Medicinal Properties of Lilium candidum L. and Its Phytochemicals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bioinformatic Assessment
4.2. Preparation of Plant Material
4.3. GC-MS Analysis
4.4. Cell Cultures
4.5. Cytotoxicity Examination
4.6. Measurement of Anti-Diabetic Activity
4.7. Measurement of Interleukin Release
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robbins, G.R.; Wen, H.; Ting, J.P. Inflammasomes and metabolic disorders: Old genes in modern diseases. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Accardi, G.; Virruso, C.; Balistreri, C.R.; Emanuele, F.; Licastro, F.; Monastero, R.; Porcellini, E.; Vasto, S.; Verga, S.; Caruso, C.; et al. SHIP2: A “new” insulin pathway target for aging research. Rejuvenation Res. 2014, 17, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thammisetty, S.S.; Pedragosa, J.; Weng, Y.C.; Calon, F.; Planas, A.; Kriz, J. Age-related deregulation of TDP-43 after stroke enhances NF-κB-mediated inflammation and neuronal damage. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Bang, E.; Arulkumar, R.; Ha, S.; Chung, K.W.; Park, M.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Yu, B.P.; Chung, H.Y. Senoinflammation: A major mediator underlying age-related metabolic dysregulation. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 134, 110891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, I.M.; Gibson, D.S.; McGilligan, V.; McNerlan, S.E.; Alexander, H.D.; Ross, O.A. Age and Age-Related Diseases: Role of Inflammation Triggers and Cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarmolinsky, L.; Budovsky, A.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Khalfin, B.; Gorelick, J.; Bishitz, Y.; Miloslavski, R.; Yarmolinsky, L. Recent updates on the phytochemistry and pharmacological properties of Phlomis viscosa Poiret. Rejuvenation Res. 2019, 22, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budovsky, A.; Fraifeld, V.E. Medicinal plants growing in the Judea region network approach for searching potential therapeutic targets. Netw. Biol. 2012, 2, 84–94. [Google Scholar]
- Budovsky, A.; Shteinberg, A.; Maor, H.; Duman, O.; Yanai, H.; Wolfson, M.; Fraifeld, V.E. Uncovering the geroprotective potential of medicinal plants from the Judea region of Israel. Rejuvenation Res. 2014, 17, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisenreichova, E.; Haladova, M.; Mucaji, P.; Budĕsínský, M.; Ubik, K. A new steroidal saponin from the bulbs of Lilium candidum. Pharmazie 2000, 55, 549–550. [Google Scholar]
- Jarić, S.; Mačukanović-Jocić, M.; Djurdjević, L.; Mitrović, M.; Kostić, O.; Karadžić, B.; Pavlović, P. An ethnobotanical survey of traditionally used plants on Suva Planina mountain (south-eastern Serbia). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 175, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigat, M.; Vallès, J.; Gras, A.; Iglésias, J.; Garnatje, T. Plants with topical uses in the ripollès district (Pyrenees, Catalonia, Iberian Peninsula): Ethnobotanical survey and pharmacological validation in the literature. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 164, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruni, A.; Ballero, M.; Poli, F. Quantitative ethnopharmacological study of the campidano valley and urzulei district, Sardinia, Italy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1997, 57, 97–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieroni, A. Medicinal plants and food medicines in the folk traditions of the upper Lucca province, Italy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 70, 235–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinbrun-Dothan, N.; Danin, A.L. Candidum . In Analytical Flora of Eretz-Israel; Plitman, U., Ed.; CANA Publishing: Jerusalem, Israel, 1991; p. 779. [Google Scholar]
- Polunin, O. Flowers of Greece and the Balkans; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; pp. 1–592. [Google Scholar]
- Mouterde, P. Lilium candidum. In Nouvelle Flore du Liban et de la Syrie; Imprimerie, C., Ed.; Editions de l’Impr. Catholique: Beyrouth, Lebanon, 1966; Volume 1, p. 236. [Google Scholar]
- Zaccai, M.; Ram, A.; Mazor, I. Lilium candidum: Flowering characterization of wild Israeli ecotypes. Israel J. Plant Sci. 2010, 57, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, N.; Huleihel, M.; Zaccai, M. Stress conditions during plant growth increase the anti-herpetic properties of Lilium candidum leaf extracts and fractions. J. Med. Plants Res. 2015, 9, 954–961. [Google Scholar]
- Trinetta, V.; Morgan, M.T.; Coupland, J.N.; Yucel, U. Essential oils against pathogen and spoilage microorganisms of fruit juices: Use of versatile antimicrobial delivery systems. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, C.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Caddeo, C.; Silva, A.M.; Musumeci, T.; Pignatello, R.; Puglisi, G.; Souto, E.B. Mediterranean essential oils as precious matrix components and active ingredients of lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 217–226. [Google Scholar]
- Bruni, N.; Stella, B.; Giraudo, L.; Della Pepa, C.; Gastaldi, D.; Dosio, F. Nanostructured delivery systems with improved leishmanicidal activity: A critical review. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5289–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben-Shabat, S.; Yarmolinsky, L.; Porat, D.; Dahan, A. Antiviral effect of phytochemicals from medicinal plants: Applications and drug delivery strategies. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mucaji, P.; Hudecova, D.; Haladová, M.; Eisenreichová, E. Anti-yeast activity of ethanol extracts of Lilium candidum L. Ceska Slov. Farm. Cas. Ceske Farm. Spol. Slov. Farm. Spol. 2002, 51, 297–300. [Google Scholar]
- Galova, E.; Kopaskova, M.; Sevcovicova, A.; Hadjo, L.; Yankulova, B.; Gregan, F.; Chankova, S.; Miadokova, E. The role of antioxidants from Lilium candidum L. and Salvia officinalis L. Extracts in phytomedicine. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 205, S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokgun, O.; Akca, H.; Mammadov, R.; Aykurt, C.; Deniz, G. Convolvulus galaticus, Crocus antalyensis, and Lilium candidum extracts show their antitumor activity through induction of p53-mediated apoptosis on human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 cells. J. Med. Food 2012, 15, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarmolinsky, L.; Zaccai, M.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Mills, D.; Huleihel, M. Antiviral activity of ethanol extracts of Ficus binjamina and Lilium candidum in vitro. New Biotechnol. 2009, 26, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolaños, V.; Díaz-Martínez, A.; Soto, J.; Marchat, L.A.; Sanchez-Monroy, V.; Ramírez-Moreno, E. Kaempferol inhibits Entamoeba histolytica growth by altering cytoskeletal functions. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2015, 204, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Park, S.E.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, S. Kaempferol inhibits thrombosis and platelet activation. Biochimie 2015, 115, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, K.P.; Malar, D.S.; Nabavi, S.F.; Sureda, A.; Xiao, J.; Nabavi, S.M.; Daglia, M. Kaempferol and inflammation: From chemistry to medicine. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, M.H.; Jia, Y.; Mok, B.; Jun, H.J.; Hwang, K.Y.; Lee, S.J. Kaempferol ameliorates symptoms of metabolic syndrome by regulating activities of liver x receptor-β. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Z. Kaempferol inhibits fibroblast collagen synthesis, proliferation and activation in hypertrophic scar via targeting tgf-β receptor type i. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Park, S.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Antika, L.D.; Habibah, N.Y.; Kang, M.K.; Kang, Y.H. Dietary compound kaempferol inhibits airway thickening induced by allergic reaction in a bovine serum albumin-induced model of asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 29980–29995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suchal, K.; Malik, S.; Gamad, N.; Malhotra, R.K.; Goyal, S.N.; Bhatia, J.; Arya, D.S. Kampeferol protects against oxidative stress and apoptotic damage in experimental model of isoproterenol-induced cardiac toxicity in rats. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchal, K.; Malik, S.; Gamad, N.; Malhotra, R.K.; Goyal, S.N.; Chaudhary, U.; Bhatia, J.; Ojha, S.; Arya, D.S. Kaempferol attenuates myocardial ischemic injury via inhibition of mapk signaling pathway in experimental model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7580731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alves, S.; Duarte, A.; Sousa, S.; Domingues, F.C. Study of the major essential oil compounds of coriandrum sativum against acinetobacter baumannii and the effect of linalool on adhesion, biofilms and quorum sensing. Biofouling 2016, 32, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutra, F.L.; Oliveira, M.M.; Santos, R.S.; Silva, W.S.; Alviano, D.S.; Vieira, D.P.; Lopes, A.H. Effects of linalool and eugenol on the survival of Leishmania (L.) infantum chagasi within macrophages. Acta Trop. 2016, 164, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Yang, Y.J.; Li, Y.S.; Zhang, W.K.; Tang, H.B. A-pinene, linalool, and 1-octanol contribute to the topical anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of frankincense by inhibiting cox-2. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 179, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehri, S.; Meshki, M.A.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Linalool as a neuroprotective agent against acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in wistar rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 38, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Seol, G.H.; Ryu, S.; Choi, I.Y. Neuroprotective effects of (−)-linalool against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced neuronal injury. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2016, 39, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabogal-Guáqueta, A.M.; Osorio, E.; Cardona-Gómez, G.P. Linalool reverses neuropathological and behavioral impairments in old triple transgenic alzheimer’s mice. Neuropharmacology 2016, 102, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seol, G.H.; Kang, P.; Lee, H.S.; Seol, G.H. Antioxidant activity of linalool in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. BMC Neurol. 2016, 16, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souto-Maior, F.N.; Fonsêca, D.V.D.; Salgado, P.R.R.; Monte, L.D.O.; de Sousa, D.P.; de Almeida, R.N. Antinociceptive and anticonvulsant effects of the monoterpene linalool oxide. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Du, E.J.; Ahn, T.J.; Choi, M.S.; Kwon, I.; Kim, H.W.; Kwon, J.Y.; Kang, K. The mosquito repellent citronellal directly potentiates drosophila trpa1, facilitating feeding suppression. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 911. [Google Scholar]
- Maßberg, D.; Simon, A.; Häussinger, D.; Keitel, V.; Gisselmann, G.; Conrad, H.; Hatt, H. Monoterpene (−)-citronellal affects hepatocarcinoma cell signaling via an olfactory receptor. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 566, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Fatima, Z.; Hameed, S. Citronellal-induced disruption of membrane homeostasis in Candida albicans and attenuation of its virulence attributes. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2016, 49, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basha, R.H.; Sankaranarayanan, C. Β-caryophyllene, a natural sesquiterpene lactone attenuates hyperglycemia mediated oxidative and inflammatory stress in experimental diabetic rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 245, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, C.C.; de Oliveira, C.V.; Grigoletto, J.; Ribeiro, L.R.; Funck, V.R.; Grauncke, A.C.B.; de Souza, T.L.; Souto, N.S.; Furian, A.F.; Menezes, I.R.A. Anticonvulsant activity of β-caryophyllene against pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures. Epilepsy Behav. 2016, 56, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Giacomo, S.; Mazzanti, G.; Di Sotto, A. Mutagenicity of cigarette butt waste in the bacterial reverse mutation assay: The protective effects of β-caryophyllene and β-caryophyllene oxide. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidyt, K.; Fiedorowicz, A.; Strządała, L.; Szumny, A. Β-caryophyllene and β-caryophyllene oxide—Natural compounds of anticancer and analgesic properties. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3007–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, M.; Benelli, G. A-humulene and β-elemene from syzygium zeylanicum (myrtaceae) essential oil: Highly effective and eco-friendly larvicides against anopheles subpictus, aedes albopictus, and culex tritaeniorhynchus (diptera: Culicidae). Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2771–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, M.; Rajeswary, M.; Hoti, S.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Benelli, G. Eugenol, α-pinene and β-caryophyllene from plectranthus barbatus essential oil as eco-friendly larvicides against malaria, dengue and japanese encephalitis mosquito vectors. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelany, M.E.; Abdallah, M.A. Protective effects of combined β-caryophyllene and silymarin against ketoprofen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 94, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, S.; Javed, H.; Azimullah, S.; Haque, M.E. Β-caryophyllene, a phytocannabinoid attenuates oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, glial activation, and salvages dopaminergic neurons in a rat model of parkinson disease. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 418, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieri, F.A.; Souza, M.C.; Vermelho, L.L.; Vermelho, M.L.; Perciano, P.G.; Vargas, F.S.; Borges, A.P.; da Veiga-Junior, V.F.; Moreira, M.A. Use of β-caryophyllene to combat bacterial dental plaque formation in dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, X.; Peng, J.; Zhong, J.; Yang, M.; Pang, J.; Lou, J.; Li, M.; An, R.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, L. B-caryophyllene protects in vitro neurovascular unit against oxygen-glucose deprivation and re-oxygenation-induced injury. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, Y.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Wu, K.W.; Chung, J.G.; Lu, C.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Wu, T.S.; Yang, J.S. Death receptor 5-mediated TNFR family signaling pathways modulate γ-humulene-induced apoptosis in human colorectal cancer HT29 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 25, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rogerio, A.P.; Andrade, E.L.; Leite, D.F.; Figueiredo, C.P.; Calixto, J.B. Preventive and therapeutic anti-inflammatory properties of the sesquiterpene α-humulene in experimental airways allergic inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldissera, M.D.; Souza, C.F.; Grando, T.H.; Moreira, K.L.; Schafer, A.S.; Cossetin, L.F.; da Silva, A.P.; da Veiga, M.L.; da Rocha, M.I.; Stefani, L.M.; et al. Nerolidol-loaded nanospheres prevent behavioral impairment via ameliorating Na+, K+-ATPase and AChE activities as well as reducing oxidative stress in the brain of Trypanosoma evansi-infected mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2017, 390, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.O.G.; Leite, L.L.R.; de Lima, I.S.; Barreto, H.M.; Nunes, L.C.C.; Ribeiro, A.B.; Osajima, J.A.; da Silva Filho, E.C. Chitosan Hydrogel in combination with Nerolidol for healing wounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Azimullah, S.; Abul Khair, S.B.; Ojha, S.; Haque, M.E. Neuroprotective effect of nerolidol against neuroinflammation and oxidative stress induced by rotenone. BMC Neurosci. 2016, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, D.; Pahwa, P.; Goel, R.K. Protective effect of nerolidol against pentylenetetrazol-induced kindling, oxidative stress and associated behavioral comorbidities in mice. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 2859–2867. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, M.; von Mering, C.; Campillos, M.; Jensen, L.J.; Bork, P. STITCH: Interaction networks of chemicals and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Campillos, M.; von Mering, C.; Jensen, L.J.; Beyer, A.; Bork, P. STITCH 2: An interaction network database for small molecules and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuhn, M.; Szklarczyk, D.; Pletscher-Frankild, S.; Blicher, T.H.; von Mering, C.; Jensen, L.J.; Bork, P. STITCH 4: Integration of protein-chemical interactions with user data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strassburg, C.P.; Strassburg, A.; Nguyen, N.; Qing, L.; Manns, M.P.; Tukey, R.H. Regulation and function of family 1 and family 2 udp-glucuronosyltransferase genes (ugt1a, ugt2b) in human oesophagus. Biochem. J. 1999, 338, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, L.; Borazan, E.; Aytekin, T.; Baskonus, I.; Aytekin, A.; Oztuzcu, S.; Bozdag, Z.; Balik, A. Increased ugt1a3 and ugt1a7 expression is associated with pancreatic cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 16, 1651–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Casado, F.L. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor relays metabolic signals to promote cellular regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 4389802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, M.K.; Balaguer, P.; Ekstrand, B.; Daujat-Chavanieu, M.; Gerbal-Chaloin, S. Skatole (3-methylindole) is a partial aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist and induces cyp1a1/2 and cyp1b1 expression in primary human hepatocytes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154629. [Google Scholar]
- Nebert, D.W.; Dalton, T.P. The role of cytochrome p450 enzymes in endogenous signalling pathways and environmental carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, J.; Kitron, A.; Pen, S.; Rosenzweig, T.; Madar, Z. Anti-diabetic activity of Chiliadenus iphionoides. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; An, J.; Zou, M.H. Immune Clearance of Senescent Cells to Combat Ageing and Chronic Diseases. Cells 2020, 9, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budovsky, A.; Yarmolinsky, L.; Ben-Shabat, S. Effect of medicinal plants on wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2015, 23, 171–183. [Google Scholar]
- Patocka, J.; Navratilova, Z.; Yokozawa, T. Bioactivity of Lilium candidum L.—A Mini Review. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2019, 18, 13859–13862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haladova, M.; Eisenreichova, E.; Mucaji, P.; Budesinsky, M.; Ubik, K. Steroidal Saponins from Lilium candidum L. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 1998, 63, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachálková, A.; Eisenreichová, E.; Haladová, M.; Mucaji, P.; Józová, B.; Novotný, L. Potential carcinogenic and inhibitory activity of compounds isolated from Lilium candidum L. Neoplasma 2000, 47, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
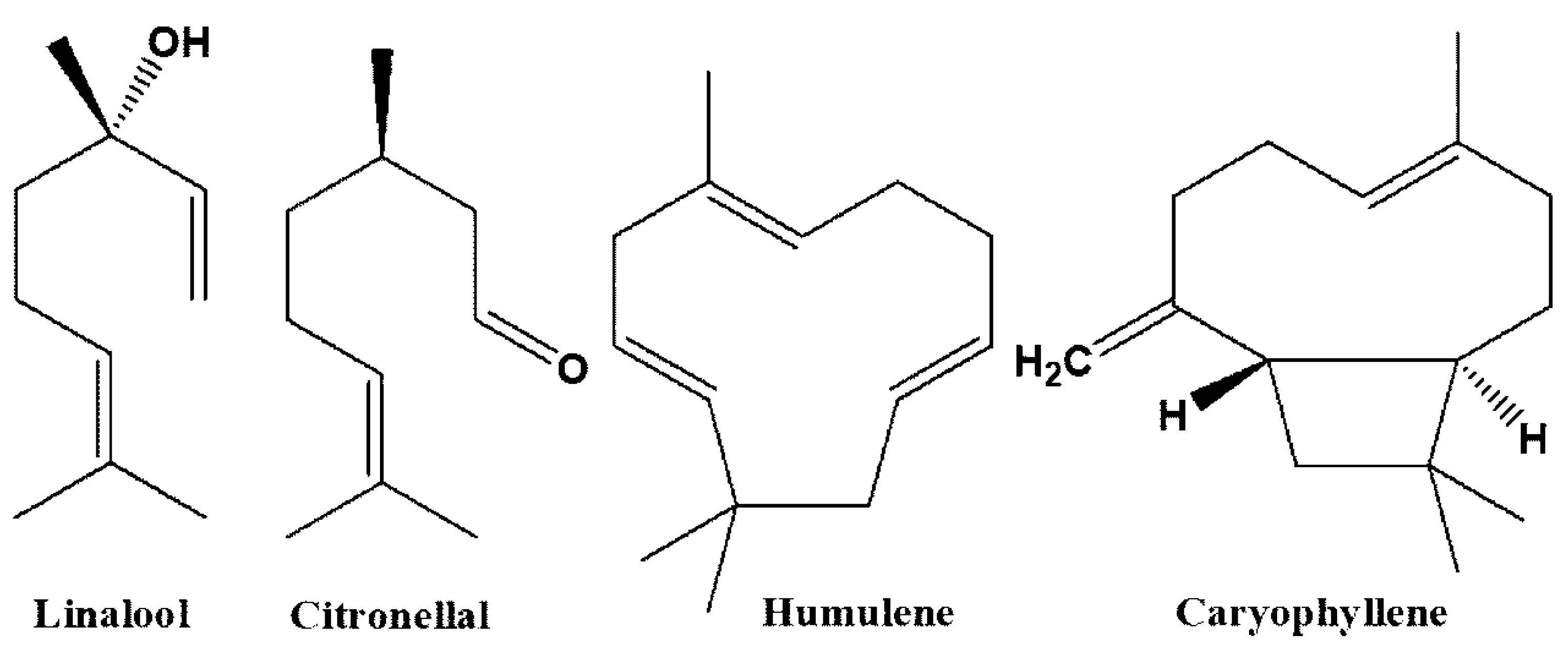



| Compound | Medicinal Uses | References |
|---|---|---|
| Kaempferol | Anti-apoptotic, pro-wound healing, anti-cancer, cardioprotective, anti-oxidant, pro-apoptotic, anti-allergic, anti-parasitic, anti-diabetic, anti-adipogenic, anti-thrombotic, anti-inflammatory, anti-metabolic syndrome, anti-bacterial, immunoregulatory, hepatoprotective, anti-atherosclerosis | [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35] |
| Linalool | Anti-parasitic, anti-convulsant, anti-cancer, anti-bacterial, neuroprotective, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-Alzheimer, anxiolytic, hepatoprotective, anti-hyperalgesic, neuroprotective | [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43] |
| Citronellal | Anti-fungal, insect repellant, hepatoprotective, anti-nociceptive, anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial | [44,45,46] |
| Caryophyllene | Anti-cancer, anti-mutagenic, anti-bacterial, oxygen deprivation protective, neuroprotective, hepatoprotective, anti-convulsant, anti-diabetic, anti-microbial, anti-Alzheimer, pro-longevity, analgesic, nephroprotective | [47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56] |
| Humulene | Insecticidal, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory | [51,57,58] |
| Neridiol | Anti-parasitic, antioxidant, neuroprotective, pro-wound healing, anti-microbial | [59,60,61,62] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaccai, M.; Yarmolinsky, L.; Khalfin, B.; Budovsky, A.; Gorelick, J.; Dahan, A.; Ben-Shabat, S. Medicinal Properties of Lilium candidum L. and Its Phytochemicals. Plants 2020, 9, 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9080959
Zaccai M, Yarmolinsky L, Khalfin B, Budovsky A, Gorelick J, Dahan A, Ben-Shabat S. Medicinal Properties of Lilium candidum L. and Its Phytochemicals. Plants. 2020; 9(8):959. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9080959
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaccai, Michele, Ludmila Yarmolinsky, Boris Khalfin, Arie Budovsky, Jonathan Gorelick, Arik Dahan, and Shimon Ben-Shabat. 2020. "Medicinal Properties of Lilium candidum L. and Its Phytochemicals" Plants 9, no. 8: 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9080959







