Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration from Sugi (Japanese Cedar, Cryptomeria japonica D. Don, Cupressaceae) Seed Families by Marker Assisted Selection for the Male Sterility Allele ms1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Somatic Embryogenesis Initiation
2.2. Selection of Male Sterile ECLs
2.3. Maturation of Somatic Embryos
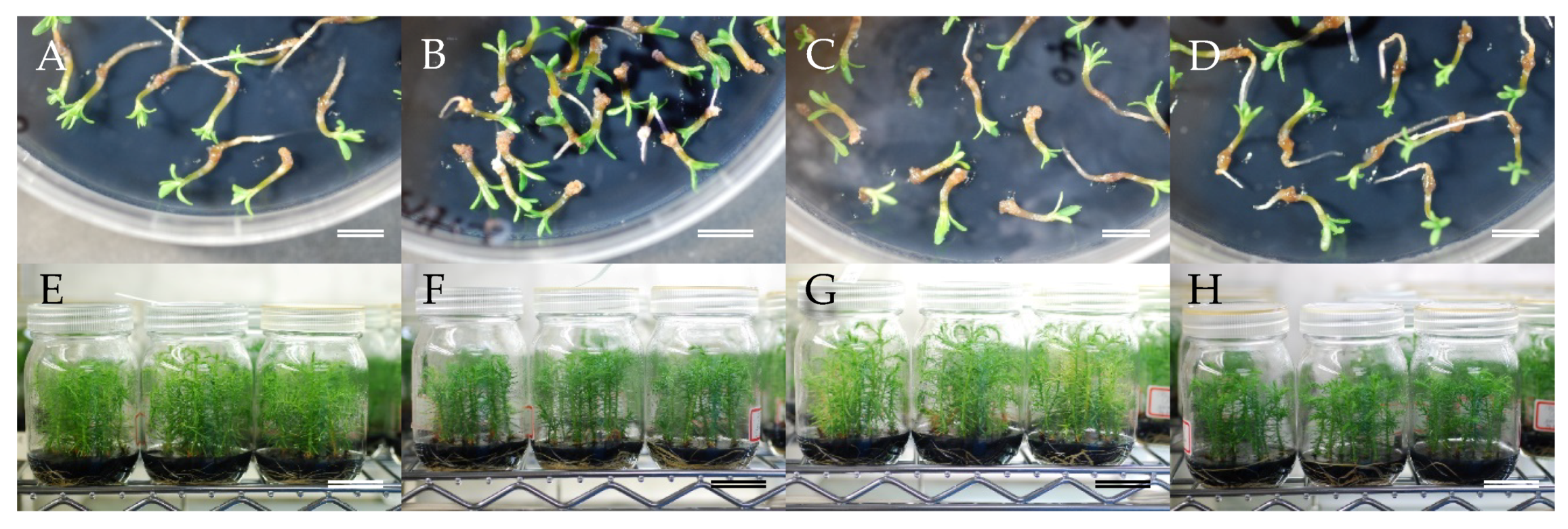
2.4. Regeneration of Somatic Plants
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Initial Explant, Medium, and Culture Conditions
3.2. Maintenance and Proliferation of ECLs
3.3. Selection of Male Sterile ECLs
3.4. Maturation of Somatic Embryos
3.5. Germination and Plant Conversion
3.6. Growth In Vitro and Acclimatization of Somatic Plants
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taira, H.; Teranishi, H.; Kenda, Y. A case study of male sterility in sugi (Cryptomeria japonica). J. Jpn. For. Soc. 1993, 75, 377–379, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi, M.; Watanabe, J.; Saito, Y.; Ozawa, H.; Saito, N.; Furukawa, S.; Ishii, Y. Breeding of Cryptomeria japonica for the countermeasure of pollinosis. Bull. Fukushima Prefect. For. Res. Centre. 2006, 39, 1–9. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Saito, M. Development status and future prospect of non-pollen cedar. For. Sci. 2008, 54, 17–20. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Ueno, S.; Matsumoto, A.; Ujino-Ihara, T.; Uchiyama, K.; Totsuka, S.; Iwai, J.; Hakamata, T.; Moriguchi, Y. Fine mapping of the male-sterile genes (MS1, MS2, MS3, and MS4) and development of SNP markers for marker-assisted selection in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taira, H.; Saito, M.; Furuta, Y. Inheritance of the trait of male sterility in Cryptomeria japonica. J. For. Res. 1999, 4, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, E. Study for the Characteristics and Applications of Nuclear Male Sterility in Cryptomeria Japonica D. Don. Ph.D. Thesis, Niigata University, Niigata, Japan, March 2007. (In Japanese). [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima, D.; Yoshii, E.; Hosoo, Y.; Taira, H. Cytological and genetic studies on male sterility in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don (Shindai 8). J. Jpn. For. Soc. 2010, 92, 106–109, (In Japanese with English Summary). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriguchi, Y.; Ujino-Ihara, T.; Uchiyama, K.; Futamura, N.; Saito, M.; Ueno, S.; Matsumoto, A.; Tani, N.; Taira, H.; Shinohara, K.; et al. The construction of a high-density linkage map for identifying SNP markers that are tightly linked to a nuclear-recessive major gene for male sterility in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriguchi, Y.; Ueno, S.; Higuchi, Y.; Miyajima, D.; Itoo, S.; Futamura, N.; Tsumura, Y. Establishment of a microsatellite panel covering the sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) genome, and its application for localization of a male sterile gene (ms-2). Mol. Breed. 2014, 33, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriguchi, Y.; Uchiyama, K.; Ueno, S.; Ujino-Ihara, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Iwai, J.; Miyajima, D.; Saito, M.; Sato, M.; Tsumura, Y.; et al. A high-density linkage map with 2,560 markers and its application for the localization of the male-sterile genes ms3 and ms4 in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. Tree Genet. Genom. 2016, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, K.; Hirao, T.; Tsubomura, M.; Tamura, M.; Kurita, M.; Nose, M.; Hanaoka, S.; Takahashi, M.; Watanabe, A. Identification of novel putative causative genes and genetic marker for male sterility in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don). BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, S.; Uchiyama, K.; Moriguchi, Y.; Ujino-Ihara, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Wei, F.J.; Saito, M.; Higuchi, Y.; Futamura, N.; Kanamori, H.; et al. Scanning RNA-Seq and RAD-Seq approach to develop SNP markers closely linked to MALE STERILITY 1 (MS1) in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. Breed. Sci. 2019, 69, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Ueno, S.; Fu-Jin, W.; Matsumoto, A.; Ujino-Ihara, T.; Uchiyama, K.; Moriguchi, Y.; Kasahara, M.; Fujino, T.; Shigenobu, S.; et al. Development of diagnostic PCR and LAMP markers for MALE STERILITY 1 (MS1) in Cryptomeria japonica D Don. BMC Res. Note 2020. (under review). [Google Scholar]
- Moriguchi, Y.; Ueno, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Tadama, T.; Watanabe, M.; Saito, R.; Hirayama, S.; Iwai, J.; Konno, Y. Marker-assisted selection of trees with MALE STERILITY 1 in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. Forests 2020, 11, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Teranishi, H. A breeding strategy of male sterile Cryptomeria japonica D. Don cultivars. Jpn. J. Palynol. 2014, 60, 27–35, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shidei, T.; Akai, T.; Ichikawa, S. Flower bud formation on Sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) and Metasequoia (Metasequoia glyptosytoboides) by gibberellic acid treatment. J. Jpn. For. Soc. 1959, 41, 312–315. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Nagao, A. Differences of flower initiation of Cryptomeria japonica under various alternating temperatures. J. Jap. For. Soc. 1983, 65, 335–338, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Isikawa, H. In vitro formation of adventitious bud and root on the hypocotyl of Cryptomeria japonica. Bot. Mag. Tokyo 1974, 87, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T. Search for the synthetic media suitable for embryo culture of Cryptomeria and Japanese black pine. J. Jpn. For. Soc. 1978, 60, 81–86, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Morohoshi, N. Tissue culture of sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) and properties of callus-lignin. Bull. Exp. For. Tokyo Univ. Agricult. Technol. 1983, 19, 39–46. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Isikawa, H. In vitro culture of forest tree calluses and organs. JARQ 1984, 18, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, T. The in vitro plantlet regeneration following induction of adventitious buds on various tissues from small sugi seedlings. J. Jpn. For. Soc. 1986, 68, 389–392. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isikawa, H. Generation of adventitious plant organs by tissue culture methods in forest trees. Bull. For. For. Prod. Res. Inst. 1987, 343, 119–153. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Isikawa, H. In vitro culture of Cryptomeria callus and organs. In Cell and Tissue Culture in Forestry, Case Histories: Gymnosperms, Angiosperms and Palms; Bonga, J.M., Durzan, D.J., Eds.; Martinus Nijhoff Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987; Volume 3, pp. 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, T. Basic studies of organ and callus culture in woody plants. Bull. For. Prod. Res. Inst. 1991, 360, 35–119, (In Japanese with English Summary). [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima, T. Tissue culture of Cryptomeria japonica, Chamaecyparis obtusa, Pinus densiflora and P. thunbergii. Bull. Shimane Pref. For. Res. Cen. 1993, 44, 13–26. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Mikawa, K. Tissue culture of sugi. Bull. Yamagata Pref. For. Res. Cen. 1994, 24, 19–24. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, T.; Kondo, K. In vitro clonal propagation of Cryptomeria japonica from current stem segments. J. Jpn. For. Soc. 1997, 79, 246–248. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Hine-Gómez, A.; Valverde-Cerdas, L. Establecimiento in vitro de Cryptomeria japonica (Taxocidaceae). Rev. Biol. Trop. 2003, 51, 683–690, (In Espanish with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ogita, S.; Ishikawa, H.; Kubo, T.; Sasamoto, H. Somatic embryogenesis from immature and mature zygotic embryos of Cryptomeria japonica I: Embryogenic cell induction and its morphological characteristics. J. Wood. Sci. 1999, 45, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogita, S.; Sasamoto, H.; Kubo, T. Selection and microculture of single embryogenic cell clusters in Japanese conifers: Picea jezoensis, Larix leptolepis and Cryptomeria japonica. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 1999, 35, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Kondo, T. Difference in ability of initiation and maintenance of embryogenic cultures among sugi (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don) seed families. Plant Biotechnol. 2000, 17, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, E.; Tanaka, T.; Hosoi, Y.; Ishii, K.; Morohoshi, N. Embryogenic cell culture, protoplast regeneration, cryopreservation, biolistic gene transfer and plant regeneration in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don). Plant Biotechnol. 2000, 17, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, K.; Maruyama, E.; Hosoi, Y. Somatic embryogenesis of Japanese conifers. In Molecular Breeding of Woody Plants; Morohoshi, N., Komamine, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Ogita, S.; Sasamoto, H.; Yeung, E.C.; Thorpe, T. The effects of glutamine on the maintenance of embryogenic cultures of Cryptomeria japonica. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2001, 37, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igasaki, T.; Sato, T.; Akashi, N.; Mohri, T.; Maruyama, E.; Kinoshita, I.; Walter, C.; Shinohara, K. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature zygotic embryos of Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. Plant Cell Rep. 2003, 22, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igasaki, T.; Akashi, N.; Ujino-Ihara, T.; Matsubayashi, Y.; Sakagami, Y.; Shinohara, K. Phytosulfokine stimulates somatic embryogenesis in Cryptomeria japonica. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 1412–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, R.; Ogita, S.; Kubo, T.; Funada, R. Effect of polyamines and L-ornithine on the development of proembryogenic masses of Cryptomeria japonica. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2006, 85, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, E.; Hosoi, Y. Polyethylene glycol enhance somatic embryo production in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don). Prop. Ornam. Plants 2007, 7, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa, T.; Tsubomura, M.; Taniguchi, T. Development of mass production technology for non-pollen cedar. For. Prod. Res. Inst. Select. Res. Results 2010, 2010, 64–65. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, K.; Hosoi, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Tsubomura, M.; Kondo, T.; Yamada, H.; Saito, M.; Suda, T.; Fukisawa, T.; Tanaka, K.; et al. In vitro culture of various genotypes of male sterile Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don). Plant Biotechnol. 2011, 28, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, E.T.; Hosoi, Y.; Futamura, N.; Saito, M. Initiation of embryogenic cultures from immature seeds of pollen-free sugi (Cryptomeria japonica). Kanto Shinrin Kenkyu 2014, 65, 107–110, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, E.T.; Miyazawa, S.; Ueno, S.; Onishi, N.; Totsuka, S.; Iwai, J.; Moriguchi, Y. Differences among families on embryogenic cell induction from seed of pollen-free sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) produced at the Niigata prefecture. Kanto Shinrin Kenkyu 2018, 69, 1–2, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, E.T.; Hosoi, Y.; Miyazawa, S.; Ueno, S.; Onishi, N.; Totsuka, S.; Iwai, J.; Moriguchi, Y. Pollen-free plant regeneration from embryogenic cells derived from sugi (Cryptomeria japonica). Kanto Shinrin Kenkyu 2019, 70, 37–40, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Finer, J.J.; Kriebel, H.B.; Becwar, M.R. Initiation of embryogenic callus and suspension cultures of eastern white pine (Pinus strobus L.). Plant Cell Rep. 1989, 8, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimaszewska, K.; Park, Y.S.; Overton, C.; MacEacheron, I.; Bonga, J.M. Optimized somatic embryogenesis in Pinus strobus L. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant. 2001, 37, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, C.; Goncalves, S.; Tereso, S.; Marum, L.; Maroco, J.; Oliveira, M. Somatic embryogenesis from 20 open-pollinated families of Portuguese plus trees of maritime pine. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2004, 76, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, C.L.; Reeves, C.B.; Find, J.I.; Gough, K.; Josekutty, P.; Skudder, D.B.; van der Maas, S.A.; Sigley, M.R.; Menzies, M.I.; Low, C.B.; et al. Improving initiation, genotype capture, and family representation in somatic embryogenesis of Pinus radiata by a combination of zygotic embryo maturity, media, and explant preparation. Can. J. For. Res. 2009, 39, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán, I.A.; de Diego, N.; Moncaleán, P. Enhancing initiation and proliferation in radiata pine (Pinus radiata D. Don) somatic embryogenesis through seed family screening, zygotic embryo staging and media adjustments. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2012, 34, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán, I.A.; Setien-Olarra, A.; Hargreaves, C.L.; Moncaleán, P. Somatic embryogenesis in Pinus halepensis Mill.: An important ecological species from the Mediterranean forest. Trees 2013, 27, 1339–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Find, J.I.; Hargreaves, C.L.; Reeves, C.B. Progress towards initiation of somatic embryogenesis from differentiated tissues of radiata pine (Pinus radiata D. Don) using cotyledonary embryos. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant. 2014, 50, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberini, S.; Danti, R.; Lambardi, M. Somatic plant regeneration from selected common cypress (Cupressus sempervirens L.) clones resistant to the bark canker disease. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2016, 124, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.H.; Tull, R.A.; Montello, P.M.; Merkle, S.A. A clonal propagation system for Atlantic white cedar (Chamaecyparis thyoides) via somatic embryogenesis without the use of plant growth regulators. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2017, 130, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Sun, Y.; Wu, B.; Duan, H.; Zheng, H.; Hu, D.; Lin, H.; Tong, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Somatic embryogenesis of immature Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook zygotic embryos. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahn, C.H.; Choi, Y.E. In vitro clonal propagation and stable cryopreservation system for Platycladus orientalis via somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2017, 131, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, C.; Hargreaves, C.; Trotin, J.F.; Lelu-Walter, M.A. Simple and efficient protocols for the initiation and proliferation of embryogenic tissue of Douglas-fir. Trees 2018, 32, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriguchi, Y.; Ueno, S.; Saito, M.; Higuchi, Y.; Miyajima, D.; Itoo, S.; Tsumura, Y. A simple allele-specific PCR marker for identifying male-sterile trees: Towards DNA marker-assisted selection in the Cryptomeria japonica breeding program. Tree Genet. Genom. 2014, 10, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Ueno, S.; Wei, F.J.; Matsumoto, A.; Uchiyama, K.; Ujino-Ihara, T.; Hakamata, T.; Fujino, T.; Kasahara, M.; Bino, T.; et al. Identification and genetic diversity analysis of a male-sterile gene MS1 in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don). BioRxiv 2020, 2020, 2005–2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Ueno, S.; Wei, F.J.; Matsumoto, A.; Ujino-Ihara, T.; Uchiyama, K.; Moriguchi, Y.; Kasahara, M.; Fujino, T.; Shigenobu, S.; et al. Development of diagnostic PCR and LAMP markers for MALE STERILITY 1 (MS1) in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. BioRxiv 2020, 2020, 2005–2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lelu-Walter, M.A.; Bernier-Cardou, M.; Klimaszewska, K. Simplified and improved somatic embryogenesis for clonal propagation of Pinus Pinaster. Plant Cell Rep. 2006, 25, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán, I.A.; De Diego, N.; Moncaleán, P. Bottlenecks in Pinus radiata somatic embryogenesis: Improving maturation and germination. Trees 2010, 24, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Moon, H.K. Enhancement of somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Japanese red pine. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2014, 8, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Moon, H.K. Enhancement of somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Japanese larch (Larix leptolepis). Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2007, 88, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelu-Walter, M.A.; Pãques, L.E. Simplified and improved somatic embryogenesis of hybrid larches (Larix x eurolepis and Larix × marschlinsii). Perspectives for breeding. Ann. For. Sci. 2009, 66, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczygiel, K.; Hazubska-Przybyl, T.; Bojarczuk, K. Somatic embryogenesis of selected coniferous tree species of the genera Picea, Abies and Larix. Acta Soc. Botan. Polon. 2007, 76, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Pullman, G.S.; Olson, K.; Fisher, T.; Egertdotter, U.; Frampton, J.; Bucalo, K. Fraser fir somatic embryogenesis: High frequency initiation, maintenance, embryo development, germination and cryopreservation. New For. 2016, 47, 453–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Kurita, M.; Itahana, N.; Kondo, T. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature zygotic embryos of Hinoki cypress (Chamaecyparis obtusa Sieb. et Zucc.). Plant Cell Rep. 2004, 23, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, E.; Ishii, K.; Hosoi, Y. Efficient plant regeneration of Hinoki cypress (Chamaecyparis obtusa Sieb. et Zucc.) via somatic embryogenesis. J. For. Res. 2005, 10, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, E.; Hosoi, Y.; Ishii, K. Somatic embryo production and plant regeneration of Japanese black pine (Pinus thunbergii). J. For. Res. 2005, 10, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, E.; Hosoi, Y.; Ishii, K. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeration in Yakutanegoyou, Pinus armandii Franch. var. amamiana (Koidz.) Hatusima, an endemic and endangered species in Japan. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant. 2007, 43, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, E.; Hosoi, Y.; Ishii, K. Somatic embryogenesis in Sawara cypress (Chamaecyparis pisifera Sieb. et Zucc.) for stable and efficient plant regeneration, propagation and protoplast culture. J. For. Res. 2002, 7, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhkov, P.V.; von Arnold, S. Polyethylene glycol promotes maturation but inhibits further development of Picea abies somatic embryos. Physiol. Plant. 1998, 104, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, E.T.; Hosoi, Y. Progress in somatic embryogenesis of Japanese pines. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoi, Y.; Maruyama, T.E. Plant regeneration from embryogenic tissue of Pinus luchuensis Mayr, and endemic species in Ryukyu island, Japan. Plant Biotechnol. 2012, 29, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruyama, T.E.; Hosoi, Y. Post-maturation treatments improves and synchronizes somatic embryo germination of three species of Japanese pines. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ. Cult. 2012, 110, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Chavez, A.; Flinn, B.S.; Egertsdotter, U. Initiation of somatic embryogenesis from immature zygotic embryos of Oocarpa pine (Pinus oocarpa Schiede ex Schlectendal). Tree Physiol. 2011, 31, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimaszewska, K.; Trontin, J.F.; Becwar, M.R.; Devillard, C.; Park, Y.S.; Lelu-Walter, M.A. Recent progress in somatic embryogenesis of four Pinus spp. Tree For. Sci. Biotechol. 2007, 1, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, N.B.; van Staden, J. Improved somatic embryo production from embryogenic tissue of Pinus patula. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant. 2001, 37, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.K.; Amerson, H.V. Slash pine (Pinus elliottii Engelm.) somatic embryogenesis II. Maturation of somatic embryos and plant regeneration. New For. 1995, 10, 165–182. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.K.; Juan, I.P. Improving the germination of somatic embryos of Picea morrisonicola Hayata: Effects of cold storage and partial drying. J. For. Res. 2015, 20, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pond, S.E.; von Aderkas, P.; Bonga, J.M. Improving tolerance of somatic embryos of Picea glauca to flash desiccation with a cold treatment (desiccation after cold acclimation). In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant. 2002, 38, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attree, S.M.; Pomeroy, M.K.; Fowke, L.C. Development of white spruce (Picea glauca (Moench.) Voss) somatic embryos during culture with abscisic acid and osmoticum, and their tolerance to drying and frozen storage. J. Exp. Bot. 1995, 46, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.R.; Sutton, B.C.S.; Flinn, B.S. Synchronous and high frequency germination of interior spruce somatic embryos following partial drying at high relative humidity. Can. J. Bot. 1990, 68, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelu, M.A.; Klimaszewska, K.; Pflaum, G.; Bastien, C. Effect of maturation duration on desiccation tolerance in hybrid larch (Larix x leptoeuropaea Dengler) somatic embryos. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant. 1995, 31, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zheng, R.; Liu, G.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Laux, T.; Zhen, Y.; Harding, S.A.; Shi, J.; Chen, J.; et al. Desiccation treatment and endogenous IAA levels are key factors influencing high frequency somatic embryogenesis in Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaneeda, T.; Maruyama, T.; Onishi, N.; Totsuka, S.; Moriguchi, Y. Trait evaluation of pollen-free sugi plants produced by tissue culture. In Proceedings of the 130th Japan Forest Society Conference, Niigata University, Niigata, Japan, 20–23 March 2019; p. 132. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, S.; Moriguchi, Y.; Taira, H. Comparison of traits between male sterile and fertile Cryptomeria japonica D. Don trees in selected stands. J. Jpn. For. Soc. 2009, 91, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullman, G.S.; Buchanan, M. Loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.): Stage-specific elemental analysis of zygotic embryo and female gametophyte tissue. Plant Sci. 2003, 164, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.P. Adjusted p-values for simultaneous inference. Biometrics 1992, 48, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ebbert, D. Chisq.posthoc.test: A Post Hoc Analysis for Pearson’s Chi-Squared Test for Count Data. R Package Vers. 0.1.2. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=chisq.posthoc.test (accessed on 23 July 2020).







| Seed Family | SE Initiation Frequency by Seed Collection Date | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 03 | July 10 | July 18 | July 24 | All Collections | |
| ♀ ‘Shindai 3’ ♂ ‘Suzu 2’ | 54/156 (34.62) | 90/191 (47.12) | 101/192 (52.60) | 39/168 (23.21) | 284/707 (40.17) *** |
| ♀ ‘Fukushima-funen 1’ ♂ ‘S3-37(1)’ | 2/324 (0.62) | 25/240 (10.42) | 37/276 (13.41) | 17/216 (7.87) | 81/1056 (7.67) *** |
| ♀ ‘Fukushima-funen 1’ ♂ ‘Oi 7’ | 11/156 (7.05) | 144/432 (33.33) | 115/204 (56.37) | 85/144 ( 59.03) | 355/936 (37.93) *** |
| ♀ ‘Fukushima-funen 1’ ♂ ‘S3-118(2)’ | 29/120 (24.17) | 55/180 (30.56) | 136/249 (54.62) | 196/468 (41.88) | 416/1017 (40.90) *** |
| All families | 96/756 (12.70) *** | 314/1043 (30.11) ns | 389/921 (42.24) *** | 337/996 (33.84) ns | 1136/3716 (30.57) |
| Family | Analyzed ECLs | Male Fertile ECLs | Male Sterile ECLs | Doubted ECLs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Shindai 3’ בSuzu 2’ | 160 | 82 | 71 | 7 |
| ‘Fukushima-funen 1’ × ‘S3-37(1)’ | 136 | 83 | 43 | 10 |
| ‘Fukushima-funen 1’ × ‘Oi 7’ | 160 | 69 | 76 | 15 |
| ‘Fukushima-funen 1’ × ‘S3-118(2)’ | 160 | 100 | 46 | 14 |
| Total | 616 | 334 | 236 | 46 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maruyama, T.E.; Ueno, S.; Hirayama, S.; Kaneeda, T.; Moriguchi, Y. Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration from Sugi (Japanese Cedar, Cryptomeria japonica D. Don, Cupressaceae) Seed Families by Marker Assisted Selection for the Male Sterility Allele ms1. Plants 2020, 9, 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9081029
Maruyama TE, Ueno S, Hirayama S, Kaneeda T, Moriguchi Y. Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration from Sugi (Japanese Cedar, Cryptomeria japonica D. Don, Cupressaceae) Seed Families by Marker Assisted Selection for the Male Sterility Allele ms1. Plants. 2020; 9(8):1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9081029
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaruyama, Tsuyoshi E., Saneyoshi Ueno, Satoko Hirayama, Takumi Kaneeda, and Yoshinari Moriguchi. 2020. "Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration from Sugi (Japanese Cedar, Cryptomeria japonica D. Don, Cupressaceae) Seed Families by Marker Assisted Selection for the Male Sterility Allele ms1" Plants 9, no. 8: 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9081029
APA StyleMaruyama, T. E., Ueno, S., Hirayama, S., Kaneeda, T., & Moriguchi, Y. (2020). Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration from Sugi (Japanese Cedar, Cryptomeria japonica D. Don, Cupressaceae) Seed Families by Marker Assisted Selection for the Male Sterility Allele ms1. Plants, 9(8), 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9081029






