Does Acid Rain Alter the Leaf Anatomy and Photosynthetic Pigments in Urban Trees?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
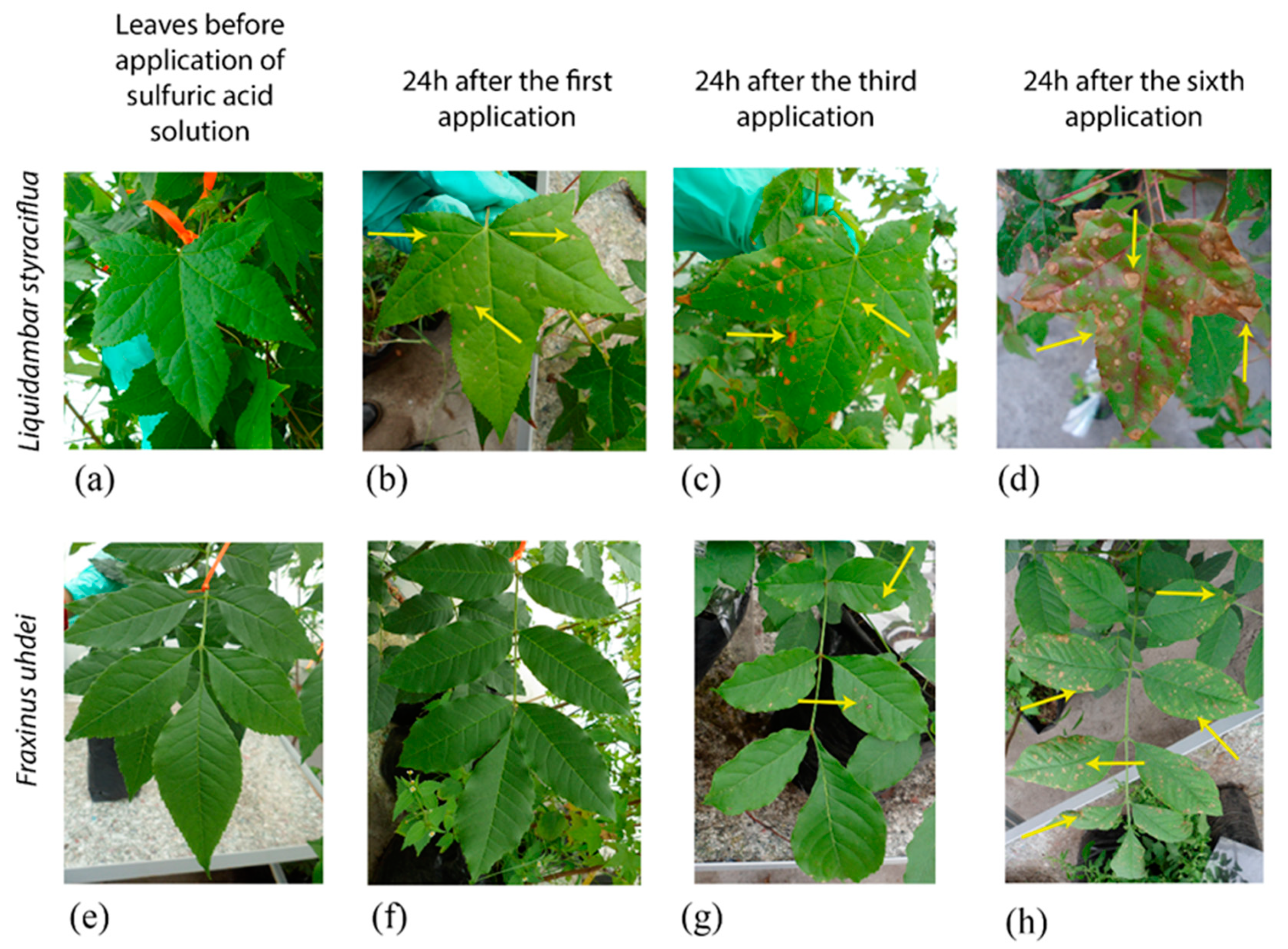
2.1. Simulated Acid Rain Causes Visible Leaf Damage
2.2. Simulated Acid Rain Causes Anatomic Leaf Alterations
2.3. Simulated Acid Rain Causes Changes in Chlorophyll a and b Content
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Species Selection
4.2. Simulated Acid Rain
4.3. Sample Collection
4.4. Cuticle Patterns
4.5. Anatomical Damage
4.6. Quantification of Chlorophyll a and b
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbasi, T.; Poornima, P.; Kannadasan, T. Acid rain: Past, present, and future. Int. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 5, 229–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clair, T.; Burns, D.; Rosas-Pérez, I.; Blais, J.; Percy, K. Ecosystems. In Technical Challenges of Multipollutant Air Quality Management, 1st ed.; Hidy, G.M., Brook, J.R., Demerjian, K.L., Molina, L.T., Pennell, W.T., Scheffe, R.D., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 139–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.; Naderi, E. The impact of acid rain on phosphorus leaching from a sandy loam calcareous soil of western Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Yang, W.J.; Ahammed, G.J.; Shen, C.; Yan, P.; Li, X.; Han, W.Y. Developmental changes in carbon and nitrogen metabolism affect tea quality in different leaf position. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 106, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zuo, Z. Initial simulated acid rain impacts reactive oxygen species metabolism and photosynthetic abilities in Cinnamonum camphora undergoing high temperature. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 135, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calva, G. Dendroquímica En Estudios Ecológicos Y Ambientales; Editorial Académica Española: Madrid, Spain, 2012; p. 176. ISBN 978-3-8473-6209-8. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, S.; Bravo, H.; Saavedra, I.; Torres, R. Acid precipitation in Mexico City Basin. In Proceedings of the Technical Conference: Urban Climatology and It Applications with Special Regard to Tropical Areas; (WMO/TD-No. 7; Abstracts); World Climate Programme/Wold Metereological Organization: Mexico City, Mexico, 1984; pp. 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Báez, P.A.; Padilla, G.H.; De González, O.G. Acid Rain Over Mexico City Valley and Surrounding Rural Areas. Geofis. Int. 1986, 25, 315–346. Available online: http://www.revistas.unam.mx/index.php/geofisica/article/view/39336/35774 (accessed on 2 July 2020).
- Peñaranda, L.F. Precipitaciones Ácidas: Metodología Para Su Caracterización Y Estudio De La Ciudad De México; Instituto Politécnico Nacional: México D.F., Mexico, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarado, F.; García, L. Estudio De La Lluvia Ácida En Corteza De Árbol Como Indicador De Contaminantes En El Volcán El Pelado. D. F; Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana Plantel Xochimilco: México D. F., Mexico, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Secretaría Del Medio Ambiente De La Ciudad De México. Informe Anual De La Calidad Del Aire Y Precipitación Ácida En El Valle De México. Gobierno Del Distrito Federal-Secretaría Del Medio Ambiente: Distrito Federal, Mexico, 2000; pp. 53–54. Available online: http://www.aire.cdmx.gob.mx/descargas/publicaciones/flippingbook/informe_anual_calidad_aire_2000/ (accessed on 2 July 2020).
- Secretaría Del Medio Ambiente De La Ciudad De México. Calidad Del Aire En La Ciudad De México, Informe 2011. Gobierno Del Distrito Federal-Secretaría Del Medio Ambiente: Distrito Federal, Mexico, 2012; pp. 76–85. Available online: http://www.aire.cdmx.gob.mx/descargas/publicaciones/flippingbook/informe_anual_calidad_aire_2011/#p=1 (accessed on 2 July 2020).
- Secretaría Del Medio Ambiente De La Ciudad De México. Calidad Del Aire En La Ciudad De México, Informe 2017. Dirección General De Gestión De La Calidad Del Aire, Dirección de Monitoreo Atmosférico. Ciudad De México. 2018, pp. 86–96. Available online: http://www.aire.cdmx.gob.mx/descargas/publicaciones/flippingbook/informe_anual_calidad_aire_2017/mobile/#p=1 (accessed on 2 July 2020).
- Secretaría del Medio Ambiente de la Ciudad de México. Calidad del aire en la Ciudad de México, informe 2015. Dirección General de Gestión de la Calidad del Aire, Dirección de Monitoreo Atmosférico. México, D.F. 2016, pp. 102–110. Available online: http://www.aire.cdmx.gob.mx/descargas/publicaciones/flippingbook/informe-2015-calidad-del-aire-en-la-ciudad-de-mexico/mobile/index.html (accessed on 2 July 2020).
- Amthor, J. Does acid rain influence plant growth? Some comments and Observations. Environ. Pol. Ser. A 1984, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.S.; Gmur, N.F.; Da Costa, F. Leaf surface and histological perturbations of leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris and Helianthus annuus after exposure to simulated acid rain. Am. J. Bot. 1977, 64, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.S. Botanical aspects of Acidic precipitation. Bot. Rev. 1984, 50, 449–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birdi, K.S.; Larsen, B.R. Y Sánchez, R. Effects of simulated acid rain on the surface tension of selected leaves. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1987, 265, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuzhu, Z.; Xiaofeng, Y.; Jinyang, Z. Effects of simulated acid rain on the injury and physiological responses of crops. J. Environ. Sci. 1994, 6, 87–92. Available online: http://www.jesc.ac.cn/jesc_en/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19940110 (accessed on 2 July 2020).
- Soukupová, J.; Albrechtova, J.; Svobodová, H.; Opatrná, J. Anatomical and histochemical changes of Norway spruce buds induced by simulated acid rain. Biol. Plant. 2002, 45, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamidele, J.F.; Eguagie, M.O. Ecophysiological response of Capsicum annuum L. exposed to simulated acid rain. Niger. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yi, L.; Yu, F.; Yin, X. Chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics and the growth response of Elaeocarpus glabripetalus to simulated acid rain. Photosynthetica 2015, 53, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X. Effects and mechanism of acid rain on plant chloroplast ATP synthase. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 18296–18306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, J.; Ma, J.; Yang, J.; Liang, Y.; Ke, Y.; Yao, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Min, X. Effect of simulated acid rain on stability of arsenic calcium residue in residue field. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 42, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Li, R.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Huang, K.; Guan, X.; Wang, S. Short-term response of soil respiration to simulated acid rain in Cunninghamia lanceolata and Michelia macclurei plantations. J. Soils Sedim. 2019, 19, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, J.; Fu, X.; Wang, L.; Teng, W. Growth and physiological response of an endangered tree, Horsfieldia hainanensis merr to simulated sulfuric and nitric acid rain in southern China. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 144, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yi, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, M.; Shao, C.; Lv, Z.; Chena, J.; Liu, Z.; Shen, C. Physiological and biochemical responses of tea seedlings (Camellia sinensis) to simulated acid rain conditions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2020, 192, 110315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cape, J.N. Effects of air pollution on the chemistry of surface waxes of Scots Pine. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1986, 31, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, H.M.; Morton, H.L.; Wharre, J.R. Environmental influences on cuticle development and resultant foliar penetration. Bot. Rev. 1975, 41, 421–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.; Alves, A.; Da Silva, E.; Oliva, M. Effects of simulated acid rain on the growth of five Brazilian tree species and anatomy of the most sensitive species (Joannesia princeps). Aust. J. Bot. 2005, 53, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Anna-Santos, B.; Campos da Silva, L.; Alves, A.; Aguiar, R. Effects of Simulated Acid Rain on Leaf Anatomy and Micromorphology of Genipa americana L. (Rubiaceae). Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2006, 49, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Moreau, M.; Ménascé, D. Urban Resilience: Introducing This Issue and Summarizing the Discussions, Field Actions Science Reports [Online], Special Issue 18 2018, Online since 15 December 2018, Connection on 08 May 2019. Available online: https://journals.openedition.org/factsreports/pdf/4629 (accessed on 2 July 2020).
- Alberti, M.; Marzluff, J.M. Ecological resilience in urban ecosystems: Linking urban patterns to human and ecological functions. Urban. Ecosyst. 2004, 7, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E.A.; Hunt, G.M. Erosion of waxes from leaf surfaces by simulated rain. New Phytol. 1986, 102, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, V.G.; Faskhiev, V.N.; Kovalenko, N.P.; Shestibratov, K.A.; Miroshnikov, A.I. Testing Transgenic Aspen Plants with bar Gene for Herbicide Resistance under Semi-natural Conditions. Acta Nat. 2016, 8, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, V.G.; Krutovsky, K.V.; Shestibratov, K.A. Effect of Phosphinothricin on Transgenic Downy Birch (Betula pubescens Ehrh.) Containing bar or GS1 Genes. Forests 2019, 10, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeld, H.S.; Jernstedt, J.A.; Haines, B.L. Direct foliar effects of simulated acid rain. New Phytol. 1985, 9, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Anna-Santos, B.F.; Campos da Silva, L.; Alves-Azevedo, A.; Marcos de Araújo, J.; Figueiredo-Alves, E.; Monteiro da Silva, E.A.; Aguiar, R. Effects of simulated acid rain on the foliar micromorphology and anatomy of tree tropical species. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2006, 58, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houbao, F.; Chuanrong, L. Effects of simulated acid rain on seedling emergence and growth of five broad-leaved species. J. For. Res. 1999, 10, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.B.; Hang, Y.H. Effects of simulated acid rain on germination, foliar damage, chlorophyll contents and seedling growth of five hardwood species growing in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 126, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.C.; Oliva, M.A.; Azevedo, A.A.; Araújo, J.; Aguiar, M. Micromorphological and anatomical alterations caused by simulated acid rain in Restinga plants: Eugenia uniflora and Clusia hilariana. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2005, 168, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, G.C.; Silva, L.C. Responses of tropical legumes from the Brazilian Atlantic Rainforest to simulated acid rain. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zobel, A.M. Phenolic Compounds Against in Defense Air Pollution. In Plant. Response to Air Pollution, 1st ed.; Yunus, M., Iqbal, M., Eds.; John Wiley: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 241–266. ISBN 0471960616. [Google Scholar]
- Vermerris, W.; Nicholson, R. Biosynthesis of Phenolic Compounds. In Phenolic Compound Biochemistry; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; Chapter 3; pp. 63–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobel, A.; Nighswander, J.E. Accumulation of phenolic compounds in the necrotic areas of Austrian and red pine needles after spraying with sulphuric acid: A possible bioindicator of air pollution. New Phytol. 1991, 117, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoddami, A.; Wilkes, M.A.; Roberts, T.H. Techniques for analysis of plant phenolic compounds. Molecules 2013, 18, 2328–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouguendia, Z.M.; Baschak, L.A. Response of two western Canadian conifers to simulated acidic precipitation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1987, 33, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.M.; Hutchinson, A. Comparison of the Ability of Leaf Surfaces of Three Species to Neutralize Acidic Rain Drops. New Phytol. 1984, 97, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellburn, A. Air Pollution and Acid Rain: The Biological Impact; Longman Scientific & Technical: Essex, NY, USA, 1988; p. 274. ISBN 0-582-01464-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kerstiens, G. Barrier Properties of the Cuticle to Water, Solutes and Pest and Pathogen Penetration in Leaves of Plants Grown in Polluted Atmospheres. In Plant. Response to Air Pollution, 1st ed.; Yunus, M., Iqbal, M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1996; pp. 167–178. [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros, C.D.; Falcaõ, H.M.; Almeida-Cortez, J.; Santos, D.; Santos, M.G. Leaf epicuticular wax content changes under different rainfall regimes, and its removal affects the leaf chlorophyll content and gas exchanges of Aspidosperma pyrifolium in a seasonally dry tropical forest. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 111, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-Andrade, G.; Nalon-Castro, L.; Campos da Silva, L. Micromorphological alterations induced by simulated acid rain on the leaf surface of Joannesia princeps Vell. (Euphorbiaceae). Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogg, G.E. Adhesion of water to the external surfaces of leaves. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1948, 3, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percy, K.E.; Baker, E.A. Effects of simulated acid rain on production, morphology and composition of epicuticular wax and on cuticular membrane development. New Phytol. 1987, 107, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichert, T.; Fernández, V. Uptake and release of elements by leaves and other aerial plant parts. In Marschner’s Mineral. Nutrition of Higher Plants, 3rd ed.; Marschner, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Chatswood, Australia, 2012; pp. 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.T.; Juniper, B.E. The Cuticles of Plants; St. Martin’s Press: New York, NY, USA, 1970; ISBN 713122455. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, L.S.; Curry, T.M. Differential responses of plant foliage to simulated acid rain. Am. J. Bot. 1979, 66, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.; Bhushan, B.; Ensikat, H.J.; Barthlott, W. Self-healing of voids in the wax coating on plant surfaces. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2009, 367, 1673–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Wang, L.; Liao, C.; Fan, C.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X. Combined Effects of Lead and Acid Rain on Photosynthesis in Soybean Seedlings. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 161, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, E.; Dong, D.; Zeng, X.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, X.; De Vries, W. Direct effect of acid rain on leaf chlorophyll content of terrestrial plants in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.F.; Feng, Z.W. Effects of Simulated Acid Rain on Seedlings of Cyclobalano glauca Oerst. In Acid Rain and Agriculture; Yang, H.X., Ed.; China Forestry Press: Beijing, China, 1989; pp. 174–178. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, Y. Effects of simulated acid rain on Pinus densiflora: Inhibition of net photosynthesis by the pheophytization of chlorophyll. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1998, 103, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Tomar, Y.S. Effect of stimulated acid rain on chlorophyll and ascorbic acid contents of Mentha piperata (Pepperiment). Agric. Sci. Digest. 2009, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mathey, J.; Rößler, S.; Lehmann, I.; Bräuer, A. Urban Green Spaces: Potentials and Constraints for Urban Adaptation to Climate Change. In Resilient Cities.Cities and Adaptation to Climate Change, Proceedings of the Global Forum 2010, 1st ed.; Otto-Zimmermann, K., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacalo, A.; Corona, V.; Esparza, N. Árboles Y Arbustos Para Aiudades; Universidad Autónoma. Metropolitana: México D. F., Mexico, 2009; p. 600. ISBN 978-607-477-157-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval, E.; Rojas, A.; Guzmán, C.; Carmona, L.; Ponce, R.; León, C.; Loyola, C.; Vallejo, M.; Medina, A. Técnicas Aplicadas a La Anatomía Vegetal; IBUNAM: México D. F., Mexico, 2005; p. 278. ISBN 9789703231317. [Google Scholar]
- Nagata, M.; Yamashita, I. Simple method for simultaneous determination of chlorophyll and carotenoids in tomato fruit. J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. 1992, 39, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 19 June 2020).




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Sánchez, V.M.; Rosas, U.; Calva-Vásquez, G.; Sandoval-Zapotitla, E. Does Acid Rain Alter the Leaf Anatomy and Photosynthetic Pigments in Urban Trees? Plants 2020, 9, 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9070862
Rodríguez-Sánchez VM, Rosas U, Calva-Vásquez G, Sandoval-Zapotitla E. Does Acid Rain Alter the Leaf Anatomy and Photosynthetic Pigments in Urban Trees? Plants. 2020; 9(7):862. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9070862
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Sánchez, Verónica M., Ulises Rosas, Germán Calva-Vásquez, and Estela Sandoval-Zapotitla. 2020. "Does Acid Rain Alter the Leaf Anatomy and Photosynthetic Pigments in Urban Trees?" Plants 9, no. 7: 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9070862
APA StyleRodríguez-Sánchez, V. M., Rosas, U., Calva-Vásquez, G., & Sandoval-Zapotitla, E. (2020). Does Acid Rain Alter the Leaf Anatomy and Photosynthetic Pigments in Urban Trees? Plants, 9(7), 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9070862





