrid performance of Fusarium head blight resistance by mid-parent values in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 130, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitonik, C.; Suresh, L.M.; Beyene, Y.; Olsen, M.S.; Makumbi, D.; Oliver, K.; Das, B.; Bright, J.M.; Mugo, S.; Crossa, J.; et al. Genetic architecture of maize chlorotic mottle virus and maize lethal necrosis through GWAS, linkage analysis and genomic prediction in tropical maize germplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 2381–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nyaga, C.; Gowda, M.; Beyene, Y.; Muriithi, W.; Makumbi, D.; Olsen, M.; Suresh, L.M.; Bright, J.; Das, B.; Prasanna, B. Genome-Wide Analyses and Prediction of Resistance to MLN in Large Tropical Maize Germplasm. Genes (Basel) 2019, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaikam, V.; Gowda, M.; Nair, S.; Melchinger, A.; Prasanna, B. Genome-wide association study to identify genomic regions influencing spontaneous fertility in maize haploids. Euphytica 2019, 215, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reif, J.C.; Zhao, Y.; Würschum, T.; Gowda, M.; Hahn, V. Genomic prediction of sunflower hybrid performance. Plant Breed. 2013, 132, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, Y.; Gowda, M.; Suresh, L.M.; Mugo, S.; Olsen, M.; Oikeh, S.O.; Juma, C.; Tarekegne, A.; Prasanna, B.M. Genetic analysis of tropical maize inbred lines for resistance to maize lethal necrosis disease. Euphytica 2017, 213, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soni, S.; Dossou-Aminon, I. Prediction of Hybrid Performance in Crop Plants: Molecular and Recent Approaches. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gowda, M.; King, C.; Würschum, T.; Liu, W.; Maurer, H.P.; Hahn, V.; Reif, J.C. Hybrid Breeding in Durum Wheat: Heterosis and Combining Ability. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 2224–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrag, T.A.; Frisch, M.; Dhillon, B.; Melchinger, A.E. Marker-based prediction of hybrid performance in maize single-crosses involving doubled haploids. Maydica 2009, 54, 353–362. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardo, R. Prediction of Maize Single-Cross Performance Using RFLPs and Information from Related Hybrids. Crop Sci. 1994, 34, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massman, J.M.; Gordillo, A.; Lorenzana, R.E.; Bernardo, R. Genomewide predictions from maize single-cross data. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, M.; Zhao, Y.; Maurer, H.P.; Weissmann, E.; Reif, T. Best linear unbiased prediction of triticale hybrid performance. Euphytica 2012, 191, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vlaming, R.; Groenen, P. The Current and Future Use of Ridge Regression for Prediction in Quantitative Genetics. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 143712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.; Singh, A.K. Marker-Assisted Plant Breeding: Principles and Practices; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Windhausen, V.; Atlin, G.; Hickey, J.; Crossa, J.; Jannink, J.-L.; Sorrells, M.; Babu, R.; Cairns, J.; Tarekegne, A.; Semagn, K.; et al. Effectiveness of Genomic Prediction of Maize Hybrid Performance in Different Breeding Populations and Environments. G3 (Bethesda) 2012, 2, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mangin, B.; Bonnafous, F.; Blanchet, N.; Boniface, M.-C.; Bret-Mestries, E.; Carrere, S.; Cottret, L.; Legrand, L.; Marage, G.; Pegot-Espagnet, P.; et al. Genomic Prediction of Sunflower Hybrids Oil Content. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endelman, J. Ridge Regression and Other Kernels for Genomic Selection with R Package rrBLUP. Plant Genome 2011, 4, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jannink, J.-L.; Lorenz, A.J.; Iwata, H.; Jannink, J.-L.; Lorenz, A.J.; Iwata, H. Genomic selection in plant breeding: From theory to practice. Brief Funct Genomics. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2010, 9, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Gowda, M.; Liu, W.; Würschum, T.; Maurer, H.P.; Longin, F.; Ranc, N.; Reif, J.C. Accuracy of genomic selection in European maize elite breeding Populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 124, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Penning, B.W.; Jamann, T.M.; Glaubitz, J.C.; Romay, M.; Buckler, E.; Redinbaugh, M. Diverse Chromosomal Locations of Quantitative Trait Loci for Tolerance to Maize chlorotic mottle virus in Five Maize Populations. Phytopathology 2017, 108, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gowda, M.; Beyene, Y.; Makumbi, D.; Semagn, K.; Olsen, M.; Bright, J.M.; Das, B.; Mugo, S.; Suresh, L.M.; Prasanna, B. Discovery and validation of genomic regions associated with resistance to maize lethal necrosis in four biparental populations. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nie, Y.; Ji, W.; Ma, S. Assessment of Heterosis Based on Genetic Distance Estimated Using SNP in Common Wheat. Agronomy 2019, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gowda, M.; Das, B.; Makumbi, D.; Babu, R.; Semagn, K.; Mahuku, G.; Olsen, M.; Bright, J.M.; Beyene, Y.; Prasanna, B.M. Genome-wide association and genomic prediction of resistance to maize lethal necrosis disease in tropical maize germplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuka, B.P.; van Biljon, A.; Cairns, J.E.; Das, B.; Labuschagne, M.; MacRobert, J.; Makumbi, D.; Magorokosho, C.; Zaman-Allah, M.; Ogugo, V.; et al. Genetic Diversity among Selected Elite CIMMYT Maize Hybrids in East and Southern Africa. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 2395–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beyene, Y.; Mugo, S.; Semagn, K.; Asea, G.; Trevisan, W.; Tarekegne, A.; Tefera, T.; Gethi, J.; Kiula, B.; Gakunga, J.; et al. Genetic distance among doubled haploid maize lines and their testcross performance under drought stress and non-stress conditions. Euphytica 2013, 192, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertiro, B.; Semagn, K.; Das, B.; Olsen, M.; Labuschagne, M.; Worku, M.; Wegary, D.; Azmach, G.; Ogugo, V.; Keno, T.; et al. Genetic variation and population structure of maize inbred lines adapted to the mid-altitude sub-humid maize agro-ecology of Ethiopia using single nucleotide polymorphic (SNP) markers. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.L.; Lv, D.B.; Wang, Y.Z.; Chen, S.J.; Tang, J.H. Study on the genetic diversity of popcorn inbreds and their germplasm relationship with normal corn inbreds using SSR markers. Maydica 2004, 49, 327–333. [Google Scholar]
- Bhusal, T.; Lal, G.M. Relationship among Heterosis, Combining Ability and SSR Based Genetic Distance in Single Cross Hybrids of Maize (Zea Mays L). Int. J. Plant Res. 2017, 30, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermail, A.; Suriharn, B.; Chankaew, S.; Sanitchon, J.; Lertrat, K. Hybrid prediction based on SSR-genetic distance, heterosis and combining ability on agronomic traits and yields in sweet and waxy corn. Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam) 2020, 259, 108817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, J.; Melchinger, A.E.; Xia, X.; Warburton, M.; Hoisington, D.; Vasal, S.; Srinivasan, G.; Bohn, M.; Frisch, M. Genetic Distance Based on Simple Sequence Repeats and Heterosis in Tropical Maize Populations. Crop Sci. 2003, 43, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchinger, A.E. Use of Molecular Markers in Breeding for Oligogenic Disease Resistance. Plant Breed. 1990, 104, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreps, R.C.; Gumber, R.K.; Schulz, B.; Klein, D.; Melchinger, A.E. Genetic variation in testcrosses of European maize inbreds for resistance to the European corn borer and relations to line per se performance. Plant Breed. 1998, 117, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longin, C.F.H.; Gowda, M.; Mühleisen, J.; Ebmeyer, E.; Kazman, E.; Schachschneider, R.; Schacht, J.; Kirchhoff, M.; Zhao, Y.; Reif, J.C. Hybrid wheat: Quantitative genetic parameters and consequences for the design of breeding programs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 2791–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oettler, G.; Tams, S.H.; Utz, H.F.; Bauer, E.; Melchinger, A.E. Prospects for Hybrid Breeding in Winter Triticale: I. Heterosis and Combining Ability for Agronomic Traits in European Elite Germplasm. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oury, F.-X.; Brabant, P.; Bérard, P.; Pluchard, P. Predicting hybrid value in bread wheat: Biometric modelling based on a ”top-cross” design. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 100, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carena, M.; Hallauer, A.; Filho, J.B. Quantitative Genetics in Maize Breeding; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Rupe, M.A.; Wei, J.; Winkler, C.; Goncalves-Butruille, M.; Weers, B.P.; Cerwick, S.F.; Dieter, J.A.; Duncan, K.E.; Howard, R.J.; et al. Maize ARGOS1 (ZAR1) transgenic alleles increase hybrid maize yield. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 65, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Maurer, H.P.; Würschum, T.; Möhring, J.; Piepho, H.-P.; Schön, C.C.; Thiemt, E.-M.; Dhillon, B.S.; Weissmann, E.A.; Melchinger, A.E.; et al. Development of Heterotic Groups in Triticale. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühleisen, J.; Piepho, H.-P.; Maurer, H.P.; Longin, C.F.H.; Reif, J.C. Yield stability of hybrids versus lines in wheat, barley, and triticale. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegary, D.; Zelleke, H.; Abakemal, D.; Hussien, T.; Singh, H. The Combining Ability of Maize Inbred Lines for Grain Yield and Reaction to Grey Leaf Spot Disease. East Afr. J. Sci. 2008, 2, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrag, T.A.; Melchinger, A.E.; Sørensen, A.P.; Frisch, M. Prediction of single-cross hybrid performance for grain yield and grain dry matter content in maize using AFLP markers associated with QTL. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 113, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, T.; Wimmer, V.; Auinger, H.-J.; Erbe, M.; Knaak, C.; Ouzunova, M.; Simianer, H.; Schön, C.-C. Genome-based prediction of testcross values in maize. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 123, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedelsheimer, C.; Brotman, Y.; Méret, M.; Melchinger, A.E.; Willmitzer, L. The maize leaf lipidome shows multilevel genetic control and high predictive value for agronomic traits. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Technow, F.; Pucher, A.; Melchinger, A.E. Genomic Prediction of Northern Corn Leaf Blight Resistance in Maize with Combined or Separated Training Sets for Heterotic Groups. G3 (Bethesda) 2013, 3, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madden, L.V.; Hughes, G.; van den Bosch, F. The Study of Plant Disease Epidemics; American Phytopathological Society: Paul, MN, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wald, A. Tests of statistical hypotheses concerning several parameters when the number of observations is large. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 1943, 54, 426–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshire, R.J.; Glaubitz, J.C.; Sun, Q.; Poland, J.A.; Kawamoto, K.; Buckler, E.S.; Mitchell, S.E. A Robust, Simple Genotyping-by-Sequencing (GBS) Approach for High Diversity Species. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradbury, P.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.E.; Casstevens, T.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E. TASSEL: Software for Association Mapping of Complex Traits in Diverse Samples. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidotti, M.S.; Matias, F.I.; Alves, F.C.; Pérez-Rodríguez, P.; Beltran, G.A.; Burgueño, J.; Crossa, J.; Fritsche-Neto, R. Maize responsiveness to Azospirillum brasilense: Insights into genetic control, heterosis and genomic prediction. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Raden, P.M. Efficient methods to compute genomic predictions. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4414–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
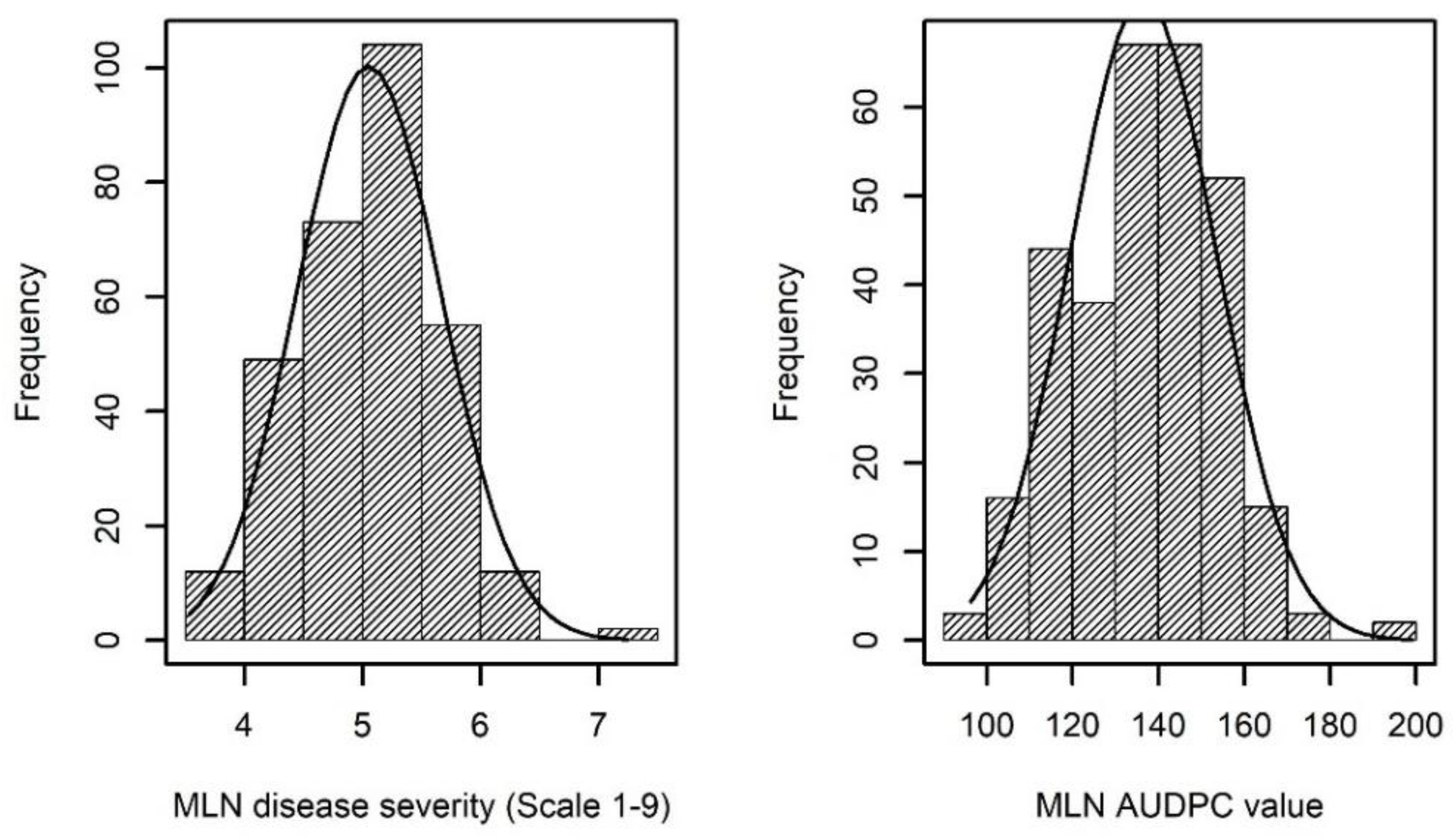
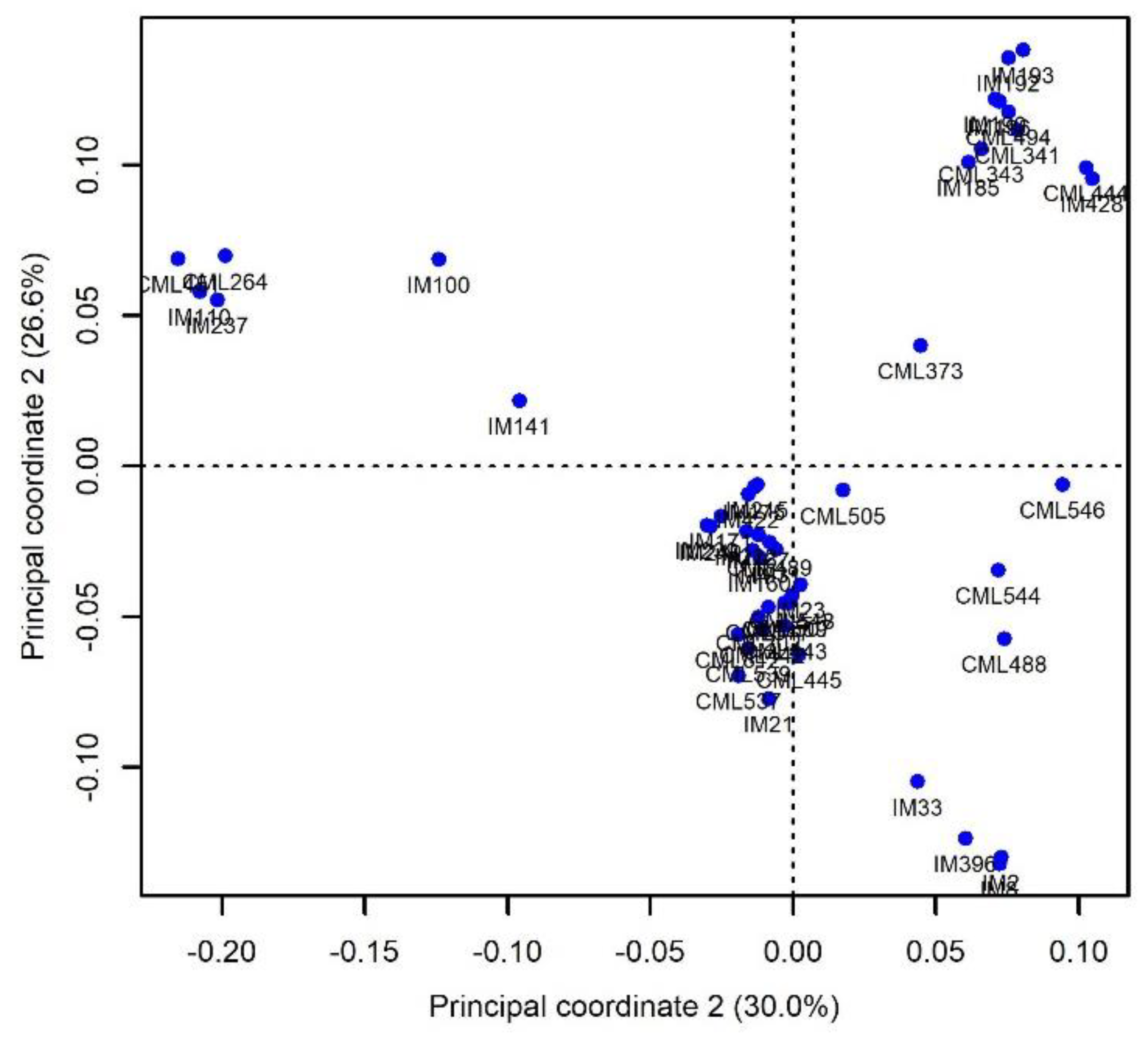


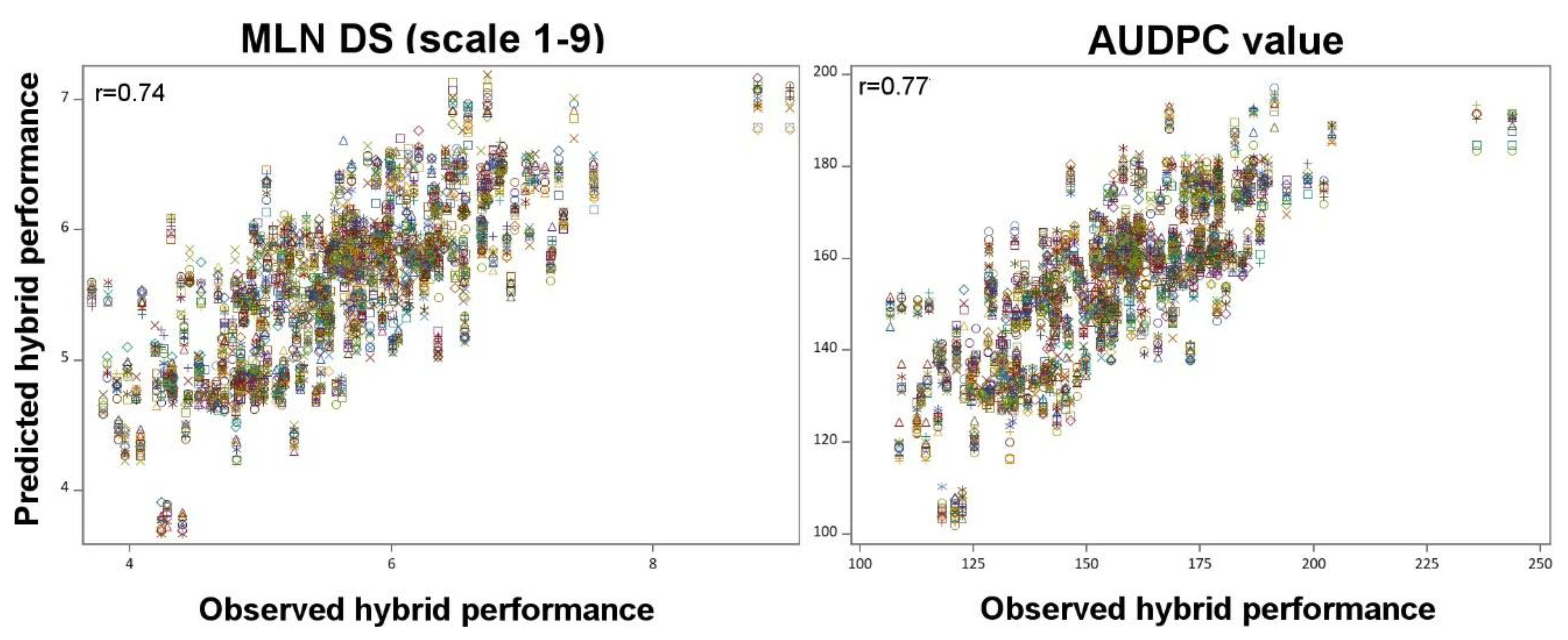
| Trait | MLN DS | AUDPC |
|---|---|---|
| Parents | ||
| Mean | 6.25 | 135.28 |
| Range | 3.44–7.12 | 58.69–216.05 |
| σ2G | 0.545 ** | 2303.16 ** |
| σ2GxE | 0.78 ** | 143.36 * |
| σ2e | 1.40 | 1267.99 |
| h2 | 0.42 | 0.86 |
| F1 Hybrids | ||
| Mean | 5.05 | 136.50 |
| Range | 3.53–7.24 | 96.30–199.10 |
| σ2G | 0.550 ** | 398.006 ** |
| σ2GCA (Female) | 0.156 ** | 114.85 ** |
| σ2GCA (Male) | 0.280 ** | 194.13 ** |
| σ2SCA | 0.114 ** | 89.02 ** |
| σ2GxE | 0.081 ** | 44.36 ** |
| σ2GCA (Female)xE | 0.030 ** | 18.47 ** |
| σ2GCA (Male)xE | 0.030 ** | 21.18 ** |
| σ2SCAxE | 0.030 ** | 11.07 ** |
| σ2e | 0.490 | 217.55 |
| h2 | 0.77 | 0.83 |
| Heterosis | MLN DS | AUDPC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute mid-parent heterosis | mean | −0.90 | 11.99 |
| range | −2.41–1.77 | −53.96–68.36 | |
| Relative mid parent heterosis | mean | −14.57 | 14.19 |
| range | −38.63–43.83 | −28.14–93.21 | |
| Absolute better parent heterosis | mean | −0.39 | 39.79 |
| range | −2.05–2.56 | −45.78–98.50 | |
| Relative better parent heterosis | mean | −4.28 | 51.19 |
| range | −36.66–74.63 | −24.93–100 | |
| r(GD:F1HP) | correlation | 0.04 | 0.07 |
| r(GD:MPH) | correlation | −0.11 | −0.12 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nyaga, C.; Gowda, M.; Beyene, Y.; Murithi, W.T.; Burgueno, J.; Toledo, F.; Makumbi, D.; Olsen, M.S.; Das, B.; L. M., S.; et al. Hybrid Breeding for MLN Resistance: Heterosis, Combining Ability, and Hybrid Prediction. Plants 2020, 9, 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040468
Nyaga C, Gowda M, Beyene Y, Murithi WT, Burgueno J, Toledo F, Makumbi D, Olsen MS, Das B, L. M. S, et al. Hybrid Breeding for MLN Resistance: Heterosis, Combining Ability, and Hybrid Prediction. Plants. 2020; 9(4):468. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040468
Chicago/Turabian StyleNyaga, Christine, Manje Gowda, Yoseph Beyene, Wilson T. Murithi, Juan Burgueno, Fernando Toledo, Dan Makumbi, Michael S. Olsen, Biswanath Das, Suresh L. M., and et al. 2020. "Hybrid Breeding for MLN Resistance: Heterosis, Combining Ability, and Hybrid Prediction" Plants 9, no. 4: 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040468
APA StyleNyaga, C., Gowda, M., Beyene, Y., Murithi, W. T., Burgueno, J., Toledo, F., Makumbi, D., Olsen, M. S., Das, B., L. M., S., Bright, J. M., & Prasanna, B. M. (2020). Hybrid Breeding for MLN Resistance: Heterosis, Combining Ability, and Hybrid Prediction. Plants, 9(4), 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040468







